( An Experimental Study at the Second Grade of Senior High School Pembangunan 1 Bogor )
The “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training In partial fulfillment of requirements
for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
Written By
Ema Ni’mah Utami
207014017978
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
i
Utami, Ni’mah, Ema, 2014, Teaching Reading Skill through Paraphrasing and Summarizing at the Second Grade of Senior High School Pembangunan 1 Bogor,
Skripsi, Department of English Education, The Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’
Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor : Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd.
Key word : Reading Skill, Paraphrasing and Summarizing
The objective of the research is to know the effectiveness of using paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading skill at the second grade of senior high school Pembangunan 1 Bogor.
The method of the research is a experimental study in a form of quantitative. The data analyzed in this research gathered through the test about teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing at the second grade of senior high school Pembangunan 1 Bogor.
By analyzing the student’s answer sheet during teaching learning process in the class. The result of statistical calculation the research showing that the value to = 16.22, and t table = 2.03 and 2.72. it is clear that t obsevation is higher than t
table :2.03<16.22>2.72. It can be seen from statistical data that using paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading can give a significant influence to increase
ii
Utami, Ni’mah, Ema,2014, Teaching Reading Skill through Paraphrasing and Summarizing at the Second grade of Senior High School Pembangunan 1 Bogor.
Skripsi, Department of English Education, the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’
Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Pembimbing : Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci : Kemampuan membaca, paraphrase dan summary
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui keefektifan penggunaan paraphrase dan summary dalam mengajar kemampuan membaca pada siswa kelas dua SMU Pembangunan 1 Bogor.
Metode penelitian ini adalah metode penelitian experimen dalam bentuk penelitian kuantitative. Data yang diteliti dalam penelitian ini di kumpulkan melalui tes tentang mengajarkan kemampuan membaca melalui paraphrase dan summary pada siswa SMU Pembangunan 1 Bogor.
iii
All praise be to Allah for His blessing, help and guidance, so this “Skripsi”
can be finished properly. May Peace and bless be upon Prophet Muhammad SAW.
The writer would like to express her greatest love and honor to her beloved parent, her mother and father, her husband Mardi, who always give his love, support, motivation, and advise to finish her study and my lovely sons M. Azmiy Aulia, M. Alfathdry Rausyan, and M. Firza Hafizhiy, and the whole family who
have given her moral encouragement to finish this “Skripsi”.
The writer would like also to address her gratitude and appreciation to :
1. All lectures in English Departement for their valuable knowledge during her study at Syarif Hidayatullah.
2. Drs. Syauki M.Pd., the head of English Departement.
3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum., the secretary of English Departement. 4. Dra. Nurlena, MA, Ph.D, the Dean of Tarbiya and Teacher’s training. 5. Drs. H. Eman Supriyatman as the head master of SMA Pembangunan 1
Bogor, giving the writer a permission to carry out this reseach.
6. Annisa . S.Pd as an English Teacher of SMA Pembangunan 1 Bogor, who has allowed the writer to take the research in her class.
Finaly, the writer realizes that this “Skripsi” still has some
weekness and mistakes. May this “Skripsi” be useful to the readers, particulary to the writer.
iv
ABSTRAK ... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iv
LIST OF TABLES ... vi
LIST OF APPENDICES ... vii
CHAPTER I :INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Identification ... 3
C. The Limitation of the Problem ... 3
D. The Formulation of the Problem ... 4
E. The Objective of the Study ... 4
F. The Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II :THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 5
A. The Reading Skill ... 5
1. The Meaning of Reading Skill ... 5
2. The Purpose of Reading Skill ... 6
3. The Kinds of Reading Skill ... 7
4. The Types of Reading Skill... 8
5. The Principles of Teaching Reading... 9
B. Paraphrasing ... 11
1. Definitions of Paraphrase ... 11
2. The Strategies in Paraphrasing ... 12
C
. Summarizing ... 131. Definitions of Summary ... 13
v
E. The Procedure of Teaching ... 16
F. Conceptual Framework ... 18
G.Theoretical Hypothesis ... 19
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY... 20
A. Place and Time of the Study ... 20
B. Method of Research... 20
C. Population and Sample ... 20
D. The Instrument of the Research ... 21
E. Technique of Data Collection ... 21
F. Technique of Data Analysis ... 21
G. Statistical Hypothesis ... 22
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDINGS AND ERPRETATION
A. Description of the Data ... 231. The Analysis of the Data ... 25
2. The Test of the Hypothesis ... 29
B.Interpretation Data ... 30
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGESTION
A. Conclusion... ... 31B. Suggestion ... ... 32
BIBLIOGRAPHY
vi
LIST OF TABLES
1. Table 4.1 the pre-test and post-test score of the experimental class...23 2. Table 4.2 the pre-test and post-test score of the control class...24 3. Table 4.3 the result calculation between experimental class and control
vii
LIST OF APPENDICES
1. Appendix 1 Rencana Pengajaran...35
2. Appendix 2 Rencana Pengajaran...38
3. Appendix 3 Rencana Pengajaran...40
4. Appendix 4 Pre-test question sheet...43
5. Appendix 5 Reading text ...48
6. Appendix 6 Reading text...50
7. Appendix 7 Reading text...51
8. Appendix 8 Reading text...52
9. Appendix 9 Reading text...53
10.Appendix 10 Post-test question sheet...54
11.Appendix 11 The answer sheet reading test...60
12.Appendix 12 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi...61
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
English is one of the International languages of the world. As an international language , it is used in all important aspect including education. learning English includes the four skill that are important for mastery of language. The four skills are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. One skill is connected with each other and they cannot be separated in a language.
Reading is one of the basic language skills and always taught to the student from Elementary School up to the University level. It is very important to learn a foreign language, because the aim of reading can provide students with some activities such as : to comprehend the text, to get pleasure knowledge, and to get information.
Reading is one of the most important skills. In fact in many instances around the world we may argue that reading is the most important foreign language skill, particularly in cases where studentshave to read English materials for their own specialist subject, but may never actually have to speak the language.1
According to Jo Aebersold and Field L, Richard, “Reading is the ability to comprehend the thought and the feelings of another of mindvia the medium oftext. Reading constituses a powerful activity that confers knowledge, insight, and
perspective on readers”.2
For a child in a school, reading is the primary source of knowledge, transmission and expression and if this exchange takes place in a week language
1
Jo MC Donough and Christoper Shaw, Material and Methods in ELT,United Kingdom : Black Well, 1993, p. 101-102.
2 Jo Ann Aebersold and Fild, Richard, From Reader to Teaching Reading : Issues and
or depends on compromised skills, the consequences for children’s education are
obvious.3
De Boer and Dallman stated in their book that:”Reading is such a complex process. Reading is not a general ability, but a composite of many specific abilities. It is therefore necessary to break down general comprehension into the specific skills which together constitute it.4
In learning reading, it is not easy to get efficient and effective to comprehend the reading materials. It is required a long process which should be leraned step by step when learning reading by the students.
