THE STUDY OF OPTIMUM CONDITION TO
PRODUCE RUBBER INDUCED POLYMER
(POLYETHYLENE)
AHMAD FARIZ BIN FAIZAL LIM
UTeM Library (Pind.1/2007)
THE STUDY OF OPTIMUM CONDITION TO PRODUCE RUBBER INDUCED
POLYMER (POLYETHYLENE)
AHMAD FARIZ BIN FAIZAL LIM
!"
#
" $ $ % & ' ()
*
+
*
+
,
-
& ! &
! &
- !) *
+
./
-
* & ( (
&
,
-
& ! &
! &
/
/
+
,
-
& ! &
! &
*
&
#
+
#
( # /
0/
+
*
&
(
+
+
#
/
1/
22 &
*
)
-- 34
-
5 - 34
!
*
&
* # (
&
+
! &
* * &
5- 3 4
3
! .6
)
!
*
&
- 34
& ( *
$& ( $
"
*
*
+
& *
* # &
)
-
-
)
&
-
+
7889 & -:5 ".79
-
:5- 5 +
9
9
/
&
/
(
$& (
-
-
<
)
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN PEMBUATAN
Rujukan Kami (Our Ref) : 15 May 2008 Rujukan Tuan (Your Ref):
Pustakawan
Perpustakawan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka
UTeM, No 1, Jalan TU 43,
Taman Tasik Utama, Hang Tuah Jaya,
Ayer Keroh, 75450, Melaka
Saudara,
PENGKELASAN TESIS SEBAGAI SULIT/TERHAD
- TESIS SARJANA MUDA KEJURUTERAAN PEMBUATAN (FAKULTI
KEJURUTERAAN PEMBUATAN): AHMAD FARIZ BIN FAIZAL LIM
TAJUK: THE STUDY OF OPTIMUM CONDITION TO PRODUCE RUBBER
INDUCED POLYMER (POLYETHYLENE)
Sukacita dimaklumkan bahawa tesis yang tersebut di atas bertajuk
“
THE STUDY OF
OPTIMUM CONDITION TO PRODUCE RUBBER INDUCED POLYMER
(POLYETHYLENE)
”
mohon dikelaskan sebagai terhad untuk tempoh lima (5) tahun dari
tarikh surat ini memandangkan ia mempunyai nilai dan potensi untuk dikomersialkan di
masa hadapan.
Sekian dimaklumkan. Terima kasih.
“BERKHIDMAT UNTUK NEGARA KERANA ALLAH”
Yang benar,
………..
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
Karung Berkunci 1200, Ayer Keroh, 75450 MelakaDECLARATION
I hereby, declared this thesis entitled “The Study of Optimum Condition to Produce Rubber
Induced Polymer (Polyethylene)” is the results of my own research
except as cited in references.
Signature
:
Author’s Name
:
AHMAD FARIZ BIN FAIZAL LIM
APPROVAL
This PSM submitted to the senate of UTeM and has been as partial fulfillment of the
requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Material
Engineering). The members of the supervisory committee are as follow:
PN. ZURINA BINTI SHAMSUDIN
(Main Supervisor)
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this study is to find the optimum condition to produce rubber induced
polymer polyethylene (PE). In this research, the used waste rubber was taken from
the old tires and the polyethylene, PE are use to produce new polymeric material that
enhance their properties. The polymer blending that involved in this study was melt
blending of two polymers which mixed up in their molten state. The methodology of
this study is prepare the raw material, mixing process by using internal mixer,
crashing process and lastly forming process of the polyethylene mix with waste
rubber. The main concern of the mixing process is the parameter such as
temperature, time and rotor speed of the mixer. The produced material of
polyethylene (PE) and waste rubber are tested for its flexural strength using the
Universal Testing Machine (UTM). The standard of the flexural strength used this
study is ASTM D790. Based on the result of the flexural testing, the best
composition for optimum condition of the polyethylene (PE) and waste rubber
produced was 90wt% polyethylene with 10wt% waste rubber. It is found out that the
rubber induced polymer polyethylene (PE) produced which is new polymeric
material do enhances the properties. Besides that, by adding some homogenizing
agent to the mixing process of the polyethylene (PE) and waste rubber can enhance
ABSTRAK
Tujuan kajian ini dikendalikan adalah untuk mencari keadaan optimum untuk
menghasilkan getah yang teraruh dengan polimer, politena. Dengan menggunakan
getah terpakai daripada tayar lama dan juga politena untuk menghasilkan bahan
polimer yang baru. Di dalam kajian ini, pengunaan getah terpakai yang diambil
daripada tayar terbuang dan juga politena, PE digunakan untuk menghasilkan bahan
polimer baru yang dapat mengubah sifat-sifatnya. Campuran polimer yang terlibat
dalam kajian ini ialah campuran cair bagi dua polimer yang dicampurkan dalam
keadaan cair. Kaedah yang digunakan dalam kajian ini ialah menyediakan bahan
mentah, proses pembancuh iaitu mesin pembancuh, proses penghancuran dan juga
proses pembentukan politena dengan getah terpakai. Bahan yang telah terhasil
daripada politena dan juga getah terpakai telah diuji kekuatan lenturannya dengan
menggunakan mesin bebas ujikaji. Piawai ujian kekuatan lenturan yang digunakan
dalam kajian ini ialah ASTM D790. Di dalam proses pencampuran, parameter
memainkan peranan penting seperti suhu, masa dan juga kelajuan pemutar.
