PR
The 1 st P The Role ofFACULTY OF ANIMAL S WE
WORLD’S POULTRY S
Faculty of Anima
PROCEEDINGS
Poultry International Seminar 2012 of Poultry in Improving Human WelfareORGANIZED BY:
L SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF ANDALAS, PA EST SUMATRA INDONESIA
AND
SCIENCE ASSOCIATION INDONESIA BRA
al Science, University of Andalas, Padan
Indonesia, 2012
PADANG
RANCH
228 1. STUDY ON MOLECULAR: GENETIC DIVERSITY IN D-LOOP
MITOCHONDRION DNA OF INDIGENOUS JAVA DUCK (MAGELANG DUCK)
Dattadewi Purwantini1), Tri Yuwanta2), Tety Hartatik2) and Ismoyowati1) 1) Faculty of Animal Science, Jenderal Soedirman University, Purwokerto, Indonesia
2) Faculty of Animal Science, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Corresponding author email: [email protected]
ABSTRACT
Individual duck in the population only inherited mitochondrial DNA from the female duck. Mitochondrial DNA had a higher rate of polymorphism than that of nucleus DNA, mainly on Loop (D-Loop) which does not decode protein (non-coding region) with the highest polymorphism in mitochondrial genome. Polymorphism (diversity) of nucleotide order of D-Loop was often used to identify and analyze individual duck’s genetic diversity inter and intra population, phylogenesis and determining the genealogy inter family, channel or breed of the female.
This research aimed to identify the genetic diversity based on nucleotide in D-loop mitochondrial DNA in the population of Magelang duck. The result gained could be used as the reference in determining the specific marker of mitochondrial DNA as the selection tool of Mallard duck conservation, breeding and propagation. The material was blood sample of Magelang ducks with eight different feather colors. Total DNA was isolated from the blood sample using DNA Isolation Kit (Geneaid). The amplification of D-Loop mtDNA with PCR technique used primary forwards DL-AnasPF and reverse DL-AnasPR. The PCR’s nucleotide produced was sequenced and analyzed.
This research succeeded in (1) Amplifying PCR towards a 718 pb fragment in D-Loop mtDNA, (2) Determining the nucleotide order of Magelang duck with feather colors of 675
pb jarakan polos (plain brown), 707 pb bosokan (dark brown), 640 pb kalungombo (brown
with wide white feather around the neck), 661 pb gambiran (mixed brown and white), 644 pb
jarakan kalung (brown with white necklace), 659 pb jowo polos (brown with specific
pattern), 665 pb wiroko (mixed black and white), and 651 pb plain white (yellow bill and feet), (3) finding variant or morph of Magelang duck from eight different feather colors with the order of Mallard duck (Anas platyrhynchos) as many as 65, 83, 63, 41, 81, 63, 8 and 79 normal variant, respectively, in different positions. The conclusion drawn was the different order of nucleotide in D-Loop DNA mitochondria showed a diverse genetic characteristic in Magelang duck population.
Key words: molecular, genetic diversity, D-Loop DNA mitochondria, Magelang duck
INTRODUCTION
229 as 73,63 ± 20,68% than Tegal ducks and Mojosari ducks or 42,42 ± 17,72 and 69,25 ± 22,16, respectively. While qualitative characteristics, feather color in Magelang ducks is more various than that of the other Mallard ducks. Ismoyowati and Purwantini (2010) reported that qualitatively Magelang ducks have nine various colors namely jarakan kalung (brown feather with white feather round the neck), coklat gambiran (mixed brown and white), wiroko (mixed black and white), kapasan (white dominating brown), putih jambul, bambangan (resembles Tegal ducks with bigger posture), putih polos (plain white) and hitam polos (plain black/cemani). The other Mallard ducks, Tegal ducks, Magelang ducks, Mojosari ducks, Bali ducks and Alabio ducks have a relatively similar feather color.
Molecular identification is apt for genetic marker to reveal any diversity intra species, philogeography, and to figure out the genealogy inter family for further use of genetic diversity study. Biomolecular approach through detection based on DNA polymorphism enables it to choose preeminent genetic ducks since each individual has different genetic structure. Zhang et al. (2002) reported that identification of genetic diversity in fowl using DNA polymorphism results in higher effectivity and sensitivity than using protein polymorphism.
