AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE MADE BY THE
ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA
A THESIS
BY
ATIKA AKHMAR 130721005
AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE TEXT MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA
A THESIS
BY
ATIKA AKHMAR REG NO. 130721005
SUPERVISOR
Drs. Chairul Husni, M.Ed. TESOL.
NIP. 19570308 198403 1 004 NIP. 19750209 20812 1 002
Rahmadsyah Rangkuti, M.A, Ph.D
Submitted to Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara Medan in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Sastra Form Department of English.
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH
Approved by the Department of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara (USU) Medan as thesis for The Sarjana Sastra Examination.
Head, Secretary,
Dr. H. Muhizar Mucthar, M.S
NIP. 19541117 198003 1 002 NIP. 19750209 200812 1 002
Accepted by the Board of Examiners in partial fulfillment of requirements for the degree of Sarjana Sastra from the Department of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara.
The examination is held in the faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara on Monday, July 6th , 2015
The Dean of Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara
NIP. 19511013 197603 1 001 Dr. H. Syahron Lubis, M.A.
Board of Examiners
Dr. H. Muhizar Muchtar, M.S. ……….
Rahmadsyah Rangkuti, M.A, Ph,D. ……….
Dr. Hj. Masdiana Lubis, M. Hum. ……….
Drs. Chairul Husni, M. Ed. TESOL, ……….
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION
I, ATIKA AKHMAR DECLARE THAT I AM THE SOLE AUTHOR OF THIS THESIS EXCEPT WHERE REFERENCE IS MADE IN THE TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS CONTAINS NO MATERIAL PUBLISHED ELSEWHERE OF EXTRECTED IN WHOLE OR IN PART FROM A THESIS BY WHICH I HAVE QUALIFIED FOR A AWARDED ANOTHER DEGREE. NO MATTER PERSON’S WORK HAS BEEN USED WITHOUT DUE TO ACKNOLEDGEMENTS IN THE MAIN TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS HAS NOT BEEN SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF ANOTHER DEGREE IN ANY TERTIARY EDUCATION.
Signed :………
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION
NAME : ATIKA AKHMAR
TITLE OF THESIS : AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE TEXT MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA
QUALIFICATION : S-1/SARJANA SASTRA DEPARTMENT : ENGLISH
I AM WILLING THAT MY THESIS SHOULD BE AVAILABLE FOR REPRODUCTION AT THE DISCRETION OF THE LIBRARIAN OF DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH, FACULTY OF CULTURAL STUDIES UNIVERSITY OF SUMATERA UTARA ON THE UNDERSTANDING THAT USERS ARE MADE AWARE OF THEIR OBLIGATION UNDER THE LAW OF THE REPUBLIC INDONESIA.
ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA” berisi tentang analisa kesalahan yang dibuat oleh siswa/siswi kelas sebelas (XI). Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk menemukan jenis-jenis kesalahan dan kesalahan yang paling dominan yang dibuat oleh siswa/i berdasarkan jenis-jenis kesalahanya. Dalam menyelesaikan penelitian ini, metode yang digunakan adalah penelitian lapangan dengan menerapkan metode kualitatif. Instrument yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data adalah dengan menyuruh siswa/i menuliskan sebuah teks narativ mengenai pengalaman mereka saat liburan. Berdasarkan grammatical aspek, kesalahan kesalahan yang dianalisis dibatasi hanya pada penggunan past tense, adjective, adverb, article, preposition, possessive, conjunction, punctuation, capitalization and spelling. Sebagai hasil penelitian, ditemukan bahwa kesalahan yang dominant adalah kesalahan informasi 32,9%, kesalahan kehilangan 26,1%, kesalahan penambahan 21,7% dan kesalahan susunan 19,3%. Dan hasil dari kesalahan secara keseluruhan, menunjukan bahwa kesalahan informasi penggunaan past tense yang paling dominan 11,0%.
ABSTRACT
Thesis entitled “AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA” contains about the analysis of errors made by the eleventh grade students. The purpose of this study is to find out the kinds of error and the dominant error made by the students based on the kinds of error. In completing this research, the method that is used is field research by applying qualitative method. The instrument used to collect data is by asking the students to write a narrative text based on their experiences during holiday. Based on the grammatical aspect, the errors should be limited in using past tense, adjective, adverb, article, preposition, possessive, conjunction, punctuation, capitalization and spelling. As the result of the research, it was found that the dominant error is Misformation Error 32,9%, Omission Error 26,1%, Addition Error 21,7% dan Misordering Error 19,3%. And from the general errors, it shows that Minsinformation Error in using past tense is the dominant error 11,0%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmaanirrahiim.
First of all, “Alhamdulillah” the writer gives praise and thank to Allah SWT who has given her the mercy such as life, healthy, times, believe, and blessing. Shalawat and Salam for the Prophet Muhammad SAW who has brought us from the darkness to the brightness.
This thesis could have been accomplished with the guidance, suggestions and comments from many people. In this occasion, the writer would like to express her sincere gratitude toward her supervisor, Drs. Chairul Husni, M.ED. TESOL and co-supervisor, Rahmadsyah Rangkuti, M.A, Ph.D, for the benefit of their wide knowledge and for their suggestions, guidance and advice in making corrections to this thesis.
Her gratitude also goes to the Dean of Faculty of Cultural Studies Dr. Syahron Lubis, the Head of English Departement Dr. Muhizar Muchtar M.S. and the Secretary of English Department Rahmadsyah Rangkuti M.A., Ph.D. She also wishes to express her thanks to all the lectures of the English Department for their helping and valuable knowledge during her study at this department.
Then, her deepest thank and love go to her beloved parents, Achyar Syauraf and Dra. Maria br. Bangun, who have patiently given moral, spiritual, and prays to their daughter. She also thank to her siblings, Yulia Akhyar, SS., Annisa Nadra, A.Md and Indra Mulia A,Md who have really support her education from the first semester until completed this thesis.
For her best friends Ingrid, Dayana, Nelfi, Yati who always gave her support, critics, and advices. Then for her dearest partner Ivana who always sat beside her during the academic years. The last but not least, thanks for her friends Sheila, Mariaty, Reza, Rummy, Siti, Tya, Winda, Hanna and Rasingan who gives contribution in supporting the writer to complete the study and her thesis.
Finally, I hope that this thesis will be worthwhile contribution for the readers. And also receive any constructive criticism to develop this thesis.
