The study assessed the technical efficiency of Pabda catfish production using stochastic frontier production function analysis. CHAPTER FOUR AN OVERVIEW OF PABDA MOSQUITO PRODUCTION IN BANGLADESH AND DESCRIPTION OF THE STUDY AREA.
Data Collection Method 91 -92
Theoretical Model of estimation of Technical efficiency
Summary Statistics of the Variables Used in the Stochastic Frontier Model
Technical efficiency index of the Pabda Catfish Producing Farm in the Study area
Policy Suggestions and Recommendation 135
It also has the potential to contribute more to the gross domestic product (GDP) of the country. Moreover, most people in Bangladesh depend on fish for their animal protein and fish provides 63.00 percent of the protein consumption (Rahman, 2009).

Statement of the Problem
Considering the above fact, the present research work was conducted to assess the effects of Pabda aquaculture on land use patterns in selected areas of Bangladesh. To our knowledge, no study has been done on these issues in relation to Pabna district or any other district in Bangladesh.
Objectives of The Study
Justification of the Study
The evaluation of Pabda catfish farming will reveal the need for catfish farmers to adopt new technologies and achieve sustainable production. This investigative approach provides a better understanding of the decision-making process of pabda catfish farming.
Framework of the Study
Limitation of the Study
It provides a theoretical basis for the study in question and helps determine the nature of the study. Indeed, research study tells a story, and the existing literature helps us identify where we are in history at the moment.
Theoretical Literature Review
Literature related with the Technical efficiency of Pabda fish farming in Bangladesh Rabbani et al., (2017) conducted a research on the technical efficiency for Setbag net fishing
Adnan et al., (2016) conducted a study on various aspects of marine fisheries and examined whether its potential exists for further contribution to the overall fish production in the country. The result of the study shows that management and cultural factors affect fish farming in ponds.
Literature related with the Technical efficiency of Pabda production in other countries
Gazi et al., (2016) conducted a study on stochastic frontier analysis of technical efficiency of cage fish farming in Peninsular Malaysia. Nades (2012) conducted a study on the technical efficiency of catfish and Nile tilapia farming in the Bangka Tengah region: a stochastic frontier production approach.
Literature Gap
72.3% of respondents were involved in rearing operations, i.e. rearing catfish to table size, while 8.4% were involved in the sole production of juvenile fish. Hence the use of stochastic production and profit models to measure the efficiency levels of the fish farmers, which are widely used in measuring efficiency.
Conclusion
That is, this chapter deals with such topics which are very important instrument to determine the technical efficiency of pabda catfish production in Pabna district. Thus, economic efficiency concerns the ability of a farm to produce the product at minimum cost, to obtain this minimum cost, the farm uses inputs in an efficient way (technical efficiency) and chooses a combination that minimizes the cost of input prices and marginal productivity.
The stochastic frontier production model
This chapter discusses production functions and some related concepts of technical, allocative, and economic efficiency. Technical efficiency involves the ability of a farm to produce maximum output from a given set of inputs using existing technology; allocative efficiency reflects the ability of a farm to choose the inputs in optimal proportions, given their input prices; and a combination of these two measures provides a measure of economic efficiency.
Production Function Analysis with Related Concepts .1 Definition and Classification of Production Function
Cobb-Douglas production function
After prioritizing labor and capital, the production function they showed was what is known as the Cobb-Douglas production function. If α+𝛽>1, the production function indicates the increasing returns to scale, if α+𝛽 <1, the production function implies the decreasing returns to scale, and if α+𝛽=1, the production function shows the constant to scale.
The marginal product of any input is defined as the change in total output due to a change in one unit of the input. The concept of elasticity can be applied to the production function to determine the stage at which farmers are allocating their resources.
