Pembangunan VIN Jakarta)
A "Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teachers Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Langnage Education
-
----Ull I
Universitas Islam Negeri SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH JAKARTAOiferirt .. rl;iri T;;J.
lnayah Rahmawati
NIIVI.205014000365
.
._.,
... ..._..____
,___
セ@.
-
....
-
...
セᄋᄋBBセMMM...
-
... .
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OFTARBIYAHAND TEACHERS TRAINING SY ARIF HIDAY A TULLAH ST A TE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
THROUGH ROLE PLAY (A Pre- Experimental Study at First Year Students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan U/N Jakarta) "was written by Inayah Rahrnawati. student's registration number 205014000365, was examined at examination session of the Faculty of Tabiya and Teachers' Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta, January 06'h, 2010. The "skripsi" has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled one of the requirements For the Degree S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education in the Department of English Education.
Chairman
Secretary
Examiner I
Examiner II
Jakarta, January 061h, 2010
The Examination committee
(\L
: Ors. Syauki, M.PdNIP. 19641211991031 002 : Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd
NIP.150293 236 : Dr. Atig Susilo, MA
NIP. 150 182 900
(
...
\
...
セ@''fit
ri
c···U'···1···)
セBGk⦅⦅L@
(
...
),.----·- ' ᄋセ@ ...,., " ,,#
セセc[⦅IGqセ@
: Drs. Sunardi Kartowisastro, Dip!. ED ( ... '7.77 .. ),
NIP. 150 002 279
Acknowledged by:
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
Saya yangbertanda tangan di bawah ini, Nam a
Tempat/Tgl.Lahir NIM
J urusan/Prodi
: lnayah Ralimawati : Sukabumi/18 Mei 1984 : 205014000365
: Pendidikan Bahasa lnggiis (PB!)
Judul Skiipsi : Improving Speaking Skill Through Role Play (A Pre-Experimental Study at First Year Students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta)
Dosen Pembimbing : Ora. Fahriany, M.Pd
dengan ini menyatakan bahwa shipsi yang saya buat benar-benar hasil karya sendiri dan saya be1ianggung jaw ab secara akademis alas apa yang saya tulis.
Pernyataan ini dibuat sebagai salah satn syarat menempuh Ujian Munaqasah.
Jakarta, 04 Jan uari 2 0 I 0
Mahsiswa Ybs.
English used as guidance for any instruction or any communication in the world involves relationship, business, networking etc. So, most of people think that English becomes a main need language after their mother tongue because it has many advantages in many aspects.
The important of speaking skill for students is in order that they can speak it forthrightly and confidently with their classmates, and then they get used in rehearsing English conversation, so that they are not clumsy in practicing it gradually.
Based on the writer observation in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, most of students have difficulties in improving their speaking. They feel anxious about their speaking ability. The students feel clumsy to speak English and to express it because they are not really interested in speaking.
In this case the teacher needs to motivate students through new atmosphere that make the students more interested in improving their speaking ability and more enjoyable to practice their speaking with certain technique.
To help the teachers create the students more interesting and enjoyable in speaking, the writer offers a teaching technique in speaking which may help the students to achieve their speaking skill better.
Next, the technique that is offered by the writer is Role Play. Role play, as Jill
Hadfield said, is a gesture game which has special purposes, rules and involve interesting aspect. A central, unique aspect of storytelling is its reliance on the audience to develop specific visual imagery and detail to complete and co-create the story.
Jakarta, 03 December 2009
APPROVEMENT SHEET ... i
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... ;... ii
WRITER'S REFERENCE SHEET ... iii
ABSTRACT . . . iv
ACKNOWLEDGMENT... v
TABLE OF CONTENT... vii
LIST OF TABLES . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ix
LIST OF CHARTS . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... x
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION... I A. Background of the Study... I B. Identification of the Problem... 5
C. Limitation of the Problem . .. . . .. .. . . .. . ... 6
D. Research question... 6
E. Significance of the Study . . . .. . . ... . . 6
F. Organization of the Writing... 6
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK .. .... .. .... ... 8
A. Speaking . . . .. . . .. . . 8
1. Definition of Speaking . . . .. . . . 8
2. Teaching Speaking... 8
a. What is Teaching Speaking? . . . . .. . . 9
b. How to Teach Speaking? . . . 10
c. How to Score Speaking Activities... 11
d. Activities in Teaching Speaking . . . ... 13 e. Purpose of Teaching Speaking
I. Definition of Role Play . . . .. .. . ... 15
2. Kinds of Role Play ... 16
C. Improving Speaking skill Through Role Play ... 17
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY ... 19
A. The purpose of Study . . . .. .. . .. 19
B. Place and Time of Study ... 19
C. Subject/Participants of Study . . . ... 19
D. Role and position of Study . . . 19
E. Data and the Source of Data . . . 20
F. Instnunents of the Research ... 20
G. Teclmique of Collecting Data... 21
CHAPTER IV FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 23
A. Data description . . . . . . 23
1. Pretest . . . . . . 23
2. \Vhilst test . . . 23
3. Post test . . . 23
4. Questionnaire . . . 24
B. Data analysis . . . 24
CHAPTERV CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 34
A. Conclusion . . . 34
B. Suggestion . . . 35
Language is one of paramount tool for communication and also one of several needs to figure out every improvement in the world. For instance, people need language for understanding international education issue, science and technology, for relating them with their needs.
English spoken because people understand globally and agreed with using English for the guidance or instruction in order that they are able to find the meaning because they are familiar with it. As that result, English is as international language and used in most places in the world, such as for interacting one another in different countries for many aspects, like business, and networking, so most of people need to learn it well because it's one of requirements of international relationship. So, English spoken by population involve more than 300 million native speakers, and between 400 and 800 million foreign users. Most of people claim that a person who doesn't know English is left behind from universe infonnation and its breakthrough due to leaving English study. 1 People now compete and increase their English qualification, for it become main need in association.
Because English is an international language, its skills are significant for everyone to be mastered, and in Indonesia English involves into education curriculum which every school runs, and as further explanation of English curriculum it can be found in Standar Kompetensi (SK) and Kompetensi Dasar (KD). Consequently, the government revealed the policy that includes English subject into national exam standard as some special subjects such as Bahasa
Indonesia, IPA and Mathematics are included.
1 Dr. G. Manivannan,
"UsingEnglish"
http://www.usingenglish.com/teachers/articles/importance-english-language. html (accessed at 21,
The curriculum that progresses now what it is called A Kurikulum Ting/cat Satuan pendidikan (KTSP) or as issued in 2006 curriculum. In this curriculum, English divided as it has four skills, Listening, Speaking, Reading and writing. Listening and reading are receptive skills which are the ways in which people extract meaning from the discourse they see or hear.2 In English curriculum of KTSP, each skill has Standar Kompetensi (SK) and Kompetensi Dasar (KD): Standar Kompetensi (SK) becomes the global explanation and Kompetensi Dasar (KD) as the specific explanation of Standar Kompetensi.