Medan, July 2015 The Writer
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION ... i
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION ... ii
ABSTRAK ... iii
CHAPTER II REVIEWOF LITERATURE ... 5
2.1 Previous Studies ... 5
2.2 Definition of Writing ... 7
2.3 The Features of Effective Writing ... 8
2.4 Text and Genre ... 9
2.4.1 Narrative Text………. 12
2.4.2The Generic Structure of Narrative Text ……… .... 12
2.4.3The Language Feature of Narrative Text ……… ... 13
2.4.4The example of narrative text ……….. .. 16
2.5 Grammar ... 17
2.6 English Tense ... 18
2.7 Definition of Error Analysis ... 20
2.7.2Sources of Error ... 23
2.7.3The causes of Error ... 23
CHAPTER III METHODEAND RESEARCH ... 25
3.1 Research Design ... 25
3.2 Population and Sample ... 26
3.2.1 Population ... 26
3.2.2 Sample ... 26
3.3 Technique of Collecting Data ... 27
3.4 Instrument of Collecting Data ... 27
3.5 Technique of Analyzing Data ... 27
CHAPTER IV ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS ... 30
4.1 Data Analysis ... 30
4.1.10Kinds of Error in Using Spelling ... 51
4.2 Findings ... 52
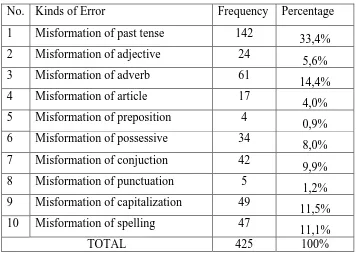
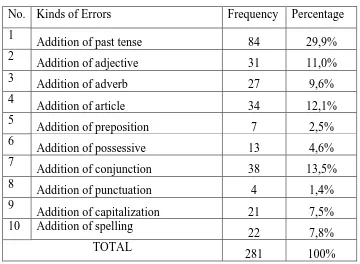
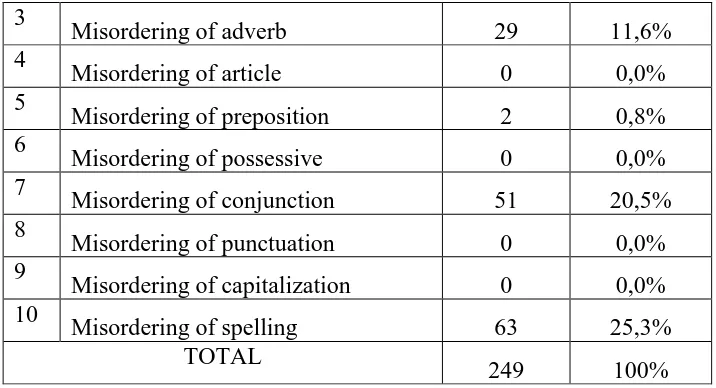
4.2.1 The Table of Erros ... 52
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 57
5.1 Conclusion ... 57
REFERENCES ... 61 `
List of Tables
Table 1. Kinds of Error……… 52
Table 2. The Errors of Misformation ……….. 53
Table 3. The Errors of Omission……….. 53
Table 4. The Errors of Addition……… 54
Table 5. The Errors of Misordering……….. 54
ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA” berisi tentang analisa kesalahan yang dibuat oleh siswa/siswi kelas sebelas (XI). Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk menemukan jenis-jenis kesalahan dan kesalahan yang paling dominan yang dibuat oleh siswa/i berdasarkan jenis-jenis kesalahanya. Dalam menyelesaikan penelitian ini, metode yang digunakan adalah penelitian lapangan dengan menerapkan metode kualitatif. Instrument yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data adalah dengan menyuruh siswa/i menuliskan sebuah teks narativ mengenai pengalaman mereka saat liburan. Berdasarkan grammatical aspek, kesalahan kesalahan yang dianalisis dibatasi hanya pada penggunan past tense, adjective, adverb, article, preposition, possessive, conjunction, punctuation, capitalization and spelling. Sebagai hasil penelitian, ditemukan bahwa kesalahan yang dominant adalah kesalahan informasi 32,9%, kesalahan kehilangan 26,1%, kesalahan penambahan 21,7% dan kesalahan susunan 19,3%. Dan hasil dari kesalahan secara keseluruhan, menunjukan bahwa kesalahan informasi penggunaan past tense yang paling dominan 11,0%.
ABSTRACT
Thesis entitled “AN ERROR ANALYSIS IN WRITING NARRATIVE MADE BY THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMK TELADAN SUMATERA UTARA 1 HELVETIA” contains about the analysis of errors made by the eleventh grade students. The purpose of this study is to find out the kinds of error and the dominant error made by the students based on the kinds of error. In completing this research, the method that is used is field research by applying qualitative method. The instrument used to collect data is by asking the students to write a narrative text based on their experiences during holiday. Based on the grammatical aspect, the errors should be limited in using past tense, adjective, adverb, article, preposition, possessive, conjunction, punctuation, capitalization and spelling. As the result of the research, it was found that the dominant error is Misformation Error 32,9%, Omission Error 26,1%, Addition Error 21,7% dan Misordering Error 19,3%. And from the general errors, it shows that Minsinformation Error in using past tense is the dominant error 11,0%.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
1.1Background of the Study
English gives a big influence to Indonesia education by adding English lesson into its curriculum starting from elementary level until University. English as the most common international language functions needs some basic skills that consist of speaking, listening, reading, and writing. From the four basic skills mentioned above, writing is much more difficult. Moreover, Hyland (2003: 3-14) states writing is not just arranging words into a sentence, linking the sentences into a paragraph, and ordering the paragraphs into a text. It also requires grammatical and lexical knowledge, understanding in applying the grammatical knowledge into different context and purposes and knowledge of topic that are going to be written.
As second foreign language, English takes an important place and has used largely in many sectors of life, such as education, culture, economic, etc. In the field of education, English plays as the subject, which is taught and learned by many people. In the course of learning English as second foreign language, students commonly make mistakes are producing utterances in speech and writing. These mistakes are judged by the rules of the foreign language.
happen because they do not realize they have made a mistake and also they do not know how to understand about the aspect in the second foreign language, actually in grammar. Grammars are needed in a text, without grammar we cannot arrange a sentence properly.
Knapp (2005:33) says that grammar therefore needs to deal with language from three perspectives: the generic, the textual, and syntactical. Error is a systematic deviation from the accepted system of target language. Mistake is a non systematic deviation from accepted system of the target language. While lapse is a non systematic deviation from the accepted system of language being learnt, it’s usually due to human limitation such as tiredness, nervous, and fatigue.
