Yogyakarta
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Muhammad Catur Setiawan 20120540112
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Muhammad Catur Setiawan 20120540112
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
I am a student with the following identity:
Name : Muhammad Catur Setiawan
NIM : 20120540112
Program Study : English Education Department Faculty : Faculty of Language Education
University : Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Certify that this thesis with the title of “Teachers’ Strategies and Challenges to Develop Students’ Critical thinking at English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta” is definitely my own work. I am completely responsible for the content of this thesis. Others’ opinion or findings
included in this thesis are quoted in accordance with ethical standards.
Yogyakarta, December 28th 2016
Almighty who gives blessing and mercy, so that I could finish this undergraduate thesis. Secondly, Sholawat and Salam may always come to Prophet Muhammad whom we’re waiting for His Syafaat.
I would like to express gratitude to my family who never gets bored supporting all things I do. To my parents Sholihul Hadi, S.Pd. and Sri
Hartatiningsih, S.Pd. I’d like to express my deepest gratitude to both of them as
everything they have given to me. I hope they both always get healthy, and I do always need their support and prayer to reach the success. To my brothers and Muhammad Mindarko, Deni Ristiawan, and Tri Kurniawan you all are amazing brothers. Maybe thousands of thanks are just not enough to express my gratitude to my family. You all are priceless in my life, and without you all I’ll never run up
to this point.
I would never forget the help, support, and motivation which come from all my friend. To my friends, Dea, Alfi, Yusuf Ikhsan, Denta, Denis, Nacil, Bermas, Haniv, Fahmi, Pees, Wahyu Tri, Temon, Fariz, Yusuf Khairul, Okta, Wanda, Chandra, Gunawan, Upik, Una, Fabyan, Zali, Eko, Aris, Kenang, Hanjaya, Fajar, Oscar, Tiar, Wahyu, Johan, Gepeng, Anja, Seroja, Hery, Rio, Akbar, Fendy, Aji, Elsa, Umami, Nisa, Ardi, Fadil, Dwi, Winda, Uli, Anjar, Venta, Windu, Firlingga and all my friends I can’t mention one by one, I send thanks for the support, joke, and laugh we’ve been through during our time here. I’ll never forget good things you all have done to me.
Statement of Authenticity ... iii
Acknowledgement ... iv
Abstract ... vi
Table of Contents ... vii
Chapter One: Introduction ... 1
Background of the study ... 1
Identification and Limitation of the Problem ... 4
Research Questions ... 5
Purpose of the Study... 5
The Significance of the Study ... 5
Chapter Two: Literature Review ... 7
Definition of Critical Thinking ... 7
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers... 8
Factors Influencing Critical Thinking ... 10
Advantages of being Critical Thinkers ... 12
Strategies to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking ... 13
Challenges to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking ... 15
Review of Related Studies ... 18
Conceptual Framework ... 20
Chapter Three: Methodology ... 24
Data Collection Method... 26
Data Analysis ... 27
Chapter Four: Finding and Discussion ... 28
Strategies in Developing Students’ Critical Thinking at the EED of UMY ... 28
Questioning strategies ... 28
Classroom debate and group discussion ... 29
Writing assignments ... 30
Problem based learning ... 31
Reading Assignments ... 32
Providing feedback ... 34
Challenges faced by the EED of UMY teachers in developing students’ critical thinking ... ... 34
Difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking ... 35
Find the right of resources ... 36
Students’ passive behaviors ... 37
Time constraints ... 38
Difficulty in designing class activities ... 39
Chapter Five: Conclusion and Recommendation ... 40
Conclusion ... 40
Recommendation... 43
Abstract
Critical thinking has been regarded as an essential aspect of education. However, it is not easy to develop students’ critical thinking. This study was conducted to find out the teachers’ strategies and challenges to develop students’ critical
thinking at the English Education Department (EED) of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (UMY). The method used in this research was descriptive qualitative that the data were gathered through interviewing two teachers of the EED of UMY selected by purposive sampling. Indeed, the participants were chosen based on two criteria. First, they should have taught at the EED of UMY for at least three years. Second, they should be teachers who created learning activities in the class requiring their students to think critically. The data collected from the interviews were analyzed into three steps of coding which are open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. The first finding of this study is about the strategies used by teachers in developing students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY. There were six strategies which were a questioning strategy, classroom discussion, writing assignments, problem based learning, reading assignments, and providing feedback. The second finding is about the challenges faced by teachers of the EED of UMY in developing students’ critical
thinking. There were five challenges, namely difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking, finding the right resources, students’ passive behaviors, time
constraints, and difficulty in designing class activities.
Chapter One
Introduction
This introduction highlights the description of the study. In this chapter, the researcher presents the background of the study, identification and limitation of the problem, research questions. The researcher also explains the purposes of the study and the significances of the study.
Background of the Study
In the 21st century, college students are expected to be independent learners. Students are encouraged to be active in a class, engaged in a class discussion or debate, to express their arguments, to write good analytical essays, and to get involved in other class activities which require a high order of thinking. The ability to think critically and to argue reasonably and rationally has been regarded as an essential aspect of education. As stated by Case (2005), critical thinking has been recognized as an important educational goal.
Critical thinking has been defined in many different ways. In brief, critical thinking is individuals’ ability to think clearly as well as rationally and to make
accordance with their level of intelligent and issues which they will encounter in real life to solve their problem.
Having good critical thinking skills gives many benefits, especially for college students. The skills will enable students to improve their attention and observation, reading concentration, ability to identify main ideas of a text instead of becoming distracted by less important materials, ability to respond to the points in a message (Cottrell, 2011). Besides, Ardington (2010) argued that students who have good critical thinking will easily reach their own learning goals, achieve better marks, and become less dependent on teachers and textbooks. A study of Mahyuddin, Lope-Pihie, Elias, and Konting (2004) showed that language learners with critical thinking ability are capable of thinking critically and creatively in order to achieve the goals of the curriculum, making decisions, solving problems, using their thinking skills, and understanding language or its contents. Moreover, it is found that students with low thinking skills got difficulty in completing tasks that require them to think independently outside of rote memorization and recall (Zachary, 2011).
taught how to think. Nickerson (1994) also noted that students need to be taught how to think more effectively, critically, coherently and creatively. Students who have not been taught how to think critically will be unable to make rational decisions in their adult life because they fail to examine the consequences, assumptions, and prejudices of issues around them (Paul, 1990). Therefore, teachers play an important role in developing students’ critical thinking.
