This thesis, The role of spirituality in the life of people living with HIV/AIDS, is my own work and has not been submitted to any university other than the University of KwaZulu-Natal (Durban). The Executive Director of the Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) argued that AIDS requires us to do business differently: not only do we need to do more and do it better; we must transform both our personal and institutional responses in the face of a truly exceptional global threat to security and stability (Piot, 2004).
Background to the Problem
Modern scientific treatment also consists of the homeostatic relationship of the patient as an individual organism. Thus, the emotional concerns and spiritual well-being of caregivers, as well as patients, must be directly addressed.
Problem Statement
In an ecological perspective that takes into account the patient and the relatives, Cooke (1992) argued that the care of HIV-infected patients is physically demanding as well as emotional. The researcher has also experienced a period of exposure to spiritual healing as part of an intercessory prayer group, as well as administering nursing care to clients and patients with chronic illnesses.
Purpose of the Study
Research Objectives
Research Questions The study was guided by the following three research questions
Significance of the Study
This study will therefore serve as a documentation of the study support group for future reference. The findings of this study are expected to enrich the knowledge base of healthcare providers regarding the role of spirituality in the care of people living with HN/AIDS, as well as other chronic conditions.
Operational Definition of Terms
People living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA): PLWHA for this study are HIV positive individuals who are members of the support group at Philani Clinic in King Edward VIII Hospital. A role does not display all the states or behavior of the entity, but the role will display state and for behavior relevant to its participation in the context.
Conceptual Framework
Another obstacle to measuring behavioral spirituality is that within a cognitive/behavioral framework, the spirituality of an act is based on the individual's own belief system. An attachment relationship can be with self, ultimate reality, environment/nature, family, friends and loved ones.
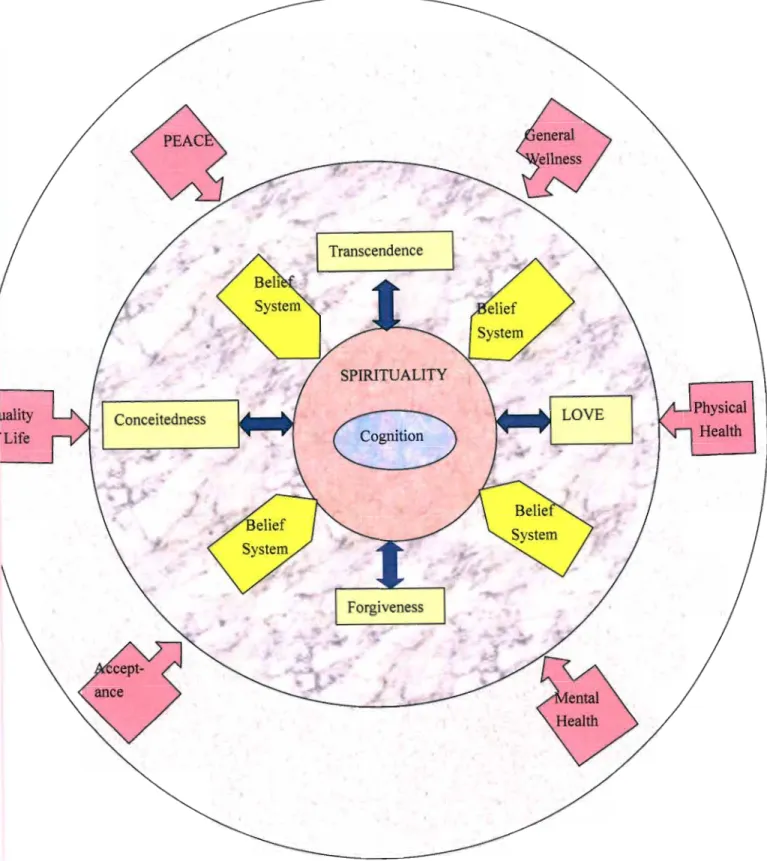
Conclusion
Introduction
This chapter reviews relevant literature on the role that spiritual beliefs play in the lives of people living with HIV/AIDS, as well as in the lives of people with other conditions. This literature suggests that spiritual beliefs can help patients cope with the uncertainty of illness, restore hope, bring comfort and support from others, and resolve the problem of existence, especially the fear of death.