In this study, the writer only explains Standar Kompetensi and Kompetensi Dasar of Speaking in class VII of the first semester. Based on cuniculum of 2006 especially in Speaking skill of the first semester of class VII has 2 SK's and 4 KD's. SK of Speaking is in the third and the fourth number in English syllabus that involves:3
S.K.3Mengungkapkan makna dalam percakapan transaksional dan interpersonal sangat sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan ling!amgan terdekat (to deliver meaning in oral simple short transactional and interpersonal conversation to be applied in the environment).
K.D.3.1. Melakukan interaksi dengan lingkungan terdekat yang melibatkan tindak tutur : orang menyapa yang be/um dikenal, memperkenalkan diri sendiri I orang lain, dan memerintah atau melarang. (Interacting with the environment which involves expression: Greeting stranger, introducing oneself I other, and giving instruction or prohibition) K.D. 3.2. Me/akukan interaksi dengan lingkungan terdekat yang melibatkan tindak tutur meminta dan memberi informasi, mengucapkan terima kasih meminta maaf dan meng1mgkapkan kesantunan. (interacting with the environment which involved: asking and giving information, giving thanks, apologizing, and delivering another polite expression)
SK.4. Mengungkapkan ma/ma dalam teks lisan fimgsional pendek sang.at sederhana untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan terdekat (to deliver meaning in oral simple short functional text and simple short monolog in descriptive and recount to be applied in the environment).
K.D. 4. I. Mengungkapkan makna tindak tutur dalam teks /isan jungsional pendek sangat sederhana (misal: instruksi, daflar belanja, selamat, pengumuman, di/) secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan !ingkungan terdekat. (To deliver oral meaning of simple short
2
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching (Third Edition), (Longman; Edinburgh: 2001), p. 199.
\
functional text in oral such as instruction, shopping lists, congratulation, announcement, etc).
K.D. 4.2 Mengungkapkan makna gagasan dalam teks lisan fimgsional pendek sangat sederhana secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan terdekat. (To deliver idea meaning in simple short oral functional text accurately, fluently, accepted to be applied in the environment).
From those 2 SK's emphasized that short transactional, interpersonal conversation, oral simple short functional text and simple short monolog are necessary to be taught in the classrom. The teacher has to get them involved in delievering those expressions in speaking activities, if not the teaching and learning activity doesn't achieve SK's target.
According to the explanation of English curriculum above that Speaking is productive skill which has 2 SK's to be achieved, the teacher must bring the students in rehearsing their speaking ability in their learning.
In fact, most of the teachers deny speaking ability even it includes to curriculum and has specific SK to be achieved; even they don't realize that students are assed with their speaking in commtrnication in their future. On other case, the teacher teaches speaking skill, but the teaching and learning activity is not enjoyable and interesting. Actually students enjoy their study not only because of the lesson is taught gradually in the classroom but also the teachers' strategy in teaching that will determine of students' comfortable in learning activity.
developing their conversational that they need in order to be effective speakers of the target language." 4
The classroom activity should be covered by any interesting teaching which makes them speak English better and practice it. What the students feel now is the serious problem that must be tackled as soon as possible.
The teacher needs technique to solve the class problem because it is a practical method or art applied to some particular task.5 The classroom will be life, students will be more active in study, and the problem will be easily covered by applying technique. So that, it can measure and lead the students to the better improvement and when one strategy doesn't work, the teacher just need to improve that strategy or to change into suitable strategy which fits with students' condition or the material being taught.
In this research, the writer offers the teacher role play which can lead the students to speak English forthrightly, bravely and confidently because it is used to express students' action normally.
Moreover Role play has useful thing for introducing students of some imp01tance aspects such sociocultural variations which have benefit for tl1em and also in providing its material, role play is based on the students' level and it gained from instruction or discussion of the speech act and its variations p1ior to the role plays tl1emselves. 6Leveling in role play is important because every stage of learners have different comprehension and study achievement. It
makes the teacher easy finding situation to be given for the students.
Stmtridge said that among classroom activities, role-play rates highly as suitable vehicles to use in a communicative approach to language teaching. Role play can reduce the classroom artificiality because it provides a reason for talking and allow tl1e learners to talk meaningfully to otl1er learners. Then, it needs to be practiced in the classroom by the teacher to help t11e students
'Roger Bowers, Applied Linguistics and English Language Teaching, (Macmillan publishers limited; London: 1991), pp. 66-67.
6
Free dictionary, Technique, http://mvw.thefreedictionary.com/technique, (accessed at 30 June 2009 ).
9
rehearse their speaking with their friends. 7 Consequently, when the students get used to practice English with their friends, they will not be clumsy to communicate with one another in English.
Role play is the liveliest form to get the class involved in speaking. Role play brings situations from real life into tlie classroom. Students inlagine and assume roles. They create a pretend situation, and they pretend to be some different persons, and of course with different act. 8 From tliat action, the students try to produce the sentence and rehearse also otl1er aspects, such pronunciation, Grammar, vocabulary and so forth because in their speaking they practice all of the many skills. In addition, they enjoy tlieir role because tliey suppose tl1eir role as tl1eir real life.
Due to speaking is important for the students; and they have some barriers in rehearsing it because of several problems tliat mentioned above, their ability in speaking skill needs to be monitored and increased if not tliey will miss this skill which is listening, reading and writing skill are combined in it. From that reason, the researcher only researches the students' improvement in speaking ability tlrrough role play.
Based on the problems above, the writer is curious to know the influence of Role Play in improving Speaking skill in the first year of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, tlie writer will conduct tlie research by the title " lmpriving Speaking Skill through Role Play", A Pre Expe1imental Study at the first grade of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.
B. Identification of the Problem
According to what the writer writes in background of the study about improving speaking skill tlrrough role play, tlie writer involves Identification of the problem involves:
a. Most of the students are still clumsy in speaking
10
Gill Sturtridge, Role Play and Simulation, (Longman; London: 1981), p. 126.
11
Purwamo, Teaching Speaking,
The first chapter is introduction. It consists of Backgrmmd of the study, Identification of the problem, Limitation of the problem, Research question, Significance of the research and Organization of the writing.
The second chapter is Theoretical Framework which includes three parts of discussions. In part A is speaking which consists of Definition of Speaking, and Teaching Speaking. Part B is Role Play which consists of Definition of Role Play and Kinds of Role Play. The last part is Improving Speaking skill Through Role Play.
The third chapter is Methodology. It contains The purpose of the research Place and Time, Subject/Participants of the research, Role aud position of the research, Data aud source of Data, Instruments of the research and Technique in Collecting Data.
The fourth chapter is Finding aud Discussion. It contains Data description, aud Data analysis.
A. Speaking
1. Definition of Speaking
Speaking skill, as the writer writes m the previous chapter is productive skill that has important role rather than other skills due to its significant and its use for communication. So that, writer will explain about the nature of speaking itself in order that gives the obvious information about what speaking is.
