THE USE OF RECIPROCAL TEACHING TECHNIQUE FOR IMPROVING SPEAKING SKILL AT THE SEVENTH GRADE
STUDENTS OF SMPN 1 MOJOANYAR MOJOKERTO THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By:
Gilang Pratama Putra D35212050
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Pratama Putra, Gilang. (2017). The Use of Reciprocal Teaching Technique for Improving Speaking Skill at the Seventh Grade Students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto. A Thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University, Surabaya. Advisor: Dr.Phil. Khoirun Ni’am.
Key Words: Reciprocal Teaching Technique, Speaking.
ABSTRAK
Pratama Putra, Gilang. (2017). The Use of Reciprocal Teaching Technique for Improving Speaking Skill at the Seventh Grade Students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto. Tesis Program Studi Pendidikan Guru Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri (UIN) Sunan Ampel, Surabaya. Penasihat: Dr.Phil. Khoirun Ni’am.
Kata Kunci: Teknik Pembelajaran Timbal Balik, Berbicara.
TABLE OF CONTENT
COVER ... i
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET...iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
STATEMENT OF THE ORIGINALITY ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ... x
LIST OF TABLE ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Questions ... 4
C. Objective of the Study ... 4
D. Scope and Limitation ... 4
E. Significance of the Study ... 4
F. Definition of Key Term ... 4
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Literature ... 7
1. Definition of Speaking ... 7
2. The Elements of Speaking ... 8
3. Point to Consider about Speaking ... 10
4. The Types of Classroom Speaking Performance ... 10
5. The Purpose of Speaking...11
6. Teching Speaking ... 11
7. Reasons for Teaching Speaking ... 13
8. The Goal of Teaching Speaking...13
9. The Roles of the Teacher during Speaking Activities...14
10. The Assessment of Speaking... 14
11. Reciprocal Teaching Technique...16
12. The Purpose of the Reciprocal Teaching Technique...18
13. How to Use Reciprocal Teaching Technique...19
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Setting of the Research ... 23
B. Subject of the Research... 23
C. Method of The Research ... 24
D. The Writer’s Role on the Study ... 24
E. Procedures of the Research ... 25
F. Technique of Collecting Data ... 26
G. Technique of Data Analysis ... 27
H. The Criteria of the Action Success ... 28
CHAPTER IV : RESULT AND DISCUSSION A. Research Finding ... 30
1. The Result of the Interview before CAR ... 30
2. The Result of the Observation before CAR ... 30
3. The Result of Pre-Test... 31
4. The Implementation of the Classroom Action Research..31
B. Discussion ... 41
1. The Result of the Interview after Classroom Action Research ... 41
2. The Result of Post-Test ... 42
3. The Interpretation of the Test Result... 46
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 48
B. Suggestion ... 49
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Research Background
Speaking is the key of communication. For the students, the achievement of English speaking is an important measure of academic success.1 Kalayo and Ansyari point out that many learners regard speaking ability as the measure of knowing a language. They regard speaking as the most important skill they can acquire and they assess their progress in terms of their accomplishments in spoken communication.2 According to Nunan speaking is the single most important aspect of learning a second or foreign language.3
A success of students in speaking is measured through the accuracy and fluency of their speaking ability. According to Harmer Speaking is using all the language at their command to perform some kinds of oral task.4 The students should always practice in classroom or out of the classroom activities. They can express their ideas with other people by speaking.
In any language education programs, it is not an easy work for teachers or facilitators to create the spoken ability among their learners, especially the English learners correctly and accurately. Besides, it needs a hard work, be professional in teaching English
1 Marianne Cecle and Murcia Lois McIntosh, Teaching English as a
Second of Foreign Language, (Los Angeles: New Bury House
University of California, 1987), p.126.
2 Drs. Kalayo Hasibuan, MEd-TESOL and Muhammad Fauzan Ansyari,
S.Pd.I. Teaching English as a Foreign Language (TEFL) (Pekanbaru: Alif Riau Graha UNRI Press, 2007), p.101.
3 David Nunan, Language Teaching Methodology a Textbook for
Teachers. (New York. 1991), p.39.
