THE EFFECT OF ANAGRAM WITH FLASHCARDS ON
STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY
A THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
FITRI MULIATI
Registration Number. 2112121010
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
ii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The greatest gratitude is expressed to Allah SWT, the Almighty and Most
Beneficial for His Grace, Guidance, and Mercy that has been given to the writer
finally accomplishes his thesis.
This thesis is aimed to fulfill one of the requirements for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan of the English Department, Faculty of Languages and Arts,
State University of Medan (UNIMED).
In completing this thesis, the writer realized that she faced some problems
and she had received the academic guidance, suggestions, and comments and got
a lot of assistance and moral support from many people. Therefore, the writer
would like to express her gratitude and special thanks to:
Prof. Dr. Syawal Gultom, M.Pd., the Rector of State University of Medan.
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., the Dean of Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan.
Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd.,The Head of English and Literature Department Dra. Meisuri, M.A., the Secretary of English Department
all at once as the her Thesis Examiner, Nora Ronita Dewi, S.Pd.,
S.S., M.Hum., the Head of English Education Program, Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan.
Dr. Rahmad Husein, M.Ed., and Neni Afrida Sari Harahap, S.Pd, M.Hum., her Thesis Advisors who have given their valuable advice, suggestion, guidance and spent their precious time in the process of
completing this thesis.
Drs. Johan Sinulingga, M.Pd., her Academic Advisor and her Reviewer who has supported her through out the academic years. Dra. Sri Juriaty Ownie, MA., Drs. Lidiman Sahat Martua Sinaga,
i
ABSTRACT
Muliati, Fitri. 2112121010. The Effect of Anagram with Flashcards on
Students’ Vocabulary Mastery. A Thesis. English and Literature Department,
Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan. 2015.
This study deals with out the effect of Anagram with Flashcards on students’ vocabulary mastery. The objective of this research was to find out the effect of anagram with flashcards on students’ vocabulary mastery. The population of this study was the students of SMP Negeri 1 Selesai, Academic Year 2014/2015. It was conducted by using experimental research design. There were two randomized groups namely experimental group and control group. The experimental group was taught by using Anagram with Flashcards while the control group was taught by using Personal Vocabulary Notes (PVN). The data was analyzed by using t-test formula. The analysis showed that the mean scores of the students in the experimental group was significantly higher than the mean scores of the students in the control group at the level of significant α= 0.05 with the degree of freedom (df) 58 with the value of observed 6.63 > the value of t-table 2.00. Therefore, null hypothesis (Ho) was rejected and alternative hypothesis (Ha) was accepted. The findings indicated that using Anagram with Flashcards significantly affected the students’ vocabulary mastery.
iv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGMENT... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iv
LIST OF TABLES ... vii
LIST OF APPENDICES... viii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. The Background of the Study ... 1
B. The Problem of the Study ... 4
C. The Objective of the Study ... 5
D. The Scope of the Study ... 5
E. The Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 6
A. Theoretical Framework ... 6
1. Vocabulary ... 6
2. Types of Vocabulary ... 7
3. Vocabulary Achievement ... 8
4. Vocabulary Teaching Technique ... 9
a. Anagram ... 10
b. Flashcards ... 13
v
d. The Advantages of Using Anagram with Flashcards in Teaching
Vocabulary ... 17
e. The Disadvantages of Using Anagram with Flashcards in Teaching Vocabulary ... 18
5. The Procedure of Teaching and Learning Vocabulary through Anagram with Flashcards ... 18
6. Personal Vocabulary Notes ... 19
a. The Advantages of Personal Vocabulary Notes (PVN) ... 20
b. The Disadvantages of Personal Vocabulary Notes (PVN) ... 20
c. The Scenario of Teaching Personal Vocabulary Notes ... 21
vi
E. Scoring of the Test ... 32
F. The Validity and the Reliability of the Test ... 32
1. The Validity of the Test ... 32
2. The Reliability of the Test ... 33
G. The Technique for Analyzing the Data ... 34
CHAPTER IV: THE DATA AND DATA ANALYSIS ... 35
A. The Data ... 35
B. Data Analysis ... 36
1. Reliability of the Test ... 37
2. Homogeneity of Variance Test ... 37
3. Normality of the Test ... 38
4. Analyzing the Data Using t- test ... 39
C. Testing Hypothesis ... 40
D. Research Findings ... 40
E. Discussion ... 41
CHAPTER IV: THE DATA AND DATA ANALYSIS ... 43
A. Conclusion ... 43
B. Suggestion ... 43
REFERENCES ... 44
vii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1.1 Students’ English Score of Grade VII in SMPN 1 Selesai ... 3
Table 3.1 Research Design ... 25
Table 3.2 The Activities of Teacher and Students in Experimental
Group ... 27
Table 3.3 The Activities of Teacher and Students in Control Group ... 30
Table 4.1 The Score of Students’ Vocabulary Mastery Score in
Experimental and Control Group ... 35
viii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX A The Score of Pre-Test and Post- Test by the Students of
Experimental Group ... 46
APPENDIX B The Score of Pre-Test and Post- Test by the Students of Control Group ... 47
APPENDIX C The Reliability of the Test ... 48
APPENDIX D Normality of the Test ... 51
APPENDIX E Table of Normality from 0 to Z... 57
APPENDIX F Table of Critical Values for the Lilifors Test for Normality ... 59
APPENDIX G Homogeneity of Variance Test ... 60
APPENDIX H F Distribution Table ... 66
APPENDIX I The Calculation of T- Test ... 67
APPENDIX J Percentage Points of the T Distribution ... 71
APPENDIX K Lesson Plan ... 72
APPENDIX L Vocabulary Test ... 87
APPENDIX M The Key Answer ... 91
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
Vocabulary as the basic element of four skills, listening, speaking, reading,
and writing plays an important role in teaching and learning English, where
mastering the vocabulary effectively is seen as a key objective for learners
(Bishop, 2009). In Indonesia, vocabulary is considered as the most important part
to be learned by the students in school. David Wilkins as quoted by Thornburry
(2002) states “without grammar very little can be conveyed, without vocabulary
nothing can be conveyed”. This statement implies if students does not know any
word of language which will be spoken, surely he or she will not able to
communicate, even though he or she knows more about the rules to construct the
sentences. Thus, it is an obligatory that students need to master vocabulary in
order to be able to communicate with other.
