(A Case Study at the First Grade of Junior High School
Of Yayasan Miftahul Jannah)
By:
Dinnie Hijrie Firdausi
108014000049
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
Yayasan Miftahul Jannah). Skripsi of Department of English Education at faculty of
Tarbiya and Teacher’s Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah
Jakarta, 2013
Keywords: Error Analysis, Types of Error.
The objective of this study was to find out their frequency of occurrence and to find out the type of errors that made by the students. Beside that another purpose is to identify kinds of personal pronouns that the students made in using subject and object pronoun.
The method used in this study was qualitative. The qualitative design applied in this study was case study. Furthermore, the subject of this study was first grade students of VII class which consist 43 students but the reasearcher only took 34 students as the sample. The data were collected by giving test to the students and.
junior high school of Yayasan Miftahul Jannah). Skripsi of Department of English
Education at faculty of Tarbiya and Teacher’s Training of State Islamic University
Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2013
Keywords: Error Analysis, Types of Error.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menganalisis dan mengelompokkan tipe-tipe kesalahan yang dilakukan oleh siswa dalammenggunakan personal pronoun. Kesalahan-kesalahan tersebut dikelompokkan berdasarkan teori Corder. Penelitian ini bertujuanuntuk memperoleh persentasi dari setiap jenis kesalahan yang dilakukan oleh siswa.Tujuan lainnya yaitu untuk mengidentifikasikan tipe-tipe dari personal pronouns yang dilakukan oleh siswa dalam penggunaansubjek dan objek pronoun.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah metode kualitatif, sedangkan pola umum atau rancangan penelitian yang digunakan oleh peneliti adalah studi kasus (case study). Selanjutnya, peneliti memilih siswa kelasVII yang berjumlah 43 siswa tetapi penulis hanya mengambil 34 siswa sebagai subjek dalam penelitian ini. Data dalam penelitian ini diperoleh melalui tes dan wawancara kepada siswa dan guru bahasa Inggris.
Hasil dari penelitian error analysis menunjukan bahwa siswa melakukan empat jenis kesalahan yaitu omission, addition, selection, and misordering.
research paper. Peace and blessing be upon our prophet Muhammad SAW, his
family, companions, and all his followers.
This paper is presented to the Department of English Education, Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah
Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of strata 1 (Sarjana
Pendidikan).
Alhamdulillah by the grace of Allah the Highest, the researcher could finish
her research paper after long hard effort of writing. Thus, she would like to express
her greatest gratitude to her beloved mom (Ir. Siti Ambarini Sabardinah) who always
pray, support, and motivate her in every part of her life especially in doing this study.
The researcher would also like to address her gratitude to her advisors Dr.
Fahriany, M. Pd and Neneng Sunegsih M. Pd for their patient guidance, kindness,
valuable advice, and correction during the development of this research.
She would like to express her deep appreciation and gratitude to:
1. All lecturers of Department of English Education who have taught her new
knowledge and have given her gorgeous experiences in study.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. and Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum. The head and secretaryof
Department of English Education.
3. Dra. Nurlena Rifa’i, Ph.D, the dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers
Training.
4. The principal and the English teacher of SMP Yayasan Miftahul Jannah
(YMJ) for permitting and helping the researcher to conduct the research.
5. Her beloved best friends who have always been in the researcher side in
facing all the laughter and tears during her study, especially for Syifa Fauziah
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all. Amin.
Finally, the researcher realizes that this research paper still has some
weakness and shortage. Thus, she would be grateful to accept any suggestions and
corrections from anyone for betterwriting.
Jakarta, 28th January 2014
ABSTRAK ... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF TABLES ... vii
LIST OF CHARTS ... viii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... ix
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A.The Background of the Study ... 1
B.The Focus of the Study ... 4
C.The Question of the Study ... 4
D.The Objective of the Study ... 4
E.The Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Error and Error Analysis ... 6
1. The Definition of Error ... 6
2. The Types of Error……… 7
3. The Definition of Error Analysis ... 10
4. The Stages of Error Analysis ... 10
B. The Pronouns ... 13
1. The Definition of Pronouns ... 13
2. The Personal Pronouns ... 14
C. The Subject of the Stud ... 18
D. The Instrument of The Study ... 19
E. The Data and Source of Data ...19
F. The Techniques of Data Collecting...19
G. The Techniques of Data Analysis...20
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING A. The Data Description of the Data ... 22
1. The Result of Test ... 22
B. The Data Analysis ... 27
1. The Description of Error ... 27
2. The Evaluation of Error ... 27
C. The Interpretation of the Data ... 28
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion……….……… 30
B. Suggestion ... 30
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 32
Table 3.1 The Table of Specification of Test Items ... 19
Table 3.2 Table of Errors Classification ... 21
Table 4.1 Frequency of Students’ Errors in Using Personal Pronoun ... 23
Table 4.2The Recapitulation of Error Types, Frequency and its Percentage ... 24
Table 4.3Frequency of Students’ Errors in using Personal Pronoun ... 28
Appendix 3: The Description of Students’ Errorsin Using Subject Pronoun...…… 38
Appendix 4: The Description of Students’ Errors in Using Object Pronoun……….60
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the study
Nowadays, English becomes an essential language subject of education
issues in Indonesia. Indonesian students’ learn English from elementary school up to university. By learning English language, they wish theyhaveability and
more confidence with English. As a matter of fact many young learners face
difficulties to understand English as their second language, which is different
from their own language, Bahasa.
The curriculum in Indonesia has been developing overtime. The curriculum
that is used now is KTSP (Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan), or (SBC)
School-Based Curriculum. This curriculum replaces the previous curriculum;
KBK (Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetensi) or (CBC) Competence-Based Curriculum in 2004. KTSP focuses on developing students’ ability to do the competence and the tasks in KTSP standard, so the students will be able to
master the specific competence. This educational program standard makes the
students have competence of the knowledge and understand every values which
is learnt because this curriculum based on the number of competence, so after the
students finish the educational program, they will master all of the competence
and apply in their own lives.