The fact shows that many students of English complain that reading is a difficult skill to perform. They are faced problem in the teaching learning process when apply the materials a teacher always ask the student to read, translate, and answer question. This could be one of the reasons why students feel bored when they get reading lessons.
Reading is a process to comprehend the contents of the text. In teaching reading the students sometimes difficult to find out the ideas in the text, and they are not understand the meaning of a passage or sentences. This difficulty, might be caused by the students lack of practice. They are still difficult to get the ideas contained in a text, to choose vocabulary, or to use the correct stucture. Learning a language is not just viewed through a set of stucture rules, and repetation of English sounds,but it is cannot be separated from practice reading. In this case, the writer uses paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading skill.
The aim of this study is to find out whether strategies of paraphrasing and summarizing can help students to increase their reading skill, but also their general language skill. In this process the writer give the students some exercises and drills to encourage and familiarize them with new form in a language.
3
Ellen Biallystok, Bilingualism in Development (Cambridge, University Press, 2001),p.174 4 De Boer, Dallman, The Teaching of Reading, (New York: Holt, Rinehart, Winston Inc.,
In the teaching learning process the teachers should have a lot of method to make reading teaching and learning activities interesting. According to Edward Anthony (1968) as in Approach and Method in Teaching Learning of Jack &
Rodger “method is the level at which choices are made about the particular skill to be taught, the content to be taught, and the order which the content will be
present.”5
Based on the background above, the writer interested in discussing about teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing. A case study at the second grade of senior high school pembangunan 1 bogor. Through this skripsi, the writer wants to give alternative way in learning reading materials. She is hope that the strategies of paraphrasing and summarizing can help students get more interesting and enthusiastic in learning reading. Beside that it is a very useful strategy for learner to improve their reading skill, but also their general language skill.
B. Problem Identification
As stated at the background of the skripsi,there are interesting problem concerning with the topic in analysis and observing teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing. Problem could be identified as follows:
1. One of the difficulties faced by the student in learning reading is difficult to comprehend the ideas in English written text.
2. The student feel bored learning English reading.
C. The Limitation of the Problem
In writing this skripsi the writer wants to give a simple description about the limitation of the study. The writer limits the problem on “teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing at the second grade of senior high school Pembangunan 1 Bogor”.
5 Jack Richard and Theodore S. Rodger, Approch and Method in Teaching Learning,
D. The Formulation of the Problem
Based on the background above, the writer would like to formulate the
problem as: “is there effects using paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading skill”?
E. The Objective of the Study
The objective of the research is to know whether paraphrasing and summarizing is effective in the teaching reading skill.
F. The Significance of the Study
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.
The Reading Skill
1.
The meaning of reading skill
Reading skill is very prominent in a language. It is a tool of learning to understand the books or other reference matrials; when we first read a book the first think we think are word and meaning. We have to memorize the meaning of words and there are unlimited in learn a language.
Reading skill is one of a language ability. In the process of reading, the students should concentrates with the subject content and the language. It is useful to provide their activities in the comprehension, interpretation of ideas, cognitive activity, and physical activity.
Harmer classified reading skill into six skills. They are: predictions, scanning, skimming, finding detailed information, recognition discourse pattern, and guessing meaning from context.6
According to Peter David Pumprey, reading is more than the ability to understand the explicit meaning of the passage presented. It is, in essence, a constructive thingking process which includes comprehension of explicit and implicit meaning. It involves application, analysis, evaluation, and imagination. It
is one activity through which the child’s cognitive development can further.7
In reading instruction for today’s children stated that reading is an activity which involves the comprehension and interpretation of ideas symbolized by written or printed language.8
6
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, New York : Longman Publishing, 1991, p. 153
7
Peter David, F, Measuring Reading Ability : concept, sources and application, :GreatBritanian :Hoder and Stoughton Educational, 1997, p.2
Reading is not only pronouncing the word loudly but also understanding
taken into consideration. As Christinc Nuttal said “it is unlikely that you were interested in pronounciation of what you read except in a tiny minority of cases, and it is even likely that you were intersted in the grammatical structures used. You read because you wanted to get something from the writing : facts, ideas, enjoyment, even feelings or family community (from letter) : what ever it was, you wanted to get message that the writer had expressed”.9
Farrel stated that ”Reading is also considered as a process of constructing
meaning through dynamic interaction among the existing knowledge, the information suggested by the written language, and the context of the reading
situation”.10
Based on those definitions above, it can be concluded that reading is the ability to understand the meaning from written langguage and it requires any other aspects such as word recognition and pronunciation.
2.
The purpose of reading skill
When people read, they read for purpose. They may read to understand (reading for full comprehension), and to get the general idea, or to find the part that contains the information.
A person may read for many purposes. If he is reading for pleasure, he may read either quickly or slowly based on the way he likes or feels. But if he is reading for information such as news, science or some line which are parts of his study or assignment it does slowly and carrefully. If a person wants to note an address, a phone number, a date or book paragraph in order to locate a special piece of information, is called scanning. But if he neds all the passage in order to know about what it deals about his reading is called skimming.11
As Harris and Smith stated that “ purpose for reading are similar for the
beginner and the mature reader. The level of thought that is required to achieve
9
Christine Nuttal, Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language, (London : Heineman, 1982 ), p. 3
Farrel, Planning Lesson for A Reading class, RELC Potrfolio Series 6, (Singapore: Regional Language Center,2002).p.1
11 Christinc Nuttal, Teaching Reading in a Foreign Language, Oxford : Heineman
the same reading purpose varies with the difficulty of selection and the skill of the reader different authorities suggest a variety of purpose of reading. We believe that most of these can be organized into five categories: (1). Finding the main idea, (2). Finding supporting detail, (3). Grasping the author’s plan of organization, (4). Following a sequence of even or thought, (5). Critically
appraising the author’s work.12
Meanwhile, Alton L Raygon, he said that :”...The purpose of this reading
is to catch all information about what the author tries to say in a printed materials to comprehension, ascension, also interpretation”.13
According to Henry Guntur Tarigan in his book, “The main purpose of reading is find and get information in content, understand in the text and get information by skimming, scanning, and comprehension”.14
From the definition above, it shows that the purpose of the reading is not only to understand the reading passage, but also to find out the ideas written by the author.
There are some reading ability to development of various reading skills such as : kinds of reading and types of reading skill.
3.
Kinds of Reading
The kinds of reading can be divided into two kinds. There are silent reading and oral reading (reading aloud).
a.
