A
STUDY OF TEACHER’S LESSON PLAN
DESIGN BASED ON STUDENTS’ NEED
AT
HOSPITALITY PROGRAM OF STATE
VOCATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 1 BUDURAN
SIDOARJO
TITLE SHEET
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By
ULIL FAUZIYAH
NIM D05212045
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN Yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini
Nama : Ulil Fauziyah
NIM : D05212045
Semester : VIII
Fakultas/Prodi : Tarbiyah dan Keguruan/Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Dengan ini menyatakan sebenar-benarnya bahwa skripsi yang berjudul “A Study of Teacher’s Lesson Plan Design Based on Students’ Need at Hospitality Program of State Vocational High School 1 Buduran- Sidoarjo”adalah benar-benar merupakan hasil karya sendiri. Segala materi yang diambil dari karya orang lain hanya digunakan sebagai acuan dengan mengikuti tata cara dan etika penulisan karya ilmiah yang ditetapkan oleh jurusan.
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET
This thesis by Ulil Fauziyah entitled “A Study of Teacher’s Lesson Plan Design Based on Students’ Need at Hospitality Program of State Vocational High School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo” is ready to be examined by the Boards of Examiners.
APPROVAL SHEET
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Sebagai sivitas akademika UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya:
Nama : ULIL FAUZIYAH NIM : D05212045
Fakultas/Jurusan : FTK/PENDIDIKAN GURU BAHASA INGGRIS E-mail address : ulilzya@gmail.com
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, menyetujui untuk memberikan kepada Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Hak Bebas Royalti Non-Eksklusif atas karya ilmiah :
Sekripsi Tesis Desertasi Lain-lain
(………)
yang berjudul :
A STUDY OF TEACHER’S LESSON PLAN DESIGN BASED ON STUDENTS’ NEEDS
AT HOSPITALITY PROGRAM OF STATE VOCATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 1
BUDURAN SIDOARJO
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan Hak Bebas Royalti Non-Ekslusif ini Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya berhak menyimpan, mengalih-media/format-kan, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data (database), mendistribusikannya, dan menampilkan/mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain secara fulltext untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya selama
tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis/pencipta dan atau penerbit yang bersangkutan.
Saya bersedia untuk menanggung secara pribadi, tanpa melibatkan pihak Perpustakaan UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, segala bentuk tuntutan hukum yang timbul atas pelanggaran Hak Cipta dalam karya ilmiah saya ini.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Surabaya, 18 Agustus 2016
Penulis
(Ulil Fauziyah)
ABSTRACT
Fauziyah, Ulil. (2016). A Study of Teacher’s Lesson Plan Design Based on
Students’ Need at Hospitality Program of State Vocational High School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo. A Thesis. English Teacher and Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. Advisor : Dra. Irma Soraya, M.Pd.
Key Words: Lesson plan, students’ needs, Hospitality program.
TITLE SHEET ... i
D. Significance of The Study ... 8
E. Scope and Limit of The Study... 8
F. Definition of Key Term ... 9
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Foundation ... 11
1. English for Spesific Puposes Definition ... 11
2. Indicators of ESP for Hospitality Program ... 13
a. The absolute characteristic ... 13
b. The variable characteristics ... 14
3. Students’ Needs ... 17
a. Necessities ... 17
b. Lacks ... 18
c. Wants... 18
4. Lesson Plan ... 19
5. The Development Principles of Lesson Plan ... 21
a. Formulating Learning Outcomes ... 22
b. The Degree of Competence from KI and KD ... 25
c. Learning Procedures ... 30
A. Research Approach and Design ... 35
B. Setting of The Study ... 36
C. Data and Source of Data ... 36
D. Research Stages ... 37
E. Data Collection Technique ... 39
F. Data Collection Instrument ... 40
G. Data Analysis Technique ... 41
CHAPTER IV : FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Research Findings ... 45
1. Finding of Students’ Needs Analysis ... 45
2. Finding of Lesson Plans Analysis ... 76
B. Discussion ... 87
1. Discussion of Students’ Needs at Hospitality Program ... 87
2. Finding of Lesson Plans in Formulating Learning Outcomes and Learning Procedures ... 94
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION B. Conclusion ... 98
C. Suggestion ... 100
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This study is about teacher’s lesson plan design based on students’ needs in
Hospitality. This chapter discusses the area of the study that will be covered in some
headings; background of study, research problems, objectives of the study,
significance, scope and limitation, then definition of the key terms.
A. Background of Study
English language teaching (ELT) in Indonesia is generally categorized into
two kinds, they are ELT for general purposes (EGP) and ELT for specific
purposes (ESP)1. However, students majoring in English are often regarded as
students who focus on EGP2. Although they may study English for a certain
purpose, the context of ELT in Indonesia they are regarded as EGP learners. On
the other hand, students majoring in subjects other than English in their study
(e.g., science, economics, and engineering) are classified as ESP students
because the focus of their English learning is on the use of English within the
specific area rather than on general use3.
1
Khan, Tariq M. et. al., “Needs Analysis of English for Occupational and Specific Purposes”,
International Journal of Social Sciences and Education, Vol. 1, No. 4, 10-2011, accessed on
www.gen.lib.rus.ac.id on: November 1st, 2015
2 Marwan, Ardi. “
ESP Teaching Challenges in An Indonesian Vocational Higher Institution”. State Polytechnic of Pontianak, Indonesia. The English Teacher Vol. XXXVIII: 1 – 12
3
Yi-Hsuan Gloria Lo, “ESP versus EGP: A case study of an ESP program for vocational high school
students of Tourism”, Taiwan International ESP Journal, vol.3, no.2, 71, 2012, accessed:
Generally, ESP is taught in vocational higher instituion or university.
However in Indonesia, it is also taught in vocational high schools level4. Thus,
English which is learned in this field also has a similar vocational context. As
Lubna stated that learners studying English in Vocational High School are
expected to master some knowledge of English usage through general class, yet
they have not learned to use language in their specialized contexts of profession
and study5. Therefore, English becomes a significant subject that needs high
attention to the development of teaching in Vocational High School.