KTSP has two components; Standard Competence (Standar Kompetensi)
and Basic Competence (Kompetensi Dasar). There are four language skills which
are learnt by the students based on Standard Competence and Basic Competence;
listening speaking, reading and writing. Besidesthose four language skills, in
English there are some language elements; grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation,
the mostcomplex and hardest language element among the others. Grammar has
many parts; pronouns, article, tenses, part of speech, gerund, etc. The students
need to learn the whole of grammar parts. They should understand, pay attention,
and need more exercise in grammar. Beside that, English and Bahasa has
different role in grammar structure.
Although grammar is not including in English four skills; reading,
speaking, listening, and writing, but grammar supports those skills. In speech or
speaking we do not concern to the grammatical rules, sometimes we did not seem
to be aware the neglect of grammatical caused miscommunication, in formal
contexts or academic. In reading, the student will understand the text and get the ideas of the writer’s if they have ability in grammar.
In this case, the researcher only took one of part of grammar, personal
pronouns. Personal pronouns have the important role. Misusing one of them can
cause the wrong meaning in one paragraph or even in the whole of it. It is
because the personal pronouns always refer to a noun, so they related to each
other.
From the Standard Competence and Basic Competence above, the students
should understand personal pronouns to be able to interact with the society by
using personal pronouns. The students should learn about personal pronouns
because personal pronouns are the basic material that they should learn.
The English grammar has different system with Bahasa. In English there
are many types of personal pronouns and they also have different position and
function, as the first person in English used as; (a) subject: I, you, (b) object: me,
them, (c) possessive adjective: my, their, (d) possessive pronoun: mine, yours, (e)
For example:
Saya melihat dia (lk) di taman I saw him in the garden
Dia (lk) melihat saya di taman he saw I in the garden (correct:
he saw mein the garden)
From the example above, it can be seen there were different system
between English and Bahasa. In Bahasa, there were no changing in subject and
object, subject and object has the same form “saya”, but in English, subject and object is different. In subject is “I” but in object change to be “me.”
Any errors produced can be caused by students’ lack of English language, less vocabulary, and their knowledge about grammar is so poor, and also because
of their mother tongue which always influences them in practicing foreign
language. The teacher should be aware of those errors and do something to avoid
them by doing some correction.
In the researcher’s experience, when the students have already understood about personal pronouns, they are still confused when they should use subject or
object pronoun, because of that there are many grammatical errors that are made
by the students. Based on this reason, the researcher chooses the personal
pronouns because the students still confused between subject and object pronoun.
This research will analyze the types of grammatical errors and what the sources
of grammatical errors.
So, the English grammatical has important roles, whether in speaking,
writing, and reading. Based on the fact above, the researcher will discuss “An
Analysis on Students’ Errors in Using Personal Pronouns” (A case study at
B. The Focus of the Study
The researcher focuses on analyzing the students’ pronouns error. However, the researcher concerns to analyze the students’ error in subject and object pronoun thatis easier to understand at the first grade in SMP Yayasan
Miftahul Jannah Ciputat.
C. The Study Questions
Based on the discussion above, the researcher would like to formulate this
problem in the following question:
1. What types error do the students make in using personal pronouns?
2. What kinds of personal pronouns error are commonly made by the
students?
D. The Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to analyze students material that easier to
understand between subject and object pronoun.According to the statement of the
problem above, the objective of the study are as follows:
1. To analyze and to classify the types of errors which students made in using
personal pronoun.
2. To identify the kinds of personal pronounserror are commonly made by the
students.
E. Significance of the Study
The research finding is expected as a contribution for (a) the English
teachers, (b) the students, (c) the further researchers.
a. The English teachers
The result of this study for the English teachers to get clearly information
made in using the personal pronouns, so they will know what should they do to decrease the students’ error in using the personal pronouns.
b. The students
The students will get right treatment in decreasing their errors in using the
personal pronouns, so they can use the personal pronouns correctly in a test.
c. The further researchers
Other researchers who are interested in analyzing on the students’ errors can get basic information from this study, so they can do their research deeper and
A. Error and Error Analysis
In this chapter, the researcher tries to give clear some descriptions of
theoretical framework that consist of definition of error, definition of error
analysis, definition of pronoun, the kinds of pronoun, and description of personal
pronoun.
1. The Definition of Error
Students make a mistake or make an error is normal. It always occurs in
process learning. Errors made by the students didn’t mean that the students couldn’t follow the lesson well but there were so many reasons why the students did an error.
In order to analyze the students’ language in a proper perspective, it is
important to distinguish between mistakes and errors. Errors and mistakes are
two synonyms that have a little bit same meaning, but in language learning,
these words have different meaning. There are various definitions of errors
and mistakes that have been presented by linguists.
According to Corder “Errors are described by the application of linguistic
theory to the data of erroneous utterances produced by a learner or a group of learners.”1
In addition, Brown said that error can look from native adult
grammar and reflecting learner interlanguage competence.2
1
S. P. Corder, Error Analysis and Interlanguage, (London: Oxford University Press, 1981), p. 36
2
Besides error, there is a mistake. Corder said in Fisiak’sbook “mistakes
are deviations due to performance factors such as memory limitation,
spelling pronunciations, fatigue, emotional strain, etc.”3 In addition Brown said in his book that “a mistake refers to aperformance error that is either a random guess or a „slip,’ in that it is failure to utilize a known system correctly.”4
According to that definition, the researcher concluded that error is when
the students make errors but they cannot fix it again, no matter how much
they make a mistake, they cannot fix it. It can be caused by the learner can’t
well understand the material; they only understand a half material or do not
understand the whole of the material. On the contrary, a mistake is a fault
that students can be self-corrected, because it is only the result of the students’ performance.
