Analisysis of Factor That Affect the Opinion of the BPK Regional Financial
Gavernment Report In Indonesia
a
Faculty of economics of Slamet Riyadi university Surakarta b
Faculty of economics of Slamet Riyadi university Surakarta Corresponding e-mail: [email protected].
Abstrak : The purpose of this study is to know BPK’s opinion on the local government financial report is the factor of discovery of the number of cases of regulatory noncompliance and the discovery of the potential value of state losses, on the quality of audit opinions on the financial statements of regional gevernments in indonesia. This research mothod is done by census. Sampling technique using the method of sampling with porposive sampling. With sampling based on subjective considerations. The purpose of this study is to determine the level of unity of regulation to the quality of the audit opinion of local financial statements in indonesia and to determine the effect of potential state losses on the quality of audit opinion of local financial statements in indonesia. Analysis motion used multiple linear regression analysis through by program eviews 9. The results of this study show that the number of cases of noncomliance and regulation the amount of potential value of the state losses has a negative affect on BPK’s opinion on the financial statements of local governments in indonesia.
Kaywords: Audit opinion; Number of cases of noncompliance regulation; Case value of potential losses of the country.
1. INTRODUCTION
In the government regulation of a country there must be regulation abaut the
mechanism of accountability
governmant/leadership state/regional leaders with the community led him as a from transparency and accountability of a budget the countries they manage The standart of government accounting (SAP) number 24 of 2005 and the low number 17
of 2004 which requires
governor/regent/mayor to submit accauntability or realization report APBN/APBD, cash flow statements and reports notes to the financial statements. In the government accounting standard (SAP) financial statements should be prepared andpresented based on principles of goverment accounting standard (SAP). Is a requirement to improve the quality of government financial reports so that the information presented in the financial statements can be understood by the use.
And meet the characteristic criteria of government financial statements as law number 24/2005 and legislation of low number 71 of 2010 on accounting standards. According to (COSO and AU319) Consideration of internal control in the financial statements audit (SAS78) identifies the five components of internal control which is interconnected ie the environment control risk assessement activity control, information, communication and monitoring activities Control, information, comunication and monitoring.
considering the relevance of the financial statements. Findings of non-compiance with statutory provisions may result in
loss of state/region/company
ineffectiveness, waste, inefficiency of badget and lack of budgetary revenues, administration.
Equalified opinion (WTP) by the supreme audit board (BPK) is very important to the local government financial statements (LKPD) to show that the LKPD has a good degree of transparency so as to create a good level of plant accountability. Compliance audit is conducted to determine whether the audite has followed a specifik set of procedures and regulations established by the higher authorities Opinion or professional statement to check the fairness of the financial information presented in the financial atatements which are based on law number 15 of 2004 on the audit of state financial management and accountability the BPK audit opinion is given based on the following general criteria: 1). Conformity with (SAP) governmant accounting standards 2). compliance with applicable laws and regulations 3). Effectiveness of the government’s internal control system (SPIP). Audit opinion of BPK RI concsists of four opinions ie unqualified (WTP), Qualified opinion (WDP), Adverse opinion (TW), and disclaimer opinion (TMP).
This study aims to analyze the effects of regulatory non-compliance and potential state losses to the quality of audit opinions given to the local government financial statements LKPD as a means of communication of financial information to parties having interests so that every financial report of the region must be in accordance with applicable laws and regulations that is SAP number 24 of 2005 and the law number 17 of 2004. The financial statements that must be reported by the head of the government agency are
one from of accountability mechanism and as a for decision making for external parties or parties that rival or stakcholder for decision making. In this study aims to whether the level of regulatory non-compliance affect the quality of audit opinion of local financial statements in indonesia and whether the potential losses of the state affect the quality of opinion audit local financial statements in indonesia.
2. THEORETICAL BASIS
A. The Agency Theory
The agency theory according to jasen and meckling (1976) is the theory that link between agents (managers of the company) with the principal (owner of the company). Which is bound in the contract. Namely the agent as the party who run s the company and take decisions and the principal is the party that evaluates the performance of the agent. Thus, the agent as the manager of the company has an obligation to report its performamce to the principal. One of the information reported by the agent to the principal is about the company’s financial statements. According to davis and friends as quoted in ( Adzani and Martani, 2014) against the assumption that principal and the agent is a homo ecomomicus, principal parties and agents together want to gain maxsimum benefit for the parties themselves which will cause a conflict of interest.
inspection of accountants accompanied by an opinion about fairness of financial statements in the check. 1) compliance with government accounting standarts 2) adequancy of disclosure 3) compliance with low and regulations 4) effectiveness of internal control system. The cualitative haracteristics of government financial statements ie normative meansure size that must be met in the accounting information so that it can achieve that objectives of
relevant, reliable,
comparable and
understandable.
