Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
BE
BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING
journal homepage: be.ub.ac.id
The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (
Rattus norvegicus
)
induced carbon tetrachloride
Lestari Dewi
1†1
Faculty of Medicine, Hang Tuah University, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Received Accepted Available online
Keywords: Lecithin,
Carbontetrachloride †Corresponding author: [email protected]
A B S T R A C T
1. Introduction
Indonesia with the biological natural resources, has a variety of plant species is efficacious as a traditional medicine. One of them is the soybean plant. Since the first, the community has been utilizing soybean plants as a food ingredient Indonesia, as one of the countries producing soybeans, soybean processed products have become daily consumption, among other dishes processed into tofu and tempe, and soy milk. Communities also use soy as a traditional medicine. Soybeans have been widely recognized and exploited as a source material of lecithin [2,56]”. Soybean oil contains a substance called
lecithin (4)”. For decades, lecithin has been
popular used for treatment of various diseases, including lowering cholesterol levels in serum [4, 17, 20, 27, 35, 36, 38]”, lowering plasma
homocysteine levels [4], and improve brain memory in patients with Alzheimer's, and dementia in patients with Parkinson's [4, 8, 13, 30, 31, 33]”. Lecithin is also an important ingredient formation of neurotransmitters [9, 34]”. Oral intake of lecithin may also help reduce the formation and healing of gastrointestinal ulcers in some animal species [30]”. Of various dietary supplement products contained in the free market, there are products that contain lecithin, derived from soy beans. The product is recognized to cure various diseases caused by free radicals, including hepatic dysfunction. Lecithin is a substance that turned out to have antioxidant effects [2, 3]”. In an in vitro study results obtained, that the soybean oil (soybean oil) contain the highest levels of antioxidants among plant oils derived from seeds [24]”. That is why lecithin from soybeans more potent as compared lecithin
Objective: To prove that the lecithin is administered orally has hepatoprotective effect on white male rats given CCl4 intraperitoneally.
Material and Methods: 45 male Wistar rats, aged 12 weeks were randomly divided into five groups. Group I, given solvent CMC - Na 0.25% dose of 0.01 ml/g bw, and were given olive oil dose of 1 ml/kg bw, intraperitoneal injection. Group II, given solvent CMC - Na 0.25% dose of 0.01 ml/g bw, and given CCl4 dose of 1 ml/kg bw,dissolved in olive oil by intraperitoneal injection. Group III, IV and V respectively given dose lecithin 90/180/360 mg/ kg bw,dissolved with 0.25% CMC-Na, and given CCl4 dose of 1 ml/kg bw dissolved in olive oil at a ratio of 1: 1, by intraperitoneal injection. On day 10, 24 hours after administration of CCl4 and olive oil , all the rats dissected, after first anesthetized with ether by inhalation. Then the blood taken from the heart to examine the level of AST and ALT in serum and hepar were taken for histopathological examination.
Results: Giving lecithin 90/180/360 mg/kg bw were accompanied CCl4 1 ml / kg body weight (group III, IV, and V), shown to reduce levels of SGOT in serum compared with the group that received only CCl4 and giving lecithin 90/180/360 mg/ kg bw with CCl4 1 ml/kg bw (group III, IV, and V) is proven to reduce ALT levels compared with the group that received only CCl4. On histopathological examination of liver cells proves that lecithin dose 90 / 180/360 mg/kg bw with CCl4 1 ml/kg bw is proven to reduce the amount of cell necrosis than the group that only received CCl4.
Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
cholesterol lowering of corn oil [25]”. Since several decades, the role of antioxidants for health has been a lot of attention from the scientific community. Hundreds of studies have been conducted and published. Physiological function of antioxidants is to prevent further damage to cellular components as a result of chemical reactions involving free radicals. Free radical production occurs continuously in all cells as part of normal cellular function. If there is excessive production of free radicals will cause oxidative stress [16]. Oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathophysiology of various diseases, including atherosclerosis, inflammatory processes, cancer, chronic renal failure, and diabetes mellitus as well as the aging process [16, 18]”. Oxidative stress also causes a major pathogen in liver disorders [22]”. Repair of fatty degeneration, fibrosis, and cirrhosis can be achieved primarily by antioxidants or agents that neutralize the collagen deposition [23]”. The liver is an organ that plays an important role in the metabolism and detoxification. Exposure by a variety of toxic materials will enhance liver damage . Potential liver damage because it is the first organ of the gastrointestinal tract after exposure to the materials - materials that are toxic. The process of metabolism by the liver to detoxify the Raw-material, but the process can produce metabolites that are more toxic than the parent material [5]”. Materials - materials that are toxic to the liver can be derived from the food we eat. Along with the advancement of civilization and technology, developments in the field of processed foods have also increased. To make food more attractive appearance, taste better, and are more durable that required certain materials are added to the food. Material - extra material is not seldom that are toxic to the liver. In addition, the drug - a drug that is used freely, not by the rules or prescribed dose, can also toxic effect on the liver [26]”. In this study, a model of liver disease, use induction potent hepatotoxins, namely carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in experimental animals [1, 5, 18, 23, 28, 29]”. CCl4 is a prototype hepatotoxic substances most commonly used in research related to hepatotoxicity, because in small doses has a clear effect, available in pure form and can give the same effect on different species, and when given orally can cause liver damage more severe compared with other organs [11, 21]”. Liver damage caused by CCl4 is due to exposure to free radicals
[30]”. Based on the above background, the activity of soybean lecithin can protect liver function with the possibility of working as an antioxidant. So in this study to prove whether lecithin from soybeans, which is administered orally to male white rats that had been induced with CCl4, has a hepatoprotective effect, by measuring the levels of AST and ALT enzymes and liver histopathology. From the results of this research can obtain information and useful scientific data on the effect of lecithin on the liver.
