i
NON-PROJECTED VISUAL MEDIA TO IMPROVE
THE SPEAKING SKILL OF THE EIGHTH GRADE
BHINNEKA TUNGGAL IKA JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL
STUDENTS: AN ACTION RESEARCH
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Magister Humaniora (M Hum) Degree
in English Language Studies
by
Asti Wahyuni Trianingsih
Student Number: 136332013
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
NON.PROJEgTED VJSUAL
MEDIA
TO IMPROVE
BI{INNEKA
TI.]NGGAL
IKA
TiINIOfi.HIGH
SCHOOL STUDENTS: A}IACTION
RESEARCHA T}IESIS
Approvd by
i;,
t:' t"
t,'--f
t,i
I i
r:Fl 'i ,I
Dr. B, B. Dwijatmoko;
ltrA
Thesis Advisor,/
fl-h,4{
ffiffi*r
{m
l?
StudentNtfber:
136332(I'+;j
A TIIESIS
NON.PROJECTED
VISUAL MEDIA
TOIMPROVE
TI{E SPEAKING
SKILL OF THE
EIGHTH GRADE
BHINNEKA
TUNGGAL
IKA JTIMOR
HIGH
SCHOOL STUDENTS: ANACTION
RESEARCHPresented by
Asti Wahyuni Trianingsih Stndent Number: 136332013
Was defended in front of the Thesis Comrni.ttee and declared acceptable
TT{ESIS COMMITTEE
Chairperson : Ilr. J. Bismoko
Secretary
: Dr" B.B. Dwijatmoko, M.AMembers
: l. F.X Mukarto, Ph.D2. Dr.E. Sunarto, M.Hum
,ft-fbr,tf
ry
Program Director
University
It
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
“Life will always have a different plan for you. If you do not give up, you will eventually get to your destination. But towards the end of your life, you may look back and realize that it was never really about the destination. It was the journey
counted.”
King Samuel Benson
“It is good to have an end to journey toward, but it is the journey that matters in
the end.”
Ernest Hemingway
“Vision without execution is a daydream. Execution without vision is a nightmare.”
Mother Teresa
“The way to get started is to quit talking and begin doing.”
Paulo Coelho
“Success is a journey, not a destination.”
Thomas Dewar
STATEMENT OT OruGINALITY
This is to certift tha! all the ideas, plraseg and srntences, unless otherwise stated,
are the ideas; p.hrasm,"and sentences of &e *resis uniter. The writer understands the fulI consequences including degree cancdtation
if
she took somebody else'sideas, phrases, or se,ntences without a proper reference.
Yogyakaxta" July 14s, 201 7
.1
Asti W-ahyuni Trianingsih
LEMBAR PERNYATAAII PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertandatangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Asti Wahyuni Trianingsih
NIM
:136332013Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan
Sanata Dharma ka.ya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
NON.PROJECTED
VISUAL MEDIA
TOIMPROVE
THE SPEAKING
SKILL
OF THEEIGHTH
GRADEBHINNEKA
TUNGGAL
IKA JUNIOR
HIGH
SCHOOLSTUDENTS:
AN ACTION
RESEARCHbeserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan
kepada' Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma
hak
untuk
menyimpan, mengalihkan, dalam bentuk media lain, mengelola dalam bentuk pangkalan data,mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan menrpublikasikan di intemet atau media lain
untuk kepentingan akadernis tanpa perlu meminta
ijin
dari
saya mauprm mernberikan royalti kepada shya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagaipenulis.
Dernikan pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakart a
Pada Tangg al: liJuli 2017
Yang menyatakan:
W,
VI
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My greatest gratitude to Allah SWT, because without His spiritual support, I could never finish this thesis. He has given me so much faith that I even cannot understand it. His angels always whispered in my ears and telling me that I could do any impossible things as long as I had a will to carry it.
My special gratitude goes to my thesis advisor, Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko,
M.A for his patience in guiding me finishing this thesis. I would like to thank him
for giving me the support to finish this thesis. He has also given me his valuable time just to give me some insights, opinion, suggestions, and critisisms to improve my thesis. Without him, this thesis will never exist. I also would like to express my sincere gratitude to all the KBI lecturers, Dr. F.X. Mukarto, Ph. D., Paulus
Sarwoto, S.S., M.A., Ph. D., Dr. Novita Dewi, M.S., M.A. (Hons), Dr. J.
Bismoko, Mr. Widya Kiswara, S.Pd., M.Hum., Ms. Josephine Sri Murwani
Pudji Lestari, M.Hum., for their enlighments, support, and knowledge during
my study in KBI. I would also thank the academic staff mbak Marni for her well cooperation during my time in KBI.
viii
one semester. This school has given me a lot of knowledge, friends, and students that will never be forgotten. Those memories will stay here in my heart forever.
My deepest gratitude goes to my whole family. I would like to say thank you to my parents, my mom and my dad, thank you for believe in me. Thank you for the prayer and thank you for taking care of my daughter while I was busy finishing my thesis. Thank you to my little brother for your patience to pick me up every day. Thank you to my big sister and my big brother for the support.
My sincere gratitude goes to all my friends in KBI. Thank you for giving me the best time of study in my life. We may be apart from each other now, but believe me, I will never forget you. You are the greatest friends that I ever have in my life. Those great memories, happines, laugh, and tears will always stay in my heart as long as I live. My special thanks goes to my best friends, Anindita
Dewanti, Sophia Anggita Kiwang Soge, and Agustina Sri Rahayu. Thank you
for giving me the great support every time I was down. Thank you for giving me the light every time I stayed in the dark.
