1
INVESTIGATING AMBIGUITY IN EFL STUDENT WRITING
Rio Giovano Setiawan
Abstract
Various interpretations are the indication that ambiguity happen in communication process. At time EFL students‟ writing indicating various interpretations, it is possible for the reader to misinterpret the meaning of EFL student writing. This current study focus on investigating ambiguity types in EFL student writing. In order to achieve the goal, 66 English Teacher Education Program students of Satya Wacana Christian University were involved in this study. The participants' writing assignments were copied and analyzed using Norton's (1975) Ambiguity Classification. The data obtained further being classified in to Scopes of Ambiguity proposed by Sennet (2011) and described in qualitative. The findings revealed that EFL students tend to make ambiguous statement especially in uncertainty as the most ambiguity types. Based on the results of this study, teachers are recommended to emphasize students with more intensive writing assignment together with peer feedback to measure their writing understanding. Further implication of this study lies on finding the method to teach ambiguity to EFL learner and reduce ambiguity especially in EFL context.
Key words: Ambiguity, Types of Ambiguity, Scopes of Ambiguity, Ambiguity Analysis
INTRODUCTION
2
Ambiguous condition occurs when speakers utter ambiguity statement during their conversation. Norton (1975) summarizes causes of ambiguity into: 1) Multiple Meanings 2) Vagueness, Incompleteness, and Fragmentation 3) A Probability 4) Unstructured 5) Lack of Information 6) Uncertainty 7) Inconsistencies and Contradictions 8) Unclear. This condition may randomly and unconditionally occurs and create confusion towards the learners since they cannot process the information correctly.
This study focuses on investigating the ambiguity done in writing assignment by EFL learners. Writing assignment become the subject of this research since EFL learners should take Guided Writing class to develop their writing skill and according to Church and Patil (1982), sentences are far more ambiguous due to the various interpretation that might occur because of the natural language processing when EFL learners working on their writing assignment. For example, consider the example below with two prepositional phrases:
(1) Put the block in the box on the table.
This has two interpretations:
(2a) Put the block [in the box on the table]
(2b) Put [the block in the box] on the table.
3
which can be investigated through the ambiguity classification as being proposed by Sennet (2011).
This research main question is what ambiguous types occur in EFL students writing. Ambiguous types will be analyzed through investigating and finding the most occurrence of ambiguous type in student writing. The frequency will be used to see which part of English cause the students confused and caused them creating ambiguous sentence .Further this research can be used as a tool to create better teaching material and teaching reflection for teacher in teaching English to reduce ambiguous sentence made by the students.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Sennet’s (2011) Scopes of Ambiguity
This study will classify ambiguity in writing into 3 scopes of language analysis according to Sennet (2011) analysis: Lexical Ambiguity, Syntactic Ambiguity, and Pragmatic Ambiguity. Related to Norton‟s classification, Sennet‟s scope of classification will be used to classify the ambiguity according to function of ambiguous element in making sentence. This scope is needed to filter the ambiguity into the bigger scope of analysis and further can be used to create a strategy to deal with the element of ambiguity.
Ambiguity Analysis
4
communication is categorized when the signal produced by the participants of communications cycle can be interpreted correctly through denoting the assigned meaning of the signal by the other participants in that communication cycle. The job of the reader as the interpreters may be easy when the signal given by the participant assigns a unique denotation to each signal. However, when the signal assigns multiple denotations, the reader must try to disambiguate to infer the producer‟s intentions. This process needs extra effort for interpreters to guess denote, moreover when the interpreters picks the wrong denote for the signal surely the chances of miscommunication occur widely between this process of communication especially in written form of language.
Chances of miscommunication happens‟ in many situations during language learning process, whether it is in classroom situations (Ely, 1995) or individually when people engage in self-instructed language study (White; 1999). The reason of this occurrence is simply because both linguistic and cultural knowledge is very limited. When the students are facing a new chapter of lexical and grammar knowledge, simply they will not understand since they need to adjust with their present knowledge of lexical and grammar knowledge, which cause further ambiguous situations such as lack of information, multiple meanings, vagueness, and so on to understand the communication process (Erten and Topkaya ; 2009).
