THE USE OF ORAL QUESTIONS IN TEACHING ENGLISH AT
SMPN 1 SALATIGA
AsaWisesaBetari
Abstract
This study discussed the oral questions used by the English teacher in teaching English at SMPN 1 Salatiga. The study aimed atanswering the research question “What are the types of oral questions used in teaching English?” One of English teachers at SMPN 1 Salatiga was selected to be the participant. The data were collected through observation. The result of this study showed that referential question was the most frequently used type of the teacher‟s oral question in teaching English at SMPN 1 Salatiga.
Key words: Teacher Talk, Teacher Question, Type of Teacher‟s Question Introduction
Teacher talk is an essential part of foreign language teaching in order to encourage student learning. The ways teachersuse language not only determines how well they teaches, but also guarantees how well students will learn. An appropriate teacher talk can create harmonious atmosphere, at the same time encourages a good relationship between teachers and students, and consequently creates more opportunities for interaction between teacher and students (Yanfen&Yuqin, 2010). Thus, the interaction between teacher and student is one of the important aspects in classroom activities, and applying teacher talk plays an important role in the teaching process.
will have an interaction, so that the teacher may be able to maintain the students‟ attention to the lesson, and also check the students‟ understanding.In addition, teachers raise some oral questions in order to get students‟ active participation in classroom.
Believing on the importance of oral questions for the success of teaching and learning, it is necessary to investigate kind of oral questions in teaching English and the reasons why it is being used. More specifically, this investigation aims to explore the use of teacher‟s oral
questions in teaching English at one of secondary schools in Salatiga.
The problem occurs when I did teaching practicum at SMPN 1 Salatiga, the school doesn‟t provide any handbook in English lesson, and limited access of AVA. The teachers have
to find other things to make a good interaction in class. One of those things is raising oral questions in teaching to make good interaction between teacher and students, check the students‟
understanding, explore the students‟ ability in learning, and maintain the students‟ attention to
the lesson. Besides, there must be other functions of the teacher questions which I want to investigate in this study. Based on the discussion above, the research question was; what are the types of oral questions used in teaching English at SMPN 1 Salatiga?
This study aimed at describing the type of oral questions used by an English teacher at SMPN 1 Salatiga in teaching English. In addition, the study aimed at describing the functions of the oral questions used in teaching English.
Review of Literature
One common influential aspect in language teaching is classroom interaction. Classroom interaction has a great influence on learning as it is an important point where the communication between the teacher and learners takes place (Hall, 2014). It seems that classroom interaction is the core element in the process of teaching and learning, which means that difficult to do teaching and learning process without interaction. Furthermore, the implementation of classroom interaction is affected directly by teacher talk.
Teacher talk is an essential part of foreign language teaching to organize activities, and the way teachers talk not only determines how well they make their lectures, but also guarantees how well students will learn (Yafen and Yuqin, 2010). It shows that teacher talk can create a harmonious circumstance which means that there will be an interaction in classroom.
Based on Mehan, (1979), the framework of teacher talk comprises follow-up and initiation. The element of Follow-up consists of informing, prompting, criticizing, ignoring, encouraging, and commenting. Moreover, the element of initiation consists of giving direction, inviting, and questioning. Mehan, (1979) also argued that one of the most frequently used in teaching is questioning because questioning strategy can encourage the learners in absorbing lesson and develop interaction with the teacher by answering the teacher‟s questions. Meng& Wang (2011: 101),stated that;
Questions stimulate and maintain students‟ interest and encourage student
said, to elicit a particular structures or vocabulary items, and to check the students‟ understanding.
Hence, the use of question in teaching English seems important in order to make a good interaction between teacher and students in class, to clarify what students have said, to elicit a particular structure of vocabulary items, and to check the students‟ understanding. Moreover, the
teacher is free to use what questions as long as it is appropriate to the teaching and learning process. Teaching English by using questions were also implied by one of the teacher at SMPN 1 Salatiga. When I observed at SMPN 1 Salatiga, the teacher wanted to check the students‟ understanding about narrative text, so she used questions related to the narrative text to know the students‟ understanding.