ix
In the end, thank you to every one whom I cannot mention one by one. Thank you for always being there for me. You will never be forgotten because you will always stay in my heart forever.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE...i
APPROVAL PAGE...ii
DEFENSE APPROVAL PAGE...iii
DEDICATION PAGE...iv
STATEMENT OF WORK ORIGINALITY...v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN UNTUK PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH ...vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS...ix
LIST OF TABLES...xiii
LIST OF FIGURES...xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES...xv
ABSTRACT...xvi
ABSTRAK...xviii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...1
1. 1 Background of the Study...1
1.2 Problem Identification...5
1.3 Problem Limitation...6
1.4 Research Question...7
1.5 Research Objectives...7
1.6 Research Benefits...8
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW...10
2.1 Theoretical Review...10
2.1.1 Non-Projected Visual Media...10
2.1.1.1 The Importance of Using Media in the Classroom...17
2.1.1.2 The Preparation of Using Media Before Teaching...18
2.1.2 The Nature of Speaking...20
2.1.2.1 The Definition of Speaking...21
2.1.2.2 Speaking as a Skill...23
2.1.2.3 The Elements of Speaking Skill...24
xi
2.1.4 Assessing Speaking...31
2.1.5 Action Research...34
2.1.5.1 Action Research for Speaking Skill...38
2.2 Review of Related Studies...39
2.3 Theoretical Framework...41
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY...45
3.1 Research Setting...45
3.2 Research Method...46
3.3 Procedure of Action Research...48
3.3.1 Planning...48
3.3.2 Acting...49
3.3.3 Observing...49
3.3.4 Reflecting...50
3.4 Data Gathering Instrument...50
3.5 Technique of Data Analysis...53
3.5.1 Analyzing Qualitative Data...56
3.5.1 Analyzing Quantitative Data...56
3.5.2 Triangulation...61
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION...64
4.1 Results...64
4.1.1 Planning for the Action...64
4.1.1.1 Pre-observation...65
4.1.1.2 Interview Before Action Research Was Applied...67
4.1.1.3 The Results of the Students’ NeedAnalysis...68
4.1.1.4 The Students’Problem in Speaking...73
4.1.1.5 The Solution to Overcome the Problems...74
4.1.2 The Cycles of Action Research...76
4.1.2.1 Cycle 1...77
4.1.2.1.1 Material and Non-Projected Visual Media...83
4.1.2.1.2 Process of Learning Speaking...89
4.1.2.1.3 Reflection...90
xii
4.1.2.1.5 Planning for the Next Cycle...93
4.1.2.2 Cycle 2...94
4.1.2.2.1 Material and Non-Projected Visual Media...97
4.1.2.2.2 Learning Process Improvement...98
4.1.2.2.3 Reflection...99
4.1.2.2.4 Test Result...100
4.1.2.2.5 Planning for the Next Cycle...101
4.1.2.3 Cycle 3...102
4.1.2.3.1 Material and Non-Projected Visual Media...105
4.1.2.3.2 Learning Process Improvement...108
4.1.2.3.3 Reflection...109
4.1.2.3.4 Test Result...110
4.2 Discussion...111
4.2.1 Learning Process Achievement...112
4.2.2 Learning Result Achievement...117
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS AND SUGGESTIONS...120
5.1 Conclusions...120
5.2 Implications...122
5.3 Suggestions...124
BIBLIOGRAPHY...126
xiii
LISTS OF TABLES
Table 3.1 The Template of the Students’ Need Analysis Result...57
Table 3. 2 The Coding of the Interview Data...62
Table 4.1 The Students’ Speaking Skill (1)...69
Table 4.2 The Students’ Speaking Skill (2)...69
Table 4.3 The Needs of English...70
Table 4.4 The Atmosphere of Learning Speaking in the Classroom...71
Table 4.5 The Use of Media for Learning Speaking in the Classroom...72
Table 4.6 The Results of the Students’ Pre-Test of Speaking...73
Table 4.7 The Comparison Results of the Pre-test and The First Cycle...92
Table 4.8 Paired Samples Test...92
Table 4.9 The Comparison Results of the First Cycle and The Second Cycle....100
Table 4.10 Paired Samples Test...101
Table 4.11 The Comparison Result Between the Second Cycle Test and the Third Cycle Test...110
Table 4.12 Paired Samples Test...111
Table 4.13 The Results of the Tests...117
Table 4.14 Paired Samples Statistics...118
Table 4.15 Paired Samples Correlations...118
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Pictures...12
Figure 2.2 An Illustration...13
Figure 2.3 A Caricature...13
Figure 2.4 A Poster...14
Figure 2.5 A Chart...14
Figure 2.6 A Diagram...15
Figure 2.7 A Bar Graph...15
Figure 2.8 A Map...16
Figure 2.9 Realia and Model...16
Figure 2.10 Board...17
Figure 3.1 The Diagram Model Based on Kemmis & Mc. Taggart (1988)...48
Figure 4. 1 Public Places & Activities...83
Figure 4.2 Was/ WereHand Out...84
Figure 4.3 Regular and Irregular Verbs Hand Out (1)...85
Figure 4.4 Regular and Irregular Verbs Hand Out (2)...86
Figure 4.5 Regular and Irregular Verbs Hand Out (3)...87
Figure 4.6 Public Places Cards...88
Figure 4.7 Activities Cards...89
Figure 4.8 Past Continuous Hand Out...97
Figure 4.9 Activities Rummy Cards...98
Figure 4.10 WH-Questions Hand Out...106
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1. The Blueprint of the Questionnaire of Need Analysis...133
Appendix 2.The Blueprint of the Students’ Reflection Interview...139
Appendix 3.The Blueprint of the Students’ Feedback Toward the Techniques.140 Appendix 4. The Interview Transcript of the Students’ Need Analysis...141
Appendix 5.Transcript of Daniel’s 1st Reflection …...143
Appendix 6. Transcript of Nathania’s 1st Reflection...145
Appendix 7. Transcript of Timothy’s 1st Reflection...147
Appendix 8. Transcript of Yoseph’s 1st Reflection...149
Appendix 9.Transcript of Daniel’s 2ndReflection ...151
Appendix 10.Transcript of Nathania’s 2ndReflection ...153
Appendix 11.Transcript of Timothy’s 2ndReflection ...155
Appendix 12. Transcript of Yoseph’s 2ndReflection ...157
Appendix 13.Transcript of Daniel’s 3rdReflection ...159
Appendix 14. Transcript of Nathania’s 3rdReflection ...161
Appendix 15.Transcript of Timothy’s 3rdReflection ...163
Appendix 16.Transcript of Yoseph’s 3rdReflection ...165
Appendix 17.The Students’ Need Analysis Questionnaire...167
Appendix 18.The Students’ Answer on the Need Analysis Questionnaire...169
Appendix 19. The Test Questions in Cycle 1 ...171
Appendix 20. The Test Questions in Cycle 2 ...172
Appendix 21. The Test Questions in Cycle 3 ...174
Appendix 22. The Results of the Tests...175
xvi ABSTRACT
Asti Wahyuni Trianingsih. 2017. Non-Projected Visual Media to Improve the
Speaking Skill of the Eighth Grade Bhinneka Tunggal Ika Junior High School Students: An Action Research, Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English
Education Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking is one of the most important skills that the students need to master among the four language skills. It is a productive skill which needs the person to think fast to deliver the ideas in an oral form. There are five elements in speaking that the person should master in order to create a better way of speaking namely vocabulary, pronunciation, grammar, fluency, and comprehension. Those elements are united into one and if a person wants to be able to speak English fluently then he or she needs to be good at them.