2
with certain educational qualification and appropriate strategy in order to achieve the goals of teaching.5
Teacher is supposed to be a model for his/her students by having good knowledge about learning process as the basic of the teaching and learning activity.6 How can the students be able to speak English, while the teachers do not use English as media of instruction.
Therefore, the teacher needs an approach, so that the students have better behaviour in speaking. There is an approach which can improve students’ motivation in speaking skill, it is Reciprocal Teaching Approach.
Reciprocal teaching approach is an effective approach that is used by the teacher in speaking subject. According to Suprapto in his journal, the influence of reciprocal teaching approach is very variety. It is influenced in communication skill, motivation, achievement, and cognitive achievement.7
Reciprocal teaching refers to an instructional activity in which students become the teacher in small group reading session. The teachers’ model, then help students learn to guide group discussions using four strategies: Predicting, Questioning, Summarizing or Retelling, Clarifying.8
Based on the observation conducted at the seventh grade of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto, the writer found that the student speaking skills was still low. It can be seen in the learning process that the students faced difficulties in comprehending of speaking skill. They needed a lot of time to understand. That condition caused the students have difficulties in speaking English.
5 Drs. Kalayo Hasibuan, M.Ed-TESOL and Muhammad Fauzan
Ansyari, S.Pd.I, Teaching English as Foreign Language (TEFL)
(Pekanbaru: Alif Riau Graha UNRI Press, 2007), p.31.
6 Drs. Slameto, Belajar dan Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhinya (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 1997), p 97.
7 Suprapto Jielwongsolo, “Reciprocal Teaching”, (accessed on February 14,2017,http://supraptojielwongsolo.wordpress.com/2008/06/17/recipro cal-teaching/).
3
Moreover, the students’ motivation was also still low to speak English. They did not want to try to speak even though they were involved in any speaking activities that were held by the teacher such as discussion, debate, English day, speech contest, storytelling, etc. When the teacher asked them for what substantively affect their motivation to speak English. The answer of some students gave such description about the real problem faced in learning English such as strategy used by the teacher, learning environment, supporting facility and many else.
Furthermore, the students will not get optimal standard achievement in speaking because they do not know what their aims to speak English, the condition and situation in the classroom have not been designed naturally for speaking, and the student still lack in use vocabulary, grammatical and acceptable interaction. Therefore, the teacher must think how the classroom interaction should best be designed to cater the student communication need.
Based on those problems above, the writer believed that Reciprocal Teaching Technique would be very useful for the teaching learning process because the students were given a large opportunity to speak and they belonged to such group discussion which also gave good motivation for them to speak among the group and also to the teacher.
In applying Reciprocal Teaching Technique, the students discussed some reading material. They thought about it, and then they were speaking each other in the group to discuss what the reading material was about. In addition, in reciprocal procedure, the students have their own job or function for a specific problem to solve in form of dialogue with the teachers or among the group. In other words, the students had much time to speak during the discussion process to show their responsibility in solving the problem of the text.
4
B. Research Questions
1. How is the implementation of reciprocal teaching technique to improve speaking skill of the seventh grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto?
2. How is the improvement of the study after using reciprocal teaching technique in the students speaking skill of the seventh grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto?
C. Objective of the Study
1. To identify the implementation of reciprocal teaching technique to improve speaking skill of the seventh grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto.
2. To find out the improvement of the study after using reciprocal teaching technique in the students speaking skill of the seventh grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto
D. Scope and Limitation
Based on the problem statement, the writer realizes that it is impossible to carry out a classroom action research based on all the problem above. The writer limits the problem to the teacher’s monotonous technique in teaching speaking skill. The writer used reciprocal technique to teach speaking of the seventh grade of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto.
E. Significance of the Study
The advantages of conducting this study:
1. For the teachers, they know the importance of reciprocal technique for teaching speaking and are able to apply it to students speaking skill.
2. For the students, they can be more skillful in speaking because they have been trained how to speak effectively by using the strategies of reciprocal techniques procedure.