If we talk about grammar, we cannot be separated it from tenses. In this thesis, the writer focuses on the past tense. Past tense as one of the most important part of language features in narrative text has a big influence in producing a good text. It is the same as what Pardiyono (2007: 114) states that past tense is one of the most frequently used tense to tell about past activities of events. Moreover, the grammatical and mechanical rules cannot be separated. It would be impossible to learn or to write something effectively without knowing the grammar and mechanics.
Based on their curriculum, there are some topics that will discuss for one year; they are tenses, grammar, question tag, exposition, conjunction and narrative text. The students have studied simple past tense in English subject which is twice a week for each class and the time 2x 40 minutes for one meeting was allotted.Furthermore, the writer needs further some evaluation of the gravity from each type of error in a communicative or pedagogical point of view. Finally, the writer needs some explanations of the causes of each type of error so that the writer undertakes appropriate remedial measure.
1.2Problem of the Study
In conducting a research, the problems must be stated clearly so that the objectives of the study and method can be meaningful. The problems of the study which the writer would like to analyze as follows:
a. What kinds of errors are made by the eleventh grader students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1Helvetia in writing narrative text?
b. What are the dominant errors in writing narrative text by the eleventh grader students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1Helvetia
1.3Scope of the Study
problems more accurately, precisely, and correctly. Therefore, the writer would like to limit the analysis grammatically in writing personal narrative.
1.4Objectives of the Study
The objectives of the studies are:
a. To find out the kinds of errors made by the eleventh graders of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1 Helvetia in using past tenses in the narrative text.
b. To find out the most errors in writing narrative text by the eleventh grader students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1Helvetia
1.5Significance of the Study
The findings of the study are expected to be useful for:
a. For the teachers, this study is useful to improve their ability in teaching writing by paying more attention to the strategy of teaching writing.
b. For the students, the result can encourage and stimulate them in improving their English ability achievement.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
2.1Related Studies
To supporting the idea of choosing the topic, some previous studies are needed such as:
Batubara (2009) in her thesisentitled An Error analysis of auxiliary Verbs Made by the 2006/2007 Ninth Grade Students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Al-Ulum
Medan, concludes that the most error made by students is the using of do (36,26%),
the using of be (32,90%), and an error in using have (30,84%).
Pujiasi (2010) in her thesis entitled The Errors of Unity and Coherence In Writing English Paragraph Made by The Sixth Semester Students of D-3 English
Study of USU : A Case Study, concludes that the percentage made by the students in
a sequence : 3.25% in using the topic and controlling idea into a good subject and verb, 9.74% in limiting the controlling idea into a good specific idea, 11.04% in using the irrelevant sentences, 2.59% in making the repetition of key nouns, 4.55% in making the constituent of pronouns, 44.15% in applicating the true transition signals, and 24,68% in applicating the chronological orders.
Napitupulu (2010), The Errors of Using Adverb by the Eleventh Years Students of SMA Negri 7 Medan, concludes that the errors made by the students are
manner 7,04%, Overgeneralization of adverb of time 9.85%, Overgeneralization of adverb of place 4.22%, Overgeneralization of adverb of manner 15.49%.
IdawatiSitumorang (2011), An Error Analysis in Using Tenses Made by the Third Year Students of SMK 7 Medan, concludes that the kinds of error made by the
students in using tenses are Misformation 78.87% (Misformation of Simple Present Tense 6.16%, Misformation of Present Continues Tense 8.27%, Misformation of Simple Past Tense 18.31%, Misformation of Pas continues Tense 25.88% and Misformation of Simple Future 20.25%), Omission 13.73% (Omission of Simple past Tense 2.11%, Omission of Present Continues Tense 7.92, Omission of Simple Past Tense 0%, omission of Past Continues Tense 3.52%, and Omission of Simple Future Tense 0%, Overgeneralization of Simple Past Tense 3.52%, Overgeneralization of Past Continues Tense 0%, and Overgeneralization of Simple Future Tense) and Incomplete Rule of Application 3.87% (Incomplete application of Rules of Simple Past Tense 2.29%, Incomplete Application of Rules of Past Continues Tense 0%, and Incomplete Application of Rules of Simple Future Tense 0%).
Rukiah (2012)An Error Analysis In Using Passive Voice Made By Eleventh Year Students Of MAN 1 Panyabungan, concludes that the percentage of correct and
incorrect answers of passive voice by students of 32 questions. Finds the most error made by students in simple future tense (27.75%), simple past tense (26.59%), and the last is simple present tense (20.23%)
Djayanti (2012) An Error Analysis of the Use of Simple Sentence Made by the Ninth Grade Students of SMP Negri 2 PancurBatu,concludes thatMisformation error
error with 25.15%, involves: -ing article, verb, preposition, reflexive pronoun, pronoun, determiner, 3rd person singular, possessive maker, and be. Misordering with 19.95%, involves: misordering of verb phrase and misordering of noun phrase. And the lowest error is addition error with 11,39%, involves: addition of determiner, plural maker (s/es), -ing, modal, be possessive maker, verb, preposition, pronoun, adjective, article, noun, and 3rdperson singular verb maker.
Sri Wahyuni(2014), Teaching Writing Design Based On the Students’ Difficulties in Writing Narrative Texts, concludes that From 35 Second Grade
Students of Junior High School, there were 9 students did not face difficulty in writing narrative text and 26 students faced difficulties as below:
a. In using Past tense occurred 152 cases or 80, 85% from all cases. b. In using conjunction occurred 26 cases or 13,83% from all cases. c. In using adjective occurred 10 cases or 5,32% from all cases.
2.2Definition of Writing
The meaning of writing is about the way we arrange a sentence. If we can arrange sentence well, we will be able to write down anything easily. Generally, EFL learners tend to write down a long and complex sentence without keeping a clear meaning related to the sentence, even the sentence has no meaning at all (Pratyasto, 2011: 1)
Writing is essential features of learning a language because it provides a very good means of foxing the vocabulary, spelling, and sentence pattern. It becomes an important aspect of students’ expression at higher stage.
Langan (2008:4) explains the important difference between reading and writing is that in writing, any idea that you advance must be supported with specific reasons or details. Supporting ideas can be expressed by words, phrase, sentence, or paragraph which consists in written text.
From those definitions, it can be concluded that writing is organizing experience, ideas or information, in the form of arranges sentences or even paragraphs. We can also add that in order to make a good written text we have to pay attention to the rules of writing when we are going to write a composition such as grammar, sentence structure, vocabulary, punctuation, spelling, adjective, adverb and capitalization.
