Edit by:
Ir. Harlianto Tanudjaja,
M.Kom,MM.
Bab 7
MOTOR
LISTRIK
Motor Listrik merupakan sebuah perangkat elektromagnetik yang mengubah energi listrik menjadi energi mekanik. Energi mekanik ini digunakan untuk, misalnya, memutar impeller pompa, fan atau blower, menggerakan kompresor, mengangkat bahan, dll di industri dan digunakan juga pada
Electric Motor Family
Tree
L
If a conductor of length 0.4m carrying a current of 10.6A is placed in a magnetic field with a flux density of 0.03T, determine the force
experienced by this conductor in newtons.
South pole Each digit of your hand must be at right
angles to both of the other two
current
field
motion
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
Force
Each digit of your hand must be at right angles to both of the other two
first finger
If the current is reversed, the direction of motion will change
The Motor Effect
Each digit of your hand must be at right angles to both of the other two
If the field is reversed, the motion will be in the opposite direction
The Motor Effect
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
I B
F first finger
thumb Each digit of your hand must be at right angles to both of the other two
field
motion
If the field is reversed, the motion will be in the opposite direction
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
South pole
North pole
field is clockwise
Current into page
field is anticlockwise
Current out of page
AC Machines
1. Select the proper ac motor type for
various applications.
2.
State how torque varies with speed
3.
Compute electrical and mechanical
quantities for ac motors.
4.
Use motor nameplate data.
5.
Understand the operation and
characteristics of three-phase induction
motors, three-phase
synchronous machines, various types
of single-phase ac motors, stepper
Sumber : http://dunia-listrik.blogspot.com/
Klasifikasi Motor Listrik Berdasarkan
AC Motors
AC motors can be divided into two
main forms:
synchronous motors
induction motors
High-power versions of either type
invariably operate from a
three-phase supply
, but single-phase
Synchronous
Machine
Synchronous machines are ac machine
that have a field circuit supplied by an
external dc source.
DC
field winding
on the rotor
,
AC
armature winding
on the stator
Origin of name: syn = equal, chronos =
time
Synchronous machines are called
‘synchronous’ because
their
MOTOR AC - SINKRON
Motor sinkron
adalah motor AC yang bekerja pada
kecepatan tetap pada sistem frekuensi tertentu.
Motor
ini memerlukan arus searah (DC) untuk pembangkitan
daya
dan memiliki
torque awal yang rendah,
dan oleh
karena itu motor sinkron cocok untuk penggunaan awal
dengan beban rendah
, seperti
k
ompres
or udara
,
perubahan frekuensi dan generator motor. Motor sinkron
mampu untuk memperbaiki faktor daya sistem,
sehingga
sering
digunakan
pada
sistem
yang
Prinsip Kerja Motor AC Sinkron
Sebuah motor sinkron dapat dinyalakan oleh sebuah motor dc pada satu sumbu.Ketika motor mencapai kecepatan sinkron, arus AC diberikan kepada belitan stator. Motor dc saat ini berfungsi sebagai generator dc dan memberikan eksitasi medan dc kepada rotor. Beban sekarang boleh diberikan kepada motor sinkron. Motor sinkron seringkali dinyalakan dengan menggunakan belitan sangkar tupai ( squirrel-cage) yang dipasang di hadapan kutub rotor. Motor kemudian dinyalakan seperti halnya motor induksi hingga mencapai –95% kecepatan sinkron, saat mana arus searah diberikan, dan motor mencapai sinkronisasi. Torque yang diperlukan untuk menarik motor hingga mencapai sinkronisasi disebut pull-in torque.
Seperti diketahui, rotor motor sinkron terkunci dengan medan putar dan harus terus beroperasi pada kecepatan sinkron untuk semua keadaan beban. Selama kondisi tanpa beban (no-load), garis tengah kutub medan putar dan kutub medan dc berada dalam satu garis (gambar di bawah bagian a).