It is not easy for teachers to develop students’ critical thinking skills. There are so many challenges in enhancing students’ critical thinking. In most
educational systems, according to Paul (1990), students gain lower order learning which is associative and rote memorization resulting in misunderstanding,
prejudice, and discouragement in which students develop techniques for short term memorization and performance. These techniques block the students' thinking about what they learn. Paul (1990) revealed that most students are accustomed to sitting back in class passively and listening to a lecture. Choy and Chey (2009) stated that teaching critical thinking is challenging because teachers have difficulty in engaging aspects of critical thinking in their lesson. Williams (2005) wrote “critical thinking requires hard work; many students would prefer
that teachers just give them answer to complex questions” (p. 182).
Based on the researcher’s observation at English Education Department of
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED of UMY), some teachers gave the students many activities or assignments in order to develop students’ critical
example, in a reflective writing activity, some students got difficulty in
accomplishing this activity. It can be seen when the teachers gave an assignment. There were students who could finish their task and there were students who could not finish their task. Therefore, there might be difficulties or challenges when the teachers tried to develop students’ critical thinking. In this study, the
researcher attempted to find out the strategies and challenges in developing students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY in depth.
Identification and Limitation of the Problem
Critical thinking is an essential skill. In order to be considered as a critical thinker, there are several characteristics such as individuals’ ability to think
rationally and make correct decisions independently. In addition, critical thinking has many advantages. Students who have developed critical thinking skills are capable of doing some activities of which other students may not be capable. However, there are challenges of developing critical thinking. The challenges can be from both teachers and students. Due to the researcher’s incapability to explore
all those mentioned problems, he limited this study to investigate the strategies that the teachers applied and challenges that teachers faced to develop students’
critical thinking at the EED of UMY in apllying the strategies.
Research Questions
Based on the background of the study, the researcher formulated two research questions. The research questions are:
1. What are the EED of UMY teachers’ strategies in developing students’ critical thinking?
2. What are the challenges that teachers of the EED of UMY face to develop students’ critical thinking in applying the strategies?
Purposes of the Study
Based on the research questions, the purposes of this study are:
1. To find out the strategies applied by teachers of the EED of UMY in developing students’ critical thinking.
2. To investigate the challenges that teachers’ face to developing students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY in applying the strategies.
Significance of the Study
This research aims at giving advantages specifically to the researcher, lecturers, and students.
The researcher. As a prospective teacher, this research may give the
researcher more knowledge of the challenges that teachers confront when
thinking teaching methods. Thus, it will be easier for him to design materials and activities at class.
Teachers. By knowing the strategies and challenges in developing
students’ critical thinking, teachers can implement creative ways in learning
process to cope with the challenges.
Other researchers. This research is expected to enlighten the other
researchers who concern with teachers’ challenges and strategies to develop students’ critical thinking. The finding of this research can be a reference for other
Chapter Two
Literature Review
This research talks about teachers’ challenges and strategies in developing students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY. In this chapter, the researcher discusses and explores the definition of critical thinking, students’ critical
thinking, factors influencing critical thinking, and teachers’ challenge to develop
critical thinking. Then, previous related studies are added as the guideline for the
researcher to conduct this research. Conceptual framework is also presented in
this chapter to describe the highlight of this study.
Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking has been defined in many different ways. Some scholars
have described critical thinking which is frequently correlated to analyses and problem solving. Chance (1986) defined critical thinking as “the ability to analyze
facts, generate and organize ideas, defend opinion, make comparisons, draw
inferences, evaluate arguments and solve problems” (p. 6). In addition, instead of the simple act of receiving information and then accepting it, critical thinking
involves an active process of thinking and analyzing what we receive (Fisher,
2001). It means that the purpose of critical thinking is to analyze what we receive,
to achieve understanding, to evaluate view-points, and to solve problems
effectively.
Critical thinking is a process where students improve their thinking quality
Fisher (2001) defined critical thinking as “active, persistent, careful consideration
of a belief or supposed form of knowledge in the lights of grounds which support it and the further conclusions to which it tends” (p. 9). Furthermore, Fahim and
Pezeshki (2012) described critical thinking as a thinking process that requires reasons as well as reflection, and rejects blind acceptance of others’ opinions. It means that a critical thinker will not easily accept others’ ideas and will prefer to
use their knowledge to make reasons and deep consideration before making a
conclusion or judgment to solve a problem.
In higher education, critical thinking is a skill that should be mastered by
students so that they can make thoughtful life decisions, solve problems creatively
and rationally, understand and analyze knowledge in and across disciplines. Based
on the aforementioned definitions of critical thinking, it is clear that critical
thinking is a skill that helps students to solve problems and to make decisions
effectively.
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers
Critical thinking was first highlighted by Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomy a
few decades ago (Duron, Limbach, & Waugh, 2006). A higher level of cognitive
abilities involving critical thinking is a feature in the analysis, synthesis, and
evaluation levels while lower levels of cognitive abilities that are knowledge,
comprehension, and application only involve remembering, relating and applying
information respectively (Duron, Limbach, & Waugh, 2006). The lower levels of
thinking skills. Duron, Limbach, and Waugh (2006) further described critical
thinkers as those who are able to analyze and evaluate information. They noted
that critical thinkers are those who are able to raise vital questions and problems,
formulate them clearly, gather and assess relevant information, use abstract ideas,
think open-mindedly, and communicate effectively with others.
In brief, critical thinking is individuals’ ability to think clearly, rationally and make correct decisions independently. It means that a critical thinker will not easily accept others’ ideas and will prefer to use their knowledge to make reasons
and complete consideration before making a conclusion to solve a problem.
Moreover, Kurland (2000) argued that critical thinkers are active, not passive.
