TEXT BY THE TENTH GRADE STUDENTS AT SMA NEGERI 2 TANJUNGBALAI
A THESIS
Submitted to fulfill the Partial Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
ROSELINA SITEPU Reg. No: 2101321007
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS
ii
patience, so that the the writer can finish her thesis as a partial fulfillment of the
requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan.
In writing this thesis, she has encountered a lot of difficulities since the
beginning to the last; many people have directly helped her in finishing this thesis.
She would like to acknowledge her deep gratitude for all of them for their
generous guidance and assistance:
Prof. Dr. Ibnu Hajar Damanik, M.Si., the Rector of State University of Medan.
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., the Dean of Faculty of Language and Arts. Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd., the Head of English and Literature Department and her Academic Supervisor.
Dra. Masitowarni, M.Ed., the Head of English Educational Study Program.
Dr. Anni Holila Pulungan, M.Hum., her Thesis Supervisor.
Prof, Dr. Busmin Gurning, M.Pd., and Dra. Sri Juriati Ownie, M.A., her Thesis reviewers.
All the Lecturers of English Department who have taught her, her throughout the academic years.
Mam Euis, the Administration Staff of English Department.
Drs. Wahidin Hasibuan, the Headmaster of SMAN 2 Tanjungbalai.
i
Regular and Irregular Verbs in Writing Recount, Narrative, Procedure and Descriptive Text by the tenth Grade Students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai. A Thesis. English Educational Program, State University of Medan, 2014
This research deals with an error analysis. The objectives of the study are (1) to identify and classify the kinds of regular and irregular verbs error find in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai, (2) to know the most dominant text getting regular and irregular verbs error by the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai, (3) to find out the causes of regular and irregular verbs error in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai.
The research design that was used in this study is descriptive research. The sources of data were taken from the tenth grade students of SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai which consists of 40 students who were chosen by taking the X-2 class as the sample. In this research, the writing text was used as collecting data. The result of the analysis shows that: (1) the errors of regular and irregular verbs in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing made by the tenth grade students of SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai were 112 occurrences of all errors. The most dominant text getting regular and irregular verbs was narrative text occurred 40 cases (10 regular verbs and 30 irregular) or (36%), it was followed by recount text occurred 36 cases (7 regular verbs and 29 irregular verbs) or (32%) then the descriptive text occurred 26 cases (7 regular verbs and 19 irregular verbs) or (23%) and the last was Procedure text occurred 10 cases (2 regular verbs and 8 irregular verbs) or (8%).
vi
Table 1.1 The Percentage of the Tenth Grade Students’ Score in Writing ...2
Table 2.1 The Example of Recount Text ...18
Table 2.2 The Example of Narrative Text ...20
Table 2.3 The Example of Procedure Text ...22
Table 2.4 The Example of Decriptive Text ...23
Table 2.5 The Examples of Simple Past with the Regular Verb Work...25
Table 2.6 The Examples of Double Consonant of Regular Verb ...26
Table 2.7 The Examples of not Double Consonat of Regular Verb ...26
Table 2.8 Some Examples of Irregular Verbs ...27
Table 4.1 Classification of Errors ... ..34
Table 4.2 The Recapitulation of Types of Error ...36
Table 4.3 Classification of Verbs’ Errors ...38
Table 4.4 The Recapitulation of Verbs’ Errors ...40
Table 4.5 The Error of Omission Suffix-ed ...42
Table 4.6 The Errors of Omission suffix-d ...43
Table 4.7 The Errors of Omissions Tobe ...43
Table 4.8 The Errors of Adding Tobe ... ..45
Table 4.9 The Errors of Tenses ... ..46
Table 4.10 The Errors of Irregular Verbs... ..47
Table 4.11 The Errors Verbs of Lexical Transfer ... ..48
APPENDIX A
WRITING TEST AT SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai
Subject : Writing
Time allocation : 80 Minutes
Source of the text : English Textbook “Look Ahead” which is published by
Erlangga for the tenth grade students
Read the Instruction Below!
