THE INFLUENCE OF TAX CONSCIOUSNESS, SERVICE TAX AUTHORITIES, AND TAX SANCTIONS ON TAX COMPLIANCE (SURVEY ON INDIVIDUAL TAXPAYER CONDUCTING BUSINESS
OPERATIONS AND PROFESSIONAL SERVICE IN JAKARTA)
By:
DIAH NUR PERTIWI
NIM : 109082100023
INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM ACCOUNTING DEPARTEMENT
FACULTY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSES STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
CURRICULUM VITAE
Personal Data
Full Name : Diah Nur Pertiwi Nick Name : Diah
Address : JL Sarbini 1 No 20 RT 008/ RW 06 Kec. Makasar, East Jakarta
Mobile Phone : 081298862069
E-mail : [email protected] Place, Date of Birth : Jakarta, March 14th 1992
Gender : Female
Religion : Islam
Nationality : Indonesia
Personality : Responsible, hard worker, good in individual and team work
Education
Elementary School SDN 05 1997-2003
Junior High School SMP Islam PB Sudirman Jakarta 2003-2006
Senior High School SMAN 10 Jakarta 2006-2007
SMAN 67 Jakarta 2007-2009
University UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta 2009-now Major: Accounting International Class Program
Informal Education
Work Experience
Internship at Koperasi Dinas Sosial Provinsi DKI Jakarta (2012)
Organization Experience
Member of BEMJ Akuntansi UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta (2010)
Seminar
Summer School “Renewable Energy-Leadership and Enterpreneurship” in Weiden, Germany, sponsored by DAAD ( September 10-18, 2011)
Activity of Co-curricular
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this research was to analyze the influence of tax consciousness, service tax authorities and tax sanctions on individual taxpayer compliance conducting business operations and professional services. The number of taxpayers are increase every year. But, it is not balanced with the level of tax compliance. The compliance problem becomes an obstacle in optimizing of tax revenue. This research examines the level of compliance of individual taxpayers conducting business operations and professional services in Jakarta by using several independent variables such as tax consciousness, service tax authorities and tax sanctions.
The data used in this research is primary data and selected by using convenience sampling method. The samples consists of 57 respondents, that is an individual taxpayers conducting business operation and professional service in Jakarta. The data is tested by using multiple linier regression analysis. The data tested using SPSS 20. Researcher also did validity and reliability test for the questioners. Classical assumption test using multicollinearity test, normality test, and heteroscedasticity test. For hypothesis testing, researcher using the coefficient of determination (R2), simultaneous test (F-test), and partial test (T-test).
Based on the results of the analysis undertaken concluded that tax consciousness, service tax authorities and tax sanctions have significant effect on tax compliance.
ABSTRAK
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk menganalisis pengaruh kesadaran pajak, pelayanan fiskus, dan sanksi pajak terhadap kepatuhan wajib pajak orang pribadi yang melakukan kegiatan usaha dan pekerjaan bebas.Jumlah wajib pajak dari tahun ke tahun semakin bertambah. Namun bertambahnya jumlah wajib pajak tersebut tidak diimbangi dengan kepatuhan wajib pajak dalam membayar pajak. Masalah kepatuhan tersebut menjadi kendala dalam pemaksimalan penerimaan pajak. Penelitian ini mengkaji tingkat kepatuhan wajib pajak orang pribadi yang melakukan kegiatan usaha dan pekerjaan bebas di Jakarta dengan menggunakan beberapa variabel bebas seperti kesadaran pajak, pelayanan fiskus, dan sanksi pajak.
Data yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah data primer yang dipilih menggunakan metode convenience sampling. Sampel terdiri dari 57 responden yaitu wajib pajak orang pribadi yang melakukan kegiatan usaha dan pekerjaan bebas di Jakarta. Data diuji dengan menggunakan analisa regresi linier berganda. Pengujian data menggunakan SPSS 20. Peneliti juga melakukan uji validitas dan uji reliabilitas untuk keusioner. Uji asumsi klasik yang digunakan adalah uji multikoliniaritas, uji normalitas, dan uji heteroskedasitas. Untuk pengujian hipotesis peneliti menggunakan koefisien determinasi(R2),Uji simultan (F-test),dan uji parsial (T-test).
Berdasarkan hasil analisis yang dilakukan maka diperoleh kesimpulan bahwa kesadaran pajak, pelayanan fiskus, dan sanksi pajak memiliki pengaruh yang signifikan terhadap kepatuhan pajak.
FOREWORD
Assalammu'alaikumWr.Wb
All Praise to Allah SWT as the Hearer, the Seer and above all an abundance of grace, Taufiq, as well as his guidance. So, because Allah SWT I can finish this research on time.
Shalawat always gives to the Prophet of Muhammad SAW and all his family and friends who always helped him in establishing Dinullah in this earth.
With the strength, intelligence, patience, and strong desire from Allah SWT, I am able to finish this mini thesis as graduation pre requirement for bachelor degree. I believe there is an invisible hand which have helped me going through this process.
My special thank for my mother, Nuri Sawitri, and my father, Soewignjo, who has been helping and support me to finish the thesis. I just can pray that Allah SWT will give you back for everything that you have done. Thank you also, you always pray for me in your sholah.
I believe I am nothing without each one of you who has helped me in finishing this thesis. Thus, in this very special moment, let me say many thanks to all of them have been helping me in the process of this thesis, including:
1. Prof. Dr. Abdul Hamid, MS as Dean of Faculty of Economics and Business
2. M. Arief Mufraeni, Lc., Msi as Head of International Program.
3. Ahmad Dumyathi Bashori, MA as Secretary of International Program. 4. Dr. Amilin, SE., Ak., M.Si as thesis supervisor I, you are my mentor
5. Wilda Farah SE., M.Si,AK as thesis supervisor II. You are the best mentor with your carefulness, specificity and punctuality. You have given me direction and guided me. Thank you so much for your time and your help. So, I can finish this thesis.
6. All lecturers who have taught me patiently, may they have given are recorded in Allah SWT almighty and all staff UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, special thank to Mr. Sugih Waluyo “thanks a lot you have taught me and gave explainantion about thesis and also for provide information and official stuffs that I needed in college”.
7. My sister, Niken and my brother, Royyan, who has always helped and supported me for my best, whatever I do and whenever it is.
8. All my friends in accounting international 2009. Thanks for the remarkable moments that we had been through together and special thanks for some of you that already shared and taught me your valuable experiences, especially in doing thesis. Thanks also for my friends in management international 2009.
9. Thanks for all seniors and juniors that had helped me during my study, comprehensive test and thesis.
I realize this minithesis is still far from perfection, thus suggestions and constructive criticism from all parties are welcome, in order to improve my thesis. Finally, only Allah SWT will return all and I hope this thesis will be useful to all parties, especially for writers and readers in general, may Allah bless us and recorded as the worship of Allah’s hand. Amin.
