Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Tivani Kusuma
- Pengajar:
- Sri Sudarsi, S.S., M.In.T.
- Indah Puspawati, S.Pd., M.A.
- Puput Arfiandhani, S.Pd., M.A.
- Sekolah: Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
- Mata Pelajaran: English Education
- Topik: The Effectiveness of Using Audio Books in Improving Students’ Listening Skill of ICT Class at SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta
- Tipe: Skripsi
- Tahun: 2016
- Kota: Yogyakarta
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction: The Rationale for Using Audiobooks in Listening Skill Development
This section establishes the foundational argument for the study. It highlights the crucial role of listening skills in language acquisition, citing research emphasizing its contribution to overall language proficiency (Renukadevi, 2014; Mendelsohn, cited in Bingol et al., 2014). The section underscores the challenges faced by students in listening comprehension, including vocabulary limitations, unfamiliar accents, and a lack of focused listening practice (Hamouda, 2013). It also addresses the pedagogical challenges in teaching listening effectively, referencing the difficulties in delivering clear pronunciation and choosing appropriate materials (Walker, 2014; Harmer, 2007). The introduction then positions audiobooks as a potential solution, aligning with the current technological landscape and the preference of digital-native learners for technology-based learning tools (Prensky, 2001). The use of audiobooks is presented as a way to bridge the gap between the need for effective listening instruction and the challenges faced by both students and teachers.
1.1 Background: The Importance of Listening and Existing Challenges
This subsection delves into the significance of listening skills as a cornerstone of language learning. It draws upon established theories of language acquisition to support the claim that strong listening skills are essential for success in other language domains, such as speaking and reading (Krashen, 1985; Hamouda, 2013; Rost, 2011). The discussion further explores the common difficulties students encounter in listening comprehension, including issues related to vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, accents, and cultural context (Hamouda, 2013; Renukadevi, 2014). This establishes a clear need for innovative teaching approaches to address these challenges and improve students' listening proficiency. The existing focus on speaking over listening in many educational settings is also critiqued (Bingol et al., 2014), setting the stage for the study's investigation into the effectiveness of audiobooks.
1.2 Problem Statement: Identifying Specific Issues in the Target Context
This subsection focuses on the specific context of SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta, detailing observations of listening skill deficiencies among students. It highlights the limited attention given to listening instruction due to factors such as its absence from national examinations (as mentioned by an English teacher at the school). The subsection also points out student-related challenges, including vocabulary gaps and difficulties with native speaker pronunciation. The lack of suitable listening materials and the underutilization of the school's ICT facilities are presented as further contributing factors to the identified problems. This section effectively links the broader issues of listening skill development to the specific realities of the research setting, establishing a clear rationale for the study's chosen methodology and focus.
1.3 Research Questions and Objectives: Defining the Scope of the Study
This subsection clearly states the central research question: whether there is a significant difference in students' listening skills after instruction using audiobooks. The corresponding research objective is to investigate the effectiveness of audiobooks in improving students' listening skills. This section establishes the specific aims of the study, providing a focused direction for the research and outlining the expected outcomes. The clear articulation of the research question and objective contributes to the overall clarity and precision of the study's design and analysis.
1.4 Significance of the Study: Highlighting Potential Contributions
This subsection articulates the potential benefits of the study for various stakeholders. It emphasizes the contribution to the researcher’s knowledge, providing valuable insights into the use of innovative teaching media. The study's significance for teachers lies in offering a practical alternative for listening instruction and providing guidance on the implementation of audiobooks. For students, the study offers a potential avenue for improved listening skills and increased engagement with learning materials. The study also benefits the school by promoting the effective use of its existing ICT resources and offers valuable data for future research on effective listening instruction. This multifaceted perspective on the study's significance strengthens its academic value and relevance.
1.5 Research Outline: Providing a Roadmap of the Study
This final subsection provides a concise overview of the study's structure, outlining the content of each chapter. This is a brief summary of what each chapter contains; Chapter One, the introduction; Chapter Two, the literature review; Chapter Three, the methodology; Chapter Four, the findings and discussion; and Chapter Five, the conclusions and recommendations. This roadmap ensures readers can easily navigate the study's content and understand the logical progression of the arguments presented.
