TRANSLATION METHODS AND PROCEDURES
OF CULTURAL ISSUES IN LITERARY TRANSLATION:
A CASE STUDY IN PAULO COELHO’S
THE ALCHEMIST
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the
Sarjana Pendidikan
Degree
in English Language Education
By
Alfonsus Rinardi Rintardo
Student Number: 071214092
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
i
TRANSLATION METHODS AND PROCEDURES
OF CULTURAL ISSUES IN LITERARY TRANSLATION:
A CASE STUDY IN PAULO COELHO’S
THE ALCHEMIST
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Alfonsus Rinardi Rintardo
Student Number: 071214092
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
iv
(Former elementary teacher’s feedback on my early learning progress)
(Buzz Lightyear’s motto on Disney’s cartoon movie Toy Story)
(Relieving spell silently recited every time I’m in trouble)
! ! " ! # !
! ! # $
! # ! " " "
(Ikal’s contemplation on Andrea Hirata’s novel Padang Bulan, p. 196)
I dedicate this thesis to:
myself,
my late parents,
…and those who become family, patrons, advisors, and close friends
vii
ABSTRACT
Rintardo, Alfonsus Rinardi. (2011). Translation Methods and Procedures of Cultural Issues in Literary Translation: A Case Study in Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This research analyzes the translation methods and procedures used in translating English version of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist into its Indonesian version, especially dealing with cultural issues found among words, phrases, or clauses within sentences.
The formulated problems are: 1) what are the translation methods and procedures used in the translated Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist and the styles of translation from the application of those methods and procedures?, 2) what is its type of text reliability? 3) what are the weakness(es) and the strength(s) of the translated The Alchemist?
To answer the problems, the researcher conducted qualitative research on content analysis. There are two sources of the research, namely primary source and secondary source. The primary source is taken from the two versions of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist, while the secondary sources consist of theories of translation, theory of culture, and the review on work’s context.
The findings of the research are: 1) the translation methods used are ‘pure’ and ‘combination’ categories of form change, modulation, adaptation, and contextual conditioning, 2) the styles of translation used are: metaphor, metonymy, zeugma, periphrasis, allusion, and allegory, 3) all in all, the translations tend to pursue fluency type of text reliability, but some in cases the so called foreignism and literalism still appear. 4) despite its accuracy and naturalness, especially in using the terms or concepts dealing with spirituality and figurative language, there are more than 25% cases (of samples provided) involving weaknesses on foreignism and literalism (including misinterpretation of meaning, inconsistency use of certain word, inappropriate or ambiguous diction, and inappropriate form.
It is suggested that the future researchers may further explore the possible studies for more detailed analysis on readability measurement of selected terms / expressions, grammatical changes of sentences, symbols which appear in the story, or characterization of the story. As for the lecturer, it is recommended that this research be used to teach Translation I class.
viii
ABSTRAK
Rintardo, Alfonsus Rinardi. (2011). Translation Methods and Procedures of Cultural Issues in Literary Translation: A Case Study in Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Skripsi ini mengkaji tentang metode dan prosedur penerjemahan yang digunakan dalam novel The Alchemist karya Paulo Coelho versi bahasa Inggris ke dalam versi bahasa Indonesia , terutama mengenai hal-hal yang bersifat kultural yang ditemukan pada kata, frasa, maupun klausa dalam kalimat.
Permasalahan yang muncul dalam penelitian ini adalah: 1) apa sajakah metode dan prosedur terjemahan yang digunakan dalam versi terjemahan The Alchemist karya Paulo Coelho dan gaya dalam penerjemahan yang muncul dari penerapan metode dan prosedur tersebut?, 2) apakah tipe text reliability dari karya terjemahan tersebut?, 3) apa sajakah keunggulan dan kelemahan karya terjemahan
The Alchemist tersebut?
Peneliti menggunakan penelitian kualitatif berupa analisis konten untuk menjawab pertanyaan-pertanyaan tersebut. Ada dua sumber yang digunakan dalam studi ini, yakni sumber utama dan sumber kedua. Sumber utama diambil dari dua versi novel The Alchemist karya Paulo Coelho, sedangkan sumber kedua meliputi teori-teori penerjemahan, teori budaya, serta konteks karya.
Hasil penelitian dari penelitian ini adalah: 1) kategori metode penerjemahan yang diterapkan merupakan variasi antara metode ‘murni’ serta ‘kombinasi’ antar metode: form change, modulation, adaptation dan contextual conditioning, 2) adapun gaya penerjemahan yang muncul dari penerapan prosedur tersebut adalah: metaphor, metonymy, zeugma, periphrasis, allusion dan allegory, 3) secara garis besar, text reliability dari karya terjemahan ini sendiri cenderung mengarah ke fluency, namun sayangnya masih menyisakan literalism dan
foreignism pada beberapa kasus yang muncul, 4) meski memiliki akurasi dan penggunaan bahasa yang natural, terutama berkaitan dengan penggunaan istilah atau konsep yang berhubungan dengan spiritualitas dan bahasa figuratif, terjemahan ini memunculkan lebih dari 25% kasus, dari keseluruhan sampel, yang berkaitan dengan kelemahan dalam hal foreignism dan literalism (termasuk kesalahan interpretasi makna, inkosistensi dalam penggunaan kata tertentu, pilihan kata yang kurang tepat atau ambigu, serta bentuk yang kurang sesuai).
Para peneliti selanjutnya disarankan untuk lebih lanjut mengeksplorasi studi untuk analisis yang lebih rinci pada pengukuran tingkat keterbacaan istilah / ekspresi tertentu, perubahan gramatikal dalam kalimat, simbol-simbol yang muncul dalam cerita, atau penokohan dalam cerita. Bagi dosen, penelitian ini disarankan untuk digunakan dalam mengajar kelas Translation I.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The whole process in conducting the research and writing the thesis was
one of greatest parts in my life. First of all, I would like to thank the Lord for
providing me with hidden blessings behind any opportunities and re-emerged
spirit in past times of stagnation and long confusion.
I would also like to convey my respect and gratitude to my advisor; Drs.
Antonius Herujiyanto, M. A., Ph. D; who gave me freedom to explore the field I
am interested in, while providing the advices and guidance necessary for
improving the analysis and presentation of research results.