2. Materials and Methods
Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
given CCl4 dose of 1 ml / kg body weight dissolved in olive oil at a ratio of 1: 1, by intraperitoneal injection. 24 hours later surgery.On day 10, ie 24 hours after administration of CCl4 and olive oil and, all rats dissected, after first anesthetized with ether by inhalation. Then the blood taken from the heart as much as 3 ml .Serum obtained was used as a sample for AST and ALT. Liver take in 10% formalin, then checked the histopatology.
2.1 Animal Etic Code
Animal was placed in a plastic box, measuring 50 x 40 cm, woven wire topped lid. Each box contains 5 rats. The boxes are then placed on a shelf plastic stacking timber, and placed in a room with lighting conditions, air circulation, good hygiene. Each was given a plastic box base from the chaff, with the aim of absorbing urine, so it does not wet the body, which can affect their health. The husks replaced every day. Plastic box also changed and washed every day. Food and beverages provided ad libitum.Giving lecithin and CMC-Na orally, performed using the sonde pediatric hose No. 8, directly into the stomach.
Administration of CCl4 and olive oil by intraperitoneal injection performed using tuberculin syringe. Before the surgery, animal anesthetized with inhaled ether. Animal anesthetized for approximately 1 minute, by the way put in a jar containing cotton that has been moistened with ether. Animals taken not to die. Then performed surgery on his abdomen using scissors, and the first organ to look for is heart. This surgical procedure is done carefully so that the scissors are not the inferior vena cava. In a state still anesthetized, the heart was still in pulsed conditions, then with 5 cc syringe of blood taken from the heart, aspirated with a syringe for up to 3 cc. Then the liver organ is taken for histopathological examination.
3. Result
The following table shows the effect of lecithin dose of 90, 180, and 360 mg / kg body weight /day, the intragastric for 9 days on levels of AST, ALT and liver histopathology white male rats (Rattus
norvegicus) induced CCl4 dose of 1 ml / kg, single
dose , intraperitoneally.
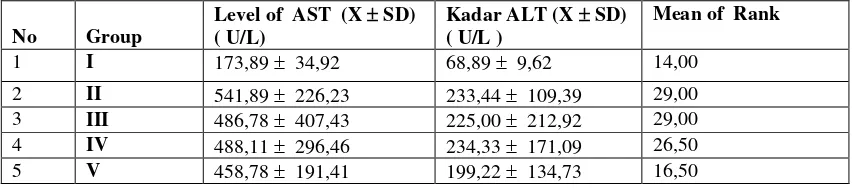
Table 1. The effect of lecithin dose of 90, 180, and 360 mg / kg body weight /day on the intragastric for 9 days on levels of AST, ALT and liver histopathology of white male rats
No Group
Level of AST (X SD) ( U/L)
Kadar ALT (X SD) ( U/L )
Mean of Rank 1 I 173,89 34,92 68,89 9,62 14,00
2 II 541,89 226,23 233,44 109,39 29,00 3 III 486,78 407,43 225,00 212,92 29,00 4 IV 488,11 296,46 234,33 171,09 26,50 5 V 458,78 191,41 199,22 134,73 16,50
In the results of the study proved that the administration of CCl4 1 ml / kg increase AST levels were significantly different (P <0.05) compared to controls. Giving lecithin 90, 180, and 360 mg / kg were accompanied CCl4 1 ml / kg proven to reduce levels of AST in serum compared with the group that received only CCl4 alone, although there was no significant difference, but there is a tendency that increasing the dose of lecithin is given, then the levels of AST decreased. Results of research on the effect of lecithin on levels of ALT, also proves that the administration of CCl4 can increase ALT levels were significantly different (P <0.05) compared to controls. Giving lecithin 90, 180, and 360 mg / kg CCl4 with 1 ml / kg proven to reduce ALT levels compared with
Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
significantly different (P <0.05) than the group that received lecithin 360 mg / bw. Giving lecithin doses 90, 180, and 360 mg / kg CCl4 with 1 ml / kg proven to reduce the number of necrotic cells than the group that only received CCl4, and there is a tendency that increased dosage of lecithin is given, the amount of cell necrosis decline. Linear regression analysis proved that there is a linear relationship in the group given lecithin with histopathological changes in the liver cells, namely a decline in the number of liver cells that undergo necrosis with increasing doses of lecithin are given.