II. Literature Review: Theoretical Underpinnings and Existing Research
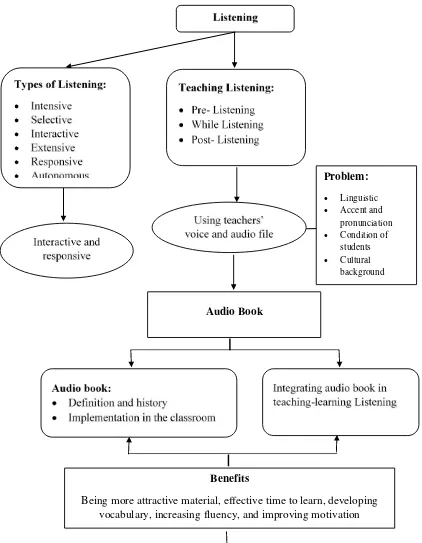
This chapter provides a comprehensive review of existing literature related to listening skills and the use of audiobooks in language learning. It explores different types of listening activities (Rost, 2011), challenges in listening comprehension (Hamouda, 2013), effective teaching methodologies for listening (Vandergrift & Goh, 2012; Brown, 2006), and methods for assessing listening skills (Rost, 2011; Vandergrift & Goh, 2012). The chapter also investigates the definition, history, and benefits of using audiobooks (Chen, 2004; Grover & Hannegan, 2008; Baskin & Harris, 1995; Talalakina, 2011; Cardillo et al., 2007; Alcantud & Gregori, 2013), including their implementation in classroom settings (Serafini, 2004; Learning Ally, 2011). The review provides a strong theoretical framework and empirical support for the study's hypotheses.
2.1 Listening Skill: Types, Challenges, and Pedagogical Approaches
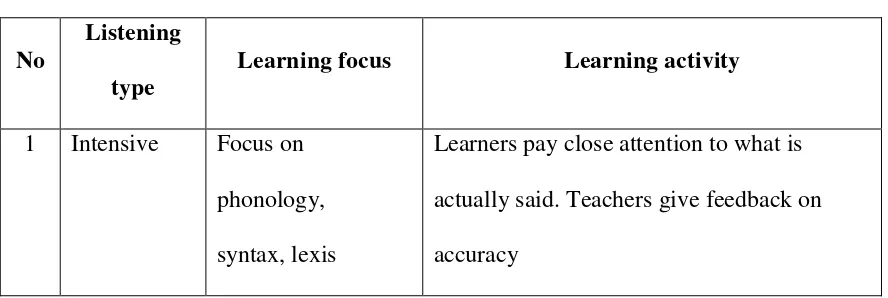
This subsection examines various types of listening, drawing on Rost's (2011) classification into intensive, selective, interactive, extensive, responsive, and autonomous listening. It details the common challenges faced by students in listening comprehension, such as vocabulary limitations, difficulties with accents, and concentration issues (Hamouda, 2013; Renukadevi, 2014). It then explores effective pedagogical approaches, including pre-listening, while-listening, and post-listening activities (Vandergrift & Goh, 2012; Brown, 2006), along with different assessment strategies for evaluating listening skills (Rost, 2011; Vandergrift & Goh, 2012). This provides the theoretical foundation for understanding the complexities of listening skill development and the rationale for employing audiobooks as a potential instructional tool.
2.2 Audiobooks: Definition, Benefits, and Classroom Implementation
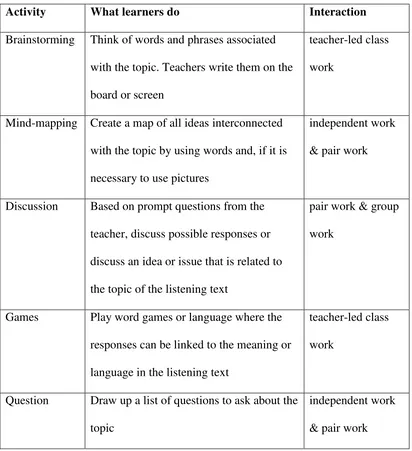
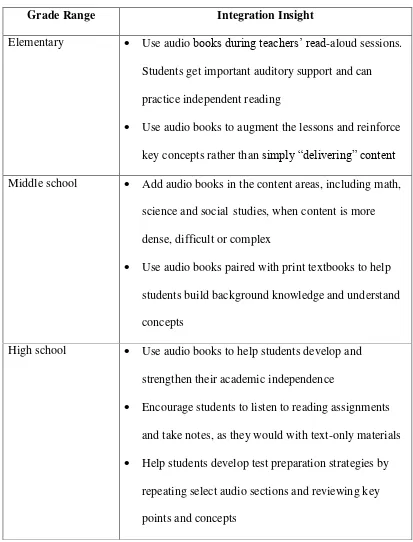
This subsection defines audiobooks and traces their historical development (Chen, 2004; Moody, 1989). It reviews the established benefits of using audiobooks in language learning, including enhanced vocabulary acquisition, improved fluency, increased motivation, and the provision of authentic listening materials (Grover & Hannegan, 2008; Baskin & Harris, 1995; Talalakina, 2011; Cardillo et al., 2007; Alcantud & Gregori, 2013). It also examines practical strategies for integrating audiobooks into classroom instruction, drawing upon examples of various activities and guidelines for effective implementation (Serafini, 2004; Learning Ally, 2011). This section builds upon the preceding discussion of listening skills, providing a clear link between the theoretical framework and the practical application of audiobooks in educational settings.
