Introduction
Rationale
This syllabus is designed for students who wish to study Chinese as an additional language and who have studied P-10 Australian Curriculum: Chinese or similar. Chinese is a general subject suitable for students interested in pathways beyond school leading to further study, vocational training or work. For example, those who value the knowledge of an additional language and the intercultural understanding it encompasses, such as business, hospitality, law, science, technology, sociology and education.
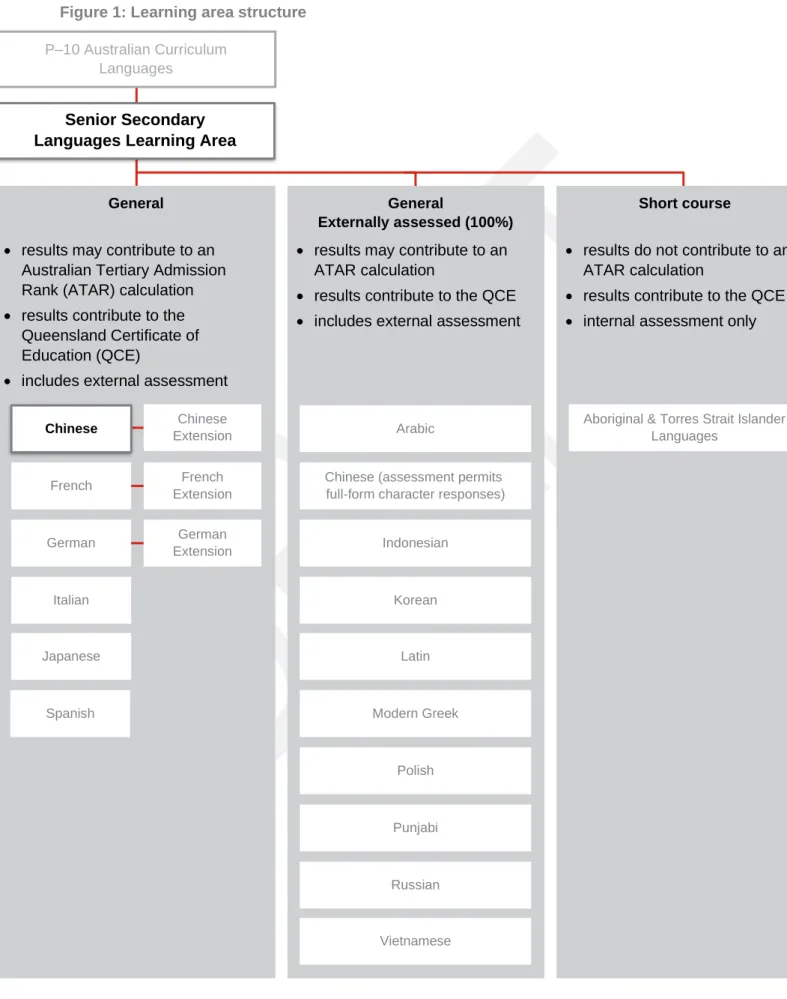
Learning area structure
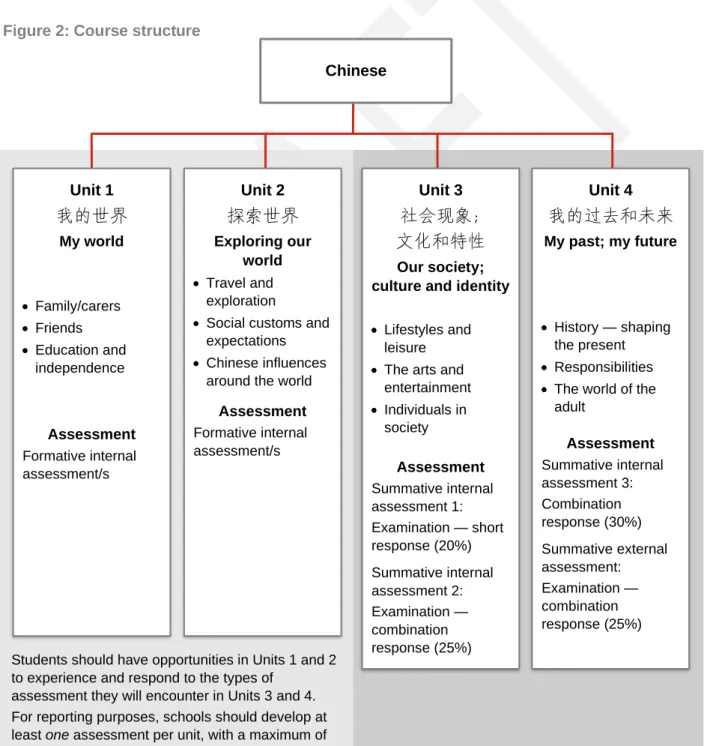
Course structure
Teaching and learning
Syllabus objectives
When students use strategies to communicate in Chinese in different ways, they use language knowledge to establish meaning and awareness of sociolinguistic conventions.
