iv
Dedication Page
This thesis is proudly dedicated to:
My beloved parents Bernadheta Sri Rejeki and Kristian Budi Santoso, S.E
My dearest husband Gede Manuel Kris Sudianto
My beloved brother Thomas Tirta Suminar
All of my friends: Ria, Manda,Dewati, Tiwi, and all of the 2006 students of
English Education & Study Program
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 7 June 2011 The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Ruth Widyasari
Nomor Mahasiswa : 061214020
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
THE DESIGN OF AN ACHIEVEMENT MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEM NARRATIVE READING TEST FOR THE TENTH GRADE PANGUDI LUHUR SANTO YOSEF SURAKARTA SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL
Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 7 Juni 2011 Yang menyatakan
vii ABSTRACT
Widyasari, Ruth. 2011. The Design of an Achievement Multiple-Choice Item Narrative Reading Test for the Tenth Grade Pangudi Luhur Santo Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This research focused on designing a multiple-choice item reading test for the tenth grade Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School 2009/2010 academic year. Designing a good multiple-choice reading test was very challenging since the multiple-choice tests are extremely difficult to design correctly. In this research, the writer designed a multiple-choice reading test as an achievement test. The writer limited the scope of reading as a skill to be tested into a genre so–called narrative. Narrative has been taught in the tenth grade of senior high school. Furthermore, the writer also investigated the validity of the test by analyzing the test items and giving questionnaire to the English teacher who taught the tenth grade Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. The aims of this research were: (1) to describe how the multiple-choice item reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School is designed; (2) to present the multiple-choice item reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School.
In addition this research was done by applying five steps of Borg’s and Gall’s R & D (Research & Development) cycle: research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, main product revision and combined those steps with Bachman’s and Palmer’s test development which consisted of three stages: design, operationalization and administration. By combining the five steps of R & D cycle and the three stages of test development, the writer were able to describe how to design the multiple-choice item reading test and present the multiple-choice item reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School.
The test consisted of five (5) narrative reading texts taken from the internet and twenty (20) questions with five (5) items. The writer distributed the test to the tenth grade students and collected the answer sheets. From the answer sheets then the writer investigated the construct validity of the test by counting the Item Facility (IF) and Item Discrimination (ID). The writer also collected the result of the questionnaire from the English teacher who taught the tenth grade students to investigate content validity and face validity. After analyzing the validity of the test, the writer revised the test. There were 3 (three) numbers that the items should be revised because of very low point of item facility and item discrimination which meant the construct validity was not good.
viii
ix ABSTRAK
Widyasari, Ruth. 2011. The Design of an Achievement Multiple-Choice Item Narrative Reading Test for the Tenth Grade Pangudi Luhur Santo Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Penelitian ini difokuskan pada perancangan tes membaca dalam bentuk pilihan ganda untuk kelas X (sepuluh) Sekolah Menengah Atas Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta tahun ajaran 2009/2010. Penulis memilih tes pilihan ganda dalam penelitian ini karena jarang digunakan untuk tes kemampuan akademik. Sebagai tes kemampuan akademik, penulis perlu mempertimbangkan kurikulum dan silabus sebagai pedoman untuk pembuatan tes. Penulis membatasi ruang lingkup membaca sebagai keterampilan yang akan diuji pada bentuk teks narasi. Teks narasi telah diajarkan di kelas X SMA. Selanjutnya, penulis juga meneliti validitas tes tersebut dengan menganalisa pilihan ganda dari tes dan memberikan kuesioner kepada guru Bahasa Inggris yang mengajar kelas X SMA Pangudi Luhur St Yosef Surakarta. Tujuan penelitian ini adalah: (1) untuk menjelaskan bagaimana tes membaca dalam bentuk pilihan ganda untuk siswa kelas X Pangudi Luhur St Yosef didesain; (2) untuk menyajikan tes membaca dalam bentuk pilihan ganda untuk siswa kelas X SMA Pangudi Luhur St Yosef Surakarta.
Lebih Jauh lagi, penelitian ini dilakukan dengan menerapkan lima langkah siklus R & D Borg dan Gall: pengumpulan informasi dan materi penelitan, perencanaan, pengembangan bentuk awal dari produk, pengujian tes awal, revisi produk utama dan dikombinasikan dengan pengembangan tes oleh Bachman dan Palmer yang terdiri dari tiga tahap: desain, operasionalisasi dan administrasi. Dengan menggabungkan lima langkah siklus R & D dan tiga tahap pengembangan tes, penulis mampu menjelaskan bagaimana merancang tes membaca dalam bentuk pilihan ganda dan menyajikan tes membaca dalam bentuk pilihan ganda untuk siswa kelas X SMA Pangudi Luhur St Yosef Surakarta.
x
memberikan tes tersebut kepada siswa kelas X dan mengumpulkan lembar jawaban dari tes tersebut. Dari lembar jawaban tersebut penulis mencari validitas konstruk melalui penghitungan item fasilitas dan item diskriminasi. Penulis juga mengumpulkan hasil kuesioner dari guru bahasa Inggris yang mengajar siswa kelas X untuk menyelidiki validitas isi dan validitas bentuk. Setelah menganalisa validitas tes, penulis merevisi test tersebut. Ada tiga nomor yang harus direvisi karena rendahnya poin item fasilitas dan item diskriminasi yang berarti validitas konstuknya tidak bagus.
xi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
In completing this thesis, I did not work alone. Some people helped me in finishing this thesis. Those people gave me supports and guidance when I wrote the thesis and did the research. In this occasion, I would like to express my gratitude to some special people.
First of all, my sponsor, Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. who always patiently gave the writer guidance in writing this thesis and doing the research and support in doing this thesis from the beginning until the writer could finish it. I still remember how I started writing this thesis enthusiastically and in the ninth semester, I did nothing. Finally, I did it. I am grateful for the assistance during finishing my thesis.
My special gratitude goes to the principal of St. Yosef Pangudi Luhur Surakarta Senior High School, Br. Agustinus Mujiya, S.Pd. and all of the teachers in Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School who gave me opportunity to do my research. My special thankfulness goes to Maria Olise C. H., S. Pd. as the English teacher of the tenth grade Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School 2009/2010 academic year who always supported me in doing the research and finishing this thesis and also became a partner to discuss everything.