This research was Action Research. The function of this research was to identify the problems during the teaching and learning process. After the problems were detected, then the researcher together with the students and the colleague tried to find the best solutions to overcome the problems. Action Research consisted of several cycles. When the first cycle was not effective enough to solve the problems then the next cycle might be conducted. The cycle might be stopped when the result of the last cycle was considered enough.
This research was conducted at Bhinneka Tunggal Ika Junior High School. The participants were the eighth graders. From the results of the observation and the pre-test, it was discovered that these students found a lot of difficulties in delivering their ideas orally. There were many things that made them quite difficult to deliver the ideas such as the lack of vocabulary, the lack of comprehending the rules of grammar, difficult to pronounce the words, lack of motivation, and less self-confidence. After having discussion with the students and the colleague, the researcher together with the students and the colleague decided to use non-projected visual media to give more speaking exercise to the students.
This Action Research consisted of four phases in each cycle, namely planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. There were three cycles in this Action Research. From the first cycle, it could be concluded that the students’motivation is getting higher. From the second cycle, it could be concluded that the students’
vocabulary was getting richer. From the third cycle, it could be concluded that the
students’ speaking skill was getting much better.
xvii
differences in two time periods. It could show whether the students performed better or worse at the second time period.
xviii ABSTRAK
Asti Wahyuni Trianingsih. 2017. Non-Projected Visual Media to Improve the
Speaking Skill of the Eighth Grade Bhinneka Tunggal Ika Junior High School Students: An Action Research, Yogyakarta: Program Pasca Sarjana Kajian Bahasa
Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbicara adalah salah satu kemampuan yang penting di antara empat kemampuan berbahasa lainnya yang perlu dikuasai oleh para siswa. Kemampuan berbicara adalah kemampuan produktif yang membutuhkan seseorang untuk bisa berpikir dengan cepat dalam menyampaikan gagasannya dalam bentuk lisan. Ada lima elemen dalam kemampuan berbicara yang harus dikuasai dengan tujuan untuk memiliki kemampuan berbicara yang baik yaitu kosakata, pengucapan, struktur kalimat, kelancaran, dan pemahaman. Semua komposisi tersebut tergabung menjadi satu dan bila seseorang ingin mampu berbicara bahasa Inggris dengan lancar maka orang tersebut harus mampu menguasai semua komposisi tersebut.
Penelitian ini adalah Penelitian Tindakan. Fungsi dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menemukan masalah yang terjadi dalam proses belajar mengajar. Setelah masalah tersebut dideteksi, kemudian sang peneliti bersama dengan para murid dan rekan sejawat berusaha menemukan solusi yang terbaik untuk memecahkan masalah tersebut. Penelitian Tindakan terdiri dari beberapa siklus. Ketika siklus pertama dianggap tidak efektif dalam menyelesaikan masalah maka siklus selanjutnya bisa dilaksanakan. Siklus bisa berhenti ketika hasil dari siklus yang terakhir dianggap sudah cukup memuaskan.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di SMP Bhinneka Tunggal Ika. Para pesertanya adalah murid kelas delapan. Dari hasil observasi dan tes awal ditemukan bahwa para murid ternyata mengalami banyak kesulitan dalam menyampaikan gagasan mereka dalam bentuk lisan. Ada banyak hal yang membuat para murid merasa kesulitan dalam meyampaikan gagasan seperti kurangnya kosakata, tidak memahami pola struktur kalimat berbahasa Inggris yang baik dan benar, susah dalam mengucapkan kata, kurangnya motivasi, dan kurangnya kepercayaan diri. Setelah melakukan diskusi dengan para murid dan teman sejawat, sang peneliti bersama dengan murid dan rekan sejawat memutuskan untuk menggunakan media visual yang tidak diproyeksikan untuk memberikan lebih banyak latihan berbicara kepada para siswa.
xix
belajar bahasa Inggris semakin tinggi. Dari siklus kedua, bisa disimpulkan bahwa kosakata para siswa semakin banyak. Dari siklus yang ketiga bisa disimpulkan bahwa kemampuan berbicara siswa semakin baik.
Untuk menghitung hasil tes, peneliti menggunakan dependent samples t-test atau paired-samples t-test. Dependent samples t-test atau paired-samples t-test digunakan dalam penelitian ini karena hanya ada satu kelompok yang diteliti. T-test digunakan untuk mengukur selisih perbedaan hasil dari dua waktu yang berbeda. T-test dapat menunjukkan apakah para siswa mengalami peningkatan atau penurunan pada periode waktu yang kedua.
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter will discuss the background of the study, problem identification, problem limitation, research questions, research objectives, and research benefit.
1. 1 Background of the Study
It is a true fact that English has become a global lingua franca in the 21st of century. English has appeared as a mean of communication between countries in all over the world which do not have the same first language. Many non-English speaking countries have used English as a bridge to work together in various fields, such as politics, economics, sports, arts, millitaries, technologies, educations, etc. Therefore, the use of English is considered very important in almost every aspect of life.
Mastering English at the early age will give more benefit to Indonesian. They can have more friends around the world. They can gain more knowledge from the book which only printed in English. They can join the exchange students program without worrying about the language that they are going to use. They can also continue their study abroad as long as they are good at English.
There are four main English skills which are very important to learn, namely speaking, reading, writing, and listening. Those four elements are one united that cannot be separated. However, above all those skills, speaking skill is the most wanted skill which become the original idea why there are many English courses in Indonesia. Since many people have realized that English is very important to learn, they are willing to pay in any prices just to master English instantly. Of course, there are many programs that have been offered by the English Courses, however, the conversation classes have always been the most favourite of all.
Looking back all of those facts above, would not it be wonderful if the young generations of Indonesia already can speak English since they were in Elementary School? However, knowing the very important facts of learning
English from the early age still does not change the government’s decision which does not let the Elementary School students to learn English. The result of this decision then will make English will be first taught in Junior High School level although there are many Elementary Schools which still teach English to their students.
School which the average ages are around 13 to 15, they tend to lose their focus during the lesson. Ahmadi and Sholeh (2005) state that at the teenage time, many negatives signs will appear. Those negatives signs are the lack of understanding to the surrounding, the lack of hard working, the lack of movement, easy to get tired or bored, and the greater need of sleeping.
The lack of understanding to the surrounding in here means that the students often make some noise during the lesson. This situation is really happened when the researcher taught in the eighth grade for one month. While the teacher was presenting the material, the students often talked to each other. They even talked very loudly although they knew that the teacher was explaining the material.
The lack of hard working in here means that the students do not really like to do many exercises during the lesson. They are willing to do one or two exercises but when the teacher gives them more exercises, they often complain that the tasks are too difficult, too many, too complicated, too tired and many other excuses that will make the teacher reduce the tasks.
