Existing knowledge suggests that Cape Town's current smart city efforts are skewed towards traditional Eurocentric markets. Tourism is one of the major contributors to the gross domestic product of Cape Town and South Africa.
Introduction and background
Research problem
- Background to the research problem
- What is the problem?
- Who does it affect?
- How is it a problem?
Compared to the existing exponential growth in international levels of inbound Chinese tourists, Cape Town is struggling to target the rapidly growing Chinese tourist. The Cape Town tourism environment does not offer the best experience to the drawn Chinese visitors, creating a tarnished image to the Chinese tourists by not meeting their expectations.
Research Problem Statement
Unlike other common tourist destinations, South Africa has seen inconsistent growth and fluctuations in Chinese tourists. Cape Town tourism is therefore not exploiting enough of the potential income from the Chinese tourist market.
Objectives and research questions
Objectives of the research
Research questions
Chinese tourism and smart destinations
- Disposable income
- China’s new travel freedom
- What is a smart city?
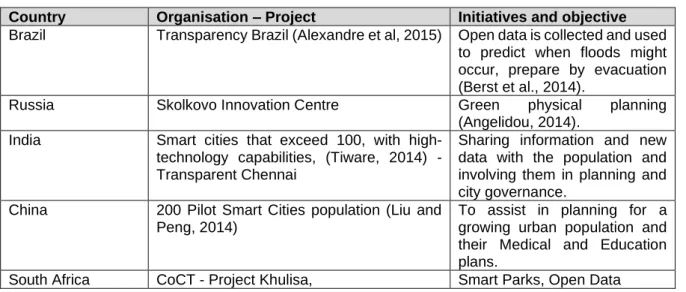
- Smart City development in Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa (BRICS)’
- Smart city initiatives in Africa
- Devices and systems in successful smart cities
- Smart tourism and smart destination
According to Neirotti et al. 2014), there is an assumption about the definition of a smart city or what its standard characteristics are. The Economic City of Tunisia in Tunisia and the city of Rabat in Morocco are some of the efforts in the African region to implement smart city initiatives.
Research design and methodology
Research philosophy
A smart destination is "an innovative space, accessible to everyone, built on the most modern technological infrastructure, which ensures the sustainable development of the space, enables interaction and integration of the visitor with the environment, and increases the quality of his experience in the destination, as well as the quality of life of the inhabitants" (Ávila et al., 2015 ).
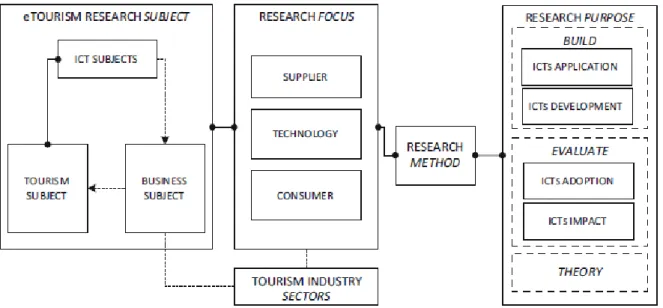
Research methodology
Research population
Sampling
Data analysis
Scope of the research
Delineation
This research did not consider all Smart Destinations stakeholders, but was therefore limited to selected Smart Destinations stakeholders that impact urban planning in Cape Town and individuals or organizations involved in the provision of tourism services such as CoCT, Cape Town Tourism, tour operators , tour operators, guides and catering service providers.
Delimitation
Ethical considerations
Significance of the research
Structure of the thesis
Introduction
Cape Town as a tourist destination
Tourist attractions in Cape Town
The tourist profile of Cape Town
In addition, the National Department of Tourism (2019) indicated the need for ways to address technology and innovations that are revolutionizing the tourism industry to strategically tailor its infrastructure development in line with the new expectations of emerging markets. An analysis of the volumes for 2016 and 2015 showed that the number of visiting tourists increased in all ten leading overseas countries, with China showing the largest increase of 38.1% (Lehohla, 2017).
Benefits of tourism to Cape Town and South Africa
In the export category, tourism is the third largest exporter after chemicals and fuels and the largest supporter of international trade (Teslya et al., 2016; UNWTO, 2018). Community-based tourism (CBT) has been used as a tool and model for developing and empowering communities in South Africa through entrepreneurship (Spenceley et al., 2016).