2. The Types of Error
According to Corder, error is divided into four categories: error of omission,
error of addition, error of selection, and error of ordering.5 Here are the
explanations:
1) The Error of Omission
Error of omission characterized is the absence of an item that should
appear.The student omits the item that should appear in the good
utterance. Omission has two types of morphemes that are omitted more
than others. They are content morphemes and grammatical morphemes.6
3
JacekFisiak, Contrastive Linguistics and the Language Teacher, (New York: Pergamon Press, 1981), p. 224
4
Brown, Op Cit., p. 165 5
Corder, Op Cit., p. 36 6
Content morphemes are morphemes that have meaning like nouns, verbs,
adjectives, and adverbs. Grammatical morphemes are little words that
have minor play in sentences like noun and verb inflections, articles,
auxiliaries, and preposition.
Example: Bobby is an actor
From the explanation and example above, the word Bobby and actor
are content morphemes because Bobby and actor is noun and has a mayor
meaning. The words is and an are grammatical morphemes because they
are verb auxiliaries and article, and they play a minor meaning in that
sentence.
According to Dulay“Omission errors are found in greater abundance
and across a greater variety of morphemes during the early stage of second language acquisition.”7
It is caused by the grammatical
morphemes are more complex, for example in using tenses, the learner
should be aware of the addition of the ending of the verb (-ed,-ing,-s)
correctly. Omit content morphemes are typically made by the learner in
the early stage. It happens because the learner still has limitation of the
vocabulary which is used in the sentences.
2) The Error of Addition
The error of addition is the opposite of omission. “Addition where some element is present which should not be there.”8
In addition, the
students add the utterance that is not needed in a sentence, or the learners
add some unnecessary element. For example: That’s the man who I saw
him
7
Ibid.,p.155. 8
From the example above, the student wants to tell that I saw the man.
She knows that to tell the object only once but she puts two items for the
same features; the man and him.
3) The Error of Selection
Dulay said in Ellis’ book that “Error of selection is the use of wrong
form of the morpheme or structure”9 This error is made by the student
when the student chooses the wrong items in the right place. Different
from omission where the items are not supplied at all, in errors of
selection, the student supplies something even though that is incorrect.
For example: They is watching movie
From the example above there was mis-selection in using to be. It should be “are” but it was “is.” The student put “is” in the sentence, and it is incorrect.
4) The Error of Ordering
Ellis said in her book The Study Language Acquisition “The incorrect
placement of a morpheme or group of morphemes in an utterance.”10Error
of ordering is the error where the items presented are correct but wrongly
sequences. For example: he is Idolacilik 2013 runner up.
From the example above, it should be he is a runner up in Idolacilik
2013.The student wrote sentence not properly. The learner didn’t put the
items in the appropriate order.
9
Rod Ellis, The Study of Second Language Acquisition, 2nd Edition, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2008), p. 52.
4. The Definition of Error Analysis
Error analysis is a way to reveal errors which are found in speaking or
writing. According to James, error analysis is the process of determining the
incidence, nature, cause and consequences of unsuccessful language.11 Another
concept of error analysis is given by Gass and Selinker “a type of linguistic analysis that focuses on the errors learner make.”12
Two definitions above clarify
that error analysis is an activity or process to observe, analyze, classify the errors
which are always made by students either in speaking or writing and also it
brings information about students’ difficulties either in speaking or writing in
English.
Error analysis can be used to analyze the errors that are made by the
students. The errors can help the teacher in teaching and learning process because
the teacher can observe the reason or background why the students do the errors.
5. The Stages of Error Analysis
In analyzing learners’ errors, there are some steps to be followed. Many
linguists have already discussed how to analyze students’ errors in their book.
Corder in Ellis’ book, he suggests five steps in analyzing students’ errors, they
are:collection of sample of learner language, identification of errors, description
of errors, explanation of errors and evaluation of errors.13
1) Collection of Sample of Learner Language
The first step of analyzing errors which suggested by Corder is
collection of sample. In this step, the researcher must decide a number of
11
Carl James, Errors in Language Learning and Use, (New York: Wesley Longman Inc., 1998), p. 205
12
Susan M. Gass and Larry Selinker, Second Language Acquisition An Introductory Course Third Edition, (New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, 2008), p. 102
13
students which is being sample for the research. Then, they will be given
regular examination in order to get data.14
2) Identification of errors
In this step the researcher must identify error from the data collection.
For identifying the error, the researcher must compare the sentence that
was produced by students to the correct sentence in the target
language.15For examples: yesterday I went to Bandung with my mom but
hedidn’t look enjoy there.The correct form in target language isyesterday I
went to Bandung with my mom but shedidn’t look enjoy there.
By comparing two sentences it can be seen that the student produced
an error in constructing subject sentence where she wroteheto refermy
mom.
3) Description of Errors
After identifying errors, the next step is description of errors. In this
step, all errors that have been identified, then they would be classified into
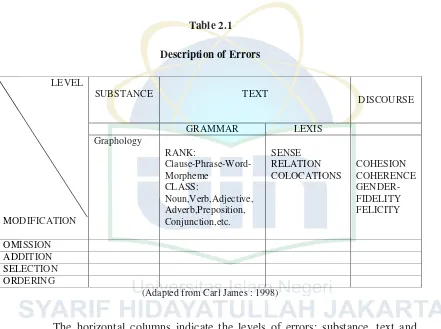
thetypes of errors. In description of error James introduces a table to make
it easy. This table can be seen as below:16
14
Ibid,.p. 47 15
Ibid., p. 48 16
Table 2.1
Description of Errors
LEVEL
MODIFICATION
SUBSTANCE TEXT
DISCOURSE
GRAMMAR LEXIS
Graphology
RANK:
Clause-Phrase-Word- Morpheme
CLASS:
Noun,Verb,Adjective, Adverb,Preposition, Conjunction,etc.