They ask questions and analyze. Students considered as critical thinkers
consciously apply strategies to find the meaning or assure their understanding. They are willing to have new ideas and know others’ perspectives. Kurland
(2000) further explained that students are considered as critical thinkers if they
meet the following requirements, namely rationality, self-awareness,
open-mindedness, discipline, and judgment. First, rationality refers to thinking skills
relying on reasons rather than emotions, supported by evidences, and focusing on
finding the best explanation. Second, self-awareness recognizes our own
assumptions, prejudices, biases, or points of view. Third, open-mindedness is a
situation when students consider a variety of possible perspectives or viewpoints,
accept a new explanation, model, or paradigm and do not reject unpopular views
and comprehensive. Last, judgment emphasizes the importance of recognizing the
relevance of alternative assumptions and perspectives.
Factors Influencing Critical Thinking
There are factors influencing students’ critical thinking in basic education institution. The factors consist of personal factors followed by other factors.
Alfaro-LeFevre (2004) identified age as one of the personal factors that influences
critical thinking. The increasing of someone’s age influences a higher level of critical thinking. The increasing of age makes someone have more opportunities
to practice in many different situations. It is because critical thinking skills
develop through experiences or education. According to Purvis (2009), another
aspect which enhances critical thinking is personal characteristics such as
curiosity, confidence, and perseverance.
Curriculum design is another key factor in promoting critical thinking.
Purvis (2009) stated that curriculum design has an impact on the development of
critical thinking skills. Besides, integrative learning activities are the other
influencing factor of critical thinking. Learning activities including tests, case
studies, and simulations help students to bring knowledge and experiences
together in their learning process to achieve understanding and consequently
improve their critical thinking skills. Meyers (1986) suggested that teaching
activities such as debates, presenting problems, and small group work lead to
enhancing their ability to define problems precisely, and then to dissect problems
into manageable portions.
Students’ comfort level and learning environment are the other factors
influencing critical thinking skills. Shea and Bidjerano (2009) suggested that a crucial factor in developing critical thinking depends on the students’ comfort
levels and instructors. Teachers should help the students to gain their comfort and
confidence during learning the activities which enable the students to develop
their critical thinking skills. People who are relaxed, comfortable, and positively
stimulated are known to be more creative and innovative. Therefore, the learning
environment can influence the development of critical thinking ability
(Mortellaro, 2015). The learning environment in the classroom plays an important
part in encouraging critical thinking among the students in order to provide a
conductive learning environment.
Indeed, different types of tests or assessments can promote critical
thinking abilities in various ways. Purvis (2009) interviewed students and findings
identified that testing or assessment methods influence the development of their
critical thinking skills. Other unique technologies such as gaming have also been
utilized as a teaching strategy in education and have been positively perceived by
the students. The teaching strategy also promotes active learning, and therefore enhances the students’ critical thinking (Royse & Newton, 2013). This may be
another component of active learning that may influence the development of
Advantages of Being Critical Thinkers
Developing the ability to think critically is an essential life skill. Many
studies have been done to determine the benefits of critical thinking. Mahyuddin,
Lope-Pihie, Elias, and Konting (2004) stated that language learners with critical
thinking skills are able to think critically and creatively, make decisions, and solve
problems, understand language or its contents, and treat thinking skills as lifelong
learning in order to achieve the goals of the curriculum. Therefore, students who
have developed critical thinking skills will have better understanding from what
they learn, and solve problems effectively.
Tishman (2008) wrote that there are many reasons why students must
learn to think skillfully so that they can make thoughtful life decisions, solve
problems creatively, and understand as well as analyze knowledge in and across
disciplines. To do any of these things well, students need to become adept at
thinking things. To be successful in the future, students need to possess abilities to
create and evaluate information, to solve problems, and to make effective
decisions.
Critical thinking is important for students to get better learning. It is
echoed by Elder and Paul (1994) saying that critical thinking is someone’s ability of developing appropriate criteria to analyze their own thinking. They also stated
that the ability to raise vital questions, gather relevant information, determine
solve a complex problem. Hence, it can be said that critical thinker can solve their
problems more effectively and efficiently.
Students will be able to gain in-depth understanding of subjects which
they are learning, and apply what they have learned in real life. If students are able
to think critically, they will be able to perform well at class. Critical thinking is a
type of higher order thinking which is not only memorization of materials but also
the use of learning materials in new situations (Pikkert & Foster, 1996). Ardington
(2010) stated that students having an ability to think critically will achieve better
marks and become less dependent on teachers and textbooks. Furthermore,
according Choy and Cheah (2009), students with higher levels of critical thinking
skills have better abilities of information processing, organizing, deduction,
inference, exploring, and openness to experience. Therefore, students who have
developed critical thinking skills are capable of doing some activities of which
other students may not be capable.
Strategies in Developing Critical Thinking
There are various strategies that teachers can use in order to develop students’ critical thinking. According to Walker (2003), there are three strategies that can be used in developing students’ critical thinking. The first strategy that
can be used is questioning. According to Groisser (1964), the purpose of the questioning strategy is to stimulate students’ interests, test their progress, promote
understanding, develop new insights, and stimulate logic and critical thinking. For
can enhance students’ critical thinking. When the students are asked by the
teacher, they may use various critical thinking skills such as interpretation,
analysis, and recognition of assumptions to make a conclusion. There is not any
right or wrong answer because the answer depends on the students understanding.
Therefore, the use of the questioning strategies in learning activities helps teachers to evaluate students’ knowledge and understanding.
According to Walker (2003), the second strategy is classroom discussion
and debates. Discussion is the way to ask the students to get involved in a group
and talk about a certain case. Classroom discussion and debates can develop students’ critical thinking. In classroom discussion and debates students must
analyze, synthesize and evaluate the knowledge they have acquired in order to
discuss and organize their points of view of an argument or topic then they are
able to discover new information and put knowledge into action. Hence, this
activity is believed as a component lifting students’ critical thinking.
The third strategy based on Walker (2013) is writing assignments. These
assignments can foster students to think and make conclusion into a written form
of their understanding. These activities promote critical thinking among students
because they should present their understanding and their conclusions into a
written form.
Another strategy that can be used is problem-based learning. Krulik and
Rudnick (1984) defined problem solving as the use of previously acquired
situation. Furthermore, Bransford and Stein (1984) stated that problem-based
learning needs students to identify what they know and need to know, define
problems, generate solutions, and test as well as evaluate their solutions. There are
a number of benefits of this strategy in learning activities. Problem-based learning increases students’ motivation, and promotes higher order thinking (Torp & Sage,
1998). Hence, using problem-based learning will encourage students to make
better decisions, and will also challenge their intuitive mind to process and
evaluate their decisions and thinking to solve their problems.