2) Non Compliance Regulation The regulationship between agents and principals according to (kurniawan, 2008) regulation is a provision used to regulate the relationships between people in a society and or a country. Accoding to (Bastian, 2010) public regulation is a provision that must be followed in obedience in the process of
managing public
aorganizations both at the
central government
organization local
government political parties foundations LSM religious oeganizations and other social organizations. According to (Bastian, 2010)
local goverments,
governors/Regents/Mayor may draft regulations on goverments accounting systems referring to government regulations and
the provisions of legislation on regional financial management (legislation regulation number 71/2010 article 6, paragraph 3). The more complete/availability of system implementers and regulatory procedures on local financial management in each SKPD it will be easier to arrange and produce quality financial reports. The potencial loss of the country/region is a real loss in the from of reduced state assets in accordance with the definition of act number 1 of 2004 article 1 point 22, but still a risk of loss if a condition that could result in loss of state/region actually happened in the future. The potential loss of the state influences the quality of audit opinion, According to (IHPS 1 year, 2015) Problems of potential regional losses in general occur because: 1) officials responsible responsible for negligent and inadequate in obeying and understanding the provisions in force, 2). not optimal in carrying out duties and responsibilities, 3). not optimal in coordinating with related parties, 4). weak in the supervision and control of assets, and 5). has
not appropriately
implemented reclamation guarantee policy
occurs due to the absence of clear accounting policies and treatment, SOP has not been established, responsible officials have not / have not
recorded accurately,
inadequate coordination with related parties, and weak in supervision or control, besides the problem of SPI weakness also occurs because the responsible officials do not comply with the existing rules and procedures and not yet optimal in following up the BPK's recommendation on
the previous LHP
(www.bpk.go.id).
B. Hypotheses
Based on the definition of oprasional and the frame of thought generates a hypothesis Influence of non-compliance Regulation and quality of audit opinion, Law No. 17 of 2003 suggests that government accountability reports or government financial statements should in turn be audited by the Supreme Audit Agency (BPK). Before being submitted to the legislature in accordance with its authority. Audit of BPK in the intention is in the framework of giving opinion (Opinion) as mandated by Law No. 15 of 2004 on audit of management and responsibility of State Finance. Examination of LKPD conducted by BPK is guided by State Audit Standards (SPKN) stipulated in BPK Regulation Number 1 Year 2007.
The issue of non-compliance resulting in state losses, potential state losses and lack of revenues is a matter of non-compliance with financial impacts explained at IHPS 1 year, 2015. While administrative
irregularities and non-compliance issues resulting in inefficiencies, inefficiencies, and inefficiencies are non-compliance issues that have no financial impact.
The results (Aryanto and Suhartini, 2009) state that compliance with laws and regulations is used to consider giving LKPD opinion. Summary of Second Semester Examination Result (IHPS) Year 2010 is prepared to fulfill the mandate of Law Number 15 Year 2004 regarding Audit of state financial management and responsibility IHPS submitted to DPR / DPD / DPRD in accordance with its authority, and to the president and the governor / regent / mayor concerned in order to obtain information thoroughly about the results of examination of the Supreme Audit Agency (BPK).
Based on the BPK Regulation No. 1 of 2007 on the SPKN, it is stated that the LHP on LKPD must disclose that the examiner has tested the compliance with the provisions of laws that directly and materially affect the presentation of LKPD
impact on the realization of accurate information delivery to the public.
The relevance of compliance to the provisions of the legislation and the effectiveness of the internal control system to the giving of opinion on the government financial statements has clearly become the basis or criteria of 4 opinions by BPK according to the Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 1 Year 2004 on the explanation of article 16 paragraph 1 According to (RM Syah Arif, 2015) more and more findings of cases of non-compliance with legislation indicate that local government performance is poor and accountability is also poor. Improper local government performance can lead to state losses.
In the study (Natuita Nuhoni,
2015) non-compliance with
legislation affects the credibility of local government financial statements represented by BPK's opinion. The
lower non-compliance with
legislation is likely to gain a better opinion on the research (justisia Sulastri M et al, 2014) that non-compliance with laws and regulations resulting in potential regional losses (NPKD) has no significant effect on the provision of TMP, TW, WDP, WTP-DPP and WTP opinion. So in this study formed the following hypothesis:
H1: non-compliance of regulation in local financial report have an effect on to quality of audit opinion of government financial report in indonesia.
1) Potential State Losses And Quality Audit Opinion The potential loss of the state / region is a real loss in the form of loss of state property in accordance with the meaning of Act No. 1 of
2004 article 1 point 22, that is causing the loss of the state which is still in the form of risk of loss, if a condition that can cause loss of state / happens later on. The potential loss of the state is very influential on the quality of audit opinion In research in (RM Syah Arief and friends, 2005) that the more findings of state losses cases are found, the lower the fairness of the financial statements and accepting the unreasonable (WT) and Not Giving Opinion (TWP) opinions. Governmental organization operates in and runs on the basis of applicable law. The results of the examination (CPC semester 1, 2014) resulted in the findings of 5,948 cases of weakness of SPI. the weakness of the control
system of the
implementation of the budget of income and expenditure is the highest with 2,498 cases or 42% of the total weakness
of SPI. The
recommendations are SPI
improvements or
for the financial statements in the audit, then detection of the level of state losses will greatly affect the level of quality of audit opinions prvided.
