THE CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ MASTERY IN
VOCABULARY AND THEIR READING COMPREHENSION
SKILL OF DESCRIPTIVE TEXT
(A Correlational Study in the Eight Grade Students of MTs Syamsul Ulum Sukabumi Academic Year 2013/2014)
By:
Siti Fatimah
109014000173
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ABSTRACT
Siti Fatimah (109014000173). The Correlation between Students’ Mastery in
Vocabulary and Their Reading Comprehension Skill of Descriptive Text; A Correlational Study in the Eight Grade Students of MTs Syamsul ‘Ulum Sukabumi Academic Year 2013/2014. Skripsi of Department of English Education at Faculty of Tabiyah and Teachers’ Training of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta, 2014.
Key Words: Correlational Study, Vocabulary, Reading Comprehension of Descriptive Text
Sukabumi Tahun ajaran 2013/2014. Skripsi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Kata Kunci: studi korelasi, kosakata, pemahaman membaca teks deskriptif
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
ميحرلا نمحرلا ه مسب
In the Name of Allah, The Beneficent, The Merciful
All praise be to Allah, the Lord of the worlds, who has given the strength, the patience, the health and the blessing to the writer, so that she can finish this skripsi. Shalawat and salam are always presented to the prophet Muhammad SAW, who becomes the inspiration in this world.
This skripsi is presented to the Department of English Education of the faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training Syaarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of first strata (S1).
The writer is particularly grateful to her parents, the late Mr. Ade Ahmad Riyad and Mrs. Pupu Maspufah. Especially her dearest mother, for the supports, hopes, and prays in each second of times. Also the writer would like to thank to the late Mr. Abdullah Manshur, for the cares and everything he has given to the writer.
It has been the writer’s privilege to accomplish this skripsi with the gifted and talented teachers in this faculty. Therefore, she would like to express her gratitude to Mrs. Nida Husna, M.Pd, MA.TESOL and Mr. Dadan Nugraha, M.Pd, for the critiques, corrections, encouragement and great advice in guiding the writer of making this skripsi.
In addition, there are many people who contribute in finishing this skripsi, the writer would like to express her appreciation to:
1. Nurlena Rifa’i, MA, Ph.D as the dean of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd as the head of the Department of English Education. 3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum as the secretary of the Department of English
Education.
6. All eight grade students in C class (8C) academic year 2013/2014 of MTs. Syamsul Ulum for good cooperation.
7. Her beloved husband, Sholehudin D. Jauhari, M.Ag for the great support, suggestion and time to share that has been given to the writer. And for her sweet baby, Rizqiya Awalia Shofa, the crying and smiling make the wonderful life for the writer. Also for her mother in law, Mrs. Pipih Sofiah, for the pray and the kindness.
8. Her sister, Siti Rahmah and family, for the supports and prays. Also all relatives who cannot be mentioned one by one.
9. The big family of Mr. Abdullah Manshur, who cannot be mentioned one by one for the cares and the kindness.
10.All friends of PBI E class year 2009, for being her new family.
11. All roommates of “Tirmidzi” and “Cemara” dorm who have became her
nice friends.
12.All people who cannot be mentioned one by one for the contribution in completing this skripsi.
May Allah protect and give the great blessing for them. Amiin.
The writer realizes that this skripsi is far of the perfect. Therefore, some critiques and suggestions are needed to make it better.
Jakarta, April 2014 The Writer
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF TABLES ... vii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... viii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ... 1
A.Background of the Study ... 1
B.Identification of the Problem ... 5
C.Limitation of the Study ... 5
D.Formulation of the Study ... 6
E. Objective of the Study ... 6
F. Significance of the Study ... 6
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 7
A.Vocabulary ... 7
1. Definition of Vocabulary ... 7
2. Kinds of Vocabulary ... 8
3. Vocabulary Learning ... 10
B.Reading ... 12
1. Definition of Reading ... 12
2. Reading Comprehension ... 14
3. Kinds of Reading ... 15
4. Types of Reading Text ... 16
C.Descriptive Text ... 18
1. Definition of Descriptive Text ... 18
2. Purpose of Descriptive Text ... 19
3. Elements of Descriptive Text ... 20
A.Place and Time of the Research ... 25
B.Subject and object of the Research ... 25
C.Method of the Research ... 25
D.Population and Sample of the Research ... 26
E. Instruments of the Research ... 26
F. Technique of Collecting Data ... 29
G.Technique of Analyzing Data ... 29
H.Statistic Hypothesis ... 30
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS ... 31
A.The Description of Data ... 31
B.The Data Analysis ... 34
C.The Test of Hypothesis ... 38
D.The Interpretation of Data ... 38
CHAPTER V CONCLUSSION AND SUGGESTION ... 40
A.Conclusion ... 40
B.Suggestion ... 40
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 42
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Social Function of Story Genres and Factual Genres ... 17
Table 3.1 Item Validity of Multiple Choices on Vocabulary Test ... 27
Table 3.2 Item Validity of Multiple Choices on Reading Test ... 27
Table 3.3 The Questions Number of Vocabulary Test ... 28
Table 3.4 The Questions Number of Reading Test ... 28
Table 4.1 Students’ Vocabulary Scores ... 31
Table 4.2 Students’ Reading Scores ... 32
Table 4.3 The Result of Pearson Product Moment ... 34
Appendix 3 The Questions of Vocabulary Try Out Test ... 49
Appendix 4 The Question of Reading Try Out Test ... 51
Appendix 5 The Result of Anates of Vocabulary Test ... 56
Appendix 6 The Result of Anates of Reading Test ... 57
Appendix 7 The Questions of Vocabulary Test (Instrument) ... 58
Appendix 8 The Questions of Reading Test (Instrument) ... 60
Appendix 9 Surat Keterangan Penelitian ... 64
Appendix 10 Tabel Product Moment ... 65
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
A.
Background of the Study
There are many international languages that are used as medium language in several fields such as in education, business, tourism, etc. One of them is English. Generally, English as an international language that is considered important has been taught in around the world including in Indonesia. Then, learning or teaching English in several countries may different with others, especially when English comes as their foreign language.
Norbert Schmitt states that learning a foreign language like English language may be difficult for some people in several countries because English has different features with their native language and there are so many aspects that must be learned in English.1 Non native students have to adapt with the letters and sounds of English. Besides that, they have to face the different rules of sentences, how the sentence can be produced, and the meaning of each word. Thus, it may need some competences that must be mastered by learners in understanding English.
According to Kumaravadivelu, there are four language competences in order to master English; those are grammatical competences, sociolinguistic competences, discourse competences, and strategic competences.2 All of the competences are important in mastering English.