Seiring dengan pembebanan, ada pergeseran kutub rotor ke belakang, relatif terhadap kutub stator (gambar bagian b). Tidak ada perubahan kecepatan. Sudut antara kutub rotor dan stator disebut sudut torque
Kontruksi Motor AC
sinkron
Motor sinkron adalah motor ac yang memiliki kecepatan konstan, namun kecepatan dapat diatur karena kecepatannya berbanding lurus dengan
Prinsip kerja 3 Phasa
1. Bila sumber tegangan tiga phasa dipasang pada kumpara
stator, maka pada kumparan stator akan timbul medan putar
dengan kecepatan
ns = kecepatan sinkronf = frekuensi sumber p = jumlah kutup
P f ns 120
2. Medan putar stator akan memotong
konduktor yang
terdapat pada sisi rotor, akibatnya pada
kumparan rotor akan timbul tegangan induksi
( ggl ) sebesar
E = tegangan induksi ggl
f = frekkuensi
N = banyak lilitan
Q = fluks
DC Machine & AC
machine
DC motor
- ends of the coil connect to a
mechanical rectifier called commutator
to
'rectify' the emf produced.
AC motor
-
No need rectification, so don’t
AC Motor
As in the
DC motor
case, a current is
passed through the
coil, generating a
torque on the coil.
Synchronous Machine
Construction
Energy is stored in the inductance
As the rotor moves, there is a change
in the energy stored
Either energy is extracted from the
magnetic field (and becomes
mechanical energy – motor)
Or energy is stored in the magnetic
Synchronous Machine
DC field windings are mounted on
the (rotating) rotor - which is thus a
rotating electromagnet
AC windings are mounted on the
(stationary) stator resulting in
three-phase AC stator voltages and
currents
The main part in the synchronous
machines are
Synchronous Machine
Rotor
There are two types of rotors used in
synchronous machines: cylindrical (or
round) rotors and salient pole rotors.
Salient pole rotors are less expensive
than round rotors.
Cylindrical ( round) rotor – low speed
machines (hydro-turbines)
Salient-Pole rotor - high speed
Synchronous Machine
Construction-Rotor
i) Cylindrical (or round)
rotor
i) Salient-pole
1. Most hydraulic turbines have to turn at low speeds
(between 50 and 300 r/min)
2. A large number of poles are required on the rotor
Salient-Pole Synchronous Generator
Stator
Salient-pole
L » 10 m
Direct-conductor cooling (using hydrogen or water as coolant)
Rating up to 2000 MVA
Turbogenerator
d-axis
q-axis
Cylindrical-Rotor Synchronous Generator
Stator
Synchronous Machine
Synchronous machine rotors are simply
rotating
electromagnets
built to have as many poles as are
produced by the stator windings.
DC currents
flowing in the field coils surrounding
each pole
magnetize the rotor poles
.
The magnetic field produced by the rotor poles locks
in with a rotating stator field, so that the shaft and
the stator field rotate in synchronism.
Salient poles are too weak mechanically and
develop too much wind resistance and noise to be
used in large, high-speed generators driven by
steam or gas turbines. For these big machines, the
rotor must be a solid, cylindrical steel forging to
Synchronous Machine
Axial slots are cut in the surface of the cylinder to
accommodate the field windings.
Since the rotor poles have constant polarity they
must be supplied with direct current.
This current may be provided by an external dc
generator or by a rectifier. In this case the leads from
the field winding are connected to insulated rings
mounted concentrically on the shaft. Stationary
contacts called brushes ride on these slip rings to
carry current to the rotating field windings from the
dc supply. The brushes are made of a carbon
compound to provide a good contact with low
Synchronous Machine
Stator
The stator of a synchronous machine
carries the armature or load winding
which is a three-phase winding.
The
armature winding
is formed by
interconnecting various conductors in slots
spread over the periphery of the machine’s
stator. Often, more than one independent
three phase winding is on the stator. An
arrangement of a three-phase stator
Synchronous Machine –
Stator construction
3 p
has
AC Synchronous Motor
Operation
41
•
Synchronous motors are like
induction motors in that they
both have stator windings that
produce rotating magnetic field
•
Unlike an induction motor, an
external DC source excites the
synchronous motor rotor and
therefore requires slip rings and
brushes
Figure: AC Synchronous Motor
ELO 2.6
AC Synchronous Motor
Operation
42
•
Synchronous motors use wound
rotor, shown in figure
•
Slip rings and brushes needed
•
Rotor is much more expensive to
manufacture than squirrel cage
rotor associated with AC induction
motors
Figure: Wound Rotor
AC Synchronous Motor
Operation
43
Starting a Synchronous Motor
•
Not self-starting, torque only developed when running at synchronous
speed
•
Needs some type of device to bring rotor to synchronous speed
Two ways of starting a synchronous motor:
1.