Challenges to Develop Students’ Critical Thinking
One of the ongoing debates in education research is whether students can
learn to think critically through their own exploration or they need to be formally
taught the skill as part of the curriculum. Sternberg and Williams (2002) noted
that critical thinking may not need to be taught as thinking is a natural process
carried by everyone. However, Black (2005) argued that students are able to
improve their thinking skills if they were taught how to think. It is a skill that can
be improved and boosted by practice (Wood, 2002). Therefore, although students
have a natural ability to think critically, it is important for teachers to guide them
in order to develop their skills.
Nevertheless, some teachers do not know steps to take in their learning
activity in order to improve their students’ critical thinking skills. For one reason, the teachers may not have mastered critical thinking so that the students cannot
clear concept of critical thinking. It will be challenging for teachers to develop students’ critical thinking when they do not understand what critical thinking is.
Hence, teachers need to improve their understanding of the concept of critical
thinking to enable them to effectively teach student to think critically.
If the teachers do not have clear understanding of critical thinking, they
will find difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking into their learning
activities. According to Choy and Cheah (2009) teaching critical thinking is
challenging because teachers have difficulty in engaging critical thinking aspects
in their lessons. Critical thinking is equated to higher order thinking skills of Bloom’s Taxonomy: analysis, synthesis and evaluation, and teachers find
difficulty in incorporating these levels into their lessons (Choy & Cheah, 2009). It
is difficult to design learning activities that meets the needs of all learners, and to seek out strategies to foster students’ ability to learn and process information.
Hence, students may not be able to think critically because their teachers are not
able to integrate critical thinking into their daily practice.
Lack of training or practices and lack of critical thinking resources are
other barriers which make teaching critical thinking is challenging. Lack of
training can impede the integration of critical thinking in education (Snyder &
Snyder, 2008). In addition, Southwest Educational Development Laboratory
(1988) argued that little training especially in teacher training programs is devoted
specifically to how to teach thinking skills. Many experienced teachers are not
trained in critical thinking methodology so that they have difficulty in
training in critical thinking methodology, the teachers can develop theirskills in
critical thinking. Moreover, according to Mimbs (2005), many teachers lack
adequate resources. Only a few provide critical thinking resources (Scriven &
Paul, 2007). Teachers do not have a wide variety of learning activities due to lack
of existing resources. These various barriers of critical thinking explain why
lecturers and instructional strategies that emphasize information dissemination are
still the dominant style of teaching in today’s classroom (Choy & Cheah, 2009; Snyder & Snyder, 2008; Southwest Educational Development Laboratory, 1988).
Another challenge faced by teachers to develop students’ critical thinking
is that students have passive behaviors in the classroom. Passive means that the
students expect the teachers to provide all of information instead of having to find
the information by them and also they keep quiet and do not participate in
classroom activity. The students are also lack of language mastery and confidence
to express their ideas, and many of them are also overly examination oriented.
According to Choy and Cheah (2009) students are very passive in learning
activities as they are not taught how to think critically since the early age.
Furthermore, Paul (1990) revealed that most students are accustomed to sitting
back in class passively, and listening to lectures because they are trained in
schools to memorize the information, and not to think critically. They expect that
that their teachers will provide all the pertinent information that students need
(Choy & Cheah, 2009). Paul (1990) also added that students are used to passing
classes and tests without thinking critically. They also rely on their teachers to
Therefore, developing students’ critical thinking is challenging when teachers
meet students who have passive behaviors in the learning activities.
One of the biggest challenges to teach critical thinking is time constraints.
According to Mimbs (2005), the challenge of using critical thinking in learning
activities is that it takes time and efforts. Critical thinking is a learning process
that needs to be constantly practiced and incorporated into daily lessons. Pogrow (1988) stated “it takes an extensive amount of time to produce results… at least 35
minutes a day, four days a week, for several months, for true thinking skills development to occur” (p. 26). Furthermore, Way and Nitzke (1998) discussed an
infusion model for teaching critical thinking, and emphasized that critical thinking
skills take time to develop and are difficult to measure. Hence, teaching critical
thinking is challenging for teachers because it takes a lot of time, and patience. On
the contrary, students just want simple solutions that do not require much time and
many efforts.
Review of Related Studies
Several studies on critical thinking have been conducted. Firstly, Zachary
(2011) undertook research to find out if the implementation of critical thinking
would improve academic achievement. The method used in this action research is
qualitative and quantitative method approach. The participants of this study were
45 students. The finding of this research showed that teaching critical thinking
Secondly, another study related to this research was carried out by Mimbs
(2005). This study was designed using qualitative and the research participants
were 25 teachers. The result showed that the challenges of using critical thinking
in the classroom were that the students were only interested in points, the strategy
took time and needed many efforts, and the teachers were lack of adequate
resources.
Another study was also presented by Aliakbari and Sadeghdaghighi
(2012).Their research was about the barriers to implementing critical thinking
skills in classes. It aimed at seeing factors which teachers perceive as barriers of
the use of critical thinking strategies in the classroom. This research involved 100
English educators as the participants. The method used on this research is
quantitative by distributing questionnaires. The findings revealed that students'
attitudes and expectations, self-efficacy constraint and lack of critical thinking
knowledge among teachers were reported as major obstacles in teachers' view.
Those three reviewed studies have correlation to this study which focuses
on challenges in developing critical thinking. However, this research also has
some differences from the related studies. Besides discussing the strategies in developing students’ critical thinking, this research also attempts to find out the
challenges in apllying the strategies so that findings of this research can be a
Conceptual Framework
This study aims at finding the strategies that teachers applied and
challenges that teachers face to develop students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY. Critical thinking was firstly highlighted by Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomy a few decades ago (Duron, Limbach, & Waugh, 2006). It was perceived that a
higher level of cognitive abilities involving critical thinking was a feature in the
analysis, synthesis, and evaluation levels while lower levels of cognitive abilities
which are knowledge, comprehension, and application only involve remembering,
relating and applying information respectively (Duron et al., 2006). They
described that critical thinkers are those who are able to analyze and evaluate
information. Indeed, it is not easy for students to be a critical thinker, and teachers
should assist the students to develop students’ critical thinking.