1. Every student in the first group write a recount text about your past experience
(on page 15), the second group write a narrative text about your own narrative
by choosing a very well-known legend, tale, myth, fable, or fairy tale (on
page 61), the third group write a procedure text about how to operate
something (on page 87) and the fourth group write a descriptive text about the
information you have gathered (on page 170).
2. Write your name, number, class and your writing genre on the peace of paper.
3. Write the outline of your writing test based on your topic.
4. Write a (recount, narrative, procedure and descriptive text) that should be
APPENDIX C
THE CLASSIFICATION OF ERRORS
Note:
RT = Recount Text: 44 cases (35%)
NT = Narrative Text: 43 times (34%)
PT = Procedure Text: 10 times (7%)
DT = Descriptive Text: 30 times (24%)
1. The Errors of Omission
NO Text
Types
Regular Verbs
Irregular Verbs
The Form of Error The Right Form
1. RT √ - We want to the zoo by bus We wanted to the zoo by bus
2. RT √ - We want to school together We wanted to school together
3. RT √ - She want to school She wanted to school
4. RT √ - He like smoking He liked smoking
5. RT √ - I ask to father to bring me go holiday to Jakarta
6. RT - √ The bird flying in the sky The bird was flying in the sky
7. NT - √ I ready to extend speech I am ready to extend speech
8. NT - √ There five students I know There were five students that I knew
9. NT - √ The day no fun it was worry The day was not fun but it was worry
10. NT √ They select him their king They selected him to be their king
11. NT √ - The parents disagree with their
relationship
The parent disagreed with their relationship
12. NT √ - I hope people help me I hoped people can help me
13. NT √ - I really understood what see want I really understood what see wanted
14. NT √ - …a special boy that I like …a special boy that I liked
15. NT √ - I want to speech I wanted to speech
16. NT √ - I like it so much I liked it so much
17. DT √ - He live in Novita’s family house He lives in Novita’s family house
18. DT √ - Every morning she prepare breakfast Every morning she prepares breakfast
19. DT √ - She like eat food cold She likes eating cold food
20. DT √ - My mother like very study English My mother likes studying English
30. PT - √ Finally fried egg ready to serve Finally the fried egg is ready to serve
31. PT - √ Make sure that the computer connected
with electricity
Make sure that the computer is connected with electricity
32. PT - √ Wait until the proccessing progress done Wait until the proccessing progress is done
33. PT - √ Next turn omelet when browns Next, turn omelet when it is brown
The Form of Errors The Right Form
1. RT √ - And after that we slept together
to prepared for tomorrow
And after that we slept together to prepare for tomorrow
She said that we were noisy
5. DT - √ We are enjoy We enjoy
6. DT - √ I’m like art teacher I like the art teacher
7. DT - √ I’m love my school I love my school
8. DT √ - I loves it very very much I love it very much
3. The Error of Substitution
We felt happy and played many games
tomorrow
16. RT - √ Another teacher telled us Another teacher told us
17. RT - √ The holiday make me fresh The holiday made me fresh
