Teacher’s Perspective on
the Use of Games in English
Teaching& Learning Process: A study at Bethany Elementary
School
Abstract
Recently, games are widly used by teachers in teaching and learning process since games are one of the important tools in EFL as stated by McCallum (1980) and Mubaslat (2012). Through this study, the writer investigated the teachers‟ perception toward the use of games in teaching English for young learners and types of games used by the teachers. This study was conducted in the first and the second grade of Bethany Elementary School Salatiga, with two participants of English teachers. Observation and interviews were used as instruments of data collection. The findings show that there were six types of games, which are Order; Connect: compare, match, group; Do: move, mime, draw, obey; Remember; Identify: discriminate, guess, speculate and Create found used by the teachers. In addition, the findings also indicate that teachers have positive perception towards games, since they can contribute to improve the students‟ language skills, build their grammar understanding, engage the students to learn the lesson, help them to expand their vocabulary and help the teachers to see the students‟ actual ability. However, the observed teachers also view that games can be boring and time consuming. Games are also demanding in terms of background knowledge and giving difficulty for the teachers to control the classroom management. Therefore, the observed teachers gave some sugggestion to minimize the problems.
For some learners, learning English as a foreign language can be hard because they need a lot of efforts to understand it. First, lerners need a relatively long time to learn. For example learners who learn English from elementary until senior high level takes around twelve years. This is in line with Fotovatnia & Namjoo‟s argument. They stated, “Foreign language learning is a hard task and a lot of effort is required every moment and over a long period of time to manipulate, understand, and produce
the target language” (Fotovatnia & Namjoo, 2013, p. 189). Second, they need to go
through series of learning process such as memorizing a lot of vocabularies and try to learn the grammar. Furthermore, they need to learn to speak, listen and write in English correctly which are not an easy job.
Due to the quite complicated process, it is not surprising that many learners face difficulties in their learning process. Fotovatnia and Namjoo (2013) conducted a study in Iran. The finding revealed that English is considered difficult to learn by the learners because most of them were lack of motivation and did not have enough opportunities to take a part in learning process. This caused learning English could be hard for them. Another research on difficulties in learning English was conducted by Kyaw and Sinhanety, K (2012). They investigated the vocabulary learning of Burmese students. The results revealed that the participants had failed to innovate the best ways that could work efficiently in their vocabulary learning because of the time limitation, the demands of language course schedule, and the exam-oriented
English, teachers need to find various techniques to the learners in order to minimize the problems.
One of the techniques that makes the English teaching and learning become fun and easier to understand is by using games. For example, in teaching vocabulary of vegetables, teachers can ask them to play a “Shopping Vegetable” game by asking them to buy some vegetables on the list given in this game, instead of asking the students to only memorize all words about vegetables. Another example is in teaching parts of body. Teachers can ask students to sing a song about parts of body. While singing, the children should touch parts of their body with their hands, such as head, then shoulders, knees, toes, when they hear each part of the body is mentioned. By doing such activities, learning English is not necessarily to be hard. Instead, it can be fun and enjoyable. In line with this idea, Fotovatnia & Namjoo argued that games are effective and cost-saving method in language education (2013, p. 189).
Besides cost-saving, games are effective and practicable for almost all levels, they are used not only for junior and senior school high students but also for young learner. The term „young learners‟ here refers to “Children from the first year of formal schooling (6 years old, in our case) to 12 years of age” (Korkut and İsisag: 2009). As mentioned by Robin (2012) “Children usually imitate their role models with spontaneity and enthusiasm and young children actively learn a second language
through games, songs, puppets, stories, projects and other activities” (p. 19). Based
Teaching English using games to young learners can be effective, since, at those period of time, young learners are more active physically and cognitively.
The important roles of games have encouraged many researchers in educational field to explore and investigate the use of games in teaching English as a second and foreign language. Griva1 and Semoglou (2012) conducted an experimental study on a game-based project in a Greek experimental primary school of 2nd grade. They were grouped into an experiment group (game-based classroom) and a control group. Both groups were given tests consist of word production. However, different approaches were implemented. The control group was taught by using PPP (Presentation- Practice-Production) context and the experiment group was taught by using games. The result showed that the test score of the experiment group was higher than the control group. The test score of children experiment group who received English language teaching in a playful context which were taught by the use of game-based project were higher than those of the control group were taught English in the convention PPP (Presentation- Practice- Production) context.
Similarly, Azarmi‟s experimental study (2007) investigated the use of adapted
skills. Also the experiment group learners performed lessons more voluntarily and showed great participation and production than the control group learners.