Norton’s (1975) Types of Ambiguity
5
of the sentence. For example, light can be used as adjective in sentence “She wore light colors because it was going to be a hot day” which defined as pale colors; as noun “The light of the sun” which defined as the natural agent that stimulates sight and makes things visible; as verb “I will light you down to the gate” which defined as
provide a light for someone so they can see where they are going.
Vagueness, according to Sorensen (2012), is standardly defines as the possession of borderlines. Borderline case is cases where it is unclear whether or not the predicate applies. For example, a word tall is not clear to what extent a thing is classified as tall, not clearly tall, or not clearly not tall. Vague predicates apparently lack well-defined extensions. Keefe (2000) specifically describe that it is the possibility of borderline cases that counts for vagueness and blurry boundary. This become very vivid since there is a gradable adjectives to measure the sentence level. Incompleteness and Fragmentation are types of ambiguity which haven‟t fulfill the requirement of a sentence to stand. A sentence need three requirements to stand; a subject, a verb, a complete thought and can stand on its own or independently. Fragmentation is divided into 3 types; no subject; no verb; a dependent clause without an independent clause. Merchant (2004) implicitly shows that this condition often occurs in form of short answers is proposed to have fully sentential syntactical structures, subject to ellipsis. Incompleteness, occurs when the fragmentation happened in a sentence, then the sentence become incomplete.
6
observations. Belief is briefly described as opinion within an event. Below is the example of a probability:
(1) Turn right here
This phrase can represent 2 kinds of phenomenon; the speaker state that phrase request to turn on that spot, or the speaker state that phrase request to turn the direction to the right.
Unstructured is type of ambiguity when a writer is unable to arrange the order of grammatical pattern accordingly.
Lack of Information is type of ambiguity which cannot fulfill the information needed to make the sentence stand. Dubois (2007) infers that lack of information or knows as incomplete information, occurs when the writers writing is subjective which cause only several people understand their utterances. Some other people need to get further information to predict the utterance of the speaker. For example if the writer only wrote:
(1) The birth date of Indonesian President
This example cause the reader only has rough idea about the birth date of Indonesian President, only few reader know precisely, some have no idea about the birth date of Indonesian President.
7
(1) John saw the man on the mountain with a telescope
This example cause the reader hardly decides who has the telescope. Is that John, the man on the mountain, or the mountain who has the telescope was unclear.
Inconsistencies and Contradictions is type of ambiguity which specifically uses negation within the writing. Khawalda and Al-Saidat (2012) briefly explain that negation has a possibility to create ambiguous sentence. Related with grammar pattern in the utterances, the use of negation cannot predict which part of the sentence is being negated by the negation itself. For instance, in a sentence like:
(1) Everyone hasn‟t finished the assignment yet
The sentence is ambiguous according to scope of negation. If the scope of „not‟ is not the subject „everyone‟ the sentence has the reading:
(a) „Everyone is in the position of not having finished the assignment yet‟
If the scope of „not‟ is „everyone‟, the sentence will have the reading:
(b) „Not everyone is yet in the position of having finished the assignment‟.
Unclear is type of ambiguity which caused by grammatical error specifically in the use of pronoun reference. A sentence is ambiguous when the pronoun used in a sentence is not referring to a particular noun in a sentence. In “Both Isabel and Barbara loved her children”, her is categorized as pronoun but it cannot tell whose
children they are.
8
ambiguous statement will be used to classify the occurrence of ambiguous statement into three big scope of ambiguous type of language learning.
Sennet (2011) analyzes the ambiguity of statement into 3 big scopes of ambiguous statement according to the language function: Lexical Ambiguity, Syntactic Ambiguity, and Pragmatic Ambiguity. These scopes will represent the categories of ambiguity listed above and further the data taken will be presented in form of most occurrences categories of ambiguity based on these scopes.
Lexical Ambiguity is dealing with the ambiguous homophones which different in meaning and syntactic categories. (Doing Semantic; 1998) Lexical Ambiguity might occur in form of a single word response in a conversation, which the meaning of that word having more than one possible meaning. Lexical Ambiguity will cover Multiple Meanings in word-choice and idioms, and Vagueness, Fragmentation and Incompleteness.
