UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS LAPORAN PROJEK SARJANA MUDA
TAJUK: The Effects of Process Parameters in Injection Moulding On Surface Quality of a Polypropylene (PP) Component
SESI PENGAJIAN: 2010/11 Semester 2
Saya MUHAMMAD AIMAN BIN YUSOF
mengaku membenarkan Laporan PSM ini disimpan di Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) dengan syarat-syarat kegunaan seperti berikut:
1. Laporan PSM adalah hak milik Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dan penulis. 2. Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dibenarkan membuat salinan
untuk tujuan pengajian sahaja dengan izin penulis.
3. Perpustakaan dibenarkan membuat salinan laporan PSM ini sebagai bahan pertukaran antara institusi pengajian tinggi.
4. **Sila tandakan (√)
SULIT
TERHAD
TIDAK TERHAD
(Mengandungi maklumat yang berdarjah keselamatan atau kepentingan Malaysia yang termaktub di dalam AKTA RAHSIA RASMI 1972)
(Mengandungi maklumat TERHAD yang telah ditentukan oleh organisasi/badan di mana penyelidikan dijalankan)
Alamat Tetap:
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
THE EFFECTS OF PROCESS PARAMETERS IN INJECTION
MOULDING ON SURFACE QUALITY OF A POLYPROPYLENE
(PP) COMPONENT
This report submitted in accordance with requirement of the Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) for the Bachelor Degree of Manufacturing Engineering
(Manufacturing Process)
by
MUHAMMAD AIMAN BIN YUSOF B050710130
DECLARATION
I hereby, declared this report entitled “The Effect of Process Parameter in Injection Moulding on Surface Quality of Polypropylene (PP) Component” is the results of my
own research except as cited in references.
Signature : ………....
Author’s Name : MUHAMMAD AIMAN BIN YUSOF
APPROVAL
This report is submitted to the Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering of UTeM as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Manufacturing Process). The members of the supervisory committee is as follow:
i
ABSTRAK
ii
ABSTRACT
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
Alhamdulillah, thanks to Allah with all His Gracious and His Merciful for giving me a chance to finish up my final project report until this end of point. First of all, I would like to take the utmost opportunity to express my sincere and gratitude to my supervisor, Dr. Nur Izan Syahriah Binti Hussein who is always giving me supports and guidance in completing this „Projek Sarjana Muda‟. I am very grateful with the co-operation given from all of my friends. Besides, thanks a lot to all lecturers and staffs of Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering.
The greatest thanks to my beloved parents and family who always pray and give the encouragement while pursuing my research and project. Their sacrifices are never being forgotten.
iv
DEDICATION
To my beloved parents, my Father, Yusof Bin Hj Awang and my Mother, Nor Lela Binti Hj Yahaya, thankful for your full support and give me an advice.
For UTeM lecturers and staffs who were involved in this thesis especially to my supervisor lecturer, Dr Nur Izan Syahriah Bt. Hussein for help and guide.