Uniformity and diversity of genetic characteristics inter individual Magelang ducks in the population can be identified through polymorphism analysis of D-Loop mtDNA. One of the commonly used techniques to analyze polymorphism of D-Loop mtDNA is PCR
(Polymerase Chain Reaction) with specific primary in order to produce short DNA fragment
that the polymorphism of D-Loop mtDNA can be directly identified and analyzed using sequence method. Polymorphism analysis is carried out after different sequence in the observed DNA fragmen or gene occurs.
Individual duck in the population only inherits mitochondrial DNA from the female duck. Mitochondrial DNA has a higher rate of polymorphism than that of nucleus DNA, mainly on Loop (D-Loop) which does not decode protein (non-coding region) with the highest polymorphism in mitochondrial genome. Polymorphism (diversity) of nucleotide order of D-Loop was often used to identify and analyze individual duck’s genetic diversity inter and intra population, phylogenesis and determining the genealogy inter family, channel or breed of the female. Genetic identification using mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in fowl group has been administered in either commercial or non commercial chicken although still relatively limited as the insight of chicken lineage (Akishinonomiya et al., 1994; Liu et al.,
2006; Niu et al., 2002 in Silva et al., 2009), while Mallard ducks get less frequent genetic identification. Leekaew et al., (2008) reported the success in studying genetic diversity of Mallard ducks in Thailand using polymerase chain reaction to amplify fragment from control area of D-loop mt DNA as much as 710 bp. The result of sequence analysis and phylogenetic relationship of the two Mallard ducks in Thailand can be identified based on D-loop segment in 667 bp with primary L78: ‘5-GTTATTTGGTTATGCATATCGTG-3’ and primary H774: ‘5- CCATATACGCCAACCGTCTC-3.
Accordingly, a research was carried out to determine genetic diversity based on the nucleotide sequence in D-loop mtDNA area in the population of Magelang ducks. The result gained could be used as the reference in determining the specific marker of mitochondrial DNA as the selection tool of Local duck conservation, breeding and propagation.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Blood sample was taken from Magelang ducks of eight different feather colors: jarakan
polos (plain brown), bosokan (dark brown), kalung ombo (brown with wide white feather
230 using DNA Isolation Kit (Geneaid). The amplification of D-Loop mtDNA with PCR technique used primary pair of forwards DL-AnasPF and reverse DL-AnasPR. The PCR nucleotide produced was sequenced and analyzed. Research method applied was experiment to (1) extract DNA through DNA isolation from duck blood sample, (2) amplify D-loop mtDNA area using PCR, (3) sequence and analyze nucleotide from sequencing result.
Magelang duck blood sample
Blood sample was taken using disposible syrink from wing vene (vena axillaries) as much as 3 ml per duck and kept in vacontainer containing EDTA anticoagulant to prevent blood clotting. In case DNA isolation was not directly carried out, the blood sample was kept in ice-filled flask or in refrigerator.
Extraction through total genome DNA isolation
Total genome Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid (DNA) was extracted from blood sample and isolated using DNA Isolation Kit (Geneaid) as follows: 25µl blood sample was put in
eppendorf tube, added with 275 µl PBS and 900 µl RBC Lysis Buffer. The formed solution
was incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes, then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for five minutes. Pellet in the tube was added with 100 µl RBC Lysis Buffer and 200 µl GB then incubated at 60 0 C over night. The formed solution was added with 200 µl absolute ethanol, then put into GD column and centrifuged 14.000 rpm for five minutes. Supernatant in the tube under was discharged, column matrix was added with 400 µl W1 Buffer, then
centrifuged at 14.000 rpm for two minutes. Supernatant was discharge again and the column matrix was added with 600 µl Wash Buffer (ethanol added), and centrifuged 14.000 rpm for two minutes. Supernatant in the tube was discharged and the dry GD column was centrifuged again at 14.000 rpm for three minutes. Supernatant under tube was replaced with the new
eppendorf coded like the sample to contain the formed DNA. 100 µl pre-heated Elution
Buffer was put right at the center of column matrix, left for three minutes then centrifuged at
14.000 rpm for one minute, added with 100 µl pre-heated Elution Buffer so that DNA in column matrix could get down into eppendorf tube, then centrifuged again at 14.000 rpm for two minutes. Solution in the eppendorf contained DNA fibre as a result of isolation. This GeneAmpRPCR systemthermocycler 2400 (Perkin Elmer) machine. Amplification of D-loop mtDNA area was carried out as follows: pre denaturation at thermocycler temperature up to 940 C for five minutes. PCR reaction process started at 940 C stable temperature. DNA
denaturation template was at 940 C for 30 seconds. Primary annealing on DNA template was
at 560 C for 45 seconds. Elongation or extension took place when PCR reaction was about to stop and the thermocycler remained at 720 C for one minute. To gain an optimum result, PCR was repeated 35 cycles. Final extension was to perfect the incomplete DNA extension at 72o C for five minutes.
