© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair
Prepared by:
Fernando & Yvonn
Quijano
4
Chapter
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 2 of 23
Chapter Outline
4
Demand and Supply
Applications
The Price System: Rationing and Allocating Resources
Price Rationing
Constraints on the Market and Alternative Rationing Mechanisms
Prices and the Allocation of Resources Price Floors
Supply and Demand Analysis: An Oil Import Fee
Supply and Demand and Market Efficiency
Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus
Competitive Markets Maximize the Sum of Producer and Consumer Surplus
Potential Causes of Deadweight Loss from Under- and Overproduction
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 3 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 4 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
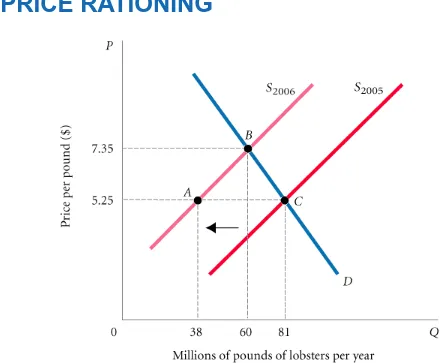
FIGURE 4.1
The Market for Lobsters
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 5 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
When supply is fixed or
something for sale is unique, its
price is demand determined.
Price is what the highest bidder
is willing to pay. In 2004, the
highest bidder was willing to pay
$104.1 million for Picasso’s
Boy
with a Pipe.
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 6 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 7 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
CONSTRAINTS ON THE MARKET AND
ALTERNATIVE RATIONING MECHANISMS
On occasion, both governments and private firms decide
to use some mechanism other than the market system to
ration an item for which there is excess demand at the
current price.
Regardless of the rationale, two things are clear:
1. Attempts to bypass price rationing in the market and to
use alternative rationing devices are much more difficult
and costly than they would seem at first glance.
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 8 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
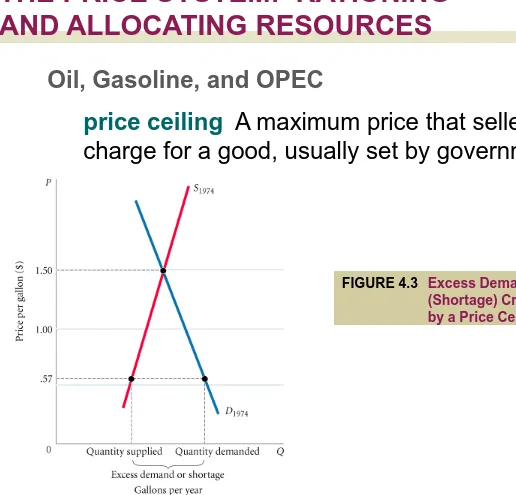
Oil, Gasoline, and OPEC
price ceiling
A maximum price that sellers may
charge for a good, usually set by government.
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 9 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
queuing
Waiting in line as a means of
distributing goods and services: a
nonprice rationing mechanism.
favored customers
Those who
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 10 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
Even when trading coupons is declared illegal, it is virtually impossible to stop black
markets from developing. In a black market, illegal trading takes place at
market-determined prices.
ration coupons
Tickets or coupons
that entitle individuals to purchase a
certain amount of a given product per
month.
black market
A market in which illegal
trading takes place at
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 11 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
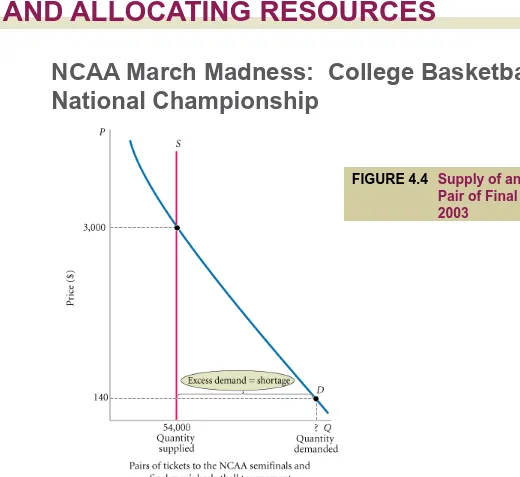
NCAA March Madness: College Basketball’s
National Championship
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 12 of 23
THE PRICE SYSTEM: RATIONING
AND ALLOCATING RESOURCES
No matter how good the intentions of private organizations and governments, it is
very difficult to prevent the price system from operating and to stop willingness to
pay from asserting itself. Every time an alternative is tried, the price system seems to
sneak in the back door. With favored customers and black markets, the final distribution
may be even more unfair than that which would result from simple price rationing.
There are many ways to deal
with the excess demand to
premiere sporting events such as
the NCAA finals, but it is hard to
keep tickets from those who are
willing to pay high prices.
CHA
© 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair 13 of 23