3. For other researchers, they can use this study to develop the similar study such as reading, listening and writing.
F. Definition of Key Term
To make easier in understanding this research, the writer defines the key terms as follows:
5
In accordance with Palinscar who introduced this technique: The formal definition of reciprocal teaching is as follows: “Reciprocal teaching refers to an instructional activity that takes place in the form of a dialogue between teachers and students regarding segments of text”.9
2. Technique
Technique is a way of doing something, especially one that needs special skills.10
3. Improve
Improve is become or make better, make a good use of something.11
4. Speaking
Speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing and receiving and processing information.12 It is form and meaning are dependent on the context in which it occurs, including the participants themself their collective experiences, the physical environment and the purposes for speaking. It is often spontaneous, open-ended, and evolving. However, speech is not always unpredictable. Language functions (or patterns) that tend to recur in certain discourse situations.13
5. Skill
Skill is capacity needed to implementing some tasks, which is the development of training results and experience gained.
9 Annemarie S Palinscar, A. and Ann L Brown. 1984, “Reciprocal Teaching of Comprehension-Fostering and Comprehension-Monitoring Activities”, Cognition and Instruction 1,2., (http://eca.state.gov/forum/ vols/vol33/no4/p29.htm, accessed on January 11, 2017).
10 Oxford University, Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2008).
11 Oxford Dictionary, Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary..., p. 216. 12 H.D Brown, Teaching by principles: an interactive approach to
language pedagogy. Englewood Cliffs, (NJ: Prentice Hall Regents, 1994).
6
6. Student
Student is person who studying at the school or university.14
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Review of Related Literature
1. Definition of Speaking
Speaking skill, as the writer writes in the previous chapter is one of the basic language skills that has important role rather than other skills due to its significant and its use for communication. So that, the writer will explain about the nature of speaking itself in order that gives the obvious information about what speaking is.
In the point of view of Jones, speaking is a form of communication, so it is important that what you say is conveyed in the most effective way. How you say something can be as important as what you say in getting meaning across.1 Based on that opinion, speaking is realized as communication. Therefore, speakers are required to be able to express what they want to say as effectively as possible in order to convey the message.
Bygate says, Speaking is a skill which deserves attention every bit as much as literary skills, in both first and second language. It is the skill which the students are frequently judged. It is also the vehicle par excellent of social solidarity, of social ranking, of professional advancement and of business.2 It indicates that as one of the language skills, speaking should get the attention from teachers and learners because it plays the important role in our society.
Meanwhile, McDonough and Shaw state, there are some reason for speaking involved expressing ideas and opinions: expressing a wish or a desire to do something, negotiating and/or solving a particular problem or establishing and maintaining
1 Rhodry Jones, Speaking and Listening, London: John Murray Publishers Ltd, 1989, p.14.
2 Martyn Bygate, Language Teaching: A Scheme for Teacher
8
social relationships and friendships. Besides, fluency, accuracy, and confidence are important goal in speaking.3
Therefore, as a language skill, speaking becomes an important component to master by the students as the main tool of verbal communication because it is a way to express ideas and opinions directly what we have in our minds. Based on the previous definitions above, it can be synthesized that speaking is the process of using the urge of speech to pronounce vocal symbols in order to share the information, knowledge, idea and opinion to the other person. Moreover, speaking cannot be dissociated from listening aspect, because speaking involves speaker and listener.
2. The Elements of Speaking
Speaking is very important skill in mastering English for students who learn English required mastering the ability to speak and communicate with each other. There are five aspects that have great influence toward speaking ability:
a. Vocabulary
Students need to learn the component of language. They need to learn what the words mean and how they are used. Meaning that, the students need to have plenty of vocabularies. Vocabulary comprises the right and appropriate use of word. One of the extreme aspects that supports speaking in English is vocabulary. Hornby states that vocabulary is the total number of words that language.4 b. Grammar
Bygate says, it is obvious that in order be able to speak foreign language, it is necessary to know a certain amount of grammar and vocabulary.5 Grammar is the sounds and the sound patterns, the basic units of meaning, such as words, and
3 JO McDonough and Christopher Shaw., Materials Methods in ELT, (Melbourne: Blackwell Publishing, 2003), p.134.
4 Albert S Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner Dictionary of Current
English. (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1984) p. 956.