In cases of non-compliance with the legislation there are 7,173 cases worth Rp. 10,928,527.26 million, of which there are indications of loss of State / Region as much as 418 cases worth Rp. 400,659.93 million. at the time of auditing the findings of non-compliance with statutory provisions may result in losses of state / region / enterprise, potential loss of state / region / company, lack of acceptance, administration, inefficiency,
inefficiency, and
ineffectiveness. Hence the hypothesis is formed as follows:
H2: the influence of the level of potential state losses on the quality of audit opinion of local government financial statements in Indonesia.
3. RESEARCH METHODS
A. Scope of Research
The scope of the study used census method with Local Financial Report (LKPD) from 2008 to 2014 that is 7 years so it can strengthen the result of previous research. Local government finance report (LKPD) year 2008-2014 data source from Indonesia financial supervisory board (BPK)
B. Types And Data Sources
1) Data type
Qualitative data, namely LKPD data in the can of quantitative data is data in the form of numbers or qualitative data. Qualitative data in this study is the data of local financial statements (LKPD) that have been audited in 2008-2014 in all provinces in Indonesia. 2) Data source.
Secondary Data,
Secondary data sources in this study were obtained from the Supreme Audit Agency (BPK), data in the form of softfile (LKPD) financial reports of local government districts, cities and provinces in Indonesia in 2008 until 2014.
C. Technical Data Analysis
Using purposive sampling method with sampling based on subjective consideration and research objectives.
D. Stages of Eviews analysis.
Technical analysis of data used is regression analysis Estimated data panel model It is the simplest technique to estimate panel data model parameters by combining cross setion and time series data as a whole regardless of time and entity differences.
E. Model Selection
1) Housman test
Is used to compare which model is most appropriate between fixed test or random effects testing if probability> 0.05 then the best model is fixed test. If Probability> 0.05 then the best model is random effects testing.
2) The LM-test
Is used to compare which model is most appropriate between fixed test or random effects testing. 3) Testing Classic assumptions
feasibility test model of panel data regression There are two types of hypotheses to the regression coefficients that can be done are:
a) F test
is intended to test the regression coefficient hypothesis together. b) T test
is intended to test the regression coefficient hypothesis one by one. F. Koefisien Determinasi
A measure to inform whether or not the regression model is being estimate. This analysis is used to determine the effect of free variables (non-regulatory compliance and potential state losses) on the dependent variable (audit opinion quality). Namely with the formula: OA = a - K_Reg - PK + e Information:
OA : Quality of Audit Opinion A : Kontanta
K_Reg : Non-compliance Regulation
PK : PotentialNational Disadvantages E : Error
4. DATA ANALIYSIS AND
DISCUSSION
A. Selection analysis regression model
1) Analisis common test
This model is used to test all models Model Analysis Using Redundent / Chow Test Chow test is done to compare which model is the best between common effect and fixed effect model. Determination is by observing the value of probability. For cross-section F. Compare niali (prob.) With α (0.05). Decision Making If the probability of chi square <0.05 then the selected is fixed effect if probability> 0.05 then the selected common effect.
Tabel III
Analisis Uji Rudendent/Chow
Effects T Statistic d.f. Prob
Cross-section F
4. 971485 (485,2914) 0.0000
Cross-section Chi-square
2051.127067 485 0.0000
From the model test the probability of chi square shows the number of 0.0000 <0.05 from the level of negligence, it can be concluded based on Chow test, that the fixed effect model is more appropriate to use.
Variable Coefficient t-Statistic Prob.
KREG -0.023777 -8.901871 0.0000
2) Model Analysis With Hosman Test
Hosman test is
conducted to compare between the most appropriate model between Fixed effect model and Random effect. To determine the model can be seen from prob. For cross cross-section. Compare Probability with α (0.05).
decision making If
probability> 0.05 then selected random effect if probbability <0.05 then selected fixed effect.
Tabel IV Analisis Uji Hosman
Test Summary
Chi-Sq. Statistic
Chi-Sq.
d.f. Prob. Cross-section
random 2.406594 2 0.3002
The model analysis table using this hosman test addresses cross-section with prob. <0.05, that is with the value of 0.3002 so it can be concluded that from this hosman test results that the Random effect model is more appropriate to use. 3) Model Analysis with
Lagrange Multipliner Test (LM)
The lagrange
multiplinier (LM) test is used to compare which model is more appropriate between the cammon effect model and the random effect model. The value (LM) count will be compared with the value of p value of the table with degrees of freedom (degree of freedem) as much as the
number of independent variables and alpa / significance of 5% (0.05). If LM counts> alpa (0,05) table then the best model is cammon effect. If LM counts <alpa (0.05) (table then the most appropriate model is the random effect model.) In this method use the breusch-food method.
