Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Rizki Lutfiah
- Pengajar:
- Dr. M. Farkhan, M.Pd
- Sekolah: Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta
- Mata Pelajaran: English Language Education
- Topik: Improving Students' Ability in Writing Recount Text by Using Mind-Mapping Technique
- Tipe: skripsi
- Tahun: 2011
- Kota: Jakarta
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. INTRODUCTION
The introduction outlines the background of the study, emphasizing the importance of English as an international language and the challenges students face in writing, particularly recount texts. The study aims to address these challenges through the implementation of mind-mapping techniques to enhance students' writing skills in recount texts. The significance of the study is highlighted, focusing on its potential contributions to teaching practices and student learning outcomes.
1.1 Background of the Study
The globalization of English necessitates its mastery, particularly in Indonesia, where English is a compulsory subject. Writing, especially recount texts, poses significant challenges for students, leading to a need for effective teaching strategies. The study aims to explore the potential of mind-mapping techniques in improving students' writing skills.
1.2 Formulation of the Problem
The study seeks to answer whether mind-mapping can improve students' writing skills in recount texts and how this teaching method can be effectively implemented in the classroom.
1.3 Scope and Limitation of the Study
The research focuses on the 8.2 class of SMPN 2 Kota Tangerang Selatan, specifically on improving writing skills in personal and procedural recount texts through mind-mapping techniques.
1.4 Objective of the Study
The primary objective is to determine the effectiveness of mind-mapping in enhancing students' recount text writing skills, as well as to evaluate the implementation process of this technique in teaching.
1.5 Significance of the Study
The study offers insights for teachers seeking alternative methods to enhance writing skills, provides students with tools to overcome writing challenges, and contributes to the overall improvement of educational quality at SMPN 2 Kota Tangerang Selatan.
1.6 Definition of Key Terms
Key terms such as 'recount text' and 'mind-mapping technique' are defined to ensure clarity and understanding throughout the study.
II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This section provides a comprehensive overview of writing, recount texts, and the mind-mapping technique. It discusses the general concepts, characteristics, and processes of writing, the specific features and purposes of recount texts, and the principles behind mind-mapping as a pedagogical tool. The relevance of these theories to the study's objectives is emphasized.
2.1 Writing
Writing is described as a complex skill that involves various competencies. It is essential for communication and requires practice to master. The section outlines the characteristics of good writing, the purposes of writing, and the writing process, emphasizing that effective writing is a structured and thoughtful endeavor.
2.2 Recount Text
Recount texts are defined as narratives that retell past events, serving to inform or entertain. The section categorizes recount texts into personal, procedural, and biographical types, detailing their linguistic features and schematic structures. This framework is crucial for understanding the specific writing task students are engaged in.
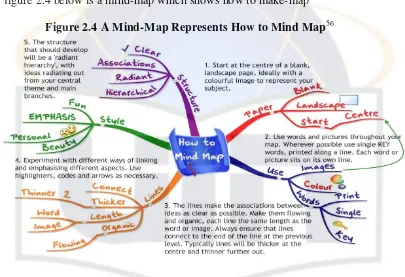
2.3 Mind-Mapping Technique
Mind mapping is introduced as a visual tool that aids in organizing thoughts and ideas. This subsection discusses its structure, functions, and benefits in the writing process, positioning it as a valuable strategy for helping students generate and organize ideas effectively.
2.4 Teaching Recount Text by Using Mind-Mapping
The integration of mind-mapping in teaching recount texts is explored, highlighting its potential to enhance creativity and engagement among students. The pedagogical implications of using mind maps in the classroom are discussed, reinforcing the study's focus on improving writing skills.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This section outlines the research design and methodology used in the study, including the collaborative classroom action research approach. It details the phases of the research process, the data collection techniques employed, and the criteria for evaluating the success of the action research.
3.1 Method of the Research
The study employs a collaborative classroom action research method, allowing for iterative cycles of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. This approach facilitates continuous improvement in teaching practices and student learning outcomes.
3.2 Subject and Object of the Research
The subjects of the research are the students of the 8.2 class at SMPN 2 Kota Tangerang Selatan. The focus is on their ability to write recount texts, thereby making the students the central participants in the study.
3.3 Writer’s Role on the Research
The writer collaborates closely with the English teacher to implement the mind-mapping technique effectively. This partnership is crucial for gathering qualitative and quantitative data throughout the research process.
3.4 Time and Place of the Research
The research is conducted during the academic year 2010/2011 at SMPN 2 Kota Tangerang Selatan, providing context for the study and its findings.
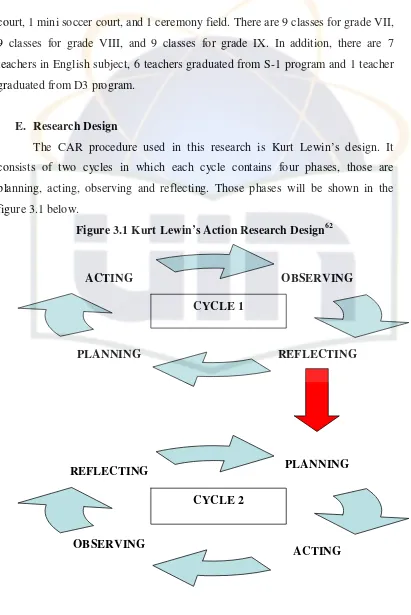
3.5 Research Design
The research design follows Kurt Lewin's model of action research, comprising two cycles of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. This structured approach ensures systematic data collection and analysis.