The lack of movement in here means that the students are quite lazy to move their body to do the practice. Although they do not find difficulties walking around the class during the lesson just to get rid of their boredom or to have a chat with other friends, they will find very difficult to move their body when the teacher asks them to work in pairs or to work in group. It takes more than one instruction to force the students to move from their chair to find the other friends to work together in doing the task.
school is quite conventional, such as too many writing activities, the lack of verbal activities, no interesting media to aid the learning process, and more to teacher-centered, the students tend to ignore the teacher and busy doing something else to get rid of their boredom such as playing with their cellphone, talking with other friends, or making excuses to go to the restroom.
The greater need of sleeping in here means that the students of Junior High School need to sleep more than the Elementary School students. The researcher has ever experienced this situation when teaching the eighth grade. When the teacher asked them to do some tasks, some students chose to sleep on their chair,
ignoring the teacher’s warning. In fact, they often slept in the classroomwhenever they found that the material was not interesting to learn.
Those situations above certainly will be great obstacles for the students to achieve the maximum output of the learning. More over, when it has a great
connection to students’ speaking ability. For the eighth grade students, English is not a new thing. They have learned English from the seventh grade and many of them have learned English from the Elementary School. However, their speaking ability is considered very low. Many of them cannot answer very simple questions related to their own personal information, such as what is your nickname?, can
you spell your nickname?, how old are you?, what does your father do?
when they make a sentence, they are influenced a lot by the first language. They also do not hesitate to use an electronic device to create the sentence in English easily, however, this electronic device just translates it technically and often misleads the students.
Teaching English to eighth grade students are not an easy thing to do. Based on the situation described above, a teacher must have a fresher idea to steal the
students’ attention, greater patience to keep survive during the lesson, and better
method to improve the students’ speaking skill. This is where the idea of this research was born.
1. 2 Problem Identification
This research is created because of the researcher taught English to the eighth grade students of Bhinneka Tunggal Ika Junior High School in the second semester. This opportunity came up when the original English teacher, Miss Agnes had an accident and had to stay at home to do the recovery for a whole semester. The researcher was assigned to teach the eighth grade students in the second semester. However, the facts that the researcher found in the field were quite surprising. It is known that Bhinneka Tunggal Ika is a three languages school means that the students will have to learn three languages in this school which are Indonesian, Mandarin, and English. For English itself, it is divided into two subjects, namely Bahasa Inggris, and English. Bahasa Inggris is the subject that the researcher taught in this school. At the first meeting, the researcher spoke English for the whole time and it surprised the students for they did not know what the teacher was talking about. This was also surprised the researcher since
the researcher taught a very simple conversation, many of them did not know the meaning of the conversation that made them keep asking the meaning of the words that they did not know.
Based on the fact above, the researcher decided to make a research on how
to improve the students’ speaking ability since speaking is the crucial part of
English which is very important to master, especially in the 21st century. However, since the students in the eighth grade of this school are considered quite unique, there are only seven students in the classroom, who are easily to get bored or to sleep during the lesson, the researcher planned to use non-projected visual
media to improve the students’ speaking ability. The use of the media in here
besidesto improve the students’s speaking ability but also to reduce the boredom factor that can steal the students’ attention and give more motivation for the
students to learn English in the classroom.
1. 3 Problem Limitation
There are many media that can be used to improve the Junior High School
students’ speaking ability. There are also many ways to attract the students’
attention during the lesson. However, the researcher only focuses to the use of non-projected visual media to improve the students’ speaking skill.
Non-projected visual media are the simplest media of all regardless of the
Besides speaking, the other three English skills such as listening, writing and reading are actually considered important too. However, since speaking is the skill which the students will use directly in the daily conversation, then the
researcher decided to do the research focus in improving the students’ speaking
skill.
1. 4 Research Question
In order to investigate the relationship between the use of non-projected visual media and the Junior High School students’ speaking skill, the following research question is raised:
1. How do the students’ speaking skill improve with the use of non-projected visual media?
1. 5 Research Objectives
There are many factors which can influence the students’ speaking skill
such as the learning atmosphere in the classroom, the motivation, and the
students’ ability in comprehending the material. Those factors can be the key to
improve or to lower the students’ speaking skill. Giving only encouragement to
the students will not be enough to motivate them to improve their speaking skill. Therefore, the correct tool is needed to help the students to improve their speaking skill. This research is conducted to find the connection between the students’
in learning because in order to improve their speaking skill they need to lessen the burden that English is difficult to learn but English is fun to learn.
1. 6 Research Benefits
There are some benefits in conducting this research. If this research is connected to the sense of creativity of the teachers to create their own media to teach, then asAsmani (2009) says that developing the teacher’s potential is a very
necessary thing to do. Ashari (2008) adds that the teachers who will have great career in the future are those who can develop their knowledge creatively and manage their time to do some productive activities. Creating their own media to teach especially non-projected visual media will help them to describe the situations that cannot be described in the classroom.
The teacher will have higher motivation in teaching English because
non-projected visual media will take the students’ attention to learn the language.
Asmani (2009) states that in this globalization era the teacher must know how to create the learning process that can stimulate the students to think creative, divergence, and collaborative. The teacher must value the learning process and must not be oriented to instant learning. The teacher should know how to stimulate English as one of the competences that the students must be able to master.
For the reader itself, hopefully this research can give more ideas in improving
10
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
The aim of this chapter is to clarify the constructs and the concepts of this study. This chapter will discuss three general concepts, namely theoretical review, review of related studies, and theoretical framework.
2. 1 Theoretical Review
The current literature on related themes in this section includes the reviews of (1) Non-Projected Visual Media, (2) The Nature of Speaking, (3) Teaching Speaking, (4) Assessing Speaking, and (5) Action Research. The discussion below is based on those reviews.
2. 1. 1 Non-Projected Visual Media
Visual media are media that can be seen or touched by the teacher and the students. Anitah (2009) says that visual media are media that can give vision or image about something only by looking at them. Meanwhile, Stoner (2009) says that visual media are something that can express a word without writing it, it can explain the abstract concepts, and it can steal the audience’s attention. Rosyada
(2010) states that visual media have strong connection with the visual sense. It is known that there are two messages carried by visual media, which are verbal message and non-verbal message. Verbal visual messages consist of words in the written form, and non-verbal messages are messages that represent in the form of non-verbal visual symbol such as pictures.
to get, and easy to use compare than the other media. They can be used everywhere regardless of the lack of the electricity. They can be used in a school that is located in a small village even without any electricity connection.