2.3 The Features of Effective Writing
According to Kathleen Cali and Kim Bowen on
effective writing as mentioned in the following: a. Focus
Focus is the topic or subject developed by the learner. b. Organization
c. Support and Elaboration
Support and elaboration is the extension and development of the topic. The students provide sufficient elaboration to present the ideas and / or events clearly.
d. Style
Style is the control of language that is appropriate to the purpose, audience, and context of the writing text. The writer’s style is evident through word choice (using appropriate, words, phrases, and description to enange the audience) and sentence fluency (using a variety of sentence styles to establish effective relationship between and among ideas, cause, and/or statements) e. Convention
Conventions involve correctness in sentence formation, usage, and mechanics. The learner has control of grammatical conventions that are appropriate to the writing task.
2.4 Text and Genre
Saragih, A. (2013) states that a text is a semantic unit not a formal one, which may be realized by a sound, word, phrase, clause, sentences of paragraph. Texts are classified into genres on the basis of the intent of the communicator.
Genre is an intuitively attractive concept that helps to organize the common-sense labels we use to categorize texts and situations in which they occur.
Based on Hartono (2011) cited i the discourse analysis, has been characterized either by Kress (1989) or Swales (1990) as being comprised of communicative events whose members share sets of communicative purposes that are recognized by parent discourse community. The purpose, then, shapes schematic structure and influences choice of content and style (Swales 1990: 58). The points from the two opinions about genre are: (1) cultural events; (2) socially recognized; (3) purposeful language activity, (4) using pattern or structure to realize meanings. Hammond et al. (1992: 2) clarifies that genres refer to culturally evolved ways of getting things done which involve use of language. Each is characterized by a distinctive schematic structure through which its social function is realized.
According to Pardiyono (2007 :18) there are thirteen types of text, they are: a. Recount
Social function: to retells events for the purpose of informing and entertaining. b. Analytical Exposition
Social function: to persuade the reader or listener that something is the case. c. News Item
Social function: to inform readers, listeners or viewers about events of the day which are considered newsworthy or importance.
d. Report
Social function: to describe the way things are, with reference to arrange of natural, man mad and social phenomenon in our environment.
e. Anecdote
f. Narrative
Social function: to amuse, entertain and deal with actual or vicarious experience in different ways; Narrative deals with problematic events which lead to a crisis or turning point of some kind, which is turn finds a resolution.
g. Procedure
Social function: to describe how something is accomplished through a sequence of actions of steps.
h. Description
Social function: to describe a particular person, place or thing. i. Hortatory Exposition
Social function: to persuade the reader of listener that something should or should not be the case.
j. Explanation
Social function: to explain the processes involved in the information or working of natural or socio cultural phenomenon.
k. Discussion
Social function: to present (at least) two points of view about an issue. l. Reviews
Social function: to critique an art work or event for a public audience. Such works of art include movies, TV shows, books, concerts, etc.
m. Spoof
2.4.1 Narrative Text
Pratyasto (2011: 39) states that a narrative text is a kind of texts which tells a series actions from time to time that is outlined through early action, cfrisi actions and then resolution. This text is to entertain the readers and even sometimes the take makes the readers are experiencing themselves the action told in the story.
Thus, Pratyasto adds that narrative text has the basic purpose namely to entertain and to gain and hold the reader’s interest in a story. Narrative may include fairy stories, science fiction, romance, horror stories, adventure stories, fables, myths and legend, historical narrative, ballads and personal experience.
2.4.2 The Generic Structure of Narrative Text
Pratyasto (2011: 39) adds the generic structure of narrative text include orientation, complication and resolution.
a. Orientation: As the first stage, orientations which introduce the major characters, the topic of story and established setting – time and place that the story happens.
b. Complication: As the second stage, complication which is the series action unfold. This stage contains the event falls on the major characters and explains a conflict among the characters. The conflict can be shown naturally, socially, or psychologically. He adds that complication is the main element in the narrative text.
success or not, but the main point is that the appeared-conlfict has become extinct.
2.4.3 The Language Feature of Narrative Text
Pratyasto (2011: 39) also gives explanation about the significant lexico grammatical features (language features) of narrative:
a. Using opening words that interesting the readers b. Focus on specific and usually individual participant
c. Use storytelling convention especially on myth and fairy story, such as once upon a time
d. Use of past tense
e. Use variated-sentences: simple compound, or complex sentence
f. Use of time words: after that, then, a few moment later, etc, to connect an event with others, and
g. A noun group describes and setting.
According to Pardiyono (2007: 97), some of grammatical patterns of writing narrative text consist of Past tense, Adjective, Adverb and Conjunction.
a. Past tense
One of the most frequently used tense to tell about past activities or events is past tense. It is marked with the use of past tense verbs in predicate.
Example:
b. Adjective
The language feature of narrative text is by using adjective with the purpose is for showing the personal attitude, for example: frightened, quite, calm, worried, confused, anxious, happy, beautiful, etc
c. Adverb
Adverb plays important in its role of contributing for better clarity of the message conveyed in the sentence. It can express the information about time, place, reason, purpose, status, and frequency. Lot of adverbs is marked with the use of prepositions: in, at, after, as, to, as, etc. Adverb can be in the form of word or phrase.
Example:
- My teacher always speak English - Please stand over there
- I will go to Bali tomorrow d. Conjunction
A sentence is a group of words that contains a subject and verb to express a complete thought, which begins with capital letter and ended with period. A sentence can be formed from one or two clauses that joined with conjunctions or relative connectors.
Example:
- He couldn’t go because he was ill.
- My mother bought me a beautiful dress and a wallet. - She is not American but British.
a. Spelling
Harmer (2004:12) says that spelling is one factor of writing. A good spelling makes meaningful writing. It will influence the meaning of the sentence; misspelling will change the meaning of the words.
b. Punctuation
Cowan and Cowan (1980: 660-661) states that punctuation is very important in indicating the writer’s purpose. It is a series of rules that are applied in sentences. Memering and O’Hare (1980: 401-421) state that one of the best tools a writer has is punctuation. They add that with a view small signal, the writer can tell the reader how to interpret the ideas on the page and how to understand the relationships among them. There are dozen significant marks in the punctuation system, they are:
a. Period (.): Open the window, please. b. Question mark (?): Is he a student? c. Exclamation mark (!): Be careful!
d. Comma (,): Mary, by the way, received your mail last night.
e. Semicolon (;): The pianist was very ill, therefore, the concert was cancelled. f. Colon (:) The following words are conjunction: and, but, or, …
g. Quotation mark (“…”): “I am going for a walk,” she said. h. Apostrophe (‘): Can’t you run faster?
i. Parentheses ((…)): If it rain (and we hope it doesn’t), the picnic will be cancelled. j. Dash (---): There are four skills in English—listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
c. Capitalization
Memering and O’Hare (1980: 438) says that the basis rule, to which there are very few exceptions, it to capitalize “first” words and words that are considered proper names or titles. They have three main purposes; to let the reader know a sentence is beginning, to show important words in a title, and to signal proper names and official titles.
