First of all, we express our sincere thanks and gratitude to Almighty Allah for His divine blessing which enables us to complete this project successfully. Our supervisor's deep knowledge and great interest in the field of wireless networks influenced us to carry out this project. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to other faculty members and staff of ETE Department of Daffodil International University.
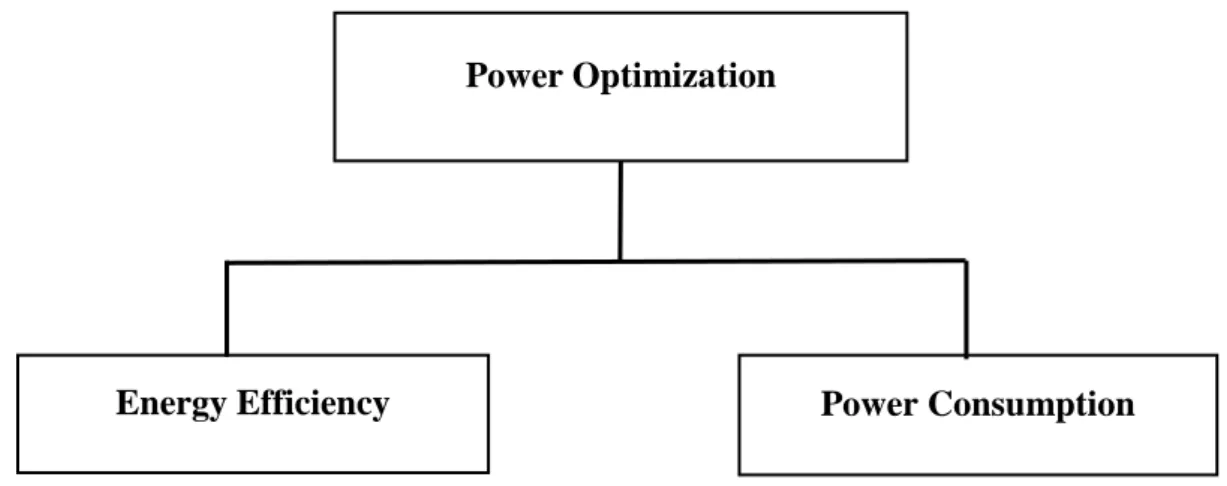
Power optimization infrastructure is needed to meet demands for increased capacity, better data speed and better quality of service of the next generation networks. The study shows some power optimization techniques and a hybrid power generation system for delivering power in the base station. The power optimization part is mainly divided by two parts, one is energy efficiency and the other one is energy consumption.
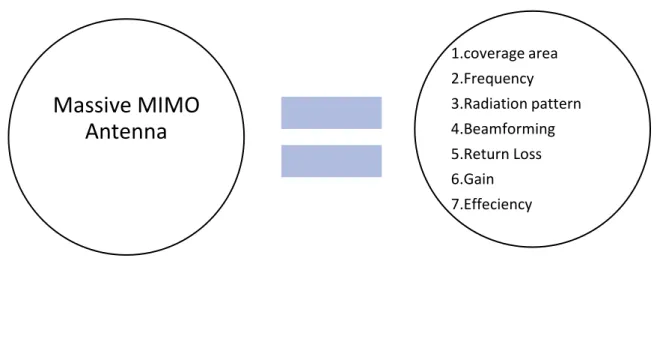
In this study the power optimization part is simulated by MATLAB software where the terminologies are coverage area, beamforming, return loss, impedance of mass mimo antenna and also sleep mode of mimo antenna during low transmission time. This project also summarized the architecture of the integrated power system using renewable energy sources and the monthly load measurement for an entire base station is simulated by Homer pro software.
Introduction
Aim and Objectives
- Aim
- Objectives
Report formation
- Communications technology
- Wireless communication
- The evolution of wireless communication
- Power Optimization
- Hybrid Energy based power generation system
- Green communication
- Smart city
In recent decades, following the first wave of mobile networks in the early 1980s, modern wireless communication infrastructure has gone through many phases. In the 1950s, Maxwell predicted the idea of wireless transmission of electricity, as demonstrated by Hertz in 1888. Analogue cellular networks (1G) such as Scandinavian mobile phones and advanced mobile phone services emerged in the early 1980s.
One of the 3G standards is the Unified Wireless Telecommunication Network, a GSM counterpart and developed by 3GP. The concept of multi-hop in-band and out-of-band relays, which can contribute to increase the coverage area and make the network more energy efficient, has been introduced in the new emerging markets such as the 3GPP LTE-A and the IEEE 802.16. j standards. The energy efficiency of the next generation networks is necessary to meet the demand of their subscribers.
