i
THE USE OF
“
FIND THE STRANGER GAME
”
TO
IMPROVE THE STUDENTS’
VOCABULARY
MASTERY AND READING COMPREHENSION
( A Classroom Action Research of the Tenth Grade Students
of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2016/2017)
GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty State
Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
BY : MUTASLIMAH
113 12 077
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF TEACHER
TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY STATE
INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN) OF
SALATIGA
v MOTTO
“THE GREATEST GLORY IN LIVING LIES NOT IN NEVER FALLING, BUT IN RISING EVERY TIE FALL”
-NELSON MANDELA-
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My beloved parents ( Suminto and Sriyanti ) thank you very much for
everything. May Allah always loves you and gives you happines in
every where you are. I love you so much.
2. My beloved husband ( Enggar Sri Wibowo) and My lovely son
(Gibran Alvaro). Thank you so much for your love and support. I love
vii
ACKNOWLEDMENT
All praises to Allah, I deliver thankfulnes to Allah Almighty
for the Blessing and Mercy Who has led me finish my graduating
paper, peace and blessing to the Allah’s Messenger, Muhammad
SAW. However, this graduating paper would not be finished without
supports, advices, help and encouragements from some people and the
institution. I would like to say thank you to :
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd as the Rector of IAIN Salatiga, thank
you for the time I spend for studying in IAIN Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M.Pd as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education
Faculty of IAIN Salatiga.
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D, as the Head of English Education Department
4. Setia Rini, M.Pd as my graduating paper counselor, thank you to
have sacrificed her vacant time to guide, give suggestions,
corrected, and encouraged me in completing my graduating paper.
5. All of my lecturers in IAIN Salatiga, thank you for teaching me
and give a lot of their worth knowledge to me along of my study
in this Institute.
6. All official staffs of IAIN Salatiga
7. My closest friends (Bilal, Agil, Arpan, Juni). Thank you for being
ix
TABLES OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
TABLES OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURES ... xiii
ABSTRACT ... xiv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Statement of the problem ... 4
C. Objective of the study ... 5
D. Limitation of the Study ... 5
E. Benefit of the research ... 5
F. Definition Key of Terms ... 6
G. Previous Research ... 8
H. Research Outline ... 10
CHAPTER II : THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK ... 11
A. Vocabulary mastery ... 11
x
2. Kinds of Vocabulary ... 12
3. The Importance of Vocabulary ... 14
4. Teaching Vocabulary ... 14
B. Reading ... 15
1. Definition of Reading ... 15
2. Reading process ... 18
3. Purpose of reading... 19
4. Developing interest in Reading ... 20
5. Principles of Teaching Reading ... 21
C.Reading Comprehension ... 22
1. Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 22
2. Basic of Reading Comprehension ... 23
3. Level of Comprehension ... 25
D.Descriptive Text ... 27
1. Definition of Descriptive Text ... 27
2. The Purpose and Kinds of Descriptive Text ... 27
3. Generic structure of Descriptive Text ... 28
4. Langauge Features of Descriptive Text ... 28
5. Example of Descriptive text ... 29
E. Find the Stranger Game ... 29
1. Definition of Game ... 29
2. Value of Game ... 30
xi
4. Procedure the Find the stranger game ... 31
5. Example Find the Stranger word card ... 32
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 34
A.Research Setting ... 34
1. General Discussion of SMK N3 Salatiga ... 34
2. Situation of SMK N3 Salatiga... 35
B.Description of the Research Schedule ... 37
C.Subject of the Research ... 38
D.Method of the Research ... 40
E. Research Procedure ... 42
F. Technique Collecting Data ... 44
G.Technique of Analyzing Data ... 47
CHAPTER IV: FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 51
A.Research Finding ... 51
B.Analysis and discussions ... 68
CAHPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 70
A.Conclusion ... 70
B.Suggestion ... 71
REFERENCES ... 73
xii
LIST TABLES AND FIGURES
Figure 1: Five basics reading comprehension processes... 25
Table 3.1: Time setting of the Research... 37
Table 3.2 List of students’ X- TSM 2 ... 39
Figure 2: Kemmis and Taggart ... 44
Table 3.3: Student’s Observation sheet for students ... 45
Table 4.1: The result of pre-test and post-test cycle I ... 55
Table 4.2: The result of pre test and post test cycle II ... 63
xiii
ABSTRACT
Mutaslimah. 2016. The Use of “Find the Stranger Game” to Improve the
Students’ Vocabulary Mastery and Reading Comprehension (A
Classroom Action Research of the First Grade Students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2016/2017).Graduating Paper. English Education Department Teacher Training and Education Faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Consultant: Setia Rini M.Pd.
Key Words: Find the stranger Game, Improve, Reading Comprehension,
The purpose of language teaching in Senior High school is to achieve functional level. In the functional level, they can develop the competence in communicating orally and written to resolve daily problems. The real problems faced by the students in the school in learning and teaching English are reading comprehension. Game is one of the solutions to overcome the research answers two problem of research (1) How is the implementation of find the stranger game to improve the students’ reading comprehension for the tenth grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic Year 2016/2017? (2) How is the result of find the stranger game in improving the students’ reading comprehension for the tenth grade students in SMK N 3 Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017?
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer presents the introduction. It explains the
background of the research, statement of the statement, objective of the research,
significance of the research, definition of the key terms, review of related
research, and organization of the graduating paper
A. Background of the Research
In Indonesia English is taught and learned as Foreign Language. In Indonesia the aim teaching English as adopted by government is to develop
communicative competence of the learners. It is taught in the schools from
primary school to high school. In addition English is one of subject which is
tested at the end both Junior and senior High School Programs.
According to Scriverner (1994: 20), there are four skills in English
language teaching; listening skill, speaking skill, vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension and writing skill According to Huyen and Nga
(2003:2), in learning a foreign language, vocabulary mastery plays an
important role; it is one element that links the four skills of speaking,
listening, reading and writing.
According to Fauziati (2005: 155), vocabulary is central to language and
of critical importance to typical language learner. Without sufficient
vocabulary mastery, one cannot communicate effectively or express his ideas
also a barrier that precludes learners from learning a foreign language.
2
reading, listening, speaking and writing skills. Vocabulary mastery is one
element that contributes to text difficulty levels or ease of reading.
Reading in a second or foreign language (SL/FL) has been a
significant component of language learning over the past forty years (Zoghi,
Mustapha, Rizan & Maasum, 2010) in Chen and Chen (2015: 156).
According to Dechant (1982: 5), reading is a language communication
process of putting a reader in contact and communication with ideas. Reading
always involves an interaction between the writer and reader. The
communication process initiated the thoughts of the writer and expressed
through symbol on the page.