Those are language competences that should be mastered by people in learning language. However, from those competences, the writer will focus on grammatical competences especially vocabulary. Vocabulary can be seen as a main position in language teaching. The observational study that has been done by Short (2002) in the ESL middle school classrooms in US shows that of the 623
1
Norbert Schmitt, Researching Vocabulary. A Vocabulary Research Manual, (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), p. 24.
2
teacher utterances that did address language, 95% focused on vocabulary comprehension or pronunciation.3
Vocabulary, as one of the grammatical competences, can be taught in any level of the study. Most non native students are usually taught vocabulary and how to sound it at the first time. Thus, some experts of language teachers and language researchers emphasized the importance of vocabulary by exploring many ways in teaching it effectively. Some of the English teachers probably use several techniques when they are teaching vocabulary such as by using flash card, using picture or memorizing it. This can be hoped that students can understand and achieve the goals of learning English. However, generally non native students assume that to master English need to master sufficient vocabulary because vocabulary will facilitate them to use English language.
In addition, vocabulary as one of the grammatical competences is important for people to master English skills. There are four English skills of; those are listening, speaking, reading and writing. By vocabulary, all of these skills can be achieved. Norbert Schmitt states that vocabulary knowledge gives a large deal to whole language success such as for reading, listening, speaking and writing, grammatical accuracy, sociolinguistic appropriateness, and language fluency.4 It can be impossible when people want to master language without vocabulary. Therefore, to get many vocabularies is needed many practices, such as by reading magazine or newspaper, watching films, listening to the music, etc. However, from those practices, the large contribution in getting vocabulary is by reading as Norbert Schmitt states that reading is a key to vocabulary improvement.5 By reading, students can get new vocabulary or they can practice to apply the vocabulary which they got.
Some experts argue that reading is not a natural ability and probably the most difficult task to be undertook by young. It is shown by some researchers that
3
Roy Lyster, Learning and Teaching Language through Content, (Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2007), p. 28.
4
Norbert Schmitt, op cit, p, 4. 5
3
the frightened task about 50 percent is reading and for about 20 to 30 percent reading becomes the most difficult cognitive task to take.6 Furthermore, to achieve the goal of reading is needed practice. The practice may be in the class or outside the class such as by reading English newspaper or magazines. Reading English may be difficult for some non native students because students are faced the foreign vocabulary which has different pronunciation and different meaning with their native language. Thus, the problem usually appears when they are facing the difficult vocabulary that causes the purpose of reading to comprehend the text is not achieved.
There were some problems when the writer taught in MTsN.19 Jakarta. First, she found most of the students did not comprehend the text. Actually they knew the vocabulary in single word, but they could not use or know it when they were reading. When they were asked to read English text, they often found vocabulary which they saw as a difficult vocabulary. They just left the word and went to the next word or predicted what actually the meaning of that word without comprehension.
There are some factors that probably cause students do not comprehend the English text, those are lack of vocabulary, lack of background of knowledge and lack of motivation. One of the factors that often appeared is lack of vocabulary. Having limited vocabulary usually makes students difficult to achieve the goal of reading. They cannot comprehend text. Students who do not have a lot of vocabulary usually get the difficult to comprehend the text rather than those who have a lot of vocabulary.
Second, based on the writer experience when she taught in MTsN 19 Jakarta, she found the students who could not answer the questions because some of them did not know many vocabularies. When they were reading, many students said that they did not know the vocabulary. The writer asked them to open dictionary and to find the meaning of that difficult vocabulary. In fact, there were many students who did not bring the dictionary. Then, when they were asked to answer the questions of their reading, they did not answer the questions well. So,
6
most of them were lazy to read English because of the difficult vocabulary which they got. Third, the problem was found in the school was, there were some students who had many vocabulary, but when they took reading test, they had a little score of reading. Otherwise, there were some students who had a few of vocabulary, but they had a good score of reading.
Moreover, the ability to read is one of the goals in learning English. Eight grade students are hoped that they can communicate functionally when they are accustomed to read. Therefore, in KTSP curriculum, the purpose of teaching reading in the eighth grade of junior high school is students can respond the meaning in the functional text and in a short text such as descriptive and recount text accurately.7 It can be meant that students are hoped to be accustomed to read and they can apply what they read in their life, so that they can solve their problems by themselves.
Meanwhile, the purpose of teaching vocabulary for the eighth grade students is to improve the communicative competences orally and written in order to achieve the language skills functionally.8 By vocabulary which students have, students are hoped to use language in communication written and orally, so that they can adapt with their time today.
Based on KTSP curriculum, it shows that there are some texts that should be mastered by eight grade students of junior high school. Those texts are descriptive, narrative, recount, procedure, and report. Whereas the texts which are learnt to eight grade students of junior high school are three texts, those are descriptive, narrative, and recount.
However, from those three texts, the writer selects only descriptive text by some considerations. First, students in second grade of junior high school have been introduced the descriptive text when they were in first grade, thus the writer considers that they can understand descriptive text. Second, description of something can be met in several ways, for that reason the writer assumes that the students may have accustomed with description. In fact, the problem appeared,
7
Standar Isi untuk Satuan Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah, (Jakarta: Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan, Kementrian Pendidikan Nasional, 2006), p. 129.
8
5
when students read descriptive text and could not comprehend the text because of the students had little vocabulary of description.
Seeing these cases, the writer is interested in doing the research to know the correlation between vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension of descriptive text at second grade of MTs Syamsul Ulum Sukabumi. Therefore, the writer conducted the research by the title “The correlation between students’ mastery in vocabulary and their reading comprehension skill of descriptive text (a correlational study in second grade students of MTs Syamsul Ulum Sukabumi
academic year 2013/2014)”.
B.
Identification of the problem
Seeing that background of the study, the writer identifies the problem such as:
1. Students could not put or could not understand the vocabulary in the context of the sentences.
2. Students had less motivation to read because they assume that reading English text is difficult.
3. Students who had many vocabulary could comprehend the descriptive text; and students who had a few of vocabulary could not comprehend the descriptive text.
4. It is supposed that students who had many vocabulary could comprehend the descriptive text, but in fact they got bad score in reading descriptive text. Otherwise, there were some students who had a few of vocabulary could comprehend the descriptive text.
5. There is a probability of correlation between students’ vocabulary and their reading comprehension of descriptive text.
C.
Limitation of the Study
In order to become more effective in doing the research, therefore the writer
D.
Formulation of the study
“Is there any correlation between students’ mastery in vocabulary and their
reading comprehension skill of descriptive text at eight grade students of MTs. Syamsul Ulum Sukabumi academic year 2013/2014?”
E.
Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to see the correlation between students’ mastery of vocabulary and their reading comprehension at eight grade students of MTs. Syamsul Ulum Sukabumi academic year 2013/2014.
F.
Significance of the Study
The study can give the contributions to enrich English knowledge for some people such:
1. The Writer
The research can give some experiences for the writer as the bridge to increase knowledge of English.