My thanks are also for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School 2009/2010 academic year. All of the students were doing a great job to help the writer finishing the research.
xii
Manuel. Those people I love so much never stopped asking me to finish this thesis as soon as possible. I really appreciate their love, support, and prayers.
My best gratitude is for all of my friends and all of my lecturers. The contribution of those people to my study is very precious for me. I learn many things from them.
Finally,” May He give you the desire of your heart and make all your plans succeed” (Psalm 20:4). God have given me success in completing this thesis. I hope that God also give all of people who helped me success in their life.
xiii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE………i
APPROVAL PAGES………..………ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……...………v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI………....vi
ABSTRACT………...………vii
ABSTRAK………ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS………....xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS………..xiii
LIST OF TABLES………....xvi
LIST OF FIGURES……….…xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES………...xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Research Background... 1
B. Problem Formulations ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Research Objectives ... 5
E. Research Benefits ... 5
F. Definition of Terms ... 6
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ... 8
xiv
2. Test ... 10
3. Design and Test Development ... 15
B. Theoretical Framework ... 19
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ... 22
B. Research Participants ... 28
C. Research Instruments ... 29
D. Data Gathering Technique ... 30
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 30
F. Research Procedure ... 31
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. How the Achievement Multiple-Choice Item Narrative Reading Test is Designed………..….35
1. Research and Information Collecting ………35
2. Planning………..39
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product………….. ……41
4. Preliminary Field Testing………...……42
5. Main Product Revising………...50
B. What the Achievement Multiple-Choice Item narrative Reading Test Looks Like ……..………..52
xiv
A. Conclusions ... 64
B. Suggestions ... 66
REFERENCES….………..68
APPENDICES………70
xiv
Page Table 4.1 Design Statement of the Test……….37 Table 4.2 Blueprint of the Test………..39 Table 4.3 The Results of Item Facility (IF) and Item Discrimination (ID)...42
Table 4.4 The Test Revision………..51
xiv
Page Figure 1.1 Test, Achievement, and Teaching………1 Figure 2.1 The Formula of Final Score………...15
Figure 2.2 Test Development………..18
Figure 3.1 The Combination of R & D and Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development……….23
xiv
Page
Appendix 1 The Interview……….…71
Appendix 2 The Lesson Plan……….73
Appendix 3 The Syllabus ……….…….82
Appendix 4 The Texts………..…..92
Appendix 5 The Answer Sheet………..99
Appendix 6 The Questionnaire………100
Appendix 8 The Result of Counting IF and ID………101
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
In Chapter I, the writer elaborates the research background, problem formulations, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
English is one of the most important subjects in senior high school in Indonesia since English is one of the subjects, which is tested in National Examination. English plays important role in National Examination because it determines the students’ graduation. Because of this reason, the process of teaching and learning English is also essential. In senior high school, English is taught from the tenth grade up to the twelfth grade. In the process of teaching English, there are also assessing and testing process to monitor the students’ mastery in English. The relationship among teaching, assessment, and test can be seen in figure 1.1 below:
Figure 1.1: Test, achievement, and teaching (Brown, 2004: 5) Teaching
Figure 1.1 shows that teaching process cannot be separated from assessment and tests. Tests are a part of assessment and teaching, while assessment is also a part of teaching.
In this research, the writer is challenged to design a test since tests are very important in teaching and learning process. Tests are very useful to record the students’ achievement and as tools for teacher to develop teaching and learning process. Brown (2004: 4) also states that
Tests are prepared administrative procedures that occur at identifiable times in a curriculum when learners muster all their faculties to offer peak performance, knowing that their responses are being measured and evaluated.
In this research, the writer focuses on designing a multiple-choice item reading test. Reading as one of language skills in learning English is chosen to design the test because reading is essential skill for success in all education contexts Brown (2004:185). Besides, in National Examination, most of the questions test the reading skill.
multiple-choice test for achievement test, because the writer wants to monitor the students’ understanding after they had been taught a certain topic.
As stated above that the writer focuses on designing a multiple-choice reading test, therefore the writer also considers the reading performance of the students. There are four types of reading performances. They are perceptive, selective, interactive, extensive (Brown, 2004: 189). In this thesis, the writer focuses on measuring students’ performance in interactive reading.
…interactive reading types are stretches of language of several paragraphs to one page or more in which the reader must, in psycholinguistics sense, interact with the text. Typical genres that lend themselves to interactive reading are anecdotes, shorts narratives and descriptions. The focus on an interactive task is to identify relevant features (lexical, symbolic, grammatical, and discourse) within texts of moderately short length with the objective of retaining the information that is processed (Brown, 2004: 189).
In addition, several reading genres are taught in schools among others descriptive, narrative, recount, and report. To limit the scope of the test the writer chose narrative. Narrative is chosen because narrative is a classroom lesson, which is taught in the second semester of the tenth grade of senior high school as stated in the syllabus. Furthermore, one interesting feature of narratives texts in particular is that they appear to induce visualization in the reader as part of reading process-readers report ‘seeing’ scenes in their head when they read such texts (Alderson, 2000: 64).
multiple-choice item test and investigate the validity of the test. The writer will only investigate the validity of the test because it is the quality that provides the major justification for using test scores or number as a basis for making inferences or decisions. In addition, evaluating the overall usefulness of a given test is essentially subjective, since this involves value judgments on the part of the test developer (Bachman and Palmer, 1996:19).
This study is very challenging since it will relate to the curriculum and syllabus, the participation of students in Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School, the English teacher of the tenth grade students in Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School and the test itself.
B. Problem Formulations
In this research, the writer proposed the following questions:
1. How is the achievement multiple-choice item narrative reading test designed?
2. What does the achievement multiple-choice item narrative reading test look like?
C. Problem Limitation
D. Research Objectives
There are two objectives of designing multiple-choice reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School:
1. To describe how the achievement multiple-choice item narrative reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School is designed;
2. To present the achievement multiple-choice item narrative reading test for the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School.
E. Research Benefits
There are three benefits of this research, as follows:
1. This study contributes to the English teacher of the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School. The teacher will have an alternative to test the students’ reading ability in narrative by using multiple-choice reading test since multiple-choice tests are infrequently used as achievement tests for classroom lesson.