The result of the studies above and the important roles of games in English teaching and learning have motivated the writer to study the use of games in Indonesian context, especially at elementary level.In Indonesia, games are used not only at senior high but also elementary level. Therefore, it is interesting to find out how teachers in Indonesia view the use of games in their classroom context. This study aimed at investigating the teacher‟s perspective of the use of educational games in teaching English at Bethany Elementary School, Salatiga, Indonesia. For that purpose, this study answers the following questions:
1. What type of games do the teachers use in their English classes?
2. What are the teacher‟s perceptions about the use of games for English teaching and learning process?
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
This section presents the definition, types, and the strength and weakness of games.
Definition of Game
There are many definitions of games explored by many experts and researchers. According to Wright, Betteridge and Buckby (2005) game is “An activity which is entertaining and engaging, often challenging, and an activity in which the learners play and usually interact with others “(p.1). Games are one of the activities that teachers use to deliver the materials in entertaining way. Likewise Arikan and
Yolageldili (2011) argue that games are “Student-focused activities requiring active
involvement of learners” (p.221). It can be said that games often become an effective way to help stimulate students in active participations. The other definition is quoted by Hadfield (1990; Quotedin Deesri, 2002, p.1) that games is “An activity with rules,
a goal and an element of fun.” It can be concluded that games are activities with
rules and goals to create a fun, entertaining, and engaging atmosphere in the classroom which stimulate students to participate actively in the classroom.
Types of game
Care and share
Caring and sharing games are kind of games which encourage the learners to share their personal information comfortably with other learners. For example
“Getting to know to each other” game. In this game the teacher asks the students to
introduce themselves, for example, I‟m Martine and I like playing football. The next learner repeats the sentence and adds his or her own information. For example one of
the students says “You‟re Martine and you like football. I‟m Robin and I have a pet
dog”. And so it continues. Getting to know to each other game, is the game which provides a fun way for the learners to share their personal information by introducing themselves to other learners.
Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey
In this game the learner is required to do something non-verbally based on the text she/ he hear. The teacher can tell a story and encourage the learners to act it out. For example the teacher says: You’ve got a little cat in a box. Put the box on your desk. Say, ‘Sit still. Don’t move.’ Now take the cat out of the box, very carefully. Put
it down. ’Show your friend your little cat’. This game includes the learner‟s
participation by doing and obeys the teacher‟s instruction.
The second example is “Listen and draw”. In this game the teacher reads a
description of a person, object, animal, or place. First, the teacher asks the learners to
listen and then draw the description that they have heard. For example “My neighbor
is a very tall, thin, woman. She wears a T-shirt. She has a square face and pointed nose. She has a long hair. She always carries her little cat in her arms”. This game
encourages the learners to participate actively by drawing about the description they have heard.
Identify; Discriminate, Guess, Speculate
In this game the learner is challenged to identify something which is difficult to identify or to hypothesize about something which is then compared with the facts.
This makes everyone participate by using the language and expressing their view by guessing the picture.
The second example is “Flashing a text”. In this game the teacher flashes her
chosen text at great speed. For example, if the teacher uses an OHP, she has to swing a book between the projector and the screen, giving the learners only a split seconds‟ view of the text between swings. The teacher encourages the learners to guess at what has been seen. Slowly, the teacher and the learners can build up the complete text together. The teacher may tell them the topic of the text. For example the text says
„don‟t put all your eggs in one basket‟. This game encourages the learners to identify
the text by guessing the words they have seen.
Describe
In this game the learner is challenged to describe something to another learner, by speaking or writing, so well that the other learner can do something, for example, draw a picture. The learner may describe something objectively or subjectively, communicating his or her own feelings and associations.
The first example is “Describe and draw”. The teacher asks a volunteer to
Here is an example:
Teacher: What‟s the shape of the picture? Learner 1: It‟s rectangle; Teacher: Artist, please draw a rectangle
Teacher: What is in the picture? Class: A house…a tree…two people…a dog…some birds.
Similar with the definition of description game, this game encourages the learners to participate actively in speaking or writing by describing an object.
The second example is “Describe from memory”. In this game the teacher
shows four pictures to the whole class. Then she/he tells the learners to decide which picture they want to describe, and not to let anyone else know their choice. Next, the teacher gives time to think and write the description of it. They should try to identify which picture has been described. For example it‟s red/green/brown apple. This game helps the learners to describe the object in English.
Connect; Compare, Match, Group
In this game the learner is challenged to connect, compare, match or group various items of information, perhaps pictures or text, objectively or subjectively. He or she uses language to describe or comment on the pairs or groups of information.
The first example is “Bingo game”. Here the teacher shows the learners how
cross it out. The first learner to cross out all four items on their list calls out Bingo is the winner.
