MANAGEMENT OF JUVENILE ANGIOFIBROMA WITH
DEGLOVING APPROACH
Ashri Yudhistira, Farhat, Rizalina A Asnir, Sri Novita
Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
Introduction
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA) is a rare tumour representing only about
0.05% of head and neck tumours. The most common presentation is a prepubescent or adolescent
male with severe, recurrent epistaxis and nasal obstruction. The epistaxis may even require a
blood transfusion 1, 2. Although not a malignant process, JNA is known for its locally invasive
spread with progressive growth that can attribute to a significant degree of morbidity commonly
related to either intracranial extension or massive hemorrhage 3. It is a typical example of locally
aggressive tumor and due to this aggressiveness; it poses a challenge to the traeting physician. It
is difficult to do a biopsy in majority of the cases due to its high vascular nature 4
An adolescent male with recurrent epistaxis and chronic nasal obstruction is highly
suspicious for a JNA. The epistaxis and nasal obstruction progressively worsen. Unilateral nasal
obstruction may progress to bilateral obstruction as the tumour grows to fill the nasopharynx.
Other common symptoms include headache, facial swelling, unilateral rhinorrhoea, hyposmia,
and ipsilateral conductive hearing loss due to Eustachian tube dysfunction
.
1
Histologically, the tumour is unencapsulated and consists of a collagenous tissue stroma
interspersed with wide vascular spaces lined by a single endothelial layer. These arterial vascular
channels are unusual in not manifesting a complete muscular layer in the vessel wall .
4
The preferred way of treating the angiofibroma is surgical, though radiotherapy and
chemotherapy is been tried for extremely unresectable tumour, but this also need surgical
treatmen later on. Many surgical approaches are describe in literature but, it all depends upon the
extent of tumour and the surgeon’s experience
.
5
. The incidence of recurrence has been reported
at 6-50% with the majority occurring within a year after surgery. Rates have been shown to
Case report
AM is a 13 year old male patient, came to H. Adam Malik general hospital on Febuary
22th
From the examination, anterior rhinoscopy and nasoendoscopy showed mass in right
nasal cavity. There is no mass seen in the left nasal cavity. Soft palate is normal and lateral wall
nasofaring showed mass preventing posterior rhinoscopy. General condition, ear and throat
examination was normal.
2014 with complaint of recurrent right nasal obstruction and intermittent right sided epistaxis
of spontaneous onset and getting worse for 5 years.
Figure 1. Nasoendoscopy of the right nasal cavity
CT scan on October 29th 2013 showing a well define mass in the nasopharynx with
extension into right nasal cavity with no destruction of bone. Results of laboratory tests (febuary
21th 2014) was: Hb 8,1 g / dl, eritrosit 3,48. 103 /mm3 and leukocytes 8,67.103/ mm3, while other
Figure 2. CT-scan of mass in the right mass in the nasopharynx
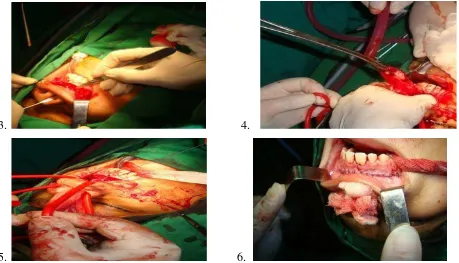
We diagnosed the patient with juvenile angiofibroma and performed degloving approach
in general anesthesia to removed the mass. After disinfection and pehacain infiltration to the
incisision site, the incision made in the sub labial, bilaterally start from maxilla tuberosity from
right to the left to the periosteum. The soft tissue then detached, the septum cartilage was cut
start from the nasal spina upto the nasofrontal suture.
3. 4.
Evaluate nasofaring, with figer and respactorium mass was detached and extracted from
its surrounding tissue. Nasofaring was evaluated endoscopically to find any residual tumor. We
used posterior tamponade (belloque) and followed by anterior tamponade to prevent bleeding.
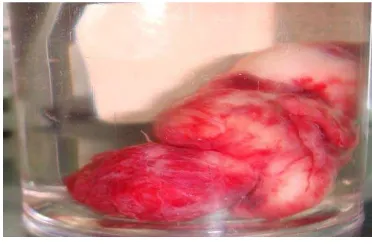
Figure 7. Mass of the nasopharynx
The mass successfully removed intact with the size 4x3x2 cm. total blood loss during
operation was 700 ml.