2. This study benefits the writer to answer the research problems and also as a teacher candidate, the writer needs to know how to make the multiple-choice item reading test and measure the quality of the multiple-multiple-choice item reading test.
F. Definition of Terms
In this study, there are four terms which are often used by the writer. To clarify the meaning of the terms, the writer provides a list below:
1. Design in general is creating a new set of materials that fix the learning objectives and specific subject area of particular learners (Hutchinson and Waters, 1994:106). While design in test development is the process of describing the purpose (s) of the test, identifying and describing tasks in the TLU (Target Language Use: a context in which the test takers will be using the language outside the test itself) domain, describing the characteristics of the language users/test takers, defining the construct to be measured, developing a plan for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, identifying resources and developing a plan for their allocation and management (Bachman and Palmer, 1996: 86-89).
2. Reading is transaction between the reader and the text in which the reader’s interpretation reflects both the meaning intended by the author and the meaning constructed by the reader (Armbruster & Osborn, 2002: 7). Reading for general comprehension is the ability to understand information in a text and interpret it appropriately (Grabe & Stoller, 2002: 9).
inference (implied detail), grammatical features, detail, excluding facts not written, supporting idea(s), and vocabulary in context.
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the writer presents theoretical description from the experts, which are useful to conduct the research and theoretical framework of the study. The theoretical description contains the theoretical description of reading, test, and design and test development. While in theoretical framework, the writer summarizes and synthesizes the theories, which are useful to conduct the research and solve the research problems.
A. Theoretical Description
The writer uses some theories as a basis in conducting this research. They are the theoretical description of reading, test, and design and test development. The theoretical description of reading is divided into definition of reading, types of reading and reading tasks. The theoretical description for the test is divided into the definition of the test, the purpose of the test, the format of the test, test validity, marking and scoring.
1. Reading
a. Definition of Reading
general comprehension is the ability to understand information in a text and interpret it appropriately (Grabe & Stoller, 2002: 9).
b. Types of Reading Performance
For considering assessment procedures, several types of reading performance are typically identified, and these will serve as organizers of various assessment tasks as follows: perceptive, selective, interactive, extensive (Brown, 2004: 189).
In designing the test, the writer focuses on interactive reading. According to Brown (2004: 189) “Included among interactive reading types are stretches of language of several paragraphs to one page or more in which the reader must, in psycholinguistics sense, interact with the text. That is, reading is a process of negotiating meaning; the reader brings to the text a set of schemata for understanding it, and intake is the product of that interaction. Typical genres that lend themselves to interactive reading are anecdotes, shorts narratives and descriptions. The focus on an interactive task is to identify relevant features (lexical, symbolic, grammatical, and discourse) within texts of moderately short length with the objective of retaining the information that is processed”. The writer designs a multiple-choice item reading test, which focuses on a certain genres that is narrative because it is in accord with the curriculum for grade X. c. Reading Tasks
various tasks, in particular: cloze tasks, impromptu reading plus comprehension questions, short-answer tasks, editing (longer texts), scanning, ordering tasks, information transfer: reading charts, maps, graphs, diagram (Brown, 2004:201-210). In designing a multiple-choice item reading test, which focuses on narrative, the writer designed two kinds of tasks: cloze tasks and impromptu reading plus comprehension questions.
According to Brown (2004: 201-206), cloze task is one of the most popular types of reading assessments task. In the written language, a sentence with a word left out should have enough contexts that a reader can close that gap with a calculated guess. While impromptu reading plus comprehension questions technique is undoubtedly the oldest and the most common. This technique covers the comprehension of these features: main idea (topic), expressions/idioms/phrases in context, inference (implied detail), grammatical features, detail, excluding facts not written, supporting idea(s), and vocabulary in context.
2. Test
a. Definition of Test
b. The Purpose of The Test
According to Brown (2004:43), the first task teacher will face in designing a test for the students is to determine the purpose of the test. Defining the purpose of the test will help teacher choose the right kind of test, and it also will help the teacher to focus on the specific objectives of the test. Based on the objectives, tests are divided into five types, in particular language aptitude tests, language proficiency tests, placement tests, diagnostic tests, and achievement tests.
In this study, the writer focuses on achievement test. Brown (2004:47) stated that an achievement test is related directly to classroom lesson, units, or even a total curriculum. Achievement tests are (or should be) limited to particular material addressed in a curriculum within a particular time frame and are offered after a course has focused on the objectives in question.
c. The Format of The Test
The writer develops an achievement test by designing a task so-called multiple-choice test, which is also known as selection items. Brown (2005: 43) states a multiple-choice format is basically receptive mode (students read and select, but produce nothing). According to Brown (2004: 55), multiple choice items, which may appear to be the simplest kind of item to construct, are extremely difficult to design correctly. Here are the characteristics of multiple choice items according to Brown (2004: 56):
2. Every multiple choice item has a stem, which presents a stimulus, and several (usually between three and five) options or alternatives to choose from.
3. One of those options, the key, is the correct response, while the others serve as distractors.
d. Test Validity
The writer also investigates the validity of the test. Validity is the extent to which inferences made from assessment result are appropriate, meaningful, and useful in terms of the purpose of the assessment (Brown, 2004: 22). There are three criteria of validity, which are investigated by the writer, as follow: face validity, content validity, and construct validity.
1. Face validity refers to the test’s surface credibility or public acceptability (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995: 172). Essentially face validity involves an intuitive judgment about test’s content by people whose judgment is not necessarily ‘expert’. (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995: 172)
2. Content validity is the representativeness or sampling adequacy of the content-the substance, content-the matter, content-the topics- of a measuring instrument. Content validation involves gathering the judgment of ‘expert’. (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995: 173)
interpretation and providing evidence justifying that interpretation ( Bachman and Palmer, 1997:21-22).
In addition, in this study, the writer measure construct validity through measuring item facility (or item difficulty), item discrimination (differentiation), and distractor analysis by using Microsoft Excel. Excel is an electronic spreadsheet program that can be used for storing and organizing data (French, 2011:1).
