This case study of this school's experience aims to understand school-based teachers' experiences of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to curriculum implementation. What are school-based teachers' experiences of a learning styles approach to teaching South Africa's NCS/CAPS Middle Stage Policy (2012).
Background to and Focus of Study
23 on what counts for good education for all in understanding teachers' experiences with curriculum implementation through learning styles. Understanding teachers' experiences of curriculum implementation through learning styles therefore requires an investigation into the extent to which the local contexts of our institutions are supported and creative, problem-solving and innovative internal cultures and conditions are established brought.
Personal Positionality, Purpose and Rationale
- As a teacher
- As an implementer of the South African National Curriculum Policy
- As a member of School Management Team
- For the sake of research
It is hoped that this study may also have the potential to spark interest in research into learning styles, a visible gap (Grosser & de Waal, 2008). THE CONCEPT/THEORIES OF CURRICULUM IMPLEMENTATION WITHIN THE SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL CURRICULUM POLICY (NCS/CAPS, 2012), LEARNER-CENTERED AND LEARNING STYLES.
What is curriculum
Thus, the chapter begins with a broad view of the concept of curriculum implementation, which requires a definition of curriculum and curriculum implementation as positioned in this study. In this study, the most appropriate definition is that of the reconceptualist's definition of curriculum as a process and a product.
Two views of curriculum development and design
The art of curriculum implementation
An academic approach to the curriculum can be incorporated into the theoretical basis of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach, an approach that was criticized in this study. Finally, the pragmatic approach is the antithesis of the above, which sees the curriculum as a dynamic, complex, irrational, fragmented and reactive process involving many interactions (Moodley, 2009).
Curriculum implementation as an art
The third method of applying the Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning style approach to individualizing instruction is the Programmed Learning Sequence (PLS) Method. 126 using Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to implementing the middle stage curriculum. These are used in curriculum delivery through Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching.
Meeting Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching was one such solution.
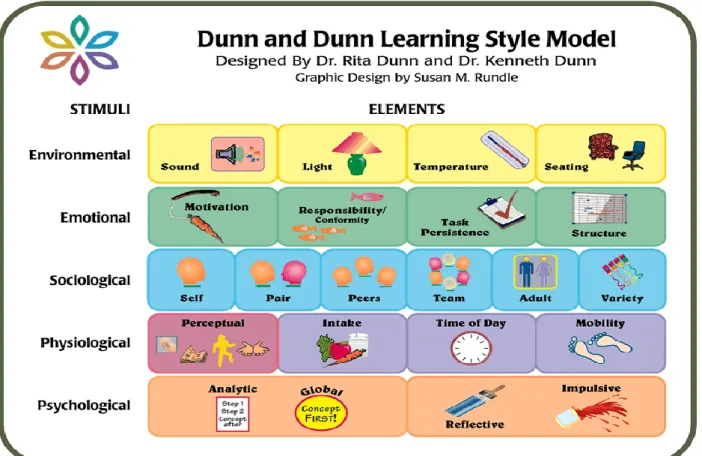
The South African curriculum statement policy (2012)
Learner-centredness: a postulated interconnection of Rousseau, Dewy,
Two influential models: Kolb‘s learning styles model and the Felder-Silverman
The hallmark of this learning style is that individuals rely on abstract conceptualization and concrete experiences. According to Moallem (2007), Felder and Silverman developed their learning style model based on a composite of different theories.
In sum
This chapter also includes an in-depth description, explanation and critique of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching in terms of curriculum implementation. 68 through Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles approach to teaching has had on how children learn and respond.
Definitions of and background to learning style theory
However, learning styles theory in general and Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach in particular, given the necessary attention, can become one of those long-awaited solutions to understanding curriculum implementation for success. in heterogeneous classrooms of the 21st century (Moodley, 2009). In doing so, it investigates the adoption of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching used to implement the Middle Stage Curriculum. Participant C clearly asserted that through Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to learning her students learned how to learn.
She found that Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles of teaching complemented her own teaching approach.
The purpose and benefits of a learning styles approach to teaching
The influence of learning styles on learner response
In direct contrast to the above, Hall (2005) found several significant problems in learning style research. It suggests that using learning styles to improve student achievement is only one type of differentiation in the classroom.
The Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles approach to teaching
- The contract activity package method (CAP)
- The multisensory instructional package method (MIP)
- The programmed learning sequence method (PLS)
- Tactual manipulatives
- Kinesthetic activities and resources
- Small group technique: Circle of knowledge
Section 83 delves into the implementation of a learning style approach to teaching, particularly the Dunn and Dunn (1978) model used by the participants in this study. This approach reduces much of the frustration and anxiety of motivated students who are often required to do so.
Implementation and use of learning styles theory
They can be seen as similar to behavioral learners who need to move and be physically involved in learning to absorb a new concept. Similar to cognitive learners who need to understand the parts of a new concept before grasping the whole, they need sufficient thinking time and an ordered thought pattern.
Critique of the Dunn and Dunn (1978) Model
Dunn and Griggs (2000) agree that learning styles change as individuals grow as students move through different school stages into adulthood. Understanding curriculum implementation through learning styles for individual pedagogy cannot afford to ignore the legitimacy and value of learning styles theory and approach.