Donald and Shaw said that Speaking is not the oral production of written language, but includes learners in the mastery of a wide range sub skills which added together, then it supports speaking skill.1 In addition, speaking is not produced without some combination of language skills, but it must be included a number of skills. So, mastering speaking is gathering skills in thought because of including some input skills in it. As the result, the mouth is delivering those skills orally.
Speaking is a skill which deserves attention every bit as much as literally skill, in both first and second language. It is the skill which the students are frequently judged. It is also the vehicle par excellent of social solidarity, of social ranking, of professional advancement and of business. So, speaking is global skills and has multifunction use.2
2. Teaching Speaking
a. What is teaching Speaking?
Teaching speaking is not as teaching other skills; it needs creativity to get students involved in speaking. Besides, to speak English needs high motivation, self-confidence, more glossaries or words. When the
1
students don't have those capabilities, they will just keep silent in speaking class. From that, role play is offered as an activity to get them active in the class with their speaking because they deserve to get success in their speaking comprehension. To know students' success in their speaking activity here are the characteristic:3
I. Learners talk a lot.
2. Participation is even or all the students get chance to speak 3. Motivation is high, that they are eager to speak.
4. Language is of an acceptable level or that is relevant with the students.
When four characteristics above are found by the teacher or they are achieved by the students, it indicates that speaking skill is success to be taught in the classroom.
Teaching speaking is generally meant that to teach learners of English to:4
I. Produce the English speech sounds and sound patterns
2. Use word and sentence stress, intonation patterns and the rhythm of the second language.
3. Select appropriate words and sentences according to the proper social setting, audience, situation and subject matter.
4. Organize their thoughts in a meaningful and logical sequence. 5. Use language as a means of expressing values and judgments. 6. Use the language quickly and confidently with few urmatural
pauses, which are called as fluency.
In those meanings of teaching speaking above, the teacher must pay attention of some important aspects, because teaching speaking is about giving several concerns include producing sentences, intonation, stress and rhythm. Those sound productions must be meaningful
3
because it must be produced logically from thoughts. Finally, the students can speak English fluently.
b. How to teach speaking
Teaching speaking is very crncial especially in teaching English. It
needs strategies to be held. So, there are some steps in performing it:5
I. Using minimal response
One way to encourage such learners to begin to participate in speaking is to help them build up a stock of minimal responses that they can use in different types of exchanges. Such responses can be especially useful for beginners.
Minimal responses are predictable, often idiomatic phrases that conversation participants use to indicate understanding, agreement, doubt, and other responses to what another speaker is saying. Having a stock of such responses enables a learner to focus on what the other participant is saying, without having to simultaneously plan a response.
2. Recognizing scripts
Teachers can help students develop speaking ability by making them aware of the scripts for different situations so that they can predict what they will hear and what they will need to say in response. Through interactive activities, Teachers can give students practice in managing and varying the language that different scripts contain. 3. Using language to talk about language
c. How to score Speaking activities?
To asses speaking activity of students' performance in Role Play, the teacher needs some criteria to score, so the writer will explain about the area of speaking assessment and criteria included in that scoring.
According to Sahanaya and Lindeck that speaking test is scored using four performance descriptors each on a band scale of 0 (didn't attend the test) to 9 (almost like a native speaker). Those four descriptors are:6
!. Fluency and Coherence
The speaker can talk without too many long pauses at what would be considered a nonnal speed. The speaker demonstrates coherence in the way she or he sequences her or his information, and by using appropriate connecting words.
2. Lexical Resource
Lexical resource means what the speaker use with his or her vocabulary. The better the vocabulary is, the more clearly and precisely speaker can communicate.
3. Grammatical Range and Accuracy
This description, relates to how good students' grammar is when speaking. Students' range is generally demonstrated through the variety of sentence structures students can use and the variation in length.
4. Pronunciation
In this section is mainly judged by the extent to which pronunciation makes it difficult for the examiner.
61-70 =good 71-80 =very good
81-90 =excellent (almost like a native speaker)
d. Activities in teaching speaking
In teaching speaking, there are some activities that can be applied in the classroom to make the class more interactive and
. . 8
mterestmg:
I.Acting from a script
The teacher can ask the students to act out scenes from plays or their course books. Students will often set out dialogues they have written by themselves.
2.Communication games
These games are designed to provoke communication between students frequently depend on an information gap, so that one student has to talk to his partner in order to solve the puzzle, draw a picture, put things in the right order , or find similarities and differences between pictures.
3 .Discussion
By discussion can aim the students to arrive at any conclusion, share any ideas and look for some solutions at final. Besides, they can get involved in agree or disagree discussion.
4.Prepared talks
In this activity, students make presentation on a topic of their own choice. But in this case, the students should speak from notes rather than from a script, or it seems more 'writing like'.
Students can design questionnaires on any topics those are appropriate. As they do so, the teacher can act as a resource, helping them in design process.
6.Simulation and Role Play
In this activity, students simulate a real life encounter, as if they were doing so in the real world.
e. Purpose of Teaching Speaking at Madrasah Tsanawiyah
Pembangunan UIN Jakarta
Based on Mariane Celcea- Murcia's opm10n that purpose of speaking component in a language class should is to encourage the acquisition of communication skills and to foster real communication in and out of class room. 9 And this purpose is still not realized in most of schools or classes because the English teachers just focus on other skills that include to National exam.
Purpose of teaching speaking at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta itself doesn't have special purposes as what Mariane Celcea- Murcia described. Its teaching purpose just based on what the curriculum and syllabus stated, then English teacher is only to support the material in English syllabus, and she is not demanded to make real communication in and out of the classroom. So that the students just speak and implicate it in around setting, and in this case is practicing English only in the classroom during English class.
f. Technique of Teaching Speaking at Madrasah Tsanawiyah
Pembangunan UIN Jakarta
Technique of teaching speaking at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta at class seventh (VII) are quite variant, the teachers gave games, pair group for practicing conversation in the class
and other techniques to make the students active and interested in their speaking activity in the classroom.
Besides, the teacher uses Expository method, because sometimes the students make some noises in the class, to handle it the teacher teaches them by lecturing, even the teacher uses that strategy but she mixes it by question and answer to handle the students noise and to keep them active in their learning activity.
The teacher also uses role playing in teaching activity for supporting speaking skill. She uses role playing in the classroom in second semester, because in that semester the students have got many material of speaking and many vocabularies. So, she doesn't implicate role playing in the first semester to anticipate lack of vocabularies in her students when performing role play.
B. RolePlay
1. Definition of Role Play
As the writer focuses this division, she will explain about the nature of Role play, as a significant thing to know in this chapter.
According to Permy Ur, Role Play refers to sorts of activities where c
learners imagine themselves in situation outside the classroom, sometimes playing the role of someone other than themselves, and using language appropriate to this new context. 10 The students will take a part in specific character as they take, and they will express the discourse of the theme which the teacher determines.
In line with 2006 curriculum, Role Play is really suitable activity to
'
years. 11 The teacher only facilitates script to the students, or explains them situation to be played. Most of the time takes for students' performance in role play, and the teacher doesn't interfere with them so much. If the teacher finds error or mistake for example, she or he doesn't give correction directly, but has to wait until the students finish the performance due to his or her interference will break their focus in acting or delivering words.