2. The English teachers
The research can inform the English teachers about students’ vocabulary that must be mastered to get their comprehension of English text, so that the English teachers can improve their method in teaching reading effectively.
3. The Students
The research can motivate students to improve their vocabulary and practice their reading activity.
4. The readers
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.
Vocabulary
1.
Definition of Vocabulary
When some people hear word “vocabulary”, the first thing in their mind is word. They may think that vocabulary is a word that has meaning. Or, may be the others assume that vocabulary is a foreign word when they are learning language. Whatever they said about vocabulary may be permitted. However, to emphasize what actually vocabulary is, the linguistic experts have argued of vocabulary definition.1
According to Troike “vocabulary (or lexicon) is the most important level of L2 knowledge for all learners to develop-whether they are aiming primarily for academic or interpersonal competence, or for broader scope of communicative competence that spans the two”.2
Ur argues what actually vocabulary is. Her opinion about vocabulary is that
“vocabulary can be defined, roughly, as the words we teach in foreign language.
However, a new item of vocabulary may be more than a single word: for example, post office, mother in law, which are made up of two or three words but express a single idea”.3 Thus, vocabulary can be said as one of the important aspects in learning a language and vocabulary can be formed from some words that create the meaning.
When people learn foreign language, the first thing they probably input is word. By knowing some words, they can be facilitated in language learning process. According to Hudson, learner’s vocabulary becomes a key in language and its acquisition and as long as they learn language, they learn lexical meaning,
1
Visnja Pavicic Takac, Vocabulary Learning Strategies and Foreign Language Acquisition, (Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Ltd, 2008), p. 4.
2
Muriel Saville Troike, Introducing Second Language Acquisition, (New York: Cambridge University Pree, 2008), p. 138.
3
syntax, and morphology, their vocabularies increase throughout their life.4 In acquiring vocabulary native speaker and non native speaker may have different ways to get it. As Lightbown and Spada state children whose their first language is English has little effort in learning vocabulary, and it is quite different with those are non native speakers.5 Native speaker of English may be easy in getting it because they are accustomed with the language. In contrast, some of non native speakers of English may not get many vocabularies as easily as native speaker because their language is different with English, they must adapt with the spelling, the letters and the meaning.
2.
Kinds of Vocabulary
Nation divides kinds of vocabulary into three or four levels based on how its frequency and how its range; they are:
a. High frequency words. These words often occur in all kinds of uses of language whether in formal and in informal uses, in speech and writing, in novels, conversations, newspaper, and academic texts. The number of high frequency words are about 2000 words of English, it can be found in a text is about 80% or more of running words in formal written text and about 90% in friendly conversation.
b. Academic words. These words are usually put or found in all kinds of academic subject area such as in academic writing that including Economic or Geography textbook, Arts, Science, Commerce, and Law. Academic words do not often occur in daily uses. Less than 2% of the running words in conversation are from academic word list. These words of academic words are important for people who will use English for academic study.
c. Technical words. These words often occur in more special purposes and very common in one particular area such as the vocabulary of Physics or
4
Thom Hudson, Teaching Second Language Reading, (New York: Oxford Universiy Press, 2007), p. 227.
5
9
the vocabulary of Applied Linguistics. In other words, most technical words occur only in one specialized area. Technical words are very important for anyone who specializes in a particular area such as a doctor, linguist, educationalist and etc. The number of technical words would seem at least 20% of the running words of technical words.
d. Low frequency words. These words do not often occur in daily use and can be found in friendly conversation about 5%, in newspaper about 10%, and in academic text about 10%. In addition, these words have a narrow scope; so that the uses of these words are rarely found.6
Different with Nation, Haycraft in Vocabulary Semantics and Language Education classifies the vocabulary in two kinds, namely receptive vocabulary and productive vocabulary:
1. Receptive vocabulary is words which come in a context that students recognize and understand in reading and listening, but they cannot produce those words perfectly.
2. Productive vocabulary is words which students understand of those words then they can pronounce and use correctly in speaking and writing.7
Read mentions two kinds of vocabulary, those are:
a. Function words. These words can be seen in grammatical aspects, such as articles, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, auxiliaries, etc.
b. Content words. These words modify the meaning and provide links to the sentences. The kinds of these words are noun, verb, adjective, and adverb.8
Those are kinds of vocabulary according to some language experts. Although they have classified vocabulary in different kinds, the important things
6
I. S. P. Nation, Teaching Vocabulary: Strategies and Techniques, (Boston: Heinle Cengage Learning, 2008), pp. 7—14.
7
Evelyn Hatch and Cheryl Brown, Vocabulary, Semantics and Language Education, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1995), p 370.
8
is how language learners can learn and apply those vocabularies in some contexts so that the meaning of texts can be achieved.
3.
Vocabulary Learning
To have many vocabularies needs some practice and techniques in reaching that. Therefore, many language experts introduce how vocabulary can be learnt effectively. Hatch and Brown identify vocabulary learning in two kinds; those are intentional learning and incidental learning.
a. Intentional learning can be said that learning vocabulary is done in class by students and teacher also by planning and designing materials.9 In other words, teachers teach the vocabulary to students, and then all students are asked to remember the words. Some of the linguists state that learning words in bilingual vocabulary list can be the act of intentional learning.
b. Incidental learningcan be described that students learn language in order to communicative purposes and it provides double advantages for time used.10 When students learn vocabulary incidentally, they can save their time because they can get vocabulary unconsciously. One of the ways to learn vocabulary incidentally can be done by extensive reading.
There are other ways to learn vocabulary that can facilitate learners: 1. Associate meanings of words together
2. Use picture or diagram
3. Classify word by word class and
4. Write synonym or antonym of words that have been found.11
In vocabulary learning, it is hoped that students can improve their vocabulary size. It can be said that there are so many size of vocabulary that has been mentioned by linguists. According to Bauer, there are 2000 set of words that is used to explain the words in The Longman Dictionary of Contemporary
9
Evelyn Hatch and Cheryl Brown, op cit, p. 368. 10
Norbert Schmitt, Vocabulary in Language Teaching, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000), p. 120.
11Michael McCarthy and Felicity O’Dell,
11
(LDEC), a dictionary written for non native speaker. It shows that non native speakers can write by using about 2000 words so that they can understand what they read well. If non native speakers know about 2000 words means that they can understand text about 80%, and if they know about 1000 words, they can understand text in 70%.12
Although English vocabulary can be said have large number, but students are not necessity to know all of them. Nation and Laufer in Cognition and Second Language Instruction mention that knowing receptive knowledge of 5000 base words is considered to be a minimal learning target.13 Another expert such as Thornburry state about the size of vocabulary that should be mastered by second language, it is about 2000 words.14It can be stated that if non native students have about 2000 words, it can indicate that they can achieve vocabulary mastery.