Berdasarkan keputusan daripada ujian kekuatan lenturan, komposisi optimum yang
diperolehi yang paling bagus adalah 90wt% politena dengan 10wt% getah terpakai.
Politena dan juga getah terpakai akan menghasilkan bahan polimer yang baru yang
dapat mengubah sifat. Dengan menambahkan agen penghomogenan di dalam proses
pencampuran politena dengan getah terpakai dapat menggubah sifat mekanikal dan
DEDICATION
To my family and my friends, thank you very much for your support and effort
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to express my gratitude and appreciation to the individuals who involve
in ensuring a successful occurrence and flow of activities throughout my final year
project. My appreciation and gratitude towards my supervisors, Mr Muhammad
Zaimi Bin Zainal Abidin, Mrs Pn Zurina Binti Shamsudin and also to my second
examiner Mr Edeerozey Abd. Manaf for their encouragement and support and for
spending time with me by providing a lot of guidance and ideas for my project
research. With their knowledge and experience really inspired and spurred myself to
learn a lot of things from them. I’m lucky to have an opportunity to work with them
and not least, my appreciation to Hairulhisham Bin Rosnan, and Azhar Shah Bin Abu
Hassan for their time and guidance to complete my research at the laboratory.
Finally, my sincere appreciation is dedicated to my parents Mr Faizal Lim Bin
Abdullah, Mrs Alawiyah Binti Ghazali and as well as the friends for their assistance
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Abstract………
i
Abstrak……….
ii
Dedication………
iii
Acknowledgement………
iv
Table of Contents……….………
v
List of Figures………..
x
List of Tables………...
xii
Nomenclature………
xiii
1. INTRODUCTION
1
1.1
Introduction of rubber induced polymer………..
1
1.2 Statement of the Purpose……….
2
1.3 Problem Statement………...
2
1.4 Objectives………
2
1.5 Scope of study……….
3
2. LITERATURES REVIEW
4
2.1 Polymer……….………...………
4
2.1.1 General View of Polymer..………..
4
2.1.2 Advantages of Polymer………...
5
2.1.3.1 Linear Polymer………
5
2.1.3.2 Branched Polymer………
6
2.1.3.3 Cross-Linked Polymer………
7
2.1.3.4 Network Polymer………
7
2.1.4 Thermoplastic……….
8
2.1.5 Thermoset…………...……….
9
2.1.6 Elastomer……….
9
2.2 Polyethylene………...………..
10
2.2.1 Classification of Polyethylene………..……...………
10
2.2.2 Properties of Polyethylene………...………
10
2.2.3 Application of Polyethylene……….………...………
11
2.3 Rubber………..………
12
2.3.1 Classification of Rubber………..
12
2.3.2 Natural Rubber………
12
2.3.3 Vulcanization………...………
13
2.3.4 Mechanical Properties of Rubber………
14
2.4 Polymer Blending..………..
15
2.4.1 Classification of Polymer Blending……….
15
2.4.2 Importance of Polymer Blending ………
15
2.4.3 Mechanical Properties of Polymer Blending..……….
16
2.4.4.1 Melting Blending……….……….
16
2.4.4.2 Solution Blending……...……….……….
17
2.4.4.3 Latex Blending……….………
17
2.4.4.4 Interpenetrating Networks..………….……….
17
2.5 Processing method of polymer………
18
2.5.1
Internal mixer………...
18
2.6 Flexural Testing Standard………
18
2.7 Flexural Strength………..
19
2.7.1 Classification of Flexural Strength………..
19
2.7.2 Three Point Flexural Strength ………
19
2.7.3 Calculation of Flexural Strength……….
20
2.7.4 Calculation of Flexural Modulus….………
20
3. METHODOLOGY………..
21
3.1 Introduction ……….
21
3.2 Raw material………
23
3.2.1
Preparation of rubber………..
23
3.2.2
Preparation of polyethylene resin………...
23
3.3.1 Internal Mixer……….
24
3.3.1.1 Material preparation……….
25
3.3.1.2 Parameter setting for internal mixer………
26
3.4 Crashing process………..
27
3.4.1 Crashing machine………...……….
27
3.5 Forming process……..……….
28
3.5.1 Hot press………...………...
28
3.5.2 Parameter of hot pressing………
29
3.6 Flexural test………...………...
30
3.6.1 Flexural test configuration………..
30
3.6.2 Specimen preparation….……….
31
3.6.3 Run flexural test
32
4. RESULTS………..………...………
33
4.1 Flexural testing………
33
4.1.1 Data collection……….
33
4.1.2 Result calculation of flexural strength………
35
4.1.3 Result calculation of flexural modulus………
36
4.1.4 Max force………
38
4.1.6 Max strain………
40
5. DISCUSSION ………...………..
41
5.1 Introduction………..
41
5.2 Flexural strength………..
41
5.3 Flexural modulus……….
42
5.4 Effect of internal mixer………
43
5.5 Homogenizing agents………..
44
6. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION…..………..
45
6.1 Conclusion………...
45
6.2 Future work………..
46
7. REFERENCE………..
47
8. APPENDICES
A
Pressure standard of hot press
B
Control panel of hot press parameter
C
Calculation of flexural test
D
Calculation of flexural test 2
E
Procedure of internal mixer
F
Process flow chart of internal mixer
LIST OF FIGURES
2.1
Polymer categories……….
5
2.2
Linear chain structure………
6
2.3
Branches chain structure………
6
2.4
Cross-linked chain structure………..
7
2.5
Network chain structure……….
7
2.6
Recycle symbols………
8
2.7
Basic Structure of polymer molecules: (a) Ethylene molecules;
(b) Polyethylene, a linear chain of many ethylene molecules………...
12
2.8
Polymerization of polyisoprene……….
13
2.9
‘cis’ configuration………..
13
2.10 ‘trans’ configuration………...
13
2.11 Vulcanization process………
14
2.12 Flexural test………
19
3.1
Flow chart of research methodology………..
22
3.2
Particles of rubber………..
23
3.3
Particles of polyethylene resin………..
24
3.4
Thermo HAAKE PolyLab Mixer OS………
24
3.5
The weighting process: (a) weight polyethylene; (b) weight waste rubber...
25
3.6
Crusher machine………
27
3.8
Schematic of hot press………..
29
3.9
Specimen of testing material: (a) polyethylene with 10wt% rubber, (b)
polyethylene with 20wt% rubber and (c) polyethylene with 30wt% rubber.
30
3.10 Specimen for flexural test……….
31
3.11 The position of specimen before run flexural test……….
32
3.12 The position of specimen after run flexural test……...……….
32
4.1
Graph of force (kN) versus stroke strain (%) for specimen PE/20% rubber
(sample 5)………...
36
4.2
The bar graph max force of polyethylene with waste rubber………
38
4.3
The bar graph max stress of polyethylene with waste rubber………..
39
4.4
The bar graph max strain of polyethylene with waste rubber………
40
5.1
The graph flexural strength of polyethylene and waste rubber……….
41
LIST OF TABLES
2.1 Application of polyethylene………
11
3.1 The composition of polyethylene and waste rubber………
25
3.2 The internal mixer parameter for polyethylene and waste rubber…………..
26
3.3 Parameter of hot press……….
29
4.1 Data of flexural testing………
33
NOMENCLATURE
° C
- Degree celcius
m
- Meter
mm
- Milimeter
N
- Newton
rpm
- Rotor per minute
Pa
- Pascal
Avg
- Average
Tg
- Glass Transition Temperature
Mpa
- Mega Pascal
Max
- Maximum
min
- Minutes
SEM
- Scanning Electron Microscope
ASTM
- American Standard Testing Material
PE
- Polyethylene
HDPE
- High Density Polyethylene
LDPE
- Low Density Polyethylene
UHMWPE
- Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
PP
- Polypropylene
PVC
- Polyvinyl chloride
PS
- Polystryene
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1
Introduction of rubber induced polymer
The use of recycled rubber taken from old tires into polymer, polyethylene and other
types of common use polymer to produce various type of characteristic polymer.
These waste rubbers from old tires suggested to be crushed into tiny bits before
mixing it with polymer resin. Polymer blend or mixing is a mixture of two or more
polymers with improvement in the properties. The important of mixing two or more
polymers are to achieve enhanced properties such as toughness, strength,
processability, chemical resistance, weatherability, heats stability, and flow behavior.