According to Tan and Nicholson (1997: 135), reading is a
multicomponent skill whereby the reader has to use a number of different
cognitive processes involving word recognition, access of word meanings,
parsing of sentences, semantic analysis of sentences, and interpretation of the
overall text
According to Gibson (1996) cited in Dechant (1982: 5), reading is
receiving communication; it is making discriminative response to graphic
symbols, it is decoding graphic sybol to speech and getting meaning from
printed page. According to Perfetti (2001:12800), vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension is an individual’s standing on some reading
assessment. According to Chen and Chen (2015: 156), reading is a complex,
interactive cognitive process where the reader is an active participant,
3
In non-native English speaking countries, the high school English
curriculum often adopts a reading skill oriented textbook that focuses on
vocabulary mastery, sentence structure, and grammar. According to Chen and
Chen (2015: 157), most learners have reading problems because they lack the
specific strategies necessary for efficient reading. According to Schiff and
Calif (2004) cited in Chen and Chen (2015: 157), explain that EFL students
have reading problems because of a lack of knowledge and awareness of how
to apply reading strategies. When foreign language read, they face some
problem such as a laborious, unpleasant, and unsuccessful process. It makes
the readers will often be unwilling to read in the target language Chen and
Chen (2015: 157).
Actually the same problems occur in SMK N3 Salatiga. Based on
the observation that conducted on May, 18th 2016 at 09.00 a.m. The writer
found some problems in English learning process. The students’ interest in
reading English text is still low. The students assume that reading is very
difficult and they have minimum vocabulary mastery therefore they have
difficulties to understand a text. Furthermore the teacher speaks too fast in
English. It is make students do not understand and the teaching learning
process ineffective.
There are many way to boost the students’ vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension. According to Krashen and Terrel (1983: 53),
language is best taught when it is being used to transmit message not when it
4
language learning is depends on the situation in the learning process itself.
One of the ways to create learning process more enjoyable is by applying
game.
According to Hadfield (1990: v) in Tuan (2012: 259), game is
activity with rules, a goal and an element of fun. Game is an organized
activity that usually has the following properties: a particular task or
objective, a set of rules, competition between players b spoken o written
language (Richard, Platt, and Platt, 1992, p. 153) in Tuan (2012:259). In this
research writer use Find the Stranger Game. Find the Stranger Game is a
game in which the players should determine the foreign word is in a group of
words or determine the word which is not the groups of it (Walidi, 2006: 14).
From the statement above, the writer wants to conduct a research
entitled THE USE OF FIND THE STRANGER GAME TO IMPROVE THE
STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY AND READING
COMPREHENSION (A Classroom Action Research for the Tenth Grade
Students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in Academic Year of 2016/2017)
B. Research Question
Based on the background of the research, the writer will formulate
the research question as follows:
1. How is the implementation of Find the Stranger Game to improve the
students’ vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension for the tenth
5
2. How is the result of Find the Stranger Game in improving the students’
vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension for the tenth grade
students in SMK N 3 Salatiga in the academic year of 2016/2017?
C. Objective of the research
Based on the statement of the problem above, the objectives of the
research are as follows:
1. To describe the implementation of Find the Stranger Game in
improving the students’ vocabulary mastery and reading
comprehension of the tenth grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the
Academic Year of 2016/2017.
2. To find out the result of the students’ vocabulary mastery and reading
comprehension after using Find the Stranger Game for the tenth grade
students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2016/2017.
D. Limitation of the Research
In order to avoid any misinterpretation of the problem, the writer
would like to limit the scope of the research. The writer wants to know
whether the use of Find The Stanger Game can improve the students’
vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension. The material is limited at the
Tenth Grade students of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the academic year of
2016/1017.
E. Benefit of the Research
Hopefully the result of this research gives additional information
6
about the effectiveness of the game to improve students’ vocabulary mastery
and reading comprehension. The writer also hopes this research will useful
for the school, students, and English teacher particularly in SMK N 3
Salatiga.
1. For English Teacher
This research can be used as an input in applying for English teacher
especially in teaching reading. They can use this method to make
teaching process more enjoyable and attractive, especially in teaching
reading.
2. For the writer
The result of this research will improve writer knowledge and
experience about teaching reading. Moreover writer knows deeply about
Find the Stranger Game
F. Definition of Key Terms
To avoid misunderstanding of the concept in this research, the writer
gives some definitions as follows:
1. Find the Stranger Game
Find the stranger is a game in which the players should determine
the foreign word is in a group of words or determine the word which is
not the groups of it (Walidi, 2006: 14).
2. Improve
Improve is to become better than before or to make something or
7
improving is to bring to a more desirable or excellent condition; to
ameliorate; to better; to make, as land or real estate, more profitable by
cultivation or construction; to make more useful; as to improve a road by
resurfacing.
3.Students
Student is a person who is researching in school, especially an
older child (Hornby, 2010:1484). Student is an individual with different
experiences both in and out the classroom (Harmer, 2001:37).
4. Vocabulary mastery
Vocabulary mastery is total number of words which (with rules for
combining them) make up a language (Hornby, 1974: 959). Vocabulary
mastery refers to words we use to communicate in oral and print
language (Handson and Padua : 2011).
5. Reading
According to Gibson (1966) cited in Dechant (1982: 5) says that
reading is receiving communication, it is making discriminative
responses to graphic symbol, it is decoding graphic symbol to speech and
it is getting meaning from printed page.
Reading is an active process. Identifying reading is often connected
with the process of reading itself. The process is the interaction between
a reader and a text which is normally silent, internal and private
8 6. Reading comprehension
According to Thorndike (1917) in Dechant (1982: 311) he says
reading comprehension includes correct meanings, the ability to reason
one’s way through smaller idea, segments, and the ability to grasp the
meaning of a larger unitary idea.
7. SMK N 3 Salatiga
SMK N 3 Salatiga is one of state Vocational High School in Jl.
Jafar Shodiq, Kalibening, Tingkir, Salatiga. The teachers and students
are Muslim. It has good building and good facilities to support teaching
learning process.
G. Previous Research
The writer takes Inayah (2015), she conduct a research about the use of
Reciprocal Teaching Technique to Improve Students’ Vocabulary mastery
and reading comprehension.The methodology of the study used Classroom
Action Research. The result of her research showed that Reciprocal Teaching
Technique can help the students of SMK N 1 Ngablak in improving
vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension.
The differences this research with this research is the game or
technique that use is difference; the subject of the research, the result of the
research is different.