A large part of the energy generated in the base station is absorbed by a large amount of energy. So, gaining energy efficiency has signed few economic benefits, not only from the producer's point of view, but also from the consumer's point of view. The energy efficiency of wireless communications is also important from the customer's point of view.
The key concept is to provide base stations in the same time-frequency network with different antennas that are used to support multiple terminals simultaneously. RETURN LOSS Return loss is the loss of power of the returned signal/expressed in the interruption of the transmission line. Energy consumption and the resulting energy pollution are becoming the main operational and economic issues in the communication space.
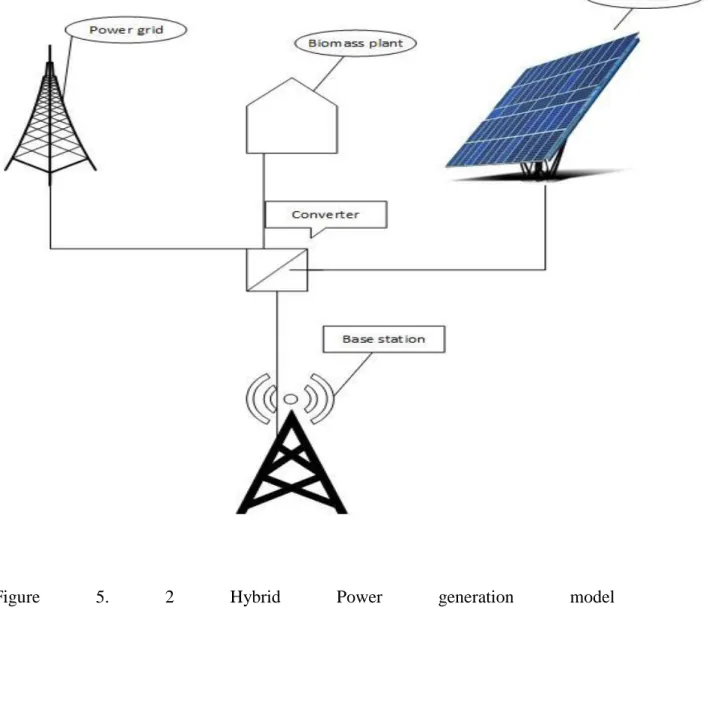
Bangladesh is an agricultural region, vegetable waste, city waste and cattle manure, which are also abundantly responsible here for the main source of biomass energy system and unlimited solar energy from the sun. In the recent past, there has been great success and competition in the telecommunications industry. Second, the cost of energy is the main element in the pro equations for telecommunications network operators.
Overview
Power optimization
Energy-efficient technologies must be implemented to meet the demands of greater capacity, better data speeds and improved service efficiency in next-generation networks. AKSHITA ABROL, (Student Member, IEEE), AND RAKESH KUMAR JHA, (Senior Member, IEEE) discuss various technologies on the energy optimization in smart cities using green communications. Imran Ashraf, Federico Boccardi and Lester Ho, Alcatel-Lucent discuss the sleep mode for the base station.
At the University of Sheffield, Mappin Street, Sheffield, S1 3JD, United Kingdom they are discussing the use of small cells for a 5G base station.
Hybrid Power Generation System
- Methodology
- Preparation
- Energy efficiency techniques
- Massive MIMO Antenna
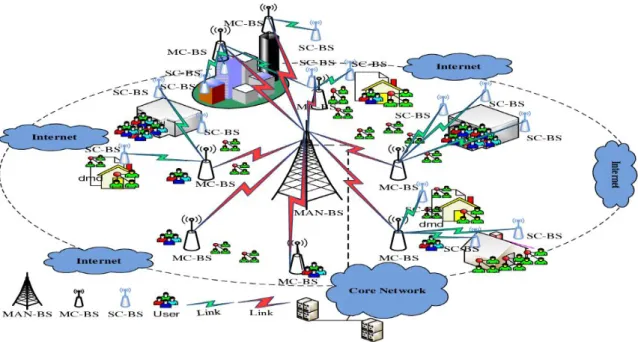
- Small cell Base station
- Power consumption
- Hybrid Energy Based Power Generation System
In every sector of the economy, whether in housing, infrastructure, manufacturing or energy generation, tremendous prospects for improvements in efficiency are present. The main purpose of small cells is to increase the capacity, speed and total network output of the macrocell's edge data. The ultimate goal is to use the renewable energy for the supply of the power that is able to defend the necessity of the power.