There are various strategies that teachers can use in order to develop students’ critical thinking. The first strategy that can be used is questioning. To
answer the question asked by teacher the student may use various critical thinking
skills such as interpretation, analysis, and recognition of assumptions to make a
conclusion based on their understanding. Therefore, the use of the questioning
strategy in learning activities helps teachers to evaluate students’ knowledge and understanding of their thoughts and others.
The second strategy is classroom discussion and debates. Classroom discussion and debates can develop students’ critical thinking. In classroom
knowledge they have acquired in order to discuss and organize their points of
view of an argument or topic then they are able to discover new information and
put knowledge into action. Hence, this activity is believed as a component lifting students’ critical thinking.
The third strategy is writing assignments. These assignments can foster the
students to think and make conclusion into a written form of their understanding.
These activities promote critical thinking among students because they should
present their understanding and their conclusions into a written form.
Another strategy is problem-based learning. Krulik and Rudnick (1984)
defined problem solving as the use of previously acquired knowledge, skills, and
understanding by an individual to encounter unfamiliar situations. Hence, using
problem-based learning will encourage students to make better decisions, and will
challenge their intuitive mind to process and evaluate their decisions and thinking
to solve their problems.
Furthermore, the challenges that teachers face to develop students’ critical thinking skills are varied. Paul (1987) argued that many teachers lack clear
concept of critical thinking. It will be challenging for teachers to develop students’ critical thinking when they do not understand what critical thinking is.
Hence, when the teachers do not have a clear understanding of critical thinking,
they will get difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking into their
learning activities. According to Choy and Cheah (2009), teaching critical
critical thinking in their lessons. In addition, lack of training can impede the
integration of critical thinking in education (Snyder & Snyder, 2008). Therefore,
by having practices and training in critical thinking methodology, teachers can
develop students’ critical thinking. Moreover, according to Mimbs (2005), many teachers are lack of adequate resources. Teachers do not have a wide variety of
learning activities due to lack of existing resources. Another challenge to develop students’ critical thinking is that students have passive behaviors in the classroom.
According to Choy and Cheah (2009), students are very passive in learning
activities as they are not taught how to think critically since the early young age.
Furthermore, Paul (1990) revealed that most students are accustomed to being passive and listening to lectures. It is difficult to develop students’ critical
thinking when teachers meet passive students. Another challenge of teaching
critical thinking is time constraints. Using critical thinking in learning activities
takes much time and many efforts (Mimb, 2005: Pogrow, 1988; Way &Nitzke,
1998). Critical thinking is a learning process that needs to be constantly practiced
and incorporated into daily lessons. Hence, the researcher uses those expert
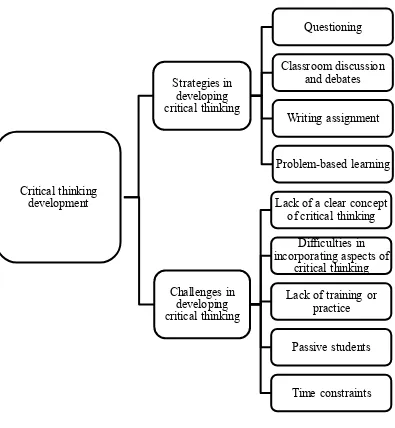
Figure 1. Conceptual Framework
Critical thinking development
Strategies in developing critical thinking
Questioning
Classroom discussion and debates
Writing assignment
Problem-based learning
Challenges in developing critical thinking
Lack of a clear concept of critical thinking
Difficulties in incorporating aspects of
critical thinking
Lack of training or practice
Passive students
Chapter Three
Research Methodology
This research discusses teachers’ strategies and challenges to develop students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY. In this chapter, the methodology
used in this study is presented. This chapter consists of research design, research setting, research participants, data collection method, and data analysis.
Research Design
Qualitative research was used as this research design. It is because qualitative research intends to explain or to reveal the participants’ personal
opinions, perspectives, experiences, and knowledge. Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2011) defined qualitative as “an in-depth, intricate, and detailed understanding of meanings from the voices of participants”, which“probes issue that lies beneath the surface of presenting behavior and actions” (p. 201). In addition, Creswell (2012) mentioned that “qualitative approach does not restrict the views of participants” (p. 205). It means that the quality research design can be employed to explore the participants’ opinions. Therefore, qualitative research
was considered as the proper research design for this study because qualitative research intends to explain or to reveal the participants’ personal opinions, perspectives, experiences, and knowledge.
Specifically, to find the detail information of the challenges that the teachers faced to develop students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY, the
when the researcher wants to know events, who are involved, what are involved, and where things take place (Lambert & Lambert, 2012). Lambert and Lambert (2012) added that the goal of qualitative descriptive studies is a comprehensive summarization, in everyday terms, of specific events experienced by individuals or groups of individuals.
Research Setting
This research was conducted at the English Education Department of UMY. There are two reasons why the researcher selected the EED of UMY as the setting of this study. First, at the EED of UMY there are learning activities which apply critical thinking such as essay writing, reflective writing, and group
discussion. Hence, this eased the researcher to get the data of the challenges that teachers’ face to develop students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY. Second,
the EED of UMY is where the researcher is currently studying. Thus, the
researcher and the participants could easily arrange the schedule to interviews to take the data. This research was started from September to October 2016.
Research Participants
selecting the two participants. First, the participants shall be the teachers whose learning activities in their class require students to think critically. Second, the participants also shall be the teachers who have taught for at least three years at the EED of UMY. With all the experiences of both teachers who have taught for at least three years at the EED of UMY in applying critical thinking in their
learning activities, they were expected to be able to give broad opinions from their experiences.
Data Collection Method
In this study, the researcher used an interview method to collect the data. He conducted the interview to the participants to find out their opinions and to gain information of their experiences when teaching at the EED of UMY. Khan (2014) stated that an interview provides an exclusive opportunity to uncover rich and complex information from an individual. Thus, by having interviews as the research instrument, the participants could express their opinions and tell their experiences. Furthermore, the interviews used the Indonesian language in order to make deeper understanding and comprehension when answering the interviews. During the interviews, the researcher used an audio recorder to store all the data when the participant answered all the interview questions.
they were scheduled to have interview based on their time availability. The interviews were conducted in certain places and time based on the agreement of both side (the researcher and participants). The duration of the interview was about 20 to 35 minutes.