4. Discussion
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a chlorinated hydrocarbon, which has been widely used in research as an inducer of hepatic damage caused by free radicals. The involvement of free radicals in the pathogenesis of liver damage caused by CCl4 toxicity has been studied and widely recognized [1, 18, 23, 28, 29]. In the liver, CCl4 requires biotransformation by cytochrome P450 to produce a metabolite that is more toxic free radicals, and more reactive, namely trichloromethyl free radical (CCl3 ●). Trichloromethyl free radical will react with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) by taking the hydrogen ions. Reaction with the PUFA initiated the process of lipid peroxidation [11, 12, 23]”. Lipid peroxidation causes dysfunction of the liver cell membrane and form a reactive aldehyde. Furthermore, both of these will cause damage to hepatocytes, and can ultimately lead to cell death (necrosis) [23]”. In this study, to know there has been a disruption CCl4-induced hepatic function then performed biochemical and histopathological examination. Damage to the liver will be marked by the release of enzymes found in the liver into the circulation. The liver is made up of thousands of enzymes, some of which are present in low concentrations in serum. If an increase in enzyme activity in serum, it showed increased serum levels are included in the result of damage to liver cells [7]. Elevated levels of AST and ALT enzymes in the blood circulation can be used as an indicator of hepatic disorders [10]”. AST and ALT testing as an indication of liver damage so far proved the most practical and the most frequently used [10,14]”. In this study demonstrated that in rat that received CCl4 induced increased levels of AST and ALT enzymes in the serum. Rat blood serum test results above
Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
"steady state", so that when induced with CCl4, liver cells will experience severe interference experimental animals that did not receive therapy previous lecithin.
The authors report no conflicts of interest
References
1. Adiwisastra A. Keracunan Sumber Bahaya dan
Penanggulangannya. Penerbit Angkasa, Bandung. 1997:33 -35.
2. Alfonso R. Gennaro. Remington Practice of The Science and
Pharmacy. 19th ed. Mack Publishing Company: Easton,
Pennsylvania 18042. 1995
3. Andreas M. Papas. Antioxidant, Status, Diet, Nutrition, and
Health. CRC Press. 1998 : 99-100.
4. David W. Johnson, David J. Mokler . Lecithin’s Therapeutic Effects. Continuing Education Module. Central Soya
Lecithin Group.2001: 2 – 6.
5. David Zakim, Thomas D. Boyer. Hepatology A Textbook of
Liver Disease. Biochemical Tests for Liver Disease. 2nd Ed.
W. B. Saunders Company.1990: 658 – 659.
6. D. Robert Dufour, John A. Lott, Frederick S. Nolte, David R.
Gretch, Raymond S. Koff, Leonard B. Seeff. Diagnosis and monitoring of Hepatic Injury. Performance Characteristics of Laboratory Tests. American Association for Clinical Chemistry, Inc.2000.
7. Eugene R. Schiff, Michael F. Sorrell, Willis C.
Maddrey.Diseases of the Liver.Evaluation of the Liver : Laboratory Tests. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.1999: 219-223: 229-230.
8. Fernstrom J. D.Dietary Precursors and Brain
Neurotransmitter Formation. Annu Rev Med (United
States).1981: 32: 413-425.
9. Fernstrom J. D.. Can Nutrient Supplement Modify Brain
Function. Am J Clin Nutr.2000:71: 1669S – 1673S.
10. Frances K. Widmann. Tinjauan Klinis atas Hasil
pemeriksaan Laboratorium.. Terjemahan Siti Boedina
Kresno, R. Gandasoebrata, J. Latu. Edisi 9. Penerbit Buku
Gastroenterologi Hepatologi. Biokimia Penyakit Hati.CV. Infomedika Jakarta.1990.58-61.
15. Hummel CW.. The UFAW Handbook On The Care And
Management Of Laboratory Animal. 4th ed. London:
Churchill, Living Stone, Edinburg.1972:199-202.
16. S. Young, J. V. Woodside.. Antioxidants in Health and
Disease. J. Clinical Pathology.2000:54: 176- 186.
17. James W. Anderson, Belinda M. Smith, and Carla S.
Washnock. Cardiovascular and Renal Benefits of Dry Bean
and Soy Bean Intake. Am J Clin Nutr .1999:70: 464S – 474S.