Silent reading
Reading is an active process, not a passive process. Silent reading suggest the student to be active. In this technique the students do not care recognize the symbol, pronounciation, intonation and rhythm, because the main purpose of this reading to get information from the texts efficiently, rapidly. In the other words, the students just focused on analyzing and understanding the text they read.
12
Harris and Smith, Reading Instruction Through Diagnostic Teaching, New York : Notl Riachart, Inc, 1972, p. 268
13
Alton L Raygon, Teaching Reading in Elementary School, Columbus : Bell and Howell, Taken from: http//www. Usergate.
14Henry Guntur Tarigan, Reading as Language Skill, ( Bandung : Angkasa Tarsito, 1986 ),
The silent reading can be developed in other valuable purposes, such as: (1). Study Reading
Study reading is the type of reading that is very important mostly for the
students. It is stated by Lyla L Miller in his book as follows : “study reading is a type in which the reader must get a maximum understanding of a main ideas and their relationship. This is the type the student must apply to his contacts, legal papers, technical manual instruction and similar materials which must read and understand now and also remember for future use.15
(2). Idea Reading
This type is intended to get key ideas which are essential to most reading. The basic meanings of most articles should be considered into a few paragraph.
b.Oral Reading (reading aloud)
Reading is not only on the pronouncing or loudly reading but also it is the
understanding taken into consideration. As said by Nuttal, “it is unlikely that you
were interested in the pronunciation of that you read expect in a tiny minority of cases, and it is even likely that you were inerested in the grammatical structures used, you read because you wanted to get something from writing : facts, ideas, enjoyment, even feelings or family comunity (from letter). What ever it was, you wanted to get the massage that the writer loud expressed ”.16
4.
The types of Reading Skill
There are four easily identifiable skills in reading : skimming, scanning, intensive reading and extensive reading.17
a. Skimming : glancing rapidly through a text to determine its general content or gist,e.g.quickly glancing through an article to see if it interest him. Being able
15
Lyle L. Miller, Increasing Reading Efficiently, (New York : Holt, Rinehart & Winston Inc., 1959 ), p.9
16
Christinc Nuttal, Teaching Reading Skill in a foreign Language, (London : Heineman, 1982 ), p.3
17 Andrew Wright, Picture for Language Learning, ( Cambridge : Cambridge University
to look over material rapidly for given purposes without reading every phrase is great asset for a reader to posses. Skimming permits people to gain a general b. Scannning : reading to locate specific information, e.g locating a telephone
number in a directory. Being able to search through material rapidly, with given purpose in mind, in order to find a specific fact or an answer to a
particular question plays a large role in much of a youngster’s reading. Scanning enables people to locate specific information without rading all the material around it.Scanning permits people to use a variety of sources with economy.
c. Intensive reading : reader is trying to absorb all the information given;e.g reading dosage instruction for medicine.
d. Extensive reading : reader deals with a longer text as a whole, which requires the ability to understand the component parts and their contribution to the overall meaning, e.g reading a newspaper article, short story or novel.
5 . The Principles of Teaching Reading
There are severals principles in teaching reading suggested by experts in order to achieve the goal or reading program. White (1981) makes some suggestions about stages which may help us to put the skill into a classroom context and to see some of it possible relationship with other langguage skills:18
a. Arouse the students’ interest and motivating by linking the topic of the text to their own experience or exixting knowledge. Give some pre-reading/focusing questions to help them to do this.
b. Give them points to search for in the reading text, or ask the students to suggest the points.
c. After reading, encourage discussion of answers.
d. Develop into writing by using the information gained for another purpose.
18
Meanwhile, Elizabeth (2006) propose some principles in teaching reading:19 a. Oral reading. The ability to attend to the individual sounds within
words (phonological and phonemic awareness) is also an oral skill that is closely associated with reading ability.
b. Phonological phonemic awareness. Phonological awareness refers to the ability to attend to the sounds of language as distinct from its meaning.
c. Fluency. Fluency is important because it is closely related to comprehension. Fluent readers recognize words quickly, but also know where to place emphasis or paused during reading.
d. Vocabulary. Vocabulary is cruciak to reading comprehension. In order to undesrtand the text, readers need to know the meanings of individuals words.
e. Prior knowledge. Readers use prior knowledge to undesrtand texts. Having more prior knowledge generally aids comprehension.
f. Comprehension. Good readers are aware of how well they understand a text while reading. Good readers also take active steps to overcome difficulties in comprehension. Students can be instructed in strategies to improve text comprehension and information use.
g. Motivation and purposes. Teachers need to be aware of their students’ learning needs, including their motivation for reading and the purpose that reading has in their lives.
h. Integrated reading and writing. Developing reading skills through writing is an effective strategy. It helps students to establish the connection between oral and written language.
i. Text. Choosing texts of the right difficulty and interest levels will encourage children to read and to enjoy what they are reading.
j. Assesment. Two forms of reading assesment are to find out how well children are reading in order to help them improve (diagnosis) and to
19
measure how much progress has been made. Both forms of assesment are needed for effective reading instruction.
k. Culture factors. Culture knowledge affects reading comprehension. Having rich but different types of cultural knowledge will affect undesrtanding and appreciation of written text.
l. Practice. Readers make progress by reading more.
There are six principles in teaching reading according to Jeremy Harmer. First, reading is not a passive skill; second, students need to be engaged with what they are reading; third,students should be encouraged to respond to the content of a reading text, not just to the language; fourth, prediction is a major factor in reading; fifth, the the task to the topic; and sixth, good teachers oxploit reading text to the full.20
B.
PARAPHRASING
1.
Definitions of Paraphrase
According to kennedy paraphrasing is translating the author’s ideas into our owns words.21 Harry Shaw stated that “The paraphrase is a kind of report on reading that is frequently requierd in collage work. Where as a pre’cis is digest of the essential meaning of an original passage, a paraphrase is a full lenght statement of that meaning. A paraphrase presents a free rendering of the sense of a passage, fully and proportionately, but in words different from the original.22Meanwhile legget defined a paraphrase is kind of report on reading that is frequently required in college work. It is represents a free passage, fully and proportionally, but in words different from the original.23
A paraphrase is a short summary of a writer’s statement (usually no more
than a sentence) in your own words concentrate only on what you think are the
20
Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach English, (England: Addison Wesley Longman Limited,1998).p.70 21
Kennedy, Mary Lynch, William J. Kennedy, Hardly M. Smith, Writing in The Diciplines, New Jersey : Simon & Chuster, 1987, p.20
22
Shaw, Harry, The Harper Handbook of Collage Composition 15th ed ), (New York : Harper and Row, 1981, p. 524
23Legget, Glenn, C.D Mend & Melinda G. Kramer, Handbook for Writers, New Jersey :
main points a writer is making, the ones for which supporting arguments are found.24
Linda Simon stated that “ paraphrase means to rephrase an author’s
statement in your own words. When your paraphrase in your paper, you always cite the source in a footnote or endnote. You need to refer your reader to the author of the idea you are presenting “.25
From the statements above the writerconclude that a paraphrase is
presentation a message from the authors’ ideas in our own words of all the information in a brief passage. Paraphrasing or wording something along side
from the original. It is make the meaning of the passage’s is clearer and more
concise. And it is a usefull skill for almost any field of study or work specially in academic reading and academic writing.