I also send my gratitude to Sr. Margaret O’Donohue, FCJ for her
kindness to take the time to correct my grammar in this thesis and became a
critical proofreader in discussion.
My sincere thanks are also for valuable moral and scholarship supports
from the Katedral Kristus Raja Purwokerto Parish, through the helps of Bu
Anik and the treasurers, and Pak Bambang, as great acquaintances of my late
parents.
Thanks also go to my siblings Nana, Fran and Lia, who are also
struggling to live in their own ways; for always reminding me of my goals for
studying in university and my obligation to graduate as soon as possible and with
x
Lastly, I give huge thanks for friends in USD EESP of all classes,
especially the class of 2007 where I belong the late four years, and juniors of E3C
and Insight International from classes below with Mbak Dhyana Paramitha as
the amazing patron, who keeps encouraging me to graduate from the university
successfully.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE………..
APPROVAL PAGES………..
DEDICATION PAGE………
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……….
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI………
ABSTRACT……….
ABSTRAK……….
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS………
TABLE OF CONTENTS………
LIST OF TABLES………..
LIST OF APPENDICES……….
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION
A. Research Background………
B. Research Problem ………
C. Problem Limitation…….……….
D. Research Objectives……….
E. Research Benefits………
F. Definition of Terms……….
xii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Theoretical Description………...
1. Theories of Translation…….……….
a. Good Translation………
b. Good Translator………..
c. Translation Process and Procedure……….
d. Meaning-Based Translation………
e. Styles of Translation……….………..
f. Assessing Translation Product………
2. Theory of Culture………...
3. Work’s Context………...
a. The Author………..
b. Work’s Setting………
B. Theoretical Framework………..
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY
A. Research Method………...
B. Research Setting……….
C. Research Participants/ Subjects……….
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique…………..
E. Data Analysis Technique………...
F. Research Procedure………
xiii
CHAPTER IV. DISCUSSION
A.
Examining the Reconstruction of the Text on Cultural Issues on Translation Methods and Procedures …...1. Part One……….
a. Language……….
b. Thought………..
c. Spirituality………..
d. Interaction………...
2. Part Two……….
a. Language……….
b. Thought………..
c. Spirituality………..
d. Interaction………...
B.
The Style of the Translation……….1. Metaphor………. 2. Metonymy………... 3. Zeugma………... 4. Periphrasis……….. 5. Allusion……….. 6. Allegory………..
C.
The Type of Text Reliability………xiv
D.
The Overall Quality of the Translation and Its Translators………1. Quality of the Translation………..
a. Strengths……….
b. Weaknesses………...
2. Quality of the Translators………...
a. Strengths……….
b. Weaknesses………...
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions………
B. Suggestions………
1. For the Students of Translation Class………
2. For the Lecturer………
3. For Future Researchers……….
REFERENCES………
APPENDICES………..
77
77
77
80
84
84
85
86
92
92
93
94
96
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 2.1 Machali’s Translation Assessment……… 18
Table 3.1 Information Derived from Questions and Their Sub-Categories… 28
Table 5.1 Distribution of Translation Method ………... 88
Table 5.2 Styles of Translation Used………. 89
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix A. Pipitta’s Reviews: Veronika Memutuskan Mati……… 99
Appendix B. Sang Alkemis………. 101
Appendix C. Covers of The Alchemist in English and Indonesian Edition.... 104
Appendix D. Map of Spain-Africa………. 105
Appendix E. Lesson Unit Plan KPE 321 Translation I……….. 106
Appendix F. Pictures for pre-Activities………. 111
Appendix G. Handout for Literary Translation……….. 113
Appendix H. Student’s Worksheet on Literary Translation Involving Cultural Issues………. 117
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of six parts, namely: research background, research
problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and definition
of terms.
A. Research Background
A good translation is expected to perform three good aspects, namely:
“accurate”, “natural”, and “communicative” (“The Role of Translation Theory”,
n. d.). Some of the translations may be well on all these aspects, while others can
just fulfill one or two aspects. An unaware translation may be accurate (means
that it produces the same possible meaning in the target language), but it sounds
unnatural and even not communicative, which finally makes it less worthy to read.
Talking about translated novels, the translator(s) (and editor) might think that
there was nothing wrong with the translation product, but however the final
judgment is on the readers. They are the devotee of a literary work itself. As a
written product, translation text certainly will serve its users.
Paulo Coelho is one of the most prominent novelists nowadays, as well as a
The researcher wants to analyze an Indonesian-translated novel of Paulo Coelho’s the Alchemist by Hamid Basyaib and Yunita as the subject of the translation study, compared to its English edition by Alan R. Clarke. In order to
do so, this thesis focuses on using theories of translation (linguistic) along with
theory of culture and review on work’s context as supporting theories.
The interest was aroused when one day the researcher found intriguing
online posts on review column and discussion board among literary work lovers in
two sites: www.goodreads.com and perca.blogdrive.com. They commented on the Indonesian version of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist by Basyaib and Yunita. One of them reviewed that the most annoying thing in the translation product is the
inappropriate pronoun of the main character itself. It carries on the whole story.
Some others in a rather informal discussion complained about ‘the language’
used. (It might be because the translation was either or both unnatural and or not
communicative). These people were so disappointed that once they decided to
stop reading any other works of Coelho, until they eventually found that the other
translation products (of other translators) were better than this one, the Alchemist
by Basyaib and Yunita.
The researcher was amazed to know this fact: if the readers judge one
translated work of an author is not really good, or even disappointing, it may
affect their perception on the other works of the same person. What a disaster! If
we see this objectively, the fault (or, to be more polite, the carelessness) is on the
translator(s). The readers will question about the capacity on the field, because in
knowledge about the settings underlying the work. In this case, researcher
believes that The Alchemist, as a masterpiece in literary world, has lots of cultural
content that makes this work special. Review and comments worldwide even
sincerely categorized it as a mind-shifter book.
This research tries to reveal how translator should work with translation,
especially literally translation which deals with cultural contents.
B. Research Problems
To translate correctly and smoothly a variety of writing from English into
Indonesian sometimes is not as easy as expected. Translation is not merely to
transfer the language, but also the meaning and the culture embedded. From the
case above, where readers perceived that the translation product of The Alchemist
is not good, then problems of this thesis are formulated as follows:
1. What are the translation methods and procedures used in the translated Paulo
Coelho’s The Alchemist and the styles of translation from the application of those methods and procedures?