According to Read, there are three components of vocabulary ability that should be mastered by students, those components are:
1. The background of vocabulary use. Vocabulary ability should draws on the various types of pragmatic, social and cultural situation which are used significantly influence the meaning.
2. Vocabulary knowledge and fundamental processes. This component consist of some aspects of vocabulary which is mentioned in four components, such as vocabulary size, knowledge of words characteristics, lexicon organization and the process to increase vocabulary knowledge by speaking and writing.
3. Meta-cognitive strategies for vocabulary use. This strategy can be used by all language users to manage the ways which they use in communication. Learners have to know and apply this strategy in communication in order to overcome their lack of vocabulary knowledge to function effectively. 15
12
Laurie Bauer, Vocabulary, (New York: Routledge, 1998), p. 12. 13
Jan H. Hulstijn, , op cit, p. 262. 14
Schott Thornburry, How to Teach Vocabulary, (Edinburgh: Pearson Education, 2002), p. 21.
15
It can be said that there are some methods in counting words that is promoted by linguist. Seashore and Eckerson in Measuring Second Language Vocabulary Acquisition stated that every different form of words in the dictionary was counted as a different word. For example, word know, knows, and knowing, all of them are different word and counted separately.16
However, according to Read, when someone takes a research about counting the number of words (in the sense of types), one of the first steps is to lemmatize the tokens (the word), so that the inflected words can be counted as the case of the same lemma as the base form.17 It can be described that words in the same lemma are counted as the base word, for example wait, waits, waited, and waiting, these words are counted as one word, that is wait.
Besides size of vocabulary, when students are learning vocabulary, they are hoped to know and use vocabulary in any possible situation. They are hoped to know the meaning in the context, in the connection with other words and in the previous knowledge. Therefore, vocabulary learning can facilitate students to improve their size of vocabulary and to apply vocabulary in any contexts.
It can be concluded the way and the strategies of vocabulary learning may
affect student’s exposure in getting vocabulary. When students can keep learning vocabulary continuously and can use it in any context, automatically their size and knowledge of vocabulary will increase.
B.
Reading
1.
The Definition of Reading
According to Alderson and Bachman “reading involves perceiving the written form of language, either visually or kinesthetically (using Braille)”.18 It can be described that reading is an activity which the reader can recognize the word in several kinds of form.
16
James Milton, Measuring Second Language Vocabulary Acquisition, (Bristol: Multilingual Matter, 2009), p. 7.
17
John Read, loc cit. 18
13
Actually, reading needs some process and the process may be complex as Harison and Salinger state that “reading is a complex activity and accomplished readers operate at a number of levels simultaneously. They are decoding and establishing meaning at the same time as they are responding to what they read, selecting particular aspects for consideration and evaluating effects”.19 Reading can be a complex activity because the reader needs to unite words by words and then try to get the meaning of the text. In addition, according to the National Council of Teachers of English (NCTE) Commission on Reading in Best Practice for Teaching Reading, reading is:
Reading is a complex, purposeful, social and cognitive process in which readers simultaneously uses their knowledge of spoken and written language, their knowledge of the topic of the text, and their knowledge of their culture to construct meaning. Reading is not a technical skill acquired once and for all in the primary grades, but rather a developmental process. A
reader’s competence continues to grow through engagement with various
types of texts and wide reading for various purposes over a lifetime.20
It is referred to those definitions that reading is a complex activity that can connects the whole capability to get and understand the meaning of the text. Therefore, the readers should become an active reader. It may be not easy for some people; but it can be achieved by practice. There are many ways to practice and to become an active reader such as the activity of guessing, predicting, checking, and asking oneself question.21 Therefore, readers are hoped to become skillful because reading consist of many process. Some people may assume that reading is passive activity, in which the reader just sit and read what they want to read; then they get what they want. Then, from those definitions of reading, it has shown that reading is an active activity, so what they assume about passive in reading is wrong.
Through reading, people can acquire new ideas and a lot of information; also can develop their reading ability. Many people provide their times to read in
19
Collin Harison and Terry Salinger, Assessing Reading Theory and Practice, (New York: Routledge, 1998), p. 89.
20
Randi Stone, Best Practice for Teaching Reading: What Award Winning Classroom Teachers Do, (California: Crown Press, 2009), p. 85.
21
order to have more knowledge or for pleasure and they choose reading as their hobbies. Reading English is one of the skills that can be mastered for those who want to improve their skill. There is much knowledge that is written in English. For that reason, it is advantageous to master reading the English text. Besides that, many students want to be able to read English text either for their careers, for study purposes or simply pleasure.22
To sum up, reading is one of four English skills that must be mastered by learners and also may become a hobby for some people. The activity of reading itself is complex because learners must decode words of the text, establish the meaning, and understand of what they read so the purpose of their reading is achieved; thus the readers are hoped to become active readers.
2.
Reading Comprehension
Achieving goals from reading can be said as the successful in reading. Sousa define reading comprehension, he states if readers are able to place the meaning of individual words into the structure and context of the entire sentence, it can be meant that they comprehend the reading material.23 It can be described that comprehensions not only know the meaning, but also the readers know the words in context and can place the word in the appropriate context of the sentence.
In comprehending the text, readers need some skills when they are reading. Linse states that “Reading comprehension refers to reading for meaning, understanding, and entertainment. It involves higher order thinking skills and is much more complex than merely decoding specific words”.24
Wallace et al, give some characteristics for good comprehension reader as follows:
1. They recall their prior knowledge of the topic they read
2. They inquire some questions about the topics before and during they read 3. They take suitable conclusions if ideas are not stated explicitly
22
Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach, (Edinburgh Gate: Pearson Education, 2001), p. 68. 23
David A Sousa, How the Brain Learns to Read, (New York: Corwin Press, 2005), p. 42. 24
15
4. They get main ideas and make a summary, then make some representation of words in the text
5. Good readers should be confident and have curiosity to carry her ideas in to reading and to question the ideas in the text.25
In addition, there are some criteria of good reading. Another expert such as Grabe in Pascoe and Wiburg (Technology and Teaching English Language Learners) state the characteristic of fluent reading. The characteristics of fluent reading should be rapid, interactive, flexible, purposeful, comprehending, and gradual.26 This characteristic can propose the reading process of EFL students to get the fluency when they are reading for academic purpose, so that they become active readers.
It can be concluded that reading comprehension is a reading activity in which the readers get the understanding and comprehension of what they read after they pass some steps such as observing and guessing what the topic, predicting what will happen in the next sentence or paragraph, asking some questions and answering or finding the appropriate answers.
3.