In line with it, State Vocational High school 1 Buduran has a vision to
become an educational and training institution which is able to produce
professional, independent and competitive graduates in national and international
social work6. To achieve that vision, vice of the head master states that English
becomes one of the main subjects which the students have to master especially
for those who are in hospitality program. For instance, one of the divisions in
Hospitality program becomes a Guest Relation Officer (GRO). This division is
directly related to the guests whom communicatively welcome and serve to
attract them to come in7. Therefore, language teachers have to prepare a lesson
4
Marwan, Ardi. ESP Teaching Challenges in an Indonesian Vocational Higher Institution” State Polytechnic of Pontianak. The English Teacher Vol. XXXVIII:1-12
5Algadrie, Lubna. “Need Analysis: Strategic Issue on the Teaching of English for Specific Purposes
for the Study of Science and Tecchnology”. University of Sidney
6
Profil smkn 1 Buduran Sidoarjo. Accessed on http://www.smkn1buduran.sch.id/profil.html
December, 4 2015.
7
for their learners in order to perform a role needed in their future job or
profession.
Thasevka states thatlanguage teachers encounter difficulties when they plan
their lessons. Some of these difficulties are immediate evidence in the lesson
plans if they are aware of their students’ competence and also their needs8. Thus,
the researcher intends to conduct a study toward the teacher’s lesson plan design
of English based on students’ needs in hospitality. The determination of the
research is taken into account in this study. Designing English lesson plan have
some differences from designing any other subjects. Instead of designing the
lesson plan based on the curriculum, the teachers also have to pay attention on the students’ needs. Moreover, the teacher also said that the first consideration
before designing lesson plans is formulating proper learning outcomes
(indicators) which meet the demands of their students’ different level of
knowledge. In addition, sometimes the teachers are still less to notice how to
formulate a proper indicator when they design a lesson plan that leads to a failure
of achieving basic competence by the learner individually9.
Concerning to the teachers’ lesson plan design, it should be based on the
applied curriculum. There are two curriculums which are applied by the
8
Tashevska, Svetla. “Some Lesson Planning Problems for New Teachers of English”. Accessed onhttp://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/lessonplans?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=soci al&utm_campaign=bc-teachingenglish
9
government in Indonesia; they are KTSP (Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan
Pendidikan) and K-13 (Kurikulum 2013). However, the curriculum applied in
State Vocational High School 1 Buduran is K-13 in which a test is given at the
beginning to accommodate their expertise based on the major10. In the
government regulation No. 70 2010 about Implementation and Management of
Education Article 80 point 1, it is stated that the majors in vocational or other
equivalent level is categorized the area of students’ expertise11. Yet, the syllabus
design is not classified based on the majors.
According to Graves’ point of view, a clear set of learning outcomes serve as a bridge between students’ need and goals. Hence, in case of formulating
learning outcomes, there are some aspects that should be considered by the
teachers before specifying them to the objectives. First, learning outcomes should
meet the demands of competence contained in the verb used in Basic
Competence (KD). Second, the learning outcomes should achieve a minimum
level of competence that can be developed to exceed the minimum proficiency in accordance with the potential and students’ need12
. Therefore, the teacher should also pay attention on what the students’ present knowledge (what they know at
that time), the students’ required knowledge (what they need to know by the end
10
Permendikbud No. 70 2013. Kerangka dasar dan struktur kurikulum SMK/MAK. p: 12
11
Ibid p: 13
12
of the class) and the last is the students’ subjective needs (what the students want
to know).
In teaching process, matching the activities and materials in lessons
becomes one of the common problems occurred in the class with a various students’ proficiency levels13. However, the English taught in vocational school
is one of ESP sub-branches areas where the teaching process should be based on the learners’ need in their respective specialized subjects14. In teaching ESP, the
teachers will also have to face three kinds of problems; materials writing,
responsibility of content and student motivation15. It is likely to happen due to
the fact that EGP learners are often exposed to a more fun learning environment
than the ESP learners. That fact is in line with Basturkmen’s point of view “the
students in ESP classes often have restricted time to learn English, it makes
sense to teach them only the bits of English they need”16.
Related to this research, there was some similar researches which had
straight relationship with this research; the first study entitled “ESP Teaching
Challenge in an Indonesia Vocational Higher Education” conducted by Ardi
13
Soraya, Irma. “English Curriculum” A handbook for English Department Undergrraduate Students. UIN Sunan Ampel press. 2014. p: 26
14
Hatchinson, Tom, – Alan Waters. English for specific Purposes: A learner centered approach. New York: Cambridge university press, 1998. Accessed: www.tu-chemmitz.edu , on: 1-11-2015.
15
Astika, Gusti. 2009. “The Role of Need Analysis in English for Specific Purposes”, accessed on:
www.journal.teflin.org , on: 1-11-2015.
16
Marwan17. Here, the researcher found some problems showed by the English
teacher in teaching ESP. The problems were students had low motivation, the
resource was hard to find, and preparing material was time consuming.
Therefore, although teaching English is considered important to be taught in
Vocational school, it practically has some complex problems. The research about students’ need also conducted by NiPutu Anggareni entitled “Syllabus and
Student Needs: An Analysis of English Syllabus at Mathematic Education
Department State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya in 2014”18. In
this study, the researcher attempted to find out the syllabus designed by
Mathematics Department whether it met with students’ need or not. However,
her study was English for Academic Purposes (EAP) oriented which concerned
researching and teaching the English needed by those who use the language to
perform academic tasks.
The effectiveness of lesson plan will be responsive to the clearly articulated
learning destination of students, needs, and also the successful outcome of the
lesson. Consequently, finding the study toward the lesson plan which
accommodates the students’ need is important. Besides, identifying the students’
need in this certain major can be source information knowledge for the teachers
to design a lesson plan better. Therefore, in the following teaching and learning
17
Marwan, Ardi. ESP Teaching Challenges in an Indonesian Vocational Higher Institution” State Polytechnic of Pontianak. The English Teacher Vol. XXXVIII:1-12
18
Anggaraeni, N. “Syllabus and Students’ Need: An Analysis of English Syllabus at Mathematic
process, it can become a set of guideline for the teachers to plan a lesson
including approach, method, technique, objectives, activity even task which in accordance with their students’ need.
B. Research Problems
Related to the research background, the problems of the study are:
1. What are the hospitality student’s needs in learning English at State Vocational
High School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo?
2. Is the teacher’s lesson plan design accordance with the students’ needs in
learning English in part of formulating learning objectives and learning
procedures?
C. Objectives of The Study
The objective of the study relates to the research problems which are
concerned in identifying the accordance of the hospitality students’ needs with the teacher’s lesson plan in part of formulating learning objectives and learning
procedures. If the lesson plan is designed appropriately based on the student`s
need, it can be a good resource for English teacher to design a relevance lesson
plan to teach English especially for Hospitality Students. However, if the lesson
plans are not in accordance with the student`s need, the analysis can be a good
tool to develop the lesson plans in order to create a better course that matches to
D. Significance of The Study
By conducting this research, the researcher hopes that it will give many
benefits for the hospitality students and teacher.