The second example is “Bingo grammar”. In this game the teacher makes
sentences in the present continuous indicating physical actions and write them on the board, for example a woman is smiling. And then the teacher can ask the learners to make a Bingo grid. The teacher asks the learners to choose any four the sentences and illustrates them with quick sketches, one in each square. If the teacher calls out the sentences in random order, the learners should cross out the picture sketched on their Bingo grid.When a learner has crossed out all of his or her pictures, he or she shouts Bingo! This game helps the learners in grammatical structure by connecting and matching the correct sentence of the game.
Order
In this game the learner is challenged to put various bits of information into an order of quality and importance, subjectively or objectively, or to put text, pictures, objects, into a developmental sequence, also subjectively or objectively.
The first example is “Jumbled texts”. The teacher asks the learners to make a
definition of order game, this game encourages the learners to be able to put the
random words becomes a correct text based on the teacher‟s order.
The second example is “Word by word”. In this game the teacher asks the
learners to make a group, and then asks the first player in each group to say a word. And then the teacher asks the next learner to add a word. The following learner will add the words based on the previous word and to say the resulting phrase of three words. For example learner 1 says „cat‟, learner 2 says „black cat‟, learner 3 says
„black cat climbs‟. Finally, in class discussion the teacher can ask each of group to
read out their completed sentences, and correct the mistakes grammatical structure. In
this game the learners are required to collect the information from the other learner‟s
word and add it with their own thought to make a correct sentence.
Remember
The second example is “Vocabulary and spelling game”. In this game the
teacher played the video to the learners about the peoples‟ activities or actions. And then teacher ask the learners to try to remember what happened or were happening from the video. Last, the learners will share their observations with the class. This game required the learners to remember and communicate what they remembered based on the video.
Create
In this game the learner is challenged or invited to make a story, write a poem or produce some other kind of material using their imagination. „Challenged‟ might include those story-making starters in which you stipulate certain features: for example, you stipulate that a certain tense form must occur very often, or that the
story must be exactly 50 words long. „Invited‟, because sometimes the best way to
stir the creative forces is to „invite‟, „encourage‟, „show interest‟, and so on.
The first example is “Visualize and describe”. In this game the teacher reads a
story to the class, and then asks the students to imagine what they hear. Then the teacher gives students time to answer the questions about what they saw or heard or felt. The last, teacher gives each of questions a number and ask them to fill in the number. Here is an example: “Close your eyes. Imagine you are in the wood. It‟s the
coming out the house”. This game challenges the learners to make their own story based on their imagination.
The second example is “Bouncing dialogue”. In this game the teacher asks the
learners to work in pairs to create a dialogue between two characters. For example, one learner can be a parent, the other a teenage child, and the situation is that the teenager was given permission to come home at midnight, but came home at two
o‟clock in the morning. And then they should read their dialogue silently. This game
encourages the learners to produce their dialogue based on their own story.
Advantages of Games
There are some advantages of games proposed by some researchers. Mubaslat (2012) stated that games are motivating and challenging. It provides language practice in the various skills such as in speaking, writing, listening and reading. They also encourage students to interact, communicate and create in a meaningful context. It can be said that games become one of the effective way in delivering the lesson because the learners can develop their language‟s ability in a comfortable way.
The other advantages of games are proposed by McCallum (1980). He argued that games provide immediate feedback for the teacher. It can be used as affirmation, review, and enrichment. It also promotes equal participation for slow and fast learners. Games can be suitably applied for all language levels of the students.
It can be concluded that the use of games in EFL teaching have many advantages for both teachers and students. Games provide motivation, challenge and active participation for the learners in the learning process. Games can be used in the various skill of target language, function as reinforcement, review, enrichment, and also can be adjusted for all language levels of the students
Disadvantages of Games
Through the advantages and disadvantage of the use of games in EFL teaching, some researchers point out how to use games in order to minimize the problem that occurs. A game must be more than just a fun. It should involve "friendly" competition and keep all of the students involved and interested. It should encourage students to focus on the use of language rather than on the language itself, and furthermore give students a chance to learn, practice, or review specific language material.
THE STUDY
This section consists of the context of the study, the participants, research instrument, and data collection procedure.
Context of the study
This study was conducted in Bethany Elementary School, Salatiga, Central Java, Indonesia. The main reason the researcher chose this place because games were actively used in teaching and learning process. Additionally, games become one of the main strategies used by the teachers to deliver the material.
The Participants
are used actively in the classroom. Second, they came from the same pedagogical background as English educators. Third, they spoke English actively in the classroom. These reasons helped the researcher to find out their perspectives on the use of games in English teaching.