The second research Herningtiyas (2014), she conducts a research
9
reading comprehension. The methodology of the research used classroom
action research. The result of the research show that that the value of
significance is 0.400 which is above the level of significance (0.05).
The differences this research with mine is the game or technique that
used is different, the subject of the research, the result of the research is
different.
The third research from Marsini (2014), she conduct a research about
improving students’ vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension using
Index Match Technique. The methodology of the research used classroom
action research. The result of the research showed that after the researcher
conducted the actions, the researcher found that Index Card Match Technique
improved students’ vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension of
narrative text at XI IPA 1 of MAN 1 Kendari.
The differences this research with mine is the game or technique that
used is different, the subject of the research, the result of the research is
different.
H. Research Outline
This research divided into five chapters. In order to make easy to
understand this paper, the writer convey the kind of the graduating paper in the
following:
Chapter I presents the introduction. It explains the background of
the research, statement of the problems research, objectives of the research,
benefit of the research, definition of key terms, limitation of the research,
10
Chapters II describes the theoretical framework including
Vocabulary mastery including definition of Vocabulary mastery, kinds of
vocabulary mastery, importance of vocabulary mastery, teaching vocabulary
mastery, definition of reading, reading process, the purposes of reading,
developing interest in reading, principle of teaching reading, reading skill
and descriptive text that include definition of descriptive text, generic
structure of descriptive text and language feature of descriptive text.
Chapter III is methodology of the research. It discusses method of
research, setting of research, procedure of research, technique of collecting
data, and technique of analysis data.
Chapter IV is data analysis. It consist of field note of cycle I, cycle II,
the discussion of cycle I, cycle II.
Chapter V is closure. It comprise of conclusion and suggestion. For
11
CH APTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter the writer tries to give clear information of underlying
theories which is definition Vocabulary mastery including definition of
Vocabulary mastery, kinds of vocabulary mastery, importance of vocabulary
mastery, teaching vocabulary mastery, of reading, reading process, the purposes
of reading, developing interest in reading, principle of teaching reading,
vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension and descriptive text that include
definition of descriptive text, generic structure of descriptive text and language
feature of descriptive text.
A. Vocabulary mastery
1. Definition of Vocabulary mastery
According to Neuman and Dwyer (2009: 385) in Alqahtani (2015:
24), vocabulary is words we must know to communicate effectively,
words in speaking (expressive vocabulary) and words in listening
(receptive vocabulary). According to Hornby (1974: 959) vocabulary
mastery is total number of words which (with rules for combining them)
make up a language.
According to Scriverner (1994: 73), vocabulary is a powerful
carrier of meaning, beginner often manage to communicate in English by
using accumulative effect of individual words.Vocabulary mastery is all
12
great knowledge about or understanding of a particular thing (Oxford,
2010 : 914).
From the definitions above, the researcher concludes that
vocabulary mastery is a group of word that arranged in alphabetical
order and has meanings that used by person in daily communication.
Vocabulary mastery mastery can be defined as great skill or knowledge
about meaningful words that used in daily communication.
2. Kinds of Vocabulary
Scrivener (1994:74) divide vocabulary into two kinds, there are
productive (active) vocabulary mastery and receptive (passive)
vocabulary mastery.
a. Productive vocabulary mastery is the sets of words that are used in
spoken communication. Good pronunciation might be encouraged
getting the sounds and the stress right.
b. Receptive vocabulary mastery is the use of words that we recognize
and understand, but tend not to use ourselves.
According to Harmer (1991) in Alqahtani (2015: 25), divided
vocabulary ino two types:
a. Active vocabulary: words that students expected to use
b. Passive vocabulary: words that students recognize when they meet
There are two types of vocabulary, word recognition vocabulary
mastery and word meaning. (Chall, 1983; as cited in Blachowicz, Fisher,
13 a. Word recognition
Word recognition is the readers’ ability to pronounce or figure out
the word by using word attack strategies.
b. Word meaning
Word meaning refers to words students know or can define.
Through we recognize the importance of both word recognition
and word meaning, the emphasis of this book will be on word
meaning.
According to Harmer (2002: 3-10) says that there are six kinds of
vocabulary mastery, they are :
a. Word classes
Word classes or parts of speech, They are devided in to eight
classes, such as: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition
and determiner.
b. Word families
It discusses about affixation of a word, such as: prefixes (pre-, de-)
and suffixes (-er, -ful).
c. Word formation
d. Multi-word units
1) Phrasal verbs: look, for, look after, wipe off, and throw on and
so on.
2) Idioms: famous last word, jack me around.
14
Two words are collocates if they occur together with more than
chance frequency. Example: this week, once more, once again, as
well.
f. Word meaning
It discusses about synonym, antonym and homonym
3. The Importances of Vocabulary
The statements from some experts about the importances of
vocabulary can be seen below:
According to John Dewey (1910) cited in Efendi (2013:78),
vocabulary mastery is critically important because a word is an
instrument for thinking about the meanings which is expresses.
In addition, Harmon et al. (2009) in Efendi (2013:78) proposed that
learning vocabulary mastery is an important instructional aim for
teachersin all content areas in middle grades schools.
From the statements above, it can be concluded that vocabulary
mastery is very important in English learning because it becomes basic
part that are needed in listening, reading, speaking, and writing.
4. Teaching vocabulary
Teacher must know learners’ strategy. Knowing learners’ strategy,
teachers can help students to acquire vocabulary mastery. Mehta (2009)
proposed three steps in vocabulary mastery learning:
15
Careful listening to the words may be a good option in teaching
vocabulary mastery items in a heterogenic classroom. "Let the
students hear the word in isolation and in a sentence. If the sounds of
the word have been mastered, the students will hear it correctly with
two or three repetitions." (Robert Lado: 121) Slow pronunciation
without distortion will help. Breaking the word into parts and building
up to the whole word will also be helpful.
b. Pronouncing the Word
Pronouncing the word enables the students to remember it longer
and identify it more readily when they hear or see it.
c. Methods of Grasping the Meaning
The teacher should try to get the meaning to the class without using
translation. This is not preferable on the ground that translation may or
may not provide the meaning of the word accurately and precisely. It
is advocated as it enables the class to go without grasping the meaning
of a word that they have learned to pronounce rather than to depend
upon the translation.
B. Reading
1. Definition of Reading
Reading is an active process. Identifying reading is often
connected with the process of reading itself. The process is the
interaction between a reader and a text which is normally silent, internal
16
they read. It is also more than recognizing words within a sentence; it
includes whole ability of thinking process to evaluate the information.
The following are some definitions of reading proposed by some experts.