1. Item facility (IF) is a statistic used to examine the percentage of students who correctly answer a given item (Brown, 2005:66). IF refers to the proportion of students who answered the question correctly, we calculated the IF using COUNTIF function for the letter corresponding to the correct answer (Elvin, 2003). The COUNTIF function is used to count up the number of cells in a selected range that meet certain criteria (French, 2011:1). Appropriate test items will generally have IFs that range between 0,15 and 0,85 (Brown, 2004: 59)
discriminating power would approach a perfect 1,0 (one) and no discriminating power at all would be 0 (zero).
3. According to Brown (2004:60), distractor efficiency is the extent to which (a) the distractor “lure” a sufficient number of test-takers, especially lower-ability ones, and (b) those responses are somewhat evenly distributed across all distractors. In addition, Elvin (2003) stated that the quality of a test item may be poor. To try to identify these potential sources of measurement error, I calculate the ratio of students answering each question to students taking the test. It can be calculated by using SUM function.
e. Marking and Scoring
In designing the test, the writer also determines how to give mark and score. There are basically two types of marking: subjective marking which is usually used for marking test of writing and speaking, and objective marking which is used for multiple-choice, true/false, error recognition and other item types where the candidate is required to produce a response which can be marked as either ‘correct’ or ‘incorrect’ (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995:106). Thus, in this research, the writer uses objective marking.
Figure 2.1: the Formula of Final Score
3. Design and Test Development
Design is in general a linear process, but in some cases some activities are iterative, that is, will need to be repeated a number of times (Bachman and Palmer, 1996: 86).
In addition, design is arranging materials into a fixed and good material. The designing is the same as creating a new set of materials that fix the learning objectives and specific subject area of particular learners (Hutchinson & Waters, 1994:106). To design the multiple-choice reading test, the writer will apply some steps of test development.
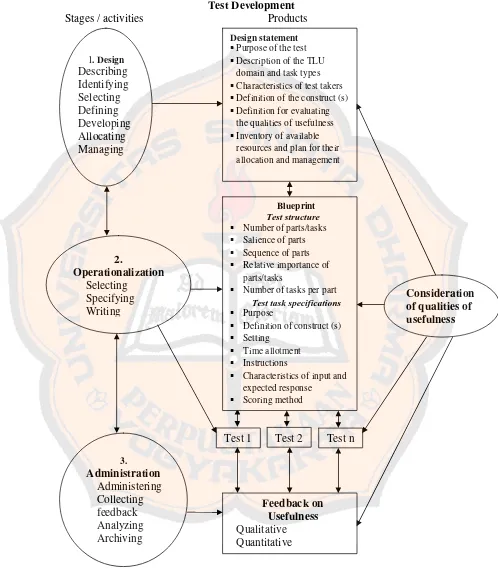
Test Development is the entire process of creating and using test, beginning with its initial conceptualization and design, culminating in one or more archived tests and the results of their use (Bachman & Palmer, 1996: 85). According to Bachman and Palmer (1996: 86-91), there are three stages of test development:
1. Stage One: Design
The product of the design stage is a design statement, which is a document that includes the following components:
a) a description of the purpose (s) of the test,
#
2
b) a description of the Target Language Use (TLU) domain and task types: Target Language Use is context in which the test takers will be using the language outside of the test itself. There are two types of TLU, real-life domain, in which language is used essentially for purposes of communication. The other type of domain consists of situations in which language is used for the purpose of teaching and learning of language, which is called as language instruction domain. While task types is in the form of multiple choice test.
c) a description of the test takers for whom the test intended, d) a definition of the construct (s) to be measured,
e) a plan for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, and
f) an inventory of required and available resources and a plan for their allocation and management.
2. Stage two: Operationalization
In addition, Brown (2004: 55) explains some practical steps to design multiple-choice test items: design each item to measure a specific objective, state both stem and options as simply and directly as possible, make certain that the intended answer is clearly and the only correct one, use item indices to accept, discard, or revise items.
3. Stage three: Test administration
The test administration stage of the test development involves giving the test to a group of individuals, collecting information, and analyzing this information for two purposes:
a) assessing the usefulness of the test, and
b) making the inferences or decisions for which the test intended.
Test Development
Stages / activities Products
Figure 2.2: Test Development (Bachman and Palmer, 1996: 86) 1. Design of qualities of usefulness Description of the TLU
domain and task types Characteristics of test takers Definition of the construct (s) Definition for evaluating
the qualities of usefulness Inventory of available
resources and plan for their allocation and management
Blueprint Test structure Number of parts/tasks Salience of parts Sequence of parts Relative importance of
parts/tasks
Number of tasks per part Test task specifications Purpose
Definition of construct (s) Setting
Time allotment Instructions
Characteristics of input and expected response
Scoring method
B. Theoretical Framework
In this section, the writer summarized and synthesized the theory above with the study. There were three theoretical descriptions in this chapter covered reading, test, and design and test development. The theoretical descriptions above were needed to give the writer a basis to do the research.
By doing the research, the writer wanted to measure students’ ability in reading. To measure the students’ ability in reading, the writer designed a test. The format of the test is multiple-choice test. Although it seemed the easiest way to make the test, the writer needed to consider some elements to design the tests. Moreover, in this study the writer did not merely design the test but also consider the usefulness or quality of the test. Considering the quality of the test, the writer needed to try-out the test and investigate the ID, IF, and distractor efficiency.
In this study, the writer focused on a reading genre so-called narrative. To design the multiple-choice reading test, the writer focused on interactive reading types. After selecting the types of reading performance, the writer decided the tasks. There were two kinds of reading tasks of the test, which the writer had designed. There were cloze tasks and impromptu reading plus comprehension questions. Both tasks were chosen because they could explore the students’ ability in understanding texts.
1. Design
In this stage the writer described, identified, selected, defined, developed, allocated, and managed the test. This stage was a preparation before writing the test. In this step, the writer produced a design statement. A design statement was needed to limit the scope of the test and to give a guideline to produce the test. A design statement contained the purpose of the test, description of the TLU (Target Language Use) domain and task types, characteristics of the test takers, definition of the construct (s), definition for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, inventory of available resources and plan for their allocation and management. To do this stage, the writer would interview the English teacher and do the library study to get the syllabus and resources.
2. Operationalization
each item to measure a specific objective, state both stem and options as simply and directly as possible, make certain that the intended answer is clearly and the only correct one, use item indices to accept, discard, or revise items. After finishing this stage, the test was ready to be tested.