Teacher question is an element of teacher talk which refers to the question given by the teacher in teaching learning process in order to maintain and create successful teaching. According to Hall (2014), teacher questions are questions raised by the teacher that support the classroom tasks and assist the students to focus on the lesson and participate in the interaction in class. Another idea about teacher question comes from Chaudron (1988) who believes that, “Teachers‟ questions constitute a primary means of engaging learners‟ attention, promoting
verbal responses, and evaluating learners‟ process.” Types of question
There are many types of teacher questions raised by some experts. Barnes (1969) divides the types of teacher questions into four; (1) questions concerning factual matters, that is the questions beginning with “what”, (2) questions of inference, that is the questions beginning with
“how” and “why”, (3) open questions which do not require any inference, and (4) questions for
other type questions into closed questions and open questions. When the students have only one acceptable answer, it is called closed question. On the other hand, when they are free to have more than one appropriate answer, then they have open questions.
Long & Sato (1983) also divides the types of teacher questions into display and referential questions. Display questions as the questions that are given by the teacher who has already known the answers. Moreover, display question is aimed at checking the students‟
understanding, whereas referential question is the other way around. A teacher who questions something which he/she has not known is called a referential question. The response from the students may add information to the teacher and other students.
The last type of questions is defined by Wilson (2014) classify five basic types of questions: factual, convergent, divergent, evaluative, and combination. The further explanation about the questions is as follows:
1. Factual – the answers are frequently either right or wrong. The questions are given straight forward based on facts or awareness.
2. Convergent - Convergent questions are questions which are given in order to get students‟ responses. Short answer often appears as the response to these questions, such as “yes”,
“no”, or other short statements.
3. Divergent - Divergent questions allow students higher level thinking to answer the questions. The students are demanded to produce their own information rather than review the previous lesson.
from different point of view before the answerer comes at newly modified information or conclusions.
5. Combinations - These are the questions that mix any combination of the type of questions above.
From those types of questions that have been raised by experts, I have categorized the types of questions into five types which I used for my research.
Open Questions (OQ)
The questions given by teacher which require more than one appropriate answer. In addition, the questions allow students higher level thinking to answer the questions.
Closed
Questions (CQ)
The questions that have only one acceptable answer. In addition, short answer often appears as the response to these questions, such as “yes”, “no”, or other short statements.
Display
Questions (DQ)
The questions that are given by the teacher who has already known the answers
Referential Questions (RQ)
The questions that are given by teacher about something which he/she has not known
Combination Questions (CombQ)
The questions that mix any combination of the type of questions above.
Functions of question
The Study
This study used descriptive method. This study described the use of teacher oral questions in details. It focused on describing the types of oral questions used by the teacher in teaching English at SMPN 1 Salatiga. The writer used “A sample of convenience” sampling
technique which means that the participant was the person who was convenient with and accessible for (Zacharias, 2011). The writer observed the teaching-learning process in the class using an observation protocol for categorizing the type of questions and described the function of the questions.
In attempting to answer the research question, this study used an observation protocol as the research instrument. The type of observation used wasevaluative or structured observation because it was based on a specific observation focus. In addition,a time-sampling protocol was also used with specific in time. Dornyei (2007), as cited in Zacharias (2011), explained, “When observing using a time-sampling protocol, you note what is happening on the stroke of the interval or chart what was happened.” Table 1is the example of time-sampling protocol.
Table1. The example of a time-sampling protocol.
Name of teacher: Date/time: Class: Duration: Topic:
Time Type of question Example Notes
This study involved one English teacher who taught the second year classes of SMPN 1 Salatiga. The teacher has taught English for 15 years. The observations were done in the second year classes consist of 8A, 8B, 8C, and 8D academic years 2014/2015. The selection of the participant is based on “A sample of convenient” sampling technique which was the participant was the person who convenient with and accessible for the writer. McKay (2006, p.37), as cited in Zacharias (2011) said that A sample of convenience is “the selection of the participant based on the people who were accessible to you.”