The Research Instrument
In this study, the data gathered through observations and interview. The observations were conducted to find out what kind of games that the teachers used in their classroom. The observations were conducted six times and they were written in an observation sheet.
Data Collection and Analysis Procedures
The data was collected through some procedures. First the researcher should prepare the observation sheet and do the observation. In the observation, the researcher took a note and classified the types of games that the teachers used in their English class. In addition to that, how each game works or not was also observed by
seeing the teacher and the learners‟ responses while doing the games in the
classroom. As for the data analysis, after the data was obtained, the researcher counted the frequency of types of games which were used by the teachers. By doing so, research question was answered.
The next procedure is collecting data from interview. The first procedure was piloting the questions. This process was needed to prepare the proper questions in order to get the data needed. The interview was an individual interview and audio-taped. The questions were given to two participants. The language used in the interview is Indonesian language. The interview began with some questions that
focus on the teachers‟ reason in using games. The questions continued with asking
The statistical data from the observation were counted to get the percentage which were presented in a form of pie chart. It was aimed to know what types of games that the participants used. After knowing the types of games used by the participants, the qualitative data obtained from the interview. The data was classified into some initial themes that emerged from the answer. It was aimed to know the
teachers‟ perception toward advantages and disadvantages of each type of games they
used.
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
This section discusses the research findings in order to answer the research
questions about “what type of games do the teachers use in their English classes?”
and “what are the teachers‟ perceptions toward the use of games for teaching and
learning process?”
Types of Games that the teachers use and how their games are applied in their
English classes
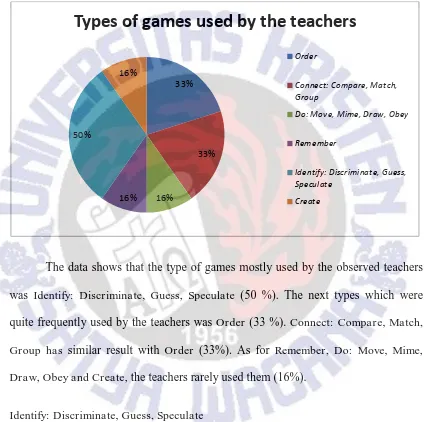
According to Betteridge, D., Buckby, M., & Wright, A (2006), there are eight types of games in teaching English, which are Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate; Order; Connect: Compare, Match, Group, Remember, Do; Move, Mime,
Figure 1: The types of games used by the teacher in English class in first and second grade.
The data shows that the type of games mostly used by the observed teachers was Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate (50 %). The next types which were quite frequently used by the teachers was Order (33 %). Connect: Compare, Match, Group has similar result with Order (33%). As for Remember, Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey and Create, the teachers rarely used them (16%).
Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate
After knowing the frequency of each game used by the teachers, it is more meaningful then to know how each type of game was used. From the observation, it was found that the first type, Identify; Discriminate, Guess, Speculate was used
33%
33%
16% 16%
50%
16%
Types of games used by the teachers
Order
Connect: Compare, Match, Group
Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey
Remember
Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate
through “guessing card game”. This game was used by the teacher in reading skill. In this activity the teacher distributed a yellow and red card to each student. After that, the teacher asked some questions related to the reading text that they had read before. The students were required to show a yellow card for the correct answer or statement. But if the statement was incorrect they should show a red card. For the example the teacher asked “Do we see a horse sleeping behind the door?” Then the students showed the red card if they thought it was false and yellow card for the correct statement. This game helped the students to understand the reading text in a fun way. It could be seen from their expressions when they could answer the questions and from their enthusiasms to follow the game.
Order
The second type is Order. The example of this type is arranging jumble words. The teacher used this game to make the students understand about the sentence structure easier. In this game, the teacher asked the students to arrange the
random words into a correct sentence. For example, “Gaby/ to wash/ the dishes/
helped”. From this game the students were pushed to review their previous material
Connect; Compare, Match, Group
The third type is Connect; Compare, Match, Group. The example of this type was when the students played a bingo game. In this game, the teacher provided some letters. In the carpet which had been provided, the students should arrange the letters into a name of animal that was on the reading text entitled “the Grandpa‟s house”. If they found the word, they should say „bingo!‟ Through this game, the students were encouraged to give their attention on the reading text in order to be able finding the words.
Remember
The fourth type is Remember. The example of this type is Chinese whisper game. The teacher divided the students into two groups. They were asked to make a line. Then the teacher chose one student as a leader to read the teacher‟s sentence. In this activity the teacher showed a sentence to the one learner, and then the learner whispered it to the next learner, and so on. The last person in the group should raise his/her hand to report what the sentence was. This game is engaging because it encourages the learners to participate actively.
Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey
The fifth type is Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey. In this type of game, the
read the text. But, if the teacher said your turn, then the students repeated what the teacher had said. Again, through this game, the reading lesson is delivered in an enjoyable way.
Create
The last type is Create. The example of this game was “Weather report”. In this game, the teacher asked the learners to make a group of two. One learner acted as a reporter and the other learner acted as a cameraman. In this play, the reporter was given a short text by the teacher about the weather and she / he should report it to the cameraman. The learners should change the roles, therefore every student had an opportunity to read a text and act as a cameraman.
Teachers’ Perception on the use of Game
The discussion of teachers‟ perception is divided into teachers‟ reason for
using games in their English teaching, the teachers‟ perception toward the advantages
and disadvantages of each type of Game and the teachers‟ perception toward the
important points to maximize the use of games.
Teachers’ Reason for using games in their English teaching
The teachers‟ view on why they used games in their teaching can be divided
Interview, participant 1). This reward motivated them to use English. This view is matched with the observation. The students looked exited when the teacher informed that the winner of the game would get some snacks that the teacher had prepared before as a reward. This game therefore motivated the students to win the game.
The second reason is because game is fun and engaging. “It‟s more fun and involving students into games activity” (source of data: Interview, participant 1). The similar statement was also given by another participant, “Through games, the children will be more interested to learn” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). The quotations indicate that the teachers used games because it helped them to create a fun learning. Therefore, the learners would not get frustrated but would be interested
to learn. The participants‟ reasons are line with Fotovatnia & Namjoo (2013) who
argued that games are not only increase the students‟ motivation, but also change the stress atmosphere into fun learning.
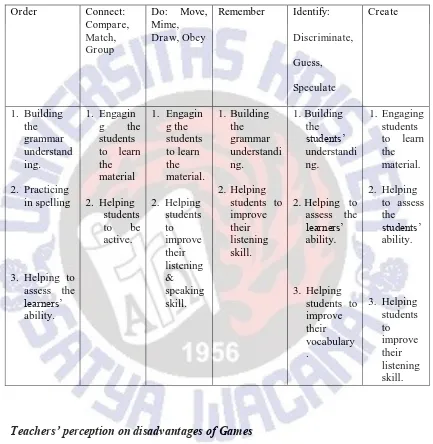
Teachers’ Perception toward the advantages of Games
Toward the advantages of using games for English teaching and learning process, the
participants‟ views games bring several advantages:
Helping students to improve their language skills (reading, listening, speaking)
This strength was clearly reflected in Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey. That was
when the teacher used “your turn and my turn game”. During the interview, the
speak by reading by themselves. I hope, from those two skills, the students will be more fluent in reading” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). This statement shows that this game helps the students improve their listening because they had to listen when the teacher was speaking. It also improved their speaking skill, because
they had to speak when the teacher said “Your turn”. Furthermore, their reading skill
was improved. When the teachers asked some questions related to the passage, the students were stimulated to develop their reading skill by answering the questions.
In addition, this advantage was also reflected in Remember. The example of
this game is “Chinese whisper game”. In this game, the learners were asked to
whisper a sentence to other learners in their group. The last person in the group should raise his/her hand to report what the sentence was. This game required the students to listen a word carefully. She stated “Teacher will get an advantage because through this game, the children listening skill will be developed more, so the teaching process from the teacher work successfully” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). What the teachers said is understandable because in this game, the students are motivated listening their friend carefully to win the game. Therefore, their listening skill can be improved.
Furthermore, the benefit can be found in Create. One of the games is used by
the teacher in this type is “Weather report game”. In this play, the students acted as
argued “Through this game, the students will describe the weather given. They will
practice how to speak and describe a thing” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). From the statement, this game helped the students to improve their speaking skill.
Based on those statements, it can be said that the use of games in English teaching provide an interactive learning, so that the learners are able to explore their reading, listening and speaking skill.
Helping students to build their grammar understanding
The potential of game in helping students to build their grammar understanding can be found in Remember. Teacher 1 said “This game can be used to teach noun phrase. Here, the children will hear some words which they have never know before. It can be applied in a form of noun phrase and a relation between adjective and noun” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). To illustrate the teachers‟ view, the following observation result is probably can help. In the Chinese whisper game, the students were encouraged to improve their grammar understanding while they were whispering some words such as white lamp and the big dining room. The statement directly shows that this game can be used to teach grammar and learn items such as noun phrase.
The benefit also can be seen in Order, especicially on “Arrange the jumbled
word”. This game encuraged the students to learn the sentence structure. As teacher 1
sentence is consist of a subject, verb and adverb” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). The statement indicates that games are able to guide the students to practice their grammar ability such as the sentence structure.
