YAHAYA1, S.H., HASIB2, H., KAMELY3, M.A., MD FAUADI4, M.H.F. and YUHAZRI5, M.Y.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka
Hang Tuah Jaya, 76100 Durian Tunggal, Melaka, MALAYSIA
1
Now adays, solid w aste management continues to be view ed as a ser ious topic for Malaysian gover nment. Effect of the alar ming rate of w aste gener ated due to the gr ow in population, affluence and changing lifestyles in Malaysia, the envir onmental r estr ictions seem to have been encounter ed w hich included the str ingent influence over w aste disposal sites, r esour ce r estr ictions, for instance; emphasizing the aw ar eness of the public about the depletion of r esour ces natur ally, the natur al disaster s' issues such as global w ar ming that caused by the gr een house effect. In other per spectives, the impr oper w aste management w ill face ser ious biohazar ds, occasionally; it might even cause death. These issues ar e gener ally addr essed as the r oadblock tow ar d the gover nment’s effor ts to attain sustainable development appr oach vision 2020.
Ros (2009) explained that the over all solid w aste gener ated per day is 18000 tones in Malaysia; sadly most of the w astes gener ated ar e dumped illegally and disposed in landfills (Figur e 1). Consequently, w aste management is a vital issue that needs the effectual solutions and r ecycling is alw ays view ed as a cr ucial aspect of an effective and efficient solid w aste management system. Billatos and Basaly (1997) said that r ecycling is the r euse of pr oducts in the same capacity for w hich they w er e or iginally manufactur ed. While Tchobanoglous et al., (1993) discussed that r ecycling involves thr ee main steps, those ar e (1) the separ ation and collection of w aste mater ials, (2) the pr epar ation of these mater ials for r euse, r epr ocessing and r emanufactur e and finally (3) the r euse, r epr ocessing and r emanufactur e these mater ials (Figur e 2). In addition, pr ocessing plays an impor tant r ole in impr oving the quality of r ecycling system (Tchobanoglous et al., 1993; Ander son and Bor din, 2005; Chenayah et al., 2007). In this study, thr ee r ecyclable mater ials ar e mostly concer ned to explor e such as discs, paper and plastics. Kosior et al., (1997) found that 10 % of the pr oduced discs ar e r ejected and disposed in landfills. Discs contain the non-biodegr adable polycar bonate, heavy metals and har mful dyes w hich lead to the ser ious pollution pr oblems w hile for the w aste paper s such as old new spaper , car dboar d, high-grade paper and mixed paper (Tchobanoglous et al., 1993) as w ell as in plastics have seven families that can be r ecycled (Table 1) as mentioned by (Vesilind et al., 2002).
Pr esently, ther e is only the existing of the conventional (manual) r ecycling system for the above mater ials w her eas not for the developed syst em in this study. For the syst em’s uniqueness, Mer it Point Incentive (MIP) system has been fully engaged to encour age the public use this E-r ecycling system efficiently. The outlines of this study mainly consist of intr oduction, follow ed by the development of E-r ecycling system model, continued w ith r esult and discussion and finally conclusion and the r elated suggestions for futur e w or k.
A BSTRA CT
Lately, M alaysians tend to generate wastes at an alarming rate, for instance; discs, paper and plastics. Abreast of that, the conventional recycling systems that have been constructed in M alaysia typically are not widely marketed and are lacking of practical applications. This study comes with an intention of concentrating on the improvement of this particular conventional renewed E- recycling system model that includes database system (generally known as M erit Point Incentive (M PI) system) and CAD model. Due to its applicability, the model is examined by Linear Static and Fatigue analyses. The comparison (cost efficiency) amongst the conventional and E- recycling systems are shown throughout this study.
Key w ords: Conventional system, E-recycling system, M PI system, CAD model.
Figur e 1 : Almost all landfills in Malaysia ar e open dumps t hat have no pollution contr ol measur es (Tan, 2004).
Reduction
Reuse
Recycling and composting
Incineration
Landfill
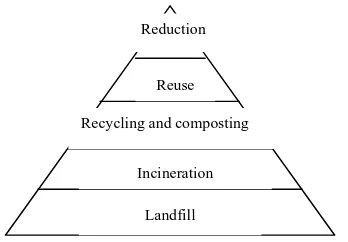
Figur e 2 : Hier ar chy of the i ntegr ated soli d w aste management (Hei mlich et al., 2009).
