State University of Makassar
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MATHEMATICS,
SCIENCES, TECHNOLOGY, EDUCATION
AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
“Recent Research and Issues in
Mathematics, Sciences, Technology, Education
and their Applications”
ICMSTEA
2014
53
thUNM
ICMSTEA
ISBN: 979-604-151-0
2014
PROCEEDINGS
Makassar, August 20-21, 2014
IN
TE
RN
AT
IO
NA
L C
ON
FE
RE
NC
E
ON
MA
TH
EM
AT
ICS
, S
CIE
NC
ES
,
TE
CH
NO
LO
GY
, E
DU
CA
TIO
N
AN
D
TH
EIR
AP
PL
ICA
TIO
NS
IC
M
S
TE
A
20
14
Makassar, August 20-21, 2014
IN TERNATIONAL CON FERENCE ON MATHEMATICS, SCIENCES,
TECHN OLOGY, EDUCATION AND THEIR APPLICATION S
Makassar, 20
th– 21
staugust 2013
RECENT RESEARCH AND ISSUES ON MATHEMATICS,
SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, EDUCATION AND THEIR
APPLICATIONS
ISBN 979-604-151-0
Mathematics and Science Faculty
SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, EDUCATION AND THEIR
APPLICATIONS
Editorial Board:
Syafruddin Side
Iwan Dini
Rahmat Syam
Sumarlin Muis
Ahmad Fudhail
Andi Irma Suryani
Ansari Saleh Ahmar
Muh. Aqil Rusli
Bustang
Muh. Hijrah
Irwan
Iswan Achlan Setiawan
Nur Wahidin Ashari
Wahyuddin Bara
Zulkifli Rais
Reviewer Board:
Prof. Max Warshauer
Prof. Susie Groves
Prof. Peter Hubber
Prof. Naoki Sato
Prof. Baharuddin Aris
Prof. Ismail bin Kailani
Prof. Duangjai Nacapricha
Prof. Muhammad Arif Tiro
Dr. Fran van Galen
Prof. Suratman Woro Suprodjo
Dr. Siti Nuramaliati Prijono
Oslan Jumadi, Ph.D.
Prof. Gufron D. Dirawan
Muhammad Abdy, Ph.D.
Dr. Ramlawaty
DESIG
Freud
Students who want to work in
room in their study for the de
research’ design and evaluation
two to four cycles: designing,
A range of data is collected,
children, classroom observations,
‘focus group’, one or more int
compare different approaches;
will often be just one class, st
strive for a presentation of the
evaluate the conclusions that t
research is a core element in
contribution to the conference
we deploy it in the curriculum
mathematics education, but de
school topics.
1
SIGNING AND DESIGN RESEARCH
Frans van Galen
reudenthal Institute, Utrecht University
Abstract
in education after their graduation, will benef
design and the evaluation of educational ac
tion go hand in hand. A typical design researc
ng, testing, retrospective analysis, redesign, test
d, amongst other things: tests to establish the
tions, video of classroom discussions, video of
interviews with the teachers. The aim of design
hes; there is no control group and as the group of
ss, statistical significance is not an issue. Inste
the empirical data that allows other researcher
hat the authors have drawn. Data triangulation is
in the study program for Indonesian students
nce I want to explain what we mean by design
um of our master students. My examples will
design research can also be used to improve e
MATHWORKS, MATH
Inquiry-based teaching and l
connected parts. First, we wi
curriculum development. Second,
the kind of investigations that
discuss math education rese
connected to teaching, learnin
Texas State for students and
University.