5 Martyn Bygate, Language Teaching: A Scheme for Teacher
9
the rules to combine them to form new sentences.6 Therefore, grammar is very important in speaking because if the speaker does not mastering grammar structure, he cannot speak English well.
c. Fluency
Speaking is an activity of reproducing words orally. It indicates that there is a process of exchanging ideas between speaker and listener. According to Hornby, fluency is able to speak or write a language or performs an action smoothly or expressed in a smooth and fluently in order to makes someone easy to understand what he or she said.7
d. Pronunciation
All words are made up of sound and speakers of language need to know these sound. Therefore, as an English teacher, you not only teach well at pronunciation, but you also make it possible for the students to acquire good pronunciation by imitating you. According to Marianne Celce-Murcia, pronunciation is a characteristic of the huge potential that only a small subset of sounds is systematically used in speaking any one language.8 To make our communication accepted by our listeners. It is better for us to pronoun the words clearly, especially with the most similar pronunciation.
e. Comprehension
The last speaking element is comprehension. Comprehension is discussed by both speakers because comprehension can make people getting the information they want. Comprehension is defined as the ability to understand something by a reasonable comprehension of the subject or as the knowledge of what a situation is really like.
6
Victoria Fromkin and Robert Rodman, An Introduction to Language,
(New York: Harcourt Brace College Publishers, 1998), p.14. 7
Albert S Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner..., p.427.
8 Marianne Celce and Murcia Lois McIntosh, Teaching English as a
Second or Foreign Language, (Los Angeles: New Bury House
10
3. Point to Consider about Speaking
Speaking is a form communication, so it is important that you say is conveyed in the most effective way. How you say something can be as important as what you say in getting your meaning across. Jones stated that there are some points to consider about speaking. They are:
a. Clarity
The words you speak must be clear if listeners are to understand what you say. This means speaking your words distinctly and separately, not running them together and slurring them.
b. Variety
Speech has its own rhythms and tunes. The voice usually rises, for instance, to indicate a question. Some words in a sentence require more emphasis than others if the meaning is to be clear. Unimportant words tend to be spoken more quickly than important ones. Consider things like pitch, emphasis, speed, variations in volume, pauses.
c. Audience and Tone
The way you speak and the tone you use will be affected by the audience to whom you are speaking.9
4. The Types of Classroom Speaking Performance a. Imitate
Imitation is this kind carried out not for the purpose of meaningful interaction, but for focusing on some particular element of language form.
b. Intensive
Intensive speaking goes on steps beyond imitative to include any speaking performance that is designed to practice some phonological or grammatical aspect of language. Intensive speaking can be self-initiated or it can ever form part of some pair work activity, where learners are going over certain forms of language.
c. Responsive
9
11
A good deal of students’ speech in the classroom is responsive, short replies to teacher or students initiated questions or comments.
d. Transactional (dialogue)
Transactional language, carried out for the purpose of conveying or exchanging specific information, is an extended form of responsive language.
e. Interpersonal (dialogue)
Interpersonal is carried out more for the purpose of maintaining social relationship than for the transmission of facts and information.
f. Extensive (monologue)
Finally, students at intermediate to advanced levels are called on to give extended monologues in the form of oral reports, summaries, or perhaps short speeches. Here the register is more formal and deliberative. These monologues can be planned or impromptu.10
5. The Purpose of Speaking
It is beneficial to understand that purpose of speaking itself. The purposes are stated as follows:
a. To expect students to have a language function skill to make themselves understand.
b. To enable students to convey meaning.
c. To make the students able to express themselves orally. d. To motivate students in order to be able to communicate
orally with native speakers.
e. To motivate students in order to use English.
6. Teaching Speaking
Teacher should consider about the difficulties of the students to learn speaking skill. In teaching speaking skill, there are some consideration that the teacher should pay attention to. In this part, the researcher present the information about teaching English speaking.
10
12
Teaching speaking gives a systematic information, instruction, or training to students about how to convey meaning to communicate with other by using correct sounds and words.
Nunan in Thomas describes what teaching involves. He stated to teach speaking means to teach language learners to: a. Produce the English speech sounds and sound patterns. b. Use word and sentence stress, intonation patterns and the
rhythm of the second language.
c. Select appropriate words and sentences according to the proper social setting, audience, situation and subject matter. d. Organize their thoughts in a meaningful and logical sequence. e. Use language as a means of expressing values and judgments. f. Use the language quickly and confidently with few unnatural
pauses, which is called as fluency.11
Bygate stated that one of the basic problems in foreign-language teaching is to prepare learners to be able to use the language.12 In other words, the teacher needs to have a good preparation and plan for teaching and learning activities in the class. The preparation includes the teaching method and teaching material. It is also important to consider the age range of the students before he or she designs teaching activities because teaching children, teens, and adults are different.