Chinese tourists
- The value of Chinese tourists
- History of travel
- Travel and service expectations and rising preferred destinations
- Tourist profile, market structure and expenditure
- Chinese’s propensity to technology
- Chinese technology and its use in Western destinations
- The future Chinese tourist
- Chinese tourists in Cape Town and Africa
Most of these destinations have special historical and cultural value for the Chinese tourists (Wang et al., 2016c). In profiling the Chinese tourists who visited the United States, Liu et al. 2016) described a shift in tourists' types and intentions for their visit.
Smart city – Smart destination
- Smart city development in BRICS’ countries
- Smart city services in China
- Apps bridging the gap over the great firewall of China
- Smart city frameworks
- Applying (Sa)6 to smart destination experience and service delivery
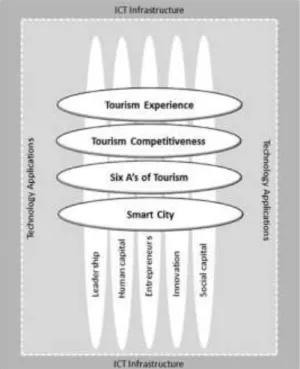
Smart destination is the application of smart principles by smart city stakeholders in the destination (Gretzel et al., 2015a). The UN smart city conceptualization calls for a more “inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable” city (Allam et al., 2018).
The theoretical framework underpinning this study
The ANT theoretical framework
The Actor Network Theory does this by making connections between controversies and following the links between the ideas (Kien, 1999). Gretzel et al., (2015c) propose open innovation ecosystems that allow actors to co-create value through. The economic power in smart tourism services depends on the access to data (Rodger et al., 2009).
Evaluation of Cape Town’s as smart tourist destination
- Smart Africa Manifesto
- Cape Town’s digital strategy and application
- Digital Infrastructure
- Digital government
- Digital inclusion
- Digital Economy – Supporting the digital economy
- Digital tourism
- Cape Town as a smart city / destination - Overview
- Summary of the literature study
Cape Town boasts an intensive broadband infrastructure program that has required a large financial investment and created employment since 2012 (Mhangara et al., 2017). Similar to Gcaba et al. 2016), Green's (2016)(Green, 2016) research points to the need for the application of robust IoT in smart city initiatives in Cape Town tourism. The different sections of the literature review aimed to report exhibitions on Cape Town tourism, Chinese tourism, smart cities (destinations) and Cape Town's smart city initiatives.

Introduction
Socio-technical research
Research paradigm
Research methodology
Research methods
Expert interviews
Expert interviewers rely heavily on interviewer skills and the context of the interview must be taken into account (Chemaly, 2012). A well-designed questionnaire facilitates the extraction of rich and detailed data. The interview questionnaire was emailed to the participants before the interview to help them prepare for the interview and avoid lengthy deliberations or missing points. In addition, after each interview, the two reflected on varying themes, comments from outsiders and opinions that emerged during the interview.
Sampling method
Data sources
Qualitative data were collected using semi-structured questionnaires that follow a designed pattern of standardized questions. Other sources of qualitative data can be texts, documents, and researcher reactions and impressions (Myers, 2009).
Ethics
Summary
Introduction
Assessing the level of sophistication of Cape Town as a destination from the perspective of Chinese tourists and knowledge of the technological needs of the Chinese market.