Tabel V
Analisis uji Lagrange multiplinier (LM)
Test Hypothesis
Cross-section
Time Both
Breusch-Pagan 1330.577 16743.44
18074. 01 P-value (0.0000) (0.0000) (0.0000)
From the above data can be concluded that the most appropriate model is the Random effect model. Can be seen at the top of cross-section food breusch table shows Lagrange Multiplier Tests for Random Effects P-value with P-value 0.0000 <0,05 alpa. So it can be concluded that the most appropriate model chosen in the Lagrange Multiplier (LM) test is the Random effect model.
models are Cammon Effect (CE), Fixed Effect (FE), and Random Effect (RE), ie Random Effetc (RE) model is better in interpreting panel data regression in this research.
B. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
Multiple linear analysis is a lenier relationship between two or more
variables of regulatory
incompatibility and potential loss of state with independent variables of audit opinion quality. This analysis is to know the correlation between independent variable with dependent whether each independent variable is positive or negative and to predict the value of independent variable increase or decrease.
1) Non-compliance of regulation and potential loss of state. Based on the data processing can be obtained the regression results seen in table 9 to obtain the equation of multiple linear lines as follows:
OA = Audit Opinion
C = coefficien
KREG = Regulation Non-
compliance
PK = Potential Losses
State
OA = C-KREG -PK
C. Test The Classical Assumption
The classical assumption test is needed to fulfill the assumption that the model can be used as a good predictor or test performed on each ordinary least square linear regression test (OLS). However, in the research data usually face some problems in the model that is problem multicollinearity, heterokedastisitas,
Autokorelasi and Normalitas so model need to be tested assumption klasi to see problem problem in that assumption.
1) Multicollinearity test
According to Ghozali (2005), this test aims to detect whether independent variables in the regression model are correlated. In the calculation is that if the variable value below 0.8 means free of multicollinearity or there is no multicollinearity.
Tabel VI Uji Multikolinieritas
Multicolinearity assumption assumed that from each independent variable from Multicollinearity problem that is variable of regulatory non-compliance (KREG) has value of 0.078826 <0,8, and variable of Potential Losses (PK) also have value of 0.078826 < 0.8 hence can be concluded this model is
free from problem
Multicolinearity. 2) Normality Test
The standard assumption test for the normality test is the most important test that shows the data must be Normal distributed. That the goal of the normality test is to test whether the regression model of the independent variable has a normal distribution of prob values. has a smaller value <0.05 then the residual distribution is said to be abnormal.
Variable KREG PK
KREG 1.000000 0.078826
Tabel VIII Uji Normalitas
Jarque-bera Probability
84.76270 0.000000
The result of residual normality test above is jarque value bera equal to 84.76270> with p value equal to 0.0000 where <0,05 means the residial is not abnormal distribution. The data in this study uses Panel data that has distrubusi that can not be measured. and the goal of normality test is to know whether the data does not deviate too far from the average value. And panel data in this research has extream value from 0 - more than 3000 range, because each of each region has different result of financial report. So in panel data resulted in abnormal distribution (Akhmad Azhari, 2016).
3) Descriptive Statistics
Analysis is done to assess the characteristics of a data. From the above data shows for the value of audit opinion with Maxsimum value of the best Opini with a value of 5 is unqualified opinion (WTP). With minimum value or low pse ng audit opinion that is 1 with disclaimer / Not Giving opinion (TMP) opinion. The value of Non-compliance Regulatory (KREG) with the highest non-compliance with 56 regencies in South Buru regency (Maluku) in 2010. And the minimum value is 0 or no cases of regulatory non-compliance. And the value of potential loss (PK) With the highest potential loss value of 1029,829.34 (In million rupiah) that is obtained by the City of
Sukabumi in 2010 and with the lowest value or Minimum is 0 million or equal to no potential losses
5. HYPOTHESES TEST
Furthermore, to examine whether the effect of regulatory non-compliance and potential state losses on the quality of BPK audit opinion, significant either simultaneously or partially (individually), tested significance. Testing starts from simultaneous testing, and if the simultaneous test results are significant it is continued with partial test.
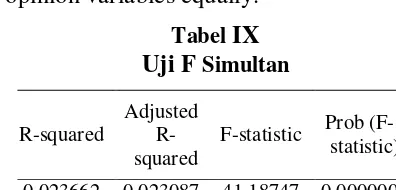
Hypothesis test of significance simultaneously (F-test) Used to prove whether simultaneously or simultaneously all independent variables ie regulatory incompatibility and potential state losses affect the dependent variable is the quality of audit opinion. Can be seen on prob. (F-statistic) ie if prob. (F-(F-statistic) has a value less than <0.05 then KREG and PK variables affect the quality of Audit opinion, If prob. (F-statistic) has a value greater than> 0.05 then KREG and PK variables do not affect the quality of Audit opinion variables equally.