Brown mentioned seven principles for designing speaking techniques. They are:
a. Using techniques that cover the spectrum of learner needs. b. Providing intrinsically motivating techniques.
c. Encouraging the use of authentic language in meaningful contexts.
d. Providing appropriate feedback and correction.
e. Capitalizing on the natural link between speaking and listening.
f. Giving students opportunities to initiate oral communication.
11
James E Thomas, Teaching Speaking Skills. Master Diploma Thesis.
(Department of English And American Studies Masaryk University,
2011)p.18.
13
g. Encouraging the development of speaking strategies.13 Another idea is from Johnson in Setiyadi. They suggested five possible learner roles that can make language learners more autonomous. One of them is “learners are member of a group and learn by interacting with others”.14 It means that by working in groups, students will have more opportunity to speak up their idea in order to learn English more effective.
7. Reasons for Teaching Speaking
Harmer stated that there are three main reasons for getting students to speak in the classroom:
a. Speaking activities provide rehearsal opportunities changes to practice real life speaking in the safety of the classroom. b. Speaking tasks in which students try to use any or all of
language they know provide feedback for both teacher and students. Everyone can see how well they are doing, both how successful they are and what language problems they are experiencing.
c. In speaking, students have opportunities to activate the various elements of language they have stored in their brains, the more automatic their use of these elements become. As a results, students gradually become autonomous language users. This means that they will be able to use words and phrases fluently without very much conscious thought.15
8. The Goal of Teaching Speaking
The goal of teaching speaking skills is communicative efficiency.16 It means learners should be able to make themselves understood, using their current proficiency to the fullest. They
13
H. Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principles an Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. (New York: Pearson Education, 2001) p.275. 14 Bambang Setiyadi, Teaching English as a Foreign Language, (Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu, 2006)p.19.
15
Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach English, (Harlow: Pearson Education Limited, 2007), p.123.
14
should try to avoid confusion in the message due to faulty pronunciation, grammar or vocabulary and to observe the social and cultural rules that apply in each communication situation.
9. The Roles of the Teacher during Speaking Activities
During speaking activities, teacher needs to play number of different roles. They can be prompter, participant, even feedback provider as viewed by Harmer as follow:
a. Prompter
When students sometimes get lost in speaking, teacher can leave them to struggle out of situations on their own, and indeed sometimes, this may best option. However, teacher may be able to help students and the activity to progress by offering discrete suggestions.
b. Participant
Teacher should be good animators when asking students to produce language. This can be achieved by setting up an activity clearly and with enthusiasm. At other times, teachers may want to participate in discussions.
c. Feedback Provider
When students are in the middle of speaking task, over-correction may inhibit them and take the communicativeness out of the activity. On the other hand, helpful and gentle correction may get students out of difficult misunderstanding and hesitations.17
In summary, when teacher being a prompter, a participant, even a feedback provider, they have to be careful that they do not force students, do not participate too much and do over correction.
10.The Assessment of Speaking
Speaking is a complex skill requiring the simultaneous use of different ability which often develops at different roles. Speaking skill are generally recognized in analysis of speech process that are pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, fluency and comprehension.
17
15
Heaton presented the sample of an oral English rating scale that used 1-6 points. Below is the frame of Heaton’s Oral English Rating Scale:
Table 2.1
6 Pronunciation good – only 2 and 3 grammatical errors - not much searching for words - very few long pauses - fairly easy to understand - very few interruptions necessary - has mastered all oral skills on course. 5 Pronunciation slightly influenced by L1 - a few
grammatical errors but most sentences correct - sometimes searchers for words - not too many long pauses - general meaning fairly clear but a few interruption necessary - has mastered almost all oral skills on course.
4 Pronunciation influenced a little by L1 - a few grammatical errors but only 1 or 2 causing serious confusion - searches for words - a few unnatural pauses - conveys general meaning fairly clearly - a few interruptions necessary but intention always clear - has mastered most of oral skills on course.