2.
The Stategies in Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing is expressing someone else’s ideas or restates a passage in
our own words. There are some strategies in paraphrasing. Kennedy the former out the systematic paraphrasing strategies as follow :26(1). Write a loose paraphrase and record necessary contextual information,(2). Substitute synonyms,(3). Change the order of ideas,(4). Compare your completed paraphrase to your loose paraphrase and the original.
According to Valiukenas another point to begin paraphrase : first, try summarizing what the original has said, then elaborate on it to whatever extent
your discussion of ideas requires. Finally, when you’re revising the first draft at your paper, polish up the paraphrase as well.27
Kathleen use the following suggestions to paraphrase effectively: 1). Read slowly and carrefully, 2). Read the material through entirely before writing
24
Eric Gould, Robert Diyanni, William Smith, The Art of Reading, New York : Random House, 1987, p. 31
25
Linda Simon, Good Writing ( A Guide and Sourcebook for Writing Across the Curriculum ), New York : ST. Martin’s Press, , p. 2
26
Kennedy, Mary Lynch, William J Kennedy, Hardly M. Smith, Writing in the Diciplines, New Jersey; Simon & Schuster, 1987, p. 21
27
anything, 3). As you read, focus on both exact meaning and relationship among ideas, 4). Begin paraphrasing sentence by sentence, 5). Reading each sentence and
identify its core meaning, 6). Don’t try to paraphrase word by word, 7). For words
or phrases about which you are unsure of the meaning, check a dictionary to locate a more familiar meaning, 8). You may combine several original sentences into a more concise paraphrase, 9). Compare your paraphrase with the original for completeness and accuracy.28
Writing a good paraphrase is not easy, for it requires that we think and think about what we read. It is need effort to undestand the passage what we read.
C. SUMMARIZING
1. Definitions of Summary
Summary is important aspect of academic writing but also linked to academic reading. It is a selection of main ideas all taking and writing involves same degree of summary.
Kennedy also say that a summary is a clear and brief work which contains only the main ideas of a text. As a consideration or compression, a summary is much shorther that the work it summarizes.29 In short, we can say that the goal of summarizing is making the original passage shorter without changing it’s meaning. According to Eric Gould a summary is a short statement in your own words which contains your interpretation of the most important ideas in a text. A summary can be a couple of statement long if it covers a short passage, or it can beconsiderablysegments there of.30 Meanwhile Linda Simon defined a summary is picks out the main points of a book, article, or other source and restates these
28
Kathleen T. McWhorter, Efficient and Flexible Reading, New York: Harper Collins Pulishers, 1992, p.301
29
Kennedy, Mary Lynch, William J Kennedy, Hardly M. Smith, Writing in the Diciplines, New Jersey : Simon & Schuster, 1987, p. 25
30 Eric Gould, Robert Diyanni, William Smith, The Art of Reading, New York : Random
points in your own words. By highlighting these main points, you will be left with a condensed version of a longer piece.31
Based on the statements above, the writer can conclude that a summary is
restatement from the author’s ideas giving only the key points of a passage. It is not a long side from the original. We just select the information presented in the original.
2. The Strategies in Summarizing
There are some strategies in summarizing. According to Kennedy, those are 1). We delete redundancy and unimportant detail,(2). We provide a general term to cover several specific the original text,(3).We locate and emphasize topic sentences, and invent ones if none are found,(4). We combine ideas in sentences and paragraph.32 Mean while Simon writes : (1). We read the text once, and try to state the point of the text in a single sentence,(2). We read the text again, and ask
our self if our sentence about the author’s meaning makes sense,(3). We go
through the text paragraphs by paragraphs, and for each paragraph we give the main point in a sentence, (4). We rewite a draft by assembling our sentences in a good order, (5). We revised, add appropriate transitional material, change words, and turn our sentences into a readable summary.33
Kathleen use the following steps as a guide in writing a summary: 1). Read the entire original work first, 2). Reread and underline key points, 3). Review your underlining, 4). Write sentences to include all remaining underlined information, 5). Present ideas in the summary in the same order in which they appeared in the original, 6). Revise your summary.34
Mean while Jordan writes the advice and suggestions for writing summaries:
31
Linda Simon, Good Writing ( A Guide and Sourcebook for Writing Across the Curriculum ), New York : ST. Martin’s Press, , p.
32
Kennedy, Mary Lynch, William J Kennedy, Hardly M. Smith, W riting in the Diciplines, New Jersey : Simon & Schuster, 1987,p.26
33
Simon, Linda, Good Writing ( A Guide, and Source Book For Writing Across the Curriculum ), New York : ST. Marti’s Press, , p.
34 Kathleen T. McWhorter, Efficient and Flexible Reading, New York: Harper Collins
a. At the beginning write the title of the book/journal, the author and article, publisher and date.
b. Quickly read (skim) the next to get an overall idea of it. c. Then read it carefully, identifying the main points. d. As you read, make brief notes of the main points.
e. Phrase are important and may be useful to quote in an essay. f. Remove examples and details.
g. Ensure that your summary is accurate and neutral.
h. As far as possible condense the ponits into straightforward statements.
i. Write clearly, concisely, coherently, and logically.35
D.Similarities and Differences Between Paraphrasing and
Summarizing
There are some similarities and differences between paraphrasing and summarizing in terms of content, vocabulary, stucture, and lenght. The similarities are about the vocabulary and the structure these are according to Sorenson 36:(1). Both paraphrasing and summarizing are strategies in language learning using
mostly cognitive strategies, (2). Both are “translating” technical of complicated
material into our own words,(3). In orther to get good result, both of them are done without looking at the original text. The differences about the content and lenght (1). A paraphrase contains all information the original, while a summary contains only the most important information, (2). The lenght of paraphrase is nearly the same as the original, usually one-fourth less, while a summary is a shorthened version of a piece of writing, (3). If a paraphrase does not reflect personal bias, a summary does.
35
Jordan R. R, English for Academic Purpose, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997, p.97
36
According to Gould a paraphrase differs from a summary in the following ways37 :(1). It is more extensive than summary,(2). A paraphrase is inclusive, a summary selective, (3). The paraphrase depends on the structure of the text, the summary does not, (4). Summaries are generally written in the present tense, (5). It is shorter than the original, but it contains all the important point, (6). It is a report on something that has already been written or presented orally, (7). The first sentence usually identifies what is sentence usually identifies what is being summarized.