18. RT - √ The games are hysteria The games were hysteria
19. RT - √ Our stomach are hungry Our stomach were hungry
20. RT - √ We choose Hill park because… We chose Hill park because …
21. RT - √ We go home We went home
22. RT - √ And he brings me some snacks And he brought me some snacks
23. NT - √ Cinderella has one step mother and… Cinderella had one step mother and…
24. NT - √ We are playing roller We were playing roller
25. NT - √ ... than we sleep at night Than we slept at night
26. NT - √ The bus was break The bus was broken
27. NT - √ We see grafe We saw grafe
28. NT - √ Train is to see animal The train was to see animal
29. NT √ - I started walking some houses I started throwing some houses
30. NT - √ So I walk alone So I walked alone
31. NT - √ The balt come and away The balt came and away
32. NT - √ ....but it does not use But it did not use
33. NT - √ Once upon there is a snow white Once opun a time there was a snow
34. NT - √ I know that he was a special boy I knew that he was a special boy
35. NT - √ The dog master come to me The dog master came to me
36. NT - √ One day my teacher bring me to One day my teacher brought me to
37. NT - √ She sitted beside me and waiting for me She sit beside me and waited for me
38. NT √ - I planed to go to with her I planned to go with her
39. NT - √ I falled I screamed I fell and I screamed
40. NT - √ Her step mother hidden her to come Her step mother hid her
41. NT - √ There we singing funny song There we sang a funny song
42. NT - √ She feeled very tired She felt very tired
43. NT - √ She heared about her uncle talked She heard about her uncle’s talking
44. NT - √ We leaved the place We left the place
45. NT - √ She went and she sleeped She went and she slept
46. NT - √ She field to the wood She fell to the wood
47. NT - √ She seed the cottage She saw the cottage
48. NT - √ Cinderella forgothen her promise Cinderella forgot about her promise
49. NT - √ Cinderella run to go home Cinderella ran to go home
50. NT - √ Finally she was driver to the place Finally she was dropped to the place
51. DT - √ I am date of birth in Medan 02 June
1997
I was born on June 2nd 1997 in Medan
52. DT - √ I’m born in Tanjungbalai I was born in Tanjungbalai
53. DT - √ My house have many facilities My house has many facilities
55. DT - √ He have brown hair He has brown hair
56. DT - √ He is pointed nose He has a pointed nose
57. DT - √ The facilities is complete The facilities are complete
58. PT √ - To bet at Ready to served
59. PT √ - Wait a minute until the eggs its soon Wait a minute until the eggs cook
60. PT - √ Place salt paper in plate Put salt paper onto a plate
61. PT - √ Eat when after you make it Eat after it is ready to served
4. The Errors of Mis-Ordering
The Form of Errors The Right Form
1. RT √ - I ask to father to bring me go holiday
to Jakarta to my brother house
I asked father to bring me holiday to
7. DT √ - My mother like very study English My mother very likes to study English
APPENDIX D
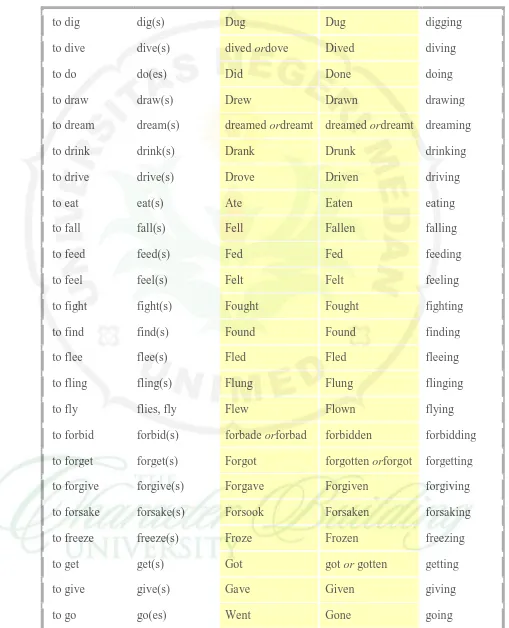
Rules F o r U s i n g I r r e g u l a r V e r b s
Know the solution.
To avoid making mistakes with irregular verbs, learn the very long chart below.