Data Analysis
After collecting the data from conducting interview, the data from interview were transcribed into a written form. Moreover, the validity of the interviews was checked by conducting member checking to the participants. According to Creswell (2012), member checking is a process to check the
accuracy of the interviews by asking each participant. The participants confirmed that there is not any mistake on the interview transcription. Afterwards, the researcher analyzed the data by coding. According to Creswell “Coding is the process of segmenting and labeling text from descriptions and broad themes in the data” (p.243). Coding eases the researcher to identify similar information (Cohen
Chapter Four
Findings and Discussion
In this chapter, the researcher presents the findings and discussion of the
research which answer the research questions. The first research question is about
the strategies in developing students’ critical thinking. The second research
question is about the challenges that teachers of the EED of UMY face to develop
students’ critical thinking. The researcher reports the findings and also adds the
theories to support this research and to attain the answers of the research questions
in the discussion.
Strategies in Developing Students’ Critical Thinking at the EED of UMY
To answer this research question, the researcher took the data by
interviewing two participants. Based on interviews, the researcher found some
strategies that were usually used by both participants to develop students’ critical
thinking. The strategies were a questioning strategy, classroom discussion and
debates, writing assignments, problem based learning, reading assignments, and
providing feedback.
Questioning strategies. The researcher analyzed, the questioning strategy can be used to develop students’ critical thinking. Both participants believed that the questioning strategy can be utilized to enhance students’ critical thinking. The
teachers were the ones who decided the topic in applying the questioning
strategies and the students answered the topic in classroom. As stated by
answered by themselves with their critical thinking skill” (P1.33). When applying the questioning strategy, the two participants applied similar strategies by giving
questions. However, participant one added that sometimes the questions from the
students. On the other hand, participant two stated, “I gave the students some
questions which can trigger their curiosity” (P2.8). In applying the questioning
strategy, participant two gave the students some questions based on what they
read and then they must answer in the discussion.
To summarize, the questioning strategy was employed by teachers to
develop students’ critical thinking because the strategy has many advantages. This
was supported by Groisser (1964), who stated that the purpose of the questioning
strategy is to stimulate the students’ interests, test students’ progress, promote
understanding, develop new insights, and stimulate their logic and critical
thinking. When the students are asked by the teacher, they may use various
critical thinking skills such as interpretation, analysis, and recognition of
assumptions to make a conclusion. Therefore, the use of the questioning strategy
in learning activities helps teachers to evaluate students’ knowledge and
understanding of their thoughts and others.
Classroom and group discussion. The data showed that both participants believe that classroom debate and group discussion are the strategy that can
develop students critical thinking. As participant one stated, “I used group discussion to increase the students’ critical thinking” (P1.30). In the
implementation, the role of the teacher was as an instructor and facilitator. The
discuss the provided topics with their own group. In addition, participant one said,
“I try to accept the students’ opinions to create secure environment” (P1.31). She further stated that when students’ opinion is accepted by teachers or other
students, the students feel confident to express their opinion in learning activity.
Participant two also used group discussion to develop students’ critical thinking.
“Sometimes, I create classroom or group discussion to develop students’ critical thinking” (P2.9). She added that from what they have read before, they will have a
discussion in class. She gave the students some cases and then they needed to
solve the problem. For example, in one of her courses, she gave an option to
students to choose between 2 textbooks, and in the end of classroom activity
students had to choose which books was the most suitable of two books based on
their idea.
Group discussion conducted at the EED of UMY had many advantages.
Besides enhancing students’ speaking skills, group discussion also increases students’ critical thinking. This research finding was actually in accordance with
Walker (2003) who stated that classroom discussion and debates can develop
students’ critical thinking. Shortly, this research revealed that applying group
discussion could increase students’ critical thinking.
Writing assignments. Another strategy used by teachers of the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking was writing assignment. In writing
assignments, participant one asked the students to read and write a conclusion
based on their understanding of what they read previously. This activity is called a
assess the students whether they have read or not” (P1.12). Moreover, Participant
one added, “I have to know what my students know. How I know what my
students know is by doing the closed book journal” (P1.28). Closed book journal
is a strategy to require the students to read. Meanwhile, participants two said “In
the end of semester, my students were required to make a text book about what
they have learned” (P2.12). In the end of the semester, for the final assignment,
students had to make a text book based on their knowledge and understanding of
the material that had been learned in one semester.
In writing assignments, the students can enhance and develop their critical
thinking skills. This research finding was in accordance with Walker (2003) who
stated that writing assignments can encourage the students to think and make
conclusion in a written form of their understanding. These assignments promote
critical thinking among students because they should present their understanding
and their conclusions in a written form.
Problem based learning. The researcher found that the problem based
learning is another strategy used at the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical
thinking. The data showed that there was only one participant saying that problem
based learning became the strategy that can develop students’ critical thinking. Participant two stated, “Sometimes, I used problem based learning activities”
(P2.11). Teachers give the students some cases and then they need to solve the
problem. For example, in material design courses teacher gives the option for
students to choose between 2 textbooks, and in the end of classroom activity
their ideas. Problem based learning aims at giving the students chances to solve
their problem. In problem based learning, the students need to identify what they
know and need to know, define problems, generate solutions, and test and
evaluate their solutions. Those statements proved that the teachers can apply
problem based learning to develop students’ critical thinking.
In brief, the research finding revealed that problem based learning was
applied by teachers of the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking.
Indeed, using problem based learning has several advantages. This was in line
with Torp and Sage (1998) stating that problem based learning increases students’
motivation, and promotes higher order thinking.
Reading Assignments. Reading assignments is the strategy used by 2
teachers of the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking. Participant one said, “I developed students’ critical thinking through reading activities”
(P1.8). Participant one added “I required the students to read by expecting the
students’ to have curiosity about what they have read and learnt” (P1.7). Hence,
students can relate their existing knowledge to new information and they get a lot
of new information.