Results and Discussion
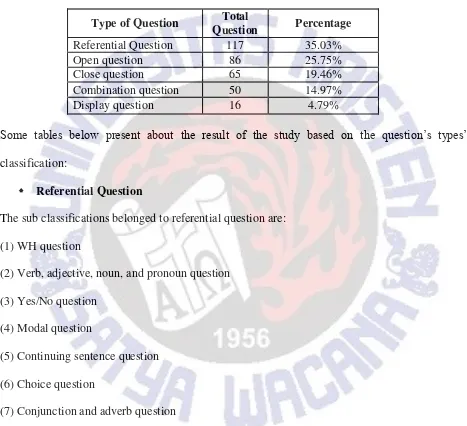
The section below presents the data analysis obtained from the observation that had been transcribed. The data were obtained from four classroom observations conducted in second year classes of SMPN 1 Salatiga. The analysis focused on the types of teacher‟s oral questions in teaching English. Table 1 represents the classification of teacher‟s question that was modified from the classification made by Barnes (1969), Long & Sato (1983), and Wilson (2014).
Table 1. Types of teacher’s question
Open Questions (OQ)
The questions given by teacher which require more than one appropriate answer. In addition, the questions allow students higher level thinking to answer the questions.
Closed Questions (CQ)
The questions that have only one acceptable answer. In addition, short answer often appears as the response to these questions, such as “yes”, “no”, or other short statements. Display
Findings from each classification
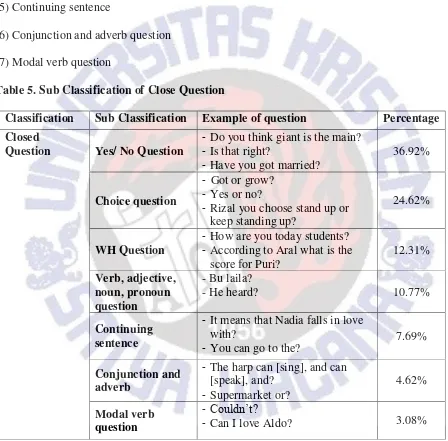
Table 2 presents the percentage of types of question used by the English teacher at SMPN1 Salatiga:
Table. 2 The Percentage of Type of Question Type of Question Total
Question Percentage
Referential Question 117 35.03%
Open question 86 25.75%
Close question 65 19.46%
Combination question 50 14.97%
Display question 16 4.79%
Some tables below present about the result of the study based on the question‟s types‟
classification:
Referential Question
The sub classifications belonged to referential question are: (1) WH question
(2) Verb, adjective, noun, and pronoun question (3) Yes/No question
(4) Modal question
(5) Continuing sentence question (6) Choice question
(7) Conjunction and adverb question
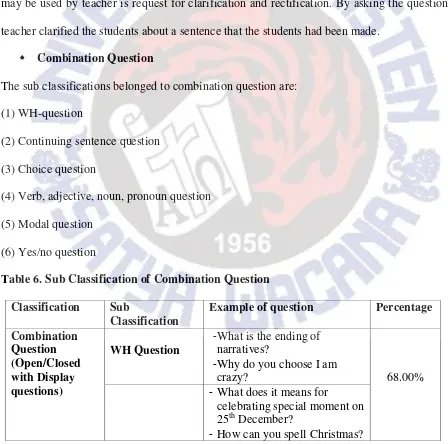
Table 3. Sub Classification of Referential Question
Classification Sub classification Example of question Percentage Referential
question WH Question
- What is it?
- Who hasn‟t finished yet? 39.32% Verb, adjective,
noun, pronoun
- Ready? - You?
question - Dentist‟s table?
Choice question - ohhDwikiapa Rizal? 5.98% Conjunction and
adverb
- Maybe you want to move to other place?
0.85%
Table 3 shows that the most frequently used sub-classification in referential question classification was WH-question, as much as 39.32%. The second rank was verb, adjective, noun, and pronoun question,as much as27.35%. Then, Yes/No question was third used by the teacher, as much as11.11%.There werealso 7.69% of modal question and continuing sentence used by the teacher. Next, choice question were used in teaching process,as much as 5.98%. The least frequently used sub-classification was conjunction and adverb, as much as 0.85%.
with one of five clear functions of questioning proposed by Tsui (1995) cited in Guinda (2011) which is request for clarification and rectification.