2
TH PROBLEMSAND MATH EDUCATION
Max
Texas State University, USA
Abstract
learning approaches have In this talk, ther
will describe Mathworks programs for stude
econd, we will provide some interesting probl
hat arise in our curriculum and math programs.
search, particularly focusing on ongoing and
ning and Math works programs. This include
nd faculty, and collaborations with KPM and
N RESEARCH
JOB ORIENTATION
OF FMIPA
Graduated from Iowa State U
Mathem
This study aimed to assess
FMIPAUNM. This study is
statistics program and receive
insight and orientation of stude
prepare for the learning proc
perspectives. This study was
after completing education at
students who participated, most
(58%), and further studies to be
professional statisticians (25%
Furthermore, the choice of suc
responsibilities, and worship in
happiness of parents (25%), w
means to earn income to make
conclusion of this research repor
the design of learning at Statist
Keywords
: job orientation, me
3
N OF UNDERGRADUATE STATISTICS S
IPA UNIVERSITAS NEGERI MAKASSAR
Muhammad Arif Tiro
e University, USA, Statistics professor at Facult
hematics, the State University of Makassar
Abstract
the job orientation and perspectives of sta
is important because FMIPA UNM has open
ve the first batch of 2013 with this study, is ex
students’thinking to prepare for theirfuture. Thus,
ocess to gain knowledge, skills, and expertise
conducted by surveying the opinions and ide
statistics study at FMIPA UNM. The results
most of them aspire to become civil servants
o become lecturers (50%). Partly of them also
25%) as well as being a business and economy en
of such work based on the meaning of the w
p in the life (30%), work as a means to achieve
, work as a struggle to achieve the goal of life
ake ends meet (18%), and work as identity and
eport will be used as inputs for improving: (1) c
tistics Studies Program of FMIPA UNM.
meaning of the work, undergraduate
STUDENTS
R
MEMBRA
EFFECTIVE ON-LINE TO
Nacapricha, D.
1,2*Ur
1
Flow Innovation-Resear
2
Department of Chemistry and
Science, Ma
3
Department of Chemist
Faculty of Science, King Mong
4
Department of Chemistry, F
5
National Doping Contro
email address: duang
Membraneless vaporization de
compounds from liquid or soli
of membraneless vaporization
suitable for flow-based analy
‘pervaporation unit’ all emplo
(donor) into a headspace pa
(acceptor). The volatile gas di
property. This change in the ph
calibration for quantitative ana
presented. Future trend in deve
of volatile compounds will be di
Keywords:
Membraneless vapor
4
RANELESS VAPORIZATION DEVICES:
OOLS FOR SEPARATION OF VOLATILE
IN FLOW-BASED ANALYSIS
*Uraisin, K.
1,2Choengchan, N.
1,3&Ratanawim
N.
1,4Wilairat, P.
1,2,5search for Science and Technology Laboratories
and Center of Excellence for Innovation in Che
Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400, Thailand
istry and the Applied Analytical Chemistry Re
Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
Road, Bangkok 10520, Thailand
, Faculty of Science, Srinakharinwirot Universi
Road, Bangkok 10110, Thailand
ontrol Center, Mahidol University, Bangkok 10400,
[email protected] and dnacapricha@gm
Abstract
devices are apparatus developed for on-line sepa
solid samples. Our group was the first to intro
ion as well as ‘membraneless vaporization uni
nalysis.
Conventional devices, such as ‘gas-di
ploy membranes. Volatile compound vaporize
partitioning between the sample section and
s dissolves into the acceptor leading to the chang
he physical property of liquid acceptor is used f
analysis.
In this talk, evolution of MBL-V
development of MBL-VP devices for simultane
be discussed.
vaporization;Separation; Flow-based analysis;V
:
ILE COMPOUNDS
imarnwong,
es (FIRSTLabs)
hemistry, Faculty of
nd
Research Unit,
bang, Chalongkrung
rsity, Sukhumvit 23
10400, Thailand.
gmail.com
CORRELATION BETWEE
ORGAN
Institute for Chemical R
Our research is devoted to
functional materials in the soli
unoccupied states of organic
inverse photoemission spectrosc
properties. Such results are appl
electronic functions.