Wassalammualaikum Wr.Wb
Jakarta, May 2013
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cover ……… i
Certification from Supervisor ……….. ii
Certification of Comprehensive Exam Sheet ... iii
Certification of Thesis Exam Sheet ... iv
Sheet Statement Authenticity Scientific Work ... v
Curriculum Vitae ... vi
Abstract ... viii
Abstrak ... ix
Foreword ... x
Table of Contents ……….. xii
List of Tables ……… xvi
List of Figures ………... xviii
List of Graph ……….. xix
List of Appendix ………. xx
Chapter I INTRODUCTION A. Background Issues ……….... 1
B. Problem Formulation ……… 11
C. Objectives Research ………. 12
Chapter II LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Literature Review……… 14
1. Taxation…..………... 14
2. Tax Consciousness…………..………. 20
3. Service Tax Authorities…….……….………… 23
4. Tax Sanction………..…. 28
5. Tax Compliance………..………… 32
6. Taxpayer Conducting Business Operations and Professional Service………... 35
B. Previous Research ……….. 38
C. Logical Framework ……… 41
D. Hypothesis ……….. 43
Chapter III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Scope ……….. 46
B. Sampling Method ………... 46
C. Data Collection Method ………. 47
D. Analysis Method ………. 48
1. Descriptive Statistics ……….. 48
2. Data Quality Test ………. 48
3. Classical Assumptions Test ……… 49
a. Multicollinearity Test ……… 50
c. Heteroscedasticity Test ………. 50
4. Hypothesis Testing ……….. 51
a. Coefficient of Determination ……… 52
b. Statistic F- Test………. 53
c. Statistic t-Test……….……….. 53
E. Operational Research Variable ………. 54
Chapter IV RESULT AND ANALYSIS A. General Description of Research Object ………... 57
1. Place and Time of Research……… 57
2. Characteristics of Sample……….. 58
3. Characteristics of Respondents……….. 59
B. Test Result of Analysis Methods………... 64
1. Descriptive Statistics ……… 64
2. Data Quality Test ………..……… 66
a. Validity Test ……….……… 66
b. Reliability Test ………. 69
3. Result of Classical Assumptions Test ……….. 70
a. Result of Multicollinearity Test……… 70
b. Result of Heteroscedasticity Test ………. 71
c. Result of Normality Test…………..……… 72
b. Result of Coefficient Determination ……… 74
c. Result of F- Test (Simultaneous) ………. 76
d. Result of t-Test (Partial)………. 77
C. Analysis……….. 78
Chapter V CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATION A. Conclusion ………. 82
B. Implication………….……… 83
LIST OF TABLES
No. Description
1.1 Domestic Revenues 2006-2011 ……….…… 2
2.1 Previous Research …..……… 38
3.1 Operational Research Variable ……….………..…. 56
4.1 Tax Revenue Target in Jakarta 2010-2012 ….………. 57
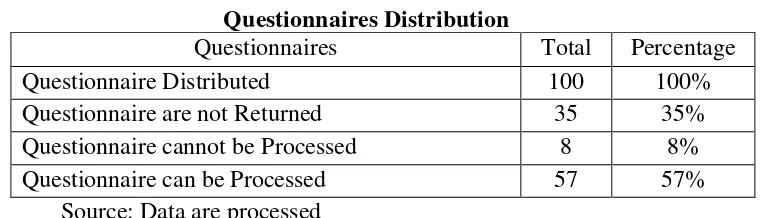
4.2 Questionnaires Distribution ……….… 58
4.3 Characteristic Respondents ……… 59
4.4 Characteristic Respondents Based on Gender …..……….... 60
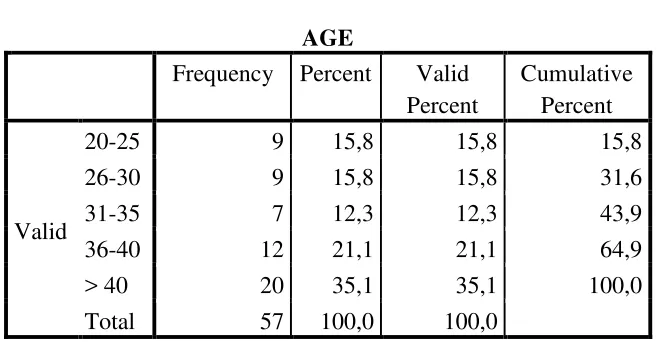
4.5 Characteristic Respondents Based on Ages……… 61
4.6 Characteristic Respondents Based on Job ……….. 62
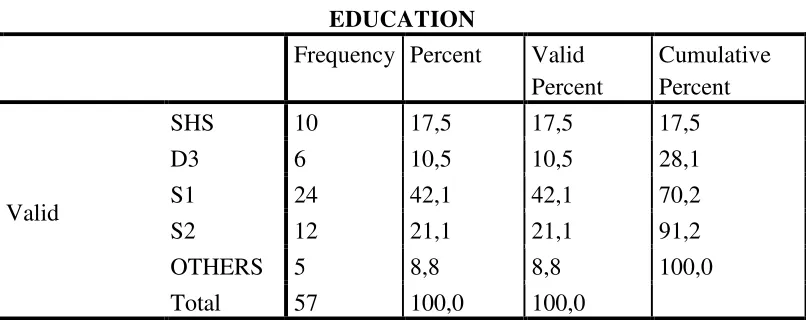
4.7 Characteristic Respondents Based on Education ……… 63
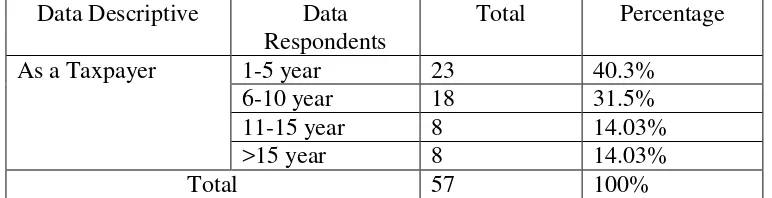
4.8 Characteristic Respondents Based on Time as Taxpayer ……… 64
4.9 Descriptive Statistics ………... 65
4.10 Validation Test for Tax Consciousness ………... 67
4.11 Validation Test for Service Tax Authorities ………. 67
4.12 Validation Test for Tax Sanctions ……… 68
4.13 Validation Test for Tax Compliance ………. 68
4.14 Reliability Test ……….. 69
4.15 Multicollinearity Test ……… 70
4.18 Statistic F Test ……… 76
LIST OF FIGURES
No. Description
2.1 Logical Framework ………... 42
4.1 Characteristic Respondents Based on Gender ………... 60
4.2 Characteristic Respondents Based on Ages ……….……. 61
4.3 Characteristic Respondents Based on Job ……..……….. 62
4.4 Characteristic Respondents Based on Education ……….. 63
LIST OF GRAPH
No. Description
1.1 Domestic Revenue 2006 -2011 ……… 3
LIST OF APPENDIXES
No Description
Appendix 1 Research Letter ………. 90
Appendix 2 Research Questioner ……….... 91
Appendix 3 Respondent Identity ………. 94
Appendix 4 List of Respondents ……….. 95
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background
Source of state revenue comes from a variety of sectors, both internal and external sectors. One source of revenue from the internal sector is taxes, while external revenue sources such as foreign loans. Source of state revenues are used to finance government spending and national development, one of which is taxed as internal sector. Tax revenues are not directly aimed at improving the welfare and prosperity of the people.
According to Soemitro (Accounting Taxation, 2010:4), the tax is a contribution to the treasury of the State under the law (which can be enforced) and did not receive reciprocal services directly demonstrated, it is used to pay for general expenses.