Laws of production
Laws of variable proportions: Short-run Analysis of Production
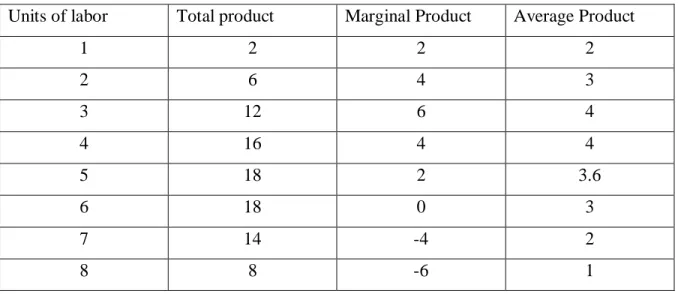
This means that until the use of certain amount of variable factor, marginal product of the factor may increase and after a certain stage it starts to decrease. From the table it can be seen that the marginal product of labor initially rises and beyond the use of three units of labour, it begins to decrease.
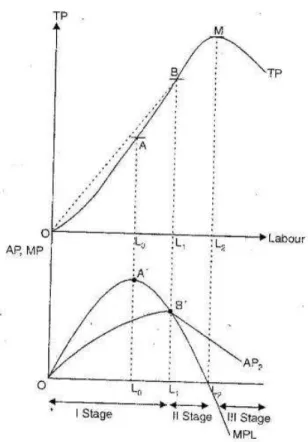
Stage of Increasing Returns
Using six units of labor adds nothing to the total production of pabda catfish. As for the average product of labor, it rises up to the use of the third unit of labor, and beyond that it declines throughout.
Stage of Diminishing Returns
Stage of Negative Returns
Law of Returns to Scale: Long-run Analysis of Production
If X* increases less than proportionally with increasing factors, we have diminishing returns to scale. It occurs when all inputs increase in a less than proportional increase in the level of output.
Productivity and Efficiency Measure
- Defining Efficiency
- Approaches of Measuring Efficiency
- Efficiency Model
It arises when an increase in all inputs leads to a more than proportional increase in the level of output. Thus, the production frontier is associated with the maximum achievable level of production, given a level of inputs, or the minimum level of inputs required to produce a given product. Technical inefficiency is attributed to the failure of the farm to produce the marginal level of output, given the quantities of inputs.
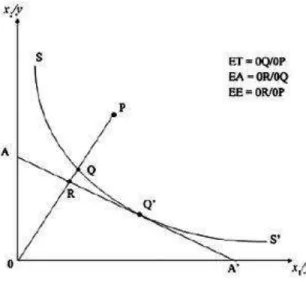
Conclusion
According to Kumbhakar and Lovell (2000), SFP function is oriented with two papers, published almost simultaneously by two teams on two continents. Unlike the deterministic model, the SFP function has a disturbance term with two components; the error component (v) and the stochastic noise (u). Furthermore, technical efficiency is the ratio of technically efficient costs to observed costs, economic efficiency is the ratio of marginal costs to observed costs, and allocative efficiency is the ratio of marginal costs to technically efficient costs.
Introduction
Aquaculture
In 2009, total aquaculture production excluding aquatic plants was 1064285 tonnes in Bangladesh (FAO world fisheries production, by catch and aquaculture, by country, 2009). According to FSRFD (2003), pond aquaculture, inland capture fisheries and marine fisheries contributed 41, 32 and 26 percent of the total fish production in Bangladesh respectively. Appropriate management strategies to develop sustainable aquaculture practices are still at a developmental stage in Bangladesh.
An overview of Fish Farming in Bangladesh
Fish is a popular complement to rice in the national diet, giving rise to the Bengali proverb Maache-Bhate ("a Bengali consists of fish and rice") (Ghose, 2014). The fishing sector plays a very important role in the national economy, contributing 3.69% to the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and 22.60%. Few reviews of the development and potential of fisheries and aquaculture in many parts of Bangladesh have been published and no studies have been published to date.