Redfield said that role play is an activity which brings the students to real communication that the teacher really brings them to the real context of life.12 They find in this activity their daily life that they find in their real condition. Then, that makes the students easy to understand the situation or role given to them.
Keith S. Folse explains that role play is the activity of the students that they use their creativity and personality to play or express the role of specific person while interacting with other person in the role play. 13The students imagine themselves to be what they are in role play and characterize in where they are. They will find this activity challenging and interesting.
2. Kinds of Role Play
In classification, Dom1 Byne divides Role Play into two kinds:
a. Scripted Role Play
In this context, the way the students know the story is through text or reading text. In order that every learner memorizes the meaning in that context or in memorably way. 14
11
Sandra Jones, Adding Value to Online Role-Plays: Virtual Situated Leaming Environments, http: www.ascilite.org.au. p.468 (accessed at 261" July 2009)
12 Michael Redfield, Role Plays Dialogues: An excellent way to practice skill, (English
Teaching forum; Vol. 19, No. 3), (July, 1981), p. 36.
13 Keith S. Folse, The Art of Teaching Speaking, (University of Michigan Press;
2. The teacher appoints some students to learn about the scenario several days before teaching and learning activity. Giving time for the students is useful to have them make good preparation for acting.
3. The teacher makes groups of students consist of five people per group. The t·.:!acher has to makes group in variant member due to their ability of speaking. So, the smart student is combined with low student.
4. The teacher explains about competence will be achieved. The teacher enlightens the students that from their performance, they will know some expression of giving thanks and it response, and giving apology and its response.
5. The teacher calls a group of students who have been chosen to play prepared scenario. Or the teacher chooses the group to perform.
6. Each student in his/her group observes scenario being performed. 7. After finishing the performance, each student is given work sheet for
discussing each group performance.
8. Every group which has performed gives conclusion about what scenario has been performed.
9. The teacher gives general conclusion. That is about the material that has been done by the students in their role play.
10. Evaluation. It is held by test to know their understanding 111 the material.
A. The Purpose of the Research
The purpose of this research is to find out students' improvement in speaking from the score derived from students' perfonnance using role play in teaching speaking at seventh grade students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah UIN Jakarta.
The performance of role play is hoped can improve sn1dents' speaking ability. Besides, the writer hopes from that activity will make the sn1dents more active and interested in learning Speaking.
B. Place and Time
I. Place of Research
The writer perfonns this research at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.
2. Time of Research
This research is started from September to November in 2009.
C. Population and Sample
The subjects or participants m this research are the students of class seventl1 E (7E) of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta which consists of 27 sn1dents.
D. Research Method
E. Data and Source of Data
Data and source of data in classroom action research consist of some resources:
I. Students, to get the data about their study result and their activity in teaching and learning.
2. Teachers, to see improvement of teaching peaking through Role Play and to see the result of student's activity in teaching learning.
3. Collaborators, is meant four data source to see the implementation of Role Play in teacher and students' side.
F. Instruments of the Research
lnstmments which used by the writers are: I. Observation
The observation was done to identify teaching and learning activities, especially speaking activities directed by the real teacher, and to reveal problem of speaking activity in classroom.
2. Pre test, whilst test, and Post test
The next steps are Pre test, whilst test, and post test. The pre test is directed to know students' existing knowledge of speaking ability. Ongoing test was used to reveal the students' speaking skill improvement during treatment, this whilst test is held in role playing pe1formance. To measure this step of test the teacher categorizes the score into criteria which referred to Sahanaya's and Lindeck's as described in the previous chapter. Next, she makes categories from score with rank value below:
::; 50 =weak 51-60 = enough 61-70 =good 71-80 = very good
The last is post test; it was used to know students' final speaking skill improvement in the last of the cycle in implementing Role Play.
3. Questionnaires
The questionnaires were divided to the students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta of Grade seven at the end of each cycle to reveal students opinion of speaking activities being conducted, to get the feedbacks of the strengths and weaknesses of Role play technique being conducted in the classroom.
4. Interview
The interview was held in the last cycle in order to show students' responses directly about the technique being conducted. It was done to support questionnaires' results.
G. Technique in Collecting Data
In collecting the data, the writer uses some teclmiques, they are:
I. Observation: is a technique for collecting data about students' activity in
teaching and learning process.
2. Test: is used for getting data of study result and students activity in teaching and learning.
3. Questionnaire: to know students' behavior and teacher about role play. 4. Interview: to get data about success of implementation Role Play in
teaching Speaking.
Then, she calculates the data obtained descriptively to see tendency that happened in learning activity by using relative frequency distribution (percentage) whose fonnula as follows according to Anas Sudjiono (2006): 1
P=fxl00% N
1
P= Percentage
A. Data description
In data description, the writer explains some data sources obtained from pretest, whilst test and post test:
l. Pre test
To know ability or existing knowledge of the students about giving thanks and apology, the teacher and collaborator give a pretest to the students to measure their comprehension of those materials.
In pretest the students were given 4 questions to know how well they understand and comprehend the new materials. Those 4 questions consist of:
I. What will you say when your mother gives you money or if someone gives you help?
2. What will you say when someone says thanks for your giving? 3. One day you break your friend's glass, what will you say for that? 4. If your friend says regret because he/she breaks your glasses, what will
you respond?
2. Whilst test
In whilst test, the teacher scores the students based on their performance in role playing because it is an activity during learning based on the crite1ia mentioned in previous chapter.
3. Post test
In post test there are 2 items, 1 item consists of 8 answers. The first item includes 4 expressions of gratefol and 4 responses of gratefol. The second item includes 4 expressions of apology and 4 responses of apology.
The questions are:
b. 4 Responses of grateful :
2. Mention 4 expressions of apology and its responses. a. 4 Expressions of apology:
b. 4 Responses of apology:
To give clear detail of students' answer, the writer explains students answer of each item below.
4. Questionnaire
Besides pre test, whilst test and post test, the author provides questionnaire data for supporting those three data. The questionnaire is enclosed.
B. Data Analysis
In data analysis, the writer will analyze and explain about the students' answer in the whole instruments.
1. Pre test
a. Question no 1
In these question 26 students answer correctly with right and variant expressions of giving thanks, I student answers inco1rnctly or that student's answer didn't fit witl1 the question.
b. Question no 2
c. Question no 3
For this number, 26 students answer correctly. They answer with the same answer with have known and practiced. That expression is "I'm sorry". 1 student answers incorrectly.
d. Question no 4
In the last number, 24 students answer correctly with 3 variant expressions there are "it's ok, never mind and no problem". 3 students answer incorrectly.