3 Pronunciation influenced by L1 - pronunciation and grammatical errors - several error cause serious confusion - longer pauses to search for word meaning - fairly limited expressions - much can be understood although some effort needed for parts - some interruptions necessary - has mastered only some of oral skills on course.
2 Several serious pronunciation errors - basic grammar errors - unnaturally long pauses - very limited expressions -needs some effort to understand much of it - interruptions often necessary and sometimes has difficulty in explaining or making meaning clearer - only a few of oral skills on course mastered.
16
Each element characteristic is defined into six chart behavioral statements as stated in frames above. The writer will objectively see the characteristic of each students speaking ability whether they achieve 1,2,3,4,5 and 6. In order to case the computation, the writer converts the small score of Heaton to scale of 100 as follow:
6= 87-100 5= 77-86 4= 67-76 3= 57-66 2= 46-56 1= below 45 18
11. Reciprocal Teaching Technique
Before implementation of reciprocal teaching technique, it is necessary to know how the reciprocal teaching technique is. Based on Farris’s description, she stated that reciprocal teaching is one of the most carefully researched, prominent strategies. In this cooperative learning procedure, the teacher and the students work together to develop an understanding of the text. There are four thoughtfully integrated comprehension strategies at the core of this approach, prediction, questioning, seeking clarification, summarization.19
It means that, reciprocal teaching technique is a process to comprehend text by using four steps which is done by the teacher and the students to build their speculation about the text.
Reciprocal teaching is an approach used by teacher in cooperative learning method by applying four learning strategy, those are questioning, clarifying, summarizing, and predicting. Moreover, Santrock indicate that reciprocal teaching approach is a model of teaching involves the teacher and the students. In this approach, the teacher is explaining and modeling the strategy in comprehending the text firstly. Afterwards, the teacher asks the
18 J. B Heaton, Classroom Testing: Longman Keys to Language
Teaching, (New York: Longman, 1990), p.70-71.
19 Pamela J. Farris, Teaching Reading a Balance Approach for Today’s
17
students to demonstrate the strategy and gives support when the students have learned. Therefore, the students will be motivated in teaching and learning process. Because it claims the students involvement or scaffolding system.20
Meanwhile, Elizabeth Walter defines, reciprocal as a reciprocal action or arrangement involve two people or groups of people who behave in the same way or agree to help each other and give each other advantages.21 In other words, reciprocal is regarded as an interaction between two people or more gain same purpose cooperatively. Meanwhile teaching derived from word teach, it is defined as to give someone knowledge or to train someone.22
According to Palinscar and Brown, there are four components of reciprocal teaching, they are questioning, clarifying, summarizing and predicting:
Questioning involves the identification of information, themes, and ideas that are central and important enough to warrant further consideration. The central or important information, themes, or ideas are used to generate questions that are then used as self-tests for the reader. Questioning provides a contexts for exploring the text more deeply and assuring the construction of meaning.
Summarizing is the process of identifying the important information, themes, and ideas within a text, integrating these into a clear and concise statement that communicates the essential meaning of the text. It may be based on a single paragraph, a section of text, or an entire passage. Summarizing provides the impetus to create a context for understanding the specifics of a text.
Clarifying involves the identification and clarification of unclear, difficult, or unfamiliar aspects of a text. These aspects may include awkward sentence or passage structure, unfamiliar vocabulary, unclear references, or obscure concepts. Clarifying
20 Jhon.W. Santrock, Psikologi Pendidikan, (Jakarta:Prenada Media Group, 2007), p.427.
21 Elizabeth Walter, Cambridge Advance Learner’s Dictionary Third
18
provides the motivation to remediate confusion through re-reading, the use of context in which the text was written and or read, and the use of external resources (e.g., dictionary or thesaurus).