v
2. LITERATURE REVIEW 6
vi
2.6 Type of Defect 17
2.6.1 Cause and Effect Diagram for Injection Moulding 17
2.6.2 Understanding the Defect 17
2.7 Surface Texture and Roughness 20
2.8 Measuring Mechanical Properties of Material 21
2.8.1 Tensile Test 21
3.3.2 The Characteristic of Polypropylene 26
3.4 Injection Moulding Process 27
3.4.1 The Injection Moulding Machine 27
3.4.2 Moulding Process 28
3.5 Mould 31
3.6 Injection Moulding Process Parameter 33
3.7 Surface Roughness 33
3.7.1 Surface Roughness Characteristics 34
3.7.2 Method to Analyze Surface Roughness 35
3.7.3 Portable Surface Roughness Tester 35
3.7.4 Surface Roughness Test Process Flow 37
3.8 Tensile Strength Testing 38
vii
3.10.4 Orthogonal Array Design 44
4. RESULT AND DICUSSION ON SURFACE QUALITY 45
4.1 Introduction 45
4.2 Design of Experiment (DOE) 45
4.3 Control Factor 46
4.4 Result of Experiment 47
4.4.1 Visual Inspection 49
4.5 Discussion on Surface Quality of Product 49
4.5.1 Introduction to Product Defect 49
4.5.2 Sprue Sticking 50
5. RESULT AND DISCUSSION ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS AND
TENSILE STRENGTH 57
5.1.5 Predicted Value of Surface Roughness 63
5.2 Tensile Strength Analysis 65
5.2.1 Result of Tensile Strength Test 65
5.2.2 Main Effect Plot for Means S/N Ratios 67
5.2.3 Main Effect Plot for Mean 69
5.2.4 Predicted Value of Tensile Strength 70
6. CONCLUSION 72
viii
6.2 Summary of Research Finding 72
6.3 Conclusion 74
6.4 Recommendation for Future Work 75
REFERENCES 76
APPENDICES
ix
LIST OF TABLES
2.1 The Control Factor and Level of optical lenses 15
2.2 Parameter Change versus property Effect 16
2.3 Troubleshooting of plastic injection moulding 17
3.1 Material Properties of Polypropylene (PP) 26
3.2 Specification of machine ARBURG ALLROUNDER 420C 28
3.3 Process Parameter of Polypropylene (PP) 33
3.4 Specification of Portable Surface Tester 36
3.5 Dog Bone Specimen Dimension 39
3.6 Universal Testing Machine (UTM) Specification 41
3.6 Selected Variable Parameter 44
3.7 Design of Experiment Orthogonal array Matrix 44
4.1 Control Factor of Process Parameter and Their Level 46
4.2 Design of Experiment Orthogonal Array Matrix 46
4.3 Result of Experiment 47
5.1 Response Table for Signal to Noise Ratio: Smaller-is-Better 58
5.2 Response Table for Means 60
5.2 Predicted Value of Surface Roughness 63
5.4 Factor Levels for Predictions 63
5.5 Tensile Strength Result 65
5.6 Dog Bone Specimen Dimension 66
x
5.14 Tensile Test Result of Dog Bone 8 67
5.15 Tensile Test Result of Dog Bone 9 67
5.16 Response Table for Signal to Noise Ratio 67
5.17 Predicted Value of Tensile Strength 70
xi
LIST OF FIGURES
2.1 Injection Moulding Machine Stage 7
2.2 A Single Screw Injection Moulding Machine for Thermoplastics 8 2.3 Feeding, transition, and metering zone of a reciprocating screw 9
2.4 Nozzle processing position 9
2.5 The moulded system includes a delivery system and moulded parts 10 2.6 Typical mould base showing the various components 11
2.7 Structure of Polypropylene 12
2.8 Categories of Parameter 13
2.9 Response Diagram of Surface Roughness 15
2.10 Defect Factors in Injection Moulding 17
2.11 Surface Roughness Characteristics 20
2.12 Test specimen under axial tension load 22
3.1 Process Flow Chart of Experiment 24
3.2 Polypropylene Resin 26
3.3 The machine ARBURG ALLROUNDER 420C 27
3.4 A Typical Injection Moulding Process 29
3.5 Plastifying Cylinder and Mould 30
3.6 Soap Container Cavity and Core Side 31
3.7 Core and Cavity of „Soap Container‟ mould 32
3.8 „Dog Bone‟ Mould 32
3.9 Measuring Surface Roughness with Stylus 34
3.10 Surface Roughness Characteristic 35
3.11 Portable Surface Roughness Tester SJ-301 36
3.12 Surface Roughness Tester Process Flow 37
3.13 Stress-Strain Curve 38
3.14 Tensile Testing Specimen Load 40
3.15 Universal Tensile Machine (UTM) 40
3.16 Tensile Test Experiment Process Flow 41
xii
4.1 Sprue Sticking 50
4.2 Part Stuck at Core Side 51
4.3 Part Stuck at Cavity Side 52
4.4 Part Flash 53
4.5 Blushing at End Area of Sprue 54
4.6 Sink Mark near Sprue of Part 55
4.7 Nozzle Drolling 56
4.8 Purging Material after Remove by Using Wire Brush 56
5.1 Main Effect Plot for Signal to Noise Ratio Graph 58
5.2 Main Effect Plot for Means Surface Roughness 60
5.3 Analysis of Variance for Means 62
5.4 Mean Effect Plot for Signal to Noise Ratio Graph 67
xiii
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
ANOVA - Analysis of Variance
DF - Degree of Freedom
DOE - Design of Experiment
F - F Statistics
FKP - Fakulti Kejuruteraan Pembuatan
MS - Mean Squares
PP - Polypropylene
P - P Value
PE - Polyethylene
PVC - Polyvinyl chloride S/N - Signal to Noise Ratio
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
Injection moulding is a practical technique used in manufacturing for mass producing plastics parts quickly and inexpensively. Nowadays injection moulding is the most important method of processing of consumer and industrial goods, and is performed everywhere in the world. As plastic parts have become more popular and critical in modem engineering applications, demand for quality has increased.