Example: I go to school every day. I live in Medan
My father and Mr. Robin arrived in Jakarta at 19.00 o’clock
2.4.4 The Example of Personal Narrative
This text is taken from https://sites.google.com/witing-links/writing-examplars/narrative--my-first-talent-show?.
My first Talent Show
Standing backstage, I could feel my heart thumping in my chest. “Just relax,” my friend Jenny whispered “You’re ready for this.” I nodded. Jenny was right. I’d been practicing my song for the school talent show for six weeks. Still, picturing an audience packed with kids, parents and teaches made me want to run out the door.
I looked out at the sea of faces. The auditorium was dark, but I could see hundreds of eyes staring back at me. The smell of candy bars and popcorn filled the room and I hope Jenny was saving some for me.
As I finished the song, the audience began to clap. I took a bow and walked offstage with a smile plastered across my face. It was such an unforgettable experience in my life, I never thought that I can stand in front of many people like that.
2.5 Grammar
A good written language should be correct in grammar and spelling. Error analysis will ensure your writing clear, precise, and comprehensible. Correct grammar and spelling make a positive impression on readers. Knapp and Watkins (2005:31) state, one of the cornerstones of this approach to genre, text and grammar is the relationship generated between genre and grammar. While systemic-functional grammar forges a relationship between context and grammar, as we have seen, such a relationship is often problematic. In many respects the gap between context and grammar is simply too wide, often resulting in deterministic relationships.
The genre and grammar-based approach creates a closer congruity as the concept of genre is not deterministic or derivative, but relies upon the relationship between social purpose and available grammatical resources. Grammar remains simply a set of rules for correctness or appropriateness.
sentences, but also with the way written English functions to communicate experiences and knowledge of the world. In addition, narrative genres often deliberately break the rules of grammar and punctuation for literary effect.
The genre and grammar model of language which are describing requires us to become aware of the forms that language takes in the social contexts in which texts are commonly used. It requires us to look at the structures and grammatical features that make up these forms, and to look at the way that language serves the intentions of those who use and produce it, as well as the effects it has for audiences.
2.6 English Tenses
In learning English language, we cannot be separated from learning grammar, especially learning tenses. When we are learning English, one of the general and base problems that are usually faced is tenses problem. Pardiyono (2007: 114) says that most of students do not understand what is spoken tense problem.
Edward (2001) says that tense is a form of a verb that shows the time of an action or condition. If someone wants to talk about tense, he or she may not escape from grammar because tense is part of structure. Grammar may be roughly defined as the way a language manipulates and combines words in order to form longer units of meaning. According to Pardiyono (2007: 114) tense is a variation of the change of verb form includes full verb, be and auxiliary that are usually used as predicate in the sentence, which should be appropriated with the kinds of time expression.
a. Simple Present Tense
Simple present tense is a tense used to assert an activity that has been a habit or action. There are two types of present tense; verbal and nominal (Sujardi et.al, 1980)
Positive (+) S + V1(s / es)
Negative (-) S + do/does not + V1 Question (?) Do/does + S + V1?
For Example:
a. She swims in the swimming pool every morning (+)
b. She doesn’t swim in the swimming pool every morning (-)
c. Does she swim in the swimming pool every morning (?)
b. Simple Past Tense
Thompson (1986: 162) says that simple past tense is used for an action whose time is not given but which occupied a period of time now interminated, or occurred at a moment in a period of time now interminated.
Positive (+) S + V2
Negative (-) S + did not + V1 Question (?) Did + S + V1 ?
For example:
a. They made a cake last week (+)
b. They did not make a cake last week (-)
c. Simple Future Tense
Present future tense is a form of time to express a plan that we will do; either it is short time planning or long time planning (Pardiyono, 2007: 68)
Positive (+) S + Shall/Will + V1
Negative (-) S + Shall/Will not + V1
Question (?) Shall/Will + S + V1 ?
For example:
a. She will study to America next year (+)
b. She will not study to America next year (-)
c. Will she study to America next year? (?)
2.7 Definition of Error Analysis
We often hear that people make a lot of mistakes in learning foreign language. Error is a deviation that is made by the learners because they do not understand the rules of the second language and cannot be corrected by themselves while they are learning.While the diminishing of errors is an important criterion for increasing language proficiency, the ultimate goals of second language learning is the attainment of communicative fluency in a language. Error analysis is used to analyze and classify the learners’ error from which the learners learning problem can be inferred.
Corder (1981: 23) cited in Ellis (2010) says that error analysis is the study analysis of the errors made by the second foreign language learners to predict the errors or the difficulties in learning foreign language. Error analysis may be carried out in order to:
a. Find out how well someone learns a language. b. Find out how well someone knows language, and
c. Obtain information on common difficulties in language learning.
Thus, error analysis is the study and the analysis of the errors made by language learners which function as to give the information on how they learn a language, how well they know the language and what difficulties faced by them in achieving the objective.
2.7.1 Types of Error
According to Dulay, Burt, and Krashen in James’ book (1998: 106) errors can be classified into four types, they are:
a. Omission Errors
Omission errors are characterized by the absence of items that must be present in a well-formed utterance.
Example: I very happy during my holiday. It should be: I am very happy during my holiday. b. Addition Errors
It should be: My mother makes a sweet cake for me. c. Misformation Errors
Misformation errors are characterized by the use of the unacceptable forms of the morphemes or structure. While in omission errors the item is not supplied at all. In misformation errors the learner supplies something, although it is incorrect
Example: She don’t know anything. It should be: She doesn’t know anything. d. Misordering Errors
The incorrect placement of a morpheme or group of morphemes in an utterance characterized misordering error. Misordering occur systematically for both L1 and L2 learners.
Example: Mark doesn’t know who is she. It should be: Mark doesn’t know who she is.
On the other hand, Ellis (2010) states, human learning is fundamentally a process that involves the making of mistakes. An error takes place when the deviation arises as a result of lack of knowledge (lack of competence) and mistake occurs when learners fail to perform their competence feature of native speaker speech: competing plans, memory limitations, lack of automaticity.