There are many kinds of non-projected visual media. Anitah (2009) says that there are ten kinds of non-projected visual media, namely picture, illustration, caricature, poster, chart, diagram, graph, map, realia or model, and board. Those non-projected visual media have their own advantages and they help the teacher to explain the material in various ways. They can be used in presentation step, practice step, or even production step.
Picture is the first non-projected visual media that has many functions. Gerlach & Ely (1980) say that a picture can represent thousands of meaning. A picture can bring the students to the place that unreachable into the classroom. Smaldono (2008) states that a picture can give a vision about anything, such as animals, people, places, or scenes. A picture can bring the abstract idea to the reality world. Edgar Dale (1963) says that a picture can transform the learning experience from the words step into the concrete experience.
There are some advantages of using picture in the classroom. First, a picture can transform the abstract idea into the concrete idea. Second, it can be found in the books. Third, it is easy to use because it does need any equipment. Fourth, it is relatively cheap. Fifth, it can be used for any studies or any levels of the students.
Pictures may also give another benefit by helping the teacher to change the situation fast in oral drill. Kreidler (1963) says that since the student’s goal in
to the students in classroom drill. The use of pictures can make the students more understand about the situation. However, there is quite a major problem that the teacher must face during the teaching and learning process which is keeping the
students’ interest. Since Junior High School students are easily to get bored, then
the teacher must prepare and carefully plan the drill.
However, the picture also has some weaknesses. First, it is too small to be shown in front of the class especially in a big classroom. Second, it cannot move. Third, the students do not always know how to interpret the picture.
There are some characteristics of a good picture. First, it is suitable with the
students’ age and the students’ level of knowledge. Second, it is simple and not
[image:31.595.95.517.230.611.2]too complicated. Third, it is realistic. Fourth, it can be touched by hands.
Figure 2.1 Pictures
Illustration comes from Latin “illustrare” which means explain or make
Figure 2.2 An Illustration
Caricature is a simple picture which is used to criticize something. Planning caricature is not easy because we have to understand first about the object that we are going to draw. It can be used as a communication tool to all level of the society. It means from educated people until those who are not educated at all. It can speak in universal language and it does not need much explanation. It is interesting and it can make clear the idea given.
Figure 2.3 A Caricature
Figure 2.4 A Poster
There are some advantages of using poster. First, it can take people’s
attention. Second, it can be used as a guide. Third, it can be used as a warning. Fourth, it can make people creative when they are making it. Fifth, it can be used as a campaign media.
Chart is a picture which is represented from lines, pictures, and words. It is used to explain relation, development, and comparison about some things. Chart is divided into eleven. They are (1) organization chart, (2) painted chart, (3) comparison chart, (4) invisible chart, (5) conditional chart, (6) pieces chart, (7) guidance chart, (8) time chart, (9) growth chart, (10) schematic chart, (11) flip chart.
Diagram is an open picture about an object or a process. It shows the picture of a piece of an object if we cut the object, for example the half cut of a flower. It can explain the picture by using lines and words.
Figure 2.6 A Diagram
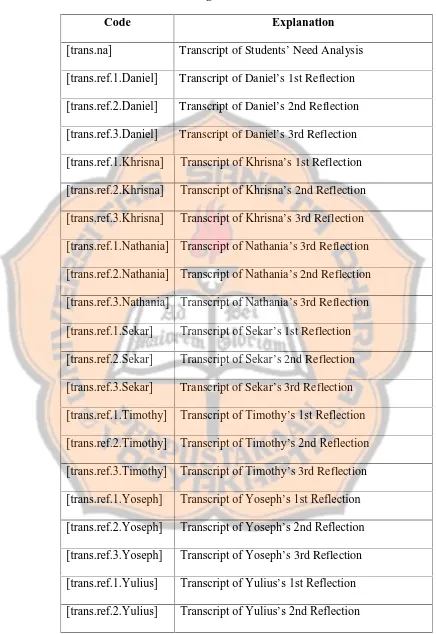
Graph is a picture which is used visual symbols to explain the statistical data. It can be in a form of lines, dots, pictures, and circles. It makes the quantitative picture simpler and understandable. There are four kinds of graph, namely line graph, bar graph, picture graph, and circle graph.
Figure 2.7 A Bar Graph
Map is a picture which is explained about the shape of the earth. It shows the size and the position of the territory based on the scale. Based on the contain, map can be divided into three, namely physic map, economic map, and politic
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
map. Based on the shape, map can be divided into four, namely blind map, three-dimension map, atlas, and globe.
Figure 2.8 A Map
Realia are the imitation of the real object in a complete form. A model is an imitation of the real object in a form of three dimensions. Model has its own scale and it can be smaller or bigger size from the real objects itself.
Figure 2.9 Realia and Model
board, display board, flannel board, fixed board, and announcement board. However, there are also some boards which are made from the paper that can be used by the teacher to drill the students to improve the students’ vocabulary or
[image:36.595.84.515.194.641.2]grammar.
Figure 2.10 Board
2.1.1.1 The Importance of Using Media in the Classroom
The use of media in the classroom is one of the ways to reduce the problems in teaching English. Ruis, et al (2009) say that the major problem of teaching English in classroom is that the learners are not interested in studying English. In order to make them interested in learning English, and make them more motivated in learning English, it is suggested that the English teachers should use media in their teaching and learning process. Media will make the class atmosphere more meaningful and enjoyable. Arsyad (2010) says that visual media hold a very
important role in the learning process. Visual media can help the students’
understanding about the material and they can make the memory stronger. Visual
Media are very useful in learning process. Ruis, Muhyidin, and Waluyo (2009) state that the teachers and the learners are helped by using media to achieve the learning goals. The teachers should apply the media in teaching and
learning activities because (1) media can solve the lack of the learners’
experiences. Since the learners have different background such as family life, society, and social economic, the learners who live in different areas will have different experiences. (2) Media can reach everything out of the classroom. There are so many things around the learners that cannot be reached by themselves, such as: bacteria, virus, etc. To know and to see those tiny things, we must use a microscope as a media. We use a picture to present things which cannot be brought into the classroom such as markets, stations, and harbors. (3) Media create the possible direct interaction between the learners and their environment. (4) Media produce some observation. The learners’ observation can be directed into the important things based on the teachers’ aims. (5) Media can keep the
basic, concrete and real concepts of the teaching. (6) The learners’ motivation is
aroused by using media in learning. (7) Media integrate the experience from the concrete things to the abstract ones.
2. 1. 1. 2 The Preparation of Using Visual Media Before Teaching
or the difficulties that might appear in the middle of the lesson. There are some steps that the teacher can do before he prepares the media.