Table 1: Seven plastic families (Vesilind et al., 2002)
Code System Chemical Name Abbr eviation
Polyethylene Ter ephthalate PET / PETE
High-Density Polyethylene HDPE
Polyvinyl Chlor ide PVC
Low -Density Polyet hylene LDPE
Polypr opylene PP
Polystyr ene PS
Mixed Plast ic O
2.0 DEVELOPMENT OF E-RECYCLING SYSTEM MODEL
2.1 MPI System
With pur pose to activate the MPI system, r ecycler w ill be asked to ent er his/ her user name and passw or d. In this system, notepad (text file) has been used as a database to stor e the login details of the r ecycler s. The system w ill then identify w hether the r ecycler is r egister ed or vice ver sa. If the r ecycler is r egister ed, the system w ill display “found” and r ecycler w ill be asked to thr ow the r ecyclable mater ials into the r ecycle bin. Else, if the r ecycler is unr egister ed, the system w ill display “not found”. In or der to use MPI system, he/ she has to cr eate a user name and passw or d w hich ar e ver y simple and convenience. After that, r ecycler w ill be inquir ed to thr ow his/ her r ecyclable mater ials into the r ecycle bin. The w eight of the r ecyclable mater ial thr ow n and the total points that ar e mer ited w ill be displayed on the scr een. The MPI w ill be standar dized w her e no matter w hich types of r ecyclable mater ials either discs, plastics or paper s. Recycler s w ill be mer ited w ith the points in accor dance to its w eight. To simplify this system, the implementation of r ecycler car ds is eliminated.
Display the weights for recyclable materials and total points earned Enter the username and password of a
recycler
Did recycler is register?
Display instruction to ask recycler to throw their recyclable material
Weighing recyclable materials by weight sensor fixed in the base of recycle bin
Receipt is printed
Register by add a username and
password
Throw the recyclable materials into recycle bin
End
Display recycler is not found
Yes No
Get the receipt
Figur e 3 : Pr ocess flow diagr am i n MPI system.
2.2 E-recycling CAD Model
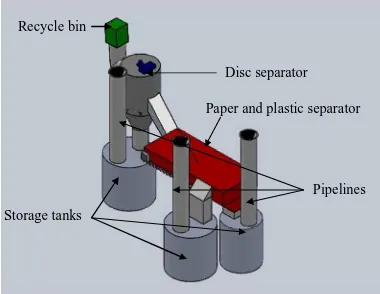
In r efer ence to Concept Design and Selection (CDS), the model may consist of r ecycle bin, w eight’s evaluation, disc separ ator , paper and plastic separator , pipelines, stor age tanks, docking station and pneumatic r efuse collection system (Figur e 4). For its pr ocedur e, the r ecyclable mater ials (discs, paper and plastics) ar e thr ow n into the r ecycle bin w her e the evaluation of w eight for these mater ials w ill be gener ated thr oughout the w eigh sensor that is fixed at the bottom of the r ecycle bin.
Hence, a door on the bottom of the r ecycle bin w ill open and the r ecyclable mater ials w ill dr op into the pipeline and go thr ough the disc separ ator . Ther e ar e eight sets of blades (w ith the gaps) in the disc separ ator that only allow the disc’s size. The discs ar e then separ ated fr om the w aste str eam and dr opped into the gap betw een the blades (w ith the constant r otating motion), and str ictly stor ed in the tanks. Pneumatic r efuse collection system is used to collect the discs thr ough the docking station. The pr ocedur es r emain the same as for the paper s and plastics. The follow ing figur e depicts the E-r ecycling CAD model using CDS and the tool, Solidw or ks. The explor ations of the r esulting of MPI system and this CAD model analysis ar e completely explained in the next section.
Recycle bin
Storage tanks
Disc separator
Paper and plastic separator
Pipelines
3.0 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Resulting of MPI System
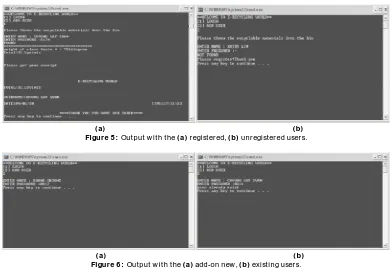
In this MPI system, w eight of the r ecyclable mater ials w ill cer tainly be automatically gener ated, and it actually has been standar dized for all sor t of r ecyclable mater ials. Basically, the system compr ises tw o par ts, w hich ar e the r egister ed user login and add user (still not r egister ed). As a w ay to keep the login details on the user s, text file is utilized as the database w her e w hen the new user name and passw or d ar e added, it w ill be automatically updated. In addition, it w ill also automatically detect for the user name that has been used and the user must use other user names except the existing name. The follow ing figur es ar e the outputs of the C++ pr ogr amming in MPI system.