At the present day, everybody approves the important of vocabulary in
learning a language. Vocabulary as the basic element of language is accepted as
even the backbone of the whole language system. But, unfortunately, vocabulary
knowledge is not attached importance according to its deserts in language study
area in the beginning. Vocabulary teaching was a matter of secondary importance
in foreign language programs. It was considered as something useless and time-
2
importance to the special vocabulary instruction in foreign language teaching all
over the world. Today almost all second language theorists and practitioners admit
vocabulary is crucial for language teaching.
Vocabulary knowledge also plays a significant role in overall academic
success. Students who are rich vocabulary will be better in listening, speaking,
reading, and writing a foreign language. Based on the statement above,
vocabulary in reading is one of the important problem for students in learning
English. There is a strong link between vocabulary knowledge and reading,
because vocabulary knowledge impacts reading and academic success, it is
significant in our daily life and can have practical as well as social and emotional
consequences (Marzano, 2004).
In reality, vocabulary becomes a problem to almost all of students at any
level of education. Vocabulary is assumed as one of the major difficult aspect of
language to be mastered since there are many students who still struggle with
mastering vocabulary. There are many reasons why students have problems in
vocabulary. One of the most obvious is simply that they have problems in
memorizing, pronouncing, and understanding the words and it makes them lazy to
study English. In line with the writer’s experience in Teaching Experience
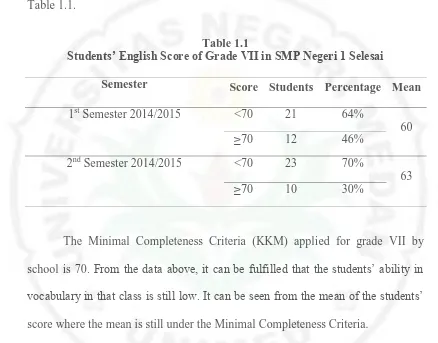
Practice (PPL) in grade VII Junior High School at SMP Negeri 1 Selesai, the
writer found that the students cannot comprehend a text and do the exercise from
the textbook because their vocabularies were still low. Most of the students get
3
Junior High School. The score of English test from the students can be seen in the
Table 1.1.
Table 1.1
Students’ English Score of Grade VII in SMP Negeri 1 Selesai
Semester Score Students Percentage Mean
1st Semester 2014/2015 <70 21 64%
school is 70. From the data above, it can be fulfilled that the students’ ability in
vocabulary in that class is still low. It can be seen from the mean of the students’
score where the mean is still under the Minimal Completeness Criteria.
In the further investigation, the writer found some problems that made the
students are difficult to master the vocabulary. The first problem is most of the
students still have limited vocabulary in English and second, the students felt
bored with the teachers’ way of teaching vocabulary, in which they were asked to
find out the meaning of difficult words in the dictionary and then memorize the
words. It seems that they need something different in studying the vocabulary.
Regarding to the problem discussed previously, the way of teaching in the
classroom needs to be improved. The use of creative and effective teaching
technique and media in teaching vocabulary is needed to perform in the classroom
4
achievement. To overcome the problem occurred, the writer acclaimed to use
anagram with flashcards.
The reason why the writer chooses anagram with flashcards is that because
anagram with flashcards is believed as an effective way in increasing students’
vocabulary achievement. Anagram with flashcards is needed to help students;
especially those who struggle with vocabulary become more interest in English
learning. Another benefit of using anagram with flashcards is to stimulate and
encourage the students to rearrange for new words to enlarge their vocabulary and
also motivate them to learn seriously through a friendly way.