The second ranks were verb, adjective, noun, and pronoun question. For example, “Ready?”. It was an adjective used by the teacher to maintain the students‟ attention when the
teacher wanted to discuss an assignment in class. In this context, the assignment was about kinds of recount text. The teacher asked students to mention kinds of recount text, after that the students had to write their answer on the white-board. Before the students wrote their answer, the teacher said, “Ready?” to begin the discussion and also to maintain the students‟ attention to the teacher.
The other sub classification such as yes/no question, modal question, continuing sentence question, choice question, and conjunction and adverb question were also used in a small number since these sub classifications may be seen as not really relevant with the topic of the lesson. These sub classifications were used to have a joke in class, or as an intermezzo to avoid boringness in class. For example, when the teacher found some money on her desk without knowing the owner, she asked the students, “May I take it?”, “Can I put it in my veil”. After that,
the students answered, “No, it is class money”. In this context, the teacher made some joke about the money, and it didn‟t relevant with the topic of the lesson on that day. The other example was
when the teacher saw one of students looks sleepy in class, she asked, “Are you tired?” the student answered, “No”. In this context, the teacher wanted to check the physical condition of the
student, and the question was not relevant with the topic of the lesson. Open Question
(2) Conjunction and Adverb question (3) Continuing sentence question
(4) Verb, adjective, noun, and pronoun question (5) Modal verbs question
Table 4. Sub Classification of Open Question
Classification Sub classification Example of question Percentage Open
question
WH question
- What else?
Based on the result above, WH-question was the most frequently used in this classification used by teacher to require more than one appropriate answer. For example, when the teacher said, “What else?” she tried to encourage students to find another answer. In this context, the teacher asked the students to mention kinds of conjunctions used in narrative text, and the students raised their hands and answer. After that, teacher said, “What else?” to know another answer from the other students. This context related with one of five clear functions of questioning proposed by Tsui (1995) cited in Guinda (2011) which is request for action.
The second ranks of sub classification of open question were conjunction and adverb question, and continuing sentence question, as much as 13.95%. The teacher used conjunction and adverb question such as, “And?” to get more than one answer from the students when she asked the students to mention main characters in a narrative text. Besides, the teacher also used continuing sentence such as,“If you want to say the supported characters, so the sentences should be?” to encourage students to answer the question in many ways. In this context, the teacher asked the students to make a sentence related to the narrative text that they had already read.
The other sub classification such as verb, adjective, noun and pronoun question, and modal verbs question were used in a small number.These sub classifications were mostly used to follow up the students‟ answer to the previous question from the teacher, so these questions may
be seen as additional question. For example, when the teacher asked, “Who‟s the main characters in the story?”, then the students answered, “Giant”. In order to follow up the students‟ answer,
the teacher asked, “Any other?”.This context related with one of five functions of questioning
proposed by Tsui (1995) cited in Guinda (2011) which is to follow up the students‟ answer. Close Question
(1) Yes/No question (2) Choice question (3) WH-Question
(4) Verbs, adjective, noun, and pronoun question (5) Continuing sentence
(6) Conjunction and adverb question (7) Modal verb question
Table 5. Sub Classification of Close Question
Classification Sub Classification Example of question Percentage Closed
Question Yes/ No Question
question, as much as12.31%.Afterward, verbs, adjective, noun, and pronoun questionwas used10.77% by the teacher. The fifth, continuing sentence question was used by the teacher,as much as 7.69%. Next, conjunction and adverb question, as much as 4.62%. And the least frequently used sub-classification of close question wasmodal verb question, as much as3.08%.
Based on the result above, it can be clearly seen that yes/no question was the most frequently used in this classification. Yes/no question was question that had only one acceptable answer.In answering the teacher‟s question, students had to mention yes or no. The example of yes/no question used by the teacher was“Do you think giant is the main?”. In this context,the teacher asked the students to mention the main characters in a narrative text. After that one student mentioned, “The giant”, and teacher seemed disagree with the student. The teacher asked other students to clarify the answer. Then the other students answered, “No”.