2008 which is the fourth amendment of the Act No. 7 year 1983 on Income Tax Act No. 36 year 2008 was passed on 23 September 2008 and came into force on January 1, 2009.
Act No. 28 year 2007 on "General Provisions and Tax Procedures", mentions that the taxpayer is an individual or entity, including taxpayers, cutting taxes, and the tax collectors who have rights and obligations in accordance with the provisions of tax legislation taxation. One form of the reaction can be seen from tax compliance to pay tax. It becomes important because it affects the amount of state income taxes.
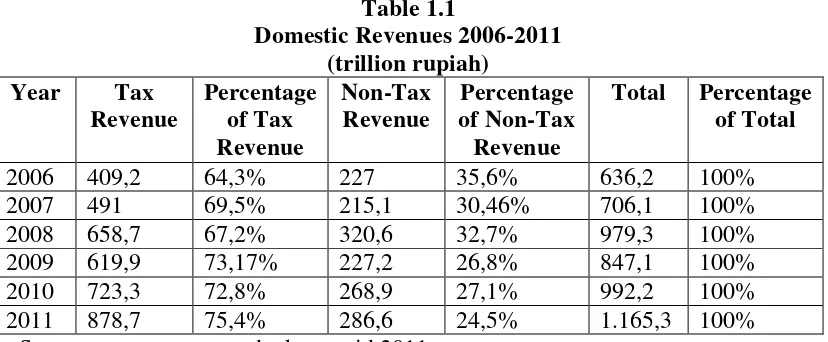
Graph 1.1
Source: Data are processed
From the graph 1.1 by table 1.1 it can be seen that the development of domestic revenue from the year 2006 to 2011 was increased, although each year fluctuated on tax revenue that could be seen in the percentage from 2006 to 2011 but in the end of year 2011 increased on the tax revenue, and when seen in non-tax revenue was decreased from 2006 to 2011 in the percentage amount, and if looked the ratio of the percentage each year in tax revenue and non-tax revenue, the amount of tax revenue is higher than non-tax revenue, as in 2006 the percentage of tax revenue was 64.3%, and non-tax revenue was 35.6%, as well as in 2011 the percentage of tax revenue was 75.4% and non-tax revenue was 24.5%, thus it can be said that tax revenue as a main source of income for the State. The increase in the tax sector as one of the sources is possible and open wide, based on the number of taxpayers, both individual taxpayer or corporate taxpayer that increases each year, with increasing population and prosperity. In addition, the tax is a sector that plays a major role for government revenues. Therefore, the amount of tax revenue that government use for national development of a country takes the role of the
0 500 1000 1500
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011
Tax Revenue
Non-Tax Revenue
community, where a willingness of the whole both individual taxpayers and entities to comply with the tax laws that hold in a country.
The role of the tax as a source of revenue for the State, efforts to increase tax revenues continue to be made by the government in this case is the task of the Directorate General of Tax in Minister of Finance. Various attempts were made in order that the Directorate General of Tax maximum tax revenues, among others, is to extensification and intensification taxes. This is done by way of extension of tax subject and object, to capture new taxpayers.
corporate taxpayer reported SPT only 466 thousand people equivalent with 3,6% of 12.9 million existing macro corporate taxpayer (Kompas, October 2011).
Several phenomena of cases occurring in the world of taxation Indonesia recently made public and concerned taxpayers to pay taxes. Of the cases that convolute the country, tax case in the second rank after case of corruption is endemic in all walks of life today. In the past, this department is known loaded with games between the employees associated with the taxpayers. One of the cases was phenomenal from the Gayus Tambunan case. Gayus arguably iconic Indonesian tax case. Former tax official IIIA group was suspected of accepting bribes and gratuities, and stored in a safe deposit box owned by him Rp 74 billion. Gayus assets totaled reached 659.8 thousand U.S. dollars and 9.68 Singapore dollars. Gayus was also involved in cases of alleged bribery prison chief Mako Brimob (Vivanews, Juny 2010). The condition can affect tax compliance and reduced public trust of taxation, because the taxpayers do not want any tax already paid by the tax authorities abused themselves. Therefore, some of the public and the taxpayer sought to avoid taxes, even though it is the duty of a good citizen.
According to John Hutagaol et al (2007) concerning the conclusion of research conducted by previous researchers Andreoni et al (1998) several aspects that affect taxpayer compliance in terms of the public finances, in terms of law enforcement, organizational structure, labor and ethics.
sanctions against those who not doing tax obligations including the government's own family or friends. When viewed in terms of organizational structure, manpower and ethics is a form of internal problems derived from the tax office. Those issues concerning professionalism in the service of an employee tax to taxpayers (Hutagaol et al: 2007).
Good service tax authorities are expected to increase taxpayer compliance. In research Supadmi (2010) mentioned that to improve tax compliance in meeting tax obligations, quality of service tax should be increased by the tax authorities. Good service tax authorities will provide comfort to taxpayers. Hospitality workers and ease the tax information system of taxation, including the taxation services. Jatmiko research (2006) found that the service tax authorities have a significant positive effect on tax compliance.
authorities can greatly affect tax compliance. If the quality of service tax authorities is very good, then taxpayer perceptions of the service will increase.
Good service tax authorities which is gives service tax authorities (serve) for the person or people who have an interest in the organization in accordance with the basic rules and procedures that have been established. Services tax authorities include the ability competencies that are have skills, knowledge, and experience in terms of tax policy, administration and taxation laws and motivation as a public servant. The tax authorities work in a transparent, voluntary helped difficulty of taxpayer (willing to provide counseling), tax authorities always maintain neatness in appearance, said keeping well and be polite, provide the tax authorities with quick and agile to help taxpayers difficulties.
If there deliberately manipulate data with the aim to make tax payments to be as efficient as possible, or not submit a SPT within a certain time, it will be subject to administrative sanctions that may be tax penalties, interest, and gains.
General provisions and procedures of tax laws has been stipulated in the Act, and the tax sanctions. Sanctions need to provide lessons for tax offenders. For example, in Article 7 of Art No. 28 Year 2007 on General Provisions and Tax Procedures when the SPT was not delivered within the period referred to in Article 3 paragraph (3) or an extension of the deadline submission of the SPT as referred to in Article 3 paragraph (4), subject to administrative sanctions in the form of a fine of Rp 500.000,00 (five hundred thousand rupiah) to the Value Added Tax SPT Period, Rp 100,000,00 (one hundred thousand rupiah) to another SPT Period, and Rp 1,000,000,00 (one million rupiah) for the Annual Income Tax of Corporate Taxpayer and Rp100.000,00 (one hundred thousand rupiah) to the Annual Income Tax of individual Taxpayer. Thus, it is expected that tax laws obeyed by the taxpayer. The taxpayer will meet the tax obligation when taxation view that sanctions would be more detrimental (Jatmiko, 2006). Research conducted by Purnomo (in Supadmi, 2010) found that perceptions of sanctions taxation taxpayer has a positive influence on tax compliance. The results Yadnyana (2009) in Muliari and Setiawan (2010) found that sanctions have a positive effect on tax compliance of taxpayers.
Muliari and Setiawan, 2010), the public must be aware of its existence as a citizen and must always uphold the Constitution of 1945 as the legal basis for organizing the state. Research conducted by Jatmiko (2006) found that consciousness of taxation has a significant positive effect on tax compliance. Research conducted by Muliari and Setiawan (2010) also found that consciousness of the taxpayer and a significant positive effect on compliance reporting individual taxpayers.