The Role of Spirituality as Described by Nursing and Researchers
Spirituality focuses on what happens in the heart, religion tries to codify that experience and capture it in a system (p. 2)". In the pursuit of psychological well-being, it is widely accepted that one's health is the best predictor of well-being Levin (1995) found that spirituality is at least equal to health itself in terms of predicting well-being and may in fact be a better predictor.
Spirituality and Alternative Treatment
This decision is because traditional healers provide a 'psychological' and a physical diagnosis that relates to the client's complaint and the social environment (Thornton, 2002). Traditional healers usually take a holistic approach, dealing with all aspects of the patient's life and providing culturally familiar ways of explaining the cause and timing of ill health and its relationship to the social and supernatural worlds.
The Role of Belief
1981, and the present, is that the disease now overwhelmingly affects poor heterosexuals in the developing world (Walker et al, 2004). Fear that condoms actually cause HIV, or that they can get stuck in the vagina (Hampton, 1991).
Relationship between Spirituality and Psycho-biological Outcomes
The average survival time of the subjects who died was 20.2 months, one and a half times the national norm. Aldridge (2001) examined the relationship between spirituality and psychological mood states in response to life changes.
Prayer and Spiritual Healing
Koss in Neid (2000) compared the effects of community mental health services in Puerto Rica with that of a spiritual leader in the treatment of patients with mental health complaints. In the treatment of alcoholism, there has been a historical influence of spiritual considerations being included in treatment plans (Bergmark, 1998; Caroll, 1993; Eisenbach-Stagl, 1998).
Spiritual Awakening
Lack of Knowledge that IIIness/Wellness is a Spiritual Issue
Parents of troubled children will put their children's names in prayer and there are always positive solutions. Modern scientific treatment also consists of re-establishing the patient's homeostatic relationships as an individual organism.
Lack of Knowledge of Cultural/Spiritual Diversity
Consequently, the literature review has provided basic information about the role that spirituality plays in the lives of people living with HIV/AIDS, as well as the role of beliefs in different life situations. Additionally, he has demonstrated the role that belief and cultural practices play in the spread of infection, the importance of prayer and spiritual healing, and the need for spiritual awakening among nurses.
Introduction
Research Design
The researcher must be welcome to follow a new lead and move the investigation into new areas in the middle of the investigation process. The study focused on the adult (18 years and over) population of people living with HN/AIDS in the support group at the Philani Clinic in Durban as study participants.
Sample Description
Nineteen participants were interviewed in four (4) focus groups: three (3) consisted of five (5) participants each, and one (1) consisted of four (4) participants. All participants were interviewed at the Philani Clinic at King Edward VIII Hospital as they were all members of the Philani Clinic Support Team.