The second rank is choicequestion, as much as24.62%. The teacher used choice question to get specific answer of the question. By answering the question, students had to choose the best answer from two or three answers that were raised by the teacher. For example, when the teacher taught simple past tense, she asked a student to read a sentence that the student had already made. Then, the student read his sentence, and made a mistake in choosing a verb. After that, the teacher used choice question,“Got or grow?”,the student answered “got”. In here, choice question was used to help the student to correct the sentence. This context related with one of five clear functions of questioning proposed by Tsui (1995) cited in Guinda (2011) which is error correction.
specific answer, and the result of the study shows that the teacher was very rare to use WH-question. The sub classification of WH questions in closed questions classification are used to greet the students in the beginning of the lesson, such as “How are you?”. In this context the
question from the teacher requires one specific answer “I‟m fine, thank you”. The other sub classification by using verbs, adjective, noun, and pronoun such as “Bu Laila?” and “He heard?” were also least frequently used because the teacher used those questions to clarify what students said.According to Tsui (1995) cited in Guinda (2001) one of the functions of questionswhich may be used by teacher is request for clarification and rectification. By asking the question, the teacher clarified the students about a sentence that the students had been made.
Combination Question
The sub classifications belonged to combination question are: (1) WH-question
(2) Continuing sentence question (3) Choice question
(4) Verb, adjective, noun, pronoun question (5) Modal question
(6) Yes/no question
Table 6. Sub Classification of Combination Question Classification Sub
Classification
Example of question Percentage Combination
Question (Open/Closed with Display questions)
WH Question
- What is the ending of narratives?
- Why do you choose I am
crazy? 68.00%
- What does it means for
celebrating special moment on 25th December?
Continuing sentence
- We call it fic? Fictive
- Opposite of unfortunately is?
16.00%
Table 6 shows that the most frequently used sub-classification in combination wasWH-question, as much as68.00%. The second rank was continuing sentenceappeared in combination (close and display) question, as much as16.00%. Then, choice questionappeared in the third rank of sub classification of combination (close and display) question, as much as8.00%.The fourth rank, verbs, adjective, noun, and pronoun question, as much as 6.00%. Next, the teacher used modal question in the classification of combination question, as much as 4.00%. And the least frequently used sub-classification of close question wasyes/no question, as much as2.00%.
The example of WH-question in combination question used by the teacher was, “What is the ending of narratives?”. In this context,the teacher asked the students to mention conjunction
that the students usually find in narrative text. Some students were able to mention some conjunctions, and the others were silent. After that, the teacher asked, “What is the ending of narratives?”, one student mentioned, “Finally”, and the teacher praised that student. Thus, WH-question was used for checking the students‟ understanding because the teacher had known the
answer.
The second rank of sub classification of combination question was continuing sentencequestion, as much as16.00%. Continuing sentence question was used to maintain students‟ attention to the lesson. The teacher used continuing sentence question to get one
specific answer of the question. For example, when the teacher taught about narrative text, she mentioned some examples of kind of narrative text. Then the teacher asked the students to mention the example of narrative text. However, the students were silent in class, so the teacher asked, “In modern narratives, we call it fic? Fictive” to maintain the students‟ attention to the lesson.
The other sub classification such as choice question, verb, adjective, noun, pronoun question, modal question, and yes/no question were used in a small number in combination question classification. These sub classification were used mostly for confirming the students‟ answer about previous question. For example when the teacher asked the students about the characteristic of main characters in narrative text, one of the students said, “Zalova is handsome”, after that the teacher asked, “Which one do you choose, Zalova is handsome, or
combination question because it mostly used just for clarification if there were any something not really clear in teaching process.
Display Question
The sub classifications belonged to display question are: (1) Continuing sentence
(2) Verb, adjective, noun, and pronoun (3) Modal question
(4) Conjunction and adverb question (5) Choice question
Table 7.Sub Classification of Display Question
Classification Sub Classification Example of Question Percentage Display
Question Continuing sentence
- Someone who likes eating very much is called blablabla?