Keywords:
Organic semiconduc
5
WEEN STRUCTURES AND ELECTRONIC P
ANIC SEMICONDUCTOR THIN FILMS
Naoki SATO
l Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011,
Abstract
to correlation studies on structures and prope
solid state. In particular, the electronic structure
nic semiconductor thin films is studied using phot
troscopies in connection with their electronic
applicable to create novel molecular systems
onductor; Thin film; Electronic property; Electroni
PROPERTIES OF
0011, Japan.
STEM AND OER
Faculty of
While STEM stands for Scienc
Open Educational Resources.
in alleviating problems related
MIT BLOSSOMS. BLOSSOMS
Studies. This presentation wil
UTM and MIT as well the Mal
are these UTM-MIT BLOSSO
teachers and UTM lecturers
BLOSSOMS that is applicabl
institution started in January
development of UTM-MIT BL
and Malaysian culture in crea
effectiveness of UTM-MIT B
project between MoE and UTM
6
ER TO STIMULATE STUDENT ENGAGEM
Baharuddin Aris
of Education, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Abstract
ence, Technology, Engineering and Mathemati
s. One of the initiatives of Universiti Teknolog
ted to STEM Education is Research and Deve
OMS stands for Blended Learning Open Sourc
ill cover the why, how and when collaborati
Malaysian Ministry of Education (MoE) evolved
SOMS. Collaborative efforts between MIT Prof
ers with respect to training and developme
cable to Malaysian syllabus in secondary sc
ry 2013. This collaborative effort goes beyon
BLOSSOMS embedded with higher order thinki
reative and contextual approach. It also involve
BLOSSOMS through UTM research grants
TM in 2013.
EMENT
REPRESENTATION CON
PEDAG
Inquiry-based teaching and lea
science classrooms (Anderson,
implementation (Minna, Levy
research-developed representa
student learning and engagem
involves challenging students
models, diagrams) that const
on the text-based, definition
a
approach is based on sequenc
constructing representations
Inquiry in the science classroom
and the selective and partial
representation construction appr
illustrations from video ethnog
ideas about matter within middl
manner in which the representa
implementation through a larg
pre-service teacher curriculum
the approach are discussed suc
approach and limited practic
based teaching approaches.
7
ONSTRUCTION: A RESEARCH DEVELO
AGOGY FOR SCIENCE EDUCATION
Peter Hubber
Deakin University
Abstract
learning approaches have long been advocated
son, 2002) but have yet been realised in ter
vy & Century, 2010). This keynote address desc
ntation construction approach to teaching and
gement with the epistemic practices of science
s to generate and negotiate the representati
onstitute the discursive practices of science, ra
al versions of concepts.
The representa
ences of representational challenges which
ns to actively explore and make claims a
room becomes inquiry into ideas and how the
tial nature of such representations. The key
approach, considered a form of directed inquiry
hnographic studies of whole topics such as forc
iddle years’ science classrooms. The address w
ntation construction approach has been translat
rge scale Professional Development (PD) workshop
um courses. Issues associated with wider scale
such as ongoing support for in-service teachers
ticum experiences for pre-service teachers in
OPED INQUIRY
inquiry-IMPROVING MATHE
221 Burw
Lesson study first came to wor
Yoshida’s (1999) doctoral diss
structured problem-solving less
Study
(TIMSS). Since then, the
for professional learning. For
“spreading like wildfire across
efforts at improving teaching
implies gradual change and
underpinning teaching and lea
can be replicated elsewhere rem
which teachers can adopt struc
presentation will describe esse
bringing about improvement i
and constraints encountered in
reference to a research project,
through lesson study,
being car
Keywords:
Lesson study; mat
solving
8
HEMATICS TEACHING THROUGH LESS
Susie Groves
Deakin University
urwood Highway, Burwood 3125, Australia
+61 3 9244 6405
Abstract
orld-wide attention as a vehicle for profession
dissertation and Stigler and Hiebert’s (1999) ac
lessons based on the
Third International Mathem
n, there has been phenomenal growth of lesson
or example, Suratno (2012, p. 212) describes
oss Indonesia”. However, as Stigler and Hieber
ng often ignore the fact that teaching is a cultu
nd the need to take into account the cul
learning. Thus questions about the extent to w
remain (Perry &Lewis, 2009), as do questions
structured problem-solving as the basis for rese
ssential features of Japanese Lesson Study tha
nt in mathematics teaching. It will aslo discuss
in its adoption and adaptation in other countr
ct,
Implementing structured problem-solving m
carried out in a small number of Melbourne school
athematics teaching; teacher professional learn
SSON STUDY
onal learning through
accounts of Japanese
athematics and Science
on study as a vehicle
bes Lesson Study as
bert (1999) point out,
ultural activity, which
cultural assumptions
o which lesson study
ons about the extent to
esearch lessons. This
that can contribute to
uss some affordances
ountries, with particular
mathematics lessons
schools.