Use a separate DC motor
2.
Embed squirrel-cage windings on the face of the rotor
•
If starting a synchronous motor with a separate DC motor, both motors
may share a common shaft
•
Upon bringing DC motor to synchronous speed, stator windings receive
AC current, DC motor then acts as a DC generator and supplies DC
field excitation to rotor of synchronous motor
•
Once operating at synchronous speed, synchronous motor is ready for
load
AC Synchronous Motor
44
Starting a Synchronous Motor
•
More commonly, a squirrel-cage winding is embedded in face of rotor
poles to start motor
•
Starts as an induction motor, speed increases to ≈95% of
synchronous speed, then direct current is applied and motor begins
to pull into synchronism
•
Pull-in torque is term for torque required to pull motor into
synchronism
•
Because of more complex nature and higher manufacturing cost,
designers rarely specify synchronous motors
•
However, large industrial applications sometimes use synchronous
motors:
–
to accommodate large loads
–
to improve power factor of transformers in large industrial
applications
–
in applications where a constant speed is important
AC Synchronous Motor
45
Knowledge Check
Select all of the statements about AC synchronous motors that are true.
A. Synchronous motors are the most commonly used motors in large
industrial applications.
B. Synchronous motors develop starting torque in the same manner as
induction motors.
C. Synchronous motors are not often used due to their more complex
nature and higher manufacturing costs.
D. Synchronous motors can continue to operate with more slip than
induction motors, thus producing more torque.
Correct answer is C.
Magnetomotive Forces (MMF’s) and Fluxes
Due to Armature and Field Windings
Synchronous Machine
Flux produced by a
stator
winding
Developing Torque –
Single-Phase
AC Motor
47
Knowledge Check
Select all of the statements about single-phase AC motors that are true.
A.
The starting winding in a single-phase AC motor is always
energized while the motor is running.
B.
Single-phase AC motors have a starting winding that is out of
phase with the main winding.
C.
The resistance and reactance of the starting winding must be the
same as the main winding.
D.
Single-phase AC motors are used for small load applications.
Correct answers are B and D.
Further Study - AC Motor Performance
Synchronous Cage Induction Wound induction
Synchronous Generator
Synchronous Speed
2
P
s
Matematis Motor AC
sinkron
Slip dari motor AC dihitung
dengan :
Di mana :
N
r= Kecepatan putar, dalam
rpm
S = Slip normal, 0 sampai 1.
Synchronous
Machine
The frequency of the induced voltage is related
to the rotor speed by:
where
P
is the number of magnetic poles
fe
is the power line frequency.
Matematis Motor AC
sinkron
Motor ini berputar pada kecepatan sinkron, yang diberikan oleh persamaan berikut :
Ns = 120 f / P
di mana :
Ns = kecepatan serempak, dalam rpm
F = frekuensi daya AC
Effect of Rotor
Inductance on Torque
c
c
c
c
L
js
R
V
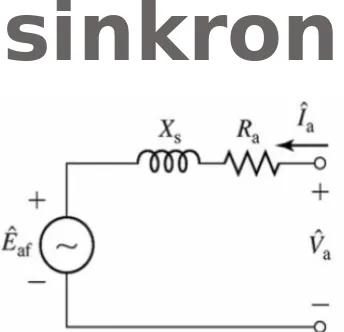
If the generator operates at a terminal voltage
V
Twhile
supplying a load corresponding to an armature current
Ia
,
then;
In an actual synchronous machine, the reactance is much
greater than the armature resistance, in which case;
Among the steady-state characteristics of a synchronous
Penggunaan Motor AC
sinkron
A three-phase, wye-connected 2500 kVA and 6.6
kV generator operates at full-load. The
per-phase armature resistance
R
aand the
synchronous reactance,
X
d, are (0.07+j10.4)
.
Calculate the percent voltage regulation at
(a)
0.8 power-factor lagging, and
(b)
0.8 power-factor leading.
