By:
Dede Rika Kurnia Anas
109014000049
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
THE SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ii
The Effectiveness of Using Card Games Technique in Teaching Vocabulary
(A Quasi Experimental Study at the Seventh Grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang)
“A Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata I (Bachelor of Art) In English Language Education
Approved by:
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS
’
TRAINING
THE SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ENDORSEMENT SHEET
The Examination Committee of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training certifies that the "slvipsi" (Scientific Paper) entitled The Effectiveness of Using
Card
Games Techniquein
Teaching vocabulary(A
euasi-Experimentalstudy at the Seventh Grade of sMP Negeri 18 Tangerazg), written by Dede
Rika Kurnia Anas,
NIM
109014000049 was examined by the Committee onMarch 26th,2014. The "slcripsi " has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled one
of
the requirementsfor
the Degreeof
S.Pd (S1)in
English Language Education at the English DepartmentChairman:
Secretary:
Examiner I:
Examiner II:
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
Drs. Syauki. M.Pd. NrP. 19641212 t99103
I 002
Zaharil Anasv. M.Hum.
NrP. 19761007 2007t0
t 002
Drs. Bahrul Hasibuan. M.Ed.
Acknowledged by
Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training
Dra. Nurlena Ri'fai. M.A.. Ph.D
NrP. 19591020 198603 2001
lll
b26th'2014
enens Sunen
KEMENTERIAN AGAMA
FORM (FR)
No. Dokumen : FITK-FR-AKD-089
UIN JAKARTA Tgl. Terbit : 1 Maret 2010
FITK No. Revisi: : 01
Jl. Ir. H. Juanda No 95 Ciputat 15412 Indonesia Hal : 1/1
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
iv Saya yang bertandatangan di bawah ini,
Nama : Dede Rika Kurnia Anas Tempat, Tanggal Lahir : Jakarta, 04 Agustus 1992 NIM : 109014000049
Jurusan/Prodi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Judul Skripsi : The Effectiveness of Using Card Games Technique in Teaching Vocabulary (A Quasi-Experimental Study at the Seventh Grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang)
Dosen Pembimbing : 1. Drs. Sunardi K. Dipl. Ed 2. Ertin, M. A. TESOL
dengan ini menyatakan bahwa skripsi yang saya buat benar-benar hasil karya sendiri dan saya bertanggung jawab secara akademis atas apa yang saya tulis. Pernyataan ini dibuat sebagai salah satu syarat Wisuda.
Jakarta, 26 Maret 2014 MahasiswaYbs.
v
Card Games Technique in Teaching Vocabulary; A Quasi-Experimental Study at the Seventh Grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang in Academic Year 2013/2014. Skripsi of the English Education at the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training of the State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Keywords: Vocabulary, Card games
Vocabulary is one of the important language components that students need to be able to use, in order to develop their language skills. A great range of vocabulary will help students understand what is written in the text, comprehend the message and help them in speaking and writing. Meanwhile in the class, the teacher uses a technique in teaching vocabulary than cannot accommodate all the students to participate in teaching and learning process. Therefore, the writer applies card games technique as a technique to teach vocabulary. The purpose of this study is to obtain empirical evidence whether card games technique is effective or not in teaching vocabulary. This study was held in January 2014 at
vi
ABSTRAK
Dede Rika Kurnia Anas (NIM: 109014000049). The Effectiveness of Using Card Games Technique in Teaching Vocabulary; A Quasi-Experimental Study at the Seventh Grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang in Academic Year 2013/2014. Skripsi, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Keywords: Vocabulary, Card games
Vocabulary merupakan salah satu komponen penting yang perlu digunakan oleh siswa, dalam mendukung perkembangan kemampuan berbahasanya. Tingginya tingkat vocabulary siswa akan mempermudah mereka dalam mengerti sebuah teks, memahami pesan yang terkandung di dalamnya serta membantu mereka dalam berbicara dan menulis. Sementara itu di dalam kelas, guru menngunakan teknik mengajar yang tidak dapat mengakomodasi siswa untuk berpartisipasi dalam kegiatan belajar dan mengajar. Karena itu, penulis mengaplikasikan card games dalam pengajaran vocabulary. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah mendapatkan bukti empiris terhadap keefektifan penggunaan teknik
card games dalam pengajaran vocabulary. Penelitian ini dilaksanakan pada bulan Januari 2014 di SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang. Metode penelitian yang digunkan adalah metode kuantitatif dengan model quasi eksperimen. Teknik pengambilan sampel yang digunanakan adalah simple random sampling. Penulis mengambil dua kelas sebagai subjek penelitiannya, satu kelas sebagai kelas eksperimen dan satu kelas lainnya sebagai kelas kontrol. Data yang di dapat kemudian di analisis dengan menggunakan rumus test-t. Dari hasil perhitungan ditemukan pada signifikansi 5%, nilai test-t ( ) ˃ table-t (6.03 ˃ 1.99). Interpretasi data menunujukan adanya perbedaan signifikan pada pemorelah vocabulary siswa dengan menggunakan teknik card games dan yang tidak. Penggunaan teknik card games dinilai efektif dan dapat diterapkan dalam pengajaran vocabulary di kelas tujuh SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang.
vii
In the name of Allah, The Beneficent, The Merciful
All praise be to Allah, the Lord of the world. The writer is sure that without His help and mercy this “skripsi”would not be completed. Peace and blessing be upon our prophet Muhammad SAW, our beloved Messenger, and his families, his companion, and his faithful followers.
This “skripsi” is presented to the Department of English Education, the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, the Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Strata I (Bachelor of Art) in English Language Education.
On this great occasion, the writer would like to thank to her beloved parents, Anasrulloh and Dra. Ikah Minarsih, for their love, sincere prayers, support, advice, motivation, and patience for the writer in finishing this
“skripsi”. She also would like to thank to her sister Rina Rahmatika Anas, for her love, support, and motivation to finish this “skripsi”.
The writer realizes that she could not finish writing this “skripsi” without help from people around her. Therefore, she would like to give her gratitude and appreciation to:
1. Her advisors, Mr. Sunardi K. Dipl. Ed and Mrs. Ertin, MA. TESOL for their valuable advice and guidance in developing and accomplishing this
“skripsi”.
2. All the inspiring Department of English Education lecturers who have already taught and educate the writer during her study at UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
viii
4. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum, the secretary of the Department of English Education.
5. Dra. Farida Hamid, M.Pd. as the academic advisor.
6. Dra. Nurlena Rifa’i, MA. Ph.D, the Dean Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training.
7. H. Sri Suyatno, M.Pd as the Headmaster of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang
and Sri Rochani, S.Pd. as the English teacher of the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang, for giving permission to have a research in this school.
8. Her beloved friends in English Education Department Class B year of 2009 who always give inspiration, ideas, and remind the writer in finishing this “skripsi”.
The words are not enough to say any appreciation for their help and contribution in this “skripsi”. May Allah, the Almighty bless them all. Moreover, the writer realized that this “skripsi” is far from being perfect.
Therefore it is really a pleasure for her to receive suggestion and criticism from everyone who will encourage her to continue her study.
Jakarta, March 2014
ix
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... iii
SURAT PERNYATAAN HASIL KARYA SENDIRI ... iv
ABSTRACT ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF APPENDIXES ... xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Study... ... 1
B. The Scope of the Study ... 4
C. The Formulation of the Study ... 4
D. The Objective of the Study ... 4
E. The Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK A. Vocabulary 1. The Meaning of Vocabulary ... 5
2. The Kinds of Vocabulary ... 6
3. The Technique Use in Teaching Vocabulary ... 7
B. Games 1. The Meaning of Games ... 9
2. The Kinds of Games Use in Language Learning ... 10
3. The Advantage and Disadvantages of Using Games a. The Advantages ... 13
b. The Disadvantages ... 14
x
1. The Steps in Using Card Games ... 16
CHAPTER III RESEARH METHODOLOGY A. The Place and Time of the Research ... 22
B. The Method of the Research ... 22
C. The Population and Sample ... 22
D. The Technique of Data Collection ... 23
E. Technique of Data Analysis ... 23
F. The Testing of Hypotheses ... 25
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING and INTERPRETATION A. The Description of Data ... 26
1. The Data of Experiment Class ... 26
2. The Data of Control Class ... 26
B. The Analysis of Data ... 27
C. Interpretation ... 32
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION and SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 34
B. Suggestion ... 34
BIBLOGRAPHY ... 36
xi
xii
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Appendix 1 : RPP Pertemuan Pertama Kelas Eksperimen
Appendix 2 : RPP Pertemuan Pertama Kelas Kontrol
Appendix 3 : RPP Pertemuan Kedua Kelas Eksperimen
Appendix 4 : RPP Pertemuan Kedua Kelas Kontrol
Appendix 5 : RPP Pertemuan Ketiga Kelas Eksperimen
Appendix 6 : RPP Pertemuan Ketiga Kelas Kontrol
Appendix 7 : RPP Pertemuan Keempat Kelas Eksperimen
Appendix 8 : RPP Pertemuan Keempat Kelas Kontrol
Appendix 9 : Soal Post-test
Appendix 10 : Kunci Jawaban Soal Post-test Appendix 11 : Validity and Reliability of Post-test
Appendix 12 : Tabel Perolehan Nilai Pre-test dan Post-test Kelas Eksperimen
Appendix 13 : Tabel Perolehan Nilai Pre-test dan Post-test Kelas Kontrol
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A.
The Background of the Study
Vocabulary is one of the crucial language components that language learners need to be able to use, in order to develop their language skills. Language learners need a great range of vocabulary to be able to understand a text written in English, comprehend the message, and also to speak and write in English. Therefore, vocabulary is one of the important language components that students should have.
As already stated above in learning English language, learners need a great range of vocabulary. It is one of the most critical language components that students need in learning English language. Vocabulary is the basic components for building their language skills, without vocabulary it will be very hard for the students to build their language skills.
In Junior High School, the students need to be able to communicate in oral and written English language. This makes vocabulary as the part of language components the students need. It is also stated on the scope of school-based curriculum competence standard for junior high school that the students are expected to be able to reach the functional stage. In the functional stage, students are expected to be able to communicate both in spoken and written English language to solve the problem in their daily life.1
Concerning the vocabulary teaching in junior high school, there are various methods and techniques have been applied in the classroom. To get
1
2
more information about the issue, the writer did an observation in SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang. She chose this school because it was her alma mater. The teaching and learning activities in this school did not changed since the writer studied there. The English teacher at that school still used the conventional teaching ways to teach vocabulary to her students. The lesson started with the English teacher provides a list of vocabulary based on the text they have read before and asked the students to read the vocabulary. After that, she wrote the translation of the vocabulary list presented before in Bahasa Indonesia. In the end of the lesson, the teacher gave homework to make a list of vocabulary related to the topic of their lesson and the students have to memorize the words and presented it in the next meeting. This condition would not lead the students to reach the functional stage as stated in their school-based curriculum.
From this observation, the conventional teaching ways is not always effective in teaching vocabulary. It is normal to use the conventional ways in teaching vocabulary, but if the teachers always use the conventional ways of teaching right after the students read the vocabulary in chorus it makes more concern in how they pronounce the words rather than the meaning itself.
The ideal condition of vocabulary teaching is the teacher should teach the meaning of the words and the kind of the words, not only translate the words and asked the students to read it in chorus. While the fact happening in the class is the students only force to remember a long list of vocabulary without a chance to use the vocabulary they knew. The English teacher did not accommodate her students with an activity to productively use their receptive vocabulary.
their receptive vocabulary. The writer analyzed, this problem happens because they did not have the opportunity to participate and practice the vocabulary they have learned.
In the other case, the teacher taught in a big class, every class consists of 40 students. The teacher has to accommodate all students to participate the teaching learning process. The conventional teaching ways is not appropriate to accommodate the students need, because it just helps some of the students in the class. So, the teacher should use other technique in teaching vocabulary which is appropriate in a big class.
This condition creates a challenge for the writer to find different ways of teaching vocabulary. The teacher should use teaching methods and technique that makes the students involve in teaching and learning process. One of the teaching techniques can be use to overcome this problem is games. Games are an effective way to teach vocabulary. All students involves in teaching learning process, they can works as a team to learn the materials and compete in the games.
There are many kinds of games that can be used in language learning such as, guessing games, search games, matching games, matching-up games, exchanging games, exchanging and collecting games, arranging games, board games and card games, and puzzle solving.2 One of the games that can effectively use in the class is card games. The card games were chosen because it develops students’ vocabulary by giving them chance to productively use their receptive vocabulary and also extending their vocabulary. Moreover, card games are fun activities and make the students relax and enjoy the lesson. Because of that reason, the writer sees that card games can overcome the problem above. In using this technique students can works as a team or individual. The students work to finish the card games based on the following instruction written on the cards.
2
4
Based on the explanation above, the writer interests to conduct a quasi-experimental research titled: “The Effectiveness of Using Card Games
Technique in Teaching Vocabulary at the Seventh Grade of SMP Negeri
18 Tangerang”.
B.
The Scope of the Study
The scope of this study covers the teaching of vocabulary as required in the school-based syllabus for the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang.
C.
The Formulation of the Study
The writer would like to formulate the problem based on the scope of the study above as follow: “Is using card games technique effective in teaching vocabulary at the Seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang?”
D.
The Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to get empirical evidence of the effectiveness of using card games technique in teaching vocabulary at the Seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang.
E.
The Significance of the Study
5
A.
Vocabulary
1.
The Meaning of Vocabulary
In learning a new language, vocabulary is one of the crucial language components that language learners have to master. Every language learner cannot master a language they learn without learning about vocabulary. Language learners need a great range of vocabulary to be able to understand a text written in English, comprehend the message, and also speak and write in English. This explains the importance of vocabulary in language learning that will help language learners in building their language skills.
There are some definitions of vocabulary given by the experts.
Harimukti Kridalaksana defines “vocabulary as a component of language that contains all of information about meaning and using word in language”.1 It means that vocabulary is a part of language involves the meaning and the use of word in language.
While according to Wilkins, “you can say very little with grammar, but you can say almost anything with words”.2
This statement explain the importance of vocabulary in language learning, a great range of vocabulary will be very helpful for the students to build their language skills and help them in communicate with others.
Allen also stated, without a great range of vocabulary it will be very hard for a language learner to build their language skills.3 In line with them
1
Harimukti Kridalaksana, Kamus Linguistik, Edisi Ke Empat (Jakarta: PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 2008), p.142.
2
Scott Thornbury, How to Teach Vocabulary, (Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2002), p. 13
3
6
Read defines “Vocabulary knowledge involves knowing the meanings of words”.4
From some definitions above, it can be concluded that vocabulary is one of the important aspects in language learning and a great range of vocabulary will help students to be able to understand a text written in English, comprehend the message, and also to speak and write in English.
2.
The Kinds of Vocabulary
Aebersold and Field classified vocabulary into two categories; they are receptive and productive vocabulary. 5 Receptive vocabulary was known as the vocabulary that the learners knew but they did not use it when they speak or write. Vocabulary that learners use in speaking and writing is known as productive vocabulary. From this explanation, it can be concluded that there are some vocabulary known by the learner but they did not use it productively in speaking and writing.
In harmony with Aebersold and Field, Fries divided vocabulary into two kinds, namely: function words and content words. 6 The function words include auxiliaries, prepositions, and conjunctions. The content words on the other hand fall into three categories: nouns, verbs, adjective and adverb. It can be concluded that the learner should know which one function word is and which one content word is. The learners also need to distinguish which one is noun, verb or adjective and adverb.
Furthermore Celce-Muria and Olshthain classified vocabulary into content and function words.7 Content words include nouns, verbs, and adjective. While function words include pronouns, auxiliary verbs,
4
John Read, Assessing Vocabulary.(Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p. 16.
5
Jo Ann Aebersold and Mary Lee Field, From Reader to Reading Teacher. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997), p. 139.
6
Charles C. Fries, Teaching and Learning English as a Foreign Language. (Rexdale: University of Michigan Press, 1978), pp. 44-47.
7
prepositions, determiners and adverbs. Celce-Muria and Olshthain explained clearly about kinds of vocabulary the learner should know. The learners need to learn both content and function words together and know how to use them.
From the explanation above there are many kinds of vocabulary the students should have known. The students should know which one is noun, verb, adjective and adverb. They are also expected to use the vocabulary they know productively.
3.
The Technique Use in Teaching Vocabulary
There are many techniques used by the teacher to teach vocabulary to their students. The teacher should determine the best technique suitable for the students. Below some techniques used in teaching vocabulary:
a. Gairns and Redman, state several techniques in teaching vocabulary, they are:
1) visual technique, includes:
flash cards, photographs, blackboard drawing, wall charts and realia (i.e. objects themselves).
mime and gestures, the mimic and gestures done by teachers to illustrate a situation when the words use.
2) verbal technique, includes:
use of illustrative situation (oral or written), teachers use illustrative situation to explain the abstract words for example
“I don’t mind”.
use of synonymy and definition, teachers often use the synonym to ease them in explaining new words and giving the definitions to their students.
contrasts and opposites, teachers use the opposites words to introduce the new vocabulary.
8
examples of the types, teachers mentioning a word with pointing or bringing the items to the class.
3) translation, teachers translate the words into students first language.8
Those are the technique used in teaching vocabulary in many classes. Teacher could choose one of the suitable ways to teach vocabulary from the list presented above to teach their students.
b. According to Nation, the meaning of word can be taught in many different ways, such as:
1) by demonstration or pictures
using an object
using a cut-out figure
using gesture
performing an action
photographs
blackboard drawing or diagrams
pictures from book
2) by verbal explanation
analytical definition, defines the word by analyzing the word from its elements.
putting new word in a defining context, teaching the word based on the context where the word use.
translating into another language, this technique can be used to save times; the teachers tend to give the translation of word in the students first language.9
8
Ruth Gairns and Stuart Redman, Working with Words: A Guide to Teaching and Learning Vocabulary. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1986),pp. 73-76.
9
Technique of presenting meaning of word explained by Nation above that is usually used in English language classroom. Teacher usually uses pictures from their textbook or translating the words into Bahasa Indonesia.
c. Allen offers several techniques in teaching vocabulary, they are: 1) using a new word in a sentence
2) using games, and
3) using pictures10
According to Allen’s statement about techniques in teaching
vocabulary, games are used as technique in teaching vocabulary to the students in this research. Games were chosen as the technique in teaching new vocabulary because leads to creative and communicative vocabulary learning.
B.
Games
1.
The Meaning of Games
A game is one of the techniques used by teachers in teaching vocabulary. The teachers use games as creative and communicative technique especially in teaching vocabulary, this way is chosen because teachers did not want to use the same practice over and over again.
Teachers needs to plan games they will use in the classroom that can make their students enjoying, convenient, comfortable and interested in
learning vocabulary. Wallace stated “The aim of vocabulary games and
exercises are to develop student’s vocabulary and practicing it through games in enjoyable activity”.11
It means that games can be used as a new way to
practice student’s vocabulary without forcing them to remember a set of
words.
10
Allen, op.cit, pp. 45-56.
11
10
Furthermore Hadfield defined “A game is an activity with rules, a goal and element of fun”.12 In line with Hadfield’s opinion the teachers could use any game that is appropriate to apply in their classes. The teachers also need to plan the games so it can make students enjoy in learning vocabulary.
Moreover Wright defined “Game as an activity in which is entertaining and engaging, often challenging and activity in which the learners play and
usually interact with others”.13
It means games lead to a creative and communicative activity that is good break the same practice use in English language classroom.
From the definition above, the writer can say that game is an activity which can be implemented in teaching vocabulary and it make students relax and feel happy in learning vocabulary, which can be carried out by a set of rules and goals.
2.
The Kinds of Games Use in Language Learning
a. Jill Hadfield divided games into two kinds, they are:
1) competitive games, in which players or teams race to be the first to solve the games.
2) co-operative games, in which players or teams work together to finish the game.14
This kind of games presented by Hadfield is good to be applied in big classroom. The teacher could choose competitive or co-operative games to be applied in their classes. It will help the teacher use games effectively in teaching vocabulary.
b. Moreover, Shaptoshvili mentioned nine kinds of games that the teacher could use in teaching vocabulary, they are:
12
Hadfield. loc. cit. 13
Andrew Wright, David Betteridge and Michael Buckby, Games for Language Learning. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), p. 1.
14
1) memory game, it begins with one student saying a sentence and the next student in turn adding a words or phrases to the sentence repeated before. Students who make a mistake cannot continue the game; the last one standing is the winner.
2) word association, this game requires students to name all the words they know associated with any lexical category. One student says a word from a category, and then the next student must immediately say another word from a category.
3) miming, it is one of a guessing game. One student mimes an action and then the other student trying to guess the word.
4) guess the tool, this game done with the help of card containing a drawing of tools related to certain jobs. This game formed in a group and the other students who did not have the card can ask certain information that might be related with the drawing.
5) human sound, in this game the students are asked to make a sound related to situation given by the teacher.
6) suggestion chain, in doing this games the students should give a suggestion to their friend according to the situation occur.
7) notices and warnings, this games use two sets of cards. The first set contains phrases and sentences of different kinds that give information or warnings. The cards in the second set contain names of places where people would see or hear each other notice.
8) exaggerate, this game gives students the opportunity to practice strong adjectives by answering a question from a card.
9) expand the sentence, this game can be use to help students practice placing an adjective in correct order.15
From the explanation guess the tool game are interesting games to do in class. Card games are easy to be applied and suitable to do in a big class.
15
12
c. Furthermore Rinvolucri and Davis stated there are many kinds of language games:
1) competitive game, this game usually uses formats taken from radio and television games. The students are paired in a small group showing collaboration to defeat the other group.
2) cognitive game, this is collaborative sentence-making game. It exercises mostly open-ended, where the students expand one sentence into two utterances by adding either one or two words. 3) feeling and grammar, in this section the students concentrate on
expressing real things about themselves and people round them. They do this using prescribe structure
4) listening to people, in this game students create a very atmosphere in a language classroom. The grammar is being practiced in a person centered atmosphere of concentration on meaning.
5) movement and grammar, this game offers student’s move while
practicing and internalizing grammar. They are moving but not wasting time.
6) meaning and translation, this game allows the intermediate until the advance students to decide whether the sentences given are meaningful or rubbish.
7) problem solving, in this game students have to find multiple solutions to technical human and cultural problems. They also express themselves within a given set of vocabulary and structures.16
From those kinds of games presented above, the writer concludes that the kind of games used in learning vocabulary depends on the materials and the situation of the class. The teacher should choose the suitable games for the
16
students. In this research the writer will only use card games as cooperative and competitive games in her classes.
3.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Games
a.
The advantages
There are many advantages from using games in language learning. Games could help reduce the boredom of drilling in language class, making students comfortable and improve their attention on the lesson.
1) Wright stated several advantages of games:
games help and encourage many learners to sustain their interest and work.
games also help the teacher to create context in which the language is useful and meaningful. The learners want to take a part in order to do so they must understand what others are saying or have written, and they must speak or write in order to express their own point of view or give information.
many games cause as much destiny of practice as more conventional drill exercise.
games can be found to give practice in all the skills (reading, writing, listening and speaking)
by making the language convey information and opinion,
games provide the key future of „drill’ with the opportunity to
sense the working of language as living communication.17 The writer highlights the point that games can motivate students in learning a language, because games are a fun activity that could be practiced in learning a language.
2) In line with Wright, Ferguson explained some benefits of using games, they are:
17
14
games help the teacher create context in which language is useful and meaningful.
games help the teacher build better class relationships and encourage class participation.
games provide language practice review and consolidation in the various skills.
games encourage the creative and spontaneous use of language and promote real communication.
games are enjoyable and challenging but not threatening. They are a nice break from the normal routine of the language class.18
The writer concluded that games can be very useful in learning new vocabulary. Games lead to creative activity, and promote real communication in class.
Based on the statement above, the writer concludes there are many advantages of using games in teaching vocabulary. Games improve student’s motivation in learning English. Games also make the usual practice becomes more interesting and help them in practicing vocabulary they knew. Communication in the classroom also increased because of the use of games
b.
The Disadvantages
Games are one of the alternative techniques used in teaching vocabulary; it also has several limitations. The writer assumes that it is not easy to use games in language learning. The teacher must understand the principle of language games first, what kinds of games that are suitable for
their students’ and if it is applicable in their classes or not.
JerotijeviĤ stated several disadvantages of using games in class, they are:
18
1) discipline issues, learners may get excessively noisy.
2) straying away from the basic purpose of the game-play activity due to inadequate rules.
3) if games already familiar, students might not get equally involved. 4) some learners, especially teenagers may find games are
unnecessary and childish.19
The teacher should carefully choose the right games in order to reach the goals. In a big class the teacher need to form the students into the small groups so they will not make a great noise.
From the statement above, the writer can conclude that games could be applied in the classroom by forming the students into small groups. There are certain materials that cannot be communicated by using games. Using games in a classroom usually make noise if teacher did not give the instruction clearly.
Even though there are some advantages and disadvantages of using games in teaching vocabulary the writer thought that this technique still can be applied in the class. The reason is, games lead the vocabulary practice to a communicative situation. By the use of games it will be easier to practice the vocabulary and it also boost their creativity. The disadvantages of using games can be solved by forming students in a small group and clearly given the instruction of the game.
C.
Teaching Vocabulary Using Card Games
Card games are one of the effective ways teachers could use in their classes. Card games are fun activities that could improve student’s motivation in learning English, memorize the word and give the students a chance to use the word communicatively.
19
Miljana K. StojkoviĤ, Reasons for Using or Avoiding Games in an EFL Classroom
16
Teaching vocabulary by using card games is the effective way to reduce the monotony of drilling in learning vocabulary. Card games are a
good alternative way in teaching vocabulary. Most of the student’s loves to
play game, with the use of card games the students could practice using vocabulary they have learnt and communicate it with their friends. Teacher could make card games with a set of pictures printed on it. The pictures itself can be gathered from books, magazines, news paper even from internet. The teacher can also use the printed or photocopied card games from a book.
1.
The Steps in using Card games
There are three steps in teaching vocabulary using games. The first step is introducing the lesson to students. The second step is introducing the new words that will be played by students. The last is, teacher begins to explain the game that students will play and let students practice the words.
The games used in this research are adapted from O’Deil and Head book’s namely Games for Vocabulary Practice. The games used are, “Who, where and what?” and “Guess my job”20
.
a.
Who, where and what?
The aim of the game is to practice basic job and workplace vocabulary. Time estimated for practicing this game is 40-45 minutes. In practicing this game teacher should provide a set of card with a profession printed on it. Teacher also needs to make a list of key vocabulary that will be taught to students.
1) Warm-up
There are some steps in this warm up stage for the teacher to follow:
In the beginning before the lesson started, the teacher shows some pictures to the students of someone doing an easily
20 Felicity O’Deil and Katie Head,
identified job, e.g. a doctor. Then ask the students to identify the job being shown in the pictures.
After they finish identified the job, the teacher ask another
question to the students like, “Where does he/she work?”
(hospital for the doctor, school for the teacher). Also ask other question that related with the picture and the job being
identified, for instance, “What does he/she use?” (stethoscope, injection, bandage, etc. for the doctor, marker, dictionary, etc. for the teacher).
Teach any word that related from the key vocabulary to students by mimicking or showing the pictures
2) Main activity
This stage requires the teacher to divide students into pairs and each pair are ask to draw three columns with the headings Who, Where, and What.
Next step, the teacher gives each pair an envelope containing a set of profession cards. Then ask students to sort the pictures into ten set of three: Who (the worker); Where (where they work); What (What they use).
When the pairs have sorted all the cards into set of three, ask them to write the words down in the columns based on the profession, the workplace and the tools that help them in work. The teacher just monitors the students on their work and gives a help if it is necessary.
When all the pairs have finished doing their work, the teacher should give pairs a score for each picture correctly named and categorized.
18
should guess the job by asking what are he/she use for works and where he/she goes to work.
3) Variation
This may also be used as a follow-up after doing the main activity or can be done in the next meeting.
In this step the students will choose one of their friends as a volunteer to start the game.
After that, the students will have a job card attach on their back and they need to guess what the job is written on their back. The student can ask three yes/no questions to the rest of their friends about the things they need for work, the work place and their responsibility.
Each student who can guess the job correctly will receive three points, the pairs with the highest score will win the game.
4) Follow-up
For follow-up activity, the teacher places an envelope of pictures in front of the classroom. Then students take turns to pick a picture from the envelope and the rest of the class have to identify what they have chosen by asking yes/no questions,
e.g. “Is it a job? Do you work outdoors? Do you use computer?”, etc.
5) Homework
For the assignment, the teacher asks the students to write a paragraph about their family or friends describing what jobs
Write sentences using all the word illustrated on the sheet and add one more item which each person might use in their job,
e.g. “A nurse works in a hospital. She uses a thermometer and a watch”.
b. Guesss my job
The aim of this game is to practice the language of jobs and their characteristics. Time allocation for doing this game is 45-60 minutes. In doing this game teacher could use the previous cards of profession and adding some other jobs to the previous cards set.
1) Warm-up
As a warm up activity, the teacher tells the class that they have a secret second job which the students have to guess by asking yes/no questions to the teacher. Choose one of the jobs from the profession cards.
Then brainstorm the kind of question the students might ask,
e.g. “Do you work outdoors? Is it a dangerous job?”
Next students try to guess the job by asking yes/no questions. Put a mark on the board for each question that have been answer. When the students have guessed the job, count up the marks on the board. These are the total point.
2) Main activity
In this stage the students are divided into pairs.
20
When the students get their card, the other students who have not get the card then ask yes/no questions to determine what
kind of job is written on their friend’s card.
Tell the student who get the job card to keep a note from the number of question asked by their friends. They win one point for each question asked. While the person who eventually guessed the jobs gets three points and is next to pick a card. But if the next student guesses further jobs correctly, that student gets three points again and nominates a different student to choose the next card.
Continue this games for an appropriate time or until all the cards have been used.
3) Variation
This may also be used as a follow-up after doing the main activity or can be done in the next meeting.
Give each pair a job card and a piece of sticky tape. Tell them to stick their card on another student’s back and make sure that the student does not know what the card is.
Students then move around the classroom asking each other five yes/no questions in order to discover their job.
The student they ask the question to looks at the card on their back and give the appropriate answer.
The game continues until all the students have identified their jobs.
4) Follow-up
students in their groups. The students explain why they would or would not like to do the jobs they marked. If there is enough time, check out with the whole class which were the most and the least popular jobs.
5) Homework
As for homework, the students need to choose any job from the activity and write a paragraph about why they would or would not like to do that job.
22
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
The Place and Time of the Research
The writer held this research at the seventh grades of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang. The address of this school is Perum Poris Indah, Blok G, Cipondoh, Kota Tangerang, Banten 15148. This research was held from January 7st to January 31th, 2014.
B.
The Method of the Research
This research used quasi-experimental method to test whether card games are effective as one of the alternative ways of teaching vocabulary. In the beginning of this research the writer held a pre-test in all the class at the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang to know their English competence. After knowing the result of the pre-test, the writer chose two classes which have relatively equal scored as the sample. The first class was chosen as the experiment class and the second one as the control class. Then, she taught the experiment class by using card games and in the control class
the writer taught the student’s by conventional teaching ways. The last, the
writer gave a post-test to both classes to know whether there was significant difference to the use of card games technique in teaching vocabulary.
C.
The Population and Sample
The population in this research is the students’ of the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang. There are 400 students’ of the seventh grade. In
was the experiment class (X) consists of 40 students’ and the control class also
(Y) consisted of 40 students’.
D.
The Technique of Data Collection
The writer did a test to obtain the data of student’s vocabulary
achievement by using card games. There are two kinds of tests in this research the pre-test and post-test. Both of the tests were an objective test, a multiple-choice test that consists of 50 questions about vocabulary. The writer used the result of pre-test and post-test from both classes to identify the effectiveness of using card games technique in teaching vocabulary. The writer used
“ANATEST” software version 4.0.9 developed by Drs. Karno To, M.Pd and Yudi Wibisono, ST to score the reliability and validity of the instrument used.
E.
The Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting the data the writer needed for this research, the writer compared the post-test score from both of the classes to know the average of gained score. The higher gained score indicated the influence of using card games technique in teaching vocabulary. According to Anas Sudijono, the formula used to test the difference between the two means is t-test.1
The procedures of calculation were:
a. Determining mean of variable X with formula:
∑
1
24
b. Determining Mean of variable Y with formula:
∑
c. Determining deviations standard variable X with formula:
√
∑
(
∑
)
d. Determining deviations standard variable Y with formula:
√
∑
(
∑
)
e. Determining standard errors mean variable X with formula:
√
f. Determining standard errors mean variable Y with formula:
√
g. Determining the differences of mean variable X and mean variable Y with formula:
√
h. Determining with formula:
i. Determining degree of freedom (df) with formula:
df = degree of freedom
f1 = total of students of experiment class
f2 = total of students of control class
F.
The Testing of Hypotheses
The writer proposes hypotheses toward this research as follow:
1) The Null Hypothesis ( there is no significant difference in
student’s vocabulary achievement in learning vocabulary by using card
game techniques. The Null Hypothesis ( is accepted if t-test ( ) < t-table and the alternative hypothesis ( ) is rejected.
26
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING and INTERPRETATION
A.
The Description of Data
To know the result of this experiment, the writer collected the students’ score in the pre-test and post-test from the two classes. The variable X represented the result of pre-test and post test from the experiment class and the variable Y is the result of pre-test and post-test in the controlled class.
1. The Data of Experiment Class
Based on the data gather from the pre-test and post-test in the experiment class, it could be seen that from 40 students in the experiment class, the mean of the pre-test is 73.2. The data shows that the lowest score achieved by students is 48 and the highest score in pre-test is 78. After giving treatment by using card games, the writer conducted a post-test to know the effectiveness of using card games in teaching vocabulary. The highest score in the post-test is 96 achieved by four students and the lowest score is 78 and the mean of the post-test is 87.6. So, the writer calculates the mean of gained score from the experiment class is 14.4. The data shows student’s achievement score after gained the treatment was increased. Further details about the students score will be presented on the appendix 12.
2. The Data of Control Class
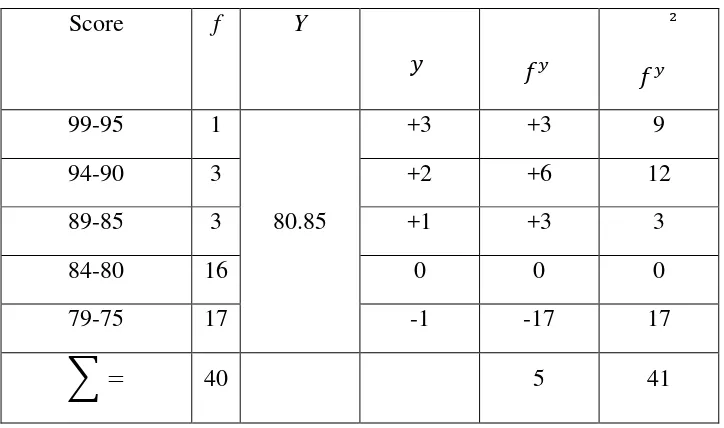
class. In the end of the research, the writer conducted a post-test. The data shows the lowest score is 78 and the highest score in the post-test is 96 achieved by one student. Meanwhile, the mean of the post-test is 80.85. So, the writer calculates the mean of gained score from the experiment class is 8.5; it is lower than the mean of gained score from the experiment class. Further details about the students score will be presented on the appendix 13.
B.
The Analysis of Data
The writer use statistic calculation to find empirical evidence and to ease the writer in hypotheses testing. The writer drew a table consist of six columns. The first column (score) showed the score interval, the second column (f) showed the frequency, the third column ( ̅) consist of the mean of
the post-test score, the fourth column ( ), the fifth column showed ( )
which was resulted from the multiplication of (f) and ( , the last column
[image:39.595.148.480.611.739.2]( ) was the multiplication of ( ) and (f). this table will be used to calculated the mean, deviations standard and standard errors of variable X.
Table 4.1
Calculation table of variable X (Experiment Class)
Score f X
99-95 4 +2 +8 16
94-90 12 +1 +12 12
28
84-80 9 -1 -9 9
79-75 2 -2 -4 8
∑ 40 7 45
The writer calculated the data based on the table above with the following formulas:
a. Determining mean of variable X with formula:
∑
(
)
)
b. Determining deviations standard variable X with formula:
√
∑
(
∑
)
√
=
√
=
√
=
5 x 1.046
c. Determining standard errors mean variable X with formula:
√
√
√
[image:41.595.132.494.362.576.2]Table 4.2
Calculation table of variable Y (Control Class)
Score f Y
99-95 1 +3 +3 9
94-90 3 +2 +6 12
89-85 3 80.85 +1 +3 3
84-80 16 0 0 0
79-75 17 -1 -17 17
∑ 40 5 41
The table 4.4 showed the calculation table of variable Y. The first column (score) showed the score interval, the second column (f) showed the frequency, the third column ( ̅) consist of the mean of the post-test score,
the fourth column ( ), the fifth column showed ( ) which was resulted
30
multiplication of ( ) and (f). this table will be used to calculated the mean, deviations standard and standard errors of variable X.
The writer calculated the data based on the table above with the following formulas:
d. Determining Mean of variable Y with formula:
∑
(
)
e. Determining deviations standard variable Y with formula:
√
∑
(
∑
)
√
√
√
√
√
√
g. Determining the differences of mean variable X and mean variable Y with formula:
√
=
√
=
√
=
√
h. Determining
32
df = (f1+f2) - 2
The writer took the value of degree of freedom (df) closer to 78 in the t-table was 80. The value of df 80 at the degrees of significance 5% in t-table is 1.99
j. The hypotheses testing
The writer formulated hypotheses toward this research as followed: 1) The Null Hypothesis ( there is no significant difference in student’s vocabulary achievement in learning vocabulary by using card game techniques.
2) The alternative hypothesis ( ), there is significant difference in students vocabulary achievement by using card game technique.
The assumption of these hypotheses, as followed:
The assumption of this hypothesis ( is rejected. It means there is a significant difference in student’s vocabulary achievement by using card game technique.
If ≤ t-table the Null Hypothesis ( ) is accepted, that there is no significant difference in vocabulary achievement by using card games technique and teaching vocabulary by conventional way.
C.
Interpretation
1) the value of df 80 at the degrees of significance 5% in t-table = 1.99
2) The value of is 6.03
The writer summarized that ≥ t-table in the significance of 5% (6.03 ≥ 1.99), it means that the null hypothesis ( ) is rejected and the alternative hypothesis ( ) is accepted.
It can be inferred that there is significant different achievement between teaching vocabulary by using card games technique and teaching vocabulary by using the conventional way.
34
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION and SUGGESTION
A.
Conclusion
Vocabulary is all the words which are existed in a particular language and it has an important role in every language. Students need to learn about vocabulary to build their language skills. In order to help students in building their language skills, the vocabulary teaching is one of the important concerns. The English teacher has to provide an activity that accommodates all the students needs to productively use their receptive vocabulary.
Card games were chosen as the alternative technique in teaching vocabulary. The reason for choosing this technique is, it gives a chance to the students participates in the teaching learning process and uses their receptive vocabulary. Therefore, the writer held a study to find out the effectiveness of using card games technique in teaching vocabulary at the seventh grade of
SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang.
According to the study that has been done, it was found that the card games technique are effective and applicable in teaching vocabulary at the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang. It could be proven by the result of t-test (6.03) that is higher than value of t-table in the significance of 5 % (1.99). It can be concluded that the use of card games technique in teaching vocabulary is more effective and applicable than the conventional teaching way.
B.
Suggestion
36
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Aebersold, Jo Ann and Mary Lee Fields. From Reader to Reading Teacher: Issues and Strategies for Second Language Classroom. Second edition.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997.
Allen, Virginia French. Techniques in Teaching Vocabulary (Teaching Techniques in English as a Second or Foreign Language). Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1983.
Celce-Muria, Marianne and Elite Olsthain. Discourse and Context in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
Coady, James and Thomas Huckin. Second Language Vocabulary Acquisition: Rationale for Pedagogy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. Creswell, John W. Educational Research Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating
Quantitative and Qualitative Research. Boston: Pearson Education, Inc., 2012.
Ferguson, Marsue and Harumi Manik Ayu. Becoming a Creative Teacher (A Manual for Teaching English to Indonesian Elementary Students). Jakarta Pusat: Regional English Language Office (RELO) Public Affair U.S. Embassy, 2009.
Fries, Charles C. Teaching and Learning English as Foreign Language. Rexdale: University of Michigan Press, 1978.
Gairns, Ruth and Stuart Redman. Working with Words: A Guide to Teaching and Learning Vocabulary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1986. Hadfield, Jill. Intermediate Communication Games (A Collection of Games and
Activities for Low to Mid-intermediate Students of English). Edinburgh: Longman, 1996.
Nation, I.S.P. Teaching and Learning vocabulary. Boston: Heinle&Heinle Publisher, 1990.
Nunan, David. Language Teaching Methodology a textbook for Teachers. Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2000.
O’Deil, Felicity and Katie Head. Games for Vocabulary Practice Interactive Vocabulary Activity for All Levels. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
Read, John. Assessing Vocabulary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001.
Redman, Stuart. English Vocabulary in Use Pre-intermediate and Intermediate. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998.
Rinvolucri, Mario and Paul Davis. More Grammar Games. Eleventh edition.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
Schmitt, Norbert. Vocabulary in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
Shaptosvili, Shalva. Vocabulary practice games. English Teaching Forum Magazine. Volume 40, January 2002.
StojkoviĤ, Miljana K. Reasons for using or avoiding games in an EFL classroom. Sarajevo: (1st International Conference on Foreign Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics, May 5-7 2011).
Sudijono, Anas. Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: Rajawali Press, 2011. Sugiyono. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif,
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, 2010
Thornbury, Scott. How to Teach Vocabulary. Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2002.
38
Wallace, Michael J. Teaching Vocabulary, English Language Book society.
London: Heinemann Education Book, 1987.
Lesson Plan Experiment Class
Nama sekolah : SMP Negeri 18 Tangerang Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Kelas/Semester : VII.1 (Tujuh Satu) / 2 Standar Kompetensi : 8. Mendengarkan
Memahami makna dalam teks lisan fungsional pendek sangat sederhana yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan terdekat.
Kompetensi Dasar : 8.2 Merespon makna gagasan yang terdapat dalam monolog sangat sederhana secara akurat, lancar dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan terdekat dalam teks berbentuk
descriptive/procedure.
Jenis teks : Descriptive text
Tema : Occupations
Aspek/Skill : Mendengarkan
Alokasi Waktu : 2 x 45 menit ( 1 x Pertemuan ) Pertemuan : Ke-1
Indikator :
- Mengidentifikasi fungsi komunikatif teks deskriptif yang di dengar.
- Menjelaskan ciri kebahasaan deskriptif teks.
- Menggunakan occupations untuk mendeskripsikan sesorang.
- Menjawab pertanyaan terkait profesinya.
- Menghubungkan antara profesi, tempat bekerja dan alat yang digunakan untuk bekerja.
40
- memahami jenis-jenis pekerjaan serta dapat mengaplikasikannya dalam kalimat sederhana secara lisan maupun tertulis.
Karakter yang diharapkan :
- Kreatif
- Inovatif, dan
- Percaya diri Materi Pembelajaran :
Descriptive
Purpose : to describe a particular person, animal, place and thing.