Post operatively, patient was given antibiotic, analgetic, antifibrinolytic and steroid. On
follow up overall result was satisfying and patient was discharged on the 4 th
Discussion
day after operation.
The result of histopatology examination of tumor tissue showed nasopharyngeal angiofibroma.
Radiology imaging has play a vital role not only in the diagnosis of this lesion but also in
accurately assesing the extension of the mass. This is of vital importance from the surgeon's
point of view. Angiogram would enable accurate identification of feeding blood vessel which
could be secured by embolisation prior to surgery there by reducing bleeding during the actual
procedure. CT scan: This study enables better delineation of bony details. Bone erosion if any
present can easily be identified by studying bone cuts. Major importance of CT scan is to study
the depth of invasion into the bone of sphenoid sinus which could predict propensity of
recurrence. The extent of invasion of cancellous bone of sphenoid sinus helps in prediction of
tendency of the lesion to recur. It is also routinely used for intraoperative navigation systems in
order to avoid damage to vital structures as well as for complete resection of the mass 7. Also,
CT scan showing a well define mass in the nasopharynx with extension into right nasal cavity
with no destruction of bone.
Various systems of classification exist for angiofibroma. The Radkowski`s classification
is currently popular, and increasing stages have been correlated with incremental rise in tumour
recurrences. And by this staging this patient was categorized as stage IA.
Surgery is considered to be gold standart JNA treatment 8. Depends mainly on the extent
of the lesion. Surgery is the preferred modality of treatment for all stages of the mass up to stage
IVa while radiotherapy is used for stage IV b. Mainly three lines of treatment are available 7
1. Surgery
:
2. Irradiation
3. Hormonal (purely supportive in nature)
Surgery has Complete excision of an extensive JNA mass is a desirable goal but is a
surgical challenge because of the limited field of work, inadequate visualisation and profuse
bleeding during surgery. Besides the deformity, scars and adhesions as a result of prior surgery
Different surgical approaches are used for complete excision. Most recent development is
excision of the tumor using endoscopes. But in certain cases with large size and different
extensions, open transfacial approaches are the choice for complete removal and for less
operative bleeding, which are the challengers for surgical excision of this tumor 9
The preferred treatment of JNA is complete surgical excision. Because of their vascularity,
the greatest risk of surgery is hemorrhage. Thus, preoperative embolization of the blood supply
to the tumor is usually performed except for the smallest of tumors. In many cases, there is
significant shrinkage of the tumor after embolization and intraoperative blood loss is minimal.
As tumor enlarge, they may derive a blood supply from multiple branches of the external carotid
artery and bilateral embolization may be necessary
.
2
.
Conclusion
We reported a 13 years old male, with complaint of recurrent right nasal obstruction and
intermittent right sided epistaxis of spontaneous onset and getting worse for 5 years. The mass
we removed intact successfully and there’s no complication found postoperatively.
References
1. Rogers D, Hartnick C, Fagan J. Open Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck
Operative Surgery. Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Surgery .Pediatric
Otolaryngology Harvard Medical School Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston,
MA, USA.
2. Ardehali MM, Ghorbani J. 2011. Juvenil Nasophryngeal Angiofibroma, New Aspects in
Management. Iranian Journal of Otolaryngology. no.3, vol. 23.
3 Quin MS. 2012. Juvenile Nasophryngeal Angiofibroma: Evaluation and Treatment.
Departement of Otolaryngology the University of Texas Medical Branch.
4 Thakar A, Hota A, Pookamala S. 2013. Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma. Review Article. vol.
6 (1).
5. Pradhan B, Thapa N. 2009. Juvenile angiofibroma and its management. NepalMed Coll J.
6. Bleier BS, Kennedy DW, Palmer JN, Chiu AG, Bloom JD, et al. 2009. Current management
of Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma :A tertiary center experience 1999-2007. 23(3):
pp. 328-330.
7. Balasubramanian T. 2012. Juvenil Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma an Overview. Disadur :
Otolaryngology online
8. Kanna P, Ray BR, Sinho R. 2013. Anaesthetic management of endoscopic resection of
juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma; our experience and review of the literature. South
Africa Journal Anesthesia Analog, 19(6).
9. Shinha NK, Rashid MH, Shaheen MM, Talukder DC, Fakir, Hussain MZ. 2011. Juvenile
nasopharyngeal angiofibroma excision through lateral rhinotomy and sublabial approach- A