INTRODUCTION TO M
Faculty
Geography focus on geospher
environments by using spatia
consist of atmosphere, lithosphe
the characteristics of geospher
be analyzed as a complex natur
of geosphere are favourable pr
system approach, a model can
in the context of planning. T
resources management. The g
mathematical model. Geographe
resources such as land, water, m
etc. By using models in geogr
the geographical resourcesca
resources can be as a basic
planning and management.
Keywords
: Geography, geogr
9
O MODELLING FOR GEOGRAPHICAL R
MANAGEMENT
Suratman
ulty of Geography Gadjah Mada University
Abstract
sphere aspect of the earth in relationship with ma
spatial, ecological and regional complex analy
hosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, andanthroph
sphere are heterogeneous from place to other pla
natural system.Ecologically, the interaction among
e processes in the developing the system. By
an be used in the determining the potential geog
. There are some types of model in geograp
he geographical models are scale model, conc
rapher will search type, pattern, and distribution
r, mineral, vegetation, land use, settlement, popul
graphy (spatial, ecological model) and also ma
scan be determined. The spatial and nume
sic for simulation in comprehensive in geog
graphical resources, system, models, resources
RESOURCES
man and other living
nalysis.The geosphere
ophosphere. Spatially,
place. Geosphere can
ong the components
By the geographical
geographical resource
raphical research for
onceptual model and
bution of geographical
population, man made
mathematical model,
numerical geographical
ographical resources
ROLE OF BIOLOGICAL
FOR
The I
The 21
stCentury has been ca
humankind’s understanding of
great scope in developing the
assurance of food security, and
animal feed . Indonesia’s strate
“green and ever-lasting Indon
process to integrate economic de
meets human needs while pre
present and the future. Achi
biodiversity and the ecosyste
sustainable use of biodiversity
Biology is a pivotal knowledge
contributing to sustainable deve
Keywords:
Biological Science
10
L SCIENCES IN DEVELOPING THE SCIE
R SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Siti Nuramaliati Prijono
he Indonesian Institute of Sciences (LIPI)
Abstract
called a “Biology Century” because of the
of the basic processes and components of lif
he scientific basis for sustainable Development
nd in the use of biology to meet the needs for m
rategic longterm development plan (2005-2025)
ndonesia.” Indonesia believe that sustainable de
ic development and natural resources and its ecos
preserving the environment so that these needs
chieving sustainable development is made
stem services that underpin all life on earth
sity, require creativity and new advances in sci
dge component to meeting humankind’s require
development.
nces, sustainable development, Indonesia.
IENTIFIC BASIS
Improvement in mathematics e growing need for mathematic teachers and administrators wh need to develop the knowled leaders working with teacher leader takes on the roles of ac instructional leader. This site aspects of the components of a must know how to support te implement mathematics profe deepen mathematical knowled level mathematics profession mathematics achievement face such as equity leadership, assessment leadership, that w There are variety of leadership office leaders, supervisors, tea instructional materials develop
11
MATHEMATICS LEADERSHIP
Ismail Kailani
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Abstract
cs education requires new kinds of leadership. T atics teacher – leaders – specialists positione
who can assist with the improvement of mathe ledge, skills and disposition, sensibilities, lo hers to take leadership for improving mathem
active observer, participant, professional devel site-based leaders will be integral in sustaini
f a comprehensive mathematics program. Thes teachers to improve mathematics teaching pr ofessional development to achieve specific go ledge needed for teaching mathematics, which ional development. Leaders who are respon ace tremendous challenges. There are several
teaching and learning leadership, curricu will help leaders implement a high-quality m ship positions in mathematics education such team leader, coach, peer coach, new teachers m loper, and inquiry team member, etc.