Reading is one of the language skills which needed to be taught
in language classroom. Reading is a process of matching information in a
text to internally activated information to interpret what we understand
from a text depends what we know previously (Widowson 1979; Carrel
and Eisterhold 1983 cited in (Grabe: 1986). Reading is a process of
interpreting or understanding the text in term of question that the reader
formulates about the text (Smith 1982) in Grabe (1986:28). Reading is
selective process that involves partial use of available minimal language
cues selected from perceptual input on the basic of readers expectation
(Goodman, 1967:108) in Grabe (1986: 26).
In his introduction to Alderson (2000) on assessing reading,
Lyle Bachman notes: "Reading through which we can access worlds of
ideas and feelings, as well as the knowledge of ages and visions of the
future, is at once the most extensively researched and the most enigmatic
of the so-called language skills. Alderson (2000) says:
Reading as interactive model as well. The interaction in reading process happens during reading. There are two kinds of interactions which are interaction between the reader and the text and interaction between the reader and the writer. The interaction between the reader and the texts happens when the reader constructs a personal interpretationof the text through recognizing the written symbols. While when the reader tries to
get the writer’s intention, the interaction between the reader and
17
of background knowledge and number of skills used in comprehending and interpreting a text. (Alderson, 2000: 3)
There are many experts who present various definition of
reading. According to Dechant (1982: 3) definitions of reading are
divided into two major types:
a. Reading as Interpretation of Experience
With the first type of reading definition, in which reading is
equated with the interpretation of experience generally, we might
speak of reading pictures, reading faces, or reading the weather.
Reading is performed whenever one experiences sensory stimulation. On the other hand, the meaning of reading based on this type is the reading readiness program in which experience with concrete object is emphasized, visual and auditory discrimination are stressed and students are required to interpret pictures and conversation. Spencer (1946) as quoted by Dechant, 1982: 4.
According to Dechant (1982: 4) reading as interpretation of
experience have three implications as followed:
a) For both the teacher and studuents who is learning to read.
Teacher must become expert in the abilities of the students in
reading. They must understand their students and must be
able to identify the personal differences in the students which
may lead to achievement differences between students.
b) The teacher needs become expert I reading symptoms of
reading
c) Another implication is that the teacher must develop
18
b. Reading as Interpretation of Graphic Symbols
In Dechant (1982: 4-5) there are presented the definition of
reading by many experts. Some of them are DeBoer and Dallmann
(1960: 19) consider that reading involves the comprehension and
interpretation of ideas symbolized by the written or printed page.
According to Bond and Thinker (1967: 22) cited in Dechant
(1982: 5) point out that reading involves the recognition of printed or
written symbols which serve as stimuli for the recall of meanings built
up through the reader’s past experience.
2. Reading Process
There are many experts promote the reading processes to find the
best way to boost the students vocabulary mastery and reading
comprehension. According to Grabe (1986) says:
The reading process must be viewed in at least two ways. First,
there is the more linguistically constrained issue is whether
different language and their different learning strategies or
various universal processes interact differently for optimal
processing in different languages. The second issue is whether
different culture imposes particular constraint on the development
of reading process that affects foreign students reading
proficiency in the EFL class. (Grabe, 1986: 29)
According to Fauziati (2010: 40) there are three main phases
needed to be followed in reading activity, namely:
a. Pre – reading : used to prepare students for reading. Activities may
19
necessary for comprehension of the text or to activate the existing
knowledge. To make students aware of the type of the text they will
be reading and the purpose for reading.
b. Whilst reading : students check their comprehension as they read, to
determines the appropriate type and level comprehension.
c. Post – reading : post reading activities function as a losing mark for
reading class.
3. Purpose of reading
There are six main purpose of reading comprehensive according
Grabe ( 2009: 8 – 10 ). The purpose includes :
a. Reading for information
The combination of scanning (identifying a specific graphic
form) and skimming (building a simple quick understanding of the
text) allows a reader to search information.
b. Reading for quick understanding (skimming)
Reading for quick understanding used for variety of other
reasons and so may be seen as a superordinate purpose. The readers
used skimming when they want to determine what a text is about and
whether or not they want to spend more time reading it.
c. Reading to learn
Reading to learn is often carried out in academic and
professional settings. Reading to learn places more processing
20
the main ideas and many supporting ideas and be able to recall this
information as needed.
e. Reading to evaluate, critique, and use information
It often also represents an increased level of demand and a
more complex interaction of reading processes.
f. Reading for general comprehension
Reading for general comprehension is the most common
purpose for reading among fluent readers, and it is the default
assumption for the term vocabulary mastery and reading
comprehension
4. Developing interest in Reading
Scott (1973) in Dechant (1982: 77), notes that overriding cause of
reading failure is lack of attention, withdrawal from the learning task and
nonuse of cognitive and perceptual power.
According to Dechant (1982: 77), pupils whose problem is
essentially motivational may be helped by awareness of their progress.
The material should also interesting and on the pupils’ instructional level.
The teacher may promote interest i reading in the following ways:
a. Develop chart to be placed on the reading table containing pupil
made jokes, riddles, statement, an stories
b. Provide a wide selection of easy reading materials
c. Guide pupils to books which they can read independently
21
e. Use book exhibits, book firs, books advertisement, periodicals and
bulletins to stimulate interest in reading
f. Give children an opportunity to share their reading experiences
through book report, panels, or a round table discussion
g. Develop a book club or hobby club
h. Introduce the children to the reading topic by illustrating the content
with TV, films, and recording
i. Provide class time for library reading
j. Stay in the background
k. Suggest the sport page, magazines, or even the comics for pupils
l. Have pupil keep record of the book they have read
m. Help pupils to look upon themselves as reader
5. Principles of Teaching Reading
According to Harmer (2001:70), there are some principles
behind the teaching of reading:
a. Reading is not a passive skill. Reading is an incredibly active
occupation. To do it successfully, we have to understand what the
words mean.
b. Students need to be engaged with what they are reading. As with
everything else in lessons, students who are not engaged with the
reading text, not actively interested in what they are doing, are less
22
c. Students should be encouraged to respond to the content of a reading
text, not just to the language. It is important to research reading texts
for the way they use language, the number of paragraphs they
contain and how many times they use relative clauses.
d. Prediction is a major factor in reading. When we read texts in our
own language, we frequently have a good idea of the content before
we actually read.
e. Match the task to the topic. Once a decision has been taken about
what reading text the students are going to read, we need to choose
good reading tasks, the right kind of questions, engaging and useful
puzzle, etc.
f. Good teachers exploit reading texts to the full. They integrate the
reading text into interesting class sequences, using the topic for
discussion and further tasks, using the language for research and later
activation.