SENSE RELATION COLOCATIONS
COHESION COHERENCE GENDER-FIDELITY FELICITY
OMISSION ADDITION SELECTION ORDERING
(Adapted from Carl James : 1998)
The horizontal columns indicate the levels of errors: substance, text and
discourse whereas the vertical columns show the types of errors which consist of
omission, addition, Misformation/misselection, and misorder.
4) Explanation of Errors
This step will explain why errors occur. This explanation concerned on
the sources of errors.17From example above, the researcher may consider
that the student above does an error in using subject pronoun instead of using
pronoun whether because of interlingual transfer/overgeneralization,
ignorance of the rule restriction, incomplete application of rules, or false
concept hypothesis.
17
5) Evaluation of Errors
In this step, the researcher must decide the criteria of errors which will
be corrected because some errors can be considered more serious than other.
The aim of evaluating errors is to distinguish which errors will be
corrected.18
6. The Pronouns
1. The Definition of Pronouns
The researcher will gives some definition of pronouns. Firstthe
definition of pronoun according to Payne in his book Understanding English
Grammar A Linguistic Introduction, he wrote pronouns are a word that can
be shorted to be noun phrase.19 In addition, Quirk and friends said on their book “Pronouns share several characteristics, most of which are absent from nouns.”20
According to some definitions above, it can be concluded that pronouns
are a word that can replace a noun.
2. The Kinds of Pronouns
Pronouns have some different types that can people use in daily activity. There are “I”, “them”, “us” etc that can people usually use. Thus, too many people only know the word of pronoun whereas words of pronoun have a
category.
18
Ibid., p. 56 19
Thomas E. Payne, Understanding English Grammar A Linguistic Introduction, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011), p. 122
20
There are six categories according to Quirk and friends, they are:21
a. central pronoun. (a) personal: subject; I, you, we, they, she, he, it. object:
me, you, us, them, her, him, it. (b) reflexive: myself, themselves, herself,
himself, ourselves, itself. (c) possessive: possessive adjective; my, your,
their, our, her, his. possessive: mine, yours, ours, theirs, hers, his.
b. reciprocal pronoun; each other, one another.
c. relative pronoun; who, where, when, which, what, that.
d. interrogative pronoun; who, what, when, which, where.
e. demonstrative pronoun; this, these, that, those.
f. indefinite pronoun. (a) positive; universal: all, both,each and every.
Assertive: some, one, half, several, enough, other and another.
Non-assertive: any and either. (b) Negative: no and neither
3. The Personal pronoun
a. The meaning of personal pronoun
Marcel Danesi stated in his book “personal pronouns are classified
according to the person(s); the person speaking (first person); the person
spoken to (second person); anyone or anything else (third person).”22
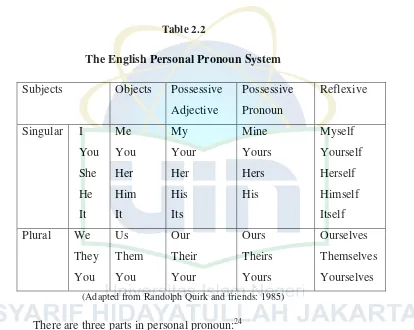
Quirk and friends distinguish personal pronouns in the table below:23
21
Ibid., p. 345 22
Marcel Danesi, Basic American Grammar and Usage, (New York: Barron’s Educational Series, Inc., 2006), p. 77
23
Table 2.2
The English Personal Pronoun System
Subjects Objects Possessive
Adjective
(Adapted from Randolph Quirk and friends: 1985)
There are three parts in personal pronoun:24
a). First person pronouns are used to refer to the person who is
speaking (I/me) or a group of people including the person who is
speaking (we/us)
b). Second person pronouns refer to the person or the group of people
to whom we are speaking (you)
c). Third person pronouns are used to refer to specific persons or
things previously mentioned. For a male (he/him), a female (she/her), an
animal or inanimate object (it), people, animals or things in the plural
(they/them).Personal pronouns change their form for person (first,
second, third), for case (subject, object, possessive), number (singular,
24
plural), and gender (masculine, feminine, neuter) except for reflexive
pronoun making the same kind of changes.
According to Beaumont &Granger’s book, there are some using of personal
pronoun:25
a. Subject pronouns as the subject of verbs
For example: Where is Simon?He is in the garage.
Sue did not go out last night. She stayed at home
b. Object pronoun as the objects of verb and prepositions.
1. Verb + object pronoun; help me, I like him, Can you see it?
2. Preposition + object pronoun; I have written to her, Look at them,
They’re waiting for us
7. Previous Related Study
There are some studies related with the pronouns error. Firstly, a research
done by Oji Fachruroji entitle “An Error Analysis on Students’Difficulties in
Learning English Pronouns”, the writer used qualitative descriptive method with
the purpose of the research was to analyze and to find out the kind of pronouns
that most students made, where the result was the highest pronouns errors was in
possessive adjective with 51,35% of error percentage.
Another study research is a research done by Restina Andriani, entitle “An
Error Analysis of Using Pronouns on Students’ Writing at SMP PGRI 1
Ciputat.” This study was carried out to identify the error of using pronouns which are commonly made by the students. The method used in this study was
descriptive analysis. With the result is the most error made by the students of
25
SMP PGRI 1 Ciputat was in Objective pronoun which caused by intralingual
transfer.