Infinitive Simple
Present Simple Past Past Participle
Present Participle
to arise arise(s) Arose Arisen arising
to awake awake(s) awoke orawaked awaked orawoken awaking
to be am, is, are was, were Been being
to bear bear(s) Bore borne orborn bearing
to beat beat(s) Beat Beaten beating
to become become(s) Became Become becoming
to bend bend(s) Bent Bent bending
to bet bet(s) Bet Bet betting
to bid [to
offer] bid(s) Bid Bid bidding
to bid [to
command] bid(s) Bade Bidden bidding
to bind bind(s) Bound Bound binding
to bite bite(s) Bit bitten or bit biting
to blow blow(s) Blew Blown blowing
to break break(s) Broke Broken breaking
to bring bring(s) Brought Brought bringing
to build build(s) Built Built building
to burst burst(s) Burst Burst bursting
to buy buy(s) Bought Bought buying
to cast cast(s) Cast Cast casting
to catch catch(es) Caught Caught catching
to choose choose(s) Chose Chosen choosing
to cling cling(s) Clung Clung clinging
to come come(s) Came Come coming
to cost cost(s) Cost Cost costing
to creep creep(s) Crept Crept creeping
to cut cut(s) Cut Cut cutting
to dig dig(s) Dug Dug digging
to dive dive(s) dived ordove Dived diving
to do do(es) Did Done doing
to draw draw(s) Drew Drawn drawing
to dream dream(s) dreamed ordreamt dreamed ordreamt dreaming
to drink drink(s) Drank Drunk drinking
to fight fight(s) Fought Fought fighting
to find find(s) Found Found finding
to flee flee(s) Fled Fled fleeing
to fling fling(s) Flung Flung flinging
to fly flies, fly Flew Flown flying
to forbid forbid(s) forbade orforbad forbidden forbidding
to forget forget(s) Forgot forgotten orforgot forgetting
to forgive forgive(s) Forgave Forgiven forgiving
to forsake forsake(s) Forsook Forsaken forsaking
to freeze freeze(s) Froze Frozen freezing
to get get(s) Got got or gotten getting
to give give(s) Gave Given giving
to grow grow(s) Grew Grown growing
to leap leap(s) leaped orleapt leaped orleapt leaping
to leave leave(s) Left left leaving
to lend lend(s) Lent lent lending
to let let(s) Let let letting
to lie [to rest
or recline] lie(s) Lay lain lying
to light light(s) lighted or lit lighted or lit lighting
to lose lose(s) Lost lost losing
to make make(s) Made made making
to mean mean(s) Meant meant meaning
to pay pay(s) Paid paid paying
to prove prove(s) Proved proved orproven proving
to read read(s) Read Read reading
to show show(s) Showed shown orshowed showing
to shrink shrink(s) Shrank Shrunk shrinking
to sing sing(s) Sang Sung singing
to sneak sneak(s) sneaked orsnuck sneaked orsnuck sneaking
to spend spend(s) Spent Spent spending
to spin spin(s) Spun Spun spinning
to spring spring(s) sprang orsprung Sprung springing
to stand stand(s) Stood Stood standing
to steal steal(s) Stole Stolen stealing
to sting sting(s) Stung Stung stinging
to stink stink(s) stank orstunk Stunk stinking
to stride stride(s) Strode Stridden striding
to strike strike(s) Struck Struck striking
to strive strive(s) Strove Striven striving
to swear swear(s) Swore Sworn swearing
to sweep sweep(s) Swept Swept sweeping
to swim swim(s) Swam Swum swimming
to swing swing(s) Swung Swung swinging
to take take(s) Took Taken taking
to teach teach(es) Taught Taught teaching
to tear tear(s) Tore Torn tearing
to tell tell(s) Told Told telling
to think think(s) Thought Thought thinking
to throw throw(s) Threw Thrown throwing
to understand Understands Understood understood understanding
to wake wake(s) woke orwaked waked orwoken waking
to wear wear(s) Wore Worn wearing
to weep weep(s) Wept Wept weeping
to wring wring(s) Wrung Wrung Wringing
to write write(s) Wrote Written Writing
Home • Terms • Exercises• Handouts • Rules • Shop • Feedbac k ©2014 by Robin L. Simmons*
BIOGRAPHY
The writer’s name is Roselina Sitepu, was born in Tanjungbalai on 31th December 1991. She was the fifth child of five children from Rikok Sitepu (deceased) and Selfia Br. Manalu. The writer stayed at boarding house on Perjuangan street number 3 in Medan.
vii
Appendix A. Writing Test ...58
Appendix B. Students’ Work Sheet ...59
Appendix C. The Classification of Errors ...67
1 A.The Background of the Study
English generally has been learned by the students since they were in the
basic level of education. When students learnt English, they are focused on
mastering four language skills: Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing.