Underpinning factors
These aspects of literacy knowledge and skills are embedded in the syllabus objectives, unit and subject objectives, and instrument-specific assessment guides (ISMGs) for Chinese. These aspects of numeracy knowledge and skills are embedded in the syllabus objectives, the unit and subject objectives, and the ISMGs for Chinese. The 21st century skills identified in the following table reflect a common agreement, both in Australia and internationally, on the skills and attributes students need to prepare them for higher education, employment and engagement in a complex and rapidly changing world.
These elements of 21st century skills are embedded in the curriculum objectives, unit and subject objectives, and ISMGs for Chinese.
Aboriginal perspectives and Torres Strait Islander perspectives
Pedagogical and conceptual frameworks
In this way, each student develops their ability to listen, read, speak, watch and write in Chinese. Using a dictionary is one of the problem-solving strategies used by language learners and is useful for. Dictionaries can also be used to confirm the literal meaning when a word or phrase is unfamiliar to a student.
Although the use of a dictionary is not an assessable skill, dictionaries may be used for assessment where this is indicated in the syllabus.
Subject matter
学生将在学习计划的第一和第二单元中接触必修的语言元素。下面的强制性语言元素提供了强调语法用法而不是指定特定词汇的句子或短语的示例。她年纪大,我小;接着就,随即;与...相同;他说话像你一样流利吗?我跑不了他那么快。
我离开。我先走了。回头见!慢慢走。慢慢吃。
Text types and structures
Kinds of writing
Assessment — general information
Formative assessments — Units 1 and 2
Summative assessments — Units 3 and 4
Evidence of student performance assessment on each criterion is matched to a performance level descriptor that describes typical characteristics of student work. When a student response has characteristics from more than one performance level, a more appropriate approach is used. When the performance level has a two-point range, it must be decided whether the best fit is the higher or lower grade of the range.
Schools and teachers should have strategies in place to ensure that work submitted for internal summative assessment is the student's own.
Reporting standards
Knowledge of the elements and structures of the Chinese language is applied to create texts that construct fragmented meaning. The student, by responding to and creating texts in a variety of contexts, demonstrates fragmented understanding of Chinese language information and fragmented application of knowledge of Chinese language elements and structures. They communicate their understanding and experiences of relationships through the use of information and ideas in texts and language, such as formal and informal spoken language, and develop a range of strategies to maintain communication.
Students generate and compare information about their own personal identity and that of others, and the cultural values associated with personal and wider lifestyles, leisure and education. The subject engages students with aspects of language and textual conventions – to convey similarities and differences, and to develop opinions about the lives and interests of young people – in familiar and unfamiliar school and home environments.
Unit objectives
Skills: Understanding how language works
Topic 1: Family/carers
Topic 2: Friends
Topic 3: Education and independence
Assessment guidance
In Chapter 2, students move beyond their personal world to how they engage with the world. They do this by exploring options for personal travel and tourism in Chinese-speaking countries and Australia, and by considering the associated cultural conventions. Their study focuses on the increasingly central role and influence of technology and media in their lives and the lives of their Chinese-speaking peers.
Students consider the ways in which Chinese culture has contributed to the world and reflect on their own experiences, compare options and express preferences, appreciating different cultural values. This provides the opportunity to develop knowledge and understanding of a variety of linguistic elements and textual structures; to communicate.
Unit objectives
Skills: Understanding how language works
Topic 1: Travel and exploration
Topic 2: Social customs and expectations
Topic 3: Chinese influences around the world
Assessment guidance
Unit description
Unit objectives
Skills: Understanding how language works
Topic 1: Lifestyles and leisure
Topic 2: The arts and entertainment
Topic 3: Individuals in society
Assessment
Summative internal assessment 1 (IA1): Examination —
Length: five short-answer written responses of up to 100 words per question with - three responses in English for tone and purpose, and analysis and evaluation - two responses in Chinese for context and audience, and analysis and evaluation. The table below summarizes the criteria, assessment objectives and mark allocation for the exam — short answer.