Syntactic Ambiguity, according to Sennet (2011), is dealing with the ambiguous words specifically when there are many language functions that correspond to the same sentence. This ambiguity is dealing with the phrasal usage, quantifier and operator scope, and pronouns preference. Syntactic Ambiguity covers the ambiguous meaning of phrase like in a Probability, Unstructured, Uncertainty, and Unclear.
9 THE STUDY
Context of Study
This research has investigated the ambiguous sentence and language usage in writing assignment. This research is conducted in English Department since this faculty requires students to use English in writing assignment. Through the investigation, the finding of the study have filtered the ambiguity occurred in EFL students writing assignment and have classified into several types of ambiguity.
Participant
The participant of this study is the 1st year students of English Department from Satya Wacana Christian University. They are chosen to be the participant because as non-native speaker of English, they have learnt and studied in English Department which requires all students to be able to communicate using English and they are still under the progress of adjusting themselves with the rule of the faculty, which use 90% of English in class communication, especially in writing assignment, it is predicted that the occurrence of the ambiguous sentence is likely high.
Method of research
10
assignment by using Random Sampling Method because, according to Bogdan (1982), random sample can represent the whole population of the participant.
Instrument and Data Collection
The writing assignments of ED Students from Guided Writing Class were collected and copied. The total of students‟ writing assignment that were involved in this research is 66 students‟ writings, taken from 5 classes of Guided Writing. By using Norton‟s Ambiguity Classification (1975), this research found 155 data to support this research from students writing assignment and the data was divided into 8 ambiguity types and classified into 3 general scopes of ambiguity.
Data Analysis
Each writing assignment of ED Students in Guided Writing Class was analyzed and the ambiguity which occurs in the writing assignment was investigated. The ambiguity has been classified into 8 ambiguity types analysis by using Norton‟s analysis of causes on ambiguity. After that, the researcher categorized the 8types into 3 scopes of ambiguity analysis by using Sennet‟s (2011) classification on ambiguity scopes. The second classification is used to identify what is the biggest problem of EFL Learner in ED when they deal with ambiguous sentence in writing assignment.
11 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
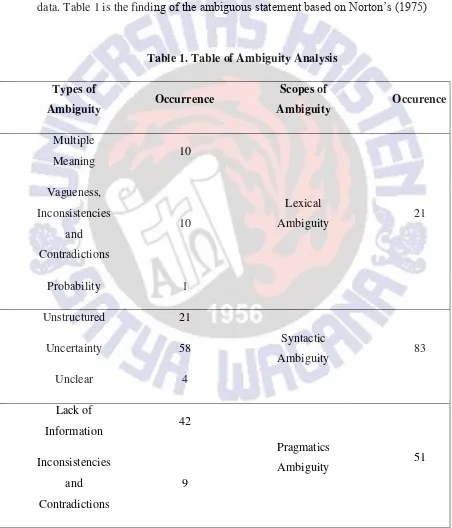
This study focuses on finding the ambiguity types done by the students by investigating their writing assignment and further noting sentences that are classified as ambiguous sentence. This research collected 66 writing assignments taken from Guided Writing class in ED. The data shows that all 8 ambiguity types appear in the data. Table 1 is the finding of the ambiguous statement based on Norton‟s (1975)
12
Norton‟s Ambiguity Classification (1975) is divided into 8, which are Multiple Meaning, Vagueness, Incompleteness, and Fragmentation, Probability, Unstructured, Uncertainty, Unclear, Lack of Information, and Inconsistencies and Contradiction. Multiple Meanings, Probability, and Vagueness, Incompleteness and Fragmentation are categorized in Lexical Ambiguity. Unstructured, Uncertainty, and Unclear are categorized in Syntactic Ambiguity. Lack of Information and Inconsistencies and Contradictions are categorized in Pragmatics Ambiguity.
Based on these findings, it is interesting that most of the students are not aware with Syntactic Ambiguity in their writing assignment. According to the data, 83 out of 155 are categorized under Syntactic Ambiguity. Syntactic Ambiguity is dealing with the ambiguous words specifically when there are many language functions that correspond to the same sentence, especially in phrasal usage, quantifiers, and pronoun reference. Most of the students use their local dialect and oral communication style in writing their assignment, therefore their writing looks informal and not well structured. Some others also didn‟t follow the requirement to make a sentence stand, for example a sentence with no verb or no subject, which cause the reader find it ambiguous especially with the structure conveyed by the students through their writing.