Engaging the students to learn the lesson
The next standing point of games is engaging the lesson to the students. This point can be found in several types of games. First is on Connect: Compare, Match, Group. The benefit on the use of games is not only for the learners, but also for the
teachers. The first teacher stated “Teacher can deliver the material more
interestingly” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). It can be seen when the
teacher and the students played “matching the pictures game”. The learners were
asked to put the name of words in the correct picture such as lamp, table, chair, which were sticked in front of the class. From the observation, it was obvious that while the game begun, all students shouted “hooray” to express their excitement in following the game. It appeared that this game can motivate the learners to learn the material in a playful atmosphere. Furthermore, it helps the teacher to make a fun learning, so she/
he will be able to attract their students‟ attention.
That game is engaging can be seen in Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey. Teacher 1
stated “This game helps teacher to teach reading becomes more interesting” (Source
the teacher to develop the reading material becomes more interesting. If it is engaging, the students will understand the text easier.
Similarly, the idea of “engaging” can be found in Create. As the teacher 2 said,
“Through this game, the student will not get bored. This game is presented with
weather news report. So, the students have their own experience becoming a reporter” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). Based on this statement we can see that Create makes the learning process become more entertaining. Through the activity of
reporting the weather, the student will not realize that they are learning, therefore they will not get bored.
Those statements emphasize that games can be used as a tool to create a fun atmosphere in language learning. It can be a way to help the teacher to design a creative learning and to motivate the learners to learn in a fun and excitement environment.
Helping the teachers to see the students’ actual ability
The third merit can be found in Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate. As Teacher 2 experienced “With this game, the teacher will be able to know if the student can understand or not about the material” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). The following observation result probably can help illustrate the
opinion. In the “Guessing a card game”, the teacher asked some questions to the
correct, the students should show a yellow card. But if the answer was incorrect, they should show a red card. It clearly shows that from this game, the teacher can assess whether the student understands or not about the material.
That game can help teacher to see the students‟ actual ability is also reflected in Order. The teacher 2 stated “The teacher will be able to know the students difficulty” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). During the observation, the students‟ achievement in understanding the material can be seen, when they were playing
“Filling the blank words”. When they performed in front of the class by filling the
blank words the students‟ ability in spelling can be seen. In this way, the teacher will
be able to assess the students‟ language level.
Similarly, this advantage also can be found in Create. The example of this
type of game is “Weather report game”. The teacher assumed “The teacher will know
whether the student can describe the weather well or not.”(Source of data: Interview, participant 2). In this point, the teacher will know the students‟ language level by looking on the way the student describes the weather.
Helping students to improve their vocabulary
vocabulary by identifying the different words. The best illustration on the opinion
above can be seen in “Guessing the pictures game”. The students were encouraged to
develop their vocabulary by guessing the pictures about the weather that the teacher showed. In this game, the students had opportunities to improve their vocabulary.
Such vocabulary improvement could also be found in Order. The example of
this type is “Filling the blank words”. Teacher 2 stated “Games can practice the
students in spelling” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). While the students fill
the missing words such as SP _ _ N _ (SPRING), it helps them to improve their spelling ability. Based on the observation and the statement, it indicates that games
can build the students‟ grammar skill, such as in spelling.
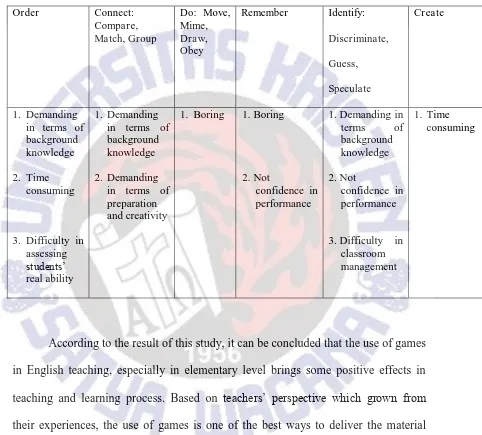
Games don’t always work
Games in teaching English do not always work because of some factors. The first one is because demanding in terms of background knowledge. For example in Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate game. According to teacher 1, “Game will
be a problem for the teacher if the teacher doesn‟t have enough patterns or enough
background knowledge” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1). Like in the guessing pictures game, the teacher should prepare some patterns to be used in the game. For example, the teachers should have enough background knowledge about the difference between the weather phenomena, such as spring, winter, autumn, summer. This statement shows that teachers may face difficulty to lead the game if they do not have enough background knowledge.