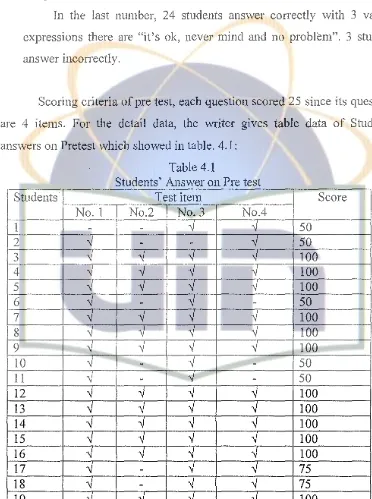
Scoring criteria of pre test, each question scored 25 since its questions are 4 items. For the detail data, the writer gives table data of Students' answers on Pretest which showed in table. 4.1:
Students
No. 1
1
-2
'1
3
'1
4 '1
5
'1
6
v
7
v
8
v
9
v
10
v
11
v
12
v
13
v
14
v
15
v
16
v
17
v
18
v
19
v
20
v
21
v
--Table 4.1
Students' Answer on Pre test Test item
No.2 No. 3 No.4
-
'1
'1
-
-
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
'1
-
v
-v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
-
v
--
v
-v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
-
v
v
-
'1
v
v
'1
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
[image:30.527.66.438.145.644.2]23 -../
-
-../ -../75
24 -../ -../ -../ -../
100
25
'1
'1
'1
-../100
26
'1
'1
'1
'1
100
27
'1
'1
'1
'1
100
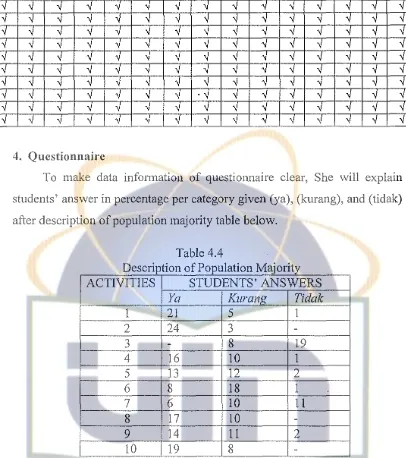
2. Whilst test
In whilst test they are scored based on what they performed. The situations are given under the theme "School Life" and "Seeing the Dentist". In school life scenario, students will be emphasized in the material "Giving Apology", and in "Seeing the Dentist", the focused on "Giving Thanks".
From students' acting, the writer provides scores data in categories fluency and coherence, lexical resource, grammatical range and accuracy, and prommciation, the scores will be enclosed. In this part the writer will provide total score obtai.ned from the students' performance.
Then those scores will be converted into some criteria as follows:
:::: 50 =weak
51-60 = enough
61-70 =good
71-80 = very good
81-90 =excellent (almost like a native speaker)
[image:31.524.67.441.145.565.2]Table 4.2
Data Description Of Whilst Test
STUDENT SCORE CATEGORY
NUMBER
1 70 Good
2 60 Enough
3 60 Enough
4 70 Good
5 70 Good
7 70 Good
8 80 Verv good
9 80 Very good
10 70 Good
11 70 Good
12 70 Good
13 70 Good
14 70 . Good
15 60 Enough
16 70 Good
17 70 Good
18 80 Verv good
19 70 Good
20 70 Good
21 80 Very good
22 80 Verv good
23 80 Very good
24 80 Verv good
25 80 Verv good
26 80 Very good
27 80 Verv good
From those data, as the author describes students in prev10us explanation into 3 categories, she finds that for "enough" (51-60) consist of 3 students, for criteria "good" (61-70) consist of 13 students and for "very good" (71-80) consist of 11 students.
3. Post test
a. Question number I.a
In question 1, 25 students answer correctly. They can answer 4 variant expressions of giving thanks such as; thanks, many thanks, thanks a million and thank you very much. 2 of the students have 3 correct answers and they have I incorrect expression of giving thanks such "Thanks is many" and "thank's amny".
b. Question 1.b
セ@
t:
La. La.
"
"O
"
I 2セ@
</)
I
"
"
2"
"
3
"
-4 y y
5
"
"
6 y y
7
"
"
8 y
"
9
"
y10
"
"
II y
"
12
"
"
13 y セ@14
"
15"
'
correct. 5 students don't have totally correct, 2 of them have 1 correct answer, 2 student has 2 correct answers, and 1 student has 3 correct answers.
c. Question 2. A
I
i.
perセsQaャ\Naan@
UT AIVIA.UIN SYMiD JAKARTA In this question, whole of students answer totally correct. They mention expressions of apology with "I'm sorry", "I'm really sorry", "I apologize", and "forgive me".
d. Question 2.b
For this last question, 3 students don't have total correct answer. 2 of them have 3 correct answers, and 1 student doesn't have correct answer at all.
[image:33.522.56.481.28.641.2]In post test the author gives more detail questions than in pretest. In this test, there are 16 items, so each answer scored 6.25 and total true answer items scored by 100. The description of student's answer will be enlightened in table 13.
Table 4.3
Students' Answer on Post test
Test ite1n number
1.a La. Lb. Lb l.b. l.b. 2.a. 2.a. 2.a. 2.a 2.b. 2.b. 2.b 2.b.
.3 4 1 .2 3 4 1 2 3 .4 I 2 .3 4
" "
"
" " " "
" " "
"
"
"
-" -"
- y-"
"
"
"
- - --"
' -"
- -"
y" "
y y y yy ' y y
-
-
y y"
y"
y y y"
'
"
-
--
"
" " "
"
"
"
-y y y y y y y y y y y y y y
-"
"
-
"
"
"
" "
"
y"
"
"
y y y y y y y y y y y y y y
"
"
"
" "
-
"
" " "
y" "
"
"
y"
y"
y"
y"
y y y y yy
"
y"
"
" "
"
y"
"
"
"
"
"
y"
" " "
"
" " "
"
" " "
y y y y y y y y y y
"
y y y"
"
" " "
"
"
"
"
"
" " " "
"
"
"
" " " " " " "
y"
y"
18 ;J y
19 y y 20 y y 21 ;J y
22
"
;J23 y y 24
"
y25 y
"
26 y y 27 ;J y
;J ;J y ;J y y y y y y y ' y y
;J ;J ;J '1 ;J ;J ;J ;J y ;J ;J ' ;J y
y y y y
"
y"
y" "
y ' y ;Jy ;J y y y y y y y y y y y y
"
"
"
" " " " "
;J"
"
" "
yy y y y y y y y y y y y
"
"
;J y y y y y y y y y y y y y
"
y y y"
"
• ;J"
;J ;J"
;J"
;Jy y y y y y
"
y"
y y"
y"
;J y y ;J y ;J y y y y y y y y
4. Questionnaire
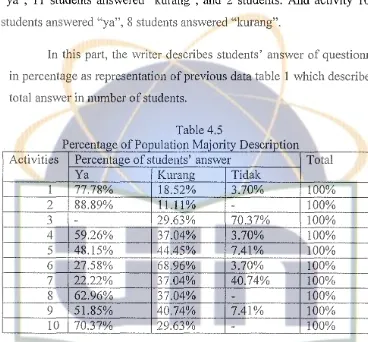
To make data information of questionnaire clear, She will explain students' answer in percentage per category given (ya), (kurang), and (tidak) after description of population majority table below.