3.6 Classroom Action Research Procedure
The procedure is broken down into phases: planning, acting, observing, and reflecting, each critical for assessing the effectiveness of the mind-mapping technique in improving writing skills.
3.7 Technique of Collecting Data
Data collection methods include observations, interviews, and tests (pretest and posttest), providing a comprehensive understanding of students' progress and the impact of the intervention.
3.8 Technique of Data Analysis
Data analysis techniques are outlined to ensure reliable interpretation of qualitative and quantitative data, allowing for informed conclusions about the effectiveness of the mind-mapping technique.
3.9 Validity of Data
The validity of data is addressed to ensure that the findings accurately reflect the students' writing abilities and the effectiveness of the teaching method.
3.10 Criteria of the Action Success
Success criteria are established based on improvements in students' writing scores and their engagement during the learning process, providing measurable outcomes for the research.
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the findings of the research, including pre-intervention data and the results of the action research cycles. It discusses the observed improvements in students' writing abilities and their experiences with the mind-mapping technique.
4.1 Before implementing the Action
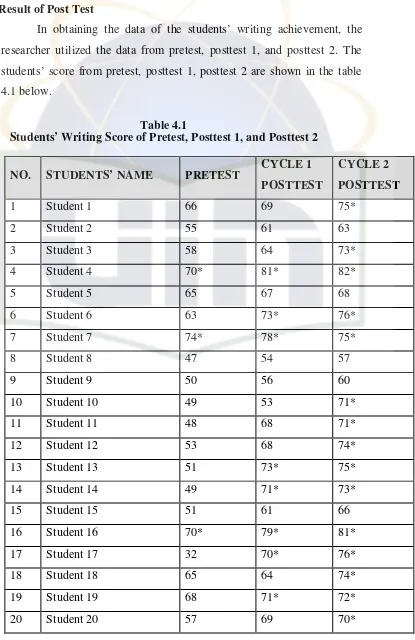
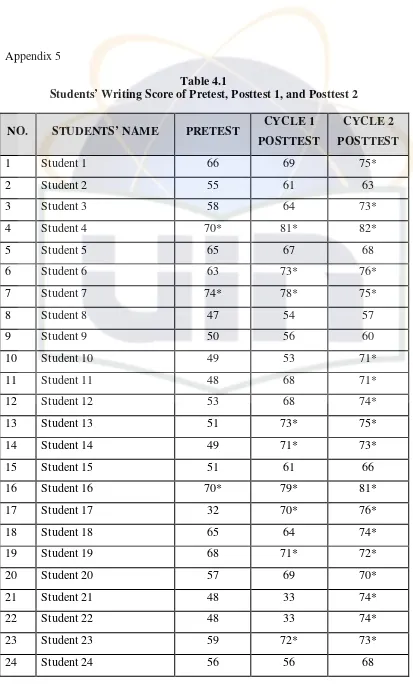
Initial observations and interviews reveal students' difficulties in writing recount texts, highlighting the need for effective interventions. Pretest scores indicate low writing proficiency, providing a baseline for measuring improvement.
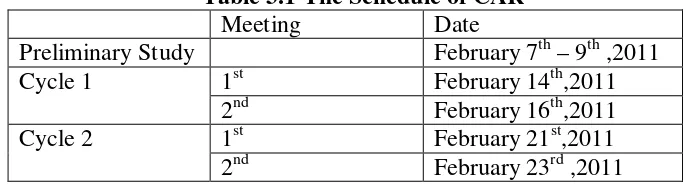
4.2 Implementation of Classroom Action Research (CAR)
The implementation of the CAR is detailed, including the planning, acting, observing, and reflecting phases for both cycles. Each cycle's outcomes are analyzed to assess the effectiveness of the mind-mapping technique.
4.3 Discussion of the Data after Classroom Action Research (CAR)
Post-intervention data indicate significant improvements in students' writing scores and engagement levels. The discussion emphasizes the positive impact of mind-mapping on students' ability to generate and organize ideas.
4.4 Interpretation of the Test Result
The interpretation of test results reveals a clear upward trend in students' writing abilities, supporting the hypothesis that mind-mapping effectively enhances writing skills in recount texts.
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study, reaffirming the effectiveness of mind-mapping in improving students' writing skills in recount texts. Suggestions for future research and practical applications of the findings in educational settings are provided.
5.1 Conclusion
The study concludes that the mind-mapping technique significantly improves students' abilities in writing recount texts. The structured approach to organizing ideas leads to better coherence and creativity in students' writing.
5.2 Suggestion
Future research should explore the long-term effects of mind-mapping on writing skills across different text types. Additionally, teachers are encouraged to incorporate mind-mapping techniques in their writing instruction to enhance student engagement and performance.
Referensi Dokumen
- Testing in Language Programs: A Comprehensive Guide to English Language Assessment ( James Dean Brown )