The first thing that a teacher must do before he plans an activity in the middle of the lesson is analyze the characteristics of the students. Latuheru (1988) states that the failure of the teacher in conducting the teaching and the learning process is caused by the teacher’s fail in analyzing the students’ characteristic.
Therefore, it is very important for a teacher to identify and to know the students specifically. The students can be identified from two types of characteristics, namely general characteristic such as age, sex, the level of the class, culture, economic factor, and special characteristic such as the level of the knowledge, ability, attitude toward the lesson that is going to be explained.
The second thing that a teacher must do before he plans the activity is matching the media with the topic that is going to be discussed in the teaching and
learning process. The media should fit with the students’ characteristics. The
correct media will help the teacher to explain the material smoothly.
After the teacher analyze the students’ characteristics, the teacher must set
the goal that he is going to be achieved in teaching and learning process. Latuheru (1988) says that the main goal in here it means something that the students will get from the teaching and learning process. For example, when a teacher wants to
teach a certain topic and the main goal is to improve the students’ speaking skill,
therefore the media that the teacher must prepare should be the media that can make the students speak more during the lesson.
use a big picture in front of the class and then ask the students to interpret the situation in the picture. Later on, the students can write about the situation in the classroom.
After the teacher has set the main goal that he is going to achieve, the teacher can choose, change or fix the media, and design the media. Many non-projected visual media are ready made. Most of them are available in the market; therefore, the school or even the teacher himself can buy them easily.
There are some factors that the teachers need to consider in choosing the right media for the students. Latuheru (1988) states that the teachers should
consider the students’ characteristics, the goal that the teacher wants to achieve,
the teaching method, and the problems during the teaching and learning process. Even though most of the visual media are available in the market, there are some media that are not sold in the market. Therefore, a teacher can make use the media that are already available in the school or the teacher can modify the media
based on the topic and the students’ need. In modifying and creating the new
media will need the teacher’s sense of creativity. That is why this step is quite
challenging for the teacher because not many teachers are able to do it and not many teachers have some available time to do it.
2. 1. 2 The Nature of Speaking
elements are wrapped into one and each of it has strong relation between one to another.
2. 1. 2. 1 The Definition of Speaking
Speaking is not always long like a sentence in a book. Luoma (2004) mentions that speaking can be considered as the units of idea. When people speak, they usually create short phrases, clauses connected with and, or, but, that, or maybe not joined by conjunctions at all but simply spoken next to each other, sometimes there will be a short pause between them. The grammar that being used in spoken language is usually simpler than the written language. This situation happens because the speaker is trying to communicate the ideas that the listener needs to comprehend at the moment of speaking. It has connection with the listener’s memory while the words are being spoken. Therefore, the units of idea
usually take time for about two seconds or seven words long.
Speaking can also be said as a try to communicate with each other in verbal language. McDonough and Shaw (1993) state that speaking is desire and purpose driven which means that it is originally an effort to communicate something and it should achieve an ending. It involves expressing ideas and opinions, expressing a wish or a desire to do something, negotiating or solving a particular problem, establishing or maintaining social relationship and friendship. Therefore, when we create some dialogs, there will always be an opening, contain, and closing.
Meanwhile, Nunan (1989) says that spoken language consists of short, incomplete utterances, and has strong connection with pronunciations. There will be some repetitions and overlaps between one speaker to another speaker. The speakers usually use the object pronoun of the things rather than saying the original name of the thingsuch as ‘this’, ‘that’, or ‘it’.
into one to make a meaningful utterance. The ideas can be short or long, they depend to the situation where the speaker is going through. Speaking is considered success when the other speaker that we are talking to is able to comprehend our message. Besides vocabulary, pronunciation is also very important in speaking. Since many words in English are not read as they are written, wrong pronunciation may create some misunderstanding between the speakers.
2. 1. 2. 2 Speaking as A Skill
Knowing the elements of the language, it does not mean that we have a great skill in speaking. Bygate (1987) says that to be able to speak a foreign language, certainly we have to master the certain amount of vocabulary and grammar. Knowledge is quite different from skill. For example, in language learning, someone is very good at memorizing the vocabulary and also very good at understanding grammar, however, if this person never tries to use it in the real life conversation or in another meaning, this person never practices to speak to others, then he or she is not that skillful in speaking. It is just like you know the whole theories about the language but then you do not know how to use it. So this
is where the skill takes part. By giving more practices and drillings, the learner’s
to make the circle complete. Knowledge can be understood and memorized but only skill that can be imitated and practiced.
2. 1. 2. 3 The Elements of Speaking Skill
Speaking also has great connection between what to say and how to say the words. Many students claimed that they found difficulties in delivering their ideas in English because they did not know what to say. They had the idea in their mind but it was very difficult to express the idea orally. They also did not know where to start the utterances. This is where the elements of speaking skill will take the most part in making the conversation.
There are five elements of speaking skill, namely pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension. Nation & Newton (2009) state that pronunciation includes the articulation of individual sounds and the distinctive features of sounds, stress and intonation. Meanwhile, Avery & Ehrlich (1992) mention that since every country has their own original accent, studying pronunciation as the native-like may not be perfect; however, ignoring pronunciation can totally be a great loss for students. Based on socio-cultural factors, they state that there are some countries that still keep their original accent as the mark of their own cultural identity. That is why we can find several dialects of English based on the place where they live, such as British English, American English, Australian English, etc. The sound system of the native language really
can affect the students’ pronunciation in three ways. First, when the students meet
the sounds in English which are not the part of their first language. Second, when the students find that the rules of combining the sounds into the words are
patterns of stress and the intonation which are quite different with the students’
first language. Learning pronunciation probably will be a very hard activity for the students especially when they learn English pronunciation. It happens because the English spelling system often fails to represent the sounds of English in direct manner. It means that often the sounds that we hear and the letters that we see on a page are quite different. However, with more practice especially in the classroom, it is hoped that the students will get used to hear the native sound like.
Grammar is one of the elements which is quite important to learn. Grammar is a study of rules to combine the words into sentences. Although some people think that grammar is not quite important to learn for speaking ability, it gives a lot of differences when we speak in grammatically correct or not. A student who learns English at school definitely will have more knowledge about grammar than a person who learns English autodidactic maybe from the movies, books, or songs. Even though it does not guarantee that the student who learns English at school will be more fluent in speaking English than a person who learns English autodidactic. However, a person who speaks English in grammatically correct definitely shows more knowledge in English rather than those who do not.
speaking skill. Improving vocabulary in thousand ways, will give a lot of benefits to the students.
