Vaal University of Technology for allowing me to conduct this study at their institution and for the cooperation of their staff members, which enabled me to complete the research project;. The primary objective of this study was to determine the relationship between transformational leadership, motivation and job satisfaction of employees tested at the University of Technology in South Africa. The findings show that all the variables considered in this study are statistically significantly related to each other.
Transformational leadership traits account for 16% of the variance in non-work self-determination motivation (NWSDM) with performance expectancy being a statistically significant predictor of non-work self-determination motivation. Characteristics of transformational leadership also explained that 29% of the variance in extrinsic job satisfaction with vision articulation and goal acceptance were statistically significant predictors of the dependent variable. However, with the inclusion of WSDM and NWSDM in the second model, the variance explained in extrinsic job satisfaction increased by 10% to 39% with vision articulation, goal acceptance, WSDM and NWSDM being the only statistically significant predictor of subjective extrinsic job satisfaction. .
Transformational leadership characteristics also explained 39% (high practical significance) of the variance in intrinsic job satisfaction, with vision articulation and goal acceptance emerging as statistically significant predictors of the dependent variable. However, with the inclusion of WSDM and NWSDM in the second model, the variance explained in extrinsic job satisfaction increased by 4% to 43%, with WSDM emerging as the only statistically significant predictor of intrinsic job satisfaction.
NATURE AND SCOPE OF THE STUDY
Introduction
Problem statement and research question
Aim and objectives of the study
- Aim of the study
- Primary objective
- Secondary objectives
Scope of the study
Rationale and significance of the study
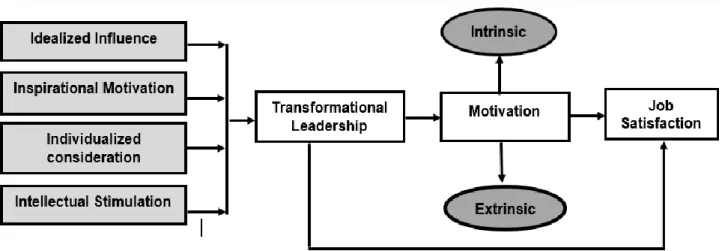
This section focuses on the conceptualization of the main constructs under investigation in this study, namely, transformational leadership, employee motivation, and job satisfaction. In addition, this section also looks at the relationships between these variables as established by previous research on the same constructs under investigation.
Transformational leadership
Those led by transformational leaders tend to improve their performance and are both loyal and successful (Cherry, 2017). Transformational leaders offer more to their subordinates, and they care deeply about their subordinates' performance and ability to achieve goals and objectives (Cherry, 2017). Transformational leaders are described as enthusiastic, charismatic, passionate, optimistic and sometimes visionary, giving them the ability to change long-held perceptions and beliefs, said Rich Hein, Senior Managing Editor of CIO.
Emotions and Behavior at Work (2018) shares the same view that transformational leaders target employees who are melancholy, sluggish, and low on energy because this leadership style makes a difference to them. Transformational leaders go beyond managing day-to-day operations and work on strategies that will take the leader's company or team to higher levels of performance and success. While providing professional and personal growth opportunities for every employee, transformational leaders set incentives and goals to encourage followers and push them to high levels of performance, says Ingram (2018).
While leading their followers, transformational leaders engage in Intellectual Stimulation, Inspirational motivation, individualized consideration, idealized influence, which are described as the 4 I's needed to facilitate transformation. Transformational leaders recognize the value of encouraging innovative ideas, building knowledge in the workplace, and not criticizing others and thereby developing employees (Kraft, 2018).
Motivation
Managers need to understand the different types of motivation to motivate employees because not all employees are the same. People are motivated by external and internal factors, as they are always the reasons why they behave, achieve, learn and react (Thompson, 2019). There are two types of motivation or rewards, intrinsic, internal motivation (the individual's motivational stimuli come from within) and extrinsic motivation, which is external (the individual's motivational stimuli come from the outside).
Examples of intrinsic motivation are self-actualization and a sense of accomplishment, while extrinsic motivation may include status and working conditions. If leaders understand the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic motivational factors, they are more likely to motivate themselves and others (Thompson, 2019). Intrinsic motivation occurs when employees can evaluate their contributions to the organization in a holistic way instead of a reward-based mechanism (Bradley, 2018).