In sum
Research gaps were highlighted by reviewing the purposes and benefits of a learning styles approach to teaching. In addition, this chapter also included an in-depth description, explanation and critique of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching in understanding curriculum implementation.
Researcher positionality and bias
The next section on methods used to collect data begins with a description of the site of data collection, a primary school in Pietermaritzburg. This is followed by a detailed description of and introduction to the analysis unit, school-based teachers and selection of the sample.
Key research question and sub-questions
Central to this case is his particular quest to understand the classroom practice of Middle Stage teachers who use Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to meet curriculum needs. What are school-based teachers' experiences of the contributions, complexities and potential contradictions of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching in the intermediate stage.
Research design / intended data analysis
Questions 3, 4 and 5 are answered in Chapter 5 (see Findings and Discussion) arising from the data collected from this sample. The table below depicts how critical questions 3, 4 and 5 are analyzed against the four datasets used in this study.
An interpretivist paradigm
Moreover, an interpretivist paradigm fits this study's exploratory, descriptive research question of asking what teachers' experiences of learning styles are. In this study, the encounter between teachers and a learner-centered, learning styles approach to their classroom practice is within the social context of this school.
A qualitative style
In this study, classroom practices and teachers' experiences with learning styles are explored and described. This study is thus an attempt to intensively understand the processes, experiences and dynamics surrounding the teachers' experiences with a learning style approach to teaching at this school.
A case study approach
Therefore, for the purposes of this study, the use of a case study approach is appropriate. In addition, the choice of a case study fits the purpose of understanding the teacher's experiences with learning styles.
Method of data collection
Unit of analysis: The Context / Site
- Demographic description
- School structure, culture and work ethic
- Confronting change
Historically, part of the school is still in original buildings, which have been declared monument status. Field trips and school camps are an integral part of the holistic learning approach inherent in the school's ethos.
Sampling
- Ethical considerations
- Profile of participants
The following is a brief description of the personal and professional profiles of the participants in this study. She believes that everyone has different strengths, that learning is a process and should be interactive, participatory and fun.
Data gathering
- Interviews
- Document reviews
- Policy documents
- School documents
- Teaching documents
- Visual data
- Artifacts
In essence, it captures an in-depth description of their practice and experience of Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning style approach to teaching the Intermediate Stage curriculum. In this case study, a sample of relevant photographs is selected that depict classroom teaching and learning through Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learner-centered model of teaching approach.
Trustworthiness
Furthermore, artifacts are used as a data collection tool in this study for triangulation and in-depth understanding of teachers' experiences of a learning styles approach to their teaching. A solution that lies in a 'judicial compromise' is suggested by Cohen, et.al. 2000). This study takes note of this throughout its iterative process used in the data collection and analysis processes.
Ethical considerations
147 validity of research conclusions are sorted and maintained for internal validity purposes (Anderson & Burns, 1989; TerreBlanche et.al., 2006). Additionally, face validity; evidence that is likely to provide a reliable description of the phenomena under study is increased when systematic procedures, the use of designs, reviews, and revisions are used (Anderson & Burns, 1989).
In sum
The research title, A Learning Styles Approach to Curriculum Implementation: A Case Study - ―Dunn and Done?‖ specifically seeks to understand teachers' experiences of implementing the NCS/CAPS (2012) Intermediate Stage Policy with Dunn and Dunn (1978) Learning. a stylistic approach to teaching as employed at a primary school in Pietermaritzburg. 150 What are school teachers' experiences of a learning styles approach to teaching South Africa's NCS/CAPS policy (2012) at the intermediate stage?, Supporting data interpretation and understanding.
Why a learning styles approach to teaching in this case?
Achievement and / or schooling success
Thus, a major reason for adopting Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching was the need to address the problem of at-risk and underachieving students. However, an even deeper purpose for adopting Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to teaching was expressed by Participant B.
Behaviour and discipline: A state of being
All the participants completely agreed that teaching through a learning style approach has definitely affected the students' morale, work ethic and motivation. Narrowing the gap between disadvantaged and high-achieving students led to the adoption towards a student-centered pedagogy, which Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles of teaching apparently allowed for academic achievement and schooling success in this case.
A learner-centred pedagogy: Individual strengths,
They saw this as extremely important as to why the Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles approach was used. Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach was found to be a suitable tool to meet such goals.
Planning, preparation and presentation
Dunn and Dunn's (1978) learning styles approach to curriculum delivery provided a context for learning and recall that was superior, novel, and best received by all three participants. By adopting the approach as part of the school's expectations, she also presented her students with opportunities to learn through their learning styles.
The Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles approach to teaching
Students were allowed to sit in groups or pairs or alone according to their individual preferences. Students were able to flip back and forth according to their pace along the way.

What are school – based teachers‘ experiences of the possible contributions,
- Facing the ―new normal‖
- Awakening awareness
- Curriculum complexities and other compromises
- Contradictions confirmed
Dunn and Done? Dynamic deviations
In sum
Summary of key findings
Why a learning styles approach to teaching in this case?
How did school-based teachers implement the Dunn and Dunn (1978) learning styles approach to
- Contradictions
- Complexities
- Contradictions
Significant insights
Teachers‘ awareness and identity
Teachers as curriculum creators
Teachers for learner access
Conclusion