3. Administration
The last stage of test development was administration, which covered administering, collecting feedback, analyzing, archiving. This stage, as stated above, involved giving the test to the test takers, collecting information, and analyzing the information. The writer would give the test to the tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Senior High School. After giving the test, the writer would collect information related to the test. The writer would get the information related to the tests from both the students and the English teacher. From the students, the writer would get the information in a form of answer sheets and from the English teacher, the writer would get the answer of the questionnaire. Then the writer would analyze the information.
22 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
In this research, the writer elaborates the methodology used for designing a set of multiple-choice item reading test for the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year. The methodology covers research method, research participants, research instruments, data gathering techniques, data analysis technique and research procedure.
A. Research Method
The method used in this research was Research and Development (R & D) because the writer designed multiple-choice reading test. Educational R & D is a process used to develop and validate educational products (Borg & Gall, 1983: 772). According to Borg, there are ten major steps in R & D: research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, main product revision, main field testing, operational product revision, operational field testing, final product revision, dissemination and implementation.
Moreover, in doing this research the writer combined R & D with Bachman’s and Palmer’s test development. The Combination of R & D and Bachman’s & Palmer’s test development can be seen in the figure below.
Stage 1:
Stage 2:
Stage 3:
Stage 4:
Stage 5:
Figure 3.1: the Combination of R & D and Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development
a. Research & Information
Collecting
b. Design: produce design
statement
Preliminary Field Testing
Operationalization: developing and writing actual test tasks, writing instructions, specifying the
procedures for scoring Developing
Preliminary Form of Product
b. Make the blueprint a. Planning =
Operationalization: selecting and specifying the materials
Administration
Main Product Revising
Figure 3.1 shows that in this research, the writer applied five steps of R & D so-called research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing and main product revising. Then the writer combined R & D and the test development, which consisted of three stages, in particular: design, operationalization, and test administration. The first stage that is design, was done after the first step of R& D that is research and information collecting. In this stage, the writer made a guideline so-called design statement before producing a multiple-choice reading test. The writer would limit the scope of the test by making design statement of the test. In the second stage of Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development, operationalization was divided into two steps of R & D, step two and three of R & D cycle, planning and developing preliminary form of product. As stated in the previous chapter that operationalization consisted of three activities: selecting, specifying, and writing. The activities of selecting and specifying the test would be done in step two of R & D cycle, while writing the test would be done in step three, developing preliminary form of product. The last one was test administration was done in step four of R & D cycle, preliminary field testing. After gathering the answer sheets, the writer analyzed the result of the test and if needed, reported to the teacher. Then, the writer revised the test’s item if needed.
1. Research and Information Collecting
other information pertinent to the planned development (Borg & Gall, 1983: 777). To obtain the literature review, the writer conducted an interview and a library study. The writer interviewed the teacher who taught the students of grade X of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. By doing the interview, the writer obtained the data on the tests specification. The writer needed the test specification because “test writer needs guidance on practical matters that will assist test construction.” (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995:11). The writer had conducted library study to obtain some theories related to the study as well as the syllabus.
After finishing this step, the writer applied Bachman’s and Palmer’s test development stage one, design. By doing the stage one, design, the writer would produce design statement which covered purpose of the test, description of TLU (Target Language Use) domain and task types, characteristics of the test takers, definition of the construct (s), definition for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, inventory of available resources and plan for their allocation and management.
know some theories about reading, test, design and test development. Moreover, the writer needed to know the school’s curriculum and syllabus to enable the writer to define the design statement. In this step, the writer had produced the overall design statement, which would be used as a guideline to produce the test.
2. Planning
In the second step, planning, Borg and Gall (1983: 781) stated that a good plan can help the developer avoid much wasted work during later phases of good R & D cycle.
The writer did the planning by doing operationalization of Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development, which was included selecting and specifying the materials to construct the test. By doing selecting and specifying the materials the writer would be able to make a blueprint of the test. A blueprint contained a test structure and test task specifications. A test structure contained number of parts/tasks, salience of parts, sequence of parts, relative importance of parts/tasks, and number of tasks per part. Test task specifications contained purpose of the test, definition of construct (s), setting, time allotment, instructions, characteristics of input and expected response, and scoring method. This step would be done by conducting library study.
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
instructional materials handbooks, and evaluation devices.” (Borg & Gall, 1983: 775)
In this fourth step, the writer applied the last activity of operationalization which was writing the test. Bachman and Palmer states that operationalization involves developing and writing actual test tasks, writing instructions, and specifying the procedures for scoring the test. Therefore, in this step the writer made the test, answers, and scoring system.
4. Preliminary Field testing
the test’s items. Furthermore, the writer also analyzed the feedback from the questionnaire to investigate face validity and content validity.
5. Main Product Revising
The last one, main product revision, the writer revised the test based on investigation of validity of the test. From the result of the validity investigation, the writer was able to make the revision because the results of validity investigation would show the quality of the test and decide which one should be revised and which one should not be revised.
B. Research Participants
The participants of this research were:
1. Participant of Research and Information Collecting
The participant of research and information collecting was the teacher of the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year. In doing the first step, research and information collecting, the writer conducted an interview to the teacher as the participant. 2. Participants of Preliminary Field Testing
test. Then their answer sheets were collected and analyzed. Then, the writer also distributed questionnaires to the English teacher of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. The questionnaires were used to investigate face validity and content validity of the test.
C. Research Instruments
There were two instruments used in this research: interview and questionnaires
1. Instrument of Research and Information Collecting
Interview was used as the instrument to do research and information collecting. The interview was done to obtain the data of the test specification. The writer interviewed the English teacher who taught the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year.
2. Instrument of Developing Preliminary Field testing
The instrument of developing preliminary field testing was questionnaires. The questionnaires were distributed to the English teacher or expert to obtain the data of face validity and content validity.
D. Data Gathering Technique
in 2009/2010 academic year, library study, and distributed questionnaire to the English teacher as the expert to obtain the feedback.
1. Data Gathering Technique of Research and Information Collecting: a. Interview was used to gather the data on research and information
collecting. The writer interviewed the English teacher who taught the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School to obtain the data on the test specifications.
b. Library Study was used to obtain the syllabus and lesson plan of the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. Library study was conducted to gather the data on research and information collecting.
