This is to certify that the thesis work entitled "A Study into the Use of the Dysfunction Mode and Effects Critical Analysis (DMECA) in a Power Plant" was carried out by Azizur Rahman in the Department of Industrial Engineering &. This is to certify that the thesis work submitted by Azizur Rahman titled "A Study on the Use of Failure Mode and Effects Critical Analysis (DMECA) in a Power Plant" has been approved by the Board of Examiners for partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Engineering in the Department of Industrial Engineering &. It will therefore be possible to assess and evaluate the criticality of the dysfunction causes.
Data for this study was collected from the respondents of the study area using the prepared questionnaire (Appendix A). In this study an application of the DMECA technique applied in an important power plant (maintenance and production for electricity) to analyze, evaluate and improve the efficiency of job management processes.
Motivation Behind The Thesis
Production and maintenance management is therefore closely linked to the success of the management process and addresses all three dimensions. In this study, the management process in the activities for production and maintenance is deepened. Management processes thus require a reliable method to assess risks and challenges in production and maintenance.
Thus, a practical method is needed that manages malfunctions related to the management process and addresses all dimensions of production and maintenance. This study includes management process dysfunctions related to plant operation and maintenance.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Related Works
Plan
- Related theory
- Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis (FMECA)
- Dysfunction Mode and Effects Critical Analysis (DMECA)
How to avoid the errors and/or mitigate the effects of the errors on the system. Assign an event rank to each error condition [i.e. estimate of the probability that the cause of failure actually occurs]. Actions likely to reduce the frequency of error conditions should also be recorded.
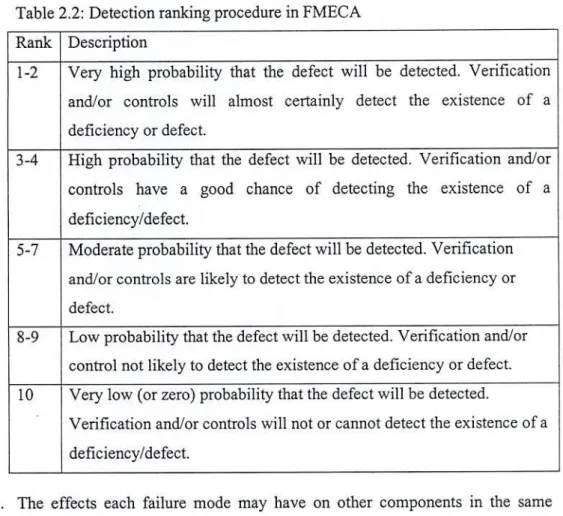
D = degree of probability that the defect will be detected before the system reaches the end user/customer. Identification of the failure modes most likely to cause the product to fail during operation.
DMEA
- General
- Research Methodology
- Prepare Process Breakdown Structure (General and detail map of the process)
- Prepare Dysfunctional Mode and Effect of the Related Activity
- Prepare Questionnaire and guideline to answer
- Data Processing and Analysis
- Organogram of Khulna Power Station (KPS)
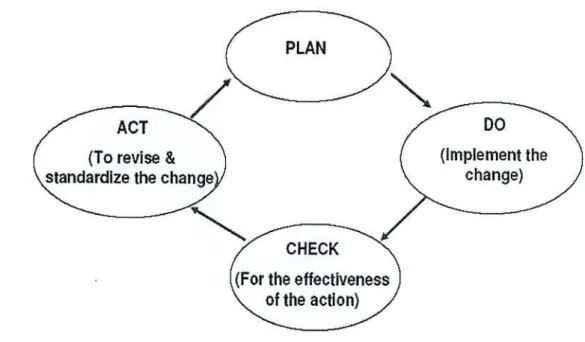
Evaluation of corrective action results - based on the results, the DMECA process can be restarted to implement new or redesigned activities. Several management personnel are requested to be interviewed to collect informational data associated with the state of dysfunction and effectiveness of the management processes. However, due to the availability of the different types of employees at a time in the factory, 5 employees were interviewed in each group.
Besides the salinity of the plant, the salinity is the main cause of corrosion of the boiler and condenser tube etc. In the rainy season, the salinity of the river is low and also less irrigation is required for the land. The causes of dysfunctional causes and its consequences of the related activities were prepared by the group discussion.
Most of the questions were close but few questions were kept open for the interest of the study. This pre-test was useful to find the gaps to detect erroneous questions and statements in the draft questionnaires to achieve the objectives of the study. Necessary additions, modifications and adjustments were made in the questions based on the feedback from pre-test.