2. What is its type of text reliability?
3. What are the weakness(es) and the strength(s) of the translated The Alchemist?
C. Problem Limitation
translation. In this study, the researcher limits the scope of discussion only on 60
prominent sentences dealing with cultural issues found among words, phrases, or
clauses within.
To note, The Alchemist is divided into two parts: the first (the beginning) and the second part (the journeys). It is not broken down into chapters just like
other common novels. Researcher takes 15 sample sentences from part one and 45
others from part two as the objects of analysis. The first part serves as an
introduction to the novel’s main character, a shepherd boy named Santiago. It also
portrays his wishes in life. In the second part, which is much longer than the
previous part, readers are invited to follow Santiago’s journey to fulfill his wishes.
In the English version the overall story seems to use simple language, but actually
contains lots of new words that are potentially unfamiliar for beginner readers
who don’t possess rich English vocabulary knowledge. Moreover, the story is
quite philosophical. This is a kind of challenge for translator to translate such
interesting and best selling novel.
With all of the restrictions, the researcher considers he could not reveal all
aspects of the novel. With open heart, further researches are welcomed to refine
this analysis or conduct deeper analyses on other aspects.
D. Research Objectives
Following the research problems formulated, the objectives of the research
thus are:
2. To look into the style in translation;
3. To look into the type of text reliability of the translation; and
4. To look into the strength(s) and (if any) weakness(es) of
Indonesian-translated The Alchemist.
E. Research Benefits
The researcher hopes that the research will:
1. Encourage intermediate-advanced students who have interest in
English-Indonesian translation to learn more about things underlying a good
translation;
2. Reveal the considerations used in translating literary works, in this case
is a novel; and
3. Appreciate a translation product in form of novel.
F. Definition of Terms
In this study, the author uses some keywords related to the theories and
discussion:
1. Translation
Translation is basically a work to transfer an object in its original
language into the target language using certain rules or considerations
and based on adequate knowledge of both languages and cultures
involved. Larson (1984) gives emphasis on changing form while keeping
source language that is replaced by the form of the receptor (target)
language.” As it also deals with transfer of meaning, “…the meaning
transferred must be held constant” (para. 3). But, to Nida, it is not
enough just to keep the meaning constant. It also needs to mind the
naturalness of the result. “Translation consists in reproducing in the
receptor language the closest natural equivalent of the source language
message, first in terms of meaning and secondly in terms of style .”
(para. as cited in Suhendra, 1994, p. 64)
2. Literary Translation
Literary translation basically is translation work on literary products.
Kwintessential defines it as “the translation of literature such as novels,
poems, plays and poems”. It then is “the highest forms of translation” by
applying interdisciplinary aspects mastered by the translator to work
with the piece (“Types of Translation”, n. d.).
3. Culture
Culture is a set of social characteristics or features that are shared by
certain community to apply in their life. Banks and McGee believe that:
The essence of a culture is not its artifacts, tools, or other tangible cultural elements but how the members of the group interpret, use, and perceive them. It is the values, symbols, interpretations, and perspectives that distinguish one people from another in modernized societies (as cited in CARLA, 2010).
Those characteristics or features that are inherited or passed down
4. Method and Procedure
In translation work, Machali (2000) refers “method deals with the
whole text work and procedure works on sentence or levels below” (p.
62). It means methods are categories used in as general, typical
strategies, while procedures are the specific treatments done with
wording and its meaning.
5. Case Study
Case study deals with the phenomenon investigation by
generalizing theories, not the samples. Then it is “not a method but a
research strategy”, and more as “a choice of what is to be studied”. It
should be defined “in terms of its theoretical orientation and interest in
individual cases” (Hartley, et al. as cited in Kohlbacher, 2006).
6. Style
“Style is used as a term distinguished from content in writing and it
stresses form or format. In other words, style means ‘how’ whereas
content refers to ‘what’ “(Lynch as cited in Shi, n. d.). Styles are the
ways translators transfer the content while preserving its language
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of two parts, namely theoretical description and
theoretical framework.
A.
Theoretical Description
1.
Theories of Translation
a.
Good Translation
An ideal translation should be: “accurate” (reproduce the same possible
meaning of the source text), “natural” (use of natural form appropriate to the kind of
text translated) and “communicative” (express all aspects that are easy to understand
by readers) (“The Role of Translation Theory,” n. d.).
Larson (1984) similarly suggests that it must: “use normal language forms
of the receptor language, communicate as much as possible the same meaning
understood in the source language, and maintain the dynamics of the original source
text” (p. 6).
Duff (1992) proposes some principles of translation to consider:
1)
Meaning: check the meaning of the original text whether or not it is
2)
Form: match ideas and words closely to the original text. However,
it allows form and word order changes in the target language, due to
language structure differences.
3)
Register: consider the tone of original text (formal/fixed or personal
expressions).
4)
Source language influence: natural means not sound like the
original language.
5)
Style and clarity: translator needs to maintain the style of original
text and simultaneously do adjustment for the reader sake.
6)
Idiom: Idiomatic expressions are commonly untranslatable. It
cannot be forcibly translated into L2 (target language) without
considering the naturalness. To work with them, translator may
retain the original word/expressions in inverted commas ‘_______’
or give literal explanation in brackets ______ (___), use
non-idiomatic translation (para. 10-11).
In discussing translation text, Robinson (1997) refers to types of text
reliability:
1)
Literalism: words-by-words translation as close as possible to the
source text.
2)
Foreignism: the translation still has a little bit strange or unfamiliar
3)
Fluency: the translation is so accessible that it feels like an original
in L2 (meaning-based translation is closely related to this kind of
text reliability).
4)
Summary: the translation summarizes only main points of the
original.
5)
Commentary: the translation simplifies the complexity or explores
the implications of the original.
6)
Summary-Commentary: the translation explores the main part and
summarizes the rests of the original.
7)
Adaptation: the translation transformed in such form that it meets the
substance for the target user.
8)
Encryption: the translation is decoded for certain group of users to
hide its messaging or meaning (para. 10-11).
Newmark believes that:
Observing the quality of a translation can focus on methods used by its
translation, whether source language oriented (translating word-by-word,
literal, or somatic) or target language oriented (adaptation, free translation,
idiomatic translation, or communicative translation) (as cited in Machali,
2000, p. 49-52).