The second problem which make the games do not always work is students‟ lack of confidance in performance. It was found in two types. The first happened when the students were playing in Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate that is
“Guessing Card Game”. In this game the students were asked to show their
understanding on the material by showing the yellow and the red card for true or false statement. All the students answered them together. Toward this game, teacher 1
stated, “Children will follow the other friends, so their knowledge cannot develop”
(Source of data: Interview, participant 1). It shows that in learning process, the negative effect that may occur is the students just follow their partner. Moreover, they
the students are not able to show their understanding confidently, because they just follow the other friends. In this way, the learners may not be able to develop their language knowledge well.
Time consuming
The second weakness of the language game is time consuming. This has something to do with duration of the game. It is reflected in conducting Order game. Here, teacher 2 argued, “The use of game will spend more time, so the learning process will no bet effective” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). This statement reveals that the use of game can be time-consuming. The clearer illustration
for the statement probably can be seen in “weather report game”. The students were
required to perform their speaking ability as a reporter and cameramen in front of the class. As the evidence from the observation, some games took a long time because they should be performed one by one. One performance took around ten minutes. The teacher should cut the time while they were performed. Such situation probably made the students did not perform their language ability maximally.
Boring
The next potential disadvantage of game is boring. Teachers 1 said “The
material delivery from the teacher by using this game for the children who are smart will get bored” (Quotation1). In learning process, the teacher also stated “For the
example is in Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey. When the students played my turn and your turn game, the students who mastered pronunciation well, they could get bored because they just copied the teachers sentence.
The teacher added, “If the teacher doesn‟t prepare well or the game that is given is not interesting, the game will be boring”(Source of data: Interview, participant 1). Here we can see that to make the game successfully done, the teacher needs to think how to make the game becomes interesting. If not, the problem which usually occurs is boredome which will make both of the teacher and the learners might lose their excitement in learning.
Difficult to control the Classroom management
The last limitation is difficult to control the classroom management. It can be seen in Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate. When the students were playing in
“Guessing the pictures game”, the teacher faced difficulty to control them at the
beginning. They kept talking and there were some students who moved around the
class. The teacher 2 said “The class atmosphere tends to be noise” (Source of data:
Interview, participant 2). Here we can see that the problem that usually occurs when game is played is the noise which are created by the students. It can be a challenge for the teacher to control the students to keep following the game.
Table 1. The disadvantages of games in Order; Connect: Compare, Match, Group, Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey; Remember; Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate; Create .
provide language practice in various skills such as in speaking, writing, listening and
reading. It is also similar with Nesselhauf and Tschichold‟s view (2002) who argued
that using games helps the students to develop their vocabulary through the games‟ activities.
However, the teachers also stated that there are some negative effects that might occur by using games in the English teaching and learning. They argued that games do not always work because of some factors. The first one is time consuming. It is coherent with Ting and Li (2012) who said that games are time consuming because they take time to play. The other factor is that for some students games are boring as proposed by Palanova, K (2010, p. 27). It becomes the other problem because it makes teachers get difficult to manage the classroom.
Teachers’ Perception toward the important points to maximize the use of games
Realizing the games is one of the important method in English teachings for young learners, the teachers have their own technique to maximize and to minimize the problem that might occur in the use of game. The first one is well preparation. Both of the teachers suggested,
“The teacher should have enough time to prepare the games. The preparation
don‟t need always costly. You can use the stuff that has been provided in
school” (Source of data: Interview, participant 1)
Those statements show that the teacher should prepare the game well with all the stuff and the things needed to make the game can be followed by the students well.
The second is considering the learners‟ language level. In this theme the
teacher stated “Game that will be used should be adjusted with the age and the
children‟s ability” (Source of data: Interview, participant 2). Here we can see that
before we decide what game which will be used, we should consider the learners‟
knowledge level to make the game becomes easily understood by the learners.
Third is the teachers should give clear instructions. Both of the teachers argued that to make a game becomes successfully done, the instructions should be given clearly. This technique is similar with Lavery‟s (2001) suggestions in managing games. She suggested, that the rules have to be as clear as possible.
The last suggestion is strictness in leading the game. The teacher 1 said on the interview about the games, that the students tend to enjoy the learning process more in a playful context. Therefore, they can lose control. Here the teacher should be assertive in leading the game.
Conclusion and Pedagogical Implications
guess, speculate and Create. They used them because of some reasons. The first one is because games are encouraging. Through games, the students are motivated to use the target language in creative learning context. Another factor is because games are fun and engaging. It helps teachers to create a fun learning for the students. Similarly, Mubaslat (2012) stated that the students are so competitive while they are playing a game. It shows that games can attract their attention and participation. Indeed, games can change a boring class into a fun one.