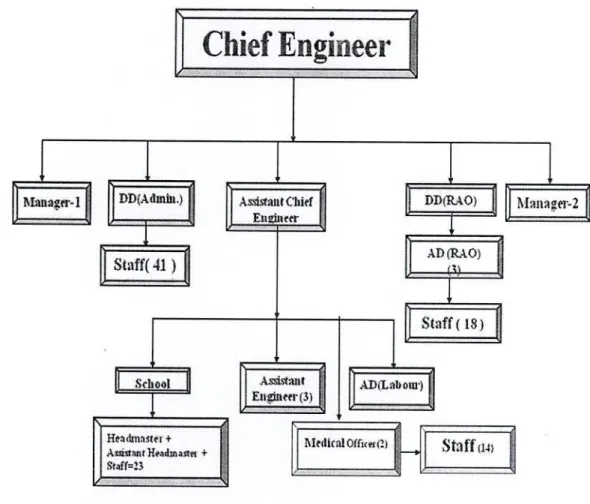
1 3.2.5 Procedure of Data Collection: Data for this study was collected from the respondents of the study area by using the prepared questionnaire. In this way, the overall picture of the study was identified to point out various dysfunctions in the management process. To analyze the management process of Khulna Power Station (KPS) it was necessary to know about the organization chart.
MANAGER-2
Management Process Identification and Process Breakdown Structure
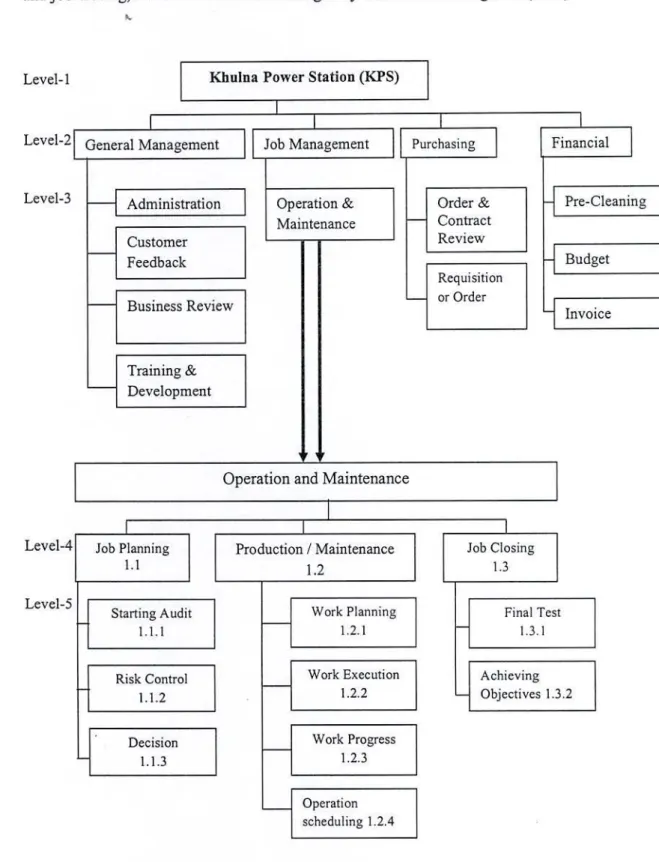
For this study, the input for mapping management processes was the five-level organizational chart reported in Figure 4.4 (breakdown of processes), where level-. In the job management process - the executive engineers are responsible for operation and maintenance, another level of managers (Sub-Divisional Engineers (SDE) and. In Figure 4.4, the 4th and 5th levels of the operation macro process were more detailed because this is the purpose of DMECA- the analysis.
The second step consists of breaking down the sub-processes of Figure 4.4 to the level of detail required for the analysis – that is, down to elementary activities as shown in Figure 4.5. In the process breakdown structure defined during the process identification phase (reported in Figure 4.4 for the firms' processes) 09 sub-processes and 57 activities of job management process were identified. Proponents of the well-known conversion tables (Table amp; 4.5) proposed to translate linguistic judgments into numerical values used to obtain a Risk Priority Number (RPN) that should not be applied in the second because it is appropriate and defined for maintenance activities, rather than management processes.
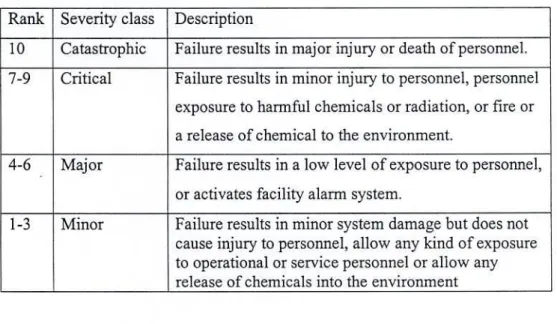
It is therefore necessary to redefine evaluation factors, acceptability limits and conversion criteria for the parameters used to determine the RPN's context of the management process. For Occurrence Dysfunction (OD), six levels (reported in Table 4.2) were identified, ranging from 'irrelevant' to 'very high' and described by Arabic numerals 1 to 10 [2]. Very high <2 weeks (< 13 days) > = 50 10 For the Detectability of Dysfunction (DD) judgement, a qualitative linguistic evaluation table was proposed as reported in Table 4.3.