Tabel IX Uji F Simultan
R-squared
Adjusted R-squared
F-statistic Prob (F-statistic) 0.023662 0.023087 41.18747 0.000000
A. Partial Test of Hypothesis T-Test
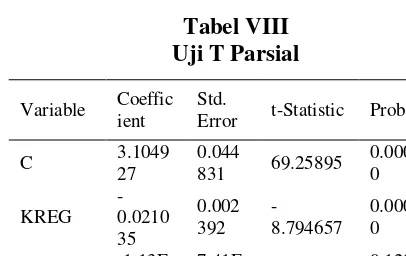
This test determines whether the presence of influences independently or influential together with the independent variable with the dependent variable. Can be said variable partially / individual effect on the dependent variable can be seen from the value of its significance if the independent variable has a prob. > 0.05 then it can be said individually These variables affect the dependent variable
Error t-Statistic Prob.
C 3.1049 study using a partial test (t-test)
That is seen from prob. The regulatory non-compliance variable (KREG) has a prob. 0.0000 <0.05. Which means the variables of regulatory incompatibility (KREG) have an individual effect on the dependent variable is the quality of audit opinion. So hypothesis one (H1) is acceptable. And reject H0, Ie regulatory unity on the financial statements of the region affects the quality of audit opinion of government financial statements in Indonesia.
H2: In the table results of this study using a partial test (t-test)
That is seen from prob. State Loss Potential Variable (PK) has prob. 0.1286> 0.05. Which means the potential variable of state losses (PK)
No individual influence on the dependent variable is the quality of audit opinion. It means Rejecting the hypothesis of two (H2) and accepting H0, ie there is no influence of the level of potential state losses on the quality of the audit opinion of local government financial statements in Indonesia.
B. Coefficient of Determination
coefficient of determination (R2 or R2 adjusted) is used to measure how much variation of the value of independent variables, can be explained by the variable independent variable. and also used to show the 0.023662 0.023087 41.18747 0.000000
From the results of this analysis shows the value of adjusted R-squared worth 0.022093 means interspestation 2.3% variation of independent variables and the remaining 98% explained by other variables. The coefficient of determination is 0.022093. This figure explains that 2.3% noncompliance and potential state losses affect the quality of audit opinions. While the remaining 97.7% of Audit opinion quality influenced by other variables that are not examined in this study.
all the information needed to predict the dependent variable variable. Imam Ghozali, 2014: 97) stresses that: the coefficient of determination is only one and not the only criterion in choosing a good model. The reason for which a linear regression estimate produces a high coefficient of determination but is inconsistent with the economic theory chosen by the study, the model is not a good estimator model and should not be chosen by empirical model.
6. DISCUSSION
A. Non-compliance Regulation affects the quality of audit
opinion Non-compliance
regulation
That is seen from prob. The regulatory non-compliance variable (KREG) has a prob. 0.0000 <0.05. Which means the variables of regulatory incompatibility (KREG) have an individual effect on the dependent variable that is the quality of audit opinion with the value of coefficien -0.021035. So that the non-compliance of regulation in local financial report have a significant effect Negative to the quality of audit opinion of government financial report in Indonesia. The fewer cases of non-compliance with regulation will result in better Audit opinion to be given to LKPD.
Hasis of this study In accordance with previous research conducted by the results of research (Aryanto and Suhartini, 2009) states that compliance with legislation is used to consider giving opinion LKPD. According to (Sipahutar and Khairani, 2013) the degree of non-compliance of the entity to the legislation and the suitability of the presentation of the
entity's financial statements affects the giving of opinion by the auditor. According to Defera (2013) materiality, SAP violations, SPI weaknesses and non-compliance with the laws and regulations do not affect disclaimer opinion. Ccording to (Darmawati, 2017), the weakness of the internal control system, the inability of the legislation and the follow-up of the recommendation of the examination result has a significant negative effect on the BPK opinion.
B. Potential losses of the state affect the quality of Audit opinion
The potential loss of the country / region is a real loss in the form of loss of state property in accordance with the meaning of Act No. 1 of 2004 article 1 point 22, but still a risk of loss if a condition that can lead to loss of state / region actually happened in the future. In this study, the State Loss Potential (PK) does not directly influence the quality of audit opinion.
The results of this study indicate that the potential value of state losses has no effect on the provision of audit opinion on the local government financial statements (LKPD) in Indonesia. this result is the same as previous research by (justisia Sulastri M et al, 2014). shows non-compliance with laws and regulations that cause potential regional losses have no effect on the provision of BPK-RI audit opinion on LKPD.
7. CONCLUSION OF
LIMITATIONS AND SUGESTIONS
A. CONCLUSION
with a total of 3403 data samples. The regulatory non-compliance variable
(KREG) of regulatory
non-compliance (KREG) has a significant negative effect on the quality of BPK audit opinion. Potential Variable State Loss (PK) potential state loss (PK) No individual influence on the quality of audit opinion. This study shows that the higher non-compliance regulation will result in the higher the value of potential losses of the state.