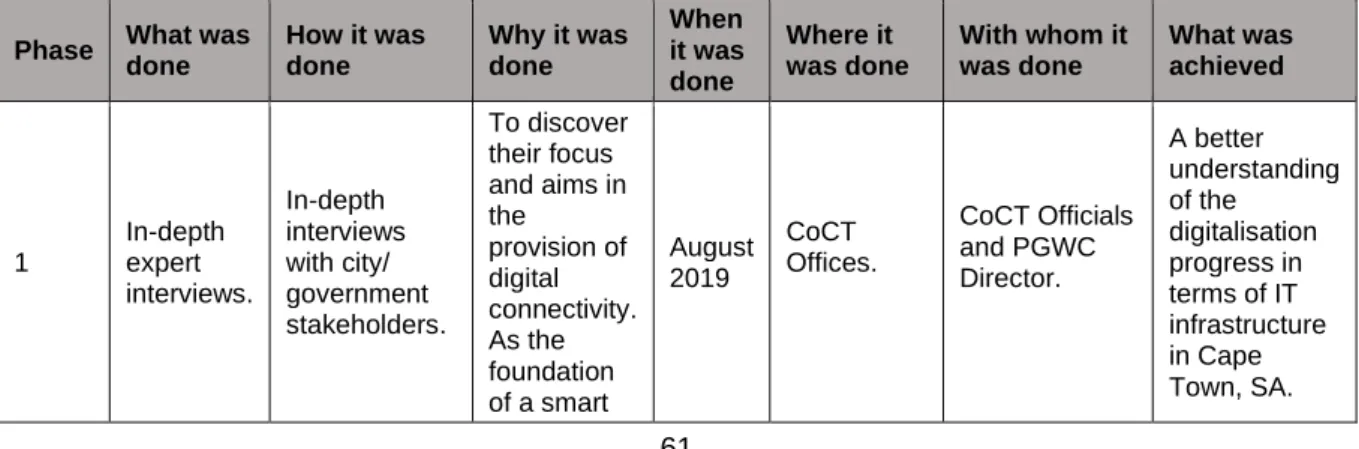
Findings of phase one
Four officials from CoCT officials and the Western Cape government were invited to participate in in-depth interviews. CoCT supports the ICT sector through financial and non-financial support of the ICT ecosystem - CoCT supports the ICT sector through annual funding and non-financial cooperation with various groups in the ecosystem - including support to sector bodies such as the Cape Innovation Technology Initiative (CITI ). CoCT collaborates with the province, CITI and private sector stakeholders in supporting skills development in the ICT sector that enables companies to obtain resources.

Findings of phase two
Do you believe that attracting Chinese tourists is a unique challenge more than tourists from other countries? They are one of the few countries in the world that do not speak as much English as other countries. R1 The Chinese tourists want to know in advance where they will sleep, the length of their stay.

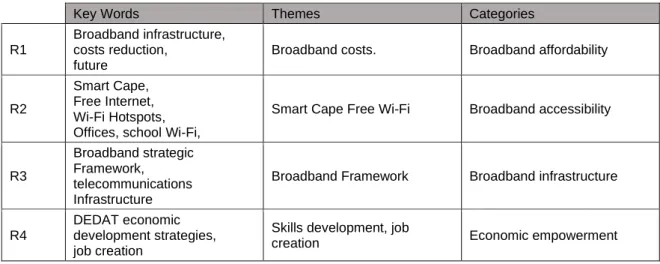
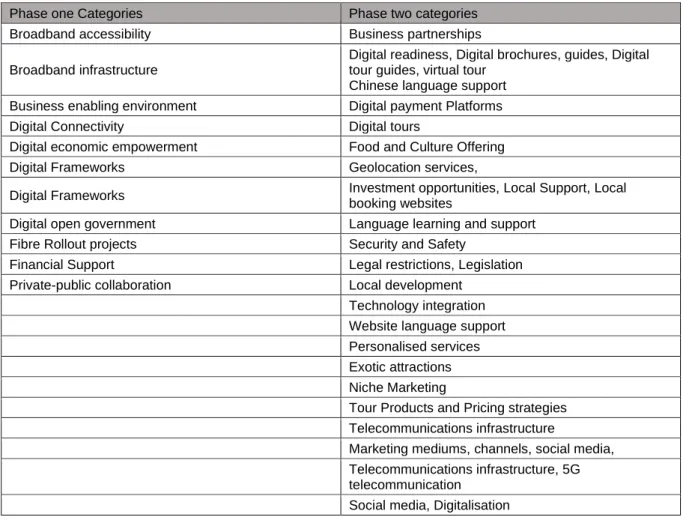
Summary of key words of findings, themes and categories of phase one
This is definitely going to pique their interest, and possibly I could end up being the next tourist. The Provincial Strategic Plan, growth and development of the provincial economy through the support of broadband use. Cape IT Initiative, Wesgro, IP Regulation - Coordination and Management in the Regulatory Environment, and the models for government.