Kinds of Reading
There are some kinds of reading:
a. Reading aloud. This reading concern on oral matter primarily. This kind of
reading focuses on “pronunciation” than to comprehension.
b. Silent reading. It can be shown that most people do reading silently and they can comprehend the text.27
Harmer divides kinds of reading in two kinds, namely intensive reading and extensive reading.28
1. Intensive reading. This reading involves the teachers that guide students to read a text in order to achieve an understanding of the text and how the
25
Jean Wallace Gillet et all, Understanding Reading Problems, (Boston: Pearson Education, Inc, 2012), p. 166.
26
Mary Ellen Butler Pascoe and Karin M. Wiburg, Technology and Teaching English Language Learners, (Boston: Pearson Education, Inc, 2003), p. 118.
27
Geoffrey Broughton et all, Teaching English as a Foreign Language, (New York: Routledge, 1980), pp. 91—92.
28
meaning is created.29 This reading activity can be done in class by teacher’s instruction to students. Intensive study of reading texts can increase
learners’ knowledge of language characteristics and can manage their
reading strategies. Then, intensive reading can drill students to read text carefully and this reading usually takes many times because there are many things that must be learnt in several kinds.
2. Extensive Reading. This reading activity is the readers read longer texts and it is usually for pleasure and involves global understanding.30 In extensive reading activity, the readers do not have to to read a whole of the text or understand each part of sentences or paragraph, however they have to need give attention extensively to the text they read, and it can develop by strategies such as scanning and skimming, the use of content list and index.
4.
Types of Reading Text
When students are reading a text, they may not know what kind of text in front of them. The introducing of types of text probably can be started when they are in junior high school to facilitate them in understanding the function of the text they read. There are many types of reading text in English.
According to Anderson and Anderson, text has two categories, those are literary and factual, in which:
1. Literary texts consist of stories, movie scripts, limericks, fairy tales, plays, novels, song lyrics, mimes, and soap operas. This category has three main text types; those are narrative, poetic, and dramatic.
2. Factual texts consist of advertisements, announcements, internet web sites, current affairs shows, debates, recipes, reports, and instructions. The main texts that are included in this category are recount, response, explanation, discussion, information report, exposition, and procedure.31
29
Christine Nuttall, Teaching Reading Skill in a Foreign Language, new edition, (Oxford: Heinemann, 1996), p. 38.
30
Francoise Grellet, op cit, p. 4. 31
17
[image:29.595.140.515.163.653.2]Meanwhile, Hartono classifies types of text into story genres and factual genres:
Table 2.1 Social Function of Story Genres and Factual Genres32
Story Genres Social Function
Narrative To amuse, entertain and to deal with actual or various experience in different ways
News Story/ items Factual text which informs readers events of the day which are considered newsworthy or important Exemplum To dealt with incidents that are in some respect out
of the usual, point to some general value in the cultural context
Anecdote To share with others an account of an unusual or amusing incident
Recount To retell events for the purpose of informing or entertaining
Spoof To retell an event with humorous twist
Factual Genres Social Function
Procedure To describe how something is accomplished through a sequence of actions or steps
Explanation To explain the processes involved in the formation or workings of natural or socio-cultural
phenomenon
Report To describe the ways things are, with reference to arrange or natural, manmade and social
phenomenon in our environment Analytical
Exposition
To persuade the reader or listener that something is the case
Hortatory Exposition
To persuade the reader or listener that something should or should not be the case
Discussion To present (at least) two points of view about an issue
Description To describe a particular person, place, or thing Review To critique an art work or event for a public
audience
Commentary To explain the processes involved in the formation (evolution) of a socio cultural phenomenon, as though a natural phenomenon
Those are kinds of text that is seen in several contexts and function. However, from those kinds of text, there are some texts which are not learnt to
32
students. According to Pelita in her blog states, students in junior high school are hoped to understand five kinds of text; those are:
a. Narrative. It is kind of text that has function to entertain the reader or listener from the factual or imaginative experience.
b. Recount. This text has function to retell the events or incidents or activity in order to entertain and to inform something.
c. Procedure. It is kind of text that gives some direction to do or not to do something through sequence action.
d. Report. It is kind of texts that has function to extend the information about something, what is in, the result of systematic observation or analysis as the effect of nature, environment, human being, or social phenomenon.
e. Descriptive. It is kind of texts that describe the characteristics of people, particular things, or place.33
From five types of text that is mentioned above, the second grade students of junior high school are learnt three types of text such as description, narrative, and recount. However, from three kinds of texts, the writer focuses on explaining a descriptive text.
C.
Descriptive Text
1.
Definition of Descriptive Text
Descriptive text is one of the text types which may be familiar with students in several ways. Siahaan and Shinoda state that description is one of the written English texts that the writer describes the objects such as person, animal, tree, house or etc, in abstract or concrete one; and it has two components; identification and description, in which the identification is the step to identify the object that
33
19
will be described and description is the next step to describe the parts of the object such as qualities and characteristic of the object.34
In addition, Zaida states that description is a text to describe particular person, place, or thing in detail. It consists of identification, description, and conclusion. Identification is part of introducing the person/thing described; description is part that describes the person or thing in details such as its qualities or its characteristics; and the conclusion (optional) is part that concludes the topic.35 It is known, that descriptive text is to describe something such as people, place or other things. As Smith and Buscemi state that description has diversity. It can be people, place and things that are described in details and it will be concrete, specific, and vivid.36
From that definition, it can be found some students may get many objects everyday in some characteristics or they may tell the object to their friends in detail; unconsciously they know the concept of describing something.
2.
Purpose of Descriptive Text
Each kind of text has the purpose itself, includes descriptive text. To know the purposes of descriptive text are important for students. There are some purposes of descriptive text:
a. Can entertain readers, it can be found in newspaper, magazine, novel, etc b. Can convey feelings or express the emotions
c. Can relate experience and share everything they see or hear about place, people, etc
d. Can inform something because it is described in detail
34
Sanggam Siahaan and Kisno Shinoda, Generic Text Structure, (Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu, 2008), p. 89.
35
Nur Zaida, Mandiri: Practice Your English Competence for SMP/MTs Class VIII, (Jakarta: Penerbit Erlangga, 2006), p. 9.
36
e. Can persuade someone, because when something or someone is described in
well description, it can move reader’s emotions to do a particular way for instance in advertisements.37
3.
Elements of Descriptive Text
As mentioned before that description is to describe something, therefore the readers should be aware of the elements of description. Those elements of descriptive text are:
a. Concrete details. It can support, reflects, or expands a writers’ attitude or purpose by specific description.
b. Image. It is known through one of the five senses, so that the image should be concrete, literal (real and actual) description of person, physical object or sensory experience.
c. Similes. Sometimes, description compares two or more things, so that the using of like or as is often found and the comparison are different in one aspect.
d. Metaphors. It can be said as the comparison between two things that has implied comparison and usually without use of like or as.
e. Connotative language. It means that description sometimes use or combine words that create the different meaning or unreal meaning with the original version.38
Those are types of text in reading and one of them is descriptive text. To sum up, descriptive is one of the types of text that describes something such as people, place, animals, event, etc. In addition, this text is usually learnt in junior high school. The students of junior high school are suggested to know the types of text in order to know the functions of text itself.