2. Data Gathering Preliminary Field Testing:
Questionnaire was used to obtain the data of face validity and content validity of the test. The writer distributed the questionnaires to the English teacher who taught the tenth grade Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data gathered from questionnaires were used to obtain the feedback from English teacher who taught the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year. These data were used for investigating face validity and content validity of the test. The data were analyzed by using descriptive analysis.
F. Research Procedure
In this research, the writer designs a set of multiple-choice reading test as an achievement test and investigates the validity of the multiple-choice reading tests, which are tested in the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School. The whole process consists of five steps:
1. Research and Information Collecting
In the first step, research and information collecting involved stage one of Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development, that is design by doing library study and interview. The writer conducted an interview to the participant who was the English teacher who taught the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year. The writer also conducted the library study to obtain some theories of reading, test, design and test development, and the syllabus and lesson plan of the tenth grade Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School.
(s), definition for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, inventory of available resources and plan for their allocation and management.
In research and information collecting, the writer would do interview to find out characteristics of the test takers and library study to obtain some aspects of design statement. They are purpose of the test, description of TLU (Target Language Use) domain and task types, definition of the construct (s), definition for evaluating the qualities of usefulness, inventory of available resources and plan for their allocation and management.
2. Planning
In the second step, planning, Borg and Gall (1983: 781) stated that a good plan can help the developer avoid much wasted work during later phases of good R & D cycle. The writer did the planning by doing operationalization, which was included selecting and specifying the materials by conducting library study. After conducting the selecting and specifying the materials, the writer would be able to make a blueprint of the test.
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
Then the writer did the third step which was developing preliminary form of product.” Developing preliminary form of product includes preparation of instructional materials handbooks, and evaluation devices.” (Borg & Gall, 1983: 775)
specifying the procedures for scoring the test. Therefore, in this step the writer made the test, answers, and scoring system.
4. Preliminary Field testing
The writer conducted preliminary field testing by doing a stage of administration (Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development). Administration consisted of four activities: administering, collecting feedback, analyzing, archiving. In administering, the writer needed participants to solve the research problem. The participants are the students of tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year as the test-takers and the English teacher of tenth grade students of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year to whom the questionnaire given.
After that, the writer collected the students’ answer sheets and feedback from the English teacher as the data, this activity was involved in collecting feedback. From the data gathered, the writer would analyze the students’ answer sheet to investigate construct validity of the test through counting IF, ID, and distractor efficiency of the test’s items. Furthermore, the writer also analyzed the feedback from the questionnaire to investigate face validity and content validity. The data then would be interpreted into descriptive analysis.
5. Main Product Revising
35 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the writer presents research finding and elaborates the research finding into a discussion.
In this research, the writer applied Research and Development cycle (R & D). The writer only used five steps of R & D process because by doing those five steps the research problems has been answered. The five steps which were used by the writer are research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, and main product revising.
A. How the Achievement Multiple-Choice Item Narrative Reading Test is Designed
1. Research and Information Collecting
In this first step, there were two main activities. They were interview and literature review.
a. Interview
The writer interviewed the teacher who taught the students of grade X of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School as a participant on Tuesday, 20th April 2010. By doing the interview, the writer obtained the data on the characteristics of the test takers (see the design statement on page 36-37).
outstanding students while most of students were not good enough in English. Some students who were outstanding students were very fluent in speaking English but they were not good enough in understanding reading text.
From the interview, the writer could draw some conclusions related to the test specification. The writer needed the test specification because “test writer needs guidance on practical matters that will assist test construction.” (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995:11).
b. Literature Review
In the first step, the writer had conducted literature review to obtain some theories related to the study and the syllabus and lesson plan of the tenth grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School so that the writer had better understanding before designing the test. The writer conducted literature review on Tuesday, 20th April 2010. From the syllabus and lesson plan, the writer obtained some data related to the test specification and teaching narrative itself.
Design Statement
Purpose of the test
The test was designed as an achievement test which aimed to monitor the students’ mastery on narrative. Achievement tests were (or should be) limited to particular material addressed in a curriculum within a particular time frame and are offered after a course has focused on the objectives in question. (Brown, 2004: 47) By doing the test, the students were expected to achieve some indicators stated in the syllabus, as follows:
a. Students are able to identify the meaning of certain words in the text;
b. Students are able to identify the meaning of certain sentence in the text;
c. Students are able to identify the rhetorical steps of the narrative.
Description of the Target Language Use
(TLU) domain and task types
a. TLU: Language Instructional b. Task Types: multiple-choice test
Characteristics of test takers
Personal characteristics:
a. Age: They are 15-16 years old b. Sex : male and female
b. Native Language: Javanese
c. Prior experience with a given test: they were taught narrative more than three meetings.
Level of language knowledge:
a. A literal understanding of a text: for most of students b.An understanding of meaning that are not directly
stated in the text: advanced students
Definition of construct (s)
Design Statement
Plan for evaluating the qualities of
usefulness
Validity: face validity, content validity, and construct validity
Inventory of required and available resources and a plan for their
allocation and management
Resources:
a.Theory of reading b.Theory of test
c.Theory of designing multiple choice test d.Theory of scoring and marking system Allocation and management:
Each resource contained a text ranging from 4 up to 8 paragraphs. The writer simplified some texts without omitting the essential events. Each text had five (5) questions.
Table 4.1: Design Statement of the Test
From the design statements, the writer concluded that the writer had to design a test to achieve the objectives of the lesson. To achieve the objectives of the test, there are some indicators which would be a guideline for the writer in writing the test. The indicators appeared in the questions of the test. Considering the reading ability of the students, the writer wrote a test which the advanced and less advanced students understand the instructions, the questions, and the items.
From the test specification and the result of interview and library study, the writer had some guidelines to do step two, planning.
2. Planning
Step two, planning, the writer collected some narrative texts which was done on Saturday 17th April, 2010. Borg and Gall (1983: 781) stated that a good plan can help the developer avoid much wasted work during later phases of good R & D cycle. So in this step, the writer developed a good plan before writing the test.
The writer did planning by doing operationalization, which was included selecting and specifying the materials to construct the test (Bachman’s and Palmer’s Test Development). By doing selecting and specifying the materials the writer would be able to make a blueprint of the test. A blueprint contained a test structure and test task specifications. This step would be done by conducting library study.