C. Reading Comprehension
1. Definition of reading comprehension
According to Thorndike (1917) in Dechant (1982: 311), reading
comprehension includes correct meanings, the ability to reason one’s way
through smaller idea, segments, and the ability to grasp the meaning of a
larger unitary idea.
According to Dechant (1982: 312) comprehension is a thinking
23
basic knowledge such as their background experience (vocabulary
mastery, knowledge, concepts and ideas) and their language skill
(knowledge of morphology, syntax and grammar). The readers use their
thinking and verbal reasoning skill to read for main ideas, for details, for
organization, for evaluation and appreciation.
Klingner, Vaughn and Broadman (2007: 8) say that reading
comprehension is a process of interaction between readers and what they
bring to the text, such as their prior or background knowledge and
strategy use. This process also includes the variables related to the text,
for example the readers’ interest of the texts and their understanding of
the genres of the texts. It means that what the readers learn and how they
respond and comprehend the text is individualistic. The process of
constructing meaning depends on the individual competencies, such as
experience and how to interpret the text.
From the statement above the writer concludes that reading
comprehension is the process of communication among reader and writer
through a text in order to grasp idea and information accurately.
2. Basic of reading comprehension
According to Klingner, Vaughn and Broadman (2007: 9-11),
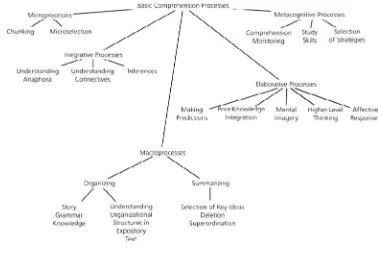
reading comprehension consist of five basic comprehension processes.
These processes work together simultaneously and complement one
another, there are:
24
Micro process it happen within individual sentences. It is the
ability to remember details idea of a text that carries meaning.
b.integrative processes
It is the process of understanding and inferring the relationships
among clauses to make connection across sentences.
c.Macro processes
Macro process is the ability to organize ideas in a coherent way.
These processes can be done through selecting the most important
information to remember and delete relatively less important details.
d.Elaborative processes
These processes connect the information provided inthe text to
the prior or background knowledge.
e.Metacognitive processes
It is the conscious awareness or control of cognitive process. In
these processes the readers try to understand the texts, select what
information to remember and decide the strategies used when reading.
The metacognitive strategies that the readers use include repeating
information to enhance recall, underlining important words or sections
of a passage, note taking,and checking understanding.
25 .
Figure 2.1
Five basics reading comprehension processes. Irwin (1991) in Klingner, Vaughn andBroadman (2007)
3. Level of Comprehension
Learning to comprehend involves complex skills. Various experts
have their level of comprehension. Lanier and Davis (1972) in Dechant
(1982: 313) say that in summarizing comprehension skills, categories
them as:
a. Literal kills
Including recognizing and recalling fact, detail, sequence, main
26 b. Interpretative skills
Including inferring, drawing conclusions, generalizing, deriving
meaning from figurative language predicting, anticipating, and
summarizing
c. Critical skills
Including judging, detecting propaganda, analyzing, checking
validity, checking author’s biases and purposes)
d. Creative skills
Include applying information and responding emotionally.
While Barret’s Taxonomy (1972) cited in Dechant (1982: 313)
identify that there are four levels of reading comprehension, there are:
a. Literal recognition or recall
The literal level is the lowest cognitive level where the reader
understands just what the words mean. The information that is stated
explicitly in the text is retrieved by the reader in the form given. Such
literal information may be the main idea, a set of specific details, or a
sequence of events.
b. Inference level.
This level requires the readers understand the literal information
from level one and go beyond it to hypothesize about relationship,
27 c. Evaluation level
It requires the reader to make judgement about the content, using
external (the teacher or authorities on the subject) or internal criteria
(reader’s personal experiences and knowledge) as points of reference.
d. Appreciation level
It relates to the emotional responses of readers to a text. It also
refers to the reader’s awareness of the literacy and stylistic techniques
used by an author to encourage a reader’s emotional responses.
Base on explanation above the writer conclude that in order to
comprehend a text the reader should read a text more than a time. The
experiences or background knowledge of the reader is prime modal to
comprehend a text.
D. Descriptive Text
1. Definition of descriptive text
Description text is a text about characteristic features of a particular
thing. According to Oshima and Hogue (1997:50), descriptive writing
appeals to the senses, so it tells how something looks, feels, smells, tastes,
and/ or sounds.
2.
Purposes and Kinds of Descriptive TextButt et al. (2001),Derewianka (1991) and Feez and Joyce (1998)
cited in Derewianka (2003: 136) the purpose of descriptive text is to
provide information about particular person, place and thing. Thereforeit
28 a. Describing people
b. Description of place
c. Description about thing
3. Generic structure of descriptive text
According to Gerot ad Wignell (1995) in Dadi (2015: 171) propose
two generic structure of descriptive text:
a. Identification: an introduction to the subject of the description.
b. Description: describe the characteristic features of the subject.
4. Language Feature of Descriptive Text
According to Cavanagh (1998) cited in Mursyid (page 5-6) said
that the language feature of descriptive text as follows:
a. Generalized participants: a whole class of things
b. Use of action verbs, especially when describing behaviour
c. Use of linking verbs (is, are, has, have, belongs to)
d. Use of present tense
e. Descriptive language; factual and precise
What they look like (color, shape, size, etc.)
What they have (body parts, components, etc.)
What they do (habits, behaviour, functions, uses, etc.)
f. Use of expressions of defining, classifying, comparing,
and contrasting (are called, belong to, can be classified as, are
29 g. Technical vocabularies
h. Formal and objective language: personal pronoun "I", "we", and the
writer's opinions are not generally appropriate.
i. Often accompanied by diagrams, photos, and illustrations.
5. Example of Descriptive text
My Beloved Mother
(Identification)
Every people certainly have a mother. It is because people are born
from her. The existence of her among us is definitely important. That is
why I love her so much. I owe great debt to what she has been doing to me
until right now. And here is my mother.
(Description)
My mother's name is Khodijah. She was born 49 years ago. She is
short, but not too short. She is little fat. And she is old. She has got short
white straight hair. She has got brown skin. She is beautiful. Her hand is so
soft, the hand that have taught me to be kind person. She never stops to
support me. She always tells me to not give up so easily. She always gives
me some fine solutions when I have some problems. The importance of
her is never denied. That is why I never reject her willing.
E. Find the Stranger Game 1. Definition of Game
According to Hadfield (1990: v) in Tuan (2012: 259) game is
activity with rules, a goal and an element of fun.
Game is an organized activity that usually has the following
30
between players in spoken or written language (Richard, Platt and Platt,
1992:153) in Tuan (2012: 257-264).