B. LIMITATIONS
The data we get using LKPD and IHPS because there is data contained in LKPD we have difficulties in determining the potential losses of the state so that we use IHPS data as a summary of the potential value of state losses. Samples that can be processed in this study as many as 486 LKPD there are areas that can not be included in this study due to lack of completeness of the data because this research data using panel data with LKPD object in all Indonesia so causing the number of samples in this research is very much n as many as 3402, so it is very difficult to determine the elaboration of Autocorrelation and Normality test so that in this research not pass Autocorrelation test of assumption test Normality. This means that the variables Regulation non-compliance and potential state losses used in this study are only able to explain 2% variability of dependent variables. 98% is explained by other variables.
C. SUGGESTION
1) For local government
In order to further improve the compliance with existing laws and conduct supervision of the Internal Control System to run in accordance with the
Standards that have been established, so that will have an impact on Decrease the findings of cases of non-compliance of regulations that will affect the acceptance of Unqualified Opinion (WTP) by BPK, and have an impact on increasing the accountability of the pablic so as to realize good governance. 2) For further research
Because the data I get in this study only contains two variables that show variables Regulation non-compliance affect the quality of audit opinion and the potential variable of state losses do not affect the quality of audit opinions that cause the value of R2 / R -Ajusted 0.022093 so that there are 98% variable The quality of audit opinion is influenced by other variables so that the researcher should continue to examine other variables with more.Such factors are the factors causing non-compliance regulation such as 1) responsible officials are negligent and inadequate in obeying and understanding the applicable provisions, 2). not optimal in carrying out duties and responsibilities, 3). not optimal in coordinating with related parties, 4). weak in the supervision and control of assets, and 5). has not appropriately implemented reclamation guarantee policy.
8. BIBLIOGRAPHY
Keuangan SKPD Di Lingkungan Pemerintah Kabupaten Simeulue.
Jurnal Akuntansi. Magister
Akuntansi Pascasarjana Volume 5, No. 2, Mei. Universitas Syiah. Kual. Adzani, A. H., dan martini, D.2014
pengaruh kesejahteraan masyarakat, faktor politik dan ketidakpatuhan regulasi terhadap opini audit laporan keuangan pemerintah daerah.
Simposium nasional akuntansi XVII.
Mataram.
Ahmad A.K. Muda, Kamus Lengkap Bahasa Indonesia, (Jakarta: Reality Publisher, 2006).
Azhari Akhmad. 2016. Uji asumsi klasik autokorelasi, heterokedastisitas, multikolineritas dan normalitas untuk data panel dengan SPSS,
Eviews dan Stata.
http://learnforfinance.blogspot.co.id /2016/02/Uji-asumsi-klasik
autokorelasi.html. Diakses tanggal 16 februari 2018.
Ardianingsi, Arum. 2012. Analisis Mekanisme Corporate Governance Pada Pemberian Opini Audit Dengan Penjelasan Going Concern.
Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis. Volume
11. Nomor 01. September.
Arens, et al. Auditing and assurance service an integrated approach sixteenth edition. Person education limited.
Arifin, I & Fitriasari, D. (2014).
Pengungkapan laporan
kementrian/lembag, karakteristik organisasi dan hasil audit BPK.
Simposium nasional akuntansi XVII.
Mataram.
Atmaja, RM Syah Arif Dan Prabohudono, W Agung Nur. 2015. Analisis audit BPK RI Terkait kelemahan SPI, Temuan Ketidakpatuhan Dan
kerugian Negara. Jurnal
AntiKorupsi INTEGRITASI (1):
81-110. Diakses tanggal 27 oktober 2017.
Badan pemeriksa keuangan RI. 2007.
Peraturan badan pemeriksa
keuangan RI No 1, tahun 2007
tentang SKPN. Jakarta: Badan
pemeriksa keuangan RI
Badan Pemeriksa Keuangan. 2011, Iktisar
Hasil pemeriksaan Semester1 tahun
2010.
Badan Pemeriksa Keuangan. 2014, Iktisar Hasil pemeriksaan Semester 1 tahun 2013.
Badan Pemeriksa Keuangan. 2015, Iktisar Hasil pemeriksaan Semester 1 tahun 2014.
Badan Pemeriksa Keuangan. 2016, Iktisar Hasil pemeriksaan Semester 1 tahun 2015.
Badjuri, achmad. 2012. “analysis faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi kualitas hasil pemeriksaan audit sektor publik (studi empiris pada bpkp perwakilan jawa tengah)”. Dinamika
Akuntansi, Keuangan dan
Perbankan. Vol. 1,No. 2,
Nopember, Hlm. 120 – 135.
Bastian, Indra. 2010. Akuntansi Sektor
pablik. Suatu pengantar. Edisi Tiga,
Jakarta : Salemba Empat.
COSO. 2013. Internal Control-Integrated Framework. The Committee of Sponsoring Organization of the
Treadway Commission. The IIAI
Research foundation, Florida.
Darmawati, 2017. Pengaruh kelemahan sistem pengendalian internal, ketidakpatuhan terhadap peraturan perundang undangan dan tidak
lanjut rekomendasi hasil
pemeriksaan terhadap opini BPK.