For this case study, the mission was proposed considering time and quality results (Table 4.4) as critical variables [2]. The next step was the evaluation of possible dysfunctions and the identification of the related causes, assigning a value to the three factors: probability, detection and gravity. In the process decomposition structure defined during the process identification phase (reported in Figure 4.4 for the companies' processes), there are 09 sub-processes and 57 activities in the job management process have been identified.
Data Collection
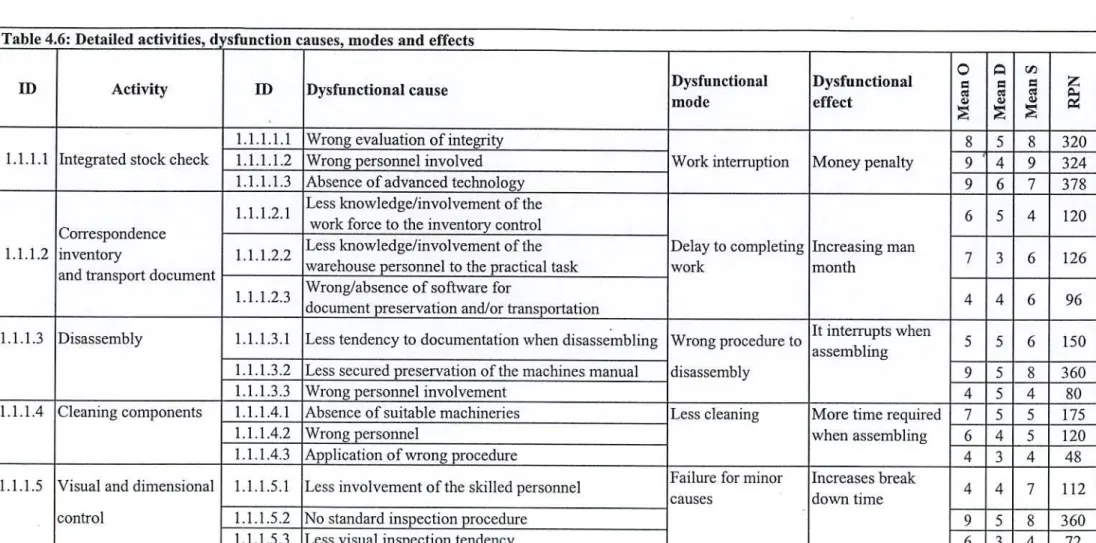
Based on the DMEA phase described above, a criticality analysis (CA) phase was performed for each identified dysfunction. A b What is the weight value of this type of dysfunction as described in Table 4.4. The mean values (from all questionnaires) of the three parameters (OD, DD and SD) for each dysfunction are then calculated.
Values for RPN can range from 1 to 1000, with 1 being the lowest possible management dysfunction. In the case of a process with a relatively high RPN, the engineering team should make every effort to implement corrective measures to reduce the RPN. Similarly, because a particular concern has a relatively low RPN, engineering teams do not overlook the causes and neglect efforts to reduce the RPN.
In this case, a low RPN can be extremely misleading, understating a cause where the severity level could be catastrophic. Overall, the purpose of the RPN was to list the various causes in the document [7]. The smaller the RPN the better - and - the bigger the worse. Missing/incorrect assessment of conformity of spare parts Delay with possibility of work interruptions Delay with possibility of work interruptions.
Identification of Critical Activities
Certification of collected redundancy and the information noise. The real data is not in order. Difficult to identify 1.1.1.7.