From the definition above the writer conclude that game is
activities which have rules with the aim for pleasure and include a value
of competition.
2. Value of game
Games are always interesting to the students who learn
vocabulary mastery because it makes fun and enjoy. Considering
language learning Stojkovic and Jerotijevic (2011: 941) propose several
advantages using game in EFL class:
a. Through fun and apparently less demanding practice, games increase
learners’ attention motivation and promote learning (Hansen, 1994)
b. Group and peer work may induce teamwork and enable successful
interaction (Rinvlucri & Davis, 1995)
c. By lowering the affective filter (Krashen 1985), games provide
favorable condition for effective language acquisition (Wierus,
1994)
d. Through a meaningful context, student are provided with
comprehensible input (Krashen, 1985)
e. Each of the four basic skills may be practiced by the use of games
31 3. Definition Find the Stranger Game
In the teaching and learning there are many kinds game that can
used to teach the students for increase their vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension. one of them there is reading race game. Find the
Stranger Game is a game in which the players should determine the
foreign word is in a group of words or determine the word which is not
the groups of it (Walidi, 2006: 14).
4. Procedure of the Find the Stranger Game
According to Walidi (2004: 14) the procedure of Find the
Stranger Game is:
a. Divide the students into teams consist of four students per group
b. Make a word list on the card such as a list of adjective or noun or verb
than insert one “the stranger word” on a certain list of noun or
adjective or verb. Example: a card with list of adjectives inserted by
one noun word as the stranger.
c. Each group go forward in turns and is represented by a team member
to take the card. Together each group must find the stranger on the
card is taken.
d. After finding the stranger, answers written on paper provided. Teams
share their answers. For every correct answer, they get one point.
e. Tally the points on the board underrespective team names.
32
g. Teams can share the meaning of each word or use it in a sentence to
get full mark.
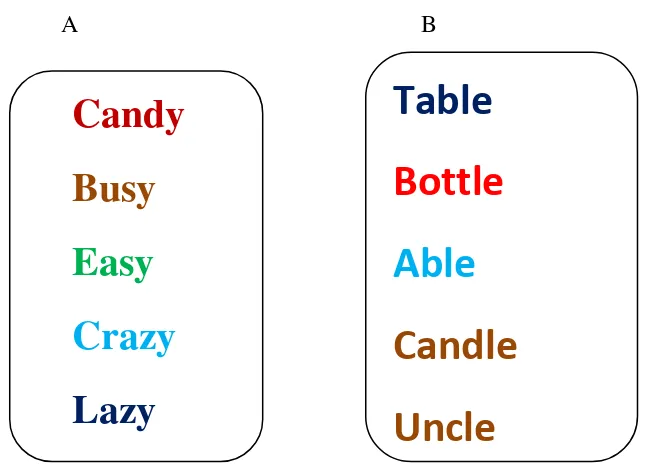
5. Example Find the Stranger
A B
From the find the stranger card above, the stranger word can be analyzed
as:
Card A: Candy (Noun)
Busy (Adjective)
Easy (Adjective)
Crazy (Adjective)
Lazy (Adjective)
The stranger word from card A is Candy, whereas candy is a noun
although the other words are an adjective
Card B:
Table (Noun)
Candy
Busy
Easy
Crazy
Lazy
Table
Bottle
Able
Candle
33
Bottle (Noun)
Able (Adjective)
Candle (Noun)
Uncle (Noun)
The stranger word from card B is able, whereas able is a adjective
34 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter the writer explains about research setting, the subject of the
research, research methodology, procedures of the research, technique of
collecting data, and technique of analyzing the data.
A. Research Setting
This research was conducted at SMK N3 Salatiga. The explanation
about this school described as follows:
1. General Discussin of SMK N3 Salatiga
SMK N 3 Salatiga is located in Jalan Ja’far Shadiq Kalibening,
Tingkir, Kota Salatiga No.Tlp: (0298) 7103119. It was built on May, 21st
2007 and built on state-own area as wide 5.2700 m2. The total number of
students SMK N 3 Salatiga in academic year of 2016/2017 is 1.321
students. They are consists of 1.136 male students and 185 female
students. The detail of the school described as follows:
Name of school : SMK N3 Salatiga
Address : Jalan Ja’far Shadiq Kalibening, Tingkir, Kota
Salatiga
Accreditation : A
Telephone : (0298) 7103119
E-mail : [email protected]
NSS : 321036202008
35
Wide : 5.27 ha
Head Master : Suripan S.Pd
NIP : 19650120 199003 1 003
Motto : Cerdas dan Berkwalitas ( Smart and Quality)
2. Situation of SMK N3 Salatiga
a. The subject and department of SMK N3 Salatiga
The subject matter that be taught in SMK N3 Salatiga are
Indonesian Language, Javanese Language, Mathematics,
Computer, Civic Education, English, Social Sciences, Natural
Sciences, Islamic Education, Guidance and Counseling, Sport,
and Arts Education.
In addition SMK N 3 Salatiga has six departments there are
Teknik pengelasan (Welding technique), Teknik Ototronik
(Ototronik Engineering), Agribisnis Tanaman Pangan dan
Holtikultura (Food crops and horticulture), Teknik Sepeda Motor
(technique of motorcycle) and Teknik geomatika (Geomatics
technique). Furthermore each department or major has practice
room or workshop.
b. The Teachers and Staff of SMK N3 Salatiga
The formal education needs qualified people to work as
teachers and some as administrators to undertake good teaching
learning process. In this school, there are 77 teachers and 18
36
this school teach different subject matter, there are: Indonesian
Language, Javanese Language, Teknik pengelasan (Welding
technique), Teknik Ototronik (Ototronik Engineering), Agribisnis
Tanaman Pangan dan Holtikultura (Food crops and horticulture),
Teknik Sepeda Motor (technique of motorcycle), Teknik
geomatika (Geomatics technique), Mathematics, Computer, Civic
Education, English, Social Sciences, Natural Sciences, Islamic
Education, Guidance and Counseling, Sport, and Arts Education.
While the staff members in this school consist of head of
administration, administrative staff, librarian, cleaning service,
gardener, and security guard.
c. Educational Facilities and Tools in SMK N3 Salatiga Salatiga in
the Academic Year of 2016/2017
SMK N3 Salatiga consists of 86 rooms to support in
teaching learning process, they are 45 classrooms and 10
productive room. The other buildings are head master room,
teacher room, library, counseling room, administration office,
health service, OSIS, cooperation room, sport facilities room, and
mosque, bathroom, laboratory, bathroom and another. The
37
d. The Extracurricular in SMK N3 Salatiga in the Academic Year of
2016/2017
The teaching learning process in SMK N3 Salatiga begins
at 07.00 a.m until 16.00 p.m everyday. Each lesson takes along 45
minutes. Beside intra curricular activities, the students also have
extracurricular activities recommended in order to improve their
skill achievements. The extracurricular activities are: computer,
football, Pasukan pengibar bendera (flag raisers), scout, Islamic
music religion club, qiro’, English club and etc.