(a) (b) Figur e 5 : Output w i th the (a) r egist er ed, (b) unr egi ster ed user s.
(a) (b) Figur e 6 : Output w i th the (a) add-on new , (b) existi ng user s.
The main pur pose of MPI system is to incentivize the user s w ho consistently use this r ecycling system. Besides, in r esponse to simplify the mer it point system, the r eceipt pr inting concepts ar e applied. This is due to the implementation of r ecycler car d w ill r educe the per centage of publics to r ecycle. As it is a difficult task for the public to apply and become a r ecycler car d holder . The pr inted r eceipt can be used to exchange the cash or the r elated token fr om the gover nment such as Majlis Per bandaran Pulau Pinang (MPPP) or in the post office. Apar t fr om that, MPI system is also used to eliminate the middleman. Hencefor th, the w in-w in system needs to be consider ed. Suppose the r ecyclable mater ials ar e RM 1.00/ kg. If publics sell the r ecyclable mater ials to the middleman, they w ill be paid w ithin the r ate of RM 0.20/ kg.
At the same time, the middleman w ill be paid w ith RM 1.00/ kg by selling the collected r ecyclable mater ials to the r ecycle center s. In this situation, if the middleman is eliminated, publics and gover nment w ill be benefited in this w in-w in situation, w her e publics can be paid RM 0.50/ kg that is RM 0.30/ kg mor e than w hat the middleman gives to them. While for the gover nment, may save RM 0.50/ kg fr om paying to the public dir ectly and not thr ough the middleman. It is unnecessar y to cr eate a database system to keep the details of the user s since the concept based on “bonus link” is implemented.
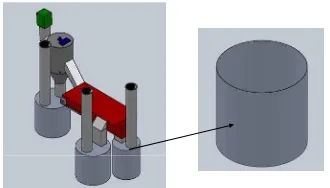
3.2 Storage Tank Model Analyses
Due to the str uctur al efficacy, stor age tank (Figur e 7) is investigated thr ough Linear Static and Fatigue Analyses. Both analyses ar e fr equently applied in physical str uctur es, for instance; str ess, for ce and displacement distr ibutions (Yahaya et al., 2012). Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is the most common tools for the analysis w hile Stainless Steel Grade 304 (AISI 304) is chosen for the selection of mater ial in this study. The character istics of AISI 304 ar e depicted in Table 2.
5.4.1 Finite Element Analysis
3.2.1 Simulation results and its safety factor
The discussion begins w ith the pr esentation of the gener ated r esults using Linear Static Analysis.
Table 4 shows the maximum Von Mises stress (υmax) distr ibutions in the model thr oughout the
r epeated loads, F. Hence, the safety factor (Sf) or also know n as a design mar gin (Michalopoulos
and Babka, 2000) can be der ived using Eq. (1) (Cliffor d et al., 2008; Shenoy, 2004) and w her e the yield str ength of AISI 304 is able to be found in Table 2.
3.2.2 Fatigue predictor using first-order newton interpolating polynomial
In r efer ence to the failur e mode above, let assume that the fatigue star ts to occur if Sf = 1.
Due to this Sf, the r elated load w ill be pr edicted using the fir st-or der New ton inter polating
polynomial. The gener al for m of this polynomial such as (Chapr a and Canale, 2010)
) 2010). The net oper ating cost of r ecycling activities is expr essed as,
Value
Ther e ar e a few assumptions ought to be made typically the pr ocessing cost is equal to RM350 per ton; labor cost equivalents to RM350 per ton; tr anspor tation cost is RM 70 per ton; r ecover ed r ecyclable mater ials sale cost is estimated as RM350 per t on as w ell as tot al w aste gener ated is 100,000 tons per year and the r ecover ed r ecyclable mater ials almost 40,000 tons per year . By applying Eq. (4), the net cost of conventional appr oximates to RM140,000,000 w hile for the cost of E-r ecycling system is near ly to RM63,000,000. This estimation r epr esents that E-r ecycling system oper ates mor e efficiently than the conventional system. Both systems have the differ ence appr oximately RM77,000,000. Thus, the calculation of efficiency is show n as in Eq. (5) (Khai et al., 2007). After applying this equation, cost efficiency for E-r ecycling system appr oaches to 55% of the saving effectiveness. Ther efor e, this pr oposed system can be concluded clear ly as the acceptable and r elevant system r egar ding the cost-saving and convenient to use.