2.7.2 Sources of Error
Communication strategies are obvious that communication is the conscious employment of verbal mechanisms for communicating an idea when linguistic forms are not available to the learner for some reasons.
2.7.3 The Causes of Error
Brown (2000: 224) says that the cause of errors can be devided into 2 categories, they are:
a. Interlingual errors,that is error caused by interference of the learner’s mother tongue. A different class of error is represented by sentences
b.Intralingual errors,that is cause of errors resulting from complicated system of the target language itself.
Richards (1985: 47) says that the intralingual errors are divided into 4 terms, they are:
a. Over-generalization
Over-generalization happens when a learner uses a certain structure that is over-generalized in the target language. It is caused the learners’ basic experience of certain structure. Generally, overgeneralization is the creation of one deviant structure in place of two regular structures, for example: “She can swim”. In this case, there is an over form of a structure verb “swim” becomes “swims”. It should be “She can swim”. Because “she” usually use verb + s. For example: She swims
b. Ignore of rule restriction
Ignore of rule restriction is failure to observe the restriction of existing structures. That is the application of rules to context where they do not apply.
c. Incomplete application of rules
Incomplete application of rules means errors are due to the occurrence of structures whose deviancy represents the degree of development of rules required to produce acceptable utterance. The learners fail to produce a correct sentence according to the standards rules.
Example: I am is student It should be: I am student
d. False Concepts Hypothesized
False concepts hypothesized means basically errors are the result from faulty comprehension of distinction in the target language.
CHAPTER III METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Research Design
This study observes the difficulties of eleventh grade of senior high school students in writing narrative texts and past tense. In order to answer the research questions on how students’ difficulty in writing narrative texts in terms of linguistic features, this study employ qualitative method which settle collected case study. Moleong (2006: 3) states that qualitative method is a procedure that generates the data in the form of descriptive words in written or spoken from people and observed behavior. The writer has the tendency to become subjectively immersed in the subject matter in this type of research method.
As Ary, et.al. (2010: 455) state, case studies can answer descriptive questions (what happened) or attempt to explain why something happened by looking at a process. They are particularistic (focused on a particular phenomenon, situation, or event), descriptive (providing as an end result a thick rich description), and heuristic (focused on providing new insights).
Moreover, Cohen, Manion and Morrison (2000: 181) say that a case study is a specific instance that is frequently designed to illustrate a more general principle. This study is not only describe the students’ difficulties but also to find out what can be proposed to help the teacher in English to solve the students’ difficulties in writing narrative text.
solve the problem. The solution made by the teachers depend on the students’ difficulties. This is the greatest advantage that the teacher can have conducting a case study.
Moreover, collective case study was used in this study to grain detail information on the phenomenon concerning students’ writing particularly in narratives. Therefore, in the present study, students’ narratives writing will be examined based on the language features by using a case study.
3.2 Population and Sample 3.2.1 Population
The population of this study is class of eleventh grade students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1which is consist of 33 students. The writer choosed this school as location of the research is terms of accessibility and the same research are never conducted in there and the finding of the study is beneficial for the teacher to help the students in improving their knowledge of writing narrative texts.
3.2.2 Sample
3.3 Technique of Collecting Data
Collecting data is a part of a process of supplying the primer data for necessary of the research. Collecting data is the systematic and standard procedure to get the needed data. There is connection between the methods of collecting data with the research problem that will be solved.
In collecting the data, the writer used written test method. The method means that the way of collecting the data by giving question in written form in accomplishment, then it is impossible to use another technique. In this research, the writer collected from the students’ work with the title “Experience During Holiday.”
3.4 Instrument of Collecting Data
In this research, the writer gives a writing test to the eleventh grade students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1 and it focuses on grammatically used in writing personal narrative of English study. Sixty minutes of allocation time was given to the students to complete the test.
3.5 Technique of Analyzing The Data
The data available in this research are analyzed by using descriptive qualitative analysis. It means that the writer tries to give the description of what types of grammatical error that the students make when they compose the personal narrative text.
while for the steps of analysis the writer used Rod Ellis; theory. The steps of analysis are:
1. Identifying Errors
In this step the writer compares the errors sentence (mention it as “original sentence”) with what seem to be moral or ‘correct’ sentences in the target language which correspond with them (mention it as “reconstruction”.
2. Describing Error
This next step is the step where the errors are described and classified into kinds.
3. Explaining Errors
This is last step of the errors analysis. In this step, the writer tried to explain how and why a sentence called be erroneous. After analyzing the errors sentence, the writer identifies the percentages of the errors made by eleventh grade students.
a. Scoring System
Bungin (2005: 40-41) states There are three kinds of research based on the location of the research i.e. library, laboratory, and field research. In this study, field research is applied.
According to Corder (1974) in Ellis ( 1985:52) , these following are the steps in any typical error analysis research :
a. Collecting the samples of learner language b. Identifying the errors
d. Explaining the errors
e. Correcting and evaluating the errors.
To identify the percentages of errors, the writer uses the theory of Bungin (2005):
� =�(�)
� �100%
Notes:
n = stands for the percentage of errors
Fx = stands for the total of frequency of the sub – categories errors N = stands for the total errors of all categories
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
4.1 Data Analysis
This chapter contain of the tabulation and the analysis of errors made by the eleventh grade students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1. The main sources of data in this study were personal narrative text written by accountancy students of SMK Teladan Sumatera Utara 1. The students were asked to write personal narrative text, in about 60 minutes, telling about their experience during holiday.
Based on surface strategy taxonomy, errors are classified into four types; omission, addition, misformation, and misordering. Grammatical competence is one of the several competences that the students have to master to be proficient in a certain language. In grammar, tenses hold an important point. Every kind of tenses has their own functions.
4.1.1 Kinds of Error in Using Past Tense 1) Omission errors
Omission errors are characterized by the absence of items that must be present in a well-formed utterance.
a. Omission of auxiliary
This table shows the samples of omission of auxiliary “did”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(1) We not celebrate the
Christmas in the village.
We did not celebrate the Christmas
(2) I was so sad because my grandmother not visit our house.
I was so sad because my grandmother could not visit our house.
Through comparing the error sentences and reconstructions, it can be seen that the students made errors. The error of those sentences is called “omission”, the students omitted “did” and “could” that must appear in those sentences. The omitting of “did” and “could” in those sentences is not proper to the sentence structure. I think that the students made error because they have not understood yet the formula of past tense.
b. Omission of suffix “ed”
This table shows the samples of omission of suffix “ed”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(3) We visit the museum before
we continue our trip again.