Based on the previous researchers above, it is known that the most difficult
material to be understood by the students’ is grammar. Thus, in this research, the
researcher intends to analyze the kinds of personal pronouns and types of errors
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. The Research Design
The method uses in this researchis qualitative method. As Bogdan and
Biklen state that qualitative is descriptive that data collected take the form of
words or pictures rather than a numbers.1 So that the researcher presented the
data collected in words rather than numbers. Furthermore, this research is
designed in a case study and she only examine a single subject like Bogdan
and Biklen state that a case study is a detailed examination of one setting or a
single subject.2 To get the data the researcher uses test. The test is done twice
to know whether it is a mistake or an error. Finally, the errors that have been
collected were analyzed to determine the types of errors by following Corder
theory. Futhermore, to know the frequency of occurence of each error type
the researcher used descriptive analysis technique (percentage).
B. The Place and Time of the Study
1. Place of The Research
The researcher conducted this researchat the first grade of SMP
Yayasan Miftahul Jannah (YMJ) which is located on Jalan Limun Nomor
27 Ciputat.
2. Time of The Research
She conducted the research at the schoolin November 2nd–25th2013.
C. The Subject of the Study
The subjects in this research is seven (VII) grade students of SMP
Yayasan Miftahul Jannah (YMJ) Ciputat. The researcher only took class VII
which contains 43 students.
1
Robert C. Bogdan and Sari Knopp Biklen, Qualitative Research for Education an Introduction to Theories and Methods, (Boston: Pearson, 2007), p. 5
2
D. The Instrument of the Study
The researcher takes the instruments of this research are writing test for a
students. The writing test divided into two parts. At the beginning, there are
10 questions about fill in the blank with the right answers, and at the second
part is 15 questions about choose the right answer between two choices.
E. The Data and Source of Data
According to Oxford dictionary “data is information and source is place, person or thing that we get something from.”3
So, the reasercher can stated
that the source of data is the information that we got from research.
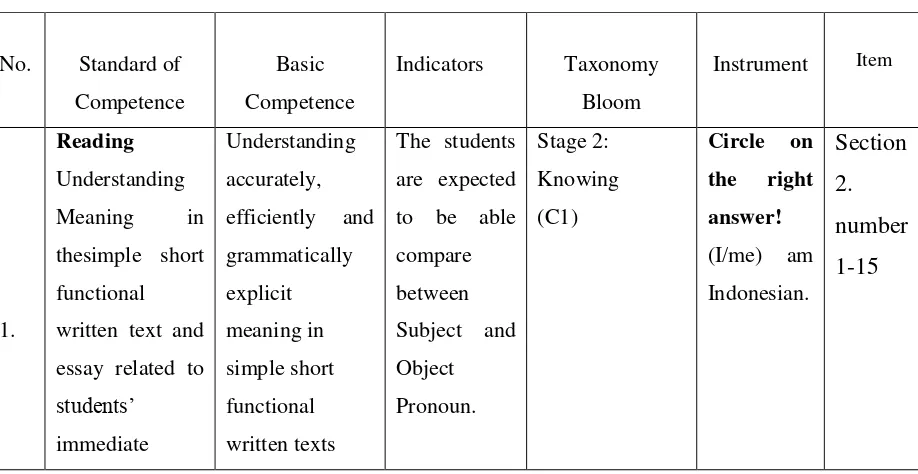
F. The Technique of Data Collecting
In this technique, the researcher gives a test to the students about
personal pronouns and it has a purpose to know which the students more
understand, it is subject or object pronoun. The stage of taxonomy bloom
which is explained in the table below.
Table 3.1
Specification of Test Items
No. Standard of Competence
Basic Competence
Indicators Taxonomy Bloom
Instrument Item
1.
Reading
Understanding Meaning in thesimple short functional efficiently and grammatically explicit meaning in simple short functional written texts
The students
3Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary New Edition,
environment related to efficiently and grammatically explicit meaning in simple short functional written texts related to
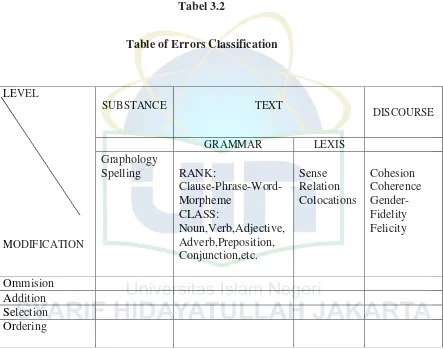
G. The Techniques of Data Analysis
Meanwhile, the data of the writing test, the researcher used the
descriptive technique. The descriptive technique is analysis which is aimed to
describe and analyze the error that is made by the students of SMP Yayasan
Tabel 3.2
Table of Errors Classification
The researcher uses the formula of frequency and percentage of errors4:
P = x 100%
P = Percentage of error
F = Frequency of false answer
N = Number of total errors occur.
4
Allan G. Bluman, Elementary Statistics: A Step by Step Approach, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004), p. 68.
LEVEL
MODIFICATION
SUBSTANCE TEXT
DISCOURSE
GRAMMAR LEXIS
Graphology
Spelling RANK:
Clause-Phrase-Word- Morpheme
CLASS:
Noun,Verb,Adjective, Adverb,Preposition, Conjunction,etc.
Sense Relation Colocations
Cohesion Coherence Gender-Fidelity Felicity
A. The Description of the Data
In the previous chapter, the techniques of completing the data have been
mentioned clearly. Furthermore, the results of collecting data could be seen as
below:
1. The Result of the Test
The researcher has given an essay personal pronouns test. There were 43
students on the absent list, but there were only 34 students in the class. Some
of them moved to another school, and another did not come to school. So, the
researcher only took 34 students as a sample. The test is an essay about
personal pronouns, which is guided by two (2) instructions. The students
needed to fill in the blank and to choose the right answer between two choices
or the students only had to follow the instructions given. After conducting the
test, the researcher analyzed the data from the students’ test to find out the
errors that students made in his/her answer.