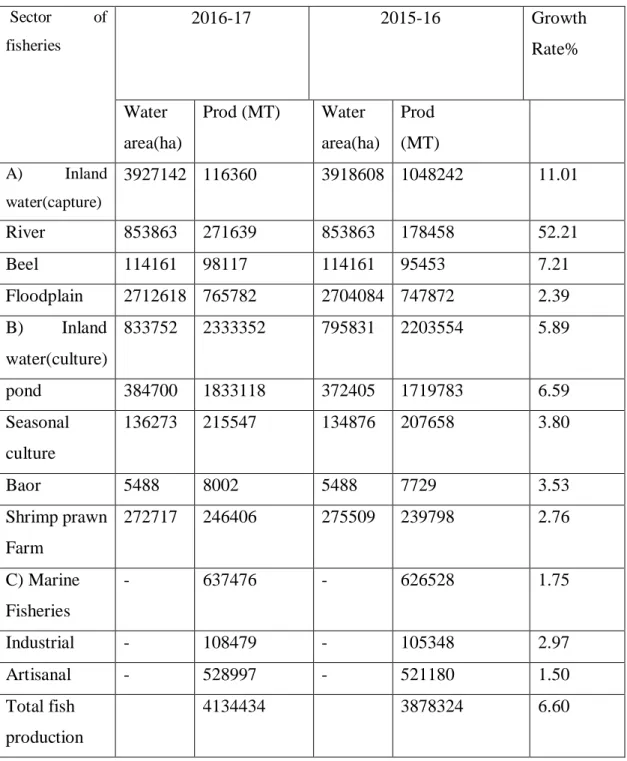
Production
- Inland Open Water (Capture) Fishery
- Inland Closed Water (culture) Fishery
- Marine Fisheries
The coastal and marine environment of Bangladesh is blessed with a warm tropical climate and high rainfall enriched with nutrients from the land, creating one of the richest ecosystems in the world with high productivity (Hossain, 2001; Islam, 2003). Exploration, exploitation and management of living and non-living resources of the Bay of Bengal can contribute significantly to the economy of Bangladesh. In particular, following the recent 2012 International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea (ITLOS) decision on the Bangladesh-Myanmar maritime boundary and the 2014 decision of the UNCLOS Arbitral Tribunal on the India-Bangladesh Maritime Boundary, sovereign rights have been established over more than 118,813 km2 of territorial sea. seas and 200 nautical miles (NM) Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and all kinds of living and non-living resources below the continental shelf up to 354 nautical miles from the coast of Chittagong (MoFA, 2014).
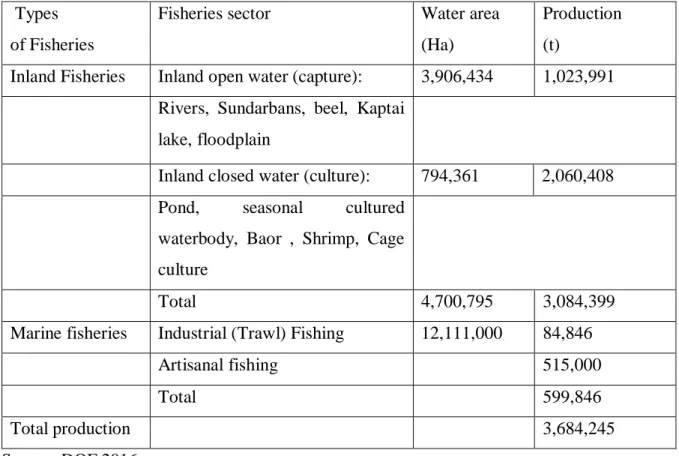
Fisheries Management System in Bangladesh
Farming systems distribution and characteristics
Three Indian large carps namely Labeo rohita, Catla catla and Cirrhinus mrigala and an exotic carp, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix now account for more than 78 percent of the total pond production (ICLARM, 2002). Setup mainly with the three Indian big and three exotic (silver, common and grass) carp, irregular use of fertilization (mostly cow dung) but no feeding. Regular use of fertilizers (both organic and inorganic) and supplemental feed consisting of rice bran and oil cakes..generally stocked and also freshwater prawns and Nile tilapia and striped catfish.
Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) Sustainable Fisheries Development Sustainable fisheries development is defined by FAO as fisheries development that integrates
Regular feeding of rice bran/wheat bran/oil cake and/or commercially produced pellet diet. Aquaculture accounted for about 43.5 percent of total fish production during 2003–2004, with inland open water fisheries contributing 34.8 percent (DoF, 2005). Taking the third position, Bangladesh produced a total of 10,48,242 tonnes of fish from inland water bodies in 2016, about 2.4 percent higher than 2015, according to FAO's fisheries and aquaculture report.
Importance of Fish Farming in the Bangladesh economy
In total aquaculture production, Bangladesh ranks fifth with production of 22 lakh tonnes in 2016, the report said. The report also said that Bangladesh produced 1,13,200 tons of fish from marine and coastal sources, ranking 11th on the list. Omega-3 fatty acids also lower the risk of age-related muscle degeneration and visual impairment; And.
Exports and Imports
The shrimp export for Bangladesh is mainly to the EU (Islam, 2008) The total imported fishery products in Bangladesh consisted of about 69.373% frozen sea fish followed by 25.353% chilled or ice fish (Fig. 8 and Table 9) (FRSS, 2016).
Environmental Impact of Fish Farming
4 Depletion of wild fish stocks for feed – wild marine fish are usually caught and pellets are made to feed farmed fish, especially shrimp. It is estimated that it takes 2.8 pounds of wild fish to produce one pound of industrially produced shrimp. Monoculture and invasive species – a major challenge for aquaculture is the need for fast-growing species that can withstand the conditions on farms.
Present situation of fish farming in Bangladesh
- Remarkable achievements and future potentials Some remarkable achievement
- Issues and plans
Citing a Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) report, Narayon Chandra claimed that the country's per capita fish consumption - about 63 grams per day - exceeded the required daily demand. To ensure continuity of the success, the government will give priority to conservation of jatka (small hilsa), protection of natural fish breeding grounds, expansion of shrimp cultivation, and collection of sea fish at a tolerable level, he said in a written statement. . The minister also said that the fisheries week will be observed across the country through various programmes, such as fair, seminar and rally.
Introduction of Catfish Farming
- Catfish varieties in Bangladesh
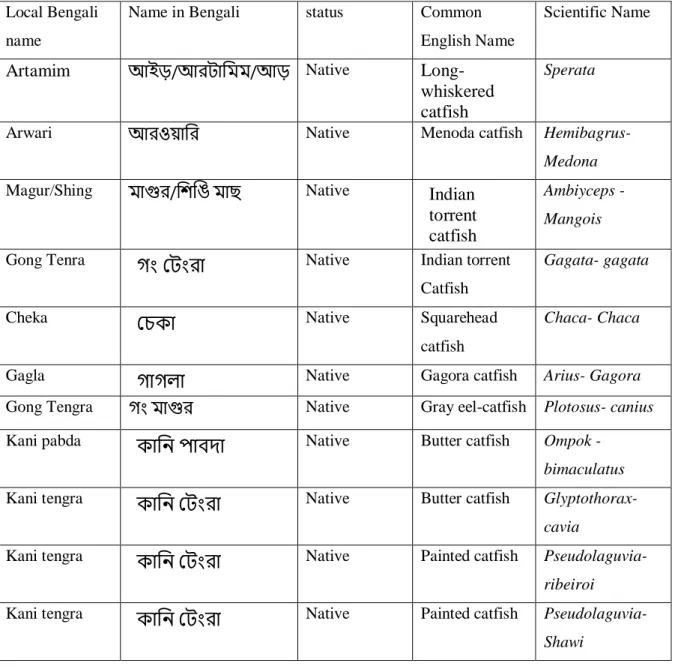
There are different types of catfish available in Bangladesh like Artamim, Arwari, Magur/Shing, Tengra, Pabda, cheka, pangus. In the case study we choose a catfish like Pabda.