Individual taxpayers conducting business or professional services must fill out SPT yearly Form 1770. Individual taxpayers conducting business or professional service is an individual who organizes activities and is not bound by a bond with the employer. Individual taxpayers conducting business enterprise carries on business as trade, services, industry, and others. While the definition of professional service is work performed by an individual who has special expertise in an effort to generate income and is not bound by a bond with the employer. Examples of professional service is in private practice as a physician, consultants, lawyers, and others. Individual taxpayers in the country with respect to employment or occupation, services, and activities of related work in the form of salaries, wages, honoraria, allowances and other payments. In this case, the tax calculation will be based on the provisions of the Income Tax Law Article 21. Income received in connection with the work of the tax will be deducted by the employer, government treasury, or event organizers.
compliance on individual taxpayers conducting business activitity and professional services, because tax compliance for individual taxpayers is still considered low to implement tax liability because most taxpayers are concerned to pay tax liability that could be misused for vested interests. Thus researchers motivated to examine the consciousness for individual taxpayers, especially taxpayers conducting business activity and professional service in Jakarta, and motivated to examine the taxpayer's perception of the service tax authorities whether it is helps, administer, and prepare all the needs of taxpayers well, and perceptions about tax sanction whether it is followed, obeyed, and complied by the taxpayer in accordance with the tax laws, by complied tax sanction given the taxpayer would not violate norms of taxation. Based on that statement, the factors to be tested in this research is the tax consciousness, service tax authorities, tax sanction and tax compliance on individual taxpayers. Based on the description above, the authors are interested in preparing thesis entitled "The Influence of Tax Consciousness, Service Tax Authorities, and Tax Sanctions on Tax Compliance" (Survey on the
Individual Taxpayer Conducting Business Operations and Proffesional
Service in Jakarta).
This research is a development from previous research, the research conducted by Muliari and Setiawan (2010). The difference of this research with previous research is as follows:
in this research, the researchers added a variable that is the service tax authorities, which suggested in previous research to examine other factors that may affect tax compliance reporting.
2. The object of this research is the individual taxpayer conducting business activity and professional services, such as doctors, teachers, lawyers in Jakarta. Meanwhile, the object of previous research are all taxpayers in the Tax Office Primary East Denpasar.
3. Previous research is conducted in 2010, whereas this research conducted in 2013.
B. Problem Formulation
Based on the description contained in the above background, the problem to be formulated as:
C. Research Objective and Benefit
1. Research Objectives
The purpose of this research is as follows:
a. Analyzing the influence of tax consciousness on tax compliance. b. Analyzing the influence of service tax authorities on tax compliance. c. Analyzing the influence of tax sanctions on tax compliance.
2. Research Benefit
The benefits of this research are as follows:
a. For General Directorate of Tax in Minister of Finance
To provide information and reference in formulating tax policy extension appropriate to improve tax compliance in relation to consciousness of taxation, service tax authorities and tax sanction primarily on individual taxpayers conducting business and professional services. To provide input to the General Directorate of Tax to determine strategies to improve adherence to pay taxes and hoped that this research can provide feedback on actions that can be taken by tax authorities in order to improve compliance of individual taxpayer that serves.
b. For Academics
c. For authors
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Literature Review
1. Taxation
Tax issue is a problem of society and the State, and any person who lives in a State have to deal with taxes, so the tax issue is also a problem of all the people in the state, thereby differing people as members of the public should be aware of all the problems associated with taxes.
Many experts in the field of taxation that describes the meaning or definition of tax on diverse taxes, but from different understanding or definition, it has a core or common purpose. Understanding or definition of taxes, according to some experts, among others:
a. According Rochmat Soemitro, on a book entitled Taxation Theory and Case by Siti Resmi (2009:1):
"Taxes are the dues of the people to the state treasury under the law (which can be enforced) and did not receive reciprocal services that goes to show, and are used to pay for general expenses".
b. According Smeets on a book written by Sukrisno Agoes, Accounting Taxation (2010:4):
c. Tax according to Article 1 No 28 year 2007 on General Provisions and Tax Procedures are:
"The contribution shall be payable to the state by the individual or entity that is enforceable under the Act, without get feedback directly and used for the purposes of the state for the maximum prosperity of the people".
After learning the definitions of tax above, it is made a conclusion of the definition of tax that the tax has some basic aspects:
1. Payment of taxes should be based on the law; 2. Characteristics can be imposed;
3. There is no immediate contra can be felt by taxpayers; 4. State tax collections by both the central and regional levels;
5. Taxes used to finance government expenditures (routine and development) for the benefit of the general public.
Meanwhile, Abdul Asri Harahap (2004) quoted by Setiyaji (2005) criticized a basic understanding of tax by revealing that the definition of tax and its implementation needs be addressed by efforts to moral consciousness and aspects of divinity in paying taxes is injected in consciousness "secular" taxation which tends to emphasize the contractual relationship between government and society.
From the several definition of tax, raised by the experts it can be conclude the definition of tax are :
a. Can be collected based on the tax law and an implementing regulation can be imposed.
Accordance with the third amendment of the 1945 Constitution article 23A which states "taxes and other levies for the purposes of the state regulated by law." So ensure legal certainty for both the tax authorities as a tax collector and the taxpayer. Tax can be imposed if the taxpayer does not meet the tax obligations and may get the sanctions in accordance with regulation.
b. Taxes levied by the central and local government.
c. In the payment of tax cannot be contra indicated the individual by the government.
For example, people who obey paying vehicle taxes are going through the same quality with those who do not pay taxes on vehicles.
Taxes have a very important role in the life of the state, particularly in the implementation of development as a source of state income, to fund all expenses including development expenditure.
According to Resmi (2009:3) in book Taxation: Theory and Cases, taxes have several functions:
1. Budgetair Function
Tax is one of the sources of government revenue to finance both routine and development expenditures. As a source of state finance, the government attempted to include as much money for the state treasury. 2. Regularend Function
Taxes as a means to organize or carry out government policy in the field of social and economic, as well as achieving certain goals beyond finance. From some of the tax functions mentioned above it can be concluded that the definition of the tax function is:
b. As a regularend function, tax can be used to achieve the goal. For example in order the capital investment, both domestic and abroad are given a variety of tax relief. In order to protect domestic production, the government set a high import duties on foreign products.
According to Resmi (2009:7), In Indonesia, for instance, the tax is classified into several categories, tax as faction, nature, and the institution of tax.
1. Tax as Faction
a) Direct tax is a tax which is borne by the taxpayer and not transferred or charged to another person or another party.
For example: Income Tax
b) Indirect tax is a tax that could ultimately be charged or delegated to other persons or third parties.
For example: Value Added Tax 2. Tax as Nature
a) Tax Subjective, is the imposition of tax at attention on personal circumstances or the taxation of taxpayers who pay attention to a state subject.
For example: Income Tax
result in the obligation to pay taxes, regardless of the subject of taxes and shelter.
For example: Value Added Tax and Sales of Luxury Goods 3. Tax as Institution
a) State Tax (Tax Center), is a tax levied by the central government and used to finance the state in general households.