[image:34.522.58.464.31.489.2]Table 4.4
Description of Population Majority
ACTIVITIES STUDENTS' ANSWERS
Ya Kuranz Tidak
I 21 5 I
2 24 3
-3
-
8 194 16 10 I
5 13 12 2
6 8 18 1
7 6 10 11
8 17 10
-9 14 11 2
IO 19 8
-From description of population majority above, showed that from students answer in activity one there are 21 students answered "ya", 5 students answer "kurang", and I student answered "tidak". In activity 2, 24 students answered "ya" , 3 students answered "kurang", no one answered "tidak". In activity 3, no one answered "ya", 8 students answered "kurang", and 19 students answered 'tidak". in activity 4, 16 students answered "ya", 10 students answered "kurang", and I student answered. In activity 5, 13
answered "tidak". In activity 6, 8 students answered "ya", 18 students answered "kurang", and I student answered "tidak. In activity 7, 6 students answered "ya'', 10 students answered "kurang", and 11 students answered "tidak". In activity 8, 17 students answered "ya" and 10 students answered "kurang", and no one answered "tidak". In activity 9, 14 students answered "ya", 11 students answered "kurang'', and 2 students. And activity 10, 19 students answered "ya", 8 students answered "kurang".
[image:35.522.70.438.147.489.2]In this part, the writer describes students' answer of questionnaire in percentage as representation of previous data table I which described of total answer in number of students.
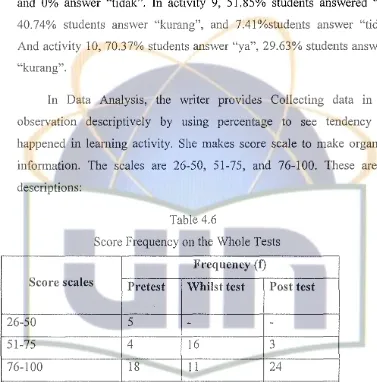
Table 4.5
p ercentage o · opu at1011 f
P
M . . D a1onty escnp·10n·r
Activities Percentage of students' answer TotalYa Kurang Tidak
I
77.78% 18.52% 3.70% 100%2 88.89% 11.11%
-
100%3
-
29.63% 70.37% 100%4 59.26% 37.04% 3.70% 100%
5 48.15% 44.45% 7.41% 100%
6 27.58% 68.96% 3.70% 100%
7 22.22% 37.04% 40.74% 100%
8 62.96% 37.04%
-
100%9 51.85% 40.74% 7.41% 100%
IO
70.37% 29.63%-
100%7.41 % students answer "tidak". In activity 6, 27.58% students answer "ya", 68.96% students answer "kurang", and 3.70% student answer "tidak". In activity 7, 22.22% students answer "ya", 37.04% students answer "kurang", and 40.47% students answer "tidak". In activity 8, .62.96% students answer "ya" and 37.04% ·students answered "kurang", and 0% answer "tidak". In activity 9, 51.85% students answered "ya", 40.74% students answer "kurang", and 7.41%students answer "tidak". And activity 10, 70.37% students answer "ya", 29.63% students allSwered
'"kurang".
[image:36.522.61.438.144.526.2]In Data Analysis, the writer provides Collecting data in that observation descriptively by usmg percentage to see tendency that happened in learning activity. She makes score scale to make organized information. The scales are 26-50, 51-75, and 76-100. These are the descriptions:
Table 4.6
Score Frequency on the Whole Tests
Frequency (f)
Score scales Pretest Whilst test Post test
26-50 5
-
-51-75 4 16 3
76-100 18 11 24
Total students (N) 27 27 27
In pre test, score scale from 26-50 achieves 5 students, in whilst test and post test no student achieves scale 26-50. In scale 51-75, 4 students include in pre test, 16 students in whilst test and 3 students in post test. In the last scale 76-100, 18 students are in pre test, 11 students in whilst test, and 24 students in post test.
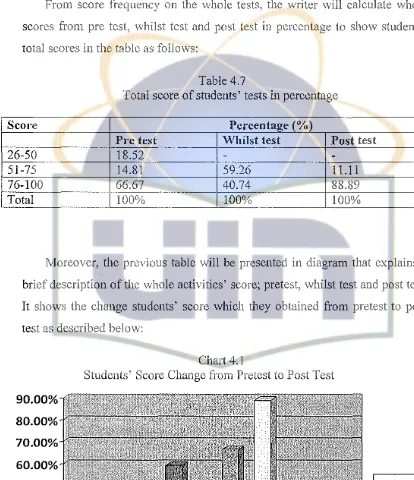
From score frequency on the whole tests, the writer will calculate whole scores from pre test, whilst test and post test in percentage to show students' total scores in the table as follows:
[image:37.521.32.446.153.633.2]Table 4.7
Total score of students' tests in percentage
Score Percenta!!e (%)
Pre test Whilst test Post test
26-50 18.52
-
-51-75 14.81 59.26 11.11
76-100 66.67 40.74 88.89
Total 100% 100% 100%
Moreover, the previous table will be presented in diagram that explains a brief description of the whole activities' score; pretest, whilst test and post test.
It shows the change students' score which they obtained from pretest to post test as described below:
90.00%
80.00%
70.00%
60.00%
50.00%
40.00%
Chart 4.1
Students' Score Change from Pretest to Post Test
fil!I pre test
Ill whilst test
B. Suggestion
In this last part, the writer will give some suggestions for the teacher and students as follows:
I. Teachers should not only focus on teaching Listening, Reading, writing and other sub skills, but also on teaching speaking because it is pi'oductive skill.
2. Teachers should apply role play in teaching speaking to increase students' speaking ability.
Bygate, Martin. Language Teaching: A Scheme for Teacher Education; SPEAKING, Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1987.
Byrne, Don. Teaching oral English: Longman Handbooks for English Teacher. Singapore: Longman Groups; 1986.
Cameron, Penny and Vanessa Todd. Prepare for IELTS Academic Practice Test, California: University of Technology; 2000.
Celce - Murcia, Marianne. Teaching English as A Second or Foreign Language (Third Edition), USA:Thomson learning; 2001.
Davies, Paul arid Eric Pearse, Success in English Teaching, Oxford: Oxford University press, 2000.
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, Model Pembelajaran Yang Efektif, (Depdiknas; Jakarta: 2009.
Direktorat Pendidikan Nasional, Sillabus Bahasa lnggris Kelas Vil
Folse, Keith S. The Art a/Teaching Speaking. Michigan: University of Michigan Press; 2009.
Harmer, Jeremy. The Practice of English Language Teaching (Third Edition), Edinburgh: Longman; 2001.
Mc Donald, et.al. Materials and 1\!Jethods in ELT, Cambridge: JB Blackwell; 1992.
Redfield, Michael. Role Plays Dialogues: An excellent way to practice skill, English Teaching forum; Vol. 19, No. 3, July, 1981.
Richards, Jack et.al. Approaches and }dethods in Language Teaching, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992.