Sekripsi (tidak dipublikasikan)
Damayanti. 2017. Pengendalian dalam
sistem informasi.
http://medium.com/@khristdamay/p
engendalian-dalam-sistem-informasi. Diakses pada tanggal 16 februari 2018.
De Anngelo. L. 1981. Auditor Independence, Low Balling, and disclosure Regulation. Jurnal Of
Accounting and Economics.
Defara, Cris. 2013. Pengaruh kelemahan sistem pengendalian intern dan ketidakpatuhan pada ketentuan perundang undangan terhadap penentuan opini. Sekripsi (tidak dipublikasikan) Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta. Gujarati dan porter. 2009. Dasar Dasar
Ekonometrika. Salemba Empat.
Jakarta
Jesen & meckling, 1976. The theory of the firm: manajerial behavior: Agency cost, and ownership structure,
jurnal of financial and economics,
3:305-306.
Justisia sulastri.M, Jenny.M, dan david P. E.Saerang. pengaruh kelemahan sistem pengendalian internal, ketidakpatuhan pada peraturan
perundang undangan dan
penyelesaian kerugian negara terhadap opini BPK RI atas laporan keuangan pemerintah daerah di indonesia.vol 5 no 2
Tobing, Halim J, Dan meiden (2004). Pengaruh Menejemen laba pada tingkat pengungkapan laporan
keuangan pada perusahaan
manufaktur yang termasuk dalam indeks LO-45. Simposium Nasional
Akuntansi VIII.
Hardiningsi, Pancawati. 2010. Pengaruh
Independensi, Corporate
Governance, Dan Kualitas Audit Terhadap Integritas Laporan
Keuangan. Program Studi Akuntansi.
Kajian Akuntansi, Vol. 2, No.1, Hal.
61-76. Pebruari 2010. Universitas Stikuban. Semarang.
Herawati, Tuti. 2014. “Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian Intern Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Keuangan (Survei Pada Organisasi Perangkat Daerah Pemda Cianjur)”. Jurnal accouting
Research. Vol XI, No. 1 – 2014.
Bandung Business School.
Hendarto, Thomas Gatot. 2006. Analisis penerapan konsep materialitas dan tindak lanjut audit atas suatu ketidakpatuhan terhadap peraturan perundang dalam pedoman audit BPK atas laporan keuangan daerah.
Tessis (tidak dipublikasikan)
Universitas Gajah Mada.
http://id.m.wikipedia.org>wiki>Ekonomi Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya
Mineral Republik Indonesia. 2014. Peraturan Menteri Energi dan sumber Daya Mineral Nomor 7
Tahun 2014.
Kurniawan, Wawan. 2008. Peraturan Perundang-undangan. Jakarta: Azka Press.
Koesoemahatmadja, R.D.H., 1979, Pengantar Ke Arah Sistem Pemerintahan Daerah di Indonesia,
Bina Cipta, hlm. 2017.
Koesoemahatmadja, R.D.H., 1979, Ibid, hlm. 30
Koesmana, Humbul., dkk. 2007. Peran auditor internal dalam mencegah dan mendeteksi terjadinya fraud menurut standart profesi. Economic Bussiness & Accounting Review, Vol 2/1:59-71.
Modul praktikum eviews 9. Analisis
regresi linier bergandan
menggunkan eviews. Fakultas ekonomi universitas borobudur.
http://www.google.co.id/search? di donwload pada tanggal 30 desember 2017.
Mulyadi. 2002. Auditing edisi keenam, cetakan pertama, jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Mulyadi 2009. Akuntansi Biaya. Yogyakarta: STIE YPKPN.
Mulyani, pujianik (2011). Analisis peran dan fungsi sistem pengendalian intern pemerintah (SPIP/PP No.6 2008) dalam meminimalisir tingkat salah sajipencatatan akuntansi keuangan pemerintah. Jurnal
organisasi manajemen vol 17 No.2
(oct. 2012).
Munawar. Nadiansyah dan Abdullah, Syukiry. 2016. Pengaruh jumlah temuan Audit atas SPI Dan jumlah temuan audit atas kepatuhan terhadap opini atas laporan
keuangan pemerintah
kabupaten/kota di Aceh. Jurnal magister akuntansi pasca sarjana
universitas Syiah Kuala. Volume 5
No. 2. ISSN 2302-0164.
Nalurita, Nuhoni. 2015. Pengaruh sistem pengendalian intern, ketidakpatuan terhadap psiperaturan perundang-undangan dan karakteristik daerah terhadap kredibilitas laporan keuangan pemerintah daerah di indonesia. Tesis. (Tidak di publikasikan) Pasca Sarjana Universitas Sebelas Maret.
Nisjar S. Karhi, 1997, Beberapa catatan Tentang Good Governance, Jurnal Administrasi dan Pembangunan, Vol. 1, No. 2, Himpunan Sarjana Administrasi Indonesia, Jakarta, hal. 19.
Nordiawan, Deddi dan Ayuningtyas Hertianti. 2011. Akuntansi Sektor
Publik. Edisi 2. Salemba Empat.