37
Barbara Fine Clouse, Patterns for a Purpose: A Rhetorical Reader, (New York: McGraw Hill, 2006), p. 103.
38
21
D.
Previous Studies
Satihat has conducted the correlation research by the title “The Relationship between Students’ Vocabulary Mastery and Reading Comprehension Achievement”. It conducted on 30 December 2007 till May 2008 at SMPN 10
Cilegon Banten. In which the sample were about 64 students of second grade of SMPN 10 Cilegon Banten. The objective of her research was to know the correlation between vocabulary and reading of the students. She used test as instruments to collect data; the test was about vocabulary and reading. Then, the test was done in two days, first day was vocabulary test and the second one was reading test by the time given of both test was about 60 minutes. To analyze the data, she used Pearson Product Moment as formula. And the result of her research was 0,734; it means that there is positive correlation between student’s vocabulary and their reading. There are the similarity and the differences between this
research and the writer’s research. The similarity of this study is both of them concern on the correlation between vocabulary and reading comprehension. Then, the instruments which was used also same, both of them used vocabulary and reading test as the instrument. Meanwhile, the differences of both studies are this study concerns on all kind of reading text, but the writer’s study concern on descriptive text only. In addition, this study was conducted on two days, and the sample had to answer the questions of both test in the different days; however the
writer’s study provided one day to give both tests for the samples.
According to her, it can be concluded that lexical access seemed to be a critical factor in enhancing comprehension. Therefore, she promoted comprehension by three factors; first was the amount of practice that given to the words, second was breadth of training in the use of the words and the third was the degree to which active processing is encouraged. The similarity of this study is both of them concern on the influence of vocabulary to reading comprehension skill. Meanwhile, the differences between both studies is this study emphasizes on teaching vocabulary by using flash card then applying it to practice reading; but in
writer’s study the focuses on the results which students got in both scores of vocabulary and reading test. Then, another difference is on applying the research. In this study, Mezynski identified 8 studies from different sample, and gave some treatments for the sample by using flash card in order to improve vocabulary on reading comprehension skill; however the writer’s study is emphasized on the result of tests not on the treatment, because there is no treatment in the correlational study.
The third is the research that was conducted by Syamsiah, Andayani and Rohmadi; they are students of Sebelas Maret University Surakarta. They conducted the research by the title “Hubungan antara Penguasaan Kosakata dan Motivasi Belajar dengan Kemampuan Membaca Cerita (Survei pada siswa kelas V SD Negeri di kecamatan Jatiroro).” The sample that was taken were about 63 students of 33 primary schools in Jatiroro by sampling technique was random sampling. This research was conducted as long as six months from June to November. The variable that was used in this research was three variables;
vocabulary mastery, students’ motivation, and reading ability. The purpose of this
research is to know the correlation between vocabulary mastery and the ability in
reading story, the correlation between students’ motivation between the ability in
reading story, and the correlation between vocabulary mastery and students’
23
of this research showed that both of vocabulary mastery and students motivation have correlation with students’ ability in reading story. Both of vocabulary
mastery and students’ motivation gave contribution about 43.5% for students’ reading ability. The similarities of both studies are both of them focus on the correlation between vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension. Another similarity is on the results of both studies, in which both of them show the positive correlation between the variables. Otherwise, the differences of both studies are there are three variables in this study such as vocabulary mastery, students’
motivation and reading skill; but in the writer’s study there are only two variables
such as vocabulary mastery and reading skills. Then, other differences are this study use test and questioner as the instruments; but in the writer’s study only use test as instrument. Besides that, the differences are on the sample of the research. The sample of this study is 63 students from 33 primary schools; but the sample
of the writer’s study is only 30 eight grade students of a junior high school.
E.
Conceptual Framework
Vocabulary is one of the important aspects of learning language. Without vocabulary, process of language learning cannot be achieved. In other words, vocabulary can be said as media to facilitate students in learning language especially achieving four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing). Therefore, students are hoped to have enough vocabulary to achieve those skills. Especially vocabulary can be found and achieved more in reading.
Reading is one of four English skills that must be mastered for students. The students should be accustomed to read in order to gain many information of the text they read. Besides that, another benefit can be gotten by reading such as improving or adding vocabulary. Therefore, vocabulary and reading cannot be separated and have may have relation each other. There are many texts that can be read to practice or improve vocabulary and reading ability. One of them is descriptive text.
students of junior high school. Students should master descriptive text as mentioned in curriculum, so that it can facilitate students in understanding an object in detail. To know how understand students in descriptive text, both of test vocabulary and reading of descriptive text can be used as instruments.
Therefore, based on the above explanations, it can be known that vocabulary probably has the great deal with reading. Thus, it can be supposed that if students have many vocabularies, they can comprehend descriptive text; otherwise if students have a few of vocabularies, they cannot comprehend descriptive text.
F.
Hypothesis
Based on the problems and theory that have been mentioned, the hypothesis will be stated as follows:
First, alternative hypothesis (ha): there is a positive correlation between
student’s vocabulary and their reading comprehension of descriptive text.
Second, null hypothesis (ho): there is no correlation between student’s
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Place and Time of the Research
1. Place of the Research
The research was conducted at MTs. Syamsul ‘Ulum that is located on Jl. Bhayangkara, Gunung Puyuh, Kota Sukabumi.
2. Time of The Research
The time of the research was on Wednesday, November, 27th 2013.
B.
Subject and Object of the Research
1. Subject of the Research
The subject of the research was 30 students in the second grade C (8C) of MTs Syamsul ‘Ulum academic year 2013/2014.
2. Object of the Research
The object of the research was descriptive text, which was shown in vocabulary and reading comprehension that will be tested.
C.
Method of the Research
The purpose of this research was to know and to find the correlation between student’s vocabulary and their reading comprehension of descriptive text. Therefore the quantitative research was selected and the method that was applied was correlational method. Correlational method associate two or more variables to know the relation between those variables.1 In order to know the correlation between those variables needs statistic. Because according to Suharsimi, statistic can be used to compare the result of two different variables to determine the relation between those variables, and this is called as coefficient correlation.2 There were two variables in this research; those were reading comprehension as dependent variable (Y) and vocabulary as independent variable (X). Therefore,
1
L.R. Gay, et al, Educational Research Competencies for Analysis and Applications, (Boston: Pearson Education International, 2009), p. 196.