Below, the researcher analyzed each student’s error in their answers. In
this study, the researcher found that the common kind of personal pronouns
error made by the students is subject pronoun and the common type of the
Table 4.1
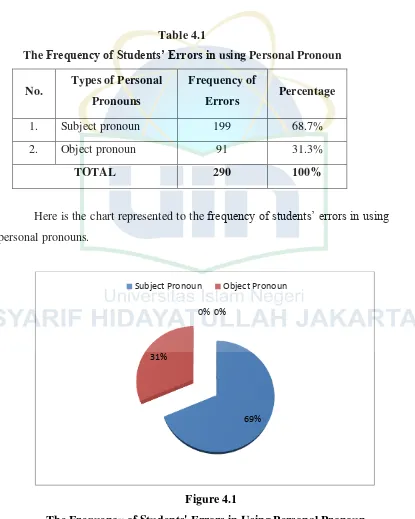
The Frequency of Students’ Errors in using Personal Pronoun
No. Types of Personal Pronouns
Frequency of
Errors Percentage
1. Subject pronoun 199 68.7%
2. Object pronoun 91 31.3%
TOTAL 290 100%
Here is the chart represented to the frequency of students’ errors in using
personal pronouns.
Figure 4.1
The Frequency of Students' Errors in Using Personal Pronoun
From the table and the figure above, it can be seen the most errors that the
students made is subject pronoun.
69% 31%
0% 0%
After identifying the data, the researcher analyzed the errors and
classified them based on the Surface Taxonomy Categories to know whether
these errors involve in omission, addition, selection, or ordering.
This calculation used the formula of descriptive analysis technique as can be
seen as below:
P =
Note:
P: Percentage;
f: Frequency of a type of error;
n: Number of total errors occur.
Furthermore, to make it easier to read, she presents it in the following table
below:
Table 4.2
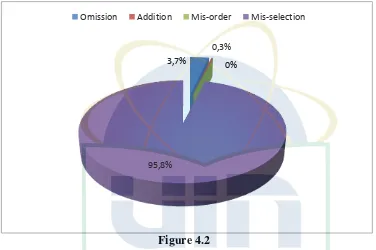
The Recapitulation of Error Types, Frequency and its Percentage
No.
Level /
Modification Substance
Text
Discourse Total Of Error
Grammar Lexis
1. Omission - 11=3.7 - - 11= 3.7
2. Addition 1=0.3 - - - 1= 0.3
3. Selection 7= 2.4 257= 88.6 - 14= 4.8 278= 95.8
4. Ordering - - - - -
Figure 4.2
The Recapitulation of Error Types, Frequency and its Percentage
Based on the calculation above, it can be concluded that the total errors of
omission were 11 errors or 3.7% in grammar text level, the addition were 1
error or 0.3% in substance level. The error of selection were 278 errors or
95.8% (error in substance level were 7 errors or 2.4%, in grammar level were
257 errors or 88.6%, and in discourse level were 14 errors or 4.8%), while
there were no errors found in mis-ordering. From the calculation of the data,
error of selection is the most frequent errors done by the first grade students
of SMP YMJ with the percentage 95.8%. Moreover, it is followed by error of
omission with percentage 3.7%, and error in addition only 0.3%. To be more
clearly the researcher explains each of the error below:
3,7%
0,3%
0%
a. Ommision
The total error of ommision were 11 errors or 3.7%. Omision error occurs
when the learner omitted a necessary element of word. Omission errors fell in
the grammar level. In this case, most of the students who made errors in this
type because they didn’t fill the answer. They let the question empty without
any answer. On the researcher opinion the blank empty answer can mentioned
in omission because the sentence didn’t complete without any answer from
students.
b. Addition
The total error of addition was only 1 error or 0.3% in substance level.
They add the unnecessary letter that is not needed in that word. For example,
*hie is in the garage. The spelling was really error. There was no need letter “i” between “h” and “e.” The student should answer *he is in the garage.
There must be omitted because it was not needed.
c. Selection
The total errors of selection that the researcher found were 278 errors or
95.8% (the errors in the substance level were 7 errors or 2.4%, in the grammar
level were 257 errors or 88.6%, and in the discourse level were 14 errors or
4.8%). This is the highest error that the students made. The students were
confused in choosing the appropriate class of pronoun (subject or object). In
this case, for example: *Her stayed at home. While the answer was supposed
to be *She stayed at home. From this sentence it can be seen that the student
was wrong to choose pronoun so they mis-selection about it.
d. Missordering
As the researcher mentioned above, she didn’t find any errors in this
B. The Data Analysis
The researcher analyzed the errors that are taken from the data description
and calculate them according to the formula as written below:
1) The Description of Error
After identifying the data, the researcher analyzed the errors and
classified them based on the Surface Taxonomy Categories to know
whether these errors involve in omission, addition, selection, or ordering. This is the following example is taken from the student’s answer sheet.
a. The Error of Ommision
The researcher analyzed the data from students’ test and she found
eleven (11) errors in error of ommision. Mostly the students didn’t answer
the question.
b. The Error of Addition
In this part, the researcher analyzed the data and she found one (1)
errors in error of addition. For example; *hie is in the garage. She was
supposed to write *he is in the garage.
c. The Error of Selection
The researcher found the most errors were in this type. There were
278 errors that students made. Mostly they couldn’t distinguish to put
subject and object pronoun. For example; *I write they a letter. The
correct sentence is I write them a letter. In this case the student was
wrong to select the pronoun, it must be „them’ for pronoun „they’
d. The Error of Ordering
The researcher couldn’t find any errors in error of ordering.