Hussain et.al (2013:831) state that writing skill is higher complex than another
skills of language. It requires much concentration, conscious effort and practice in
composing, developing and finalizing and also needs stages and steps of intensive
revision to have final draft in hand. As Mansur (2008) states that in writing
process needs the control of content, format, sentence, vocabulary, punctuation
spelling.
Based on the premilinary observation of the English teacher of SMA
Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai on March 18th 2014, the writer asked the teacher about the
students’ writing score list for the first semester. Then the writer also asked about
the minimum criteria mastery for writing. The writer saw the minimum criteria
mastery (KKM or Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum) was applied 80 meanwhile the
students’ writing score were still low. Most of students could not exceed the
minimum criteria mastery (KKM) which applied by school for English lesson. For
Table 1.1 The Percentage of the Tenth Grade Students’s Score in Writing
1stSemester >80 ≥80 <80
X-1 18 Students(42,9 %) 2 Students(4,8%) 22 Students (52,4%)
X-2 10 Students(24,4%) 3 Students(7,3%) 28 Students (68,3%)
X-3 11 Students(26,8%) 5Students(12,2%) 25 Students (60,8%)
X-4 15 Students(38,5%) 0 Students (0%) 24 Students (61,5%)
X-5 10 Students (25,3%) 2 Students (4,7%) 31 Students (72,1%)
X-6 12 Students(23,8%) 3Students(7,14%) 27Students (69,1%)
Source: The students’ accumalated score of the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai academic year 2013/2014
From the previous data, it can be concluded that the students’ ability in
writing is still low. It can be seen from the most of students’ score percentage are
under the KKM.
Reffering to the Educational Unit Oriented Curriculum (Kurikulum
Tingkat Satuan; KTSP) 2006 of Senior High School, the students are required to
be able to write various types of writing genres, such as descriptive, narrative,
recount, report, procedure, explanation, analytical exposition, hortatory
exposition, news item and anecdote. Meanwhile in the syllabus that stated in
Competence Standard of the tenth grade students curriculum of English Subject,
there are four writing genres that must be learned by students such as recount,
narrative, procedure and descriptive. So the writer uses the recount, narrative,
descriptive, and procedure text as the writing genres in this study.
Recount is purposed to inform the reader or people about the last
to amuse the reader or listener about the last activity or event in the past that has a
problematic experience and resolution. Procedure has the purpose to tell the
reader how to do something. While descriptive has the purpose to describe a
particular person, place, or things. One of the language feature of the texts use
verb (Pardiyono, 2007). So the students are expected to be able to write a recount,
narrative, procedure and descriptive text by using verb to describe the action in
the texts.
Pardiyono (2002:98) states that verb is divided into two groups; a regular
verb and an irregular verb. In regular verb, the verb changes regularly in the past
tense form or the past participle. Such as, it is added by suffix-ed to the base form
of verb. The irregular verbs do not have the form of fixed and do not change
regularly. The irregular verbs have to memorize because the changes are not
permanent.
As the writer’s interview of the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2
Tanjungbalai on March 18th 2014, The writer found some mistakes in students’
writing such as they wrote the past of regular verb “stop” became “stoped” and
“plan” became ”planed”. But the correct forms were “stopped” and “planned”.
The irregular verb “fly” became “filed” and “go” became “wen”. The correct
forms were “flew” and “went”. Even most of students forgot and did not know
about regular and irregular verbs. But sometimes the teacher did not aware about
these mistakes. Then the students made their mistakes repeatedly because they did
not have the correction, more practice and it was called as error (Emmaryana,
Fang and Mei (2007:10) state that few teacher could not tolerate to the
students’ error. They think that the error correction spend their time. So the
students feel upset, and great a gap between themselves and their teachers in
dealing with errors and understanding of error correction.
According to Erdogan (2005: 263) mistakes can be self-corrected when
attention is called. Whereas, an error can not be self-corrected that the use of
linguistic item in a way that a fluent or native speaker of the language regards it as
showing faulty or incomplete learning.