13
negation in their sentence without knowing the meaning of using negation and how to build a sentence with proper comparison between the main sentences with the supporting details.
Lastly, 21 out of 155 data are categorized under Lexical Ambiguity. Lexical Ambiguity deals more with the ambiguous homophones which cause multiple interpretations when EFL learner is not aware with explaining the meaning of the word and the context of the statement. Students under this ambiguity are not recognizing that some words that they used have more than one literal meaning when it was used in a sentence. Some of the students also unable to differentiate adverb and noun which further cause the meaning of the sentence changed.
Lexical Ambiguity
Multiple Meaning, Probability, and Vagueness, Incompleteness and Fragmentation are categorized in Lexical Ambiguity. Types of ambiguity in Multiple Meaning occur in these examples,
“I get a spirit when I look at his picture”
This sentence can cause the reader interpret the phrase “get a spirit” as gaining motivation by seeing the picture or gaining unseen creature by seeing the picture. When the reader gets more than 1 kind of interpretation in reading a sentence, this can cause the reader to interpret the sentence wrongly. To avoid ambiguity, this sentence needs to be corrected by using either „getting more motivation or catching an unseen creature during the time the writer look at his own picture‟.
14
This example also ambiguous because the writer can cause the reader interpret the phrase “in one touched” as hit the enemy with one touch or probably can win the battle easily without any significant effort to beat his enemy. In order to reduce the chance of ambiguity, the writer should explore more their ideas and explain it descriptively by giving another supporting details.
Types of ambiguity in Probability occurs in this example,
“I don’t know why, but maybe it is because Charlotte is small than Wilburn”
This example shows probability ambiguity because the word small cannot explain which small condition that the writer wants to emphasize. Therefore, the reader might interpret that small is related with the body size between Charlotte and Wilburn, or small is related with the connection built between them. In order to reduce chance of ambiguity, the writer should add more detail information about the word small, for example, the writer might say probably it is because Charlotte‟s body is smaller than Wilburn; or Charlotte‟s connection is smaller than Wilburn.
Example of Vagueness, Incompleteness, and Fragmentation occur in these examples,
From that point, Po starts the most hardest training ever with his teacher, Master
Shifu. (Vagueness)
This example show vagueness ambiguity that occurs in “the most hardest (supposed to be the hardest)” phrase. The reader might think that the most hardest training is not
15
But he keep train until he get though. (Fragmentation and Incompleteness)
This example shows sentence fragmentation that causes incompleteness of a sentence to stand. The incompleteness occurs when the component of a sentence to stand is not being added in that sentence, for example when a sentence has no subject, no verb, or a dependent clause which need independent clause to stand. This sentence is ambiguous because this sentence is dependent clause which needs more information to make the sentence stand. By recognizing this requirement, this sentence will reduce random interpretation for some particular information that might be not the real message of the writer. For example, maybe the writer may add more information about what kind of training that the subject took and why the subject need to be tough according to writer.
Lexical Ambiguity may cause confusion, especially with some certain words which cannot be clearly explained. Readers may be students that learn English writing style which need to learn from their peer also. If students are not guided well especially in dealing with Lexical Ambiguity, students will get the impact of not knowing the meaning of certain words and the use of words in that sentence. Even though the finding shows only 21 data of participant conducting Lexical Ambiguity, Lexical Ambiguity cause confusion when the readers gets more than 1 kind of interpretation in reading a sentence and they might interpret the sentence wrongly. Moreover, certain words cannot be explained well will also increase the chance of misinterpretation to readers in dealing with Lexical Ambiguity. Especially when Lexical Ambiguity occurs in several types, it will causes the readers interpret the meaning of the words wrongly.
16
Uncertainty, Unstructured and Unclear are categorized in Syntactic Ambiguity. Example of Uncertainty occur in these examples,
“Moreover, my father is not as boring as other fathers”
This example show uncertain ambiguity occurs in the basic form of the sentence. The reader possibly might interpret that writer‟s father is boring, but compared to another father, the writer‟s father is not that boring; or the reader might interpret that writer‟s father is more than one, since the writer mention other fathers as the parameter of „the boring‟. By recognizing this ambiguity, the writer shall reduce the chance of ambiguity by giving more information that give specific details about the meaning of the sentence. For example, the writer might not use comparison especially the use of comparison, or probably just simply say that writer‟s father is more than one and one of them is not boring.