Kathleen stated that a summary contains only the gist of the text, with limited background, explanation, or detail. Although summaries vary in lenght, they are often one-quarter or less of the length of the original.38
A paraphrase and a summary are a useful technique in several situations and useful in a variety of reading situations. Mainly to get information for several paper, to get detailed comprehension, and to understanding difficult passages.
E. The Procedure of Teaching
In the teaching learning process, there is an interaction between teacher and student. The writer should prepare all components are related to teaching learning process such as she make lesson plan before presenting the concept would be learned:
1. Greeting
The writer entered the class and greets the students, and than the writer
checked the attendance list by calling the student’s name one by one.
Before starting the lesson the writer introduced herself. The writer tells the students some information about the topic that would be learned.
37
Eric, Gould, Diyanni, Robert, Smith William, The Act of Writing, New Yprk : Random House, 1989,p.77
38 Kathleen T. McWhorter, Efficient and Flexible Reading, New York:Harper Collins
2. Presentation
Before the writer begins the teaching learning process, she tells the students the objective of the lesson. Then she gives exercise and test for feedback and encouragement to the students in the class.
The steps of teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing are described as follows:
a. Before starting the lesson the writer gave motivation to the students on reading skill, for example: what is the use of reading skill?
b. The writer gave explanations related to reading skill. The writer asked the students to ask some question about it.
c. The writer gave the first reading text about “Tobacco Convention
Becomes Law Sunday”. The writer asked the students to read the
passage carefully, and answered some questions.
d. The writer gave the second reading text about “Analogy” to each students, and asked them to read the passage carrefully. After that the writer asked some question to the students.
e. The writer distributed a handout about paraphrase. Then she gave explanations including all those strategies to make a paraphrase.
f. The writer asked the students to make paraphrase from reading text
“Analogy”. Before that the writer asked them to read the passage
carefully, find the main idea, and the detail.
g. The writer asked the students to read their presentation and conclution about the passage to be paraphrased.
h. The writer gave the third reading text about “The Composition of
Food”. She ask them to read the passage carefully and than answer
some questions orally.
j. The students given the fourth passage about “The First European Settlement” to be paraphrased. The writer asked them to read the passage carefully to look for topic sentences or the main information. k. The passage “Culture and The Natural Environment” were distributed
to the students to be summarized. The teacher asked them to skim the text to get an overall idea of it.
l. The writer asked some students to read the reading text by turns and discuss the conclution of the text.
m. The writer tells the students to discuss the vocabularies that the students do not understand and asking them to tells their problems in learning process.
n. The writer evaluates the students.
After gives some explanations and exercises. The writer gave a handout reading text related paraphrase and summary, and asked the students fill the instrument sheet.
In this evaluates, the students need some efforts to get a maximum understanding or they should understand the passage organization as the process in applying their own ideas. It is to find out how efficient the paraphrasing and summarizing strategies are for students to learn a language especially in reading subject.
F. Conceptual Framework
the details of the passage. And they feel bored when they get reading lesson. Based on the background above, the writer give an alternative technique in learning reading using paraphrase and summary in teaching reading skill. It is can help student to write ideas and information required in the reading, and it can give the students new experience and knowledge about reading skill, paraphrase, and summary.
G. Theoretical Hypothesis
The writer calculating the obtained data prove the hypothesis the result by using t test formula and to (observation) as follows:
a. Formulating the null hyphotesis (Ho): there is no significance effect of paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading skill.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Place and Time of the Study
The writer did her research at SMA Pembangunan 1 which is located on Jl. Poras No. 7 Sindang Barang Loji Bogor. She began the research from March 12, to April 10, 2007. On March 12, the writer asked permission to the headmaster of the school. Then in March 13, up to April 10, the writer held the research by applying the uses of paraphrasing and summarizing in the teaching reading skill in the class.The writer entered the class five times. In the first meeting, she gave pre test. In the next meeting, she taught reading and gave post test.
B.Method of Research
The method of this research is experimental in a form quantitative research about teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing. The experimental research was done in one class. To obtain the data in this research the writer gave pre-test at the first time before the material had not been given to the students, and the post-test was given in the last when the material had been given to them. The test was given in the same form.
C.Population and Sample
D.The Instrument of the Research
The research instruments used by the writer was written test to the second grade of SMA Pembangunan 1Bogor. The test was given twice to the students. The first test was pre-test, and the second was post-test. This test was done to know how well the students master learning reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing.
E.Technique of Data Collection
The writer gave two test as a technique of collecting data in this research. The test were pre-test and post-test. The first test was given before teaching and the second test was given after teaching.
F.Technique of Data Analysis
In analyzing the data from teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing the writer used the statistical calculation. The writer calculated by using these steps:
a. Determining the Mean of Variable X by using formula: Mx =
b. Determining the Mean of Variable Y by using formula : My =
c. Determining the Standard Deviation Score of Variable X by using formula :
SDx = √
d. Determining the Standard Deviation Score of Variable Y by using formula :
e. Determining Standard Error Mean of Variable X by using formula : SEMX =
√
f. Determining Standard Error Mean of Variable Y by using formula : SEMY =
√
g. Determining the Standard Error of different Mean of Variable X and Mean of Variable Y by using formula:
SEMX– SEMY = √
h. Determining to by using formula:
to =
i. Determining the degree of freedom (df) by using formula: Df = N1 + N2 - 2
G.Statistical Hypothesis
Statistically, the hypothesis stated as follows: Ho : µA= µB
H1 :µA > µB
The criteria for the hyporhesis testing are:
[image:33.595.111.479.124.558.2]CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND INTERPRETATION
A.
The Description of the Data
[image:34.595.151.518.258.750.2]As mentioned in previous pages, in taking the data the writer conducted both library research and field research. To know the result of the test, the writer observed the class, and taught the student to take students score before the teaching began and after the teaching or in the last meeting of the research.
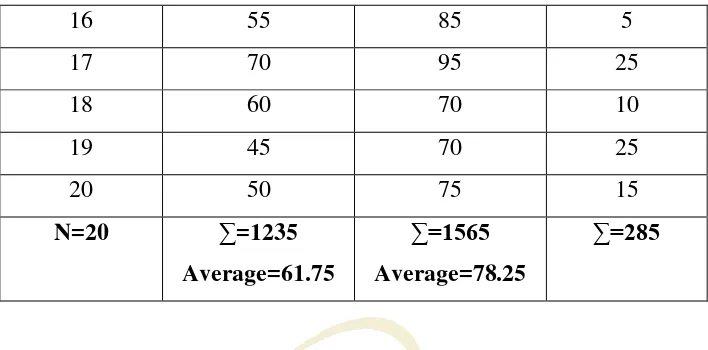
Table 4.1
The score of the experiment class students pre-test and pos-test
using paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading.