Summative internal assessment 2 (IA2): Examination — combination
The conversation should be recorded as evidence of the quality of the student response and made available for quality assurance processes. Time: 10 minutes of planning with a new, unseen stimulus text in Chinese plus up to 7 minutes of student-centered conversation in Chinese.
Unit objectives
In Unit 4, students focus on what it means to be a citizen of a community, and how that is shaped by the experiences of the past and the challenges of the future. This includes research into historical patterns and contemporary developments, and how these may impact students in their post-school future. Students consider possible plans for their future and how their plans, responsibilities and ambitions compare to those of young Chinese speakers.
As students research and discuss, and then create texts relevant to post-graduate students, they consolidate their knowledge and understanding of a range of language elements, structures and text types. Students are provided opportunities to use the Chinese language and explore their perspectives on issues related to their future and the future of their peers.
Skills: Understanding how language works
Topic 1: History — shaping the present
Topic 2: Responsibilities
Topic 3: The world of the adult
Assessment
Summative internal assessment 3 (IA3): Combination response (30%)
Criterion: Creating a multimodal response in Chinese (15 points) Criterion: Exchanging information and ideas in Chinese (15 points).
Summative external assessment (EA): Examination — combination
Criterion: Analyzing Chinese Texts in English and Chinese The Criterion requires students to:. respond to three to six Chinese stimulus texts, of which at least one is written and one is audio or audiovisual, which are. related to the subject of Unit 4. written text/s and transcripts of up to 1000 characters in length, when combined. respond in English and Chinese to unseen questions, scenarios and/or problems, e.g. interpretation of graphs, tables or diagrams. completing items requiring short and/or extended answers - responding to unseen stimulus texts. interpreting ideas and information in Chinese texts. analyze, synthesize and evaluate questions, scenarios and/or problems in response to Chinese language text/s. write in complete sentences, as appropriate, constructing a response so that ideas are retained, developed and justified. Students respond in Chinese to unseen Chinese questions, scenarios, problems, and/or stimuli. short written responses, up to 100 words per item. Total answer up to 400 words - answer in Chinese. No ISMG is provided for external assessment. performed highly trained or skilled in a particular activity; perfect in knowledge or training; expert. the condition or quality of being true, accurate, or correct; freedom from error or defect; accuracy or precision; correctness; in science, the degree to which a measurement result represents the quantity it is intended to measure; an accurate measurement result includes an estimate of the true value and an estimate of the uncertainty. accurate and precise; straight to the point; in accordance with or exactly. in accordance with a known truth, standard, rule, pattern, convention or fact; without errors or defects; punctual; correct in all details. the process by which a language other than one's mother tongue is learned, including culturally appropriate communication habits; also referred to as "second language acquisition". skilled very/very skilled or good at something; adequate satisfactory or acceptable expert in quality or quantity equal to. decomposes to ascertain and examine its component parts and/or their relationships; dissect or examine in order to identify essential elements, features, components or structure; determine the logic and reasonableness of the information; to examine or consider something in order to explain and interpret it, in order to find meaning or relationships and to identify patterns, similarities and differences. acquisition and application of knowledge, understanding and skills in real world or life contexts which may include workplace, industry and community situations; it emphasizes learning by doing and incorporates theory and application of theory, linking subject knowledge and understanding with the development of practical skills. a subject whose main path is work and vocational education; emphasizes applied learning and community connections; a subject for which a syllabus has been developed by QCAA with the following characteristics: results from courses developed from applied syllabuses contribute to QCE; results can contribute to ATAR calculations. use knowledge and understanding in response to a given situation or circumstance; to perform or use a procedure in a given or particular situation. value estimate the value, importance or status of something; judge or consider a text or work. appraise know or make a judgment about the worth or value of something; fully understand; understand the full implications of. suitable acceptable; suitable or suitable for a purpose, circumstance, context, etc. suitable for the purpose or occasion; adaptation, appropriate study area a division of, or a section within a unit. argue give reasons for or against something; challenge or debate an issue or idea; convince, prove, or try to prove by giving reason aspect a particular part of a feature of something; an aspect, phase or part. measure, determine, assess, rate, or make a judgment about the value, quality, results, outcomes, size, importance, nature, or extent of something. assessment is the deliberate and systematic collection of information about student achievement. assessment instrument a tool or device used to collect information about student achievement. drawn from the unit objectives and contextualized to the requirements of the assessment instrument. see also 'curriculum objectives', 'unit objectives').