The principle of injection moulding is very simple. Injection moulding is process in which a plastic material is heated until it becomes soft enough to force into a closed mould at which point the material cools to solidify and from a specific product. The action that takes place is much like the filling of jelly donut. A reciprocating screw style cylinder and nozzle inject the heated plastic into an opening creates in closer container (mould). The material is allowed to harden, a finished part is ejected and the cycle is represents as often as necessary to produce the total number of pieces required.
2
The material will be use in this project is polypropylene. This material has a different properties and parameter from other material. The accurate result for polypropylene can be finding and can conclude of the quality of product. The surface roughness of the specimen must be measured by using Surface Roughness Tester. The tensile test of the product produced must be carry on and analysis the result of the test using the Universal Tensile Machine (UTM). One of the major activities of manufacturing engineering is the assessment of the effects of changing process parameter values on part characteristics.
The primary use of process models is to predict these effects. Often process models are inadequate for this task, usually because the process is very complex or because accurate material behavior descriptions at processing conditions are unavailable. So the defect of from the result produce should be analyze and try to improve the surface quality of the product. Outcome of the defect will be defined to produce the better parameter.
1.2 Background of Problem
3
1.3 Problem Statement
There are several main points needed to be concentrated and questions need to be answered at the end of the topic:
i. How different processing parameters affected surface quality of polypropylene (PP) material?
ii. How different processing parameters affected tensile strength of polypropylene (PP) material?
1.4 Objectives of Project
Objective of this project is:
1. To study the effect of process parameter in plastic injection moulding of polypropylene (PP).
2. To measure the surface roughness of sample product from optimized process parameter.
3. To determine the maximum tensile strength value of polypropylene (PP).
1.5 Scope of The Project
This project to study the effect of process parameter in plastic injection moulding, so for the started to optimize the parameter, the sequence of the process was:
i. Material selection for polypropylene. Pure polypropylene have been used to investigate the parameter setting in injection moulding
ii. Produce the specimen using Plastic injection Moulding. The parameter should be setting based on the parameter selection.
iii. Measure surface roughness for the produce specimen and other defect involve in surface quality.
4
v. Analyze the result and find the optimum result for this investigation for parameter setting of Plastic Injection Moulding.
1.6 Overview of the Thesis
Chapter 1 provides the principle of injection moulding and its applications. Overview of the activity and background of this research involve in this study also include in this chapter. Problem statement and objectives of this experimental research are stated based on the task given.
Chapter 2 is more presents a review on the literature about injection moulding, machine component, materials and its properties and its commercial application. Beside, the literature about process parameter of injection moulding also reviews in this chapter. The properties of polypropylene material are also provided in relation to its process parameter, surface roughness, and tensile strength. Summary of literature review is provided at the end of this chapter.