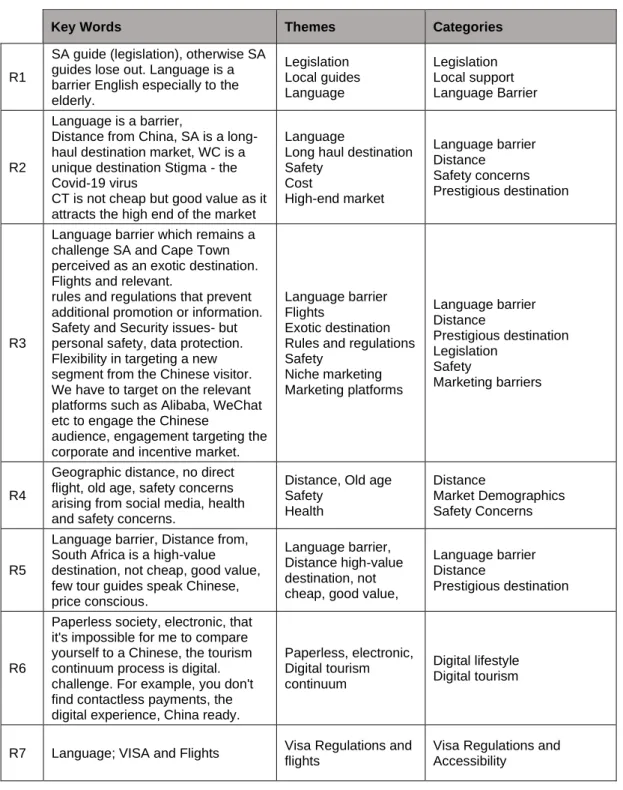
Summary of keywords and findings of phase two of the data collection
Geographical distance, no direct flight, advanced age, safety issues due to social media, health and safety issues. Network Coverage, Cape Point, Environmental Law, Walk-in Video Tour - no Chinese language support, more websites and applications are needed. WeChat is more convenient than UnionPay, technology enabler, Cape Town's fresh air and free open country.
Summary
Cape Town can attract more Chinese tourists by offering personalized services, better pricing and payment platforms. The study revealed Cape Town's efforts to develop into a smart city and thus a smart destination. The previous interviews revealed the challenges that tourism faces and how Cape Town can utilize technologies in tourism while attracting Chinese tourists.
Introduction
Findings and interpretations of phase one
Findings and interpretations of phase two
China is an emerging crucial tourism resource market that sees Cape Town as an exotic and prestigious destination. Cape Town's tourism stakeholders recognize China as an emerging tourism market with great revenue potential. The development of broadband infrastructure will accelerate digital connectivity in Cape Town and prepare it for the widespread use of 5G.
Summary of Interpretations
Cape Town needs to get ready for China by becoming digitally connected and preparing for widespread adoption of 5G and IoT devices. Although WCPG's strategic framework recognizes tourism as one of the focus areas of its digital strategy in Cape Town, their smart city initiatives focus on the citizens of Cape Town. In parallel with one of the objectives of the NDT, the tourism sector recognizes China as a potential emerging tourism market.
Introduction
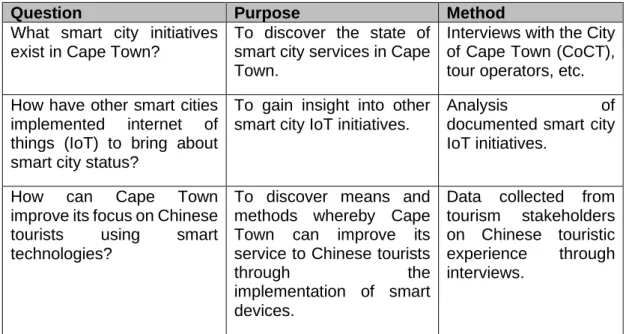
To determine the extent to which Cape Town can satisfy Chinese tourists in terms of smart city technology and services. Systematic literature review Analysis of literature and findings led to the recommendation of the Cape Town Smart Destination Development Framework. Suggestions on how Cape Town can improve its services to Chinese tourists through the implementation of smart devices and through the Cape Town Smart Destination Development Framework.