231 from Electrophoresis Documentation and Analysis System 290 (EDAS 290) with UV ray ( = 300 nm).
DNA Sequencing of Magelang Duck
DNA amplification from amplification (PCR product) was carried out by Genetika
Science Indonesia Ltd. Sequencing result was nucleotide sequence and electrophoregram
graphic with colored peaks to differ nitrogen bases (nucleotide) in that green for Nucleotide A (Adenine), black for nucleotide G (Guanine), blue for nucleotide C (Cytosine) and red for nucleotide T (Thymine).
Analysis of Nucleotide sequence Result
Analysis of nucleotide sequence result to determine any new variant or diversity was compared to the sequence from GeneBank (GenBank: HM010684.1, 2010) database. It showed the base sequence at D-loop DNA mitokondria complete genome area in Mallard duck (Anas platyrhynchos) was 1049 pb.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
DNA Extraction Result through DNA Isolation of Duck Blood Sample
DNA extraction is basically DNA molecules separation from the other components by lysis method. This research used DNA Isolation Kit (Geneaid). DNA extraction result was put in electrophoresis at 1% gel agarose to ensure the success of isolated DNA. DNA solution with qualitatively high concentration showed thick and bright DNA bands figures; contrarily, low concentrated DNA showed pale smear bands. Figure one shows DNA extraction electrophoresis result of Magelang duck blood sample based on various feather colors.
A B C D E F G H
Figure 1. DNA extraction electrophoresis result of Magelang duck blood sample using 1% gel Agarose
Note: Blood sample of Magelang duck A (Jarakan polos), B(Bosokan), C (Kalung ombo), D (Gambiran), E (Jarakan Kalung), F (Jowo polos), G (Wiroko), H (plain white)
232 DNA Amplification in D-Loop mitochondria area of Magelang Duck using PCR
PCR utilized primary pair of DL-AnasPF (L56) as forward primer and DL-AnasPR (H773) as reverse primer with duck whole genome as DNA template. DNA isolation result was used as PCR template without purification for PCR result. PCR result in specific size according to the used primary pair was resulted from optimizing PCR process.
To figure out the amplification success, PCR product of DNA fragments was separated using electrophoresis in 1% low-melting agarose gel with buffer 0,5x TBE in
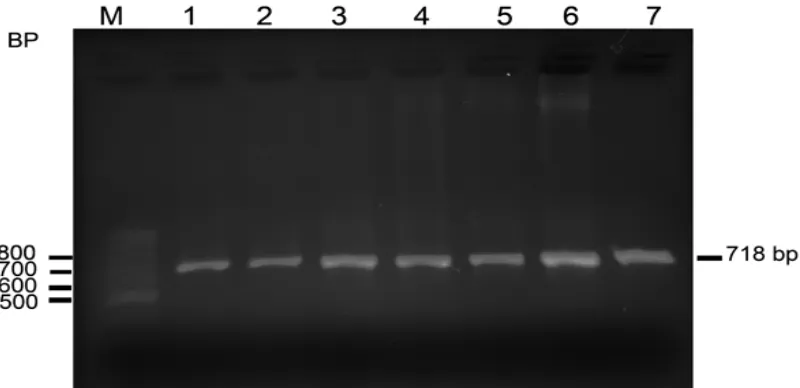
Submarine Electrophoresis (Hoefer, USA). Figure 2 shows the electrophoresis result of PCR
product with blood sample primary pair of DL-AnasPF (L56) and DL-AnasPR (H773) from Magelang duck and other Mallard ducks using 1.5% agarose gel.
Figure 2.The electrophoresis result of PCR product with blood sample primary pair of
DL-AnasPF (L56) and DL-AnasPR (H773) from Magelang duck using 1,5% gel Agarose
Figure 2 showing bright strings from PCR process with primary pair, indicated that the primary pair used was specific and successful to amplify DNA fragments at D-Loop mitochondria area in Magelang duck.