For example: Income Tax, Value Added Tax and Sales Tax on Luxury Goods, Land and Building Tax, and Stamp Duty.
b) Local Tax, is a tax levied by local governments both Local and Regional Level I and Level II are used to finance the household each area.
a) Provincial tax, for example: Motor Vehicle Tax and Motor Vehicle Fuel Tax.
b) Taxation regency/city, for example: Hotel Tax, Restaurant Tax and Entertainment Tax.
According to Resmi (2009:11-12), the system of tax collection can be divided into:
a. Official Assessment System
b. Self Assessment System
It is a tax collection system that gives authority, trust, and responsibility for taxpayers to calculate, estimate, pay, and report their own amount of tax to be paid.
c. With Holding System
Tax collection system that gives authority to a third party who appointed to determine the amount of tax payable by the taxpayer in accordance with the tax laws and regulations. The appoinment of third party is done according to the tax laws, presidential decrees and other regulations to cut and collect taxes, deposit, and account for through taxation means available.
2. Tax Consciousness
Consciousness is an element in human beings to understand reality and how they act or behave towards reality. Jatmiko (2006) explains that consciousness is a state of knowing or understanding. Irianto (2005) in Widayati and Nurlis (2010) outlines some form of consciousness pay taxes that encourage taxpayers to pay their taxes. The realization that taxes are a form of participation in supporting the country's development. Knowing this, the taxpayer would pay taxes because they are not be aggrieved from the collection of tax.
object. Thus it can be said that the tax consciousness in paying taxes is a form of taxpayer behavior or outlook feelings involving knowledge, belief and reasoning with tendency to act on the stimulus provided by the system and the tax provisions.
In Jatmiko (2006), Sumarso (1998) stated that low public consciousness of taxation often be one of the reasons many potential taxes that could not be captured. Still in Jatmiko (2006), Larche (1980) also suggests that consciousness of taxation is often a constraint in the public issue of tax collection. Empirically also been demonstrated that higher of tax consciousness it will be the higher level of tax compliance (Suyatmin, 2004 in Jatmiko, 2006).
As one important part to rotate state economy, taxes are points that must be recognized and doing by society whose are taxpayers. Taxpayers consciousness to fulfill their tax obligations needed to realize that taxes have an important contribution in the State as a means of development progress, economic evenly and prosperity for the country.
From the literature and research above, it can be obtain several dominant internal factors that make a taxpayer consciousness to comply, which are : a. Taxpayer Perception
perception that include paradigm will be the tax function for financing development, usability taxes in the provision of public goods, as well as justice (fairness) and legal certainty in the fulfillment of tax obligations. Availability public goods is a matter of taxpayer trust in the use of taxes paid. If taxpayers feel that the taxes paid cannot be properly managed by the government, so the taxpayers feel do not get benefit of tax paid, then taxpayers would not be obey to pay tax.
2. The level knowledge on the provisions of the applicable tax.
The level knowledge and understanding of taxpayer on the provisions of tax that existing, effect on behavior of tax consciousness. Taxpayers whose do not understand the tax laws are clearly likely to be a taxpayer whose do not obey, and conversely the taxpayers whose understand the tax laws, more conscious of the sanction that will accepted if shirking their tax obligation. Research conducted by Fikriningrum (2012) gives the result that the taxpayer understanding of the tax rule has a positive and significant influence on taxpayer consciousness in its tax reporting.
3. Taxpayer financial condition.
than companies with low profitability. Companies with low profitability in generally are experiencing financial difficulty and tend to tax non-compliance. Similarly, the cash flow with liquidity conditions.
Taxpayer that have consciousness (Manik Asri, 2009) in accordance with the following:
1. Know the laws and tax regulations.
2. Determine the function of taxes for state financing.
3. Understand that the tax liability must be carried out in accordance with the applicable regulations.
4. Understand the function of taxes for state financing. 5. Calculate, pay, tax reporting voluntarily.
6. Calculate, pay, tax reporting correctly.
3. Service Tax Authorities
Service is a way to serve (help administer or prepare all the necessary requirements a person). Meanwhile, the tax authorities is a tax officer. Thus, service tax authorities can be interpreted as a way of tax officer to help, to administer, or to prepare all the necessary needs someone who in this case is the taxpayer (Jatmiko, 2006).
register to obtain a NPWP is through by service . Still in the Ilyas and Burton (2010), explained that the good attitude of the tax authorities or the ministry was to be given to all taxpayers, because to pay tax the person does not have reciprocity directly. If there is a saying in the world of commerce "Buyer is King", the phrase "Taxpayer is King" also needs to be promoted, so that taxpayers eager to pay taxes.
Provisions that control a duty and authorities of the tax authorities, Art No 28 year 2007 on General Provisions and Tax Procedures (KUP). Article 35 Paragraph (1) that said, if in carrying out inspection tasks, billing, tax or criminal investigations required information or evidence from banks, public accountants, notaries, tax consultants, administrative agency, or other third parties who have a relationship with a taxpayer, the Directorate General of Taxation written request the parties shall provide the requested information or evidence. Paragraph (2), in which case the parties are duty bound to keep, then for the purpose of examination, billing, tax or criminal investigations, secrecy obligation was abolished. Especially for bank secrecy obligation was abolished upon written request the minister.
a. The obligation to foster taxpayer.
In order to carry out the functions of development, the Directorate General of Taxation shall give guidance to taxpayers as in the implementation of accounting/record keeping, calculation of tax liability tax reporting, invoicing tax and tax administration.
b. The obligations issued a tax overpayment.
If in a given tax period, or the taxable year by a taxpayer calculating the overpayment occurred, the taxpayer may apply for its return (restitution). After a thorough investigation/examination by the tax authorities, if it is in accordance with the provisions of overpaid tax bill, the tax authorities will issue refund overpayment for tax overpayments.
c. Obligations to keep taxpayer data.
Confidentiality of taxpayer data on existing taxpayer data and submitted to the tax authorities, kept secret for interests outside the Directorate General of Taxation.
Meanwhile, there are also the rights of tax authorities set in Tax Law, among others:
b. Right to issue tax assessments. Upon inspection done, KPP will issue tax provisions (such as SKP, STP, SPPT), as the basis for determining the amount of legal tax due by the taxpayer.
c. Rights issue Forced Letter and Warrant Implement Foreclosure. When to maturity payment has passed and been reprimanded, then the tax debt, KPP (through a bailiff) issuing and executing Forced Mail (SP), and seizure (SPMP).
d. Rights of inspection and sealing. In carrying out the functions of guidance, the Directorate General of Taxation conduct tax audits of taxpayers to determine the level of compliance of the implementation of tax obligations or other purposes. In the case of an uncooperative taxpayer, did not provide the document/file requested by examiner, then conducted over the sealing of the document/file.
e. Right to conduct an investigation. When taxpayer allegedly committing a crime of taxation, there will be an investigation into the taxpayer. Investigations carried out by civil investigators. If convicted of a crime of taxation, will be submitted to the Court for a sequel.
the tax system will affect the taxpayer's noncompliance, although a simple tax system does not guarantee taxpayers will obey (Suryadi, 2006).
Taxpayers and tax authorities can work together to achieve their respective goals. This condition will be achieved if in every activity of life in carrying out the rights and obligations of each party consciously rely on the values of a good relationship. Transparency, accountability and responsibility are some of the many values of life in the world of tax that should be the ideal value carried in the interest-based model of bilateral relations between the taxpayer and the tax authorities.