18. Jason D. Morrow, Joseph A. Awad., Tatsuko Kato, Kihito
Takahashi, Kamal F. Badr, L. Jackson Roberts II, Raymond F. Burk. Formation of Novel Non- cyclooxygenase-derived Prostanoids (F2-Isoprostanes) in Carbon Tetrachloride
Hepatotoxicity. An Animal Model of Lipid Perxidation. J.
Clin. Invest.1992: 90: 2502-2507.
19. Jose C. Fernandez-Checa. Alcohol-induced Liver
Disease:when Fat and Oxidative Stress Meet. Annals of Hepatology.2003.
20. J. T. Knuiman, A. C. Beynen and M. B. Katan. Lecithin
Intake and Seru Cholesterol. American Journal of Clinical
Nutrition.1989: 49: 266 – 268.
21. Kaye s. Handbook OF Emergency Toxicology. 2nd ed.
Charles C, Thomas, Springfield.1961: 132-134.
22. Laura Cesaratto, Carlo Vascotto, Sebastian Calligaris,
Gianluca Tell. The Importace of Redox State in Liver Damage. Annals of Hepatology. 2004
23. Lutz W. D. Weber, Meinrad Boll, and Andreas Stampfl.
Hepatotoxicity and Mechanism of Action Haloalkanes: Carbon Tetrachloride as a Toxicological Model. Critical
Reviews in Toxicology ;33,2:Pro Quest Medical
Library.2003:105- 136
24. Nicoletta Pellegrini, Mauro Serafini, Barbara Colombi,
Daniele Del Rio, Sara Salvatore, Marta Bianchi, Furio Brighenti. Total Antioxidant Capacity of Plant Foods, Beverages and Oils Consumed in Italy Assessed by Three Different In Vitro Assays. American Society for Nutritional Sciences. 2003.
25. O’Mullane J. E., Hawthorne J . N.. A Comparison of The Effects of Feding Linoleic Acid- Rich Lecithin or Corn Oil on Cholesterol Absorption and Metabolism in The Rat.
Atherosclerosis.1982: 1: 81 – 90.
26. Marian Maltese Eschleman. Introductory Nutrition & Diet
Therapy 2nd ed. J. B. Lippincott Company.1991:111:114.
27. Mary S. Anthon. Soy and Cardiovascular Disease :
Cholesterol Lowering and Beyond. American Society for Nutritional Sciences. J. Nutr.2000: 130: 662S-663S.
28. Pandit S., Sur T. K., Jana U, Debnath P. K., Sen S.,
Bhattacharyya D.. Prevention of Carbon
Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats by Adhatoda Vasica Leaves.
Indian Journal of Pharmacology.2004:36:5: 312-313.
29. Raymond F. Burk, James M. Lane, and Kuldeep Patal.
Relationship of Oxygen and Glutathione in Protection against Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Hepatic Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation and Covalent Binding in The Rat. Rationale for the Use of Hyperbaric Oxygen to Treat Carbon Tetrachloride Ingestion. J. Clin. Invest.1984: 74:1996-2001.
30. Russett, J. C.. Lecithin and Equine Ulcers. Specialty Products
Research Notes.2002
31. Sandra L. Ladd, Susan A. Sommer, Stephen LaBerge, and
Please cite this article as: Dewi,L. The effect of lecithin on liver function of white rats (Rattus Norvegicus) Induced Carbon
32. Sandritter. Color Atlas and Textbook of Histopathology. 7th
ed. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publisher Inc.1984: 184-211.
33. Satoru Suzuki, Hideyuki Yamatoya, Masashi Sakai, Akito
Kataoka, Masayoshi Furushiro and Satoshi Kud. Oral
Administration of Soybean Lecithin Transphosphatidylated Phosphatidylserine Improves Memory Impairment in Aged
Rats. Nutritional Neurosciences. J Nutr. 2001:131: 2951-
2956.
34. Wurtman R. J., Hefti., Melamed E.Precursor Control of
Nurotransmitter Synthesis. Pharmacol Rev.1980:32:4: 315-
335.
35. Y. Nagata, K. Tanaka, and M. Sugano. Serum and
Cholesterol levels of Rats and Mice Fed- Bean Protec or
Case. J Nutr Sci Vitam.1981:27:6: 583 – 593.
36. Yongzhi Jiang, Sang K. Noh, and Sung I., Koo. Egg
Phosphatidylcholine Decreases the Lymphatic Absorption of
Cholesterol in Rats. Nutrition Interactions and Toxicity.2001: 2358- 2363.
37. Young S. N. Behavioral Effects of Dietary Neurotransmitter
Precursors: Basic and Clinical Aspects. Neuroscience and
Biobehavioral Reviews (USA).1996:313 – 323.
38. Y.Y. Kesaniemi and S. M. Grundi. Effects of Dietary