2.3 ICT Class at SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta: Contextualizing the Study
This subsection describes the specific technological resources available in the ICT classroom at SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta, highlighting the relevance to the study's methodology. The availability of technology, such as LCD projectors and sound systems, is emphasized as facilitating the successful implementation of the audiobook intervention. This establishes a clear connection between the research setting and the chosen methodology, demonstrating the feasibility and appropriateness of using audiobooks in the specified context. The description of available technology also provides important contextual information for interpreting the study's findings.
2.4 Review of Related Studies: Building upon Existing Knowledge
This subsection summarizes relevant prior research on the effectiveness of audiobooks and other technology-based interventions in improving listening comprehension skills. It provides a comparative analysis of existing findings, highlighting similarities and differences with the current study's design and objectives. This helps to position the current research within the broader academic context, demonstrating its contribution to the existing body of knowledge. By summarizing and critically evaluating relevant prior studies, this section strengthens the study’s methodological rigor and enhances its academic contribution.
2.5 Conceptual Framework: Integrating Key Concepts and Hypotheses
This concluding subsection presents a visual representation of the study's conceptual framework, illustrating the relationships between key variables. It articulates the hypotheses guiding the research, clearly stating the expected outcomes based on the integrated theoretical and empirical considerations presented in the literature review. This is crucial for understanding the study’s design, interpreting the results, and evaluating the study's contribution to the field. The clear articulation of the conceptual framework and hypotheses ensures transparency and allows for rigorous evaluation of the research findings.
III. Research Methodology: Design, Instruments, and Procedures
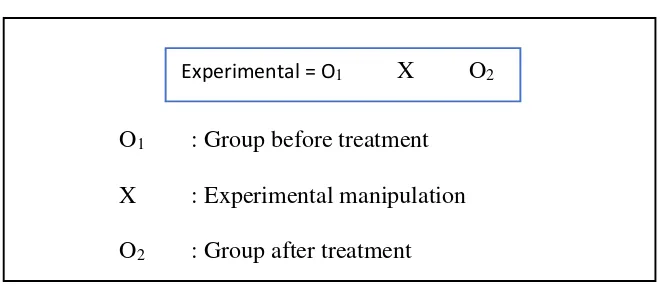
This chapter outlines the research design, participant selection, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques employed in the study. It details the quantitative experimental approach, specifying the one-group pretest-posttest design used to measure the effectiveness of the audiobook intervention. The chapter explains the selection of participants through purposive sampling, focusing on the ICT class at SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta. It describes the research instrument used to assess listening skills, outlining its validity and reliability. The data collection procedures are described in detail, including the administration of the pretest, the implementation of the audiobook-based instruction, and the administration of the posttest. Finally, the chapter explains the statistical methods used to analyze the data, providing a transparent account of the research process.
3.1 Research Design: Choosing an Appropriate Approach
This subsection details the quantitative experimental design employed in the study, justifying the choice of a one-group pretest-posttest design. The rationale for this choice is clearly articulated, considering its suitability for evaluating the effectiveness of the audiobook intervention within the constraints of the research setting. This ensures that the reader understands the strengths and limitations of the chosen design in relation to the research question and objectives. The justification provided enhances the study's methodological rigor and strengthens the validity of its findings.
3.2 Population and Sampling: Selecting Participants
This subsection explains the selection of participants using purposive sampling, focusing on the ICT class at SMP Muhammadiyah 1 Yogyakarta. The rationale behind this sampling method is clearly articulated, emphasizing the suitability of the ICT class for testing the effectiveness of technology-based learning materials. This choice is justified based on the availability of resources and the suitability of the context. The clear explanation of the sampling procedure strengthens the study's internal validity and allows for a better understanding of the generalizability of the findings.
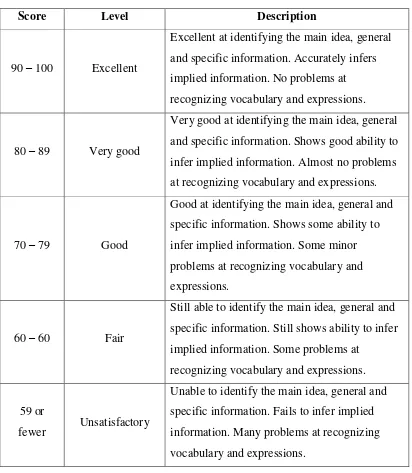
3.3 Research Instrument: Measuring Listening Skills
This subsection describes the instrument used to measure students' listening skills, including details about its construction and validation. The reliability and validity of the instrument are discussed, providing evidence to support its suitability for measuring the targeted construct. The description of the instrument ensures that the reader understands how the data were collected and the potential sources of error or bias. Detailed information about the instrument enhances the study’s transparency and strengthens the trustworthiness of the findings.