%
This study has pr esent ed an E-r ecycling system model t hat involves MPI system and CAD model. MPI system is intr oduced to encour age the user s to use this E-r ecycling system. Cur r ently, this E-system is developed par ticular ly w astes such as plastic, paper and disc. CAD model is designed for the simulation pur pose using Linear Static and Fatigue Analyses. As a r esult, the st or age tank design r emains the same str uctur al (in safety mode) if F < 29.8893E05 kN. Resulting fr om its cost efficiency, the developed syst em has 55% of the cost-saving w hen compar e to the conventional system appr oach. In futur e, CAD model w ill be impr oved w hich ideal in all fields such as households, industr ies and tow ns. In addition, the pr ototype of an E-r ecycling system model may build. Apar t fr om that, it is equally suggested to constr uct the pr ototype model w ith full-size and fully functional that w ill be used to demonstr ate the pr acticality of this developed system.
ACKNOWLEDMENTS
REFERENCES
[ 1] Ander son, H. and Bor din, M.H. (2005): The Consumer ’s Changing Role: The Case of Recycling. Jour nal of Management of Envir onment al Qualit y, Vol.16, No. 1, pp.77-86.
[ 2] Billatos, S.B. and Basaly, N.A. (1997): Gr een Technology and Design for the Envir onment. Univer sit y of Connect icut St or r s, CT: Taylor & Fr ancis, pp.57-70.
[ 3] Chapr a, S.C. and Canale, R.P. (2010): Numer ical Met hods for Engineer s, 6t h Edn. McGr aw -Hill, New Yor k. [ 4] Chenayah, S., Agamuthu, P. and Takeda, E. (2007): Multicr iter ia Modelling on Recycling of Municipal Solid
Waste in Subang Jaya. Jour nal of Science, Vol.26, No.1, pp.1-16.
[ 5] Cliffor d, K.H., Bibeau, T.A. and Quinones, A.Sr. (2008): Finite Element Analyses of Continuous Filament Ties for Masonr y Applications: Final Repor t for the Ar qui n Cor por ation. SAND2006-3750, Sandia National Laborator ies Albuquer que, Califor nia, USA.
[ 6] Heimlich, J.E., Hughes, K.L. and Chr isty, A.D. (2009): Extension FactSheet: Integr ated Solid Waste Management. The Ohio St at e Univer sit y, USA.
[ 7] Khai, N.M., Ha, P.Q. and Obor n, I. (2007): Nutr ient Flow s in Small-Scale Per i-Ur ban Vegetable Far ming Systems in Southeast Asia-A Case Study in Hanoi. Agr icult ur e, Ecosyst ems and Envir onment, Vol.122, No.2, pp.192-202.
[ 8] Kumar , P., Ver ma, M., Wood, M.D. and Negandhi, D. (2010): Guidance Manual for t he Val uat ion of Regulat i ng Ser vices, Publishing Ser vices Section, UNON, Nair obi-Kenya.
[ 9] Kosior , E., Shah, G. and Stepanov, N. (1997): Recycling of Compact Discs: CHE 498. RMIT Polymer Technology Cent r e.
[ 10] Michalopoulos, E. and Babka, S. (2000): Evaluation of Pipeline Design Factor s. GRI 00/ 0076, The Har tfor d Steam Boiler Inspection and Insur ance Company, Har tford, USA.
[ 11] Ros, S.S. (2009): Solid Wast e Collect ion in Univer sit i Teknologi Malaysia and Aw ar eness of Recycling among t he St udent s, Degr ee Thesis, Univer siti Teknologi Malaysia.
[ 12] Shenoy, P.S. (2004): Dynamic Load Analysis and Optimization of Connecting Rod. M.Sc. Thesis, Univer sity of Toledo.
[ 13] Tan, C.L. (2004): New Guidelines Dictate That Landfills, Now Simply Abandoned When Full, Must Be Safely Closed and Monitor ed. St ar Publicat ions (M) Bhd.
[ 14] Tchobanoglus, G., Theisen, H. and Vigil, S. (1993): Int egr at ed Solid Wast e Management (Engineer ing Pr inciple and Management Issues), McGr aw Hill: New York, pp.456-890.
[ 15] Vesilind, P.A., Wor r ell, W. and Reinhar t, D. (2002): Solid Waste Engineer ing, Thomson Lear ning: UK, pp. 239-259.
[ 16] Yahaya, S.H., Ali, J.M., Yazariah, M.Y., Haer yip Sihombing and Yuhazr i, M.Y. (2012): Integr ating Spur Gear Teeth Design and its Analysis w ith G2 Parametr ic Bézier -Like Cubic Transition and Spir al Cur ves. Global