From the explanation above it can be concluded that the success rate of tax revenue is influenced by the tax payer is also influenced by tax policy, tax administration and tax law. The latter three factors attached and controlled by the tax authorities themselves, while the tax payer-dominated factor of the taxpayer's own self. Tax authorities in carrying out their duties to serve the public or taxpayers greatly influenced by the existence of tax policy, tax administration and tax law.
4. Tax Sanctions
Sanctions are an act of punishment given to those who break the rules. Regulations or laws are signposts for someone to do something about what to do and what should not be done. Sanctions need to be rules or laws are not violated. Sanctions taxes is an assurance that the provisions of tax laws (taxation norms) will be followed, observed, complied, in other words, the tax penalty is a deterrent so that taxpayers do not violate norms of taxation (Mardiasmo, 2006 in Muliari and Setiawan, 2010).
The view of these tax sanctions is measured by indicators (Yadyana, 2009 in Muliari and Setiawan, 2010) as follows:
a. Criminal sanctions for violators of the rules imposed heavy taxes. b. Administrative sanctions imposed for violators of tax laws is ethereal. c. The imposition of heavy sanctions is one means of educating taxpayer. d. Sanctions should be imposed on violators tax without tolerance. e. Imposition of sanctions for violations of the tax can be negotiated.
taxpayer reward obedient and has included the Notice has not been pay on time. Currently, the Directorate General of Taxation is still focusing on the negative sanctions demanding that taxpayers complied with the tax laws. When associated with the applicable tax bill, according to Ilyas and Burton (2010), there are four things that are expected or required of taxpayers, namely:
a. Demanded adherence (compliance) in taxpayers paying tax implemented with full awareness.
b. Demanded responsibility taxpayers in submitting or entering the Notice on time according to Art No. 28 year 2007.
c. Demanded honesty taxpayers in filling out the Notice in accordance with the actual situation.
d. Impose sanctions (law enforcement) are more heavily to taxpayers who do not obey the regulations.
Here are the tax sanction stipulated in Art No 28 year 2007:
a. Article 7 (1): administrative sanction in the form of fines of Rp 500,000.00 (five hundred thousand rupiah) for Value Added Tax SPT Period, if SPT not delivered within a maximum period of 20 (twenty) days after the end of the tax period.
b. Article 7 (1): sanction administrative fine amounting to Rp 100,000, 00 (one hundred thousand rupiah) for SPT another period when the SPT is not delivered within a maximum period of 20 (twenty) days after the end of the tax period.
c. Article 7 (1): sanction administrative fine amounting to Rp 1,000,000 00 (one million rupiah) for SPT Income Tax Taxpayer when SPT is not delivered within a maximum period of 4 (four) months after the end of the tax year.
d. Article 7 (1): sanction administrative fine amounting to Rp 100,000, 00 (one hundred thousand rupiah) Annual Income Tax for individual taxpayers later than 3 (three) months after the end of the tax year.
The purpose of the imposition of administrative sanctions such as fines as provided in this paragraph is for the interest of the orderly administration of taxes and increase taxpayer compliance in fulfilling the obligation to submit the SPT.
followed/observed/complied, in the other words tax sanction is a deterrent in order to the taxpayer does not violate the norms of taxation (Mardiasmo, 2006:39). Taxpayers will meet tax payments when looking at the tax penalty would be more detrimental (Jatmiko, 2006). The higher or severity of sanctions, it will be more detrimental to the taxpayer. Therefore, the tax penalties are expected to affect the level of tax compliance in paying taxes.
In essence, the imposition of sanctions imposed taxation to create taxpayer compliance in implementing tax obligations. It is important for taxpayers to understand tax penalties thus knowing the legal consequences of what was done or not done.
5. Tax Compliance
a. Definition of Tax Compliance
In General Indonesia Dictionary, compliance means submission or obedience to the teachings or rules. Meanwhile, according to Gibson (1991) in Agus Budiatmanto (1999) as quoted by Jatmiko (2006), compliance is the motivation of a person, group or organization to act or not act in accordance with the rules set. In the tax rules that apply are Tax Law. Thus, tax compliance is a compliance of person, in this case is the taxpayers, towards regulation or taxation laws.
According to Simon James et al, quoted by Gunadi (2005), the notion of tax compliance is having the willingness of taxpayers to meet their tax obligations in accordance with applicable rules without need for the holding of the examination, thorough investigation, a warning or a threat, the application of law and administrative sanctions. Santoso (2008) defines tax compliance as a situation where the taxpayer meets all tax obligations and enforce rights of taxation.
According Nurmanto in Rahayu (2010:138) says that tax compliance can be defined as a state where the taxpayer meets all tax obligations and enforce rights of taxation.
legislation, filling out tax forms with complete and clear, calculate the amount of tax payable correctly, pay the tax due on time (Devano, 2006 in Supadmi, 2010).
Muliari and Setiawan (2010) explains that the criteria taxpayer abiding by the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia Number abiding taxpayers 192/PMK.03/2007 as follows:
a. Timely in submitting the Notice;
b. Has no tax arrears for all types of taxes, unless the delinquent taxes that have been licensed in installments or defer payment of taxes; c. Financial Statements audited by a public accountant or a public
financial supervisory agency with unqualified opinion for 3 (three) years in a row;
d. Never convicted of a crime in the field of taxation based on court decisions that have been legally binding for a period of 5 (five) years. b. Types of Tax Compliance
Formal compliance, which can be measured by assessing adherence to enroll, the deposit compliance, and compliance reporting. Material compliance is more important, because it may be formally demonstrated taxpayer compliance, but what was deposited and reported by the taxpayer is not necessarily in line with what it should be. Indicators that can be used to measure compliance is the result of the examination material. In an effort to improve taxpayer compliance, administrative corrective measures are expected to encourage taxpayer compliance through:
a. Taxpayers comply because getting good service, fast, and pleasure, and the taxes that they pay will useful to the development of the nation. b. Taxpayers will comply because they think they will get severe
sanctions due to taxes that they are not report detected by information system and tax administration.
Tax compliance is the fulfillment of tax obligations by taxpayers in order to contribute the development expected in the fulfillment given freely. Hopefully with the fulfillment of voluntary compliance, the tax revenue target will be met.
correct that SPT accordance with the provisions of the tax laws and submit to the tax office before the deadline.
With the compliance, then it implies that tax revenues will go fluently, because tax compliance has been shown that the taxpayer has properly implement tax obligations. Tax compliance defined as a situation where the taxpayer meets all tax obligations and implement rights of taxation in accordance with the provisions of applicable legislation. In order for tax target achieved, need to be grown continuously for public’s consciousness and compliance to fulfill tax obligations. Consciousness of taxation arising from within its own taxpayers without regard to any tax sanction. While tax compliance arising due to aware of any tax sanction.
6. Taxpayer Conducting Business Operations and Professional Service
employment. The willingness of the taxpayer of professional service in paying taxes is important for the state as a source of revenue from individual income tax.
Individual taxpayers conducting business or professional services are those that organize business activities and is not bound by a bond with the employer. The definition of running the business activity in question is any effort in many areas, agriculture, industry, trade, or otherwise. While commonly associated with professional services expertise or profession carried on by the relevant experts such as lawyers, accountants, consultants, notaries, or doctor. That is, the independent actor opened his own practice with his own name. If the work is concerned only or employee status, such as an accountant working in the Office of Public Accountants, so it does not include professional individual taxpayer.