Each of extra activities is held once a week on Saturday.
Besides improving students’ skill and achievements, the activities
are also aimed to train the students’ discipline, growing up their
talent ability, and developing their positive attitude and behavior
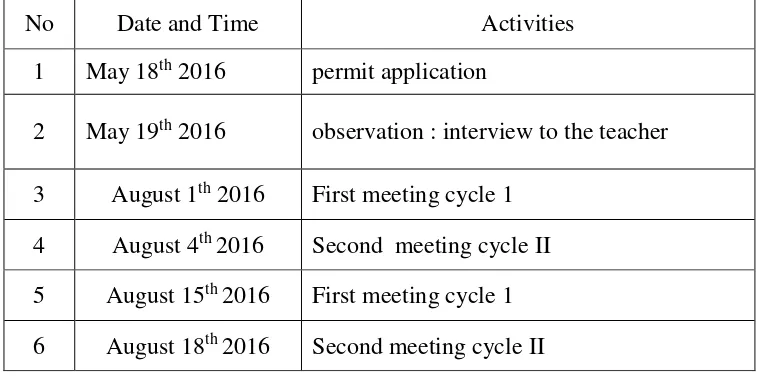
B. Description of Research Schedule
The research was conducted in May but the process during the
research began from August. In this research the writer as a teacher and the
collaborator Dini Wahyu Tri Utami in teaching learning process. The table
38
Table. 3.1 Time setting of the Research
C. The Subject of the Research
In this research, the writer choosed SMK N 3 Salatiga as subject of
the research especially the tenth years students. The tenth years students
consist of 12 class groups, but the writer took one class group, X Teknik
Sepeda Motor (TSM) 2 ( Technique motorcycle). The number of the
students are 34 students. They are 1 girl and 33 boys. Their native language
is Javanese . The average age of the participants are 16 years. The English
lesson is taught two times n a week and which is each meeting along with
two hours lesson; one hour lesson is 45 minutes.
The problems that the students faced when read English text are the
students have lack of vocabulary mastery, less interest in reading English
text. In addition the tudents assumed that English is difficult. In teaching
and learning process, the tenth years students of SMK N 3 Salatiga faced
some difficulties when their teacher explain the materials. It seen at their
No Date and Time Activities
1 May 18th 2016 permit application
2 May 19th 2016 observation : interview to the teacher
3 August 1th 2016 First meeting cycle 1
39
response in English learning. Some of them are bored, sleepy and did not
pay attention to their teacher explanation.
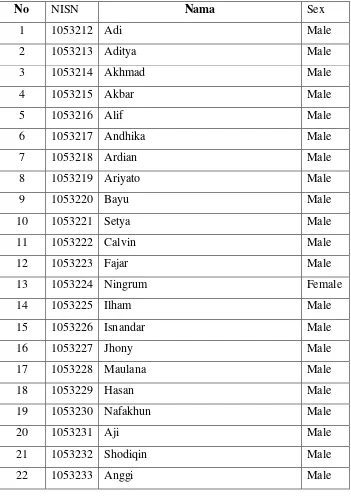
TABLE 3. 2
List of X- TSM 2 Class Group of SMK N 3 Salatiga in the Academic
40
23 1053234 Anwar Male
24 1053235 Bagas Male
25 1053236 Ngainul Male
26 1053237 Ulinuha Male
27 1053238 Habibi Male
28 1053239 Mamcribo Male
29 1053240 Arga Male
30 1053241 Rual Male
31 1053242 Septian Male
32 1053243 Tegar Male
33 1053244 Sutiyono Male
34 1053245 Yuswan Male
Source SMK N 3 Salatiga
D. Method of the Research
The research method used in this research is action research.
According to Suhasimi Arikuto (Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, 2010: 130)
methodology of this research stands from three words, classroom, action
and research. So there are three term can be explained.
1. Research
Research is activities to observe object of research that use a way and
a methodology together information or data to boost quality of thing
which is very interesting and important for teacher.
2. Action
41 3. A Classroom
A classroom is not limited just one room of class, but in term that more
specific. A classroom is a group of student in same time that already to
catch same material from same teacher.
Beside definition above, there are some definitions of action
research. The first definition is given by Kemmis (1983) in Hopkins
(1993:44) that action research is a form of self reflective enquiryundertaken
by participants in social situation in order to improve the rationality and
justices, their understanding of these practices and the situations in which
the practices are carried out.
Second, according to Ebbutt (1985) in Hopkins (1993:45), action
research is about the systematic research of attempts to improve educational
practice by groups of participants by means of their own practical action and
by means of their own reflection upon the effects of those actions.
Third, definition is given by Robert Rapport in Hopkins (1993:45)
that action research aims to contribute both to the practical concerns of
people in an immediate problematic situation and to the goals of social
science by joint collaboration within a mutually acceptable ethical
framework.
Based on many definitions above about action research; the writer
concluded that classroom action research is a research which is must stands
for three elements; there was improvement, treatment and certain sequence
42 E. Research Procedures
This research used classroom action research in SMK N 3 Salatiga on
August 2016, therefore in this case the writer used some steps as Kemmis and
Taggart. There are two cycles in this action research and each cycle consist of
two meetings.
According to Kemmis and Taggart (1990) in Burn (2010: 8) the
procedure of classroom action research are as follows.
1. Planning
The Activities in the planning which do by writer are:
a. Preparing materials, making lesson-plan and designing the steps
indoing the action.
b. Preparing list students’ name and scoring
c. Preparing teaching aids (e.g. cards, text, rewards, etc)
d. Preparing sheets for classroom observation (to know the situation of
teaching-learning process when the method or technique or mode is
applied)
e. Preparing a test. (to know whether students’ vocabulary mastery and
reading comprehension improves or not)
2. Action
a. Introduction/ greeting
b. Check of the present of the students
c. Giving pre-test.
43
e. Giving Occasion to the students to ask any difficulties or problem
f. Giving post-test.
3. Observation
Observation is one of the research instruments used in collecting
the data. As a scientific method, observation can be systematically used
to observe and note the phenomena investigated like students feeling,
thinking and everything they do in teaching learning process. The writer
plans this observation flexible and open to record the unexpected case.