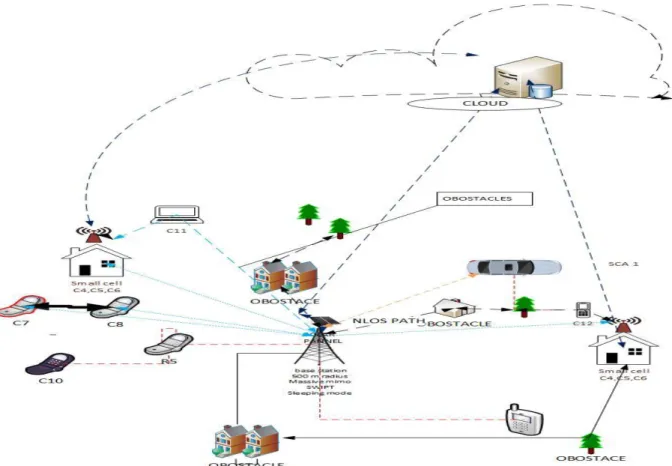
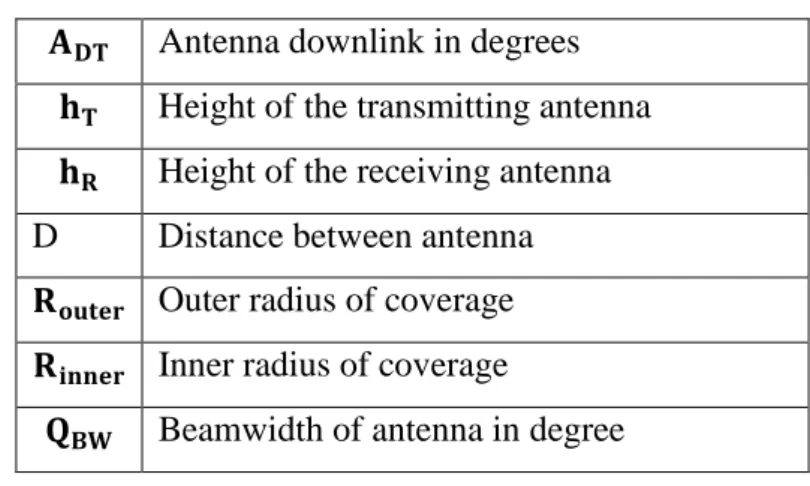
Such base stations maintain the network coverage of the cell that can be used to transmit voice, data and other service types. The antenna turns off in degree, outer radius of the antenna, inner radius of the antenna can be found from the coverage area of the antenna. Beamforming is essentially the linear combination of the product outputs, which can be measured with a beam.
Power gains, or simply antenna gains, are a key performance figure that correlates with antenna directivity and electrical efficiency. Antenna output power is a measure of the energy received by the antenna compared to the antenna's power output. Most of the energy at the source of the antenna radiates from high.
When the load is high, which means during the office hours, the required power is high, but the rest of the time, except the office hours, the necessity of the power is less. According to the vacuum movement of all light waves at the same time, the number of wave crests that reach a point in one second depends on the length of the wave. When the base station enters sleep mode during the low power transmission time, it used 60% of the power.
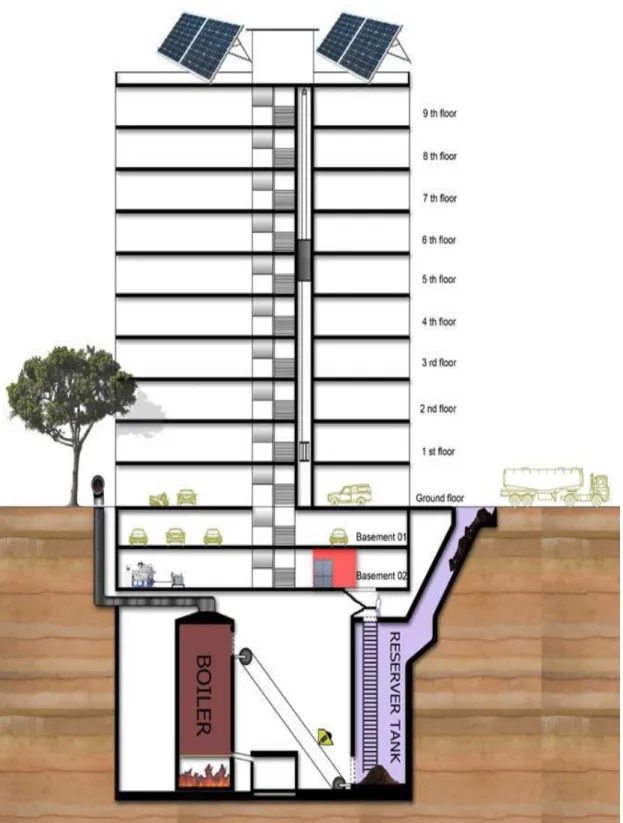
If it remains active during the low power transmission time it requires 100% of the output power. The variation of the hybrid power generation system per month is shown in Figure 6.18 Per day for a base station covering 200 𝒎𝟐 area requiring 11 kw of power. One of the major limitations is the implementation of small cell technology under one base station.