Fostering intrinsic value in your staff is an ongoing and ongoing process so that your employees feel good about the work they do, even when they are not physically rewarded (Bradley, 2018). Workers enjoy what they do, so this motivation can serve as an incentive for them.
Job satisfaction
Transformational leadership and Motivation
Transformational leadership and Job satisfaction
Transformational leadership, motivation and job satisfaction
Motivation and job satisfaction
Theories of motivation and job satisfaction
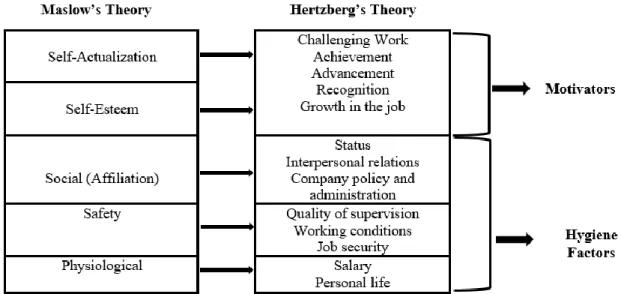
Mark (2014) suggests that “the presence of hygiene factors does not increase satisfaction and motivation, and their absence causes an increase in dissatisfaction”. Both motivational and hygiene theory must be constantly improved for a happier and most productive workforce. According to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs theory, each person has a set of needs that must be met for self-actualization (Burton, 2012).
The hierarchy explains the general human motivation and it is used to explain job satisfaction (Adeogun, Fapojuwo and Ajayi, 2011). Managers need to understand the hierarchy of needs to understand that “motivation causes goal-oriented behavior” (Juneja, 2019) and to understand its contribution to job satisfaction (Adeogun, Fapojuwo, & Ajayi, 2011). Social need, need to feel love or belonging – to be accepted by others and to be part of the group.
Self-actualization needs are the highest stage of human motivation, where employees need to develop and grow to become what they want to be. Basic or lower needs must be met or satisfied by an organization to improve employee job satisfaction before moving on to meet higher order needs.
Research design and methods
Study population
Research paradigm
Sample characteristics
Measuring instruments
Statistical analysis
RESEARCH ARTICLE
This study aimed to determine the relationship between transformational leadership, employee motivation and job satisfaction. The primary question in this study was what is the relationship between transformational leadership, motivation and job satisfaction. How are transformational leadership, employee motivation and job satisfaction conceptualized according to the literature;.
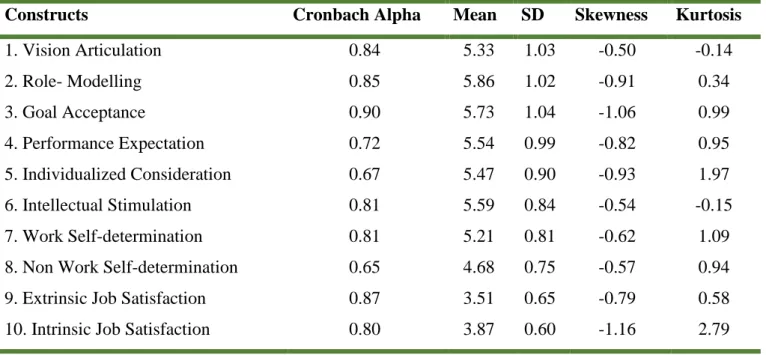
The primary objective of this study was to investigate the relationship between transformational leadership, motivation and job satisfaction. Job Satisfaction: The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ): A short form developed by Weiss, Dawis, England, and Lofquist (1967) was used in the present study. NWSDM was also statistically significantly related to extrinsic job satisfaction (medium effect) and intrinsic job satisfaction (medium effect).