In line with the teachers’ creativity for developing students’ mastery of
vocabulary, the researcher wants to help in teaching and learning process by using
anagram with flashcards in teaching vocabulary. It is expected that the use of
anagram with flashcards can motivate and make the students interested and
relaxed in learning vocabulary. It means that after learning vocabulary by using
anagram with flashcards, the student’s achievement in vocabulary will be
improved. Therefore, this study chooses anagram with flashcards to increase
students’ vocabulary mastery.
B. The Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the study, the research problem of this study
is formulated as follows:
“Is there any significant effect of using anagram with flashcards on students’
5
C. The Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to find out the significant effect of using
anagram with flashcards on students’ vocabulary mastery.
D. The Scope of the Study
The scope of this study is limited on the effect of using anagram with
flashcards on students’ vocabulary mastery in reading on grade VII at Junior High
School.
E. The Significance of the Study
The result of this study is expected to contribute either the theories or
practices for:
1. Theoretically:
a. It is useful for the reader, to add reference or give alternative way in
teaching and learning vocabulary.
b. It is providing some information for those who are interested in conducting
the further research, especially in vocabulary.
2. Practically
a. It is useful for the students to increase their vocabulary mastery in learning
English.
b. It is useful for the English teacher in order to use anagram with flashcards in
43
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions
After analyzing the data, it was concluded that there is a significant effect
by using anagram with flashcards on students’ vocabulary mastery, since tobserved >
ttable (6.63> 2.00; df= 58, α = 0.05). It means that the null hypothesis (H0) was
rejected and the alternative hypothesis (Ha) was accepted because there was
significant effect of using anagram with flashcards on the students’ vocabulary
mastery.
B. Suggestion
Based on the conclusion above, the researcher gives some suggestion as
following:
1. The English teacher was suggested to apply anagram with flashcards
in teaching vocabulary and facilitated the students to learn
independently.
2. The students guided by the teacher were suggested to apply anagram
with flashcards in a group or individually to make them to be more
active, enjoyable and have deeper understanding of a word.
3. Other researchers should try to apply Anagram with Flashcards in
teaching vocabulary on different level of learners through different
topics to prove the effectiveness of anagram with flashcards on
44
REFERENCES
Arikunto, Suharsimi. 2002. Prosedur Penelitian: Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: PT Asdi Mahasatya
Ary, D. et al. 2010. Introduction to Research in Education. Eighth Edition. The United State of America: Nelson Education.
Beck, I.L., McKeown, M.G., & Kucan, L. 2002. Bringing Words to Life: Robust Vocabulary Instruction. New York: Guilford Press.
Bishop, A., Yopp, H, R., & Yopp, H,K. 2009. Vocabulary Instruction for Academic Success. Huntington Beach: Shell Education
Bromberg, M & Gale, C. 1998. Vocabulary Success. Barron’s Educational series.
Brown, Douglas. 2001. Teaching by Principles An Interactive Approach and Language Pedagogy, Second Edition. Longman: Inc
Collins, William. 2003. Collins English Dictionary. Princeton University
Dale, I. 1971. Priming and Aging, Evidence of Preserved Memory Function in an Anagram Solution Task. The American Journal of Psychology, 105 (4), 541-548
Harmer, J. 2003. The Practice of English Language Teacher Third Edition. Harlow: Pearson Edition.
Hills, J. 2008. Assessing Vocabulary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Hornby. 2002. Oxford Advanced Learners Dictionary of Current English. London: Oxford University Press
Kamil, M.L., and Hiebert, E.H. 2005. Teaching and Learning Vocabulary: Bringing Scientific Research to Practice. Mahwah. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates
Kurzweil, J. 2002.Journal of Personal Vocabulary Notes Technique. http://iteslj.org/techniques/Kurzweil-PVN.html. Accessed on February 24th, 2015.
Macmillan, Collier. 1997. The Key to English Vocabulary. London: The Macmillan Company
45
Milton, James. 2009. Measuring Second Language Vocabulary Acquisition. Toronto: Multilingual Matters
Pavicia Takak and Vinsja. 2008. Vocabulary Learning Strategies and Foreign Language acquisition. Clevedon: Cromwell
Pikulski, John. J and Shane, T. 2004. Teaching and Developing Vocabulary: Key to Long Term Reading Success. United State of America: Houghton Mifflin Company
Presley, Susan. 2006. Definition of Flashcards. Retrieved on February, 20, 2015 from http://www.ehow.com/facts.6300729-definition-flash-cards-html.
Richard, J. C and Rodgers, S.T. 1988. Approaches and Method in Language Teaching. Cambridge: LUP
Schmitt, N & Schmitt, D. 1995. Vocabulary Notebooks. ELTJournal, 44(2), 133-143
Shen, Zhifa. The Roles of Depth and Breath of Vocabulary Knowledge in EFL Reading Performance. Journal of Asian Social Science, Vol. 4, No. 12 (135- 137)
Th1ornbury, Scott. 2002. How to Teach Vocabulary. England: Bluestone Press
1