Moreover, participant two also used reading assignments to develop their
students’ critical thinking. Participant two said “I asked my students to read”
(P2.7). In reading assignments, the students should be critical thinkers. They were
required to read a book, a novel or journal articles, and then they should formulate
that the reading assignments force the students to read and understand what they
read.
Reading assignments have some advantages. First, the assignments can
also be applied with other strategies to develop students’ critical thinking.
Usually, reading assignments are followed by writing assessment and discussion.
Participant one stated, “After the reading assignments, I conducted a closed book
journal activity to assess the students’ awareness of reading” (P1.12). Closed
-book journal is a reflective writing where students have to read a -book and then
they express their conclusion by answering questions from the teacher based on
what they have read. Moreover, participant two stated, “After reading assignment,
students will do discussion in class, in the discussion they will evaluate what they
have read, or they will synthesize what they have read” (P2.9). Second,
conducting the closed book journal and discussion after a reading assignment was
believed as a good strategy because the students practiced it continuously.
Participant one said, “Using the closed book journal can encourage students to
read and develop their critical thinking” (P1.28).
In further analysis, the use of reading assignments as a strategy to develop
students’ critical thinking has been proposed in several literature. For instance,
this was in line with Tung and Chang (2009), who stated that using reading
assignment can encourage students to think critically. Therefore, reading
Providing feedback. The teachers of the EED of UMY provided feedback
to motivate students in developing their critical thinking. The data showed that
there was only one participant saying that providing feedback was a strategy in
developing students’ critical thinking. Participant one said, “Feedback is the most important aspect in developing students’critical thinking” (P1.29). In this
strategy, the teachers gave the feedback on the students’ paper assessments. Thus,
the students would know which part they should improve.
The research finding revealed that providing feedback was applied by
teacher of the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking. According to
Duron, Limbach, and Waugh (2006) the purposes of feedback is to enhance the
quality of students learning, performance and it help students learn how to asses
their own performance in the future. Based on the result, the researcher concluded
that providing feedback to students was considered as a good strategy to develop
students’ critical thinking at the EED of UMY.
Challenges Faced by Two Teachers of the EED of UMY in Developing Students’ Critical Thinking
This section discusses findings of the second research question. From the
interviews, the researcher found that the EED of UMY teachers faced five
challenges in developing students’ critical thinking. Mainly, the challenges could
be categorized into several themes, namely difficulty in incorporating aspects of
critical thinking, lack of resources, students’ passive behaviors, time constraints,
discusses the challenges in detail followed by other researchers’ or experts’ findings.
Difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking. The findings presented that both participants got difficulty in engaging aspects of critical
thinking in their lesson. In developing students’ critical thinking, the teachers also
faced several challenges. The main challenge was because developing critical
thinking needs a good strategy and the teachers have to endeavor to design
classroom activities that meet the need of all learners. Participant one said,
“Connecting subject contents to an activity that increases critical thinking is also challenging” (P1.20). Furthermore, “the students met difficulty in linking their existing knowledge with the materials that they learnt” (P1.23). Participant one
revealed the reason why students have difficulties in linking their existing
knowledge with the materials that they learn. First, students are not accustomed to
think critically. “Students are not familiar with critical thinking that makes them
confused” (P1.24). Second, students are trained in schools to memorize the
information, and not to think critically. “The difficulty for students to think
critically is that they have grown accustomed to memorize information” (P1.25).
Third, teacher-centered learning that have been taught in school does not
encourage students to be curious. “Teacher-centered learning does not encourage
students to be curious” (P1.26).
Another challenge was also stated by the other participant. Participant two
students also became a challenge. Moreover, Participant two said “It was difficult
to give questions which can encourage students to respond the questions and to
state their opinions” (P2.6).
In a further analysis, the researcher found that the challenge found in the
EED of UMY was actually in line with a study of Choy and Cheah (2009). They
maintained that teaching critical thinking is challenging because teachers get
difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking into their lessons. It is
difficult to design learning activities that meet the needs of all learners, and to
seek out strategies that foster students’ ability to learn and process information.
Find the right resources. In developing students’ critical thinking at the
EED of UMY, the teachers also faced several challenges. Mainly, in developing
students’ critical thinking, the challenge was that the teachers have difficulty in
finding right resources for students. The data showed that there was only one
participant who said that selecting the right of resources for students was the
challenge in developing students’ critical thinking.
First, students were hard to understand the resources when they got
materials in English. Participant one said, “The challenge was finding the right
resources or materials for the students that were not too easy and not too hard to
understand” (P1.9). Second, it was difficult for the students to understand if the
Thus, it can be concluded that the challenges in developing students’
critical thinking is due to lack of resources. The challenge was actually a common
challenge in teaching non-English students. Moreover, according to Mimbs
(2005), many teachers lack of adequate resources. The teachers do not have a
wide variety of learning activities due to lack of resources. Therefore, it can be
concluded that there will always challenges in developing students’ critical
thinking.
Students’ passive behaviors. Another challenge in developing students’
critical thinking was that the teachers faced students who have passive behavior
during learning activities. Both participants answered that teaching students who
have passive behaviors are the challenges to develop students’ critical thinking. As stated by participant two, “Students’ awareness to read is low, so when asked
to read by teachers before the class started, they started to read in class instead”
(P2.2). Hence, students did not have much information and opinion to express in
the learning activity because they did not read enough. Participant two added,
“Only a few of students were active in the classroom activity” (P2.3). Most of
students keep quiet and do not participate in classroom activities; this situation
makes the classroom activity not run well.
Besides, the students’ performance in the class also becomes a challenge
in developing their critical thinking. Based on the interviews, a research
participant said that there were a few students who were willing to think.
Participant two stated, “Only a few students tried to think when the teacher asked
Participant one said, “Students were accustomed to memorizing information” (P1.25). Participant one added, “teacher-centered learning does not encourage
students to be curious” (P1.26). Hence, it will be difficult to develop students’ critical thinking because they are accustomed to memorizing information rather
than thinking critically.
Paul (1990) stated that students are used to passing classes and tests
without thinking critically. Hence, the students get used to relying on their
teachers to provide them with the information. Consequently, this habit stunts
their ability to analyze. Therefore, developing students critical thinking is
challenging when teachers meet students who have passive behaviors in the
learning activities.