PCR product above was used to identify polymorphism diversity of D-Loop mitochondria area in Magelang duck by sequencing method. Polymorphism analysis could be done due to diverse sequences at the observed DNA fragments or gene.
Magelang Duck DNA Sequencing
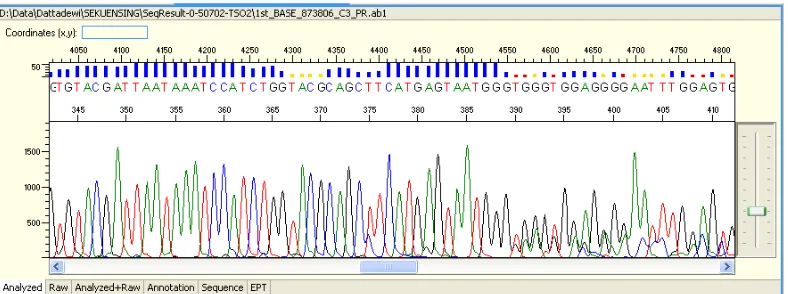
233 Figure 3. DNA sequencing result of jarakan polos-feathered Magelang duck
Figure 4. Electrophoregram result of DNA sequencing of jarakan polos-feathered Magelang duck
after editing.
Figure 3 shows nucleotide sequence of jarakan polos-feathered Magelang duck (plain brown) as much as 675 pb, Figure 5 shows nucleotide sequence of bosokan-feathered Magelang duck (dark brown) as much as 707 pb.
234 Figure 6. Electrophoregram result of DNA sequencing of bosokan-feathered Magelang duck after editing.
This research determined nucleotide sequence of Magelang duck namely 640 pb in
kalung ombo (brown with wide white feather around neck), 661 pb in gambiran (mixed
brown and white), 644 jarakankalung (brown with white feather around neck), 659 pb in
jowopolos (brown with specific pattern), 665 pb in wiroko (mixed black and white) and 651
in plain white (yellow bill and feet). Diverse variant or morphs of Magelang duck with eight types of feathers were figured out based on database of GeneBank (GenBank: HM010684.1, 2010). It was found out that base sequence of complete genome D-loop mitochondrial DNA area in Mallards duck (Anas platyrhynchos) was 1049 pb. It was therefore found 65, 83, 63, 41, 81, 63, 8 and 79 normal variants in various position.
Sequencing result and analysis of electrophoregram DNA sequence result of Magelang duck after editing indicated that nucleotide sequence of each duck showed diversity with certain similarity, so did with Magelang duck with different feathers. Mirza and Kurniasih (2002) stated nucleotide sequence from the same species did not show diversity, but different species accordingly had different sequence.
CONCLUSION
DNA fragment as PCR product was perfectly amplified as much as 718 bp at D-loop mitochondrial area of Magelang duck and other Mallard duck population. Nucleotide sequence diversity at D-loop mitochondrial area indicated that Magelang duck population had diverse genetic characteristics.
REFERENCES
GenBank: HM010684.1, 2010. Anas platryrhynchos breed Shaoxing mitochondrion, complete genom.
Haqiqi SH. 2008. Mengenal Beberapa Jenis Itik Petelur Lokal. Fakultas Peternakan Universitas Brawijaya. Malang.
Ismoyowati and D Purwantini. 2009. Isolasi dan Identifikasi DNA Itik Lokal untuk Memperoleh Keragaman Genetik sebagai Sumber Gen-Gen Unggul. Laporan Penelitian Fundamental. Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi. Departemen Pendidikan Nasional. Fakultas Peternakan Universitas Jenderal Soedirman. Purwokerto.
Leekaew P, T Songserm, A Choothesa and Boonyaprakob. 2008. A simple method to extract mitochondrial DNA in a non-invasive phylogenetic study of domestic native Thai ducks.
Kasetsart Journal (Nat Sci) 42 : 41- 50
235 Purwantini D, Ismoyowati, Prayitno and SS Singgih. 2002. Polymorphism blood protein as indicator for production characteristics of indigenous Java duck. Proceeding of International Seminar and Conference on “Technology and Policy on Indonesia
Resources Utilization” September 20 – 22, 2002. Hamburg. Germany. P 32 – 37
Ratnayani K, IN Wirajana and AAIAM Laksmiwati. 2007. Analisis Variasi Nukleotida Daerah D-Loop DNA Mitokondria pada Satu Individu Suku Bali Normal. Jurnal Kimia 1(1) : 7-14.