Identification of Corrective Action
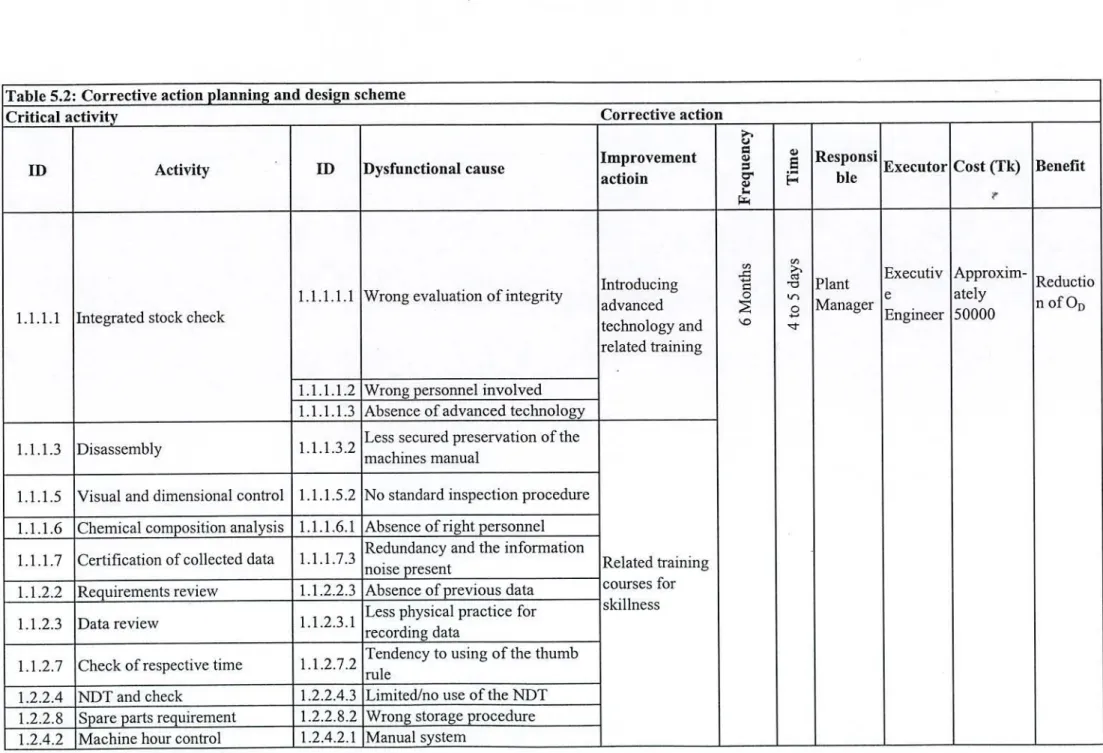
Similarly, checking the capabilities of welders and machine operators can eliminate two dysfunctional problems associated with welding and machine operation activities, respectively. For the activity 1.1.1.6 Chemical Composition Analysis, a related chemical composition analysis training was proposed as a corrective action to reduce the relative RPN factor, as listed in Table 5.2.
Conclusion
To analyze the managerial dysfunction in any organization, DMECA approach is very effective and it involves low cost as found in the research work. So it is cost effective and can be used to identify deficiencies in management personnel which will be useful for uninterrupted production and/or maintenance. An application of the DMECA technique implemented in important power plant industry (maintenance and production for electricity) to analyze, evaluate and improve the efficiency of job management processes suggests that it would also be interesting to apply the method in the area where the measurement of process efficiency is more difficult than the production activities.
There is already an application of the DMECA technique in a major power plant to analyze, evaluate and improve the process efficiency of task management. Ensure that all personnel who will be involved in the DMECA are made aware of the potential benefits arising from DMECA and the need for corrective action. DMECA is more cost-effective in the early phase of the management plan than in a later phase, when the plan is nearing its final stages.
It is never to ignore the participation of a less influential individual and allow important dysfunctions to be easily overlooked with comments such as,.
Recommendation for Further Study
Specification Risk Analysis: Avoiding Product Performance Deviations Through an FMEA-Based Method', International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, Vol. Pristop k analizi procesov, ki temelji na FMEA", International Journal of Process Management and Benchmarking, Vol. 1995) "Uporaba in ocena IDEF3 – metoda zajema opisa toka procesa", International Journal of Operations and Production Management, Vol. Total Quality Management", Pearson Prentice Hall, P Ed. model analize', International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, letnik 2004) 'FMECA pristop k sledljivosti izdelkov v prehrambeni industriji', Food Control.
Procedures for performing a failure mode, effect and criticality analysis, Department of Defense, USA. 2000) 'Monte Carlo simulation approach for a modified FMECA in a power plant', Quality and Reliability Engineering International, Vol. 2002) 'Design, implementation and integration of FMEA methodology with the HACCP system in a food company', Food Control, Vol. 1993) 'Failure mode modeling and impact analysis', International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, Vol. Delay with loss of efficiency 1.2.1.3 Checking workloads 1.2.1.3.1 Missing/wrong discovery of resource saturation opportunity and. 1.2.1.3.2 Missing/wrong finding of overlapping use of machines for work allowance interruptions, fines 1.2.1.3.3 Missing/wrong planning with GANT1' chart.
1.2.1.4.2 Missing/wrong finding of suitable machines for non-external work. 1.2.1.4.3 Missing/misallocation of suitable space for work compliance.