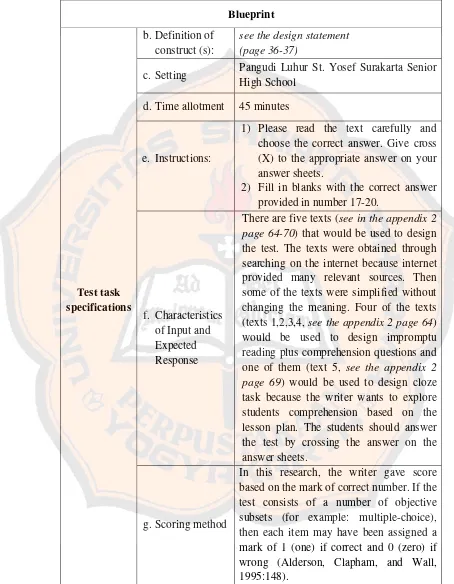
Research result of this step is a blueprint that can be seen in Tabel 4.2 below:
Blueprint
Test structure
a. Number of parts/tasks
The test was organized into two tasks. The tasks of this test will be cloze tasks and impromptu reading plus comprehension questions.
b. Salience of
parts Parts are clearly distinct Test task
specifications a. Purpose see the design statement
Blueprint
Test task specifications
b.Definition of construct (s):
see the design statement (page 36-37)
c. Setting Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School
d.Time allotment 45 minutes
e. Instructions:
1) Please read the text carefully and choose the correct answer. Give cross (X) to the appropriate answer on your answer sheets.
2) Fill in blanks with the correct answer provided in number 17-20.
f. Characteristics of Input and Expected Response
There are five texts (see in the appendix 2 page 64-70) that would be used to design the test. The texts were obtained through searching on the internet because internet provided many relevant sources. Then some of the texts were simplified without changing the meaning. Four of the texts (texts 1,2,3,4, see the appendix 2 page 64) would be used to design impromptu reading plus comprehension questions and one of them (text 5, see the appendix 2 page 69) would be used to design cloze task because the writer wants to explore students comprehension based on the lesson plan. The students should answer the test by crossing the answer on the answer sheets.
g.Scoring method
In this research, the writer gave score based on the mark of correct number. If the test consists of a number of objective subsets (for example: multiple-choice), then each item may have been assigned a mark of 1 (one) if correct and 0 (zero) if wrong (Alderson, Clapham, and Wall, 1995:148).
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
Step three, developing preliminary form of product.”Developing preliminary form of product includes preparation of instructional materials handbooks, and evaluation devices.” (Borg & Gall, 1983: 775)
The research results of this step were as follows:
a. Multiple-choice items test (see the appendix 3 page 71)
The test consisted of five (5) narrative texts and twenty (20) items. Four (4) texts were used to design impromptu reading plus comprehension questions and one (1) of them would be used to design cloze task. Each item had five (5) choices named A, B, C, D, E.
b. The answer
The answer key of the test: 1. C
2. B 3. A 4. E 5. D
6. B 7. C 8. C 9. A 10.B
11.D 12.B 13.A 14.D 15.E
16.B 17.C 18.E 19.B 20.D
c. Scoring and marking system
For the scoring system, the writer assigned a mark of 1 (one) if correct and 0 (zero) if wrong. The total number of correct answer would be divided by two (2) to get the final mark.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
In the fourth step, preliminary field testing, the writer conducted the test to the students of X grade of Pangudi Luhur St. Yosef Surakarta Senior High School in 2009/2010 academic year on April 29, 2010. The students were asked to read the texts and give cross (x) to the correct answer of the questions in forty-five minutes (45’).
After conducted the test, the writer obtained the answer sheets of the students, counted IF, ID, and distractor efficiency and also the result of the questionnaire. Here are the research results of Preliminary Field Testing:
a. The result of counting IF, ID, and distractor efficiency
Item
No. IF ID
Number of student answer the distractor A B C D E 1. 0.40 0.56 19 103 96 16 2
2. 0.76 0.40 17 179 18 18 1 3. 0.44 0.42 105 61 30 14 25
4. 0.60 0.33 1 2 6 84 143
5. 0.03 - 0.01 3 201 23 8 1
6. 0.48 0.70 36 112 47 16 20 7. 0.57 0.59 47 8 135 15 26
8. 0.78 0.42 7 10 185 12 22 9. 0.01 0.01 3 203 12 15 3
Item
No. IF ID
Number of student answer the distractor A B C D E 11. 0.43 0.45 21 25 72 102 12
12. 0.78 0.18 29 185 7 11 3
13. 0.74 0.24 174 47 12 0 3 14. 0.30 0.06 31 7 44 70 81
15. 0.80 0.27 19 16 5 7 187
16. 0.56 0.60 50 132 24 22 5 17. 0.66 0.36 22 45 155 3 10 18. 0.39 0.47 81 26 21 13 92
19. 0.36 0.35 102 85 28 8 11
20 0. 37 0.26 25 3 7 88 112
Table 4.3: The Results of Item Facility (IF) and Item Discrimination (ID) From the table above, the result of IF and ID could be seen. This result was used for determining next step, which is Main Product Revising. Appropriate test items will generally have IFs that range between 0.15 and 0.85 (Brown, 2004: 59). In addition, Brown (2004: 68) also stated high discriminating power would approach a perfect 1.0 (one) and no discriminating power at all would be 0 (zero). Good test items should fulfill the criteria of adequate point of IF and ID. While the test items, which could not fulfilled the criteria should be revised.
While 96 students answer number 1 correctly. The result of IF was 0.40; it meant that number one had appropriate test items. While the result of ID was 0.56, it meant that number one had moderate discrimating power. It could be concluded that the distractors for number one were acceptable.
Number 2 had the IF point 0.76 and the ID point was 0.40. The correct answer was B. there were 17 students were lured by item A, 18 students were lured by item C, 18 students were lured by item D and only 1 student was lured by item E. there were 179 students answer number 2 correctly. The distractors for number 2 were acceptable. Number 2 had appropriate test item because the IF point was 0.76. The discriminating power for number two was 0.40, which meant that it was not very low discriminating power.