The extent to which Cape Town can satisfy Chinese tourists using technology and
How have other smart cities implemented internet of things (IoT) to achieve smart city status? Identify and make recommendations to smart city stakeholders on how a smart destination specifically targeting the Chinese market can be. Cape Town has implemented smart city initiatives through several projects and has recognized tourism as a strategic focus area for technology.
Cape Town’s current state as a smart city (destination)
However, the main focus was on broadband and infrastructure roll-out and skills development, with less effort on the application of digital trends in tourism. While smart technologies are anchored by an integrated and reliable broadband infrastructure, WCPG's broadband projects should simultaneously deliver smart city services and educate citizens about the use and importance of digital services to revitalize declining public services.
Smart City IoT initiatives in smart cities in the world
Through capital investment, pragmatic government policies and support, the city continues to develop and implement smart city initiatives with various objectives aligned with the principles of the Smart Africa Alliance and the UN's Africa Socio-Economic Development Agenda. Creating high urban value encourages socio-technical systemic solutions for Cape Town, such as smart city investor crowdfunding schemes. The development of a smart tourist destination requires leadership, vision, coordination, strategic management and constant evaluation.
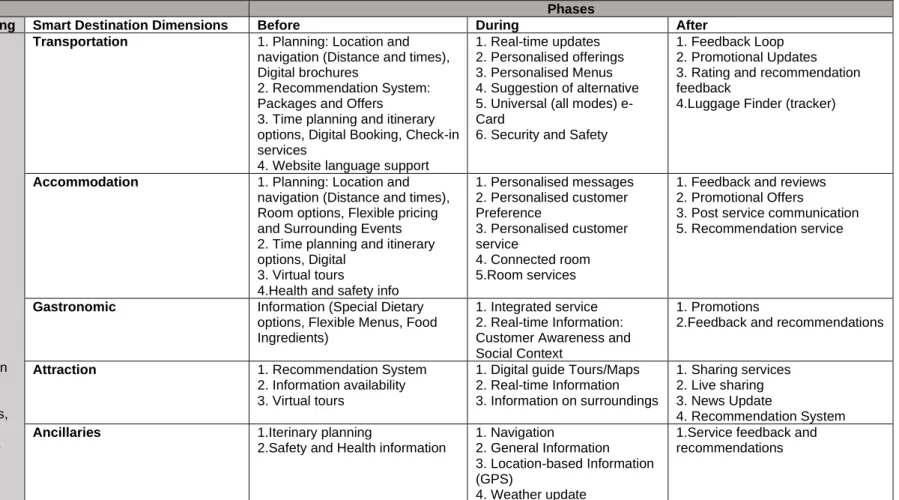
Cape Town Smart Destination Development Framework
The tourism challenges that the Government of Western Cape (2018a) aims to address are in line with the identified aspects that Cape Town as a smart destination is bypassing. Attractiveness - the study and findings identify Cape Town's attractiveness as having great potential, particularly the cultural and heritage centers that highlight its unique history. The smart city initiatives explicitly benefit citizens by providing open data portals for every aspect of government services to citizen services.
Contributions
Similarly, the research adopted a two-stage data collection process across the IT and tourism disciplines, collecting data from the City of Cape Town and tourism stakeholders respectively. Cape Town's Smart Destination Development Framework provides a concise framework that guides how digital tourism can be improved. The innovation of the research lies in improving the city life of citizens and tourists and developing sustainability and diversity in Cape Town and across South Africa.
Limitations and future research
Conclusion
Government needs to support Cape Town smart tourism small businesses to articulate the shift from e-tourism to 4IR experiential tourism through digital transformation in the tourism industry. Smart destination ideology is an underdeveloped area of research in the annals of African tourism. Building on BRICS: Unveiling Tourism and Investment Opportunities at the 2018 BRICS Summit.
R1 CoCT has enabled the environment by providing over 848 km of broadband infrastructure in Cape Town that will help reduce telecommunications costs in the near future. R1 CoCT supports the ICT sector through financial and non-financial support of the ICT ecosystem - CoCT supports the ICT sector through annual funding and non-funding collaboration with various groups in the ecosystem - including support to sector bodies such as the Cape Innovation Technology Initiative (CITI).