Time constraints. The research findings presented that time constraints is
another challenges in developing students’ critical thinking. The data showed that
there was only one participant who said that time constraints was the challenge in
developing students’ critical thinking.
Participant one said, “Giving feedback is challenging because it takes a lot of time” (P1.13). Feedback is one of the strategies used by teachers of the EED of
UMY to develop students’ critical thinking. This was supported by Mimbs (2005)
that enhancing critical thinking during learning activities takes much time and
many efforts. Hence, teaching critical thinking is challenging for teachers because
Difficulty in designing class activities. In developing students’ critical
thinking, the challenge was difficulty in designing class activities. The data
showed that there was only one participant who said that difficulty in designing
classroom activities was the challenge in developing students’ critical thinking. Participant one explained “designing teaching activities is challenging to develop students’ critical thinking” (P1.21). Actually, designing class activities is
important.
Based on the aforementioned results, the researcher concluded that
designing classroom activities was included as a challenge in developing students’
critical thinking at the EED of UMY. According to Mimbs (2005) challenges
using critical thinking in the classroom is the students’ interest in points only.
Most teachers find difficulty in designing classroom activities which meet the
Conclusion and Recommendation
This chapter consists of two major parts namely conclusions and
recommendations. First, the researcher presents the summary of the research.
Second, the researcher points out several recommendations after conducting this
research.
Conclusion
This research mainly aimed at exploring the strategies and challenges of
teachers of the EED of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking. This research found the strategies used by the EED of UMY teachers to develop students’
critical thinking. The strategies were questioning strategies, written assignments,
classroom debate, or group discussion, problem based learning, reading
assignments, and giving feedback. Furthermore, this research also revealed the
challenges of EED of UMY teachers’ to develop students’ critical thinking skills. The challenges were difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking, lack of
resources, students’ passive behaviors, time constraint, and difficulty in class
activity designs.
Two teachers of the EED of UMY used question strategies to develop
students’ critical thinking. The methods can foster the students to use various
critical thinking skills such as interpretation, analysis, and recognition of
The use of reading assignments was believed as the most effective strategy
to develop students’ critical thinking. This statement indicated that the reading assignments force the students to read and understand what they read.
Furthermore, the reading assignments can also be applied with other strategies to
develop students’ critical thinking. Reading assignments were usually followed by writing assignments. Writing assignments were also effective to develop students’
critical thinking. In writing assignments, the students can enhance and develop
their critical thinking skills. These activities promote critical thinking among
students because they should present their understanding and their conclusions
into a written form.
Classroom debate and discussion were also used by 2 teachers of the EED
of UMY to develop students’ critical thinking. Indeed, these two strategies were
usually combined as one. Debate and discussion were expected to improve
students’ critical thinking and teamwork. Indeed, debate and discussion were designed to increase students’ ability to respond quickly and spontaneously to
other students’ arguments. However, the delivered arguments should be based on academic and scientific resources.
Teacher of the EED of UMY used problem based learning as a strategy to
develop students’ critical thinking. The aim of problem based learning is to give
These research findings proved that the teachers can apply problem based learning
to develop students’ critical thinking.
The last revealed strategy which the teacher of the EED of UMY used to
develop students’ critical thinking is providing feedback. The teachers gave
feedback to motivate students to develop their critical thinking. In this strategy,
the teachers gave the feedback on the students’ paper assessments. Thus, the
students knew which part they should improve.
In developing students’ critical thinking, the teachers found that teaching
students who have passive behaviors was the hardest challenge. When only a few
students were active in class activity, the classroom activity would not run well.
Besides, another challenge was that only a few students thought and answered
when the teacher asked a question. The other challenge was that students were
accustomed to memorizing information. Therefore, developing students’ critical
thinking is challenging when teachers meet students who have passive behaviors
in the learning activity.
Difficulty in incorporating aspects of critical thinking in learning activity
also becomes a challenge in developing students’ critical thinking. It is difficult to design learning activities that meet the needs of all learners, and to seek out
variety of learning activities. Therefore, it can be concluded that there are always
challenges in developing students’ critical thinking.
A time constraint is another challenge in developing students’ critical
thinking. Teaching critical thinking was challenging for the teachers because it
took a lot of time and patience.
The last revealed challenge which teachers faced to develop students’
critical thinking is regarding class activity designs. In designing class activities,
the teachers should create the classroom activities which meet all learners’ needs,
so that it is challenging to create class activities that can enhance students’ critical
thinking skills.
Recommendation
After the research was conducted, there are some recommendations for the
teachers and other researchers.
For teachers. In this research, there are some challenges and strategies
that faced and used by teachers to develop students’ critical thinking. Teachers
are responsible for helping students to develop their critical thinking skills. As
teachers, they should be able to apply the strategies as good as possible. The
researcher suggests the teachers to find certain strategies which meet needs of
their own students. Hopefully, the strategies could help the teachers in developing
and also strategies used by teachers to develop students’ critical thinking. The
researcher recommends other researchers to conduct research discussing how to
overcome the challenges in applying the strategies to develop students’ critical
thinking. Those other researchers can use case study in this research to find the
strategies, challenges, and the teachers’ ways to cope with the challenges in real situation.
However, it needs to be acknowledged that the participants of this research
were only two lecturers of the EED of UMY, so the number of participants in this
study was too limited to be representative. Therefore, the result from this research
Aliakbari, M. & Sadeghdaghighi, A. (2013). Teachers' perception of the barriers to
critical thinking. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 70. 1-5
Alfaro-LeFevre, R. (2004). Critical thinking and clinical judgment (3rd ed.). St.
Louis: Elsevier Science.
Ardington, A. (2010). Developing critical thinking skills. Sydney: The University
of Sydney.
Black, S. (2005). Teaching students to think critically. The Education Digest,
70(6), 42-47.
Bransford, J. D., Sherwood, R. D., & Sturdevant, T. (1987). Teaching thinking
and problem solving. In J. B. Baron & R. J. Sternberg (Eds.), Teaching
thinking skills: Theory and practice. New York: W. H. Freeman and
Company.
Bransford, J., & Stein, S.B.(1984) The ideal problem solver: A guide for
improving thinking. Learning, and creativity. New York, NY:
W.H.Freeman
Cas