4. Reflection
The result of the observation is analyzed. It is to remember
what happened that has been recorded in observation. Reflection seeks
to make sense of the process, problems and issues in strategic action.
It looks account of the variety of perspectives possible in the social
situation and comprehends the issues and circumstances in which they
arose. Reflection has evaluative aspect; is asks the writer to weight the
experience, to judge whether effects (and issues which arose) were
desirable and suggest ways of proceeding. The writer’s reflection is
done by discussing with his collaborator. The target of passing grade
was 75%. The passing grade was 75. If the target could not reached,
44
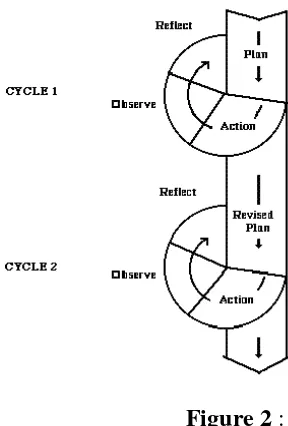
The procedures above are briefly ilustrated in the following
scheme.
Kemmnd Taggart (1990)
Figure 2 :
Kemmis and McTaggart (1988: 14) as quoted by Hopkins (1993:
48)
F. Technique of Collecting Data
In this research the writer uses test, observation and documentation in
collecting the data.
1. Test
Arikunto (2010: 226) stated that test is used to measure the
students basic ability and achievement. He mentions that there are two
kinds of achievement test which usually used by school:
a. Test made by the teacher; that arranged by certain procedure, but it has
not been examined many times so its characteristics and strength has
45
b. Standardized test; a test that usually has been available in a testing
institution and has been guaranteed its effectiveness.
In this research, writer collected data by using test made by teacher.
From the result of the test the writer is able to know the improvement of
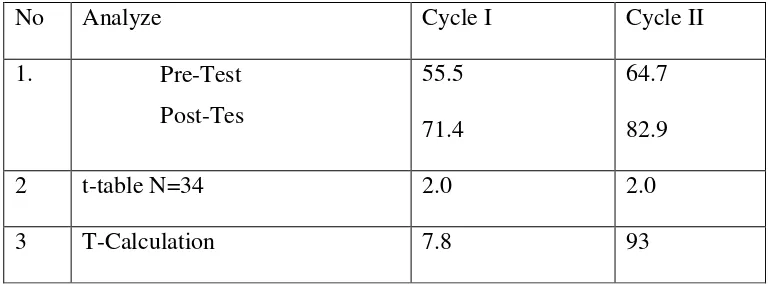
students’ comprehension. The writer made pre- test and post- test in each
cycle. Pre- test is used to know the students’ ability in learning English
especially in reading lesson. While post-test, it is used to measure how
far their improvement after apply the game in reading lesson. Pre-tes and
post-test use to know the differences of the students’ ability before and
after the teacher applied the game.
2. Observation
According to Arikunto (2010: 199) observation is a limited
activity to observe something using eyes.
Observation would be used to monitor the students’ activity
during English teaching and learning process in reading. Based on the
observation, can be known interest, motivation and the improvement of
students’ vocabulary mastery and reading comprehensions that occured
in learning process.
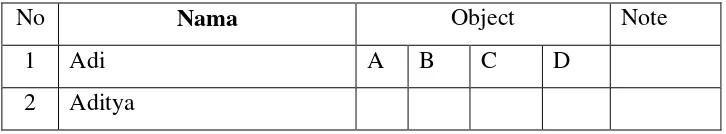
. The table below show the example of observation sheet as follow:
TABLE 3.3
Student’s Observation sheet for students
No Nama Object Note
1 Adi A B C D
47 33 Sutiyono
34 Yuswan
Explanation:
A. Pay attention C. Activeness in responding question
B. Activeness in asking question D. Enthusiasm in doing test
3. Documentation
In this research, the researcher used documentation as one of the
instrument. According to Arikunto (2010: 274), documentation is an
activity to look for variable like notes, transcribes, books, newspapers,
magazines, etc. In this method, writer holds a check- list to look for the
variable that had been decided.
The writer collected all the data from the school and the teacher
document such as students’ reading result in pre-test and pos-test and
also the students’ reading scores in pre-test and pos-test. Photo in this
research will be used to documented all situation in this class.. Another
instrument was the data from the school and from the teacher about the
situation of the SMK N 3 Salatiga, and especially the students in X
TSM 2 of SMK N 3 Salatiga. Beside the writer also prepare some video
as documentation.
G. Technique of Analyzing Data
The writer conduct the actoin research of the implementation of
48
reading comprehension. To analyzing data, there are two ways to analyze
the data, they are:
1. Descriptive technique
The writer used the descriptive technique to analyze students
participation, interest, and students behaviour during the teaching
learning process. The writer described all activity that happened in the
classroom. In descriptive technique, the researcer analyzed the
observation sheet which has been made by the collaborator.
2. Statistical technique
A statistical technique was used to calculate the result of the test,
before and after applied using Find the Stranger Game to improve
students’ vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension. According to
Sudijono (2008:81) by using formula:
a. Mean
M = ∑XN
Where,
M : Mean of students’ score
∑X : The sum score of students’ reading test
N : The total number of students
b. Percentage of students’ passing grade
According to Sudijdono (2008: 43) the formula to sought
percentage of students’ passing grade is:
P=𝑓
49 Where:
f= frequency were sought the percentage
N= numer of cases (students who pass the passing grade)
P= Number of percentage
D : Difference between pre-test post-test
N : Total number of students
d. T-test
To be able to know whether there is a significant
improvement or not between pre-test and postest, writer using
t-test after calculate the SD. The formula is :
o
50
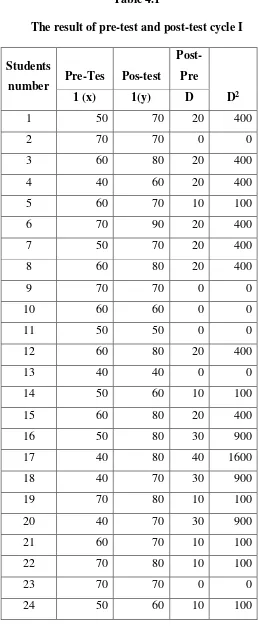
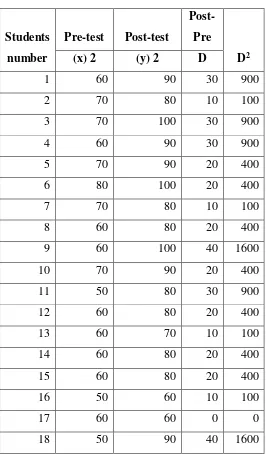
D : Different between pre-test and post-test