Based on the result above, the most frequently used this classification was continuing sentence question. Continuing question in display question was used to help the students to answer the teacher‟s question, so the students become more active in class. Tsui (1995) cited in
Guinda (2001) stated the functions of display questions were to simplify a broader initial question to facilitate comprehension and help recall knowledge. The example of continuing sentence question in teaching process is when the teacher asked the students to mention the supporting characters in a narrative text that the students read. Some students answered the teacher‟s question correctly, but some students were silent. Then, the teacher asked, “Someone
who likes eating very much is called blablabla?” the students answered, “Giant”. Thus, the teacher used continuing sentence question to encourage the students to facilitate comprehension and help recall knowledge.
The other sub classification such as modal question, conjunction and adverb question, and choice question were used in a small number in display question classification.These sub classification were used as an intermezzo to avoid boringness in class, and may be seen as not really relevant with the topic of the lesson. For example, when the teacher asked, “Can I love Dafa?”, she inserted moral value to the students about politeness. The teacher expected the
Conclusion, Limitation, and Suggestion
The study has examined the use of teacher‟s oral question in teaching English by one of teachers at SMPN 1 Salatiga. The finding shows that the most frequently type of teacher‟s question used by the teacher was referential question, as much as35.03%.This type of question was used for gaining the information that the teacher has not known. The response of this type of question may provide information to the teacher and other students. The data from observations show that referential questions were mostly used to request for clarificationand maintain the students‟ attention to the lesson. On the other hand, the least frequently type of question used
was display question, as much as 4.79%. This type of question is given by the teacher who has already known the answers. According to the data, the functions of display question were mostly for correcting error and comprehension checking. The result from this study is expected to be useful for teachersnot only to maintain the students‟ attention to the lesson, but also encourage
Acknowledgment
References
Barnes, D. (1969).Language in the secondary classroom.In D. Barnes et al. (eds.) Language, the Learner and the School.Harmondsworth: Penguin.
Chaudron, C. (1988). Second Language Classrooms: research on teaching and learning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Guinda, S. (2011). Tips for Presenter/Audience Interaction: Typology and Function of Questions. Journal of Oral Presentations Seminar for MERIT Project (UPM-ICE, 21 Nov. 2011), 1, 2
Hall, J. K. (2014). Second and Foreign Language Learning Through Classroom. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Long, M. H. & Sato, C. (1983). Classroom foreigner talk discourse: Forms and Functions of teachers‟questions. In H. W. Seliger& M. H. Long (eds.), Classroom Oriented Research in SecondLanguage Acquisition. Rowley, Mass.: Newbury House.
Mehan, H. (1979). Learning Lessons: Social Organization in the Classroom.Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press.
Meng, X & Wang, X. (2011).Action Study of Teacher‟s Language on EFL Classroom Interaction.Theory and Practice in Language Studies, vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 98-104
Wilson, L. O. (2014). Five Basic Types of Questions. Retrieved from http://thesecondprinciple.com/teaching-essentials/five-basic-types-questions/
Yanfen, L&Yuqin, Z. (2010).A study of teacher talk in interactions in English classes.Chinese Journal of Applied Linguistics (Bimonthly), vol. 33, No.2, pp.76-86.
Appendix
10.10 Continuing sentence At the end of the story, you use what?
Combination or continuing??? 10.12 Open question What else?
What is it? 10.16 Close question Is it your friend?
Is he funny?
Is bu laila horrible? 10.17 Referential question What‟s first?
What‟s Ana..first? 10.22 Display question How do you say in English?
Bu laila semaking langsing. How do you say in English? Grow bentuk 2 nya menjadi? 10.24 Display question If in the past tense? Bu laila?
10.26 Verb, pronoun, noun Can you decide who is main character?
What is the title of the story? 10.35 Close question Is he like Ahmad Dhani?
Is he like he tell a story? 10.36 Choice question Thumb or down?
Up or down?
According to bu Laila it is so good. How about you? Up or down?
11.03 Referential question Who wants to go first? 11.08 Referential question According to..what is the
score?
According to..what is the score?
Repeated
11.11 Referential question Finish? Students are
doing an assignment about narrative text