Sudijono, Drs. Anas, Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan, Jakaiia: PT Raja Grafindo Persada: 2006
Ur, Penny. A course in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1996.
Wallace, Michael J. Action Research for Language Teachers, Cambridge: · Cambridge University Press; 1998.
Adding Value to Online Role-Plays: Virtual Situated Leaming Environments. By Sandra Jones. http: www.ascilite.org.au. p.468 (accessed at 261h July 2009)
Teaching Speaking: Activities to Promote Speaking in a Second Language. By
Hayriye Kayi. http://iteslj.org!Techniques!Kayi-TeachingSpeaking.html (accessed at August, 17 2009
"Using English". By Dr. G. Manivannan.
http://www.usingenglish.com/teachers/articles/importance-english-language.html (accessed at 21, June 2009) ..
Teaching Speaking: Strategies for Developing Speaking Skills
http://v.'WW.nclrc.org/essentials/speaking/goalsspeak.htm. (accessed on August, 17 2009)
Teaching Speaking. By Purwamo.
ウ。ケセ@
3. You're welcome 4. I sav vour \Velcome
5. Your welco1ne 6. Thank you 7. Your \Velcon1e 8. You're \velcome
9. I will say your welcome to her or his 10. I can your \Velcome
11. I will say thank's back 12. I \Vill say "your welcome" 13. You're \velcome
14. Your \velcome 15. Your \Velco1ne 16. You are \Veicome
17. I will sav "no oroblem'
18. I your to that sorneone
19. I \Vill say "you're \Velcome"
20. Thank YOU
21. You're \velcome 22. Yau \Velco1ne
23. Thanks mom/thank vou
24. I say "your \Velcome" to that someone 25. Your \Velcome
26. I \Vill say, vou're \Velco111e
4. I sav iam sorrv 5. Im sorry
6. I'm sorry, one day , I give you new glass 7. I'm sorry
8. Im son'\', because this mv false
9. I \vill say sorrv to mv friend or chan2e \Vith the new e:lass IO. I say I'm sorry friend, I break your glass
I I. I a111 \Vil! say 'I'n1 sorry"
12. I will sav "I'm sorry if! break vour elass"
13. I'm sorry
14. I'n1 son-v
15. I am sorry 16. I a1n son)'
17. I will say "I'm son,,, I regret I will give you some money, to change it" 18. I'm sorry
19. I say "I'1n sorrv)'
20. I am sony because I break your glass 21. I'm so sorrv. l regret to break vour elass 22. Im so sorrv I will pay for your bill in the ootic 23. I'm sorry. I will give you a new glass/ I will fix it 24. I sav I'm sorrv , because break vour glasses
25. 1'111 so sorry, because I break your glass, I \Viii fixine: vour elass 26. I'm sorry, I already break your glass
4. That's ok 5. No problem
6. Oh, just prepare my glass 7. It's ok no problem 8. Ooh ... no problem!
9. 1 will say no problem or verv well 10. Oh, I not protect vour glass
11. No!
12. I will say "is okay but you have to change with new glasses" 13. No problem
14. No problem
15. I don't care it's ok I still have it 16. It's ok, no problem
17. I will sav "veah, no oroblem. That's ok" 18. I'm apologize
19. I \Vill say, "oke, I'll forgive you, but you have to pay it"
20. Okey, this is no problem
21. "It's ok, but you must change my glass!" 22. No problem I can fix it again in optic 23. It's okay, I will buy a glasses again 24. I will say that's okay
Thank you very much Thanks a lot
Many thanks
2 Thank's a lat Thank' s verv mach Thank's million Many thanks
3 Thanks
Thank's amnv Thank's a million Thanks very much
4 Thank vou
Thank's a lot Thank's so much Thank's a million 5 Thank you very much
Thanks Thanks a lot Many thanks
6 Thank vou very much Thank's
Thank's a lot Thank's a million 7 Thank you very much
Thanks a million Thanks is many Thanks
8 Thanks a lot
Thanks
Thanks a million Thank you very much
9 Thank you
Thanks a lot Thanks
Thanks a n1illion 10 Thank you very 1nuch
'fhank's a lot
Thank's Many thank's
I I Thank you very 1nuch
Thanks a lot Thanks a million Thanks
12 Thank you
Thanks a lot Thanks a million Many thanks 15 Thanks a lot
Thanks million Many thanks Thanks
16 Thank vou very nH1ch
Thank a lot Many thanks Thanks a million
17 Thanks you ve1y much Thanks a lot
Thanks a million Thanks
18 Thanks
Thanks a lot
Thank you very much Thanks a million
19 Thank vou
Thanks a lot Thanks a million
Thank you so rnuch
20 Thank you ve1y much Thanks a lot
Thanks a million Many thank
21 Thanks a lot
Thanks
Thanks a million Thank you very much
22 Thanks
Thanks a millions
Thanks a lot
Thank you ve1y much
23 Thanks a lot
Thanks a n1illion
Thanks
Thank vou very 111uch
24 Thank vou very n1uch
Thanks a lot Thanks a million Many thanks
25 Thank vou very much Thanks a lot
27
Thanks Thanks a lot Thanks a million
No. I. b. Response of Giving Thanks
Student Ans\ver
I You 're \Ve I come
Don't mention it
My pleasure That's mv oleasure
2 Have welcorne
Thanks Welcome To many thanks
3 Mention it
Your \Velcorne Thanks my plusuare It's plusuare
4 Your \Velcome
Don't 1nention it Pleaserf Don't pleasurf
5 You 're \velcon1e
-6 Mv pleasure
You are \Velco1ne
Its pleasure
Don't 1nention it
7 No problem
That mv please my
Yure \Velcon1e
Forget it
8 That's my pleasure
My nleasure
Don't 1nention it Youre \Velcome
9 Your \Velco1ne
Don't 111ention it
Forgife me
That's 111y n1ention
IO Your \Velcon1e
It's ok
12 Forget it
My pleasure
Your welco1ne Don't mention it
13 You 're \Velcon1e
Thats my pleasure Mv pleasure
Don't n1ention it
14 Your \Velco1ne
Dont mention it
That mv pleasure Forget it
15 Your welcome
Mv pleasure Thats mv oleasure Dont mention it
16 You're welcome
Forget it
Don't mation it
That's my pleasure
17 Forget it
You 're \Velcome Don't mention it
Thats my pleasure
18 Forget it
You're \Velcorne
My olusure
Thanks yo plusure .