Fluency is considered very important in speaking skill because whenever the students want to learn a new language, what they seek in the end of the course is the fluency of the language. Even when a person is looking for a job which involve the mastering of certain language, what the company needs is the people who can speak the language fluently. Burns and Goh (2012) state that fluency is speech where the message is communicated or delivered coherently with only few pauses and little hesitations. Therefore, the listeners will get the idea easily without causing any difficulties or confusion while they are grasping the speaker’s
words. Fluency is more focus on meaning. A student who can deliver his idea smoothly without thinking too much, without giving many pauses on his words by using mmm, errr, or aaa, may consider fluent in English. The speed of the speech can also be a measure whether a student is fluent in English or not.
Comprehension is certainly being the most important element of speaking skill. Comprehension is the power of the mind to grasp something. This is the reason why comprehension is considered very important because the conversation between two or some people will never be happened when there is no understanding between them. Understanding in here means that those people who are talking to each other, understand what each other say or mean. In that way, those people can ask and give some answers which is connected to the questions.
When a student has a lack of comprehension in understanding the other speaker’s
2. 1. 3 Teaching Speaking
The main purpose of learning English as a foreign language is to master the language and to be able to apply it in the real world. However, this idea has been so long gone in the ideal world of grammar, structure, reading, and writing. Especially, when the students meet the final test in the end of the semester, the test that they have to go through is reading and writing. As a result, many English teachers at school give more focus on the learning of grammar and reading rather
than give more focus on students’ speaking and listening ability. Another result is the students are created to be the passive ones rather than the active ones. This condition can be seen from the eighth grade students of Bhinneka Tunggal Ika Junior High School. If they have learnt English for one year in the previous level, seventh grade, then why they cannot even speak the simplest words of English such as introduction? Giving more focus on grammar and reading are not the wrong things to do. However, as a teacher, we need to teach the English skills in balance, means how much you teach written skill in the classroom will be as much as you teach oral skills to the students. One point that the teacher must remember, when the students graduate from the school and start to face the real world by looking for some jobs to survive their futures and lives, the person who can speak English fluently will have more chance to survive especially in the 21st of century when the government has opened the free trade with many countries. Many foreign investors will come to Indonesia and how can we work together with them if we cannot even understand their language?
speak fully English in the classroom. This assumption has led the teachers to teach English with the first language such as Indonesian, and sometimes even with Javanese. This poor condition of course does not give any benefit at all to the students. How can the students be able to speak English if they never heard the teacher communicate in English? How can they be brave to speak English if the teacher never gives encouragement to the students to practice the language? Surely hiring a native speaker to teach English is a good way to do, but of course it is not an easy way to do if the school financial cannot support it. Therefore, a local teacher can be a replacement model of the native speaker.
Teaching speaking can be a hard way to do if the students are not quite familiar with the vocabulary. Therefore, as a teacher, we need to supply the vocabulary to the students, teach them how to say it, and how to apply it in the real conversation. Since the language of speaking can be a bit different than the language of writing, the teacher should give the clear explanation about it. If the students only imitate the words from the text book, the result is their language will
sound very bookish. This is where the teacher’s part is highly needed to give more
examples about how to give more communicative language to the students. The teacher can start it by giving simple instructions in the classroom. Between the
instructions, ‘listen to the conversation and fill in the missing words’ and ‘I want
you to listen to the conversation and after that I want you to fill in the missing
words. Do you understand?’, the second instruction sounds more communicative
important because in the real time those kind of things would be readily processed and the learners will find easy to understand and those are the kind of language that good teachers use.
If we want to teach speaking to the students, we need to pay attention to several aspects. Willis in Pawlak & Klimzcak (2015) mentions that there are three basic conditions that the teacher must pay attention if the aim of the lesson is to teach conversation effectively. First, we must have a clear idea of what conversation is like. Is it conducted in the formal or non-formal situation? What kind of expressions that the students can use? Therefore, we need to think of it carefully. Second, we must communicate this to our students. As a teacher, we do not just give the task to the students without explaining what they are going to do. The students may be misled if the teacher does not give the correct direction. Third, we must bring into the classroom samples of language which bear a real resemblance to spontaneous spoken language.
The role of the teacher is considered very important for the development of
the students’ speaking skill. Richards (2012) says that there are three key factors in successful language learning. They are teachers, materials, and the learners. The role of the teacher is to help the learners to acquire the language and the
skills. Without the teacher’s help the learners will not be able to achieve the progress even though they have worked hard. Teachers can be a great observer.
By being an observer, teachers may understand more about language learner’s
active in providing input, support, and feedback. Creating activities that enable the students to communicate with their classmates is only a part of the learning experience that teachers can provide for the students. However, those activities will be considered not enough because they will not learn new skills and language if there is little linguistic and background knowledge about them. Therefore, the
role of the teacher is to structure the students’ learning experiences to support
their speaking development, in and outside the classroom. Teachers may do this by designing interesting and appropriate materials.
Materials in teaching speaking should be the materials that will support the second language speaking development. Richard (2012) states that there are three categories of good materials for speaking. First, the materials should provide the speaking practice. They should provide contextualized, varied, and interesting prompts and scenarios so that the talk can take place. Second, the materials should promote the language and skills learning. It means that the materials should focus on selected elements of the talk, or model spoken texts to increase learners’
relevant linguistics knowledge and control of speaking skills. Third, the materials should facilitate meta-cognitive development. In other words, the materials must
raise the learners’ knowledge and control of learning processes, and can train them in using communication and discourse strategies.
and the demands of speaking. They also must critically consider the strategies that can facilitate their oral communication. Learners may work collaboratively with their peers.
2. 1. 4 Assessing Speaking
Assessing speaking is considered as a challenging activity because teacher as the examiner often finds difficulties in deciding of how well the students speak the language. Luoma (2004) states that there are so many factors which can influence the teacher impression about the students’ ability in speaking the language. It happens because the teacher expects the test scores to be accurate and appropriate for the purpose. Sometimes, it will be very difficult to judge the
students’ speaking skill if the teacher only gives focus to one out of the five elements of speaking skill, namely pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension. Because it is often found in the field that there are many students have large vocabulary but they are lack of grammar. Meanwhile, there are some students that have good pronunciation and grammar, but they only have small vocabulary. Some students are very talkative in delivering the idea, in the other hand, they often mispronounce the words. Other students are not talkative. They only speak few words but they speak accurately and grammatically correct. Those factors often give the teacher a lot of considerations before he or she decided the score. In this situation, the teacher must give a fair judgment to the students.
Creating a language test to measure the students’ ability in speaking is sometimes confusing. As a teacher, we are often wondering what is the best
teachers create the test, they must think of it carefully. Hughes (1989) state that the test or the testing system should consistently provide accurate measures of precisely the abilities in which the teachers are interested. It must have a beneficial effect on teaching, especially in the cases where the test is likely to influence teaching. It is also economical in terms of time and money.