507
Hendra Jaya1, Sapto Haryoko2
1,2Department of Electronics Education, Faculty of Engineering,
State University of Makassar, Parang Tambung, Sulawesi Selatan, Indonesia. e-mail address: [email protected] , [email protected]
Abstract
A hands-on approach in which the vocational students actively participate in obtaining results is used. Vocational students are taught a step-by-step procedure for applying the simulation technique which helps them answer questions about the behavior of real processes under varying conditions. They feature statistical topics that are important to students, a wealth of hands-on activities, real data sets and active experiments which motivate student participation, and graphical methods instead of complicated formulas or abstract mathematical concepts. There are numerous examples of practical problems which can be simulated using this approach and which are interesting and motivating for vocational school students. Simulation has a good transfer of learning , as studied in simulations usually good transfer to the real situation. a) The other way to increase the efficient learning is to equip students with an environment that is more conducive to study one of the real activity; b) simulation offers other advantages as well. Simulation is safe , comfortable , and can be controlled; c) simulation is also more convenient in the real world activity. d) the simulation can be used as a test. simulation is an ideal mechanism for providing the teacher to explain the lesson, to drawing conclusions and making inferences.
Keywords:laboratory simulation, real world problem.
1. Introduction
Laboratory is a scientific research, experiments, measurements or scientific training done. Laboratories are usually made to allow these activities in a controlled manner. Scientific laboratories usually differentiated according to the discipline, such as physics lab, chemistry lab, biochemistry lab, computer lab and language lab. Laboratory is used as an academic support unit in educational institutions, in the form of a closed or an open room, or a permanent move, managed systematically for testing activities, calibration, and / or production on a limited scale, using equipment and materials based on a particular scientific method, in order to implement education, research, and community service. Various efforts were made by the teacher or administrator educators to further enhance and support the learning process more effective and efficient. Although many factors that determine the quality of education or learning outcomes.
508
reality environment called reality (Virtual Reality). VR is a form of human computer interaction in which a real or imaginary environment is simulated and the users can touch and move the world. In the most successful virtual environment, users feel that they are truly present in the simulated world and that their experience in the virtual world is comparable to what they would have done to the environment sebenarnya.Virtual Reality can be applied to various fields. In the research techniques and lmiah, virtual labs can help overcome the problems in vocational beragai especially for productive vocational subjects such as for work on hazardous equipment including the very high voltage or with expensive equipment better implemented through simulation. Simulation is a method that can be used to transfer the functions of the real problem into a form that can be represented by a computer program.
2 . Laboratory
The emergence of more complex interactive multimedia supported by the development of computer technology which gave birth to the more complex types of media as well as the combination of audio media,
video and communications, known as
multimedia computers that can be used as an alternative medium of supplements lab at the school referred to as laboratory simulation.
Laboratory is a scientific research, experiments, measurements or scientific training done . Laboratories are usually made to allow such activities in a controlled manner . Scientific laboratories are usually distinguished by the discipline, such as physics lab, chemistry lab, biochemistry labs, computer labs, and language labs.
3 . Simulation Model
Simulation is the imitation of the operation , according to the time, a real-world process or system. According to Law and Kelton (1991) simulation is a technique mimics the operations or processes that occur in a
imitating a real system that is full of complex probabilistic nature without having to experience the real situation (Ellyns, 2009) .