The correct answer for number 3 was A. There were 105 students answered A. there were 61 students were lured by item B, 30 students were lured by item C, 14 students were lured by item D, and 25 students were lured by item E. The result of If was 0.44, which meant that it had appropriate test items. While the result of ID was 0.42, which meant that it had not very low discriminating power. It could be concluded that the distractors for number 3 were acceptable.
Number 5 had D as the correct answer. There were only 8 students who could answer correctly. 3 students were lured by item A, 201 students were lured by item B, 23 students were lured by item C, while 1 student was lured by item E. The IF point was 0.03. The IF point was too low. Therefore, number 5 did not have appropriate test item. While the result of ID was -0.01. Since it has negative point, number 5 did not have discriminating power. The ID point was negative because the number of lower ability students who could answer correctly was higher than the upper ability students.
The correct answer for number 6 was B. there were 36 students were lured by item A, 47 students lured by item C, 16 students were lured by item D, and 20 students were lured by item E. The result of IF was 0.46 while the Id was 0.70. The IF point showed that number 6 had appropriate test items. While the ID point showed that number 6 had high discriminating power. Therefore, the distractors were acceptable.
For questions number 7, the correct answer was C. there were 112 students chose C. There were 47 students were lured by item A, 8 students were lured by item B, 15 students were lure by item D, and 26 students were lured by item E. The IF point was 0.57 and the ID point was 0.59. From the IF point, it could be concluded that number 7 had appropriate test item. While ID point showed that number 7 had moderate discriminating power. The distractors for number 7 were acceptable.
students were lured by item D and 22 students were lured by item E. The IF point was 0.78. It meant that number 8 had appropriate test items. While ID point was 0.42. It meant that it had moderate discriminating power. The distractors were acceptable.
The correct answer of number 9 was A. there were only 3 students answer correctly. There were 203 students answered B, 12 students answered C, 15 students answered D and 3 students answered E. The IF point 0.01. It meant that number 9 did not have appropriate test items since only 3 students from 236 students answered correctly. The ID point was 0.01, which meant that number 9 had very low discriminating power. Therefore, the disctractors were not acceptable and should be revised.
Number 10 had B as the correct answer. There were 66 students answered correctly. 64 students were lured by item A. 27 students were lured by item C. 39 students were lured by item E. The IF point was 0.28 and the ID point was 0.46. The IF point showed that number 10 had appropriate test items. While the ID point showed that number 10 had moderate discriminating power. Therefore, the distractors were acceptable.
Number 12 had B as the correct answer. There were 185 students answered correctly. There were 29 students answered A, 7 students answered C, 11 students answered D, and 3 students answered E. The IF point was 0.78 and the ID point was 0.18. Number 12 had appropriate test items and adequate discrimination power. The distractors were acceptable.
For number 13, the correct answer was A. there were 174 students answered correctly. 47 students were lured by item B. twelve students were lured by item C. and 3 students were lured by item E. The IF point for number 13 was 0.74 and the ID point was 0.24. The IF point showed that number 13 had appropriate test items. While the ID point showed that number 13 had adequate discrimination power. The distractors were acceptable.
The correct answer for number 14 was D. There were 70 students answered correctly. Item A was chosen by 31 students. Item B was chosen by 7 students. Item C was chosen by 44 students. While item E was chosen by 81 students. The IF point was 0.30 and the ID point was 0.06. Number 14 had appropriate test items. It can be seen from the IF point. On the other hand, the ID point was very low and approached zero. It meant that number 14 had very low discriminating power. Therefore, the distractors were not acceptable. Number 14 should be revised.
The correct answer for number 16 was B. there were 132 students answered correctly. 50 students were lured by item A. 24 students were lured by item C. 22 students were lured by item D. 5 students were lured by item E. The IF point was 0.56 and the ID point was 0.60. From the IF point, it could be concluded that number 16 had appropriate test item. While from the ID point, it could be concluded that number 16 had high discriminating power. Therefore, the distractors were acceptable.
C was the correct answer for number 17. 155 students answered correctly. 22 students answered A, 45 students answered B, 3 students answered D, and 10 students answered E. The IF point was 0.66 which meant that number 17 had appropriate items. While the ID point was 0.36, which meant that number, 17 had discriminating power. The distractors were acceptable.
For question number 18 the correct answer is E. The IF is 0.39 and the ID is 0.47. There are 81 students were lured by item A, 26 students are lured by item B, 21 students are lured by item C, and 13 students were lured by item D. While 92 students answer number 18 correctly. The result of IF was 0.39; it meant that number one had appropriate test items. While the result of ID was 0.47, it meant that number one had moderate discrimating power. It could be concluded that the distractors for number 18 were acceptable.
number 19 were acceptable. Number 19 had appropriate test item because the IF point was 0.76. The discriminating power for number two was 0.40, which meant that it was not very low discriminating power.
The correct answer for number 20 was D. There were 88 students answered correctly. Item A was chosen by 25 students. Item B was chosen by 3 students. Item C was chosen by 7 students. While item E was chosen by 112 students. The IF point was 0.37 and the ID point was 0.26. Number 20 had appropriate test items since the IF point was adequate. The ID point showed that number 20 had adequate discriminating power. Therefore, the distractors were acceptable.
b. The Questionnaire
The questionnaire was given to the English teacher who taught class X. from the result of the questionnaire, it could be inferred that the test was well-constructed, expected format with familiar tasks. The writer divided the test into two parts which were impromptu reading plus comprehension questions and cloze task.
most of the students were lured but some students could answer correctly. The test had a clear theoretical definition of the construct to be measure.
Furthermore the items and tasks are congruent with the contain domain definition. The tasks were relevant to the purpose of the test and the test was relevant to the indicators of the syllabus.
The teacher added that the writer had designed the test well, in the case of choosing the type of the test, the texts and the items (questions). Unfortunately most of the students were not familiar with long texts. Therefore they felt that the test was difficult for them.
5. Main Product Revising
After finishing four steps of R & D cycle, the writer had enough consideration to revise the test. The revision was made because the writer wanted to design an appropriate reading test based on the analysis of IF, ID, and distractor efficiency and the result of the questionnaire. In this step, the writer revised the items. Therefore, the item would be clearer for the students.