According to the teachers, there were five standing points of advantages on the use of games. Playing educational games helped the students to improve their language skills, built their grammar understanding, engaged them to learn the lesson, helped them to improve their vocabulary and helped the teachers to see the students‟ actual ability through their performance. Through games, the students did not get worried to make mistakes of grammar structure when they communicated. Therefore, their ability in listening, reading, speaking, grammar and vocabulary knowledge would naturally develop because they learnt in a real and fun atmosphere.
However, some negative effects were found in type of games used by the teachers based on the interview. The games do not always work because of several factors. The first one is if both the teachers and the students lack of background knowledge, the game will not be understood and followed well. Game is also time consuming because it takes a lot of time. The next weakness is because games
them well. The last limitation is games can be a boring activity. It happened when the students have mastered the material. They will get bored because there is no challenge in the game.
As the implications for pedagogical practices, if the teachers use games they should consider the students‟ language level. The teacher can decide which game is appropriate to their students. The second is well preparation. The third is the teachers should give a clear instruction in order to make the students able to follow the games. Finally the last step is strictness. The teachers should be consistent with the rules and the consequences of the games in order to control the learners. If those entire steps have been done by the teachers, the games will run smoothly.
Acknowledgement
First and above all, I would like to express my gratitude to my God and my savior Jesus
Christ, for being my strength during the writing of my thesis. Thank you for Your love and
Your power that are given to me.
I am using this opportunity too to express my sincere gratitude to my supervisor Debora Tri
Ragawati, SS, MA-ELT for the continuous support of my research. Thank you for your
patience, motivation, enthusiasm, and the guidance helped me in all the time of research and
writing of this thesis.
Besides my supervisor, I would like to thank to my thesis examiner Mr. Dian Toar Sumakul
for the encouragement and the necessary criticism.This thesis cannot be completed without
his advice.
I also sincerely thank to the headmaster and the teachers of Bethany Elementary School, Salatiga. It would not have been possible without the cooperation and kind support from them.
I express my warm thanks to Mas Kristian Y. Thanks for your support, love, and your
guidence in completing the thesis. I am so thankful that I have you in giving me such
attention, help and time.
Also I thank my best friends friends: Dyah, Tia, Ester, Ellisa, Eva, Via. Thank you for
becoming part of my life. Love you always guys.
Last but not the least, I would like to thank my family: my parents and all my sisters for
References:
Al-Issa, A.S. 2009. ELT games and teacher beliefs: The use of games in teacher education in Oman. Reflections on English Language Teaching 8 (1): 35–52.
Anyaegbu, R, Ting, W., & Li, Y. (2012). Serious game motivation in an EFL classroom in Chinese primary school. TOJET: The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 11(1), 154–164.
Azarmi, S. (2011). The use of authentic games in English language teaching Ekev Akademi Dergisi, 15 (47), 411-422. Retrieved November 2, 2013, from Ebscohost Web database.
Isisag, U. & Tavil, M. (2009). Teching vocabulary to very young learners through games and songs. Ekev Akademi Dergisi, 13(38), 299.
Fotovatnia, Z., & Namjoo, M. (2013). The Effects of Cooperative versus Competitive
Word
Games on EFL Learners' Vocabulary Gain, Motivation, and Class
Atmosphere. Mediterranean Journal Of Social Sciences, 4(1), 189-208.
Hadfield, J. (1990). A collection of games and activities for low to mid-intermediate students of English: Intermediate communication games. Hong Kong: Thomus and Nelson and Nelson and Sons.
Kalendová, E. (2008). The Use of Game-Like Activities in Teaching English To Young Children.Masaryk University in BRNO. Department of the English Language.
Kyaw, K. & Sinhaneti, K. (2012). A Study of the Role of Rote Learning in Vocabulary Learning
Strategies of Burmese Students. US-China Education Review, A(12),987-1005
Lavery, Clare. "Games in the language Classroom." TeachingEnglish. British Council, 2 Dec. 2011. Web. 13 Nov. 2013.
McCallum, G. P. (1980). 101 word games: For students of English as a second or foreign language. Oxford:Oxford University Press.
Mubaslat, M. (2012). The Effect of Using Educational Games on the Students‟ Achievement in English Language for the Primary Stage. Retrieved from:
Nesselhauf, N., Tschichold, C. (2002). Collocations in CALL: an investigation of vocabulary- building software forEFL. Computer Assisted Language Learning 15, (3): 251-280.
Pálanová, K. (2010). Use of games in English language teaching (Bachelor‟s thesis). Retrieved from: http://is.muni.cz/th/266189/pedf_b/thesis.doc
Robin, A. (2001). Guidelines for Teaching to Young Children,
http://web.educastur.princast.es/proyectos/keltic/documentos/cong/robin.pdf(1
3.11.2013).