Pabda (Ompok- Pabda)
The size of the pond for the cultivation of pabda fish can be any depending on the type of land available. You can use clay/natural, plastic, fiber, glass or concrete pond for breeding pabda fish. Pabda fish farming business requires relatively less investment and the profit from this business is very high.

Prospect and potential of Pabda catfish production in Bangladesh
You can expect to harvest the fish after 10-12 months of settling them in the pond. Pabda fish farming can create a great opportunity for people, especially the unemployed educated youth. According to the People's Republic of Bangladesh, in 2010 the country spent over N100 billion importing over 780,000 metric tonnes of frozen fish.
Constraints to Sustainable Fisheries Development in Bangladesh
The lack of fish supply in the country has resulted in a low annual per capita fish consumption rate of only 7.5 kilograms compared to 15 kilograms per year as recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FGN, 2011). Therefore, it is crucial to increase domestic production to meet the demand-supply gap and diversify the country's resources. Profit maximization requires that a firm produce the maximum output given the level of inputs used (that is, it is technically efficient), using the right mix of inputs given the relative price of each input (that is, it is allocative of inputs). efficient) and produce the right mix of outputs given the set of prices (that is, they are efficient in allocating output). Pabda catfish farming also plays a key role in boosting Bangladesh's aquaculture sector by directly and indirectly creating jobs for millions of people that help diversify the country's resources, earn foreign exchange through potential exports and help the country achieve the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).
Pabna district
- Chatmohar upazila Area and location
- Bhangura Upazila Area and Location
The area of high, medium and low land in the study area is high land 48 percent of total land while low and medium land is 8 and 44 percent respectively. In the study area there is no local meteorological center to record temperature and rainfall. Religious institutions in the study area at Atgharia Upazila of Pabna district are about mosque 161, temple 17, church 1.
Conclusion
This chapter also provides a description of the explanatory and dependent variables used in the study and the relationship between them. The design of any survey is primarily determined by the nature, aims and objectives of the study. The design of the survey for the current study in this chapter mainly involves the following steps.
Selection of Sample
- Selection of the study areas and Rationale
- Sampling Technique and Sample Size
- The questionnaire for data collection
- Data collection method
It was not possible to include all the farmers of the study area due to time, money and personal constraints. A multi-stage random sampling technique was followed in the present study to minimize cost, time and to achieve the ultimate objectives of the study. The second category contained information related to the costs and returns of the two selected crops.
Secondary Information
The third category of information was related to limitations and problems faced by the farmers in the production of Pabda fish. A combination of the participatory, qualitative and quantitative methods was used for the collection of information through rapid evaluation. The advantage of RRA over other methods is that it allows wider participation from the community, therefore the information collected is likely to be more accurate (Chambers, 1992; Chambers, 1994).
Mapping Workshop
Primary Study
- Method of analysis
- Theoretical Model for estimation of Technical Efficiency
- Selection of the Form of Production Function
- Model Specification and Estimation
- Choice of the Variables
- Stochastic Frontier Production Model
- Explanation of the variables used in the Model
- Variables used in Estimation of the inefficiency effect model
- Description Statistics
- Presentation of Result
- Distribution of the respondents in sample area
- Distribution of the Respondent according to age group
- Distribution of the respondent according to sex
- Marital status of the Respondent
- Distribution of the Farmer According to Family size
- Distribution of the Farmer according to the Number of children
- Educational status of the Farmers
- Main occupation of the respondent
- Distribution of the farmers according to experience
- Distribution of the farmers by receiving aquaculture training
- Farm Holding Size of the Respondent
- Source of aquaculture information of the respondent
- Distribution of the farmers according to cultivation technique
- Nature of problems of Pabda farmers in the study area
- Conclusion
- Production types and technologies
- Culture System
- Factors Determining/ Affecting Farm inefficiency
- Results of the Cobb-Douglas Production Frontier for Pabda catfish production The maximum likelihood estimates of the parameters of Cobb-Douglas frontier are estimated
- Effects on Economic Factors on Production
- Conclusion
- Major Findings and Conclusion
- Policy suggestions and recommendation