Student Pre-Test Post-test Gained Score
1 45 90 33
2 60 70 10
3 55 60 5
4 60 65 5
5 75 95 20
6 65 95 30
7 75 85 -3
8 65 70 5
9 70 80 10
10 60 70 10
11 60 85 20
12 70 75 5
13 75 90 15
14 65 80 15
16 55 85 5
17 70 95 25
18 60 70 10
19 45 70 25
20 50 75 15
N=20 ∑=1235
Average=61.75
∑=1565
Average=78.25
∑=285
[image:35.595.162.516.111.286.2]Based on the tabel above, the writer concluded that the lowest score of the pre-test is 45 and the highest score of pre-test is 75 with average 61.75. And the lowest score of the post-test is 60, and the higher score of post-test is 95 with average 78.25.
Table 4.2
The score of the control class students pre-test and post-test using
paraphrasing and summarizing in teaching reading.
Student Pre-Test Post-Test Gained Score
1 45 60 15
2 40 60 33
3 60 75 15
4 55 65 10
5 60 75 15
6 60 75 15
7 60 76 16
8 70 65 -5
9 50 80 30
10 66 78 12
11 45 70 25
13 65 64 -1
14 72 60 -12
15 70 65 -5
16 40 50 10
17 58 55 -3
18 56 57 1
19 65 70 5
20 60 65 -3
N=20 ∑=1667
Average=58.35
∑=1330
Average=66.5
∑=168
Based on the table above, the writer concluded that the lowest score of the pre-tes 40 and the higher score of the pre-test 70 with the average 58.35. The lowest score of post-test is 50 and the higher score of the post-test 80 with the average 66.5.
1. Analysis of the data
[image:36.595.130.517.117.488.2]The following is the table the result of the data from the score experiment class student and the score of the control class student.
Table 4.3
The result calculation of test between experiment class and control
class
Student X Y x y
1 90 60 -11.75 6.5 138.06 42.25
2 70 60 -8.25 6.5 68.06 42.25
3 60 75 -18.25 -8.5 333.06 72.25
4 65 65 -13.25 1.5 175.56 2.25
6 95 75 -16.75 -8.5 280.56 72.25
7 85 76 -6.75 -9.5 45.56 90.25
8 70 65 -8.25 1.5 68.06 2.25
9 80 80 -1.75 -13.5 3.06 182.25
10 70 78 -8.25 -11.5 68.06 132.25
11 85 70 -6.75 -3.5 45.56 12.25
12 75 65 3.25 1.5 10.56 68.06
13 90 64 -11.75 2.5 138.06 6.25
14 80 60 -1.75 6.5 3.06 42.25
15 80 65 -1.75 1.5 3.06 2.25
16 85 50 -6.75 16.5 45.56 272.25 17 95 55 -16.75 11.5 280.56 132.25
18 70 57 -8.25 9.5 68.06 90.25
19 70 70 -825 -3.5 68.06 12.25
20 75 65 3.25 1.5 10.56 2.25
N=20 ∑=1565 Average
=78.25
∑=1330
Average
=66.5
∑=0 ∑=0 ∑=2133.7 ∑=19401.87
Based on the data on the table 4.3, the writer conclude that the statistical calculatioan as follows:
Mx =
=
My =
=
= 0.5835
SDx = √
= √
= √ = 10.328
SDy = √
= √
= √ = 31.146 SEMx =
√
= √
= √
=
SEMy =
√
= √
= √
=
= 7.146
SEMx - SEMy = √
= √
= √ = √
= 4.360
to =
=
=
Df = N1 + N2 – 2 = 20 + 20 – 2 = 40 - 2 = 38
If to (observe) > tt (table) : there is a significant difference so the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and the null hypothesis is rejected.
If to < tt : there is no a significant difference so the alternative hypothesis is rejected, the null hypothesis is accepted.
According to the result of the statistics calculation, it can be seen that the value of to is 16.22 and the degree of freedom (df) is 38 obtained from (N1 + N2)
– 2; 40 – 2 = 38. By using the degree of significance of 5% and 1%. It can be seen in the table of significance that on df = 38, the value of the degree of significance that on the df = 38, the value of the degree of significance are 2,03 and 2,72. Because to score obtained from calculating result is higher that tt score in the table of significance, it means that Ha is accepted and Ho is rejected.
2. The Testing of the Hypothesis
The writer calculating the obtained data prove the hypothesis the result of hypothesis by using t test formula and to (observation) as follows :
a. Formulating the null hypothesis (Ho) : there is no significant improvement between variable x and y.
b. Formulating the alternative hypothesis (Ha) : there is significant improvement between variable x and y.
Based on the table above, df at significance level 5% and 1% are: t tabel at significance level of 5%= 2.03
So the result is= 2.03<16.22>2,72
From the result of statistic calculation indicates that the role of teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing is has significance effect on
students’ ability in learning reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing.
B.Interpretation
The data collected from the test gained from experiment class and control class, before and after taught using paraphrasing and summarizing in the teaching reading skill showed that the average scores of test in experiment class was 78.25. while the average scores of control class was 66.5.
From the result of analysis on the table 4.3 above, it can be concluded that the students score who learn reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing almost same as with the score students without using paraphrasing and summarizing in learning reading skill. It means that the effectiveness of using paraphrasing and summarizing is not different both experimental class and control class.
According to the result hypothesis testing. It is “there is significant
difference between teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing and without paraphrasing and summarizing technique for the second year of SMA
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A.
CONCLUSION
In the last chapter, the writer will describe some conclusion from the explanation shown in the previous chapter. It is meant to give the result in teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing at SMA Pembangunan 1 Bogor has run well even there are some difficulties in teaching and learning reading.
Paraphrase and summary are important aspect of academic reading and writing. It is the effective ways in teaching reading. It is can develop not only students confidence in writing, but also their competence in general language skills such as, extending vocabulary, and improving reading comprehension skills.
After carrying out the research, the writer has some result of student’s test at second year of SMA Pembangunan 1 Bogor. Based on the data analysis the writer makes conclution that the role of teaching reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing is significant different between experimental class and control class. The value of tt and the value of to is 2.03<16.22>2.72. Although
there is not successful in the teaching reading through paraphrasing and summarizing,it can be seen from the score af the experiment class and control class perhaps have same score. The writer through this technique hope that the student have interesting and developing the students’ motivation in learning English.
The writer found that most of them are interested in learning reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing. It is highly challenging activities for the
students. They are expressing some one else’s from the reading materials in their
their ideas in a English and to be understand after lookingt up the words in the dictionary.
While in the teaching learning process, reading skill through paraphrasing and summarizing. They can understand the explanation given by the teacher and they can do some exercise. Finally, they are realize that learning it are use full skill and they so must be learnt and practiced.