2
Pearson Product Moment was used in this research to know the correlation of both variables.
D.
Population and Sample of the Research
The population of this research was about six classes of second grade which consist of 177 students. Because the number of population was too big, the writer considered to take sample for collecting data. In taking sample, the writer used purposive sampling techniques because of some considerations. The first thing was the ability of the population was same. The 8C class was selected as sample of this research because this class has the same ability with other classes, so that this class can be representative one. The consideration of practicality and efficiency of time, energy, and fund could be another issue in taking this sample.
E.
Instruments of the Research
In conducting a research, it is necessary to use an instrument for collecting data. The instruments can be a test, interview or questioner based on the research need. In this research, the instruments which were used were test and the result of the test. Because the variables were vocabulary and reading, the test consisted of vocabulary test and reading test.
1. Vocabulary test.
The questions of vocabulary test were compiled from second grade books and other sources that were appropriated with their level and their material. Then, kinds of vocabulary tests were to find the synonym, antonym, and meaning based on the context of the descriptive sentences.
2. Reading Test
Students were asked to read and answer the questions of reading. The
reading material and its question were selected from students’ book and
27
The questions of vocabulary and reading that were compiled were about 30 questions each of them, so the total was 60 questions (appendix 3 and 4). Before doing the research, those questions were tried out to other students that had the same level with the sample of the research in order to know the quality of the instruments such as validity, reliability, index difficulty and discriminating power. So that the instruments are appropriate for the sample of the research.
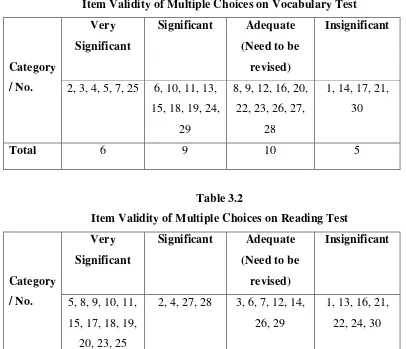
[image:39.595.111.513.342.517.2]After conducting the try out, the writer found the result of vocabulary and reading score and put it into Anates application to count the quality of the questions. The result shown some questions of vocabulary and reading that were valid, very significant, significant, and adequate (should be revised).
Table 3.1
Item Validity of Multiple Choices on Vocabulary Test
Category
/ No.
Very
Significant
Significant Adequate
(Need to be
revised)
Insignificant
2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 25 6, 10, 11, 13, 15, 18, 19, 24,
29
8, 9, 12, 16, 20, 22, 23, 26, 27,
28
1, 14, 17, 21, 30
[image:39.595.110.516.344.693.2]Total 6 9 10 5
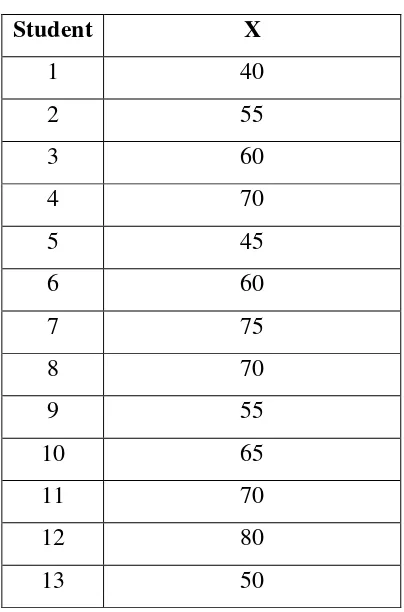
Table 3.2
Item Validity of Multiple Choices on Reading Test
Category
/ No.
Very
Significant
Significant Adequate
(Need to be
revised)
Insignificant
5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 15, 17, 18, 19,
20, 23, 25
2, 4, 27, 28 3, 6, 7, 12, 14, 26, 29
1, 13, 16, 21, 22, 24, 30
Total 12 4 7 7
From that result of the quality of both tests, the writer did not use all questions to be tested for sample. The writer decided to take 20 questions for each test. In point insignificant, the writer did not use it because it was not valid question. The writer used very significant and significant point, also adequate question after revising the question. The questions that were used for vocabulary test were:
Table 3.3
The Questions Number of Vocabulary Test
No
Very Significant Significant Adequate (Need to
be revised)
2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 25 6, 10, 11, 13, 15, 18, 19, 24, 29
8, 9, 12, 16, 20, 22, 23, 26, 27, 28
In column very significant and significant, all questions were used. However, in column adequate, only five questions with the bold sign that were used after they were revised. So, the total questions that were used were 20 questions.
Like vocabulary test, reading test also used 20 questions for the sample of the research. These were the questions of reading test that were used:
Table 3.4
The Questions Number of Reading Test
No
Very Significant Significant Adequate (Need to
be revised)
5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 15, 17, 18, 19, 20, 23, 25
2, 4, 27, 28 3, 6, 7, 12, 14, 26, 29
[image:40.595.116.516.549.632.2]29
F.
Technique of Collecting Data
1. Observation
The first thing of collecting data that was done by the writer was observation. The writer observed the school by meeting with the headmaster and the English teacher of second grade in this school. Then, the writer asked about English class, the situation, the condition, and students when they were studying English.
2. Test
After the writer observing and selecting the instrument that was suitable for students, it was the time to select data from samples. In this section of collecting data, the students were asked to take vocabulary and reading test. Testing was conducted in a same day. First test was vocabulary that provided time about 40 minutes and the second was reading test by the same time about 40 minutes. Students must answer 20 questions that were provided in vocabulary and reading test.
H. Technique of Analyzing Data
In analyzing data the writer used Pearson Product Moment. Pearson Product Moment is a technique that was created by Karl Pearson and this technique is often used to find the correlation between two variables.3 This is the formula of Pearson Product Moment:4
=
√{ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ }{ ∑ ∑ }In which:
correlation of the score of each item
N = the number of the subject
∑ score in each item
∑ from each subject
∑ = the sum of the square of the total score in each item
3
Anas Sudijono, Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 2010), p, 190
4
∑ = the sum of the square of the total score from each subject
∑ the sum of the multiple of the score from each subject with total
score.
The next step was to test the significance of the variables in order to know the meaning of the correlation between variable X and Y. Therefore, the result of
PPM was tested by formula of to = √
√
.
5
In which: to = t value
r = the result of correlation coefficient n = number of sample
Then, to know how many contributions of the dependent variable to independent variable, it can be known by this formula: KP = x 100%.6
In which: KP = value of determinant coefficient r = value of correlation coefficient
I. Statistic Hypothesis
In the correlational research, the statistic hypothesis can be stated as follows: Ha: ro > rt
Ho: ro < rt
ro = the result of Pearson Product Moment rt = r table (Pearson Product Moment Table)
Ha: The alternative hypothesis is accepted, means that there is correlation
between students’ mastery in vocabulary and their reading comprehension.