There are some purposes why the testing is conducted. Hughes (1989) mentions that the purpose of the testing is to measure the language proficiency. That is why testing is often conducted after one or some materials have been finished to discuss. Testing is also to discover how successful students have been in achieving the objectives of a course of study. Testing is to diagnose students’
strength and weaknesses, means to identify what they know and what they do not know. It is to assist placement of students by identifying the stage of or part of teaching program most appropriate to their ability.
A test can be said valid if it measures accurately what it is intended to measure. In assessing speaking, the teachers should be clear with the purpose of
the test. If the main purpose is to find out the students’ skill in talking the
language, then the teachers will not give the focus to students’ reading or writing
means that the researcher should not expect that the students’ speaking skill will
be much better than the students in the ninth grade. The second form of evidence relates to the content of the test is criterion-related validity. It relates to the degree to which results on the test agree with those provided by some independent and
highly dependable assessment of the students’ ability. In other words, the material of the test for eight grade junior high school may not be mixed with the material for the ninth grade of Junior High School.
Having validity in scoring is also very important. Hughes (1989) says that not only the items that should be valid but also the score. It is no use having excellent items of testing if they are scored invalidly. When the teachers wish to
measure the students’ speaking skill, it is not enough to elicit speech in a valid
fashion. The rating of the speech should be valid too. The teachers may give different score to the students who can deliver the idea smoothly to those who need more time to speak the idea.
2. 1. 5 Action Research
Action Research (AR) is one of the best ways for the researcher to find the problem during the teaching and learning process, analyze it, and then find the best solution for it. McNiff & Whitehead (2002) state that AR is a practical way to check whether how the way you are teaching in the classroom runs just the way that you are planning or expecting. If you think that your practice is satisfactory, then you may explain how and why that makes you think that this is the case. Later on you can provide some evidences to prove your claims. However, when you think that your practice is the opposite or less satisfactory, then you may take an action to improve it. Later on, you may produce the evidences to show that in what way that your practice has changed and improve.
Action Research is quite important to apply in the classroom. It can help the teacher to find the solutions of the problem that is found during the teaching and learning process. Mills (2011) says that AR can be defined as systematically investigation conducted by the teachers, the administrators, the counsellors, or anyone else which has a special interest in teaching and learning process in order to gather some information about their school, how the way the teachers teach, and how the way the students learn. Meanwhile, Johnson (2008) says that AR is a kind of research which is conducted by the teachers and for their own beneficial.
aim of AR is to improve the work quality of others. Practically, this research purpose is to improve the quality of the research subject. The subject of the research may be a group of people or only an individual who have the same purpose which is to improve the quality of their work. Syamsuddin and Damaianti (2006) conclude that AR is more emphasize to the activity (action) by experimenting the ideas through the practice or the real situation in a micro scale, and it is hoped that the activity may repair and improve the quality in a certain situation, teaching and learning process for the example. Parson & Brown (2002) mention that AR can make the teachers to study about their own classes. It includes the method that the teachers use during the teaching and learning process, study about the students, and study about the teachers themselves. AR is applied in the classroom to gain better understanding and to improve the quality and the effectiveness of the teachers themselves. The research is focus on the unique characteristics from a population.
Action Research has some characteristics. Syamsuddin and Damaianti (2006) mention that the researcher is the active agent in the main activity. They also mention that the researcher is the agent of change. Meanwhile, the participant of the research will have the benefit from the result of the action which was given regularly by the researcher. Besides that, Stringer (2007) states that AR is democratic because it gives many chances for the people to participate. AR is
equitable because it gives value to every person’s work. AR is liberating because
it provides the people’s freedom from pressure situations and weak conditions.
AR is life enhancing because it is able to show the expression of the people’s
It is known that there are some advantages in doing AR. Syamsuddin and Damaianti (2006) state that when a teacher does AR, he or she does not need to leave the place of work. The teacher can also feel the result of the action that he or she has been planned. Beside the teacher, the respondent will also feel the effect of the action that has given by the teacher. Those advantages are the benefits that only belong to AR. There is no other research that can give those benefits. Mertler and Charles (2011) also mention the importance of AR. There are some benefits in conducting AR in the classroom. First, it deals with your own problem in the
classroom, not with somebody else’s problem. Second, AR can be done anytime. It can be started now, or whenever you are ready, and it can also give direct feedback. Third, AR gives more opportunities to the teachers to understand better and to improve their practice. Fourth, AR as a process may build stronger relationship between teachers for they share the same problem and they try to solve it together.
There are some stages in doing Action Research. According to Kemmis and McTaggart (1998), the major author of AR, AR usually involves four broad phases in a cycle of research. The first cycle may be continued into several cycles until a satisfactory result has been achieved and it is considered that it is the time to stop the cycles. In a cycle of AR, it consists of planning, action, observation, and reflection.
are dealing with. This is the phase where the researcher must consider about what kind of investigation which is possible in dealing the situation and what are the potential improvements that considered possible in the situation.
The second stage is action. In this phase, the plan should be carried out carefully since there will be some interventions during the teaching situation and the researcher will put the action over an agreed of time. Those interventions will be critically informed when the researcher questions the assumptions about the current situation and then later on the researcher must plan new and alternative ways of doing something. In this case means that the researcher must be well prepared in conducting the plan because sometimes the plan is not doing well as it has been planned before.
The third stage is observation. In this phase the researcher must observe the effects of the action systematically and the researcher also must document the context, actions, and the opinions of those who are involved in the research. We
can call it as a data collection phase where the researcher must use ‘open eyed’
and ‘open-minded’ tools to collect the information about the situation which is happening during the research.
2.1.5.1 Action Research for Speaking Skill
Stringer (2007) defines Action Research as an approach which is quite systematic to the investigation and this research can make the people to find the best solutions for each problem that they have to deal every day. Different from traditional experimental or scientific research which provides general explanations that can be applied to all contexts, AR more focuses on certain situations and certain solutions. AR is a collaborative approach to the investigation which supplies people with the certain equipment to do some specific action to handle the problems. The scope of this research is quite local. It does not provide all answers for all problems, however, the systematically actions that have been taken by the researcher can be a great insight for other people that work in the same field and face the same problem. The aim of this research is to improve the effectiveness of the quality of work where the people live.
the students’ opinion about the teaching and learning process. The researcher in
here also collaborated with her colleague which teaches English in the same class. Her opinion, advice, and also her insight have been very useful for the researcher to improve the teaching and learning quality in the classroom.
Doing Action Research in the field of speaking skill will give many advantages for the p