“Po was a brave panda, he told the truth to his father and faced Tai Lung”
This example also shows uncertain ambiguity in the basic form of the sentence. The reader might interpret that to be a brave panda, the panda have to tell the truth to his father and face his natural enemy, or wonder the reason for a panda to be brave is through telling the truth which is unclear and face his natural enemy which is unnecessary. In order to reduce the ambiguity, the writer need to explore their idea and describe it in sequence according to their idea. For example, the writer might explore their idea of a brave panda and find related reason to support that idea such as being bold during their difficult time, tough in his daily exercise, and so on.
Types of ambiguity in Unstructured occur in these examples,
17
This example shows unstructured ambiguity because the writer cannot arrange grammar pattern accordingly. This sentence is ambiguous because the writer uses adverb and noun to explain the writer‟s friend. The ambiguous part of this sentence lies on the dual interpretation of the adverb and noun used by the writer which may confuse the reader to classify which word is classified as adverb and which one as noun. For example, the writer may reduce the chance of ambiguity by saying „it is a miracles to have a crazy and wise friend‟, or the writer might say it is very difficult to have an extraordinary friend with wisdom inside him.
“She adviced her children to positive thinking if we have problems and didn’t gave
up”
This example also shows unstructured ambiguity because the writer cannot arrange grammar pattern accordingly. This sentence is causing multiple interpretation especially in the use of verb and adverb and confusing the reader to classify the word used from the sentence. In order to reduce the ambiguity, the writer might say that she gave her children an advice to think positively during their hard time and not to give up easily.
Types of ambiguity in Unclear occurs in this example,
“She made it from her web, and it is so amazing”
18
amazing, or that the spider made the word from her web and the process of making the web was so amazing. Another consideration is that not to put two pronoun references „it‟ in a sentence like what occurs in the example.
Syntactic Ambiguity may cause confusion since Syntactic Ambiguity occurs in the basic form of the sentence, cannot arrange grammar pattern accordingly which cause dual interpretation of the adverb and noun, and unclear use of pronoun reference. What becomes the problem is, readers are might not that aware in understanding the focus of ambiguous meaning of a sentence seen from the syntactic structure. Most of the finding shows that students writing assignment is ambiguous because they cannot relate their idea in structure. This issue is being supported by the finding that shown most of the students trapped in Uncertainty ambiguity which can be concluded that students are not well structured in writing down their idea. If this problem continues, their mistake will affect their peer understanding and teacher understanding in assessing their writing related to the writer‟s idea.
Pragmatic Ambiguity
Lack of Information and Inconsistencies and Contradictions are categorized in Pragmatic Ambiguity. Types of ambiguity in Lack of Information occurs in these examples,
“The last things that make Po is the smartest panda ever is because he can find unique
way to do something”
19
smart panda. This statement is the example of Pragmatics Ambiguity in Presuppositional Ambiguity. In order to reduce the chance of ambiguity, the writer might write that Po is smart because he can find unique way in doing certain activity such as eating or sleeping.
“Another reason why I said that he is a humble person is because both of us have the
same hobby, that is playing card games”
This sentence is lack of information which confuse the reader and only the writer that can understand the meaning of this sentence. The writer write that his friend is humble because both of them have the same hobby, which might confuse the reader whether a parameter of a person to be humble is by having the same hobby with the reader, or might be playing card, or any other interpretations. In order to reduce the chance of ambiguity, the writer might write that my friend is humble because even though he is rich but he wants to play card games with me and other common friends.
Types of ambiguity in Inconsistencies and Contradictions occurs in this example,
“I like to feed my child, but Po like kungfu”
This example shows that the information given is inconsistent and cause the reader wonder the relation in comparing feeding the writer‟s child to kungfu. This sentence needs more detail explanation in order to make the reader understood the meaning of the writer writes the sentence. For example, the writer might write that the daily routine of a panda is feeding their child but Po as a panda in Kungfu Panda movie has different daily routine which is doing kungfu everyday.