Referring to Article 28 paragraph (1) and (2) of Art No 28 year 2007 which is the bookkeeping required to hold an individual taxpayer conducting business or professional services and agencies in Indonesia taxpayer. Exempted from the obligation to keep books but must keep records, an individual taxpayer is conducting a business or professional services in accordance with the provisions of tax laws allowed calculating net income using the norm calculation of net income (the gross income in a year is less than Rp 4.800.000.000) and individual taxpayers who do not do business or independent.
Bookkeeping is the recording process is done on a regular basis to collect data and financial information including assets, liabilities, capital, income and expenses, and the total acquisition price and the delivery of goods or services, which closed with the preparation of financial statements in the form of balance sheet and income statement for the period of the tax year.
Recording is the collection of data collected on a regular basis about the turnover or gross receipts and/or gross income as the basis for calculating the amount of tax payable, including income tax is not an object and / or subject to final tax.
do cash transactions. Therefore, a lot of transactions and investments actually happens but not recorded. Based on this, a study of individual taxpayers conducting business and professional services is deemed interesting to do.
B. Previous Research
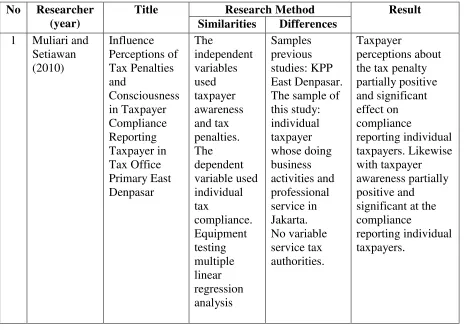
This research on the effect of tax consciousness, service tax authorities, and tax sanctions towards tax compliance has been done by previous research with variable and different analysis methods. The previous results from previous studies on topics related to this study can be seen in Table 2.1
Table 2.1 Previous Research
No Researcher
(year)
Title Research Method Result
Similarities Differences
No Researcher (year)
Title Research Method Result
Similarities Differences
No Researcher (year)
Title Research Method Result
No Researcher
Source: Adapted from various references
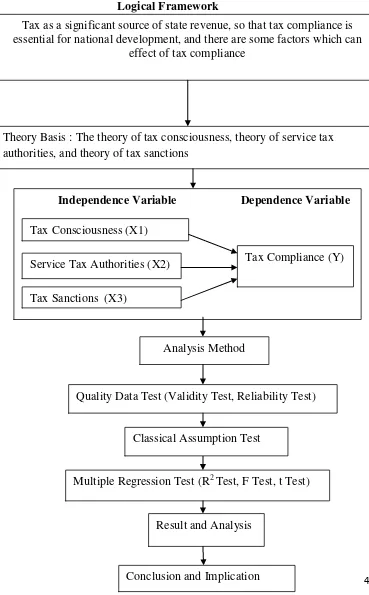
C. Logical Framework
Figure 2.1 Logical Framework
Tax as a significant source of state revenue, so that tax compliance is essential for national development, and there are some factors which can
effect of tax compliance
Theory Basis : The theory of tax consciousness, theory of service tax authorities, and theory of tax sanctions
Independence Variable Dependence Variable
Tax Consciousness (X1)
Tax Compliance (Y) Service Tax Authorities (X2)
Tax Sanctions (X3)
Analysis Method
Quality Data Test (Validity Test, Reliability Test)
Classical Assumption Test
Multiple Regression Test (R2 Test, F Test, t Test)
D. Hypothesis
1. Tax Consciousness on Tax Compliance.
Tax consciousness is a condition in which the taxpayer know, understand and correctly implement tax provisions and voluntary. The higher level of awareness of the taxpayer's tax liability, the better implementation so as to enhance compliance (Muliari and Setiawan, 2010). Taxpayer consciousness of the functions of taxation as state funding is needed to improve tax compliance (Jatmiko, 2006).
Pancawati Hadriningsih (2011) states that the taxpayer consciousness affect tax compliance. Soemarso (1998) in Jatmiko (2006) suggested that low public awareness of taxation often be one of the reasons many potential taxes that could not be captured. Taxpayer consciousness is needed in improving tax compliance (Jatmiko, 2006). Tax consciousness on taxation is required in order to increase the willingness of the taxpayer to pay the tax. The higher consciousness of taxpayers in paying taxes the higher willingness of taxpayers to pay taxes. Based on that, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H1: Tax consciousness has significant influence on tax compliance
2. Service Tax Authorities on Tax Compliance
The tax authorities have competence in the sense of having the expertise, knowledge and experience in terms of tax policy, tax administration and tax laws. Besides the tax authorities should also be highly motivated as a public servant (Ilyas and Burton, 2010).
The tax authorities are expected to provide a good service to the taxpayer, that taxpayer would pay taxes payable. The better the services provided to the taxpayer's tax authorities, greater willingness of taxpayers to pay taxes. Based on the description it can be said that the service tax authorities are expected to influence the tax compliance in paying taxes. Therefore, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
H2: Service tax authorities has significant influence on tax compliance.
3. Tax Sanctions on Tax Compliance
Tax sanctions created with the aim that taxpayers are afraid to violate the Law on taxation. Taxpayers will comply with tax payments when it considers that the sanctions would be more detrimental (Jatmiko, 2006).Tax sanctions is an assurance that the provisions of tax laws (taxation norms) will be followed/observed/complied, in other words, the tax sanctions is a deterrent so that taxpayers do not violate norms of taxation (Mardiasmo, 2006 in Muliari and Setiawan, 2010).
outlook on sanctions taxpayers are expected to affect the level of tax compliance in paying taxes.
Therefore, the view of taxpayers suspected of tax sanctions will affect the tax compliance in paying taxes. Under these conditions, the hypothesis is formulated as follows:
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
The Scope of ResearchThe study was conducted to analyze the effect of tax consciousness, service tax authorities and tax sanctions towards tax compliance on personal taxpayer conducting business activity and professional services. This study is a survey, in which researchers directly involved in the research. The population in this study is the individual taxpayer either live or work in Jakarta area.
B.
Determining Sample MethodThe sampling technique is done by convenience sampling method, which is a general term that includes variations in the level of respondent selection procedures the member population sampling technique is based on convenience alone. Someone sampled by chance people had been there or investigators know the person. This type of sampling is very good if used for research assessment, which is then followed by advanced research sample taken at random (Sugiyono, 2007:56).
taxpayers conducting business operation and professional service who living or working in Jakarta area.
C.
Data Collection MethodsData collection methods refers to the way which is needed in this research it can be obtained. In this regard, the data collection techniques can be used directly through the combination.
The data obtained in this study, researchers used two ways, namely library research and field research.
1. Library Research
Researchers obtained data related to the problem being researched through books, journals, theses, internet, and other devices related to their topic. 2. Field Research
respondents and later respondents were asked to answer according of their opinion. To measure the opinion of respondents used a Likert scale of five numbers starting from number 5 to the opinion strongly agree and 1 for strongly disagree. The breakdown is as follows:
Figures 1 = Strongly Disagree Figures 2 = Disagree
Figures 3 = Less Agree Figures 4 = Agree
Figures 5 = Strongly Agree
D.