Error analysis is an activity to identify, classify or describe the errors
made by someone in speaking or in writing. Khansir (2012) states that error
analysis is a type of linguistic analysis that focuses on the errors learners make. It
consists of a comparison between the errors made in the target language and that
target language itself. Erdogan (2005) states that error analysis enables teachers to
find out the sources of errors and take pedagogical precautions towards them.
Thus, the analysis of learner language has become an essential need to overcome
some questions and propose solutions regarding different aspects.
Hussain et.al (2013: 828) states error analysis is caused by the slip of the
tongue and pen are termed as lapses or the cause of errors performance. Such
incidents in spoken or written medium happen when the learners are tired,
stressed or at least absorbed in some non-linguistic activity.
The advantages of error analysis for the students are to show the students
error made by the students, to know the source or the cause of error and the
students can learn from their mistakes in order that they will not make some errors
repeatedly. For the teachers, it is required to evaluate themselves whether they are
successful or not in teaching English. So based on the problems that the writer
found on students’ error of regular and irregular verbs, the writer is interested to
analyze the regular and irregular verbs error in students’ writing of recount,
narrative, procedure and descriptive text that supported by relevant theories.
B. The Problems of the Study
Based on the background of the study on the previous, the problems are
formulated as follows.
1. What kinds of regular and irregular verbs error find in recount, narrative,
procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade students at SMA
Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai?
2. What is the most dominant text getting regular and irregular verbs error by
the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai?
3. What are the causes of regular and irregular verbs error find in recount,
narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade students at
C.The Scope of the Study
The study deals with the errors analysis. The study focuses on the
identification, classification the kind of errors, to know the most dominant text
getting regular and irregular verbs error, and to find out the causes of errors on
using regular and irregular verbs in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive
writing by the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai.
D.The Objectives of the Study
Based on the statement of the problems above the writer has some purposes.
1. To identify and classify the kinds of regular and irregular verbs error find
in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade
students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai.
2. To know the most dominant text getting regular and irregular verbs error by
the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai.
3. To find out the causes of regular and irregular verbs error in recount,
narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade students at
SMA N 2 Tanjungbalai.
E.The Significance of the Study
The study is expected to have both theoretical and practical perspectives.
a. The result of the research can be useful for teaching regular and
irregular verbs in recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive
writing.
b. The result of this research can be used as a reference for those who
want to conduct a research about the regular and irregular verbs in
recount, narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing.
2. Practical perspectives
a. For the teachers
The writer hopes that this research will be inspiring for English
teacher to give correction and more exercises about regular and
irregular verb clearly.
b. For the students
The students are more be able to use the regular verb and irregular
53
This chapter presents the conclusion of the result of the study that has been
discussed in previous chapters and suggestion for English teachers and students
and another reseacher.
A. Conclusion
Based on the data analysis and research at the tenth grade students of SMA
Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai, the writer wants to present the conclusion. The conclusion
consists of several points that are related to the statement of problem, there are:
1. The kinds of regular and irregular verbs error find in recount,
narrative, procedure, and descriptive writing by the tenth grade
students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai were errors of omission,
addition, substitution, and mis-ordering.
2. The most dominant text getting regular and irregualr verbs error by
the tenth grade students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai was narrative
text. It occurred 40 cases (10 regular verbs and 30 irregular) or (36%).
3. The causes of regular and irregular verbs error find in recount,
narrative, procedure and descriptive writing by the tenth grade
students at SMA Negeri 2 Tanjungbalai were interlingual transfer, and
intralingual transfer. Interlingual transfer which is caused of the
interference of first language/mother tongue, Intralingual transfer
knowing the rules and the structure of the language and the inability to
apply what they have learned.
B. Suggestions
Considering the conclusion above some suggestions are presented in this
part. As discussed in the previous chapter, this study will hopefully contribute
both theoretical and practical perspectives.