Chapter 3 explains an experimental method of this research including experimental flow, equipment involve and design of experiment. Method and approach in selecting an optimize parameters for this experimental research also stated in this report. Furthermore, design of experiment method that help to run the experiment also describe in this chapter.
Chapter 4 describes the detail result on surface roughness and their quality of each specimen that running based on Design of Experiment (DOE) selected. The produce specimen is investigating and inspect by using Mitutoyo Portable Surface Roughness Tester that available at UTeM Laboratory. The discussion on possible source of error of surface defect and the quality of product also involve in this chapter.
5
Chapter 6 is the conclusion sections that will be summarize the study on a achievement of objectives, completion of research, the future work and the suggestion.
1.7 Activity Planning
6
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
This chapter reviews the literature on injection moulding and basic working principle, process parameter, materials, mould and commercial application. In addition, the literature about defect of injection moulding and properties of injected material also review in this chapter. Background knowledge on surface roughness, tensile testing and mechanical properties of propylene material is also provided in relation to its process parameter. Summary of the literature review is outlined at the end of this chapter.
2.2 Injection Moulding
Injection moulding is widely used technique for fabricating thermoplastic and thermosetting material. It also is perhaps the most common and versatile method of forming plastic into plastics. Injection moulding process is a process in which polymer is heated to highly plastic state and forced to flow under high pressure into mould cavity, where it solidifies. Moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest component. The moulded part called is moulding, is then removed from the cavity.
Generally injection moulding has four stage starting the filling, packing, cooling and finally ejection. According to Bozdana et al. (2002) is said injection moulding
7
filled with hot polymer melt at injection temperature. After the cavity is filled, in the "packing stage", additional polymer melt is packed into the cavity at a higher pressure to compensate the expected shrinkage as the polymer solidifies. Next, the mould is cooled until the part is sufficiently rigid to be ejected, and this stage is the "cooling stage". The last one is the "ejection stage" in which the mould is opened and the part is ejected, after which the mould is closed again to begin the next cycle. For thermoplastic materials, the injection moulding machine converts granular or pelleted raw plastic material into final moulded parts via melting, injection, packing, cooling and ejection cycle. Polypropylene is tough and flexible material and used for containers, polyethylene, and polyvinyl chloride or PVC is more common in extrusions as used for pipes, window frames, or as the insulation on wiring where it is rendered flexible by the inclusion of a high proportion of plasticize as reported by Osswald et al. (2002).
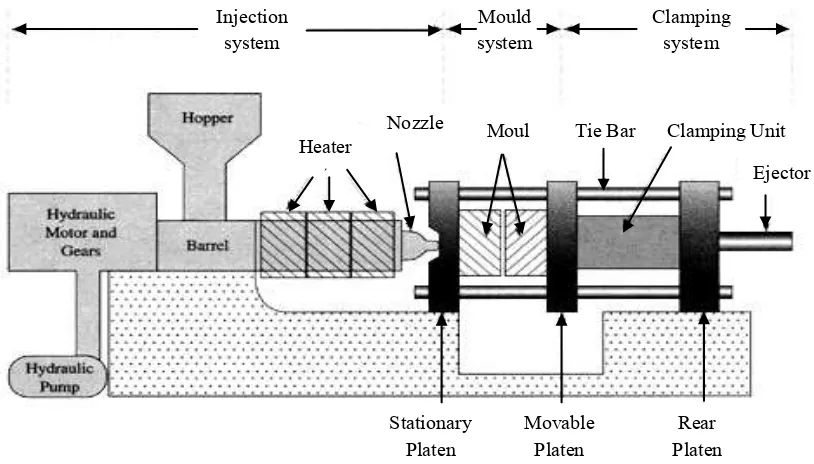
Figure 2.1: Injection Moulding Machine Stage (Strong, 1996).
2.2.1 Machine Component
The injection system consists of a hopper, a reciprocating screw and barrel assembly, and an injection nozzle, as shown in Figure 2.2. This system confines and transports
Mould system Injection
system Clamping system