Analysis MethodsThe data analysis method using descriptive statistics, test data quality, classic assumption test and hypotheses test.
1. Descriptive Statistic
Descriptive statistics provide a picture or description of the data as seen from the average (mean), standard deviation, maximum, and minimum (Ghozali, 2009:19).
2. Data Quality Test
a. Reliability Test
2009:45). Ghozali (2009:46) states that the reliability of the measurement can be done in two ways, namely:
1. Repeated Measure, here someone will present with the same questions at different times, and then see if he remains consistent with his answers. 2. One Shot or measurement once, here measurement only once and then
the results were compared with another question or measure the correlation between the answers to the questions.
Criteria testing conducted using test Cronbach Alpha (α). A variable is
said to be reliable if it delivers value Cronbach Alpha > 0.60 (Priyatno, 2012:108)
b. Validity Test
Validity test is used to measure whether a legal or valid questionnaires. A questionnaire as valid if the questions in the questionnaire were able to reveal something that will be measured by questionnaire (Ghozali, 2009:49). Testing the validity of the study using Pearson Correlation is by calculating the correlation between the values obtained from the questions. If Pearson Correlation earned value below 0.05 means that the data obtained are valid (Priyatno, 2012:101).
3. Classical Assumptions Test
a. Mulitcollinearity Test
Mulitcollinearity test aims to test whether the regression model found a correlation between the independent variables. A good regression model should not happen correlation between the independent variables (Priyatno, 2012:61).
Detect the presence or absence mulitcollinearity in the regression model can be seen from the amount VIF (Variance Inflation Factor) and tolerance. Free mulitcollinearity regression if the value of VIF < 10 and tolerance values > 0.10 (Priyatno, 2012:61).
b. Normality Test
Normality test aims to measure whether the regression model the independent variables and the dependent variable both have normal or near-normal distribution. A good regression model is to have a normal or near-normal distribution. In this study, test for normality using the Normal Probability Plot (PP Plot). A variable is said to be normal if the distribution of the image data points are spread around the diagonal line, and the spread of data points in the same direction following the diagonal line (Priyatno, 2012:60).
c. Heteroscedasticity Test
observation permanent it is called homoskedasticity and if it is different called heteroscedasticity. Good regression model that is homoskedasticity (Ghozali, 2009:125).
Detect the presence or absence heterocedastisity presence or absence can be seen with a certain pattern on the charts scaterplot. If there is a pattern that has occurred indicating heteroscedasticity. But if there is no clear pattern and the points spread above and below 0 on the Y axis, then it does not happen heteroscedasticity (Ghozali, 2009:125-126).
4. Hypothesis Testing
Hypotheses testing using a multiple regression analysis. Regression equation as follows:
Y= a + β
1 X1 + β 2 X2 +β 3 X3 +e
Y = Tax Compliance
X1 = Tax Consciousness X2 = Service Tax Authorities
X3 = Tax Sanctions
a = Constanta
β 1, β2, β 3 = Regression coefficients
e = Error Factor
Hypothesis testing is done in the following ways: a. Coefficient of Determination
b. Statistic F Test
F Test performed is to determine the effect of joint independent variables on the dependent variable. The significance level used was 5%, with degrees of freedom df = (nk-1), where (n) is the number of observations and (k) is the number of variables. This test is done by comparing the calculated F with F tables with the following conditions: H0 is accepted if f count < f table for α = 5%
H1 accepted if f count > f the table for α = 5%
According to Santoso (2004:120) basis on decision making as follows: 1. If the probability is greater than 0.05, H0 is accepted or rejected Ha, this means that all independent variables have no influence or free together or bonded to the dependent variable.
2. If the probability value of less than 0.05, then H0 rejected and Ha accepted, this means that all free variables have an independent or jointly influence on the dependent variable or bound.
c. Statistic t Test
Significance level used is 5%, with degrees of freedom DF = (nk-1), where (n) is the number of observations and (k) is the number of variables. This test is done by comparing the calculated t with t table with the following conditions:
H0 is accepted if t count < t table for α = 5% H1 accepted if the t count > t table for α = 5%
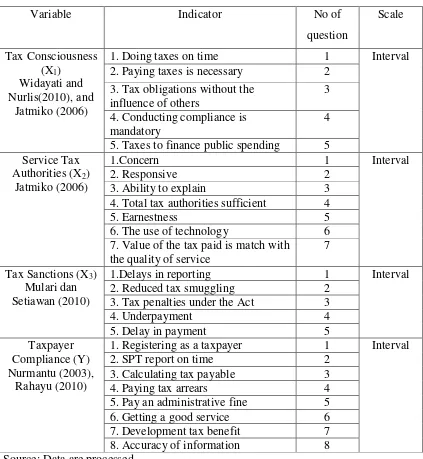
E. Operational Research Variable
Variables Operational Definition is the definition given to a variable or construct a way to give meaning or specifying activities. Operational variables used are:
1. Tax Consciousness (X1)
2. Service Tax Authorities (X2)
Service tax authorities can be interpreted as a way to help tax officers, administer, or prepare all the necessities needed someone who in this case is the taxpayer (Jatmiko, 2006). All item questionnaire measured using interval scales (Likert), 1 to 5. The answers will be made scores are: the value of (1) strongly disagree, (2) disagree, (3) less agree, (4) agree, and (5) strongly agree. 3. Tax Sanctions (X3)
Tax sanctions is an assurance that the provisions of tax laws (taxation norms) will be followed/observed/complied with, in other words, the tax penalty is a deterrent so that taxpayers do not violate norms of taxation (Mardiasmo, 2006 in Muliari and Setiawan, 2010). All item questionnaire measured using interval scales (Likert), 1 to 5. The answers will be made scores are: the value of (1) strongly disagree, (2) disagree, (3) less agree, (4) agree, and (5) strongly agree.
4. Tax Compliance (Y)
Table 3.1
Operational Research Variables
Variable Indicator No of
question
2. Paying taxes is necessary 2 3. Tax obligations without the
influence of others
3 4. Conducting compliance is
mandatory
4
5. Taxes to finance public spending 5 Service Tax
4. Total tax authorities sufficient 4
5. Earnestness 5
1.Delays in reporting 1 Interval
2. Reduced tax smuggling 2
3. Tax penalties under the Act 3
1. Registering as a taxpayer 1 Interval
2. SPT report on time 2
3. Calculating tax payable 3
4. Paying tax arrears 4
5. Pay an administrative fine 5
6. Getting a good service 6
CHAPTER IV
RESULT AND ANALYSIS
A. Research Object
1. Place and Time of Research
This research was done on individual taxpayers conducting business operations and professional service who living and working in Jakarta. Researchers try to measure the effect of tax consciousness, service tax authorities and tax sanctions towards tax compliance, where objects in this study were individual taxpayers conducting business operations, and professional services in Jakarta area.
Tax revenues in Jakarta is the country's primary source of funding and revenue sources that are important in development that aims to improve State prosperity and welfare. Tax revenue target in DKI Jakarta in 2010-2012 contained in Table 4.1 are as follows:
Table 4.1
Tax Revenue Target in Jakarta 2010-2012
Source:Jakarta.go.id
The collection of data on the research methods is done through the questionnaires is given directly to individual taxpayers conducting business
Year Tax Revenue
2010 12,819 trillion
2011 14,821 trilllion