20
information given is inconsistent and cause the reader interpret wrongly. Readers may found it difficult in understanding the writing because what the writers wrote is what they thought and might don‟t understand with their idea development in the sentence. Moreover, Pragmatics Ambiguity deals more with the perception of the students, so it will be very difficult for other students to follow or to give peer feedback in order to develop the students. Further, teachers also will find difficulties in assessing students writing since teacher might not expect that students giving ambiguous expression and sentence within their works, but we cannot deny that they are new students in this faculty which need more guidance in understanding the material and focus of the study. Therefore, it is very crucial for teachers to be aware with this ambiguity.
This is interesting that EFL learner has a chance to do dual ambiguity because some of the data taken may be categorized into more than one kind of ambiguity classification. For example,
“He is not afraid to leave his house, he knows that he can’t defeat Tai Lung but because of his father advice he go to the place where he can find Tai Lung, and
because he has a strong will he can defeat Tai Lung alone”
21
finding might indicate that EFL learners are need more drill and monitory from their lecturer in order to avoid the occurrence of ambiguous sentence in their writing assignment.
CONCLUSION
This research main question is what are the ambiguity types done by EFL students in writing and the result is what occurs the most is Syntactic Ambiguity. Pragmatic Ambiguity and Lexical Ambiguity also occur but not as often as Syntactic Ambiguity. These researches have discussed the problem of EFL learner in making a sentence in English especially dealing with scopes of ambiguity. Sentence ambiguity happen to EFL students is because they need time to adjust and learn about basic structure of syntactic structure and further apply it in their writing assignment. According to the finding, some students are unable to differentiate meanings of words used in a sentence that can cause confusion to the readers.
22
Suggestion to overcome ambiguity problem might in be in form of developing the teachers in order to emphasize syntax understanding in students writing and the use of multiple meaning in a sentence to make students understand with the meaning of words and further able to avoid ambiguity. Further students also might be assigned to have peer feedback to measure their friends understand with their writing.
23
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
24
REFERENCES
Bogdan, R. C., & Biklen, S. K. (1982). Qualitative research for education. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Church, K., & Patil, R. (1982). Coping with Syntactic Ambiguity or How to Put the Block in the Box on the Table. American Journal of Computational Linguistics , 139-149.
Dubois, D., Lang, J., & Prade, H. (2004). Possibilistic Logic
Dubois, D., (2007). Uncertainty Theories: A Unified View
Ely, C.M. (1995). Tolerance of ambiguity and teaching of ESL. In Reid, J. M. (ed.). Learning styles in the ESL / EFL classroom. Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Erten, I. H., & Topkaya, E. Z. (2009). Understanding tolerance of ambiguity of EFL learners in Reading Classes at tertiary level. Novitas-Royal, 3(1), 29-44
Gillon, B. S. (1990). Ambiguity, Generality, and Indeterminacy : Test and Definitions. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Keefe, R. (2000). Theories of Vagueness. United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Khawalda, M. I. & Al-Saidat, E. M., (2012). Structural Ambiguity Interpretation: A Case Study of Arab Learners of English. Global Journal of Human Social Science, 12(6), 1-7
Merchant, J., (2004). Fragment and Ellipsis. Kluwer Academic Publisher, 27, 661-738
Marzban, A., Barati, H., & Moinzadeh, A. (2012, January). An Investigation into Ambiguity Tolerance in Iranian Senior EFL. English Language teaching , pp. 76-85.
Norton, R. W. (1975). Measurement of ambiguity tolerance. Journal of Personality Assessment, 39, 607-619.
Sennet, A, "Ambiguity", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2011 Edition),
Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL =
25
Sorensen, Roy, "Vagueness", The Standford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2013 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), URL =
http://plato.standford.edu/archives/win2013/entries/vagueness/
Wasow, T., Perfors, A., & Beaver, D. (2005). The Puzzle of Ambiguity. Morphology and the
web of grammar: Essays in memory of Steven G. Lapointe, 265-282.
26 APPENDIX
Appendix 1. Table of Ambiguity Analysis
Table of Ambiguity Analysis
Scopes of
Ambiguity Ambiguity Classification Ambiguous Statement
Lexical Ambiguity
Multiple Meanings
Vagueness
Probability
Syntactic Ambiguity
Unstructured
Uncertainty
Unclear
Pragmatic Ambiguity
Lack of Information