2) The Evaluation of Error
From the explanation above, the researcher found any errors in using
put subject and object pronoun. They were confused in choosing the
appropriate class of pronoun (subject or object). For example: My friend,
Alex, love read a book. So, me will borrow my book to him.
If the sentence above is translated to Bahasa, it will become “teman
saya, Alex, senang membaca buku. Saya akan meminjamkan buku saya ke
dia” In Bahasa it will be accepted, but in English it cannot be accepted.
Therefore, this error should be treated intensively because this error will
hinder the message to be understood.
C. The Interpretation of the Data
In this Part, the researcher will interpret some errors that students made as
follow:
Table 4.3
Frequency of Students’ Errors in using Personal Pronoun
No. Types of Personal Pronouns
Frequency of
Errors Percentage
1. Subject pronoun 199 68.7%
2. Object pronoun 91 31.3%
TOTAL 290 100%
As shown on the table above, subject pronoun is the most frequent errors
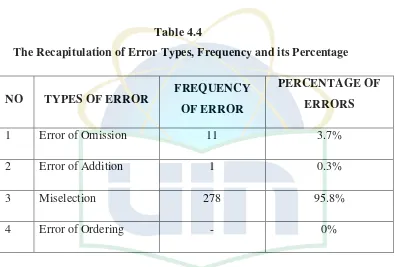
Table 4.4
The Recapitulation of Error Types, Frequency and its Percentage
NO TYPES OF ERROR FREQUENCY
OF ERROR
PERCENTAGE OF
ERRORS
1 Error of Omission 11 3.7%
2 Error of Addition 1 0.3%
3 Miselection 278 95.8%
4 Error of Ordering - 0%
As shown on the table above, error of selection is the most frequent errors
that done by the first grade students of SMP YMJ with the percentage 95.8%.
They did it because some students found difficulties in distinguishing between
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
Based on the explanation and the description in the previous chapters,
subject pronoun is the most frequent errors that done by the first grade
students of SMP YMJ with the percentage 68.7%. Besides, the researcher
concluded that the total errors of omission were 11 errors or 3.7% in grammar
text level, the addition were 1 error or 0.3% in substance level. The error of
selection were 278 errors or 95.8% (error in substance level were 7 errors or
2.4%, in grammar level were 257 errors or 88.6%, and in discourse level were
14 errors or 4.8%), while there were no errors found in misordering. From the
calculation of the data, error of selection is the most frequent errors done by
the first grade students of SMP YMJ with the percentage 95.8%. Moreover, it
is followed by error of omission with percentage 3.7%, and error in addition
only 0.3%. So, the types of error that were made by the students of the first
year of SMP Yayasan Miftahul Jannah (YMJ) in their pronoun from the
highest percentage to the lowest are error of selection, addition, omission and
error of ordering.
B. Suggestion
Errors in teaching learning process of foreign language are something
unavoidable. Although it seems natural, students should learn more about
grammar to enhance their ability in English lesson. The researcher intends to give
some suggestions as follow:
1. The teacher has to keep giving students practice in using personal
pronoun. By these tasks, the students will be familiar with the difference
2. The teacher has to make the students aware of their mistakes by letting
them correct their errors with partner. Besides, this will make students
find out their own mistakes; this also will motivate them in teaching
learning process by doing it in pair.Beside that, the teachers have to pay attention to the students’ errors and make them aware about their errors so they can make a correction by themselves and will not do the same error.
3. The teachers should explain more about personal pronoun for the students
can really understand.
4. The students have to pay more attention when teacher give explanation.
Appendix 1: The Recapitulation of Student’s Errors
Students’ Number
Errors Classification Total
Students’ False Omission Addition Mis-order Mis-selection
1 - - - 9 9
2 - 1 - 6 7
3 - - - 4 4
4 - - - 4 4
5 - - - 6 6
6 - - - 4 4
7 1 - - 6 7
8 - - - 16 16
9 - - - 6 6
10 1 - - 7 8
11 - - - 11 11
12 - - - 4 4
13 - - - 10 10
14 - - - 5 5
15 - - - 13 13
16 - - - 10 10
17 - - - 9 9
18 1 - - 12 13
19 1 - - 12 13
20 - - - 6 6
21 - - - 5 5
22 - - - 10 10
1. The Error of Omission =
3.7%
2. The Error of Addition =
3. The Error of Selection =
4. The Error of Misordering =
24 2 - - 6 8
25 1 - - 12 13
26 - - - 9 9
27 - - - 7 7
28 - - - 7 7
29 - - - 10 10
30 - - - 6 6
31 - - - 12 12
32 - - - 3 3
33 1 - - 9 10
34 - - - 10 10
Appendix 2: The Description of Errors (Numbers in bracket indicate students’
list number)
LEVEL
MODIFICATION
SUBSTANCE TEXT
DISCOURSE
GRAMMAR LEXIS
Graphology
Spelling RANK:
Clause-Phrase-Word-
Addition *hie/he (student
2)
- - -
Selection *hie/he (student
2)
*my sister and me/my sister and I (student 1, 2, 5,
*her/they (student 1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 11, 13, 15,
*her/him (student 7, 18)
*him/she (student 7, 11, 19)
*them/they (student 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 33, 34)
*they/them (student 2, 11, 15, 24, 25, 31, 33, 34)
*he/him (student 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 17, 18, 19, 21, 23, 25, 29, 34)
*I/me (student 8, 11, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 26, 29, 33, 34)
*we/us (student 8, 9, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 23, 24, 26, 29, 31, 32, 33, 34)
*us/we (student 11, 17, 32)
*she/her (student 13, 16, 18, 25, 26, 33, 34)
*he/she (student 12, 33, 34)
*my/they (student 23)
*she/he (student 23)
No. Students’
Number Wrong Answer Correct Answer
Types of
(mereka) always go
together.