We visited the museum before we
on December 24th, 2014.
My Father arrived in Medan on
December 24th, 2014.
(6) During holiday, I just stay at
home because I was sick.
During holiday, I just stayed at
home because I was sick.
(7) So I just celebrate
Christmas and new year
with my mother and my
sister also my nephew at
home.
So I just celebrated Christmas and
new year with my mother and my
sister also my nephew at home.
students used “listen” instead of “listened” to show an activity in the past. I personally think that they make those errors because lack of understanding about form of verb tense
c. Omission of “to be”
This table shows the samples of omission of “to be”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(8) We very happy and enjoyed
the holiday
We were very happy and enjoyed
the holiday
(9) I just stayed at home
because I sick
I just stayed at home because I was
sick
Related to the sample above, we can see that the omission of to be “were and was” is not correct. The adjective must be added by the proper “to be”. The omission error happens because the students omitted the “to be”, while it must appear in those sentences. It might occur because the students do not understand well about how to put to be in a sentence.
d. Omission of “ing”
This table shows the samples of omission of “ing”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
sentence above is by adding suffix “ing”, the students used “sing” instead of “singing”. Furthermore, it is the same with the second sample above. This error might occur because the students do not understand the use of suffix “ing” well.
2) Addition errors
Addition errors are the opposite of mission errors. They are characterized by the presence of an item which must not be present in a well-formed utterance..
a. Addition of “ed”
This table shows the samples of addition “ed”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
I met my family in Siantar
The error sentences also become grammatically incorrect because they added “ed” for “read”. “Read” must not be added by “ed” because it is an irregular verb, thus the verb does not change into the other form or added by “ed”. Most verbs are regular, but many common verbs have irregular past form. This error occurs because of the students’ lack of knowledge in using suffix “ed” well.
b. Addition of “to be”
This table shows the samples of addition of “tobe”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(14) My mother was made
some cakes in my sister’s
house
My mother made some cakes in my
sister’s house
(15) I was bought a beautiful
red wallet for my mom
I bought a beautiful red wallet for
(16) I am went to village. I went to village.
Related to the samples above, addition errors occur because the students added to be “was, were” that must not appear in those sentences. To make those sentences above become correct sentences, they must delete to be in those sentences. Be careful, the simple past in English may look like a tense in our own language, but the meaning may be different. It implies that the error happened because the students lack understands about how to use to be properly.
3) Misinforamtion Errors
Misformation errors are characterized by the use of the unacceptable forms of the morphemes or structure. While in omission errors the item is not supplied at all. In misformation errors the learner supplies something, although it is incorrect.
a. Misformation of Irregular Verb
This table shows the samples of misformation of irregular verb.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(17)Time so fast by gone and
come back home in the evening
Time so fast by gone and came back
home in the evening.
(18)We go to the church at night. We went to the church at night.
(19)I buy souvenir from Samosir
to my friends.
I bought souvenir from Samosir to
my friends.
such as: “Go – Went” and “Buy – Bought”. There is no way to tell what form an irregular verb is going to take in a change tense, the only option for an English speaker is to commit the changes to memory.
I assume that the students in Indonesia commonly make errors in using past tense because there are some differences between Bahasa Indonesia and English when we talk about something in the past. In English, if we want to talk about something in the past, we do not only put the adverbs of time, but also change the verbs into past form.
b. Misformation of “to be”
This table shows the samples of misformation of to be.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(20) I am very happy during
holiday
I was very happy during holiday
(21) We are singing all day
in my house
We were singing all day in my
house
c. Misformation of “auxiliary”
This table shows the samples of misformation of “auxiliary”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(22) Because tomorrow morning
I will go to school.
Because tomorrow morning I
would go to school.
(23) After that, we have rest
for waiting the night of new
year.
After that, we had rest for
waiting the night of new year.
(24) Our grandmother can
embroider since she was
young.
Our grandmother could
embroider since she was young.
The table shows that there are errors in using auxialiary, the students used the wrong form of auxiliary use. The auxiliaries “will”, “have”, and “can” are not in the correct form based on their function as the auxiliary of sentence. To make them proper with the structure of the sentence, there must be “would”, “had”, and “could”. Auxiliaries are helping verbs that express a wide range of meanings (ability, permission, possibility, necessity, etc.), thus most of the modals have more than one meaning. I think the errors occur because the students do not understand the use of auxiliary in simple past tense well.
d. Misformation of “change into negative (-) form”.
Related to the sample above, the students produced error because they used the wrong form in negative sentences. The students still did not understand or they were likely confused with the change from the positive (+) into negative sentence (-). We can see that the students used the wrong verb “went” instead of “go” and “visited” instead of “visit”. I think the students made this error because their lack of knowledge in changing the verb.
4) Misordering Errors
The incorrect placement of a morpheme or group of morphemes in an utterance characterized misordering error. Misordering occur systematically for both L1 and L2 learners.
a. Misordering error.
This table shows the sample of misoredering
Error Sentence Reconstruction
(27) I went to home my
family’s
I went to my family’s house
4.1.2 Kinds of Error in Using Adjective 1) Omission Errors
Omission errors are characterized by the absence of items that must be present in a well-formed utterance.
a. Omission of “-ed”
This table shows the samples of misformation of “ed”.
Error Sentence Reconstruction
(28) I was interest playing
guitar.
I was interested in playing guitar.
According to the table above, the type of error is omission error because the students omitted “ed” of the adjective form that must be appeared in the sentence. There is certain adjective that must be followed by “ed”. I think the reason of the students making this error is because they do not understand the use of “ed” form after adjective well.
b. Omission of “-ing”
This table shows the samples of omission of “ing”.
Error Sentence Reconstruction
(29) The party was surprise us
last night.
The party was surprising us last
night.
c. Omission of “-ful”
This table shows the samples of omission of “ing”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(30) The waterfall was really
beauty
The waterfall was really beautiful.
Related to the sample above, the students omitted “ful” in the adjective. It is not correct form because there must be certain with “ful” before the adjective. I think this error occurs because of the students’ lack of knowledge of the form of adjective. Therefore, the students do not know how to put the proper form of adjective well.
2) Misformation Errors
Misformation errors are characterized by the use of the unacceptable forms of the morphemes or structure. While in omission errors the item is not supplied at all. In misformation errors the learner supplies something, although it is incorrect
a. Misformation of “ed”
This table shows the samples of misformation of “ed”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(31) During holiday, I was
boring just stayed at home.