1. For Hospitality Students
The researcher expects that the result of the study can bridge student`s
necessities and student`s objectives in order to maximize their potentially to
be successful in acquiring English in Hospitality program.
2. For the Teachers
The study can also give the clear indicators for teacher especially in
hospitality to make an effective lesson plan which is based on student`s need
in learning English by gathering information from students’ perspective.
3. For English Teacher Education Department
Recognizing that the study will be conducted in Vocational High School, the
researcher also look ahead the study can give more insight to the Department
to not only prepare students with EGP but also with ESP.
E. Scope and Limit of The Study 1. Scope of the Study
This research is focused on the English teacher’s lesson plan design in
hospitality program. As stated in background, there are some terms used to
design a good lesson plan including learning objectives, procedures,
only focus on two parts of lesson plan, which are; formulating learning
outcomes and procedures.
These two parts are considered from Development Principles of
Lesson Plan in K-13 that the teachers should notice on students’
characteristics of early education units such as their abilities, needs, students’ learning motivation and cultural background. A learning procedure
designed to provide a learning experience that involves mental and physical
processes through interaction between learners, teachers, environment and
other learning resources in order to achieve the basic competence (KD).
2. Limits of the Study
This research is limited to tenth grade of hospitality major at State
Vocational High School 1 Buduran, Sidoarjo. There are 2 classes in this
major.
F. Definition of The Key Terms 1. Lesson Plan
A lesson plan is the teachers’ guide for running a particular lesson, and it
includes the goal (what students are supposed to learn), how the goal will be
reached (the method, procedure) a way of measuring how well the goal was
reached (test, worksheet, homework etc)19. For this study, lesson plan means
19
a set of assumptions of what teacher will do in teaching English for
hospitality students at State Vocational High School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo.
2. Students’ Need
John Macalister argues that needs is divided into two terms; they are target
needs (what the learners need to do in target situation) and learning needs
(what the learners need to do in order to learn)20. Thus in this research, students’ needs refers to what the learners need to learn and what they want
to learn as a process to establish some aspects of students’ basic need
generated by need analysis. It is as a preference of learning process which can equip teachers’ domain to formulate goals and objectives related to the
provided indicators in syllabus.
3. Hospitality Program
Based on Cambridge Advance Learner Dictionary, hospitality is defined as a
term when people are friendly and welcoming to guests and visitors21. In this
study, hospitality refers to a group of students at State Vocational High
School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo who learn particular topics for hospitality where
the English is needed to be used in certain situation especially for dealing
with hotels’ customers.
20
Macalister, John. Language Curriculum Design. New York: Routledge Tailor and Francis Group, 2010. p. 24
21
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher will explicate several theories through
reviewing some literatures related to this study. This theoretical construct deals with
four main areas, they are English for Specific Purposes (ESP), Students’ need, lesson
plans and the development priciples of lesson plan.
A.Theoretical Foundation
1. English for Specific Purposes Definition
In term of English as foreign language or English as second language, ELT is
divided into two main categories; they are English for General Purposes (EGP)
and English for Specific Purpose (ESP). ESP is a technical name that denotes
English for Specific Purposes which means teaching a specific genre of technical
English to students with specific goals, majors or jobs1. ESP is in fact a
learner-centered approach to teaching English as a foreign or second language. In the
sense of linguistic terminology, ESP means what learners needs in target situation
or what they want about his function of language usage or what are their needs
according to their own views2. It closely refers to what the students require
regarding the language they will use in certain situations.
1
Abu-Zahra, J. Majid, “Is ESP a Need? Birzeit Public Administration Students”, Department of Languages & Translation Birzeit University, accessed on 5 Jan, 2016.
2
Khan, Tariq M. et. al., “Needs Analysis of English for Occupational and Specific Purposes”,
International Journal of Social Sciences and Education, Vol. 1, No. 4, 10-2011, accessed on
www.gen.lib.rus.ac.id on: November 1st, 2015
Moreover, Pauline also defines ESP as Goal-oriented language learning that
means student has a specific goal that is going to be attained3. Through the
experience of ESP Need Analysis research conducting in Pakistan, ESP is
presupposed that the learners will use the language practically which is meant to
meet their needs in a special context. For that purpose, the course is designed and is expected to provide the required competence to fulfill the students’ needs
through language learning.
In general school, English for General (EG), the subject is designed for the
students to the potential of language in general which is used by the learners
whenever they will come across the situation in future4. Here, the restriction is not
possible to specific tasks to achieve the specific ability. However in vocational
school level, the learners are not only purposed to master four skills of language
but also to support the certain skill through a language. Here is English for
Specific Purpose (ESP) applied in the teaching and learning process. Thus, what
distinguishes English for Specific Purpose (ESP) from General English (GE) is not
the existence of a need as such but rather than awareness of the need5. Yet, this
distinction is not applicable in Indonesian vocational school, due to most of the teacher are not aware of what their students’ needs in learning English.
3
Robinson, Pauline C.,ed. Hywel Coleman, Working with Language: A Multidisciplinary Consideration of Language Use in Work Contexts. New York: Mouton de Gruyter1989, p 398
4
Yi-Hsuan Gloria Lo, “ESP versus EGP: A case study of an ESP program for vocational high school
students of Tourism”, Taiwan International ESP Journal, vol.3, no.2, 71, 2012,
5
2. Indicators of ESP for Hospitality Program
The indicators of a good ESP can be seen by looking at the core
principles and the characteristics of ESP. If the ESP course fills the core
principles and the characteristics of ESP means that the ESP course is good.
The core principles of ESP are: needs driven, specificity, and relevance46. In
addition, the expert of English shares their idea about the characteristics of
ESP. Laurence Anthony cited in Duddley - Evan explains that ESP has some
characteristics. The characteristics are divided into two groups according its
´absolute´ and ´variable´ attributes.
a. The absolute characteristics are:
1) ESP is defined to meet specific needs of the learner.
2) ESP uses of the underlying methodology and activities of the discipline
it serves.
3) ESP is centered on the language (grammar, lexis, and register), skills,
discourse and genres appropriate to these activities.
b. The variable characteristics are seen in five points:
1) ESP uses specific teaching situations, a different methodology from
that of general English.
2) ESP is designed for adult learners, either at a tertiary level institution
or in a professional work situation.
6
3) ESP is generally designed for intermediate or advanced students.
4) Most ESP courses assume some basic knowledge of the language
system, but it can be used with beginners7.
Beside the principle and characteristic, activity is also
important aspect in a teaching process. In term of teaching English in
vocational high school context, here are some activities for
Hospitality students8.
a) Speaking: speaking to foreign visitors, taking care to customers’ arrival, speaking on the phone, taking part in
meetings, taking part in conferences, giving presentations.
b) Writing: business letters, e-mail, memorandums, reports, essay,
summaries of articles.
c) Reading: business letters, e-mail, memorandums, reports, price
lists, standard operational procedure.
The activities above are related to the job areas that the
students will have when they are in work field. Some job areas for
hospitality students are9:
a) General Manager: The general manager has duties walking
around to each department in the morning to check in with the
7Milevica Bojović,, Teaching Foreign Language for Specific Purposes:
Teacher Development, 487
8
Kyunghee. Need Analysis of Tourism and Hotel Industry. Hanyang Women’s Collage
9
staff in different departments taking care of any issues that may
have come up while he was out of the office and others.
b) Front Officer: this job represents the hotel to the guest
throughout all stages of the guest's stay. This front officer has
also to determinate a guest's reservation status and identifies
how long the guest will stay.
c) Housekeeping: this job area is charged with cleaning and
maintaining the rooms and premises in and around a hotel. This
may involve sweeping, waxing and polishing floors, emptying
waste baskets, changing sheets, folding and ironing clothes and
cleaning the rooms and hallways.
d) Laundry Service: the duty of this laundry attendant is to clean
garments and linens. This job is to set up cleaning machines
depending on the garments that needs washing. The laundry
worker is responsible for repairing minor damages on a client
or others.
e) Ticketing Service: this job is Responsible for serving the
general public by selling event related tickets. And the
responsible for this job is cash management and compliance
and this job is also operates a cash register and/or credit card
3. Students’ Need
The relevance of ESP and students’ needs is elaborated by Khan. He stated
that to make a clear assumption that ESP is based on how the students use the language according to the students’ content areas10
. Similarly, he also mentioned
the definition of a need itself as a condition or situation in which something is
required. This is why the awareness of a need takes a significant vitality for the
learners or teachers to know why they learn English and to influence on what will
be acceptable and reasonable content in learning language. In sum, the course
designed should be based on an analysis of need. As a reason that needs analysis
makes sure that the course will contain relevant and useful things to learn11.
To understand more what the students’ need is, let see a brief explanation
regarding to the different school level; as mentioned above that vocational school
is generally different from general school. In vocational school, a placement test is
given at the beginning to accommodate the expertise of students based on the
major. The need of the students can be seen clearly due to the variety of
department is also offered in this school. The tendency of the language need in
each department is also quite different. It is influenced by the skill that will be
achieved in the department regarding to the purpose of learning English.
10
Khan, Tariq M. et. al., “Needs Analysis of English for Occupational and Specific Purposes”,
International Journal of Social Sciences and Education, Vol. 1, No. 4, 10-2011
11
According to the theory of English for Specific Purpose (ESP), the teacher has considered the target need to find out the students’ needs in learning English12.
Those terms are able to figure out by conducting an analysis for students’ needs, or
it is familiarly known as need analysis. Needs analysis is a process which is
undertaken by trainers, teachers and course designers to ascertain the
pre-requisites for developing a course and its implementation13. It could be declared
that needs analysis is name of providing all the things and collecting all the
information which are necessary to start a journey to reach the destiny14. Citied by
Macalister, Hutchinson and Waters defined that target Need is something an
umbrella term which has practice hides a number of important distinctions. It is
more useful to look at the target situation in term of necessities, lacks, and wants.
a) Necessities
Necessities can be defined as the type of need determined by the demands
of target situation; that is what the learner has to know in order to function
effectively in target situation15. For example, one of the divisions in
Hospitality becomes a Guest Relation Officer (GRO). This division is
directly related to the guests whom communicatively welcome and serve to
12
Hatchinson, Tom, – Alan Waters. English for specific Purposes: A learner centered approach. New York: Cambridge university press, 1998. Accessed: www.tu-chemmitz.edu , on: 1-11-2015.
13
ibid
14
Nurhayati, Siwi. 2014. Teacher’s Perception on The Student Needs in Learning English and Its
Impact to The Teaching Strategies at Pastry Student of SMKN 2 Trenggalek. (IAIN Tulungagaung, 2014) p. 19
15
attract them to come in. In line with it, the student is supposed to acquire
speaking skill and enough knowledge related to their job.16.
b) Lacks
Since the concern is in ESP with the needs of particular learners, it is also
important to identify what the learners already know, so that the teachers can decide which of the necessities and the learners’ lacks (present knowledge).
Analyzing the learners’ present knowledge is aimed to get some particular
details to decide the necessities of students. Thus, the teacher can make a gap
of those two matters.
c) Wants
Two previous points above are considered on target need only in an
objective senses with the passive role learners. However, the learners must
have their own interest related the material they want to learn. It is named “wants”. As Richterich, citied by Hutchinson, stated that a need does not
exist independent of a person, it is people who build their images of their
needs on the basis of data relating themselves and their environment17.
Therefore, it is also important for the teacher to know what the hospitality
students expect in learning English related to their real field.
16
Hatchinson, Tom, – Alan Waters. English for specific Purposes: A learner centered approach. New York: Cambridge university press, 1987. P. 55 Accessed: www.tu-chemmitz.edu , on: 1-11-2015.
17
4. Lesson Plan
Before going to the classroom, teachers need preparation to what to do in
the classroom. This planning learning phase is called a lesson plan. As Lorin
elaborated that planning in teaching and learning is a process of the teachers to
visualize and design an outline to guide their proceedings in the future.18 Meanwhile, planning, according to Scrivener, is “imagining the lesson before it
happens which includes prediction, anticipation, sequencing, organizing, and simplifying.”19
Planning helps most teachers to predict what they will perform
by using a guide.
According to O’Bannon, a lesson plan is a teacher’s complete course’s
explanation and description of instruction for one class.20 He further explains
that details may be varied depending on the teacher’s preference, covered
subject, and students’ interest and need. This statement means that a lesson
plan is designed for guiding teacher to run the activities based on the students’
need, the subject, and the school system related with it.
Planning is often viewed as a key aspect in achieving a successful
teaching21. A lesson plan as it is operationally defined in most colleges of
education consists of an introduction, objectives (behavioral or not), materials,
procedures, and evaluations, all produced by an individual teacher candidate
18
Lorin W. Anderson, The Effective Teacher, (Singapore: McGraw Hill Book Company, 1989), 47
19
Jim Scrivener, Learning Teaching 2nd edition, (Oxford: Macmillan, 2005), 109
20
O'Bannon, B. "What is a Lesson Plan?" Innovative Technology Center, (The University of Tennessee, 2008), Cited in http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lesson_plan
21
or classroom teacher22. A successful lesson in teaching learning is mostly
determined before the teaching learning process.
In designing a lesson plan, teachers should be able to determine the
main teaching techniques and activities to present in the classroom. A large
variety of techniques and activities can be drawn on when designing lessons.
There are four major types of activity in the lesson plan which is covered by
Macalister:23
a) Experience activities; trying to keep as much as possible of the knowledge
needed to perform the activity within the learners’ previous experience.
b) Shared activities; involving the learners achieving group work which cannot
be accomplished when working alone.
c) Guided activities; involving the learners doing already partly completed task.
It is the activities which involve the teachers to provide what part is needed so
that the learners’ task is made easier and less likely to result in error.
d) Independent activities; is the ultimate goal of the other three. This activity
involves the learners work with no assistance or preparation.
22
Jalongo, Mary Renck. Planning for Learning. New York and London: Teachers College Press: Columbia University, 2007. p. 12
23
5. The Development Priciples of Lesson Plan
As stated in Research Background that there are two curriculums which are
applied by the government in Indonesia; KTSP (Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan
Pendidikan) and K-13 (Kurukulum 2013). However, the school, where the
research is conducting, applies K-13 which means the concern of designing lesson
plan should also be based on K-13. This curriculum applies the definition of
competence stated in the Law on National Education System of the three
integrated dimensions; attitudes, knowledge, and skills. Thus, it has also a rule that
the teachers should notice some points before designing a lesson plan. The rules
are laid on subheading four “The Principles in Designing Lesson Plan”. Those
principles are24:
a) Lesson plan design is aimed to administer the characteristics of the
educational unit as early ability of learners, interest, learning, motivation,
talent, potential, social skills, cultural background, etc.
b) Lesson plan design should be based on learner center approach.
c) Lesson plan should contain a draft of program providing positive feedback,
reinforcement, enrichment, and remedy.
d) Lesson plan is prepared intended to the connected and coherence between
Core Competence (KI) and Basic Competence (KD), learning materials,
24
activities (procedures), assessment, and learning resources in the integrity of
the learning experience.
Since the object of this study is lesson plan, the definition is as same as the statement of O’Bannon that lesson plan is a comprehensive description of the
teaching for one class. Details will vary depending on the teacher’s preference,
subject being taught, and the students’ need. A good lesson plan is outlining the
teachers about the content of the materials to be taught, the techniques to motivate
learners to be used, well-arranged procedure and activities for students to be done,
the instructional materials and the evaluation process to be utilized in the
classroom. However, for this study the researcher only focuses on 2 parts in
designing lesson plan, they are; formulating learning outcomes and learning
procedures, below are the theories regarding those concerns.
a. Formulating Learning Outcomes
Learning outcomes, familiarly known as objectives is statements
describing the behavior of students that teachers expect after completing a
particular learning process25. In principle, formulating objectives before
teaching is a good thing. But practically, it might also become one of the
hardest aspects of lesson design for the teacher. In addition, studies on the teachers’ planning process showed that teachers are primarily focused on the
25
“concretes” of the classroom: what they will teach, how they will teach it,
the students in the classroom26. Otherwise, formulating objectives (learning
outcomes) and learning procedures in the lesson plan can be the first step to
guide the teacher in setting what and how they will teach in the classroom.
Not all teachers set language learning objectives for the activities they
use in class. Teachers are primarily concerned with making sure that the
learners have something to do and that they are happy while doing it27. On
the other hand, there are two bigger obstacles of formulating objectives. One
is lack of time. Generally, the teachers who have full days in teaching at
school do not really have much time to formulate objectives for their lesson. The other is that people don’t know how to formulate them. Thus, this
subheading is meant to elaborate how to formulate the objectives in a way that makes sense to the students’ need.
Since the school where this study conducted applies curriculum 2013,
it is significant to comprehend the competencies hierarchy of K-13 includes
Standard Competencies (SKL), Core Competence (KI), and Basic
Competence (KD).
Standard Competencies (SKL) is used as criterion regarding the qualifications of graduates’ abilities including attitudes, knowledge and
skills. The Core Competencies (KI) is the level of capability that should be
26
Graves, Kathleen. “Designing Language Course”. Heinle & Heinle Publishers. 2000. p: 74
27
possessed by the students in each grade and also as a base to the
development of Basic Competence. Meanwhile, Basic Competence is a
number of capabilities of minimum that should be mastered by the learners
to the certain Standard Competence which is used as references to the
development of learning outcomes28.
According to Nur Dewi, the first step in formulating learning outcomes
is to analyze the level competence from KD29. It is necessary to meet the
demand of minimum standards. The level of competence can be seen
through the operational verb used in KD. In addition, it can also be classified
into three parts of level. They are; knowledge, process and the application.
The operational verbs which are used in level of knowledge are lower than at
the process and application level.
Thus, in formulating learning outcomes, the teachers should notice the
following qualifications30:
1) Each Basic Competence is developed into at least three objectives.
2) The overall objectives should meet the demands contained in the verb
used in Basic Competence and can be developed beyond the minimum
competence in accordance with the potential and the needs of learners.
28
PERMENDIKNAS No. 41 tahun 2007
29
Nur Dewi, “Merancang Pencapaian Kompetensi Dasar Melalui Pencapaian Indikator” accessed onhttp://www.lpmpsulsel.net/v2/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=361:pencapaia n-kompetensi-indikator&catid=42:ebuletin&Itemid=215 Dec, 9 2015. Artikel E-Buletin Edisi Maret 2015 ISSN. 23553189
30
3) The objectives accommodate the characteristics of the lessons and focus on students’ behavior.
4) The objectives develop beyond the minimum competence in
accordance with the potential and the needs of learners.
5) Specific and measurable action verbs are used to describe what
students are expected to demonstrate proficiency through some
observation action or generation of appropriate product.
6) Learning objectives clearly convey the expected student action.
7) Formulations of objectives develop into a number of assessments that
includes the realm of attitudes, knowledge and skills.
8) The objectives align with the needs and capabilities of the students at
this stage of their intellectual development in this stage of their
curriculum.
b. The Degree of Competence from KI and KD
The first step in formulating learning outcomes is to analyze the competence
degree from KI and KD. This step is aimed to fulfill the minimum demands of
competence that can be a national standard. The degree of competence can be
seen through operational verbs that are used in KI and KD and it can be
application31. The verbs in knowledge level are lower than those which are in
level of process and application. The level of application is the higher
demands competence which is expected. The classification of competence
based on verbs used is displayed on the table below32.
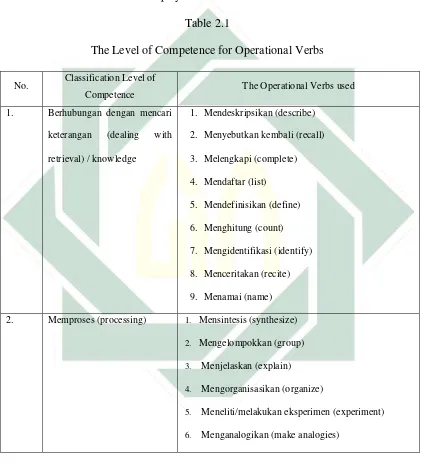
Table 2.1
The Level of Competence for Operational Verbs
No. Classification Level of
Competence The Operational Verbs used 1. Berhubungan dengan mencari
2. Memproses (processing) 1. Mensintesis (synthesize)
2. Mengelompokkan (group)
Panduan Pengembangan Indikator. hal, 5
32
7. Mengurutkan (sequence)
8. Mengkategorikan (categorize)
9. Menganalisis (analyze)
10. Membandingkan (compare)
11. Mengklasifikasi (classify)
12. Menghubungkan (relate)
13. Membedakan (distinguish)
14. Mengungkapkan sebab (state causality
3. Menerapkan dan
mengevaluasi (Application
and evaluation)
1. Menerapkan suatu prinsip (applying a principle)
2. Membuat model (model building)
3. Mengevaluasi(evaluating)
4. Merencanakan (planning)
5. Memperhitungkan/meramalkan kemungkinan
(extrapolating)
6. Memprediksi (predicting)
7. Menduga/Mengemukakan pendapat/ mengambil
kesimpulan
(inferring)
8. Meramalkan kejadian alam/sesuatu (forecasting)
9. Menggeneralisasikan (generalizing)
10. Mempertimbangkan /memikirkan
kemungkinan-kemungkinan
(speculating)
11.Membayangkan /mengkhayalkan/ mengimajinasikan
12. Merancang (designing)
13.Menciptakan (creating)
14. Menduga/membuat dugaan/ kesimpulan awal
(hypothezing)
However, the development of learning outcomes should accommodate the level
competence which is accordance with the tendencies used in KI and KD. In addition,
the use of operational verbs in learning outcomes show the emphasizing the expected
aspect of what the students’ need to comprehend at the end of teaching process.
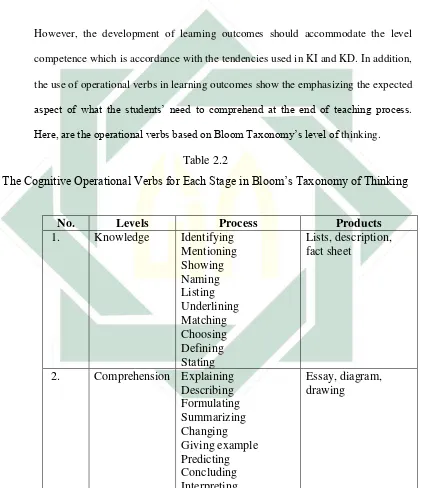
Here, are the operational verbs based on Bloom Taxonomy’s level of thinking.
Table 2.2
The Cognitive Operational Verbs for Each Stage in Bloom’s Taxonomy of Thinking
No. Levels Process Products
1. Knowledge Identifying Mentioning
Replacing Developing Proving
Interpreting Discussing Estimating
Choosing between Differentiating Supporting Refusing
c. Learning Procedures
Learning activities at school in Indonesia which has been a tradition is
teacher centered. This staging is commonly carried out the steps; instance,
while teachers is explaining the rules, formulas, showing images, the students
are listening to get understand; at the end of class, the learners have the exercise
in classroom. Thus, the teacher centered of learning activities may not be
implemented without the use of textbooks as the main source of learning, due to
the lesson taught by the teacher, it still requires the uniformity of teaching
materials.
Basically, learning procedures is designed to provide students learning
experience. It involves both mental and physical processes through interaction
among learners, between learners and teachers, environment and other learning
resources in order to achieve (basic competence)33. Thus, learning experience
may be able to be achieved through the variety of Scientific Approach with
students centered learning.
33
According to Ministry of Education and Culture, Scientific Approach in
curriculum 2013 underlies to determination and selection of learning steps,
attitudes, knowledge and skills, which includes five learning activities: to
observe, to ask, to gather information, to associate and communicate34. This
approach is integrated in formulating the elements of the learning framework,
from defining learning objectives up to carrying out the evaluation of learning
outcomes.
Learning procedures in a Scientific Approach can be elaborated as
follow35;
- To observe
Learning procedures carried out at this stage is the activities that maximize
the senses in a way to see, hear, and read, or watch. The things should be
observed by the students is material in the form of social function, the
structure of text, which is heard or read from any sources. For that, when
conducting these stage, the teacher should prepare the observation guide in
the form of task format.
- To ask
At the stage of this activity is the process of constructing knowledge about
the function of the social, linguistics element and the structure of the text
34
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. 2013. Kerangka Dasar Kurikulum, Struktur, Implementasi dan Evaluasi Kurikulum. Jakarta. Kemendikbud.
35
through a group of class discussion. This process is meant to develop
curiosity and critical thinking of students, which is required to obtain a
good observation. At the same time, the students may also learn to ask
reasonable and meaningful questions in English.
- To collect information
This stage is undertaken through trying or exploring activities which is
aimed to internalize the current knowledge and skills that has been learned.
In this process, the learners practice to state what they have learned and try
to declare in the real context, outside/inside the class. This process is an
individual learning activity conducted through collaborative learning within a group under teacher’s guidance.
- To associate
This activity is the process of developing the ability to categorize and
compare a variety of ideas and events to set it into a fragment of memory.
For English subject, at this stage the learners are guided to classify and
compare the text based on social function, the text structure and also
linguistics elements.
- To communicate
These activities are aimed to develop the ability to present knowledge and
skills that have been mastered either orally or in writing. At this stage, it is
not only knowledge or skill that should be communicated / presented, but
Communication activities may include verbal interaction during the
learning process, an oral presentation in front of the class orgroup.
B.Review of Previous Study
Here, the researcher reviews some researches which were related to this
research, as follows:
There were some similar researches which had relationship with this research:
The first study was in a form of journal and done by Kyunghee Choi, Hyang
Women College in year 2005. The title was “Need Analysis of Students of Tourism
English”36. In this research, the subject was the student of tourism. Kyunghee’s
research was aimed to find out the material of English that college student of
tourism want to learn in the conversation classes, and find out the way to help
them to achieve better result, licenses and got the job.
Other similar study was done in 2012, entitled “ESP Teaching Challenge in
an Indonesia Vocational Higher Education” conducted by Ardi Marwan37. Here,
the researcher found some problems showed by the English teacher in teaching
ESP. The problems were: students had low motivation, the resource was hard to
find, and preparing material was time consuming. Therefore, although teaching
English considers important to be taught in Vocational school, it practically has
some complex problems.
36
Choi, Kyunghee. Need Analysis of Students of Tourism English. Hyang women college. 2005
37
The newest research was done by NiPutu Anggareni in 2014 with the
research entitled “Syllabus and Student Needs: An Analysis of English Syllabus at
Mathematic Education Department State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel
Surabaya”38. In this study, the researcher attempted to find out the syllabus
designed by Mathematics Department whether it has met with students’ need or
not. However, her study was English for Academic Purposes (EAP) oriented
which concerned researching and teaching the English needed by those who use
the language to perform academic tasks.
Seeing from the studies that have been conducted before, the researcher
concludes that all the previous studies have the similarity and different areas of
study. Those previous studies could be the foundation of conducting this research.
The previous studies mostly focus on the ESP materials, syllabus design and the
challenges in teaching ESP, while in this research, the researcher focuses on the
lesson planning which is design by English teacher in Vocational high school.
In addition, related to the object of the research, some of the objects of the
previous research above are the syllabus design that the format is all aspects of
syllabus and the concern is in English for general purposes, while in this research,
the researcher focus on the designing lesson plan on certain aspects such as
objectives and learning procedures which analyze its accordance with the students’
needs.
38
Anggaraeni, N. “Syllabus and Students’ Need: An Analysis of English Syllabus at Mathematic
35
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODS
This chapter deals with the procedures of conducting the research, it
covers research approach and design, setting of the study, data and source of data,
data collection technique, research instruments, data analysis technique.
A.Research Approach and Design
Uwe Flick states that Research design is a plan for collecting and
analyzing evidence that makes it possible for the researcher to answer the
questions he or she has posed1. Thus, this research was typically designed as
descriptive with qualitative approach because it concerned with social
phenomena dealing with teacher’s lesson plan and students’ needs in learning
English in Hospitality at state Vocational High School 1 Buduran Sidoarjo. It
was in line with Beverley Han cock’s theory that qualitative research was
concerned with developing explanations of social phenomena2.
In addition, descriptive approach is the information describes the
phenomena happens at the present3. In this study, it described the result of students’ needs and analyzed the teachers’ point of view toward the analysis
result as their reference in designing lesson plans. It would deal with the teacher’s formulation of objectives based on regulation of standardization in
1
UweFlick, An introduction to qualitative research fourth edition (Singapore: SAGE Publications, 2009), 143
2
Beverley Han cock, Elizabeth Ockleford, Kate Windridge, An Introduction To Qualitative Research, national institute for health research, 7
3
Education and Culture Ministry which was used to plan and decide learning
procedures.
B.Setting of The Study
The subject of this study was the first grade of Hospitality program. This
study was held at State Vocational High School Buduran Sidoarjo. The
researcher conducted the research for Hospitality students in tenth grade. There
are 2 classes in Hospitality major. The location was decided because of some
considerations bellow:
1) Tenth grade was chosen because the students in this level were prepared
to master skills that they will use to have a job training outside the
schools in eleventh grade.
2) Hospitality major provides opportunities for students to interact with
many people in term of tourism and also hospitality itself. Thus, this
major has special communication strategies in ways to teach the students
how to serve the customers. State Vocational High School Surabaya is
the only school which has its own hotel, named Edotel, located in the
center of Sidoarjo regency. This school has already got chances to
interlace with some hotels in Indonesia and overseas.
C.Data and Source of Data
The data in this study are about students’ need and lesson plan. Those data
were collected from source data as follow; the first source was tenth grade of Hospitality students to get data of students’ needs, the second was the English
in designing lesson plans based on students’ need, and the last was documents
of teacher’s lesson plans that have formulated before.
D.Research Stages
Based on Suharsimi’s point of view, there are five steps that the
researcher do in conducting a research. They are preliminary study, research
preparation, research action, analyzing data and writing result of the study4.
Thus, the researcher implements those steps in this study. They are described
as follows:
1) Preliminary Study
This step is regarded as the researcher’s preparation of the study.
The preparation was done by asking some questions dealing with the
lesson plan designed by English teacher at Hospitality program. In this
study, the researcher has conducted this step on October 24, 2015.
Proposing a good title, formulating research questions were included in
this step. It was conducted to make research proposal to know the
possibility of the research.
2) Research Preparation
After conducting the preliminary study about lesson plans at
Hospitality program, the researcher did research Preparation. In this step,
the researcher managed the research design, and prepared the instrument
related to collect the data about students’ needs and also teacher’s point of
view in designing English lesson plan.
4
3) Research Action
The researcher conducted the research action after the researcher has
prepared for the study. This research action was completed during May 2nd
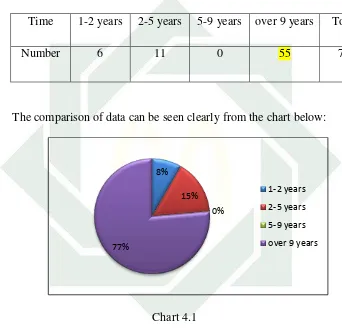
2016 to August 8th 2016. This step had three main purposes. The first, the
researcher distributed the questionnaire to 72 students of Hospitality
program at tenth grade (APH 1 and APH 2) and interviewed some students
who have answered of questionnaire and also some students from eleventh
grade as the complement informant. The second part was interviewing the teacher related the lesson plans and the students’ need at Hospitality
program. And the last was documentation study to describe how the
teacher designed lesson plans.
4) Analyzing Data
The researcher used the data from the instruments which have been
obtained from the research. Then, the researcher analyzed the instruments
to clarify and answer the research questions because the researcher had to
present some conclusions based on related literatures and experts. The
researcher has examined the analysis which was started from May 20th,
2016 to June 16th, 2016.
5) Writing the Result of The Study
This step gave opportunity to the researcher to arrange the design of
analyzing the data which have been obtained from the study, the researcher
also wrote the result of the study.
E.Data Collection Technique
In case of collecting the data of the research, the researcher needed the
instrument. In this study, the researcher obtained the data by distributing the
questionnaire, conducting interview and doing checklist. In short, the process
of collecting the data was specified in the table below:
Table 3.1 Techniques for Collecting Data Based on Research Questions Techniques
1) To answer the first research question about what the hospitality students’
needs in learning English at state vocational high school 1 Buduran, the
researcher obtained the data by distributing the questionnaire to the
hospitality students to analyze the target needs. Then, the result of the
questionnaire would be used as a tool to examine the lesson plans designed
by English teacher.
2) To answer the second question if the students’ need in learning English was accordance with the teachers’ lesson plan design in part of
formulating learning objectives and learning outcomes, the researcher
vocational high school 1 Buduran. This technique was used by researcher to find out the teacher’s points of view regarding his students’ need and
his lesson plans design.
F. Data Collection Instrument
To answer the research questions, some instruments were used as follow:
1) Questionnaire
The questionnaire is useful in gathering data for a large number of
participants5. In this study, it was used to get data to answer the research
question. Giving the questionnaire to the students was intended to get
information about their needs to learn English. Furthermore, student’s
needs is an abstract thing, it cannot be seen by observation. Therefore, students’ need analysis was used to examine the needs in Hospitality
students. The instrument of the questionnaire was formulated as follows
(see Appendix 1).
2) Observation sheet
The observation sheet in this study was used to get the data related to
the formulation of objectives and learning procedures in the lesson plans
designed by English teacher in Hospitality major. In this section, the
instrument was designed by considering some theories regarding to students’ needs analysis and the lesson plans. This instrument is used to
assist information about how the lesson plans designed regarding the needs
of Hospitality students (see Appendix 2).
5Mother and child health. “Qualitative field research” www.o
3) Interview guideline
This interview guideline was used by researcher to find out the teacher’s point of view about his students’ need and his lesson plan (see
Appendix 3). By having the interview, the researcher could collectthe data
and examine them with the lesson plans.
G.Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis technique is a process of resolving data into its constituent
components, to reveal its characteristic elements and structure. Based on
Robert K. Yin, data in qualitative research is analyzed in five- Phased
technique: (1) Compiling, (2) Disassembling, (3) Reassembling (and
Arraying), (4) Interpreting, and (5) Concluding. However, the data in this study
were analyzed in four phases because disassembling and reassembling phase
could be combined (assembling). The steps and figures will be depicted as
1. Compiling (Assessing students’ needs)
The first stage of this study was called Compiling. This stage was
used to conduct the need analysis of the students. In this stage,
questionnaire was distributed to the hospitality students to obtain data
about their needs. Besides, interview to some students was also done in
this step. The researcher interviewed some students from tenth grade
related the answers of questionnaire and three students from eleventh
grade as the complement informant.
2. Assembling (Interview the teacher)
After distributing the questionnaire, the second step that the
researcher did with the instrument was interview to the English teacher at
Hospitality program. In this step, the researcher asked the teacher’s point of view in designing lesson plan and also their students’ needs.
3. Interpreting (Examining the result of questionnaire and document study)
In this stage, the researcher analyzing the result of need analysis that
was conducted before and continued by analyzing the documents studies
which means here the lesson plan designed by English teacher using the
observation sheet.
4. Concluding (Elaborating the findings and stating conclusions)
In the last section of analysis data, the researcher could decide to
draw the findings about the data obtained, representing it in tables or
charts to summarize and explain the conclusions in words to provide
answers of the research questions6. The result of collected data then would
be analyzed by using descriptive qualitative, means that data was
described as the way it was whether the lesson plan which means here
learning outcomes and learning procedure are accordance with the students’ needs or not.
6
44 CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter deals with the research findings and discussion of the study.
The researcher describes and analyzes the data which are obtained during the
research process. It includes the results of interview, questionnaire, and
observation sheet for document studies analysis. The researcher distributed the
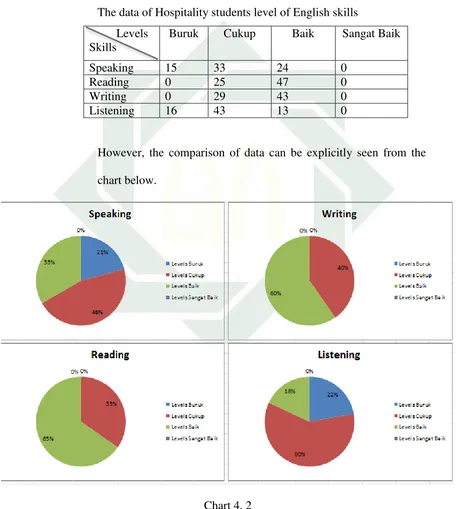
questionnaire to students of Hospitality program at State Vocational High School
1 Buduran Sidoarjo (Appendix 1). There are 72 students of Hospitality program
which is divided into two classes, APH 1 and APH 2. The researcher also did an
interview to some students from tenth grade and three students from eleventh
grade as complement informant to get data regarding the answers of questionnaire
which need more reasons.
After distributing the questionnaire, the next step was doing interview with
the English teacher of Hospitality program using interview guideline (Appendix
3). This step is aimed to get the data regarding the needs’ of Hospitality students
based on the teacher’s perception and also the data of lesson plans which is
designed by the English teacher. Afterward, the researcher collected the last data
that is Document Studies. The document studies in this research are Lesson plans
designed by English teacher of Hospitality program. Then this data was analyzed
by using observation sheet (Appendix 2). In addition, this chapter also contains the
discussion about the answer of the research problems. The research problems are:
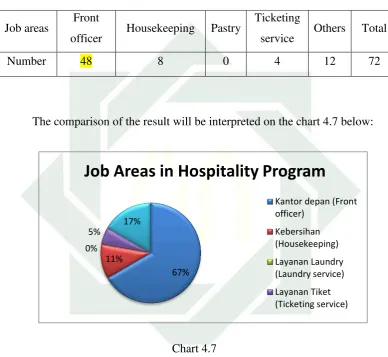
1. What are the hospitality student’s needs in learning English at State