B.SUGGESTION
Based on the all research result, the writer tries to draw some suggestion in this chapter, those are :
1. The English teacher hoped gives some exercises and drills to the students mainly in the teaching learning process as an effort to make them recognize and understand the subject.
2. The English teacher hoped gives clear explanation when explains the lesson and more gives attention to the students in the teaching learning process. 3. The English teacher should be creative to get the subject in various technique
or method and stimulate in order for the students’ interest and motivation in
learning English.
4. To get succes in a study, the students should be able to be active and creative in developing their English competence.
5. The students hoped many read a book, magazine, or text in English to get the habit of making paraphrase and summary.
6. The students hoped try to write own sentence using paraphrase and summry in different context.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Aaron, Jane E, The Compact Reader, New York: ST Martin Press,1987. Al-Issa, Ali SM, Train Them toSummarize, English Teaching Forum,36, 2, 1998.
Axelrod, Rise B and Charles R. Cooper, Reading CriticallyWritingWell, (2nd ed),
New York: ST Martin Press, 1990.
Aebersold. JO Ann and Richard Field (ed), From Reader TeachingReading : Issue and Srategic for second languageclassrooms,New York: Cambridge
University Press, 1997.
Durning, Alexandra, Summarizing Succss, English Teaching 35.4,1997. Donough JO MC and Shaw Christoper, Methods Material andin ELT,United Kingdom: Black Well, 1993.
David,Peter F, Measuring Reading Abilities Source, Concept,andApplication, Great Britanian: Horder and Stoughton Educational,1997.
DeBoer J John, Dallmann Martha, The Teaching of Reading,(New York:Holt, Rinehart, Winston Inc., 1964), p.7
Harmer Jeremy, The Practice of English Language Teaching, New York: Longman Publishing, 1991.
Jordan R.R, Academic Writing Course, Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 997,p.97
Kennedy, Mary Lynch, Kennedy William J, Smith Handly M, Writing inthe Diciplines, Newq Jersey: Simon & Schuster, 1987.
Legget, c.o Mend Glenn & Krammer Melinda G f, Handbook orWriters, New Jersey: Simon & Schuster, 1988.
Michael L, ET AL Long, Reading English for Academic Study,Massachasetters: Newbury House, 1980.
Miller Lyle L, Increasing Reading Efficiently, New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston Inc, 1959.
Nuttal Christinc, Teaching Reading Skill in a foreign Language,London: Heineman, 1982.
Raygon Alton R, Teaching Reading in Elementary School, Columbus:Bell and Hovel com, 1985.
Rebecca L Oxford, Language Learning Strategies, New York: Newbury House, 1990.
Smith Nilla B and Robinson Alan H, Reading Instruction forToday’sChildren, New Jersey: Practice Hall Inc, 1980.
Shaw, Harry, The Harper Handbook of College Composition(5th ed), New York: Harper and Row, 1981.
Sonka, Amy, L, Skillful Reading, New Jersey: Practice Hall, 1981.
Simon, Linda, Good Writing ( A Guide and Source Book forWritingAccors the Curriculum), New York: St Martin’s Press, 1988.
Smith and Harris, Reading Instuction Through DiagnosticTeaching,New York: Holt Rinchart, Inc, 1972.
Sorenson Sharon, Students Writing Handbook, New York: PrenticeHall, 1988. Suryaningrum Dwi Tanti, S.Pd, Bank Soal Bahasa Inggris, Bandung:CV.
M2S,2006
Sundayana Wachyu, Contextual Learning, Bandung: Grapindo Media Pratama, 2005
Tickoo, Makhan, L, Reading and Writing, Singapore: RELC, 1995.
35 APPENDIX 1
RENCANA PENGAJARAN
Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Tema : ”Tobacco Convention Becomes Law Sunday“ Materi : Reading Skill
Kelas : XI. 1 Semester : II
Waktu : 2 x 45 menit Aspek utama : Membaca Aspek pendamping :Meyimak
I. Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum
Siswa dapat menguasai materi tentang Reading Skill dengan baik dan dapat menerapkannya baik secara lisan maupun tulisan.
II. Tujuan pembelajaran khusus
Siswa dapat menemukan informasi tertentu dari teks “Tobacco Convention
Becomes Law Sunday” dengan cara membaca cepat.
Siswa dapat menemukan pikiran utama yang tersurat maupun yang
tersirat dari teks “Tobacco Convention Becomes Law Sunday” dengan cara menjawab pertanyaan.
Siswa dapat memperoleh informasi utama dari teks tersebut yang disampaikan dengan lisan.
36 III. Materi
Reading is a tool of learning, student need a variety of Reading Skill to understand books or other refence materials.
Harmer classified reading skill into six, they are : prediction, scanning, skimming, finding detailed information, ricognition discourse, and guessing meaning from context.
IV. Kegiatan Belajar Mengajar A. Pendekatan
1. Pendekatan Kooperatif 2. Pendekatan Kontextual 3. Pendekatan Komunikatif
B. Metode : ceramah, tanya kawab, penugasan C. Langkah – langkah :
1. Pendahuluan :
a. Salam dan tegur sapa b. Guru mengabsen siswa c. Guru memberi motivasi
d. Guru menjelaskan inti pembelajaran 2. Kegiatan inti
a. Guru menjelaskan pengertian Reading Skill dan beberapa bagian – bagiannya.
b. Guru menjelaskan tujuan dari Reading Skill.
c. Guru menyajikan materi tersebut dengan mengaplikasinya melalui beberapa reading teks.
37 3. Penutup
Menyimpulkan kegiatan belajar mengajar
V. Media dan Sumber
1. Media : papan tulis, handout berupa materi Reading Skill, teks book dan anak.
2. Sumber : teks book bahasa inggris kelas 2 SMA/2004. Karangan Wachyu Sundayana, dkk.
38 APPENDIX 2
RENCANA PENGAJARAN
Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris Tema : “Analogy” Materi : Paraphrase Kelas : XI. 1 Semester : II
Waktu : 2 Jam Pelajaran Aspek Utama : Membaca Aspek Pendamping : Menulis
I. Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum
Siswa dapat menguasai materi tentang paraphrase dengan baik dan dapat menerapkannya secara lisan maupun tulisan.
II. Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus
- Siswa dapat menemukan informasi tertentu dari teks
“Analogy” dengan membaca cepat.
- Siswa dapat menemukan pikiran utama yang tersirat
dari teks “Analogy” dengan cara menjawab
pertanyaan.
- Siswa dapat memperoleh informasi utama dalam
teks “Analogy” yang disampaikan secara lisan.
- Siswa dapat menggunakan paraphrase melalui tulisan dengan baik dalam bentuk kalimat maupun dalam bentuk paragraph.
III. Materi
Definition of paraphrase
A paraphrase is an presentation in our own words of all information in a brief passage.
Paraphrase stragegies
1. Write a loose paraphrase and record necessary contextual information.
39 3. Change the order of ideas
4. Compare your completed paraphrase to your loose paraphrase and the original.
IV. Kegiatan belajar mengajar A. Pendekatan
1. Pendekatan kontextual 2. Pendekatan komunikatif
B. Metode : ceramah, tanya jawab, penugasan. C. Langkah – langkah
1. Pendahuluan
a. Salam dan tegur sapa b. Guru mengabsen siswa c. Guru memberi motivasi
d. Guru menjelaskan tujuan inti pembelajaran 2. Kegiatan inti
a. Guru menjelaskan definisi paraphrase dan memberikan contohnya.
b. Guru menjelaskan kegunaan dari paraphrase c. Menyajikan materi paraphrase melalui reading teks d. Guru membagikan handout berupa reading teks dan
meminta siswa untuk membuat paraphrase dari reading teks tersebut
3. Penutup
Menyimpulkan kegiatan belajar mengajar V. Media dan sumber
1. Media : papan tulis, handout berupa materi reading teks, anak 2. Sumber : Reading for Academic Study by Long, Michael L
40 APPENDIX 3
RENCANA PENGAJARAN
Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Tema : “The Composition of Food” Materi : Summary
Kelas : XI.I Semester :II
Waktu : 2 Jam Pelajaran Aspek Utama : Membaca Aspek Pendamping : Menulis
I.Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum
Siswa dapat menguasai materi tentang summary dengan baik dan dapat menerapkan secara lisan maupun tulisan.
II. Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus
a. Siswa dapat menemukan informasi tertentu dari “The Composition of
Food” dengan membaca cepat
b. Siswa dapat menemukan pikiran utama yang tersirat dari teks “The
Composition of Food” dengan cara menjawab pertanyaan
c. Siswa dapat memperoleh informasi utama dalam teks tersebut yang disampaikan secara lisan
41 III. Materi
Definition of Summary
Summary is aclear and brief work which contains only the main ideas of the text
Summarizing strategies : 1. Delete redundancy 2. Delete unimportant detail
3. Provide a general term (superordinate) to cover several specific items from the original text
4. Locate and emphasize sentences
5. Invent topic sentences if none are found 6. Combine ideas in sentences and paragraphs IV. Kegiatan Belajar Mengajar
A. Pendekatan
1. Pendekatan kontextual 2. Pendekatan komunikatif
B. Metode : ceramah, tanya jawab, penugasan C. Langkah – langkah :
1. Pendahuluan :
a. Salam dan tegur sapa b. Guru mengabsen c. Guru memberi motivasi
d. Guru menjelaskan tujuan inti pembelajaran 2. Kegiatan inti
a. Guru menjelaskan definisi summary dan memberikan contohnya
b. Guru menjelaskan kegunaan dari summary
c. Guru menyajikan kegunaan materi summary melalui reading teks
d. Guru membagikan handout berupa reading teks dan meminta siswa untuk membuat summary dari reading teks tersebut 3. Penutup
42 V.Media dan Sumber
1. Media : papan tulis, handout berupa materi summary dan reading teks, anak
2. Sumber : Reading English for Academic Study by Long Michael L Writing in the Diciplines by Kennedy, Mary Lynch
43 APPENDIX 4
Pre-test question sheet
Put a cross (x) on either a, b, c, d, or e for the right answer Question number 1 -5 are based on text 1.
Work and careers
Sometimes we say that someone we know is “a square peg in a round hole”. This simply means that the person we are talking about is not suited for the
job he is going. He may be a bookkeeper who really wants to be can actor or mechanic who tikes cooking. Unfortunately many people in the world are “square
peg”. They are not doing, for are reason or another. As a result they probably are
not doing a very good job and certainly they are not happy.
Choosing the right career is very important. Most of us spend a great part of our life at our jobs. For that reason we should try to find out our talents are and how we can use them. We can do this through aptitude test, interviews with specialist, and study book in our filds or inteest.
There are many careers opened to each of us. Perhaps we like science. Then we might prepare ourselves to be chemists, physicist, or biologists, may be our interests take us into the business, world and such work as accounting, personal management or poblic relations. Many person find their places in the government service. Teaching, newspaper work, medicine, engineering, and many other fields offer fastinating careers to person with talent and training.
1. Why is it important for us to choose the right career?, because... a.Our career will determine our future
b.We spend most of our life at our jobs
c.The fild of work provides us with various kind of job d.We must know what we are able to do well
e.There are many careers opened to us
44 b.Careers
c.Talen d.life e. reasons
3.The saying “a square peg in a round hole” means...
a.a person who has a side jobs besides him main job b. a person who workstoo hard
c. a person whose dream comes true
d. a person who is not suitable for the he has e. a person who really loves his/her job
4.If we like science, the following jobs might be suitable, except... a. a book keeper
b. a physicist c. a biologist d. an engineer e. a chemist
5.The words “their” in the last paragraph refers to.... a. talent and training
b, chemist, physicists, biologist
c. accounting, personal manager, public realtion d. teaching, newspaper work, medicine, engineering e. many person
45
resources. Second , it has a large number of workers available for employment in industry. finally, Brazilian business and economic planners have encouraged investment.
6.what is the topic of the paragraph?...
a. the factors leading to the Brazil’s increase in its GNP b.Brazil’s advantageous physical condition
c.the change in Brazil’s GNP
d.the policy of economic planners in Brazil
e.the number of workers in Brazil’s industry
7.what is the main idea of the text?...
a..Brazil’s industry has grown rapidly because of large number of human resources
b.Brazil’s physical chracteristics have contributed to the increase in Brazil’s GNP
c.Brazilian needs a lot more investment
d.there are three factors that have caused a rapid increase in Brazil’s GNP e.Brazil’s GNP has greatly changed the face of Brazil’s economy
saudi Arabia is a country rich in oil, but poor in one of a contry’s most
critical natural resources, fresh water. Without it, agriculture becomes extremely difficult and costly. Many areas are removing the salt from the seawater that surrounds the Arabian Peninsula. Other efforts might be floating of an ice cap all the way from North Pole and digging of wells to reach water that is underground. 8.what is the topic of paragraph?...
a. fress water
b.how to improve agriculture c.problems faced by Saudi Arabia d.reasons of wayer shortage
46 9.what is the main idea of the text?
a.fresh water is one of the most critical natural resources of contry b.several effors are being made in Saudi Arabia to get fresh water
c.water supply in Saudi Arabia is provided by removing the salt from sea water
d.many area in Saudi Arabia are in habitable due to the lack of fresh water e.agriculture in Saudi Arabia is difficult and costly
10.The word “it” in the second sentences, refers to... a.Saudi A