Proteksi Motor AC sinkron
Ada banyak metode kendali motor AC (motor induksi, motor
sinkron) dengan kelebihan dan kekurangannya. Namun secara
umum metode ini dapat dikelompokkan sebagai berikut:
1.Kendali Skalar (v/f Konstan)
Proteksi Motor AC sinkron
Sesuai dengan namanya proteksi motor ini menggunakan panas sebagai pembatas arus pada motor. Alat ini sangat banyak dipergunakan saat ini. Biasanya disebut TOR, Thermis atau overload relay. Cara kerja alat ini adalah dengan mengkonversi arus yang mengalir menjadi panas untuk mempengaruhi bimetal.
Bimetal inilah yang menggerakkan tuas untuk menghentikan aliran listrik pada motor melalui suatu control motor starter. Pembatasan dilakukan dengan mengatur besaran arus pada dial di alat tersebut. Jadi alat tersebut memiliki range adjustment misal TOR dengan range 1 ~ 3,2 Amp disetting 2,5 Amp. Artinya, kita membatasi arus dengan TOR pada level 2,5 Amp saja.
Proteksi Motor AC Sinkron
Overload Motor Protection, yang dimaksud motor ini adalah electric motor yang oleh orang awam disebut dinamo. Dan disini dikhususkan yang terjadi pada motor AC 3 phase. Fungsi dari motor ini adalah sebagai penggerak atau untuk mengkonversi energi listrik menjadi mekanik / gerak seperti lift, conveyor, blower, crusher dll.
Pengukuran Motor AC
sinkron
Pembangkitan Torka
•Interaksi antara medan putar stator (Bs) dan medan rotor (Br) yang
membangkitkan torka seperti terlihat dalam persamaan berikut :
T = Bsx Bs(sin δ)
•δ disebut sudut beban karena besarnya tergantung pembebanan. Pada saat
beban nol nilai δ = 0. Jika dibebani, medan rotor tertinggal dari rotor sebesar δ,
kemudian berputar sama lagi. Beban maksimum tercapai pada δ = 90o. Jika
beban dinaikkan terus melebihi batas itu, maka motor akan kehilangan
Pengukuran Motor AC
Tiap arus fasa membangkitkan ggm F yang merupakan fungsi sudut ruang seperti :
ia à Fa.cos θ. Dengan Fa=Fm. sin ωt
Maka ggm F tiap fasa yang dibangkitkan :
Fa = Fm sin ωt.cos θ
Fb = Fm sin (ωt-120o).cos (θ-120o)
Fc = Fm sin (ωt-240o) .cos (θ-240o)
Pengukuran Motor AC
sinkron
Jika kemudian disederhanakan dengan persamaan trigonometri akan diperoleh:
F(θ,t) = 3/2 Fm.cos (θ-ωt)
Karakteristik Motor AC
sinkron
Gambar di atas memperlihatkan bahwa Torka (Torque) adalah fungsi sin δ, dengan δ adalah sudut daya. Pada motor sinkron nilai δ negatif dan nilainya positif pada generator sinkron. Torka maksimum dicapai pada δ= +/- 90o. Jika
Karakteristik Motor AC
sinkron
Gambar Model Motor Sinkron (Model dan Diagram Fasor)
Pengaruh Penguatan Medan
• Untuk membangkitkan fluksi dibutuhkan daya reaktif yang bersifat induktif.
• Pada motor sinkron, ggm dibangkitkan arus medan (DC) pada belitan rotor. Jika arus medan ini
cukup, maka motor tidak membutuhkan supply energi reaktif dari sisi stator yang bersumber dari jaringan listrik. Sehingga motor bekerja dengan faktor daya = 1.
• Jika penguatan arus medan kurang, maka motor sinkron akan menarik daya reaktif yang bersifat
induktif dari sisi stator. Sehingga motor bekerja dengan factor daya (pf) terbelakang (lagging). Artinya motor menjadi pembangkit daya reaktif yang bersifat induktif.
• Kebalikannya jika kelebihan penguatan arus medan, maka motor sinkron akan menarik daya reaktif
Synchronous Generator
Phasor diagram of a synchronous generator
The phasor diagram is to shows the relationship among
the voltages within a phase (E
φ,V
φ, jX
SI
Aand R
AI
A) and
the current I
Ain the phase.
Leading P.F. Lagging P.F