Jakarta.
Peraturan Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 24 tahun 2005 tentang peraturan pemerintah no 60 tahun 2008. tentang sistem pengendalian Interen pemerintah (SPIP).
____, peraturan pemerintah No. 58 tahun 2005 tentang pengelolaan dan pertanggungjawaban keuangan daerah.
____, peraturan pemerintah No. 6 tahun
2006 tentang pengelolaan barang
milik pemerintah/daerah
____, keputusan menteri dalam negeri
Nomor 12 Tahun 2003 tentang
pedoman penilaian barang daerah. _____, Peraturan menteri dalam negeri
nomor 17 tahun 2007 tentang
pedoman teknis pengelolaan barang milik daerah.
Republik Indonesia, Undang Undang Dasar tahun 1945 pasal 23 (1) tentang keuangan negara.
_____, Undang undang no 17 tahun 2003 tentang keuangan negara.
_____, Undang undang No. 1 tahun 2004 Tentang pembendaharaan negara _____, Undang undang No. 12 tahun
2008 tentang pemerintah daerah.
Jakarta ; Republik Indonesia.
_____, Undang undang No. 12 tahun
2011 jenis dan hiraki peraturan
perundang undangan
_____, Undang Undang No. 15 tahun
2004 tentang pemeriksaan
Pengelolaan Dan tanggung jawab Keuangan Negara.
_____, Undang- undang No 17 tahun 2013 tentang keuangan Negara. _____, Undang undang no 32 tahun 2004.
Tentang pemerintah daerah.
Septariana, Niegita. 2012. “Pemetaan Opini Audit Bpk Pada Kabupaten Dan Kota Di Provinsi Jawa Timur”.
Sekripsi (Tidak Dipublikasikan)
fakultas ekonomi universitas. Jember.
Setyarno, Eko Budi, Indira Januarti dan Faisal. 2006. “Pengaruh Kualitas
Audit, Kondisi Keuangan
Perusahaan, Opini Audit Tahun
Sebelumnya, Pertumbuhan
Perusahaan Terhadap Opini Audit Going Concern”. Simposium. fakultas ekonomi universitas diponegoro. Semarang.
Setiawan, Wahyu. 2012. “Pengaruh Akuntabilitas Laporan Keuangan
Pemerintah Daerah (LKPD)
Terhadap Tingkat Korupsi
Pemerintah Daerah Di Indonesia”.
Sekripsi (Tidak dipublikasikan)
Fakultas Ekonomika Dan Bisnis Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang. Siregar, Silky Raditya.2012. “Faktor –
Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Pertimbangan Opini Auditor Atas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta”.
Sekripsi (tidak dipublikasikan)
Jurusan Akuntansi Fakultas Ekonomi, Universitas Negeri Semarang, Indonesia.
Sipahuntar, H dan S. Khairani. 2013. Analisis perubahan opini LHP BPK
RI atas laporan keuangan
pemerintah daerah kabupaten
empat lawang. SETIE MPD. Jurnal.
Suhartini dan Dodik aryanto. 2012. pengaruh pemeriksaan interim, lingkup audit, Dan independensi terhadap pertimbangan opini auditor (Studi kasus pada BPK RI perwakilan provinsi Bali). Jurnal
Ilmiah Akuntansi dan bisnis Vol.5,
No. 1 Januari 2010.
Sussanto, Herry dan Nur Mettani Aquariza.2013. “Analisis Pengaruh Opini Audit Tahun Sebelumnya, Kualitas Auditor, Profitabilitas, Likuiditas, Dan Solvabilitas Terhadap Pemberian Opini Audit Going Concern Pada Perusahaan Consumer Goods Industry Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia”. Proceeding PESAT (Psikologi, Ekonomi, Sastra, Arsitektur & Teknik Sipil) Vol. 5 Oktober 2013 Bandung, 8-9 Oktober 2013.
Syarif, Nuh H.Muhammad. 2012. “Hakikat pertanggungjawaban pemerintah daerah penyelenggaraan pemerintah”. Jurnal Fakultas
hukum. Universitas Muslim
Indonesia Makasar.
UU NKRI 1945, penerbit Sekjen MPR RI 2014.
Widar jono, Agus 2007. Ekonometrika : Teori dan aplikasi untuk ekonomi
dan bisnis. Edisi ke 2. Jogjakarta:
ekonisia FE Universitas islam indonesia.
Widodo, oka purnawan dan Sudarno.
2016. “Pengaruh temuan
kelemahan sistem pengendalian intern dan temuan ketidakpatuan terhadap ketentuan peraturan perundang undangan terhadap opini BPK atas Laporan keuangan pemerintah daerah”. Skripsi (tidak dipublikasikan) fakultas ekonomika dan bisnis universitas diponegoro. Semarang.
www. BPK.go.id
Yustrianth, Rahmawati Hanny. 2012.
Beberapa Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Audit Judgment Auditor Pemerintah. jurnal
Akuntansi, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu