Qualifications, at most, develop teaching competence in three school subjects, but the practice of teaching across the curriculum often requires teachers to teach more than three school subjects to a class. My study is a focus on the narratives of teachers' experiences of teaching across the curriculum in primary school.
Introduction and Background to the Study
This study attempts to understand the implications of systemic changes on quality issues related to educational provision. New demands have been placed on teachers within this transformed agenda and the effects of these demands form part of the remit of this study as it attempts to understand the challenges these teachers face.
FOCUS AND PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
The teachers' experience of teaching across the curriculum is also placed within the country's transformation agenda, where equality of educational provision is striven for. Therefore, the policy governing various aspects of school education is also under review in this study as it affects teachers' abilities, training and management of their teaching responsibilities.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
How do teachers cope with teaching across the school curriculum in a primary school?
The Rationale for the Study
Methodology
Outline of Chapters
Despite all the difficulties, teachers are willing to teach according to the curriculum, but there is a lack of expertise, professional development and training to help these teachers. By working together, all teachers could contribute to the planning and preparation of teaching across the curriculum.
Limitations
Introduction
The emergence of teaching across the curriculum within the school curriculum in South Africa
This curriculum was introduced only from grades 1-9 in the GET (General Education and Training) band. The Revised National Curriculum (RNCS) was developed in the General Education and Training band, which made schooling compulsory.
Policy issues and the impact on the curriculum
The change in the norms and standards in teacher education was within the parameters set by the National Qualifications Framework (NQF) and the South African Qualifications Authority (SAQA) Thomen (2005, p. 813). All teachers need to develop their skills, not necessarily their qualifications, to deliver the new curriculum.
Review of the Curriculum 2005
What do we understand by the concept, Teaching across the Curriculum
The above two iterations of cross-curricular teaching and/or learning are slightly different from the South African notion of teaching across the curriculum. When teaching across the curriculum, the teacher usually has a single grade and must plan, prepare and teach each subject in the curriculum.
Teaching and Learning when Teaching across the Curriculum
As effective an approach as it is, our education and training for teachers does not allow them to be effective in the classroom. The curriculum shift from subject-based teaching to teaching across the curriculum needs to be fully understood.
Enhancing Continuing Professional Development
Continuing professional development” is necessary because teacher education programs cannot incorporate all the propositional understanding needed in the classroom Knight (2002, p. 230). While professional development seems to ensure that teachers are pointed in the right direction, there is little support from the Ministry of Education.
Construction of Teacher Identity in the Classroom Practice
There must be a lot of planning and preparation in the nine learning areas. Administrative work has increased because there must be planning and preparation for all learning areas in the classroom.
Framing of the study in terms of the concepts of Norms and Standards
Therefore, the Norms and Standards policy was necessary to regulate teacher training in the new curriculum and training system, by specifying the Seven Roles and competencies of teachers, as well as minimum specialist requirements for specialization, according to DoE requirements for phase and learning area/subject. Instead of outlining the necessary subjects that teacher training should contain, the policy describes what teachers are expected to do. Norms and Standards were developed by the Chief of Education Committee for Teacher Education Policy (COTEP), which came up with the idea of outcome-based education.
Summary
This triggered the implementation of a more competency-based National Core Curriculum and the accreditation of qualifications Welch & Gultig (2002). The “competency-based change to the education and training system” saw the introduction of the National Qualifications Framework (NQF) for each level in the Parker and Adler system (2005, p. 63). Education was linked to the NQF organized and monitored by the South African Qualifications Agency (SAQA) Parker and Adler (2005).
Methodology 3.2 Introduction
What opportunities and challenges are presented to teachers who teach across the school curriculum in a primary school?
How do these teachers feel about teaching across the school curriculum in a primary school?
Research Methodology: Narrative Inquiry
The focus of my study is teaching across the curriculum and how different teachers relate their experiences to this phenomenon. I used the qualitative approach to explore and understand the experiences of teachers who teach across the curriculum. It is important to my study because it helped me understand other teachers' experiences of teaching across the curriculum.
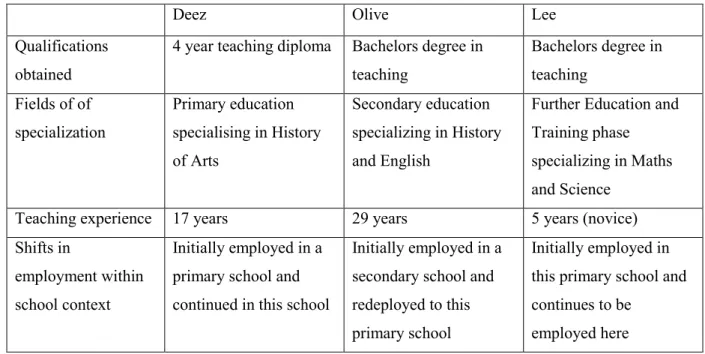
Participants and Context
In my research it should be kept in mind that the teachers are currently teaching the whole curriculum, and this can change to teaching a specialization if necessary. That is why this school site became a site for rich data, because it includes teachers from all kinds of specializations: those who are trained to teach languages in a secondary school, but teach in a primary school, those who are trained to teach in the primary school with some subject specialization, but teaching a number of subjects for which they were not qualified, as well as novice teachers trained within an OBE framework, with some subject specialization, but teaching across the curriculum. This study has given me insight into how curriculum coherence can be achieved through the experiences of teachers teaching across the curriculum.
DATA COLLECTION METHODS .1 Interviews
DOCUMENT ANALYSIS
I have examined the number of assessments per learning area to see whether there is an intensification of teachers' work. Interrogating documents gave me answers to the research question about experiences of teachers teaching across the curriculum. Documents are a useful source for providing solid evidence of the intensification of teachers' work, or are first-hand accounts of the phenomenon under investigation, according to Cohen et al (2007).
Trustworthiness
Keeping all of this in mind will help me with the challenges that teachers face in their classroom practice. This data collection approach was intended to provide data that would be useful in answering the research questions. I would make a thorough report of the research process available to create a clear audit trail for anyone wishing to continue the process in the future.
Ethical Issues
The transcribed interview would be returned to the participants to check that their ideas were adequately presented. This means that the researcher must avoid activities that could negatively affect the participant, physically, emotionally or psychologically. The researcher had to ensure the confidentiality of all data that could be traced back to the participants.
Data Analysis
Limitation of the Study
CONSTRUCTION OF NARRATIVES
The collective experiences of the three participants were collected so that I could identify, describe and explain the teachers' experiences of teaching across the curriculum in a way that would illuminate issues at the systemic level. I conducted face-to-face interviews with my participants to understand the lived experiences of these teachers. I had to listen to the transcripts several times to identify recurring themes that emerged from the data about these teachers' experiences.
Description of School Site
A New Beginning
In the composition of each story I used the first person as it makes the narration more authentic. I did not want to report on what my respondents said, but wanted their own voices to be brought to the fore. I was last in the department; therefore I had to step down first because it was the rationalization and redeployment policy guideline for schools.
A Tough Road Ahead
I had to make a big adjustment from a high school to teaching elementary school. Teaching across the curriculum became a "nightmare" because I had to teach nine learning areas for the first time in my teaching career. Back then I had to deal with the large class sizes and now, even worse, the teacher becomes the facilitator.
Overworked and Managing to Survive
I need to join a professional organization like AMESA so that I can feel confident teaching math in the classroom. This would ease the tension in the classroom for both the teacher and the student. The workshops contribute to the intensification of the work and do not help me in actual classroom practice.
I have been given a number of policy documents in different learning areas to start planning and preparing before the start of the new year. This describes what grades children will receive in nine learning areas and a breakdown of how each will be assessed. I followed the schedule and went from one class to another in the same class, and the students were sometimes overwhelmed by the pace and speed.
NARRATIVE 3: LEE
I was thrown into the 'deep end' because I had so many worksheets to plan for the day. I just had to follow what the others were doing because I didn't want management to think I wasn't following protocol. This was not an easy task as I had to make time for this in between my hectic schedule in class.
5.1 Data Analysis
Theme 1: How did teachers come to teach in a school context requiring them to teach across the curriculum?
According to Lee, “There was very little support from department officials in the different learning areas. According to Deez, "I knew I had to give myself time and adapt my strategies in the classroom. Incidental and informal learning was undertaken by three of the teachers in my study to empower them to be confident in the classroom.
Theme 3: Dealing with deployment into classes that required teaching across the curriculum
The context of the school is not taken into account and teaching across the whole curriculum is expected to work regardless. Olive faces the practical realities of the class: “I couldn't immediately get the attention of the class to start my lesson. Teachers were eager to borrow and borrow their work schedules and learning programs from each other.” It was not learning to teach across the curriculum, but how to plan and execute testing programs regardless of context.
Theme 4: Challenges experienced in teaching across the curriculum
Deez comments on the fact that teachers have to actually account for any apparent discrepancies in their record keeping: "It's not always feasible because of the current topics to be discussed, but I have to give an explanation to the subject advisor when he's going through my books and the students' books." I always feel that I don't need to give a reason for sometimes deviating from my daily schedule.” Teachers also do not have time to meet, plan and share during the school day; therefore, they must try and sometimes plan individually for the nine learning areas.
CONCLUSION
Summary and discussions of the main findings
There are no specific qualifications in teacher education that develop teachers to teach across the curriculum. Although the policy states that primary school teachers are expected to teach all subjects, there is no formal training for all these specialist teachers to adapt to teaching across the curriculum. The professional development that teachers are exposed to in order to support teaching across the curriculum has been quite inadequate.
Limitations
The heavy workload had an effect on their health which in turn had an impact on their classroom practices.
Reflections
It was encouraging that the teachers in my study chose to rise above the obstacles they faced.
Conclusion
Norms and Standards for Teacher Education, Training and Development: Discussion Paper, Technical Committee on the Review of Norms and Standards for Teacher Education. Technology and the coming transformation of schools, teachers and teacher training. 2002), Developing a teacher identity: the impact of critical friend practices on the student teacher. Paper presented at the Education for Democracy and Sustainability conference in Mauritius, April 16 and 17, 2009.