Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:S:Structural Change and Economic Dynamics:Vol11.Issue1-2.Jul2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
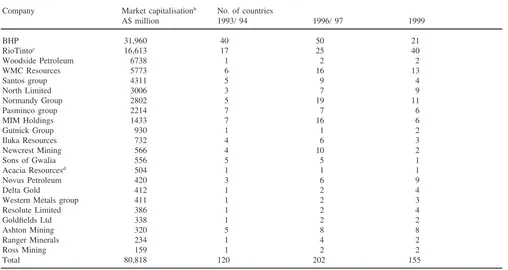
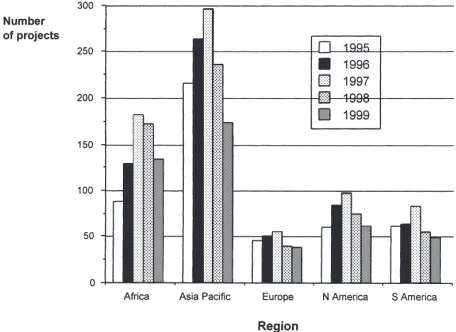
Dokumen terkait
In a constant-returns-to-scale production system in which each commodity is produced by primary factors alone and is subject to Hicks-neutral technical progress (HNTP), the
(Marshall, 1873, pp. The restrictions Marshall imposes on this very generous principle — which allows economists to use their own experiences and judgement as part of the
Keywords : Economic structures; Structural change; Exchange and production approaches; Leontiev – Sraffa horizontal models; Vertically integrated models (Pasinetti);
2. Responses to balanced stimuli. There are systems that are complex enough to react constructively to general top-down stimuli. In these cases, a pattern of structural evolution
As a result, special emphasis has been laid upon the analysis of growth in a wider context, and thus on topics such as technological change, the institutional and bureaucratic
The cornerstone of that framework is the zero - bequest sa 6 ing function which represents the aggregate cross-sectional saving rate that satisfies the zero-bequest
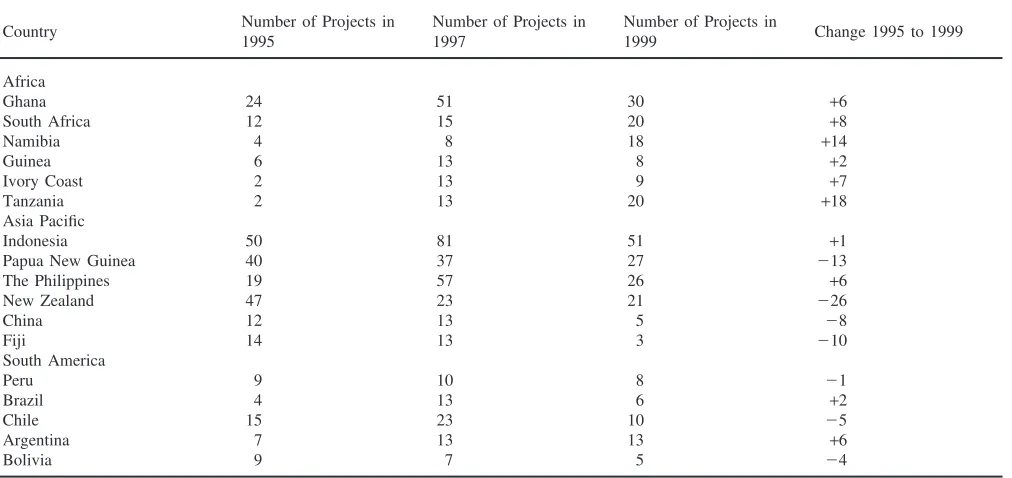
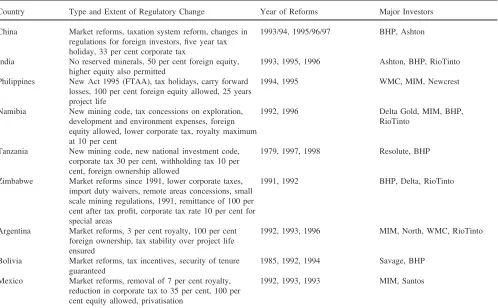
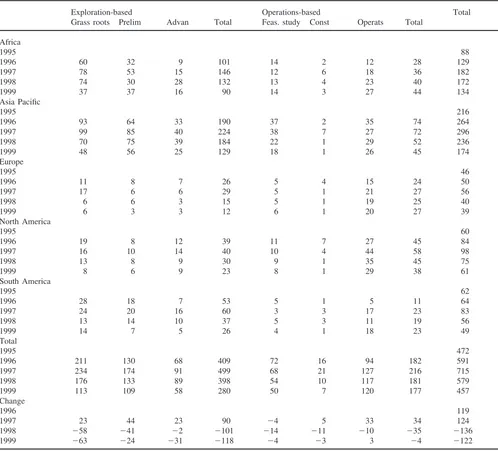
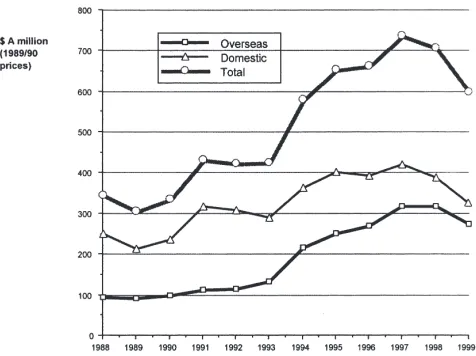
Data from the centralised performance tests for young beef bulls in South Africa were used to determine the minimum test duration required to obtain an accurate measure of feed
In sum, in contrast to White (2000), the sustain- able ecological footprint criterion for nations may not yield a welfare maximizing sustainable world, the solution to malnutrition