3.4 Validity and Reliability: Ensuring the Quality of Data
This subsection focuses on the steps taken to ensure the validity and reliability of the data collected. It explains the measures employed to establish the construct validity and internal consistency of the research instrument. The procedures for ensuring the reliability of the data collection process are detailed, addressing potential sources of error or bias. A strong emphasis on validity and reliability strengthens the credibility and trustworthiness of the study's findings.
3.5 Data Collection Procedure: Implementing the Intervention
This subsection provides a step-by-step account of the data collection process, including the administration of the pretest, the implementation of the audiobook-based intervention, and the administration of the posttest. It describes the timeline of the study, clarifying the duration of the intervention and the intervals between assessments. The detailed description ensures the reproducibility of the study and enhances the transparency of the research process. This detailed account strengthens the study’s methodological rigor and allows for independent scrutiny of its procedures.
3.6 Data Analysis: Processing and Interpreting Data
This final subsection outlines the statistical methods used to analyze the data collected, explaining the specific techniques used to assess the effectiveness of the audiobook intervention. The choice of statistical tests is justified based on the nature of the data and the research question. This transparency ensures that the reader understands how the conclusions were drawn from the data and the limitations of the statistical analyses employed. The clear articulation of the data analysis plan strengthens the study's methodological rigor and facilitates the assessment of the findings’ validity.
IV. Findings and Discussion: Interpreting the Results
This chapter presents the results of the data analysis and discusses their implications in relation to the research question and existing literature. It presents descriptive statistics summarizing the students' pretest and posttest scores, illustrating the changes in listening proficiency after the audiobook intervention. The chapter then presents inferential statistics, such as t-tests, to determine the statistical significance of the observed changes. The discussion section interprets the findings in the context of the literature review, comparing the results to existing research and exploring possible explanations for the observed effects. It also acknowledges any limitations of the study and suggests avenues for future research.
4.1 Findings: Presenting the Empirical Data
This subsection presents the descriptive and inferential statistical findings of the study in a clear and concise manner. It presents the mean scores, standard deviations, and other relevant descriptive statistics for both the pretest and posttest data. The results of any inferential statistical tests, such as t-tests, are presented, indicating whether the observed differences in listening skills between the pretest and posttest were statistically significant. Tables and figures are used to present the data visually, enhancing the readability and accessibility of the findings.
4.2 Discussion: Interpreting and Contextualizing the Results
This subsection interprets the findings in relation to the research question and the literature review. It discusses the implications of the statistical analyses, explaining whether the results support or refute the study's hypotheses. The findings are contextualized within the broader literature on listening comprehension, effective teaching methodologies, and the use of technology in language learning. Potential explanations for the observed effects are explored, considering factors such as the nature of the audiobook intervention, the characteristics of the participants, and the limitations of the study design.
V. Conclusion and Recommendations: Synthesizing Findings and Suggesting Future Directions
This chapter summarizes the main findings of the study and draws conclusions regarding the effectiveness of using audiobooks in improving students' listening skills. It restates the research question and objectives, synthesizing the key results in relation to these aims. Based on the findings, recommendations are provided for educators on how to effectively integrate audiobooks into listening instruction. It also suggests areas for future research to expand upon the findings and address any limitations of the current study. This chapter provides a concluding synthesis of the study's contributions, highlighting its practical and theoretical significance.
5.1 Conclusion: Summarizing Key Findings
This subsection summarizes the main findings of the study concisely, restating the research question and objectives. The key results are presented in a clear and accessible manner, highlighting whether the hypotheses were supported or refuted. The conclusions drawn are directly linked to the evidence presented in the previous chapters, ensuring consistency and coherence. This section provides a clear and concise summary of the study's key contributions and their implications.
5.2 Recommendations: Suggesting Practical Implications and Future Research
This subsection provides practical recommendations for educators based on the findings of the study. It suggests specific strategies for integrating audiobooks into listening instruction, considering various pedagogical approaches and classroom contexts. It also identifies areas for future research to address limitations of the current study and explore other related questions. This section ensures that the study's findings have practical relevance for educators and inspires further research in the area.
Referensi Dokumen
- The Whispering Palms
- The Little Pianist