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
2. 2. 1. My sister and me
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and (mereka) always go
4. 4. 10. Where is Simon?
(mereka) always go
together.
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
6. 6. 16. (he/him) is my
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
have dinner with Lisa
this night.
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
9. Sue did not go out
last night. Hem (dia
We (kami) will have
dinner with Lisa this
10. Where is Simon? school at 6 o’clock
My Daddy gives two
6. My Daddy gives
two books to Maya
and I (saya).
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
dinner with Lisa this
night.
We (kami) will have
dinner with Lisa this
night
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together. school at 6 o’clock
25. (I/me) am writing
a letter to my
grandma.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
dinner with Lisa this
night.
6. My Daddy gives
two books to Maya
and I (saya).
We (kami) will have
dinner with Lisa this
last night. Her (dia pr)
My Daddy gives two
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
letter to my grandma
Selection
(saya) like pop music
and I (saya).
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together school at 6 o’clock
Selection
My Daddy gives two
Selection
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Her
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
dinner with Lisa this
night.
We (kami) will have
dinner with Lisa this
night
6. My Daddy gives
two books to Maya
and I (saya).
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. My
(mereka) always go
together. school at 6 o’clock
23. (he/him) is so nice
to me.
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
Indonesian. school at 6 o’clock
23. (he/him)Ө is so
(mereka) always go
together.
16. (he/him) is my
brother.
My sister and I
(saya) like pop music
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
21. (I/me) arrived at school at 6 o’clock
school at 6 o’clock
26. 26. 7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Selection
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
best friends. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
My sister and I
(saya) like pop music
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friends. They
(mereka) always go
together
Selection
Selection
garage.
(mereka) always go
together.
My Daddy gives two
two books to Maya
and I (saya).
7. Nia and Maya are
best friend. Them
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
together
(mereka) always go
together.
9. Sue did not go out
last night. Her (dia pr)
stayed at home.
My Daddy gives two
books to Maya and
me (saya)
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
garage.
letter to my grandma
Selection
dinner with Lisa this
night.
23. (he/him) is so nice
to me.
We (kami) will have
dinner with Lisa this
night
(mereka) always go
Nia and Maya are
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
9. Sue did not go out
(mereka) always go
together.
best friend. They
(mereka) always go
Appendix 4: The Description of Students’ Errors in Object Pronoun
No. Students’
Number Wrong Answer Correct Answer
Types of
Errors
1. 1. 2. I write her (mereka) a letter.
I write them (mereka) a letter
Selection
2. 2. 19. Their mom will
give (they/them) to
watch a movie
their mom will give
breakfast with I
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
breakfast with I
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
17. I will borrow my
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
5. Our mother is very
these chocolates are
14. these chocolates
are for (we/us)
24. I still remember
(he/him)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
24. 24. 14. these chocolates
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
24. I still remember
12. I will give it to
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
their mom will give
32. 32. 14. These chocolates
are for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
these chocolates are
for (we/us)
Selection
Selection
19. Their mom will
give (they/them) to
watch a movie
their mom will give
(they/them) to watch
a movie
Subject and Object Personal Pronoun
Nama :
Kelas :
Hari/Tanggal :
Mata Pelajaran : BahasaInggris
PETUNJUK UMUM
1. Periksalahdanbacalahsoal-soaldengantelitisebelummenjawab.
2. Dahulukanmenjawabsoal-soal yang dianggapmudah.
3. Kerjakanlangsungpadalembarsoal.
4. Kerjakandenganmenggunakanpensil.
5. Apabilaadajawaban yang dianggapsalah, daningindiperbaiki,
hapuslahjawabanandadengankaretpenghapussampaibersih, kemudianisidenganjawaban yang benar.
I. Fill in the blank with the right answer! 1. My sister and …. (saya) like pop music.
2. I miss my friends, so I write …. (mereka) a letter.
3. …. (kami) will have dinner with Lisa this night.
4. My parents have breakfast with ….. (saya)
5. Our mother is very angry with …. (dia lk)
6. My Daddy gives two books to Maya and .... (saya)
7. Nia and Maya are best friend. …. (mereka) always go together.
8. we saw …… (dia lk) at the show.
9. Sue did not go out last night. ….. (dia pr) stayed at home.
1. A: What is your name? and may I know your nationality?
B: My name is Sue. (I/me) am Indonesian.
2. A: Hay, Bob! Will give you Samantha a cupcake?
B: I don’t think so. I like the watch that I saw in the shop. So, I will give it to (she/her)
3. A: What is your mom occupation?
B: My mom is a fashion designer and (she/her) is very pretty.
4. A: Hay Bobby and Daniel! What is that?
B: Hay David! Bobby and I love sweet and these chocolates are for (we/us)
5. A: Who is he?
B: He is Bob. Bob is my dad. (He/him) is a waiter.
6. A: Where is your brother?
B: On the left you can see Simon. (He/him) is my brother.
7. A: Why do you bring that thick book?
B: My friend, Alex, love read a book. So, I will borrow my book to (he/him)
8. A: Are (they/them)twins?
B: yes, they are twins.
9. A: I heard, Dona and Doni’s mom will give a gift to them if they can pass the exam, is it right?
B: yes, Dona and Doni like watch a movie. Their mom will give
B: Today (She/her) lives in Japan.
11.A: What time did you arrive at school this morning?
B: (I/me) arrived at school at 6 o’clock
12.A: Do you know Sule?
B: yes, I know (he/him). He is comedian.
13.A: What do you think about Mr. Eaglestone? B: (he/him) is so nice to me.
14.A: Do you still remember Jo?
B: Sure! I still remember (he/him). He is our old friend.
15.A: What are you doing?