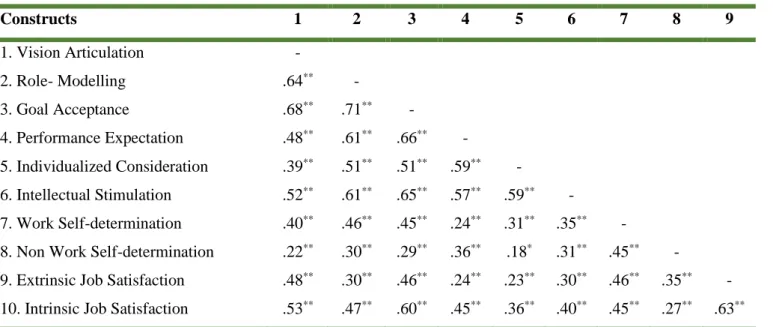
We were also interested in the impact of transformational leadership traits as predictors of WSDM, NWSDM and extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction. Regression analysis with transformational leadership characteristics as predictors of WSDM, NWSDM and extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction is presented in Table 4 below. Characteristics of transformational leadership also explained 29% (medium practical significance) of the variance in extrinsic job satisfaction with vision articulation (β=.36 / t=3.48) and goal acceptance ((β=.40 / t=3.12) which appeared to be statistically significant predictors of the dependent variable.
41 Traits of transformational leadership also explained 39% (high practical significance) of the variance in intrinsic job satisfaction with vision articulation (β=.24 / t=2.49) and goal acceptance (β=.39 / t=3.32), proving that statistically significant are predictors of the dependent variable. However, with the inclusion of WSDM and NWSDM in the second model, the variance explained in extrinsic job satisfaction increased by 4% to 43% (great practical significance), with WSDM (β=.22 / t=2.59) being the only to be a statistically significant predictor of intrinsic job satisfaction. The findings suggest that transformational leadership characteristics were statistically significantly related to each other and to WSDM, NWSDM, and extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction.
More specifically, vision articulation, role modeling, goal acceptance, performance expectations, individual considerations, and intellectual stimulation were related to WSDM, NWSDM, extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction. Transformational leadership characteristics also explained 39% of the variance in intrinsic job satisfaction with vision articulation and goal acceptance, proving to be statistically significant predictors of the dependent variable. However, with the inclusion of WSDM and NWSDM in the second model, the explained variance in extrinsic job satisfaction increased to 43%, with vision articulation, goal acceptance, and WSDM proving to be the only statistically significant predictors of job satisfaction. internal work.
WSDM was also related to NWSDM, extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction, and extrinsic job satisfaction was related to intrinsic job satisfaction. The findings also suggest that vision articulation, goal acceptance, and WSDM were found to be predictors of extrinsic and intrinsic job satisfaction.
CONCLUSIONS, LIMITATIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
These findings are consistent with previous empirical findings that confirmed relationships between transformational leadership (and its dimensions) and intrinsic, extrinsic motivation (Barbuto Jr, 2005; . Conchie, 2013) and job satisfaction (Risambessy, Swasto, Thoyib & Astuti, 2012) ). Specific Objective 3: To determine the role of transformational leadership in employee motivation in an academic institution. Transformational leadership characteristics account for 16% of the variance in WNSDM, with performance expectancy found to be a statistically significant predictor of NWSDM.
Specific objective 4: To determine the role of transformational leadership and employee motivation in job satisfaction in an academic institution. Previous empirical findings have also confirmed the links between transformational leadership (and its dimensions) and intrinsic, extrinsic motivation (Barbuto, 2005; Conchie, 2013) and job satisfaction (Risambessy, Swasto, Thoyib & Astuti, 2012). The results show that transformational leadership characteristics also explained 39% of the variance in intrinsic job satisfaction, with vision articulation and goal acceptance proving to be statistically significant predictors of the dependent variable.
One can, for example, test whether the transformational leadership hypothesis - employee motivation hypothesis and whether the transformational leadership - job satisfaction hypothesis holds for an employee at different levels of the hierarchy. Transformational leadership and job satisfaction: Assessing the impact of organizational contextual factors and individual characteristics, 20 (4). The mediating role of psychological empowerment in the relationship between transformational leadership and employee organizational identification.
The mediating role of self-efficacy in the relationship between transformational leadership and subjective experiences of work success. Examining the Effects of Transformational Leadership on Employee Job Satisfaction with Organizational Learning Culture Interaction. Impact of Transformational Leadership on Job Satisfaction; mediating role for employee empowerment and moderating role for employee training.
Transformational leadership principles of management. https://www.wisdomjobs.com/e-university/principles-of-management-tutorial-293/transformational-leadership-9508.html. 2012).