Furthermore , the simulation model is basically a learning strategy that provides a more concrete learning experience through the creation of a clone - clone form experience approaching the real atmosphere . From the definition of the experts above , it can be concluded that the simulation is a form of presentation by manipulating an object and make copies for the purpose of reducing misperceptions of the material - the material is complex or abstract . Variety of learning media will be able to turn the learning environment , encourage and facilitate the learning motivation understand abstract concepts or complex (Munir, 2001).
The simulation model consists of two types, namely the analog simulation and symbolic simulation. According Sunarno (2008) analog simulation using the physical representation to describe the characteristics of
a problem, while the simulation of
mathematical models that emulate symbolic solution using computers, called computer simulations . Simulation is generally used to solve a variety of problems : difficult to be solved by analytical means such as the complex electrical circuits; has a data size and high complexity; very difficult to implement directly since it requires very expensive, when the relationship between variables is not linear , and when the model has a random variable .
In the simulation approach , to solve complicated problems will be easier to do when starting to build an experimental model of a system . Learning model simulation aims to: (1) specific skills training is both professional as well as for everyday life, (2) gain an understanding of a concept or principle , (3) trained to solve problems , (4) increase the activity of learning , (5) motivate students to learn , and (6) foster students' creative power(Djati, 2007) .
509
2) conceptual models , a description of the model will be developed ; 3) computer models , a simulation model is applied to the computer . ; and 4) solutions / understanding , is the result of a process of experimentation.
Fig 1.
Key Stages and Process of Simulation
Motivation in performing a simulation is the recognition of some of the problems that occur in the real world that would cause concern for it is necessary to run for a simulation . to propose a model that is suitable to handle it . Thus , conceptual modeling consists of the following sub - processes :
1. Develop an understanding of the problem situation
2. Determine the purpose of modeling 3. Designing conceptual models : input ,
output and content models
4. Collecting and analyzing the data needed to develop a model
In the model coding conceptual model is converted into a computer model . Here , coding is defined in the most general sense and does not have to mean computer programming . In contrast refers to the development of computer models . The model can be encoded using a spreadsheet , a special simulation software or programming language . The assumption here is that the simulation was built and performed on the computer . it should be noted that other forms of physical simulation is
to find solutions to real-world problems . One of the models developed in the study are presented by Figure 1. Consists of material, discussion forums, perogress reports, examinations, assignments, exercises, and additional files search. All of which will be presented in the form of a website through a virtual learning activities.
4 . Characteristics Simulation
The desire to do interactivity , active involvement and support of navigation in the simulation are important characteristics that contribute to the educational outcomes of these tools. In addition , an important characteristic of simulation is its validity . Various types of validity can be distinguished . Content validity revealed the degree of simulation environments in accordance with the relevant aspects , activities and operational parameters of the real environment to simulate , construct validity reveal the level at which the construction , the knowledge and skills students should have evolved in a simulated environment resembling that we use in the real world .
As according (Wiharjo, 2007),
simulations are used to demonstrate something ( skills ) so that students feel like being in a real situation . Simulation is widely used in the learning material harm , difficult , or costly , for example, to train pilots or fighter aircraft .
510
teachers convey the message of learning to students . In the simulation model , students manggunakan computer and obtain learning materials are packaged in the form of
animations that can strengthen the
responsiveness of students to instructional material that is packaged in the form of
animations that can strengthen the
responsiveness of students to the learning material .
Basically different simulation programs with drill and practice programs , the simulation program , the students did not respond to questions but rather on creating an atmosphere closer to the actual situation , which is probably the real situation that is too expensive or too dangerous to be done by the student , but with the use of simulation it can be overcome , because the strength of the simulation is the fact that response by the computer based on the choices made by the students themselves .