The optimum condition to produce polymer blend can be determined by studying the
mechanical properties of the blend. It depends on the composition of blend elements
and method of producing it such as internal mixer. Main components that are needed
to be consider in producing Rubber-polyethylene, PE polymer are the ratio of
material (waste rubber and polyethylene, PE), particle size, process parameter
(temperature and time) and method of producing it such as internal mixer, machine
and hot press for forming the rubber induced polymer. After the polymer blend has
been produce, flexural test is conducted to determine the best composition and
process parameter in producing the waste rubber induce polypropylene polymer
1.2
Statement of purpose
The purpose of this research is to study and analyzed the flexural strength of the
optimum condition to produce waste rubber induced polymer (Polyethylene, PE) that
depends on the composition of the material, the process of blend and the parameter
setting during blending process.
1.3
Problem statement
Rubber and commonly used polymer such as polyethylene (PE) have different
characteristics for example elasticity, heat resistance and also durability. By
combining these various characteristics of the both material hope to get a new
polymeric material that have a good flexural strength based on the composition of the
material. The correct method of mixing the both material need to be determine so
that the suitable process and parameter would create a new polymeric material.
1.4
Objectives
The objectives of this study are:
i) To study the method of producing the waste rubber induced polymer,
polyethylene (PE).
ii)To analyze the flexural strength of the waste rubber induced polymer,
polyethylene (PE).
iii)To find the optimum condition of waste rubber induced polymer, polyethylene
1.5
Scope of study
The polymer material (Polyethylene, PE) induced the waste rubber only will be cover
in this study. By doing mixing process on both materials based on the composition,
the ideal temperature and mixing time are obtain to produce new polymer. The
process that involve in the study is the mixing process by using internal mixer
machine, where else there are forming process such as hot press involved in this
study concerning about the optimum condition to produce waste rubber induced
polymer (Polyethylene, PE). The mechanical testing that involve in this study is
flexural testing that based on ASTM D790. This study does not cover the others
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1
Polymer
2.1.1
General view of polymer
The word polymer is derived from the classical Greek words poly meaning “many”
and meres meaning “parts” (Joel R. Fried, 2003). Simply stated, a polymer is a
long-chain molecule that is composed of a large number of repeating units of identifical
structure. Certain polymers, such as proteins, cellulose, and silk, are found in nature,
while routes. Polymers naturally can be produced synthetically. Polymers that are
capable of high extension under ambient conditions find important application as
elastomers. Others polymer may have characteristics that permit their formation into
long fibers suitable for textile applications.
In the contrast to the usage of the word polymer, those commercial materials other
than elastomers and fibers that are derived from synthetic polymers are called
plastics. A typical commercial plastic resin may contain two or more polymers in
addition to various additives and fillers. These are added to improve a particular
property such as process ability, thermal or environmental stability, or modulus of
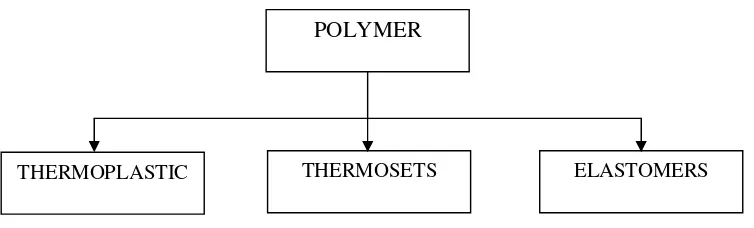
Figure 2.1: Polymer categories
2.1.2
Advantages of polymer
The advantages of the polymer that have been widely used in the application today in
term of the following characteristics:
1. Corrosion resistance and resistance to chemicals
2. Low density
3. Low electrical and thermal conductivity
4. High strength-to-weight-ratio, particularly when reinforced
5. Noise reduction
6. Wide choice of colors and transparencies
7. Ease to manufacturing and complexity of design possibilities
8. Relatively inexpensive
2.1.3
Structure of polymer
2.1.3.1
Linear polymer
Linear structure (Refer Figure 2.2) has a sequential structure based on the properties
of the polymer that depends on the monomers and the arrangement of the molecular
structure. A linear molecular is not necessarily straight in shape. Generally, a POLYMER
polymer may consist of more than one type of structure; a linear polymer may
contain some branched and linked chains. As a result of branching and
[image:24.612.257.408.160.262.2]cross-linking, the polymer’s properties might change (R.A Higgins, 1998).
Figure 2.2: Linear chain structure
2.1.3.2
Branched polymer
Branched polymer is determined by the properties of the polymer that depends on the
type of monomers and the arrangement of the molecular structure. The branched
polymers are side-branch chains that attach to main chain during the synthesis of the
polymer. The branching interferes with the relative movement of the molecular
chains as for the result, deformation resistance and stress crack are increased (R.A
Higgins, 1998). The density of the branched polymer might also effect the efficiency
of the packing polymer chains. The entanglement of the branches makes the
movements more difficult, a phenomenon akin to increased strength.
[image:24.612.256.407.553.653.2]