Text Organization : - Identification
(mention the name, occupation, place etc.)
- Description
(mention the physical appearance, personality, place, habitat, etc.)
Language Features : - The use of adjectives
e.g.: a) Debby is brown-skinned.
b) Debby looks attractive and beautiful.
- The use of preposition of place and time
e.g.: a) There is a white board in front of our class. b) I go to school at 6 a.m.
Pokok bahasan : Occupations
List of vocabulary presented:
1. A cashier 2. Supermarket 3. Till
4. A dentist 5. Dental surgery 6. Drill
7. A farmer 8. Rice field 9. tractor 10.A hairdresser 11.Hair salon 12.Scissors
13.A nurse 14.Hospital 15.Thermometer 16.A police officer 17.Police station 18.Walkie-talkie 19.A receptionist 20.Hotel
28.A waiter 29.Restaurant 30.Plates 31.A tailor
32.Clothes factory 33.Measuring tape 34.Make furniture 35.A postman 36.Post office
40.Animals hospital 41.A carpenter 42.Furniture factory 43.A mechanic 44.Garage 45.Drill
Script for listening:
Listen to your teacher and complete the dialogs below!
1. Ary : Who is he? Beta : He is a …
Ary :Where does he work? Beta : He works at …
2. Didi : What does your mother do? Caca : She is …
Dedi : What does she do? Caca : ….
Script for Reading:
Read aloud the following text!
My Family
My name is Randi. I am an SMP student. I live on Jalan Suryakanta. My father’s name is Mr. Rahman. He works in a hospital. He is a doctor. My mother is a teacher. My parents have three children. Ely, the eldest, works as a programmer in a private company. Wulan is the second child, she goes to SMA 3.
Script for speaking:
Practice dialogue above with your partner in front of the class!
Script for writing:
Match the jobs written in the column below with their work place, and what they use in their jobs!
No. Job Work place Tools
1. A tailor Restaurant Measure tape
2. A cashier Clothes factory Board
3. A carpenter Rice fields Walkie-talkie 4. A farmer Furniture factory Postman bag
42
6. A postman Police station Till
7. A dentist Supermarket Scissors
8. A hairdresser Hospital Tractor
9. A receptionist School Computer
10. A policeman Hair salon Drill
Model Pembelajaran : Communicative approach
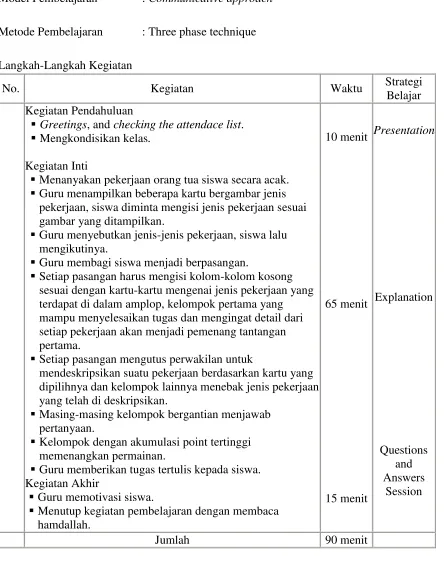
Metode Pembelajaran : Three phase technique Langkah-Langkah Kegiatan
No. Kegiatan Waktu Strategi
Belajar Kegiatan Pendahuluan
Greetings, and checking the attendace list.
Mengkondisikan kelas.
Kegiatan Inti
Menanyakan pekerjaan orang tua siswa secara acak.
[image:54.612.74.520.156.726.2] Guru menampilkan beberapa kartu bergambar jenis pekerjaan, siswa diminta mengisi jenis pekerjaan sesuai gambar yang ditampilkan.
Guru menyebutkan jenis-jenis pekerjaan, siswa lalu mengikutinya.
Guru membagi siswa menjadi berpasangan.
Setiap pasangan harus mengisi kolom-kolom kosong sesuai dengan kartu-kartu mengenai jenis pekerjaan yang terdapat di dalam amplop, kelompok pertama yang mampu menyelesaikan tugas dan mengingat detail dari setiap pekerjaan akan menjadi pemenang tantangan pertama.
Setiap pasangan mengutus perwakilan untuk
mendeskripsikan suatu pekerjaan berdasarkan kartu yang dipilihnya dan kelompok lainnya menebak jenis pekerjaan yang telah di deskripsikan.
Masing-masing kelompok bergantian menjawab pertanyaan.
Kelompok dengan akumulasi point tertinggi memenangkan permainan.
Guru memberikan tugas tertulis kepada siswa. Kegiatan Akhir
Guru memotivasi siswa.
Menutup kegiatan pembelajaran dengan membaca hamdallah.
10 menit
65 menit
15 menit
Presentation
Explanation
Questions and Answers
Session
Buku teks English in Focus for Grade VII, karangan Artono Wardiman, dkk. 2008. Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuaan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
Satu set kartu vocabulary Gambar-gambar yang relevan
Laptop
Proyektor
White board Penilaian
Indikator Pencapaian Kompetensi
Teknik Penilaian
Bentuk
Instrumen Instrumen/ Soal
1. Siswa dapat
menjawab mengenai
jenis-jenis pekerjaan. Tes Tulis Menjodohkan.
Match the jobs written in the column below with their work place, and thing they use for works!
Pedoman Penilaian a) Tes tertulis
1. Untuk setiap nomer, jawaban yang benar di beri skor 10. 2. Jumlah skor maksimal x 10 = 100
3. Nilai maksimal = 100
4. Nilai siswa = x10 al SkorMaksim
han SkorPerole
b) Tes Lisan 1. Siswa menjawab pertanyaan dari teks yang sebelumnya telah mereka baca.
Penilaian difokuskan pada content yang disampaikan.
No. Aspek Skor
1. ACCURACY
1. Mudah dipahami dan memiliki aksen seperti penutur asli (pronounciation)
2. Mudah dipahami meskipun dengan aksen tertentu (intonation) 3. Ada masalah pengucapan yang membuat pendengar harus
5 4 3
Uraian Skor
Jawaban benar Jawaban kurang tepat Jawaban salah
44
konsentrasi penuh dan adakesalahan (diction, pronounciation, stress)
4. Banyak kesalahan pada pengucapan setiap kata (grammar, diction)
2
2 FLUENCY
1. Lancar seperti penutur asli
2. Ke