5. Enable Students to Solve Real-World Problems
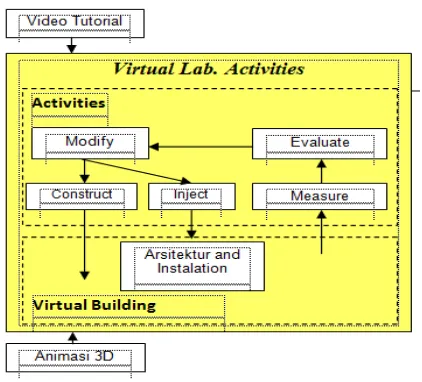
Simulation enables students to
incorporate systems adjacent to their area of focus, and gives them the freedom to explore designs without the risks and limitations of hardware testing. By enabling safe exploration of solutions and failures, students can develop optimized designs.Simulation makes it possible for multidomain systems such as Digital Electronics subjects: Modify the electrical circuit, construct component, inject the circuit and component, measure component in electric circuit, and evaluate the practicum (Figure 1). Models of physical systems built using simulation laboratory (Hendra, 2013:187). Exploring integrated systems helps students understand how design decisions at the
subsystem level affect system-level
performance.
Fig 2. The Scope of Simulation Process
511
(a)
(b)
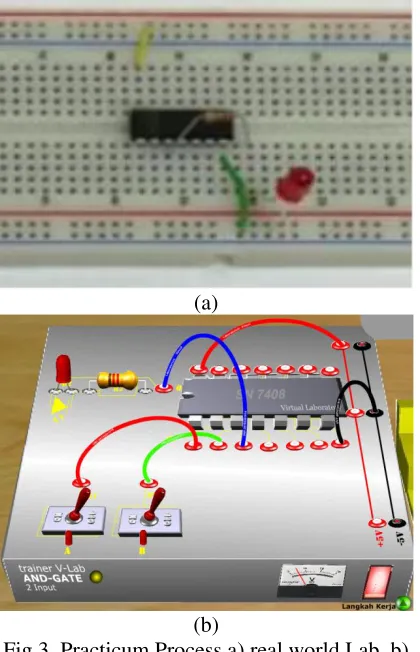
Fig 3. Practicum Process a) real world Lab, b) Simulation Lab
Besideshavingadvantages, simulationalso hasdrawbacks, including: 1) Experience gainedthroughsimulationis
notalwaysappropriateandin accordancewith thefacts on the ground; 2) poormanagement.
simulationis oftenused as ameans
ofentertainment, so thelearning objectivesto be neglected; 4) Psychological factorssuch asthe
loss ofactivity ofHands-on that are
affectingstudentsbecauseoftenperformsimulatio ns.
6. Conclussions
Simulation has a good transfer of learning , as studied in simulations usually good transfer to the real situation. a) The other way to increase the efficient learning is to equip students with an environment that is more conducive to study one of the real activity; b) simulation offers other advantages as well. Simulation is safe , comfortable , and can be controlled; c) simulation is also more convenient in the real world activity. d) the
and making inferences.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank DP2M Dikti for financial support in fiscal year 2014.
Reference
(1) Djati, Bonett., & Satya Lelono.(2007).
Simulasi, Teori dan Aplikasinya.
Yogyakarta: Penerbit ANDI.
(2) Ellyns. (2009). Definisi Simulasi, [online]. Tersedia: (http://ellyns.wordpress.com/ 2009/08/28/definisisimulasi-2/, diakses pada tanggal 26 juni 2011.
(3) Hendra Jaya. 2013. Pengembangan
laboratorium simulasiPraktikum
elektronika digitalDi SMK. Dissertation. Yogyakarta State University. Yogyakarta.
(4) Hendra & Sapto Haryoko. 2014. 3D Simulation Laboratory Model Of
Web-Based Interactive To Improve
Accessibility, Desire To Learn, And
Competence Of Student Vocational
Subject. Prosiding. ICVET 2014.
Yogyakarta.
(5) Munir. (2001). Aplikasi teknologi
multimedia dalam proses belajar
mengajar. Jurnal Mimbar Pendidikan, 3, 9
– 17.
(6) Robinson, stewart. (2004). Simulation: The Practice of Model Development and Use. Southern Gate Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
(7) Sunarno, W. (1998). Model Remediasi
Miskonsepsi Dinamika dengan
menggunakan Animasi Simulasi dengan
Komputer. Desertasi doktor, tidak
512