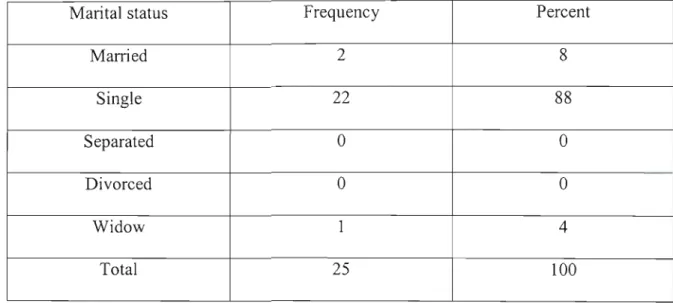
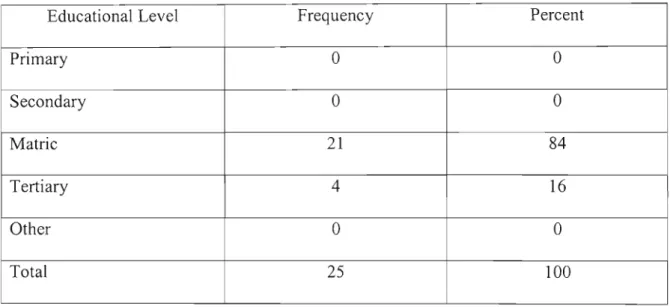
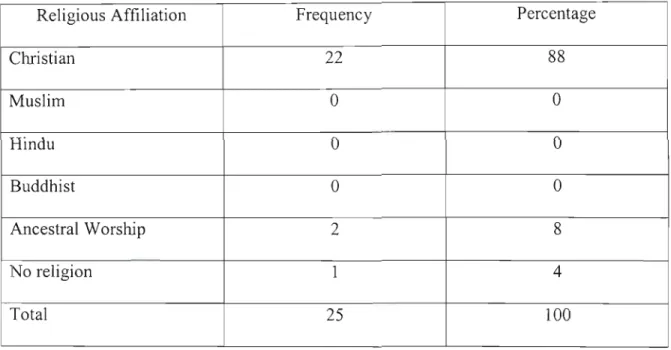
Socio-demographic characteristics of study
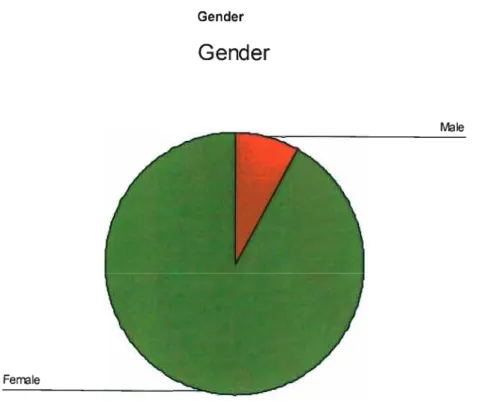
Gender
Data Collection and Instrumentation
The instrument was used to obtain rich descriptions of the role of spirituality in the lives of people living with RN/AIDS. The one-on-one participants were not the same as those of the focus group.
Data Analysis
The interview guide was then applied to the data collected and the main themes and sub-themes and categories that emerged were discussed. The fourth chapter also presents the various subcategories that were observed in some categories.
Trustworthiness
- Credibility
- Transferability
- Dependability
- Confirmability
The researcher validated the information by allowing the participants to read the transcript of the data. The researcher also has the transcript that was used for data analysis.
Dissemination of Findings
Ethical Consideration
Those who volunteered to participate in the study signed the consent page of the permission letter. The open, emergent and unpredictable nature of qualitative research is acknowledged to make informed consent problematic (Robley, 1995).
Conclusion
Due to the nature of the methodology, issues may arise in the interview for which the participants and the researcher were not prepared. As a way forward, consensual decision-making or process-informed consent has been used, in which consent is reassessed throughout the research process (Streubert & Carpenter, 1999).
Introduction
Presentation of findings
- Sub-theme 1: Spiritual Expressions
- Sub-theme 1: Spirituality provided strength to deal with stigma and discrimination
- Category 1: Spirituality provided emotional strength
- Sub-theme 2: Spirituality provided strength for positive living
- Sub-theme 4: Spirituality facilitated interpersonal relationship
- Category 1: Spirituality facilitated love
- Category 2: Spirituality facilitated forgiveness
- Category 3: Spirituality facilitated connectedness
- Sub-theme 5: Spirituality provided protection
34;]it is nice to have friends around, but your spiritual needs are not fed by your friends; you must be the food of your own spirit." 34;The most important thing in everything I do is to ask God to help me, and He helps me."
Theme 3: Beliefs about the cause, prevention and cure of HIV/AIDS
- Sub-theme 2: HIV/AIDS is God's plan
- Sub-theme 4: HIV/AIDS is a blessing
34;In my opinion, the HIV virus can only be prevented by faithfulness in marriage; I don't think condoms can prevent it.” Those participants who believed that the infection could be prevented through marital fidelity also believed that only God could cure it.
Theme 4: Benefit of belief in helping people living with HIV/AIDS to cope with the infection
- Sub-theme 1: Spiritual belief promoted restoration of relationship
- Category 1: Restored relationship promoted healing
When a relationship with God is restored, participants reported that God empowers you from within to fight HIV/AIDS and overcome its challenges. 34; When you are alone in your room, you can just pray, especially when you have problems, God is always there and you feel that he can heal you.
Conclusion
Essentially, it empowered people living with HIV/AIDS to continue with life, provided hope for the future, facilitated interpersonal relationships, and provided protection from imminent fear. A major benefit of the participants' spiritual beliefs that played a significant role in helping them cope with the infection was.
Introduction
The benefits of spiritual belief in helping people living with HIV/AIDS to cope with infection.
Discussion of definition of spirituality in relation to literature
This statement is consistent with the study because it was found that people need a relationship with a higher power in the same way that they need a relationship with other people. Similarly, this study found that a good relationship with oneself, the higher power and with others gives the person a sense of inner peace and hope.
Discussion of the Role of Spirituality
- Dealing with stigma and discrimination
- Positive living with HIV/AIDS
- Inspiring hope
- Spirituality facilitated relationship with God/Ultimate Reality, the self and others
- Spirituality facilitated love
- Spirituality facilitated forgiveness
- Spirituality facilitated connectedness
- Spirituality provided protection
- Beliefs about the prevention of HIV/AlDS
- Prevention through the use of condoms
- Prevention through abstinence
- Prevention through faithfulness in marriage
- Belief about the cure of HIV/AIDS .1 An ordinary cure
- Belief about a "God cure"
- Belief about a "virgin cure"
- Other beliefs about the cure of HIVIAIDS
This is also consistent with the result of the study because some participants said HIVIAID was meaningful. However, in this research, it was found that the majority of participants believed that HIV/AIDS was God's plan.
Benefit of spiritual belief in helping people living with HIV/AIDS to cope with the infection
The ultimate goal of a relationship with ultimate reality is the good of humanity (Todeschi, 2004). Restoring the relationship with ultimate reality proved to be the way forward for the HN/AIDS dilemma.
Limitations
Therefore, nurses must be provided with the knowledge they need on how to guide people living with HIV/AIDS in the process of restoring their relationships with whoever they may refer to as their superior. If national as well as international health organizations are to deal effectively with the HIV/AIDS situation, there is an urgent need for them to include the role of spirituality in dealing with the infection in their policies.
Conclusion
Approve or condemn the condom: lesson you can learn from Ugandans http://www.kit.nl/frameset.asp?/ils/exchange contentlhtml/2004- 1.0 October 30, 2005. Spirituality and treatment of people living with HIV /AIDS: Providing HIV/AID care in a changing environment.
ANNEXURE A
COPIES OF LETTERS REQUESTING PERMISSION TO CONDUCT RESEARCH
The title of my research is: THE ROLE OF SPIRITUALITY IN THE LIVES OF PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS. This research was approved by the Research Ethics Committee at the aforementioned university.
UNIVERSITY OF
KWAZULU-NATAl
They will also be assured that confidentiality will be respected and that their names will not appear anywhere in the research report. A summary of the research proposal and participant interview guide are attached, including a copy of the University of KwaZulu-Natal Research Ethics Committee approval.
ANNEXUREB
LETTERS OF PERMISSION TO CONDUCT RESEARCH
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH
The Management of King Edward VIII Hospital reserves the right to terminate the consent for the study if circumstances so require.
ANNEXUREC
ETHICAL CLEARANCE FROM UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL
RESEARCH ETHICS COMMITTEE
ANNEXURED
LETTER WRITTEN TO PARTICIPANTS REQUESTING PERMISSION
This study aims to explore the role of spiritual beliefs in the lives of people living with HIV/AIDS and the importance of these beliefs in helping them to live with the infection. Confidentiality will be respected and your name will not be mentioned anywhere in the completed document.
ANNEXUREE
DATA COLLECTION TOOL
DATA COLLECTION TOOL Questionnaire-l
Gender: Male/Female