1. For the Teacher
a. The teachers are expected to give proper emphasis on teaching
regular and irregular in present or past tense.
b. The teacher should use an interesting strategy that can help students
to memorize easier.
c. The teacher should give more exercises continuously to their
students. So, they would be able to know about regular and irregular
verb. Then, they discuss the errors in front of the class. By doing so,
the students are expected no to do the same errors.
2. For the Students
a. The students should be able to comprehend the form of regular and
irregular verb in recount, narrative, procedure and descriptive
writing.
b. The students have to memorize the present and past form of verbs
both regular and irregular form.
c. The students are suggested to pay more attention to their study of
using regular and irregular verbs in recount, narrative, procedure and
descriptive writing.
d. The students are expected to study or practice more about the use of
regular and irregular verbs in certain context, so their error can be
reduced and they can master the use of regular and irregular verb in
present and past form.
e. The students should be aware of their errors and avoid repeating the
same errors in their further learning.
3. For other researcher
It finally suggested that other researchers should conduct a further study
about regular and irregular verbs in recount, narrative, procedure and descriptive
56
Ary, D. Jacobs, L.C. & Razaevich, A. 2002. Introduction to Research in Education. Sixth Edition. United States of America: Wadsworth Group
Brown, H.D. 2000. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. Fourth Edition. Englewood Cliffs: Wesley Longman, Inc
Emmaryana, F. 2010. An Analysis on the Grammatical Errors: A Case Study of the First Year Students of SMA Negeri 1 Cigudeg-Bogor. Unpublished Thesis. Jakarta: Syarif Hidayatullah’ State Islamic University
Erdagon, Vaside. 2005. Contribution of Error Analysis to Foreign Language Teaching. Mersin University Journal of the Faculty of Education. I (2)
Fang, X., and Mei, F. 2007. Error Analysis and the EFL Classroom Teaching Learning. US-China Education Review Journal. IV (9)
Gass, S.M. et.al. 2008. Second Language Acquisition an Introductory Course. Third Edition. New York: Routledge
Hussain, Z. et.al. 2013. An Error Analysis of L2 Writing at Higher Secondary Level in Multan. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Busines, IV (11)
Khansir, A.A. 2002. Error Analysis and Second Language. Journal of Theory and Practice in Language Studies. I (5)
Knapp, P., and Watkins, M. 2005. Genre, Text, Grammar: Technologies for Teaching and Assesing Writing. Australia: University of New South Wales Press Ltd
Lawless, L.K. 2010. Simple Past of Regular Verbs. Retrieved from http://www.elearnenglishlanguage.com/blog/learnenglish/grammar/simple -past-regular-verbs/.html accessed on 1 April 2014
Mansur. 2008. An Error Analysis in Recount Writing on the Use of Simple Past Tense by the Tenth Year Students at Smk PGRI 2 Tuban. Unpublished Thesis. Tuban: University of PGRI Ronggolawe (Unirow) Tuban.
Menhook, 2010. Regular and Irregular Verb. Retrieved from http://menhook.wordpress.com/2010/08/07/daftar-irregular-verb-beserta-arti-bahasa-indonesia/ accessed on 25 June 2014
Pardiyono. 2007. Pasti Bisa: Communicative Grammar for Easy Conversation. Yogyakatra: Andi Offset
Pardiyono. 2007. Pasti Bisa: Teaching Genre-Based Writing. Yogyakarta: Andi Publisher
Ramli, Doni. 2013. An Analysis on Students’ Errors in Writing Recount Text. Teacher Training Research Journal of the Faculty of Education, pp. 1-9
Sembiring, I.E.P, 2013. The difference of Grammatical Errors in Writing Recount Text between Natural Science and Social Science Student. Unpublished Thesis. Medan: State University of Medan
Simmons, R.L. 2014. Rules: For Using Irregular Verbs. Retrieved from http://www.chompchomp.com accessed on 8 April 2014
Sudarwati, T.M,. and Grace, E. 2007: Look Ahead: An English Course for Senior High School Students Year X. Jakarta: PT Gelora Aksara Pratama