This methods observation makes measurement on translation quality easier
b.
Good Translator
To produce a good translation, there is a need also to be a good translator.
Nida argues that a translator should be capable to: have an adequate knowledge of the
source language (can not just rely on the dictionary), to understand the contents of the
message of source language and to retain the subtlety of certain emotive meaning and
value of the source language vocabulary and style that will determine the taste of the
message delivered (para., as cited in Suhendra, 1994, p. 64).
Polet suggests these must-have qualities:
1)
The translator must perfectly understand the sense and material of the
original author although he should feel free to clarify obscurities;
2)
The translator should have a perfect knowledge of both SL and TL, so as
not lessen the majesty of the language;
3)
The translator should avoid Latinate and unusual forms;
4)
The translator should avoid word for word rendering; and
5)
The translator should assemble and liaise words eloquently to avoid
clumsiness (as cited in Munday, 2001, p. 27).
Robinson (1997) calls for translator reliability regard to the text within these
aspects:
1)
Attention to the details;
2)
Sensitivity to the user’s needs (type of translation desired);
3)
Research on specific unknown terms or words; and
4)
Checking by proofreader to avoid doubt (p. 12-14).
To be more specific about literary translators, Suryawinata believes that they
need to:
2)
Control and able to understand the target language well, correctly, and
effectively;
3)
Know and understand the literature, appreciation of literature, as well as
translation theory;
4)
Have sensitivity to literary works;
5)
Have the flexibility of cognitive and socio-cultural; and
6)
Have the tenacity and strong motivation (para. as in Haryanti, 2006, p.
169).
c.
Translation Process, Methods, and Procedure
According to Nida and Taber, translation process, basically covers:
1)
Analysis: the translator looks on grammatical context, words meaning,
textual meaning and contextual meaning to analyze the sentences of
original text;
2)
Transfer: the translator digests the meaning of analyzed original text;
3)
Restructuring: the translator finds equivalent words, expressions and
sentence structure in L2 to maintain the content, meanings and messages
of the original text; and
4)
Evaluation and Revision: translator rechecks the translation product by
comparing to the original one to get the closest equivalences (para., as in
But, Suryawinata and Hariyanto (2003) find that basically the process works
on analysis of original text and its messages/meanings and then retell those
messages/meanings with acceptable words or sentences of target language (para. 19).
Machali (2000) states some proper procedures in translation. She differs
between method and procedure. “Method deals with the whole text work and
procedure works on sentence or levels below” (p. 62). The methods focus on:
1) Shift / Transposition/Form Change
There are four groups of grammatical form changes due to language gap.
It is only needed when the target language does not have the same
grammatical structure for a text of source language. The changes are as
elaborated below.
The first group:
•
Plural-noun in English converted into singular one in bahasa
Indonesia;
Ex: ‘a pair of jeans’ = ‘sebuah celana jeans’
•
Adjective reduplication in bahasa Indonesia as variation for English
plural-noun;
Ex: “Rumah di Jakarta bagus-bagus.” from English “The houses in
•
Reverse of pattern adjective + noun into noun + adjective and the
order of adjectives.
Ex: ‘beautiful woman’ = ‘wanita (yang) cantik’.
The second group:
•
The adjustment not to put object in the beginning of a sentence;
Ex: “Buku itu harus kita bawa.” = “We must bring the book.”
•
The adjustment not to put verb in the beginning of a sentence.
Ex: “Berbeda penjelasannya.” = ”The explanation differs.”
The third group:
•
The conversion of noun/noun phrase in source language into verb
in target language;
Ex: “... to train intellectual men for the pursuits of an intellectual
life.” = “untuk melatih para intelektual untuk mengejar kehidupan
intelektual.”
•
Adjective + noun turned into noun + noun;
Ex: ‘medical student’ = ‘mahasiswa kedokteran’
•
Clause underlined in source language is explicitly stated in target
Ex: “The cells
carrying
the germs are dangerous.” = “Sel-sel yang
membawa/mengandung ...”
•
Noun phrase with adjective on source language turned into noun
clause.
Ex: ‘thinking person’ = ‘orang yang berpikir’.
The fourth group:
•
A textual focus signal on source language is stated grammatically in
target language;
Ex: “Perjanjian inilah yang diacu.” = “It is this agreement which is
referred to (not anything else).”
•
The commonly change from word in source language into
clause/phrase, phrase into clause, and so on.
Ex: ‘adept’ = ‘sangat terampil’ or ‘interchangeability’ = ‘keadaan
dapat saling dipertukarkan.’
2)
Meaning Change / Modulation
Modulation is needed by changing the perspective when there is no
equivalence for words, phrase, or structure on the target language.
•
Only one between two words has the equivalence on target
Ex: ‘lessor’ and ‘lessee’ = ‘orang / pihak yang menyewakan’ atau
‘pemberi sewa’ dan ‘penyewa.’
•
Active sentence changed into passive voice;
Ex: “The problem is hard to solve.” = “Masalah itu sukar (untuk)
dimusnahkan.”
•
Split subject structure needs a clarification;
Ex: “Buku tersebut telah disahkan penggunaaannya oleh Dikti.” =
“The use of the book has been approved by Dikti.”
•
Specific words share general and particular meaning of a word in
target language.
Ex: ‘society’ = ‘masyarakat’ (social relationship) and ‘community’ =
‘masyarakat’ (group of people).
3)
Adaptation
It is a kind of cultural adjustment on two situations.
Ex: ‘Dear Sir’ = ‘Dengan hormat’ not ‘Tuan yang Terhormat’.
4)
Contextual Conditioning
Put the information within a context so that its meaning is clear to the
Ex: ‘selamat malam’ could be translated as ‘good night’ or ‘good
evening’.
“Hari ini adalah 40 harinya ibunya.” = “This day is the fortieth day of
her mother’s death.”
5)
Footnote Conditioning happens only if there is a deadlock in
translating the text (para. 62-72).
d. Meaning-Based Translation
Larson (1984) points out on the goal of any translator, which is “to keep the
meaning constant” (p. 11). It means a meaning-based translation allows translator to
change the form of source text wherever necessary, as long as its meaning is not
distorted.
e. Styles of Translation
Friedman further describes the kinds of style in translation. According to
him, it includes:
1)
Metaphor
is a transfer of some quality from among objects based on
resemblance;
2)
Trite Metaphor
is a metaphor that overused in speech and often turns
3)
Metonymy
is a transference of meaning which is based on contiguity of
notions;
4)
Irony
is a simultaneous realization of two opposite meanings: the direct
and implied;
5)
Zeugma
is an application of two different meanings of the word at once
that creates a pun (direct and figurative meaning at once);
6)
Periphrasis
is a process of renaming, that sometimes applied by
creating
euphemism
;
7)
Allusion
is an indirect reference to a historical or literary fact (or
person) contained in the text.
8)
Allegory
is a use of objects or characters figuratively, representing some
more general things, good or bad qualities, including
personification
(para. as cited in Goumovskaya, 2007).
f.
Assessing Translation Product
Machali (2000) comes with a table of translation assessment as follows:
Table 2.1 Machali’s Translation Assessment
Category Score Indicators
Almost Perfect 86 – 90 (A) Fluent translation, no mispell, no
gramatical mistake, no diction
Category Score Indicators
Very Good 75 – 85 (B) No meaning distortion, no literal
translation, no diction confusion, only
few grammatical / spelling mistakes
appear.
Good 61 – 74 (C) No meaning distortion; few literal
translations; grammatical, diction, and
idiomatic mistakes appear but no more
than 15 % of all text.
Average 46 – 60 (D) Sounds like a translation.
There are some literal translations;
idiomatic or grammatical mistakes, and
unproper dictions but no more than 25%
of all texts.
Poor 20 – 45 (E) Sounds really like a translation; there are
literal translations, meaning distortions,
and improper dictions more than 25% of
all texts (para. 119-120).
2.
Theory of Culture
In translating sometimes unaware translation can possibly translate the
original work inappropriately, especially when it contains certain foreign cultural
aspects. This problem may appear for the lack of knowledge on the translator. He or
she should know the cultural settings related to the work translated, something called
Further about culture, the researcher refers to a theory about culture. It
defines that culture refers to the following Ways of Life, including but not limited to:
1)
Language
: the most complicated medium of expression;
2)
Arts & Sciences : the most advanced and refined forms of human
expression;
3)
Thought
: the ways people perceive, interpret, and understand the
surrounding world;
4)
Spirituality : the contemplated value system transmitted through
generations that is expressed through language and deeds;
5)
Social activity : the shared purposes within a cultural community,
demonstrated in events and celebrations; and
6)
Interaction: the social aspects of human contact, as applied in giving and
taking of socialization, negotiation, protocol, and conventions (para.
“Definition of Culture”, n. d
.).3.
Work’s Context
a.
The Author
As acknowledged previously in the background of study, Paulo Coelho is a
His life is reviewed by Wikipedia as follows. He knew that he wanted to be
a writer soon after entering Jesuit school as a teenager. Tried to live his own way, her
parents once sent him into mental institution when he was under 20. He finally
entered law school to fulfill his parents’ wish, but then he dropped out to travel
around the world: South America, Mexico, North Africa and Europe. After that, he
had a hard life by performing hippie’s life and committed subversive actions during
60’s-70’s period. He took another amazing trip to a famous place in Spain. That was
Santiago de Compostella, a hundred –miles road of ancient pilgrimage. This long
journey enlightened him spiritually, inspiring him to work with his novel entitled
Pilgrimage
soon after he came back home. He wrote his most famous work,
The
Alchemist
, the following year. This work later was recorded in The Guinness Book
of Records as the most translated book by a living author (in 71 languages, over 65
million copies worldwide).
Totally, Coelho has published 29 books (all were originally in Portuguese).
He distributed his work firstly by peer-to-peer file sharing network. Two of them,
The
Pilgrimage
and
The Valkyries
, are autobiographical, while the rest mostly are fiction,
although rooted in his life experiences. Here is the list of his books:
The Manifest of
Krigha
and
Theater for Education
(1974);
Hell Archives
(1982);
Practical Manual of
Vampirism
(1986);
The Pilgrimage
(1987);
The Alchemist
(1988);
Brida
(1990);
The
Greatest Gift
(1991)
; The Valkyries
(1992);
Maktub
and
By the River Piedra I Sat
Down and Wept
(1994);
The Fifth Mountain
(1996);
Love Letters from a Prophet
and
Words
(1998);
The Devil and Miss Prym
(2000);
Fathers, Sons and Grandsons
(
2001);
Eleven Minutes
(2003);
And on the Seventh Day, The Genie and Roses,
Journeys
(2004);
The Zahir
and
Revived Path
(2005);
Like The Flowing River
and
The Witch of Portobello
(2006);
Life: The Selected Quotations
(2007);
The Winner
Stands Alone
(2008); and
The Aleph
(2010).
b.
Work’s Setting
As many reviews said, Coelho’s
The Alchemist
is a story with delicate
symbols embedded. It combines simple wordings with abundant symbols of a fable.
The story takes place in the Andalusia countryside (Spain) at the beginning,
where the shepherd Santiago as the main character used to graze his sheep flock. As
the story goes, Santiago travels across the sea to Tangier, Morocco (Africa).
Afterward, the story introduces the adventure on the desert and pyramid of Egypt.
Eventually, the whole story end back where it began: an abandoned church in
Andalusia.
No specific time informed in the story, since it is a fable. But, if we look
deeper and see the details, especially the meeting of Andalusia people with the Moors
(Moslems of Western Africa), we may link it back in history to the post
Reconquista
era, after the fall of Islamic caliph (Umayyad) which formerly had reigned in Spain,
especially in some prominent areas like Seville, Toledo, and Granada. Another signal
to the rather modern age is the use of revolver as revealed in a dialogue between
B.
Theoretical Framework
Those theories reviewed above are used to help the researcher conducting
this research, which focuses on analyzing the translated sentences related to cultural
issues. The theory of good translator and good translation in general later will help in
making the conclusion of data analyzed. The theory about translation process &
procedure, culture, style, meaning-based translation, and translation assessment are
used to conduct deeper research on the selected data.
A good translator should have perfect knowledge on languages involved in
work as well as the matter or culture involved. The knowledge of language
encompass: the grammatical rules, the meaning complications (including idiomatic
expressions), the diction, the register, the styles, and the translation rules and process
that requires extra attentions to the details (Robinson, 1997; Nida, as cited in
Suhendra, 1994; Polet, as cited in Munday, 2001). To work on literary work
containing cultural contents, an aware translator should also understand the
underlying principles of literature and its appreciation. Further research on culture
embedded may also be conducted to help adjusting the translation product to meet the
readers’ needs without distorting the original content (Robinson, 1997; Suryawinata
as in Haryanti, 2006). After all, to Robinson (1997), a kindness to consider and apply
useful criticism and suggestion obtained from the proofreaders will really help
maintaining the quality of the translation (para. 14).
A good translator will eventually produce a good translation product. A
communicative”. It means a translation work not only produce the same meaning as
its original work, it should also use of natural form appropriate to the kind of text
translated that is easy to understand by the readers (para. “The Role of Translation
Theory,” n. d.) . In his “Meaning–Based Translation” concept, Larson (1987)
described it as to change the form of source text wherever necessary, as long as its
meaning is not distorted (para. 11).
In accordance with Duff’s proposal on some principles of translation to
consider, a translation process will undergo some steps: “analysis”; “transfer”;
“restructuring”; “evaluation and revision” (Duff, 1992; Nida and Taber, as in
Suryawinata and Hariyanto, 2003). Research on Paulo Coelho’s
The Alchemist
specifically looks on “restructuring” step, in which covers translation methods
classified by Machali (2000). Researcher will work on this level to reveal the
methods procedures applied to the 60 assorted sentences under six common cultural
categories as suggested by Roshan Institute, accompanied by Friedman’s theory on
styles on translation (“Definition of Culture”, n. d
.;Friedman, as cited in
Goumovskaya, 2007). From the data analysis, later researcher could summarize the
quality of the translation, whether it is source language oriented or target language
oriented. The orientation could be specified to show its type text of reliability
(Newmark, as cited in Machali, 2000; Robinson, as cited in Munday, 2001). Finally,
from the intertwined analyses, researcher will be able to conclude the strength(s) and
25
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter consists of six parts, namely: research method, research
setting, research participants / subjects, instruments and data gathering technique,
data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
To look into translation methods and procedures applied on the
translated Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist, the researcher conducted a qualitative research. The type of research chosen was content analysis. It could also be
considered as a specific form of typological analysis. Weber defined this type as
“look at documents, text, or speech to see what themes emerge.” It then tends to
be theory driven with specified rules for data analysis (as cited in Ratcliff, n. d.).
The text examined was in a form of novel. It then used a case study with
sentences as the strategy. This strategy used to reveal the patterns / schemes in
data and any possible relationship among them.
B. Research Setting
The researcher conducted the content analysis research during February
C. Research Participants / Subjects
The subjects of the research in this thesis were in the form of texts,
which were two versions of Paulo Coelho’s the Alchemist novel. One of them was a 177-page English edition by Alan R. Clarke, which was published by Harper
San Francisco in 1999. Another one was a 196-page Indonesian edition by Hamid
Basyaib and Yunita, which was published by Pustaka Alvabet in 2004. Data used
for analysis were sample of words, phrases, and clauses within sentences in the
novels. Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (2008) defined sampling as “the
process of systematically selecting that which will be examined during the course
of a study”. Type of sampling fitted to the data was stratified purposive sampling.
Patton stated this type of sampling as “samples within samples and suggests that
purposeful samples can be stratified or nested by selecting particular units or cases
that vary according to a key dimension” (as cited in Ratcliff, n. d.)
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
As Patton mentioned about research instrument in qualitative research,
researcher functioned as the "human instrument" of data collection (as in Hoepfl,
1997). The other instruments accompanied were list of sub-categories pre-defined
to gather eligible data (as summarized in Table 3.1 in this chapter). To obtain the
representative data, researcher took 60 sentences from the two parts of the novel:
15 from the first half part and 45 from the other part. The ratio 1:3 taken was in
accordance to the ratio of pages between both parts, in which the second part is
E. Data Analysis Technique
In analyzing data, the researcher referred to process on analyzing
qualitative as data described by Powell and Renner (2003):
1. Get to Know Data
The researcher needed to read the text several times to really understand the
data desired. Only quality data would be picked as samples. The sampling
took limitation only words, phrases, or clauses within sentence level involving
cultural issues.
2. Focus the Analysis
The researcher referred to the objectives of the research to decide what exactly
to find among abundant data and the targeting few questions. As stated in the
problem formulation, then, researcher focused to look on translation methods
and procedures, translation style, and translation type of text reliability to later
summarize the whole quality of the translation product of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist and its translators.
3. Categorize Information
The researcher identified themes or pattern on selected sentences through
ideas or terminology used to organize them into coherent sub-categories of
culture suggested by Roshan Institute: “language”, “arts and sciences”,
“thought”, “spirituality”, “social activity” and “interaction” (“Definition of
Culture”, n. d.). As suggested by Weber in his theory on Content Analysis
each of them fitted a category and, overall, some of possible
sub-categories (para. as cited in Ratcliff, n. d.).
Table 3.1 Information Derived from Questions and Their Sub-Categories
Question Sub-Categories
a. What are themethods (and procedures) used in the translated Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist?
Form Change (FC), Modulation (M), Adaptation (A), Contextual Conditioning (CC), and Footnote Conditioning (FtC)
b. How they (the procedures and methods) influence
the styles?
Metaphor (M), Trite Metaphor (TM), Metonymy (My), Irony (I), Zeugma (Z), Periphrasis (P), Allusion (A), Allegory (Ay)
c. What is its (the translation) type of text reliability?
Literalism (L), Foreignism (Fo), Fluency (Fl), Summary (S), Commentary (C), Summary-Commentary (SC), Adaptation (A), Encryption (E)
4. Identify Patterns and Connections Within and Between Categories
The researcher identified the possibility of same procedures applied on
sentences under a sub-category and even might link sentences between
categories for their related ideas.
5. Interpretation
The researcher used themes and connections revealed among sub-categorized
information to attach meanings and significances to the analysis.
F. Research Procedure
Overall, the steps taken in the research were as follow.
1. Setting literary translation fan-based cases in internet postings as the
background of the research and formulated the problems of the research
2. Preparing two versions of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist and related literature fitted to the research topic from both printed and electronic sources.
3. Selecting the theories to be synthesized in the theoretical framework.
4. Reading the two versions of Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist simultaneously to get the understanding on the whole text.
5. Gathering eligible data in forms of words, phrases, and clauses within
sentences from the novel using sampling limitation by research’s topic
(cultural issues) and pages ratio on parts of the novel (1:3).
6. Analyzing data to get major findings through a process of categorization,
identification, and interpretation to fulfill the objectives of the research.
7. Drawing the conclusion and possible additional suggestions from the findings
30
CHAPTER IV
DISCUSSION
This chapter, which is intended for answering the problems formulation,
consists of four parts, namely: Examining the Reconstruction of the Story on
Cultural Issues on Translation Methods and Procedures, The Style of the
Translation, The Type of Text Reliability and The Overall Quality of the
Translation and Its Translators.
A. Examining the Reconstruction of the Text on Cultural Issues on
Translation Methods and Procedures
Referring to Machali’s theory on translation procedures (2000), the
researcher examined the whole text of the two versions of The Alchemist to find eligible sentences containing cultural issues. In accordance to Roshan Institute’s
theory on culture, the issues later were specified into six possible sub-categories,
to obtain effective generalization among abundant data. The categories are:
“language”, “arts and sciences”, “thought”, “spirituality”, “social activity”, and
“interaction” (“Definition of Culture”, n. d.).
Considering that the proportion of the data (sentences) between the two
parts of the translated novel is almost 1: 3, on which part one consists of 53 pages
ratio on the limitation of data sample. Researcher would only take 60 selected
sentences among similar others, under categories that had firmly planned, from
both the English version by Clarke, and the Indonesian by Basyaib and Yunita.
1. Part One
In this part the researcher took only 15 sentences as prominent data by
referring some possible similar or related, but not-taken, sentences or parts. There
are four major categories found among selected data in this part: “language”,
“thought”, “spirituality”, and “interaction”.
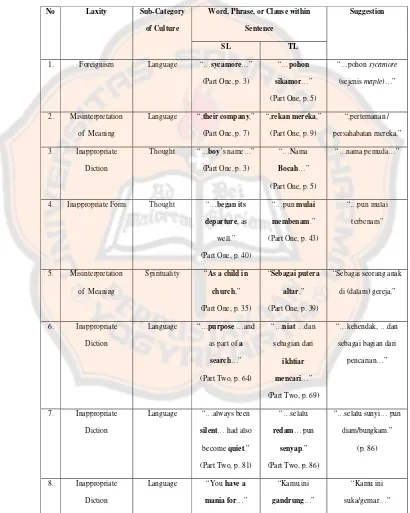
a. Language
1) The roof had fallen in long ago, and an enormous sycamore had grown on the
spot where the sacristy had once stood (p. 3).
Atapnya sudah lama runtuh, dan pohon sikamor yang sangat besar tumbuh di
titik tempat sakristi pernah berdiri (p. 5).
Method of Translation : Adaptation.
Procedure of Translation : Translators found a difficulty to get an equivalence of word ‘sycamore’, as Hornby (2004a) mentions it as “a kind of European
tree of maple family”, that is not typically Indonesian vegetation (p. 1318).
‘pohon sikamor.’ The phrase created a feel of “foreignism”. Robinson (1997)
points out that foreignism occurred as “the translation still has a little bit
strange or unfamiliar feel, though the readers consider it not as an original
work” (p. 10). Theoretically this situation is almost similar to Modulation
Method, but without trying to change the perspective. The word ‘sacristy’
underwent the same procedure. But this word fortunately is a bit recognized in
Indonesia, for it also belongs to religious context; a typical of Catholic’s
vocabulary; as Hornby mentions (2004b) it refers to “a room in a church
where a priest prepares for a service and where various objects used in
worship are kept” (p. 1127). So, translators took a risk to simply use the
Indonesian wording, with hope that most of the readers (even the
non-Catholics) would understand with no need for further information. The case on
‘sycamore’ appeared in the sentence, refers to Robinson (1997), requires the
translators to research on specific unknown terms or words (p. 13). To Duff’s
principles of translation (1992), it indicates “source language influence”, in
which the translation sounds like the original (para. 10).
2) "Well, if you know how to read, why are you just a shepherd? (p. 5)"
“Eh, kalau kamu bisa baca, kenapa cuma jadi gembala? (p. 8)”
Method of Translation : Modulation
'well' is quite vary, sometimes can be interpreted as other opening expressions,
which are usually used in informal conversations. This case is closely related
to Duff’s (1992) “register” (p. 10). The tone in the translation version
transformed into the less formal form. Here were the other alternative
expressions with word ‘well’ found on Part One of the novel:
"Well, interpret the dream," he said (p. 14). “Oke, tafsirkan mimpi itu, “ katanya (p. 17).
“‘Well,' asked the wise man, 'did you see the Persian tapestries that are hanging in my dining hall? (p. 33)”
“Nah,” tanya orang bijak itu, “apakah kamu melihat tapestri Persia yang tergantung di ruang makanku? (p. 36)”
And also in Part Two:
"Well, why don't you go to Mecca now?" asked the boy (p. 57). “Kok, Bapak tidak pergi ke Mekah sekarang?” tanya si bocah (p. 61).
3) They were content with just food and water, and, in exchange, they generously
gave of their wool, their company, and—once in a while—their meat (p. 7).
Mereka puas hanya dengan makanan dan air, dan, sebagai imbalannya,
mereka dengan murah hati memberikan wol, rekan mereka, dan – sesekali –
daging mereka (p. 9).
Method of Translation : Contextual Conditioning
relationship of the meaning of 'friend'. Researcher believed in this sentence,
the intended meaning for word ‘company’ was more likely as ‘friendship’
than ‘friend.’ If it means ‘friend’, the sense collides with the next phrase,
about giving their own flesh. 'Giving their friend' can also mean choosing
between them for slaughter. In the end means the same: give the meat. This
was one of translators’ inaccuracies that can cause unnaturalness sensed by the
reader who is quite meticulous in understanding the meaning of the text. Duff
(1992), in his principle “meaning”, suggests translator to “check the meaning
of the original text whether or not it is clear enough or underlying
implications” (p. 10).
4) At other times, at a crucial moment, I make it easier for things to happen (p.
24)
Di waktu lain, pada saat genting, aku mempermudah terjadinya hal-hal
yang muskil (p. 27).
Method of Translation : Contextual Conditioning
Procedure of Translation : Translators put information within a context to clarify the meaning. ‘Things’ later clarified as ‘hal-hal yang muskil’ to
emphasize the difficult ones. ‘Muskil’ itself is a word that was adopted uptake
of Arabic, which happened to fit appropriate setting of this story, which also
b. Thought
5) The boy's name was Santiago (p. 3).
Nama Bocah Itu Santiago (p. 5).
Method of Translation : Adaptation
Procedure of Translation: Adapted the subject or doer into local / target
language perception. Here ‘boy’ translated as ‘bocah’. This may be the
weirdest and most annoying detail that carried throughout the story. This even
triggered a critic in a internet fan page review of the novel. ‘Bocah’ in
Indonesian perception will be considered as ‘any kids, usually at
pre-teenage’, or Pusat Bahasa Departemen Pendidikan Nasional Republik
Indonesia through KBBI Daring refers it as ‘anak (kecil); kanak-kanak’
(“Bocah”). If we go into the details of the story scattered throughout this
novel, it is known that at minimum Santiago the shepherd was a teenager, and
more suitable for the so-called 'pemuda', or; another alternative; 'anak muda’
that indicates a bit of maturity. The use of the imposed meaning ‘bocah’
would violate some parts of the story that create the sense of maturity of the
main character himself, such as follows.
This part clearly indicates that the boy falls in love with a girl, a psychological
condition that generally are experienced by young men.
That he had attended a seminary until he was sixteen (p. 8).
This apparently estimates that the age of the young man now is more than
sixteen years old, during which some time ago he decided to quit from the
seminary to become a wandering shepherd with his sheep.
Some other situations that also support the view of the maturity of the main
character: the wine he drinks as part of his dinner, philosophical talks with
Melchizedek the Old King of Salem, and his desire to have a sword when he
saw it in a marketplace of Tangier. Overall, those were things that seemed
impossible to be owned or performed by a character who is a child, or younger
than teenage. As Robinson’ principles of translator reliability (1997),
translator needs to give “attention to the details” (p. 12). To Suryawinata this
then means that the translators had less flexibility of cognitive and
socio-cultural (para. as cited in Haryanti, 2006, p. 169).
6) There, he could exchange his book for a thicker one, fill his wine bottle,
shave, and have a haircut; he had to prepare himself for his meeting with the
girl, and he didn't want to think about the possibility that some other shepherd,
with a larger flock of sheep, had arrived there before him and asked for her
Di sana dia dapat menukarkan bukunya dengan buku yang lebih tebal, mengisi
botol anggurnya, bercukur dan potong rambut; dia harus mempersiapkan diri
untuk pertemuan dengan gadis itu, dan dia tidak ingin memikirkan
kemungkinan ada gembala lain, dengan kawanan domba yang lebih banyak,
sampai duluan di sana dan melamarnya (p. 14).
Method of Translation : Form Change and Contextual Conditioning
Procedure of Translation : Translators translated figurative expression of ‘ask one hand’ into ‘melamar’. An accurate translation, although the imperceptive
readers may need to imagine themselves further of the context: the scene of a
young man knelt down and grabbed a young woman’s hand to kiss, to say a
proposal. A perfect image that quite often appears in romantic tales
well-represented by a single verb: ‘melamar’. To Duff’s principles (1992), this
case belongs to “style and clarity”, in which suggests translator to “maintain
the style of original text and simultaneously make adjustment for the reader’s
sake” (p. 10). To Robinson’ (1997), it indicated “sensitivity to the user’s needs
(type of translation desired)” (p. 13).
7) "It describes people's inability to choose their own destinies … (p. 18)”
“Ia menggambarkan ketidakmampuan orang untuk memilih Legenda Pribadi
mereka sendiri … (p. 21)”
Procedure of Translation : Quite intriguing to look at this sentence translators took the initiative to create a new phrase itself as an alternative translation for
the word 'destiny', which is actually quite easy to digest in Indonesian context
as the popular: 'takdir' or 'nasib'. But researcher tends to assume that they
decide to 'borrow' a direct translation for the phrase 'Personal Legend' that
will appear later in the story, and use the translation for both original words /
phrases alternately.
8) "Rather than finding a saintly man, though, our hero, on entering the main
room of the castle, saw a hive of activity: tradesmen came and went, people
were conversing in the corners, a small orchestra was playing soft music, and
there was a table covered with platters of the most delicious food in that part
of the world … (p. 32)”
“Tanpa mencari orang bijak itu dulu, pahlawan kita langsung saja memasuki
ruang utama istana itu, melihat macam-macam kegiatan: para pedagang
datang dan pergi, orang-orang berbincang di sudut-sudut, orkestra kecil
memainkan musik yang lembut, dan ada sebuah meja yang dipenuhi
piring-piring makanan terlezat yang ada di belahan dunia tersebut … (p. 35)”
Method of Translation : Adaptation and Contextual Conditioning
Procedure of Translation : The phrase 'a saintly man' in English, which borrows the concept of respect for 'saint' or 'santo; orang suci' in
of the Moslem majority in Indonesia, which may have different language
expressions of respect for their religious figures. The next part, once again, is
an imaginative translation. 'A hive of activity' as an image of
‘macam-macam kegiatan', or we can simply call it 'kesibukan', as in a hive of bees,
where each of them seems busy doing something specific, just like people
busy doing their own business.
9) The sun began its departure, as well (p. 40).
Matahari pun mulai membenam (p. 43).
Method of Translation : Contextual Conditioning
Procedure of Translation : The translation of this figurative sentence applied a personification. The sentence describes that the Sun 'began its departure', as if
he would go, leaving his original position. This was then interpreted as a
change of time between light and dark, between noon and evening, at which
time the sun ‘mulai terbenam', which in this sentence was expressed as ‘pun
mulai membenam’, unusual in word ‘membenam’. Duff’s “form” principle
allowed “form and word order changes in the target language, due to language
structure differences”, but in this case translators were less natural in using
form as it should, which was also suggested by Larson: “use normal language
forms of the receptor language” and Polet: “the translator should avoid
Latinate and unusual forms” (Duff, 1992; Larson, 1984, Polet, as cited in
10)In half an hour, he had cleaned all the glasses in the w