During holiday, I was bored just
stayed at home
(32) We were really tiring We were really tired.
The Error Sentence become grammatically incorrect because the students put the wrong form of the adjective, it is “boring”, it must be “bored”, and “tiring, it must be “tired”. This error might occur because the students do not understand well about how to use adjective in a sentence.
1) Misformation Errors a. Misformation of adverb
Misformation errors are characterized by the use of the unacceptable forms of the morphemes or structure. While in omission errors the item is not supplied at all. In misformation errors the learner supplies something, although it is incorrect.
This table shows the samples of misformation of “ly”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(33) I couldn’t celebrate
Christmas with happy.
I couldn’t celebrate Christmas
happily
(34) We practice very strong We practice hard
From the Error Sentence, we know that the type of error is misformation. Misformation occurs because the students used the wrong form, it is “with happy”, it must be “happily” and “very strong” it must be “hard”. I think that the students do not know the use of adverb well.
4.1.4 Kinds of Error in Using Article 1) Omission Errors
Omission errors are characterized by the absence of items that must be present in a well-formed utterance.
a. Omission of definite article “the”
This table shows the samples of omission of “the”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(35) After that, I and my
family went to Zoo.
After that, I and my family went
to the Zoo.
activities during holiday activities during holiday.
Based on the samples above, the students omitted the article “the” that must be appeared in those sentences. By using “the”, we are signaling to our listener or reader that she/he is very likely to know what we are referring to and that the context of our conversation should help them to identify the object. These errors might occur because of the inability of the students understanding the use of article.
b. Omission of indefinite article “a”
This table shows the samples of omission of “a”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
Related to the sample above, the students omitted indefinite article “a” for I am “a” Moeslem that must appear. Here, it could be seen that the students do not well about the indefinite article “a” use.
2) Addition Errors
Addition errors are the opposite of mission errors. They are characterized by the presence of an item which must not be present in a well-formed utterance..
a. Addition of Definite Article “the”
This table shows the samples of addition of “the”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(39) My father and my
mother quarreled
because she wanted to
return to her village but
My father and my mother
quarreled because she wanted to
return to her village but father
the father did not allow
(40) to gather with the
brothers there.
to gather with my brothers there.
Related to the error sentence, the students made error because they added article “the” in the wrong place. Article “the” used to indicate a noun that is definite or has been previously specified in the context. I assume that this error might occur because of lack of knowledge about article use.
b. Addition of Indefinite Article “a”
This table shows the samples of addition of “a”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(41) So many a clothes for my
mother.
So many clothes for my mother.
Related to the sample above, we can see from the Error Sentence is found addition error because the students added item “a” that must not appear in grammatical sentence. The error might occur because they do not understand well about the use of article.
3) Misformation of Article
a. Misformation of Indefinite Article “a/an”
This table shows the samples of addition of “a/an”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(42) We practiced for the
hour before performance.
We practiced for an hour before
performance.
(43) My mother bought me
an beautiful dress
My mother bought me a beautiful
Based on the sample, the errors occur because the students use the wrong form of indefinite article “a/an”. The students used “the” instead of “an” and the second sentence used “an” instead of “a”. I think this error occurs because of the students’ inability in using article well.
b. Misformation of Indefinite Article “a/an”
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(44) We went to a beach for
holiday
We went to the beach for holiday
(45) My sister told me to buy
eggs in a shop
My sister told me to buy eggs in
the shop
From the samples above, we can see that the student do the errors. The errors occur because the students use the wrong form of definite article “the”. Furthermore, I think these errors occur because the students confused how to use article properly.
4.1.5 Kinds of Error in Using Preposition
1) Omission Errors
Omission errors are characterized by the absence of items that must be present in a well-formed utterance.
a. Omission of preposition
This table shows the sample of omission of preposition.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(46) The 1st January, we were
going to the church.
At the 1st January, we were going to
the church.
because the traffic jam. traffic jam.
If we look to the Error Sentence, the students made error because they omitted the preposition “at” and “of” in those sentences. Preposition is one of the items of English grammar. If the students do not have the knowledge of preposition, they will not able to use English well. Preposition usually comes before the word they control. They indicate various relationships between words of phrases the most usual being those of time, space (position or direction) or emotional attitude. It is as a prove that the students do not understand the use of preposition.
2) Addition Errors
Addition errors are the opposite of mission errors. They are characterized by the presence of an item which must not be present in a well-formed utterance.
a. Addition of preposition
This table shows the sample of addition of preposition.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(48) I could to meet my
grandmother and my
grandfather in my house.
I could meet my grandmother and
my grandfather in my house.
(49) My brother and I rode
the motorcycle to go to
there.
My brother and I rode the
motorcycle to go there.
pronouns, adjectives, and verbs. I personally think that the error occur because the student do not understand the use of preposition.
3) Misformation Errors
Misformation errors are characterized by the use of the unacceptable forms of the morphemes or structure. While in omission errors the item is not supplied at all. In misformation errors the learner supplies something, although it is incorrect.
This table shows the samples of misformation of preposition.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(50) I spend time on my
village
I spend time in my village.
(51) Made my parents proud
in me
Made my parents proud of me.
The Error Sentence are incorect, the students made error because they used the wrong form of “to”and “at” in those sentences. The students used “on” instead of “in” in the sentence “I spend my time in my village”. It is because they think that the used of “on” had same meaning with “in”, but in grammatical it is proper to use “in”. I personally think that the error occur because the student do not understand the use of preposition.
4.1.6 Kinds of Error in Using Possessive
1) Omission of apostrophe “’s”
This table shows the samples of omission of apostrophes “’s”. Error Sentences Reconstruction
(52) We were going to my uncle
house.
We were going to my uncle’s house.
(53) My brother face was pale. My brother’s face was pale.
By looking through the Error Sentence, the type of error is omission because the students omitted “’s” of noun that must appear in those sentences. The apostrophe is a punctuation used to indicate the possessive case (ownership) and the omission of letters (contraction). I think the reason of the students making this error is because they do not understand the use apostrophes form well.
2) Addition of apostrophes “’s”
Addition errors are the opposite of mission errors. They are characterized by the presence of an item which must not be present in a well-formed utterance.
This table shows the samples of omission of apostrophes “’s”.
Error Sentences Reconstruction
(54) Which has family’s name
same as me.
Which has family name same as me.
(55) I and my brother’s were
playing guitar.
I and my brother were playing
guitar