Hybrid power generation model
𝐀𝐃𝐓 Antenna downlink in degrees 𝐡𝐓 Height of transmitting antenna 𝐡𝐑 Height of receiving antenna D Distance between antenna 𝐑𝐨𝐮𝐭𝐞𝐫 Outer coverage radius 𝐑𝐢𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐫 Inner coverage radius. The power generation system is set up for a small area where a base station can cover 200 𝐦𝟐. Where running one base station per day requires 8 kW of power per hour. When the business hour is over and the base station goes into sleep mode, it may consume power and then our old LTE mode is active.
The power delivery system is based on hybrid power generation system that includes biomass, solar power and the grid.
Data Analysis
- Massive MIMO antenna
- Coverage analysis of MIMO antenna
- Beamforming
- Return loss
- Impedance of mimo antenna
- Gain of the MIMO antenna & SISO antenna
- Efficiency of massive MIMO antenna & SISO antenna
- Power consumption by sleeping mode
- Power Delivery from Hybrid Model
- The analysis of Hybrid power system
Multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) is a multi-path network method for increasing network connectivity.[1] MIMO has become an essential element in the wireless communication protocols, including IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi), IEEE 802.11ac, HSPA+ (3 G), WiMAX (4 G) and Long Term Evolution (4 G LTE) standards and multi-path multi-input and multi-output (Wi-Fi) system. Return loss is the power loss in the signal that is reported/reflected in the transmission line or optical fiber in telecommunications. The return loss is related to both the SWR and the reflection coefficient. A low-efficiency antenna loses most of its power as defects in the antenna or as a result of a defect in its impedance.
In 5g for driving one single base station requires 192kw power to cover 200 𝐦𝟐. But there are so many small base stations that are also needed to implement the 5g. When data traffic is high, it can be on active mode, but when the office hours end and the ratio of data traffic is low, it can go to sleep mode, respectively. To analyze the hybrid power generation, some data were collected from the MSW collection and energy efficiency research or investigations in Bangladesh.
Results
- Massive MIMO Antenna
- Coverage of MIMO antenna
- Beam-forming
- Return loss
- Impedance
- Gain of the massive mimo vs siso antenna
- Energy efficiency in massive mimo Vs siso antenna
- Power consumption
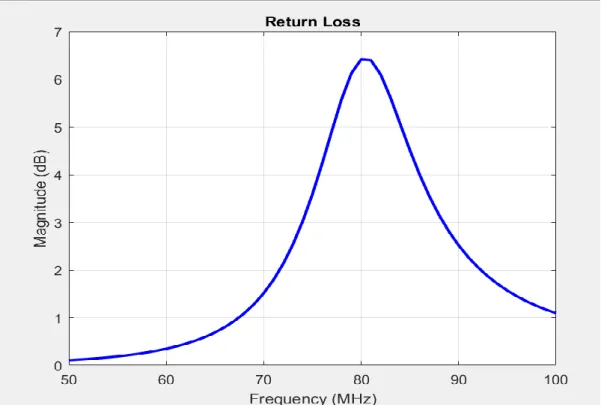
From the return loss analysis, we found that the return loss in mimo antenna for 200 𝐦𝟐 is 6.02 db. The return loss for SISO antenna is approximately 15 dB and the MIMO antenna is 6.02 dB. So the return loss of the MIMO antenna is less than the SISO antenna. With distance from the antenna, the impedance changes and shows opposite distributions for the dipole and the circuit.
The dipole, the primary radiation source of the electric field, shows a small distance from the radial ring, α/2μ, while the magnetic dipoles which can be called a circle show a limit in the impedance. This crossover takes place very close to the system and the strong separation means that we are in a receptive environment. The wave impedance for the dipole and the layer increases and increases beyond the beam-sphere distance (β/2α), respectively.
The wave impedance has not even converged at a distance from the antennas of 5 μ/2т-1μ, which means it is still not far enough. The values of wave impedance are almost equal to 377 regular at a distance of kα/2α=1 and higher.
Conclusion
Limitation
Scope of future researches
34;Multi-objective optimization of 5g mimo massive wireless networks towards power consumption, uplink exposure and downlink." Energies. 34;TOKA—Energy Aware Radio and Network Technologies IEEE 20th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications.
34;Characterization of Energy Efficiency and Implementation Efficiency Relationships for Green Architecture Design IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops. 34;Green cellular—Optimization of the cellular network for minimal emission from mobile stations IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronics Systems.