19 You 're \velco1ne
Don't mention it
Never think about it Fomet it
20 You're \velco1ne
Don't tnention it
Thanks 111y pleasure
Mv pleasure
21 'r.' ou're \\'elcon1e
-My pleasure
Don't tnention
Forget it
22 That's n1y eleasure
Mv pleasure
You're \velco1ne
Forget it
Your welcome
25 My plesure
You're welcome
No oroblem That's my pleasure 26 Don't mention it
Forget it
You 're \Velcon1e
That's my pleasure
27 Mv pleasure
You 're welcome It's my pleasure It's mv pleasure No problem
2 .a. A •DO OQV
Student Answer
1 Im sorrv
I apologize
In1 so sorrv
Im really sorry
2 I auologize
Im sorry In1 so sorry
Im very sorry/Im really sorry
3 I'n1 sorrv
I' 1n very som1
I'm apologize
l'n1 so sorry
4 I'm aooJogize
I'm sorry
Forgive it
I'm sorrv
5 Im sorry
fn1 so sorry
Forgive 1ne
1!11 sorry so 1nuch
6 I'in sorrv
Im so sorry
rm apologize
Forgive n1e
7 I'm sorry
I' 111 so sorry
I'm apologize
I'm very sony
I'm so sorry Forgife me
10 I apologize
I'm sorry
I'm so sol!l'._
Forgive me
11 Im sorry
Im very sorry Im a_g_ologize IIn so sorry
12 Sorry
I so sorry Forgive me I apologize
13 I'm sorry
I'n1 so so!:_!)'._ I'm really sorry Forgive me
14 I'm sorry
I'm so sorry I'm really sorrv For give me
15 Sorry
1 a1n (_!Eoloqv I am very sorry
I a1n so sony
16 I'n1 sorry I'1n apologize l'n1 so sorry l'm very som
17 I'rn sony
I 'n1 so sorry
Sorry Forgive me
18 I'n1 sorry I apologize I'm so sorry I ve1y sony
19 I apologize
1'111 so sorry
1'111 sorry
I'1n sorry so 1nuch
20 l'1n ウッイセ[G@
I apologize
I'n1 so sorry
I'm very/ really sorry
21 l apologize
I apolo1>;ize
23 l'tn sorrv
I'm reallv sorrv
Forgive me I'm so sorry
24 I'm so sorrv
I apologize
I'm so sorrv
I' 111 reaHy sorrv
25 I'm sorry
I)m so sony I apologize Forgive n1e
26 I'm SO!Ty
I apologize I'm reallv sorrv Forgive 1ne
27 I'm sorry
I'm so sorry Fonzive me I apologize
2.b. Responses o f a )O oov
Student Ans,ver
I Never 111ind
Its ok Thats all right 'fo give 1ne
2 l sorry
I-lave apologaze
Apology My aoolegace
3 Never n1ind
It's all right It's ok No problem 4 That's all right
Never 1nind
It's ok No oroblem
5 It's ok
No oroblem
Never 1nind
Thank all right
6 Never n1ind
That's all right No problem
21 Never mind
It's ok No problem Don 1
t \Vorrv
22 Never inind
That's all right No oroblem It's ok
23 Nevern1ind
It's okav That's all right No problem 24 Never mind
that's all right That's ok All right
25 That's all right
It's ok!
No oroblem Never 111ind
26 Never mind
No oroblem It's ok
That's all right
27 Never mind
That's all right It's ok
I. Mention 4 expressions of grateful and its responses. a. Expressions of grateful
I.
2. 3.
4.
b. Responses of grateful
I.
2.
3.
4.
2. Mention 4 expressions of apology and its responses. a. Expressions of apology
I.
2. 3. 4.
b. Responses of apology I.
2.
3.
Interviewee : Prastya Arghawaty, S.Pd Day/date : Saturday/I 0 October
1. How long have you been teaching English at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan?
I have been teaching English at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Pembangunan for a half and a year.
2. What are strategies or techniques do you use in teaching speaking?
The strategies or techniques I use in teaching speaking are repetition and role play.
3. What kind of difficulties do you find in teaching speaking?
When I find my students have different comprehension because they have limited vocabularies for speaking.
4. How is your students' achievement especially in Speaking? They achieve 68 % in average for speaking.
5. What should the English teacher do to improve the students' ability 111 speaking?
The English teacher should vary the techniques; give the vocabularies before giving the theme of speaking.
6. I-lave you ever implicated role play in teaching speaking in the classroom? Yes, I have ever implicated it.
7. How were the students' responses for that? They were good in responding it
2. What will you say when someone says thanks for your giving? 3. One day you 「イ・セォ@ your friend's glass, what will you say for that?
4. If your friend says regret because he/she breaks your glasses, what will you respond?
Put vour answer here.
l. 1. L L
PRETEST
lead these questions carefully, and answer each number with the best answer. What will you say when your mother gives you money or if someone gives you help? What will you say when someone says thanks for your giving?
One day you break your friend's glass, what will you say for that?
If your friend says regret because he/she breaks your glasses, what will you respond?
A. PERHITUNGAN ALOKASI WAKTU TIAP SEMESTER
Semester I
Ne Bulan Banyaknya pekan Seme:1ter Gasal Keterangan
Seluruhnya Tdk Efektif Efektif
1 Juli 5 2 3 LIBUR SEMT 2 LANJUTAN, MOS & !SRA Ml'RAJ
2 Agustus 4 1 3 17 AN & LIBUR AWAL RAMADHAN 1430 H
3 September 5 3 2 LIBUR RAMADHAN DAN IED FITR 1430 H
4 Oktober 4 0 4 LIBUR LANJUTAN IED FITR 14301-i
5 Nopember 4 0 4
6 Desember 5 4 1 PERSIAPAN RAPOR, LIBUR SEMESTER 1
I Jumlah 27 10 I 17 17X4=68 JAM PELAJARAN
Semester 11
Ne Bulan Banyaknya Pekan Semester Genap Keterangan
Seluruhnya Tdk Efektif Efektif
·1 Januari 5 0 5
2 Februari 4 0 4
3 Maret 5 0 5
4 April 4 1 3 UN
5 Mei 4 1 3 us
6 Juni 5 3 2 PERSIAPAN RAPOR DAN LIBUR SEMT 2
セセBMM
Mセセ@
jMゥセ@
--
ャセZMMMセセセM
セ@
___
mis 4 1 11 ·13 25
セ[]セ」]ゥ]QMセセiセQセQAセZQMZセM⦅Z⦅⦅L⦅ᄋZ⦅ZZZ⦅⦅MM⦅MM⦅MM⦅⦅L⦅M
__ ___,
1-1ari Efektir = 20---MARET 2010 URA IAN KEGIATAN KE LAS
QQY⦅イQZL⦅ZMMjセセZQMZZZ⦅@
14--f=2-i
MMセゥウ@---ヲセセセ]M GZZZ⦅Qセ
Q⦅ZZZ⦅@ セ@
'' -セ@ セZエ@ セエZ@ ZZ[セセ@
1ilu
' ---i--- -- ---- ' -- ---
3 'I 0 17--- -- '
24 31 2 -31 Belajar Efel1tilQ
QBQ
QQ
L[エLゥャGセL
Q@
r
QVMMセゥM MQセSMMMM
1 21ッセ@ セRセW@
- , Hari Efeklif =
MMセMMセMMセMMQMMMMQMMMMM
-7 - 9.
23
A PR IL 2010 TAMGGAL I UR/\ IAN KEGIATAN KELllS
LM[MァMァセ@
_±_l:::_
11 _
_:IL