Ho: The null hypothesis is accepted, means that there is no correlation
between students’ mastery in vocabulary and their reading comprehension.
5
Riduwan and Sunarto, Pengantar Statistika: untuk Penelitian Pendidikan, Sosial, Ekonomi, Komunikasi dan Bisnis, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2011), p. 81
6
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
A.
The Description of Data
As the purpose of this research, to know the correlation between students’
mastery in vocabulary and reading comprehension of descriptive text, the writer used the quantitative research by the correlational method. Therefore, calculations of statistic were needed.
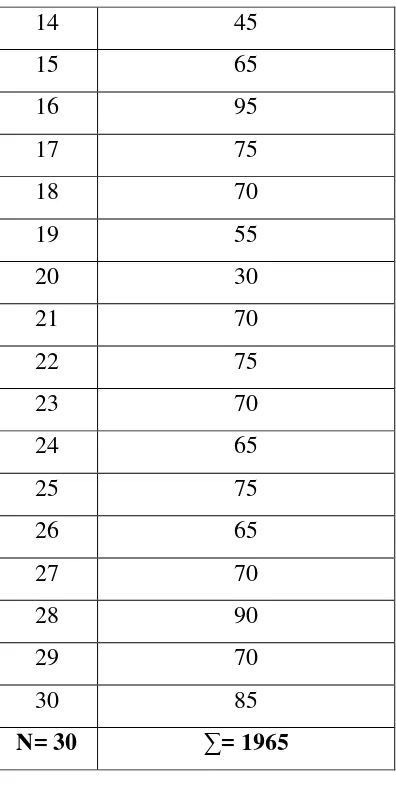
[image:43.595.211.413.437.743.2]The instrument of this research was two kinds of test; vocabulary and reading test. Both of these tests consisted of 20 questions, so the sample was asked to take both of these tests. Then, after conducting the research for 30 students as the sample, the writer got the result of vocabulary and reading test. For each question, the writer gave value 5 for correct answer and 0 for wrong answer. These are the result of both tests:
Table 4.1
Student’s Vocabulary Score
Student X
1 40
2 55
3 60
4 70
5 45
6 60
7 75
8 70
9 55
10 65
11 70
12 80
14 45
15 65
16 95
17 75
18 70
19 55
20 30
21 70
22 75
23 70
24 65
25 75
26 65
27 70
28 90
29 70
30 85
N= 30 ∑= 1965
From that table, the lowest score of vocabulary test was 30 and the highest score was 95. Then, the mean score of this test was 65.5.
[image:44.595.214.412.110.503.2]Table 4.2
Student’s Reading Score
Student Y
1 45
2 55
3 95
4 90
33
6 70
7 65
8 90
9 50
10 85
11 70
12 95
13 55
14 40
15 75
16 90
17 85
18 80
19 50
20 55
21 75
22 60
23 65
24 70
25 75
26 60
27 75
28 100
29 70
30 80
N= 30 ∑= 2120
B.
The Data Analysis
Having finished the quantitative research by using vocabulary test and reading comprehension test, the writer used statistic calculation of the Pearson Product Moment Formula to analyze the data of both tests. To make easier, the writer made a table with six columns; those were (No), (X), (Y), (X2), (Y2), and (XY). Column X was for vocabulary score of the sample, column Y was for reading score of the sample, column X2 was for quadrate of each score in column X, column Y2 was quadrate for each score in column Y, and column XY was for the result of multiplying score X and Y.
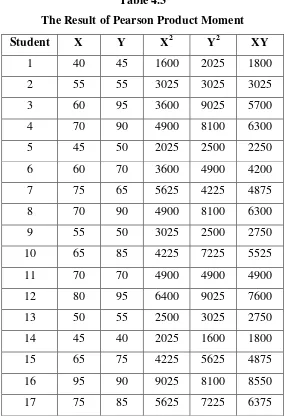
[image:46.595.169.457.331.751.2]These were the table of the above explanations:
Table 4.3
The Result of Pearson Product Moment
Student X Y X2 Y2 XY
1 40 45 1600 2025 1800
2 55 55 3025 3025 3025
3 60 95 3600 9025 5700
4 70 90 4900 8100 6300
5 45 50 2025 2500 2250
6 60 70 3600 4900 4200
7 75 65 5625 4225 4875
8 70 90 4900 8100 6300
9 55 50 3025 2500 2750
10 65 85 4225 7225 5525
11 70 70 4900 4900 4900
12 80 95 6400 9025 7600
13 50 55 2500 3025 2750
14 45 40 2025 1600 1800
15 65 75 4225 5625 4875
16 95 90 9025 8100 8550
35
18 70 80 4900 6400 5600
19 55 50 3025 2500 2750
20 30 55 900 3025 1650
21 70 75 4900 5625 5250
22 75 60 5625 3600 4500
23 70 65 4900 4225 4550
24 65 70 4225 4900 4550
25 75 75 5625 5625 5625
26 65 60 4225 3600 3900
27 70 75 4900 5625 5250
28 90 100 8100 10000 9000
29 70 70 4900 4900 4900
30 85 80 7225 6400 6800
∑ = 30 1965 2120 134675 157550 143900
Those are the result of the classifications of each score. After getting the above results, it was the time to calculate the equations to Pearson Product Moment Formula:
r = ∑ –
√{ ∑ ∑ }{ ∑ }
=
√{ }{ – }
=
√{ }{ }
=
√
=
=
ro = 0.74
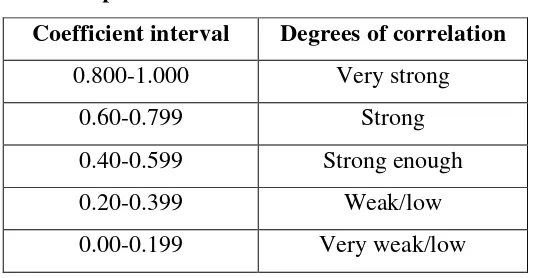
That was the result about 0.74 of Pearson Product Moment, the next step was to find out how much significant the result of correlation. To know the
significance of the correlation, the writer used “r” table by significance of 5% and 1%. Before going to “r” table, the writer found out the degree of freedom by the following formula: df = N-2
In which: df : degrees of freedom
N : Total number of respondents
Therefore, df = N - 2 30 - 2 = 28. It can be seen on Pearson Product Moment Table, that 28 at the degree of significance of 5% is 0.374.
Based on the calculation of ‘ro’ and ‘r’ table, it can be meant that:
In 5% : ro > rt = 0,74 > 0.374.
In addition, the result of coefficient correlation (ro) was also compared to ‘t’
table in order to test significance of the variables. This step was used to know the meaning of the correlation variable X (vocabulary) to variable Y (