Chapter 5
The Self
By Michael R. Solomon
•
What depresses Lisa about the magazine
models?
•
Lisa feels that women don’t look like
models in “real life.” Do you agree?
•
If Lisa doesn’t consider herself
unattractive, why does she consider
cosmetic surgery?
•
Does Lisa want to improve herself for Eric
or herself?
Perspectives on the Self
•
Does the Self Exist?
–
1980’s called the “Me Decade”
–
March 7
thdesignated “Self Day” by
Self
magazine
–
Western societies emphasize uniqueness of self.
–
Collective self:
Eastern culture’s belief that a
person’s identity is derived from his or her social
group.
Self Concept
•
Self Concept:
– The beliefs a person holds about his or her own attributes and how he or she evaluates these qualities
•
Dimensions of the Attributes of Self Concept:
– Content – Positivity
– Intensity
– Accuracy
Self-Esteem
•
Self-esteem:
– Refers to the positivity of a person’s self-concept.
•
Social Comparison:
– A process by which consumers evaluate themselves by
comparing themselves with others (particularly comparisons with idealized images of people in advertising)
•
Self-esteem Advertising:
Real and Idealized Selves
•
Ideal Self:
– A person’s conception of how he or she would like to be – Partially molded by elements of a consumer’s culture
•
Actual Self:
– A person’s realistic appraisal of the qualities he or she does and
does not possess
•
Fantasy: Bridging the Gap between the Selves:
– Fantasy: A self-induced shift in consciousness
– Fantasy appeals: Marketing communications aimed at
Multiple Selves
•
Role Identities:
– Different components of the self
•
Symbolic Interactionism:
– Stresses that relationships with other people play a large
part in forming the self
– Self-fulfilling prophecy: By acting the way we assume others expect us to act, we wind up confirming these perceptions
•
The Looking-Glass Self:
Self-Consciousness
•
Self-Consciousness:
– A painful awareness of oneself magnified by the belief that
others are intently watching.
•
Public Self-Consciousness:
– A heightened concern about the nature of one’s public
“image”
– Results in more concern about the appropriateness of
products and consumption activities
•
Self Monitoring:
– Awareness of how one presents oneself in a social
Consumption and Self-Concept
•
Products that Shape the Self: You are What
you Consume:
– People use an individual’s consumption behaviors to help them make judgments about that person’s social identity.
– Symbolic self-completion theory: People who have an
incomplete self-definition tend to complete this identity by acquiring and displaying symbols associated with it.
•
Self/Product Congruence:
– Consumers demonstrate consistency between their values and the things they buy.
– Self-image congruence models: Products will be chosen
The Extended Self
•
Extended Self:
– External objects that consumers consider a part of themselves
•
Four Levels of the Extended Self:
– (1) Individual Level: Personal possessions – (2) Family Level: Residence and furnishings
– (3) Community Level: Neighborhood or town one is from – (4) Group Level: Social groups
– A consumer may also feel that landmarks, monuments, or sports teams are part of the extended self.
Advertisements Extending the Self
•
This Italian ad
• Some consumers feel that a sports team is part of the extended self. At www.flameheads.com they celebrate fanaticism toward the Tennessee Titans football team.
• How does affiliation with a sports team affect self perceptions? What other affiliations are part of the
Sex Roles
•
Sex Identity:
–
An important component of a consumer’s self
concept
•
Gender Differences in Socialization:
–
Agentic goals
(Males): Stress self assertion and
mastery
Satirical Ad of Exploitation
•
This French shoe ad
pokes fun at ads that
demean women by
proclaiming: “No
woman’s body was
Sex Roles (cont.)
•
Gender Versus Sexual Identity:
– Sex-Typed Traits: Characteristics stereotypically associated with gender
•
Sex-Typed Products:
– Many products are sex-typed (i.e., they take on masculine or feminine attributes and are associated with gender)
•
Androgyny:
– Refers to the possession of both masculine and feminine traits
Culturally Bound Sex Roles
Sex Roles (conc.)
•
Female Sex Roles:
– Female sex roles are still evolving
•
Male Sex Roles:
– Masculinism: The study of the male image and the cultural
meanings of masculinity
•
Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual, and Transgender
(GLBT) Consumers:
– GLBT population is an attractive segment to marketers
Reinforcing Gender Stereotypes
•
This ad rebels
somewhat against
Targeting GLBT Consumers
•
This ad for Alize, a
VIDEO: Subaru
•
Survey data told
Subaru that it was
overlooking the
female demographic.
Body Image
•
Body Image:
–
Refers to a consumer’s subjective evaluation of his
or her physical self
•
Body Cathexis:
–
A person’s feelings about his or her body
•
Ideal of Beauty:
Ideals of Beauty
•
Is Beauty Universal?
– Men are attracted to an hourglass shape
– Women prefer men with a heavy lower face, above-average
height, and a prominent brow
•
The Western Ideal:
– Big round eyes, tiny waists, large breasts, blond hair, and blue
eyes
•
Ideals of Beauty over Time:
– Periods of history tend to be characterized by a specific
Beauty Ideals in the 1950’s
Working on the Body
•
Fattism:
–
Our society is obsessed with weight
•
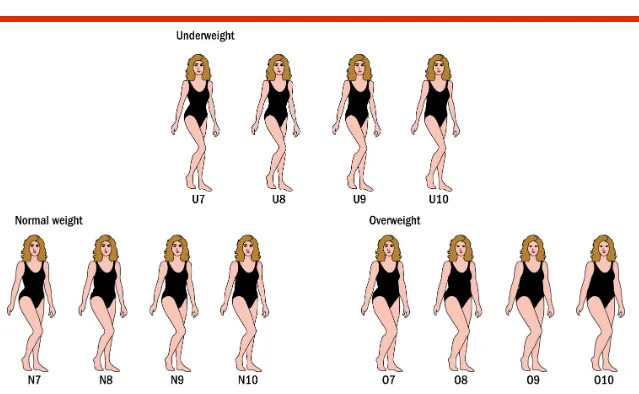
Body Image Distortions:
–
Women’s ideal figure is much thinner than their
actual figure
–
Anorexia:
Starving oneself in a quest for thinness
–
Bulimia:
Binge eating followed by purging
Unrealistic Body Shape Expectations
•
This ad for an online
weight-loss site drives
home the idea that the
media often
• In this advertisement, it is insinuated that this
model’s physique was
achieved partially through drinking milk. (Notice that the model is so thin you can see her ribs.)
• Is her physique really ideal? What kind of
distorted message is this sending to young girls
Cultural Emphasis on Thinness
• Society’s emphasis on thinness makes many consumers
Working on the Body (cont.)
•
Cosmetic Surgery:
–
Consumers are increasing electing to have cosmetic
surgery to change a poor body image or enhance
appearance.
–
Men are increasingly having cosmetic surgery too.
•
Breast Augmentation:
–
Our culture tends to equate breast size with sex
appeal.
–
Some women have breast augmentation procedures
Body Decoration and Mutilation
•
Purpose of Decorating the Self:
– To separate group members from nonmembers
– To place the individual in the social organization – To place the person in a gender category
– To enhance sex-role identification
– To indicate desired social conduct – To indicate high status or rank
– To provide a sense of security
Body Piercing
•
Body piercing has
Tattooing
•
Tattooing is becoming