Predicting involves combining the reader’s prior knowledge, new knowledge from the text, and the texts structure to create hypotheses related to the direction of the text and the author’s intent in writing. Predicting provides an overall rationale for reading to confirm or disconfirm self-generated hypotheses. Santrock states that using reciprocal teaching is to increase the students’ ability to do some strategies to increase their understanding in reading.23
Trianto says that reciprocal is one of the approaches to teach the students about the learning strategies, those are questioning, clarifying, summarizing, predicting. In reciprocal, a teacher teaches the students about the important cognitive skills by creating studied experience, attitude modeling and helping the students to increase their skills for effort themselves by motivating, supporting and scaffolding system.24
12.The Purpose of the Reciprocal Teaching Technique
Pallinscar and Brown stated that, while students and teacher apply reciprocal teaching procedure, its purpose that the teacher prompts and shapes the students participation by using corrective feedback.25 It means that, the teacher as guidance to maintain the activity and to give respond correctively in the classroom.
Moreover, Farris researched that careful supervision and practice will help students to master the step in an educationally interactive dialogue.26 In this point, students can develop their
23 Jhon. W. Santrock, Psikologi Pendidikan…, p.427.
24 Trianto, Mendesain Model Pembelajaran Inovatif-Progressif. (Surabaya: Prenada Media Grup: 2009), p.174.
25 Annemarie Pallinscar and Anna Brown, “Reciprocal Teaching: A means to a Meaningful End”, in Jean Osborn, (ed), Reading Education: Foundations for a Literate America, (Urbana Campaign : D.C Health and Company, 1985), p.299.
19
understanding the steps within the dialogue between the teacher and the students.
Furthermore, Cotteral said that, firstly the strategy training allows them to gain confidence and expertise as they apply the four strategies to a variety of texts.27 Using the reciprocal teaching technique, students could build their confidence for many kinds of texts. She also explained that the purpose of this interaction notion is to engage students’ attention to the meaning of the text, it could bring students to identify the kind of problem they are finding, and to seek clarifications in a text. In short, by dialogue between students and the teacher will help the students concentrate and identify the text.
13.How to Use Reciprocal Teaching Technique
In applying reciprocal technique, the researcher distributed the material to be discussed by the students. Since of the procedure of reciprocal strategy demanded students to be able to predict where the students are asked to make a prediction what will the reading material be about. In this process the student tried to make a correlation their prior knowledge to the information consisted in the material. From the first cycle until the second cycle the researcher had given about reading material to be discussed. And the materials enriched students’ vocabularies.
In accordance with Palinscar and Brown who introduced this technique, the formal definition of reciprocal teaching is as follows: Reciprocal teaching refers to an instructional activity that takes place in the form of a dialogue between teachers and students regarding segments of text.28 Therefore, in order all students got more active in the dialogue process of discussion in applying predicting, summarizing, clarifying, and questioning
27Sara Cotteral, “Reciprocal Teaching: A problem Solving Approach to
Reading“, Guidelines a Periodical for Classroom Language Teachers 12 (1991), p.31-39.
20
about reading material given, the researcher and collaborator gave any help to lead the student involve in those activities. In other words, the researchers gave scaffolding to the students until they could lead and do discussion in good order. Summarizing provides the chance to identify the most important information of the text. Questioning reinforces the summarizing strategy and carries the learner one more step along in the comprehension activity. Clarifying gives an opportunity to students to clarify any unfamiliar message, difficulty word and if they have problem they might reread the difficulty one for asking help in discussion.
B. Previous Study
There are some previous studies that related with the tittle of this research. The first study was done by Ika Fhatma Sari Putu Wara Sukma Wardana, entitled “The Effectiveness of Using Reciprocal
Technique on Students’ Reading Ability of Narrative Text”.29In this
research, the researcher used quasi-experimental method, while the writer used mixed qualitative and quantitative method. The researcher just focused to use reciprocal technique on students’ reading ability of narrative text, while this writer focused on the improving speaking skill on article texts.
The second previous study is about “Reciprocal Teaching to Improve English Reading Comprehension of a Group of Form Three Students in Hong Kong”. The author is Leung Won Gay, Faculty of
Education at University of Hong Kong. The purpose of this study was to explore and experiment with a modified reciprocal teaching in a local ESL classroom context, examine whether there were any qualitative differences between students’ reading comprehension processes when reading texts prior to and after the intervention and investigate the effectiveness of Reciprocal Teaching on improving reading ability. The method used in this study was an experimental research.30 In this research, the researcher just focused to use
29Ika Fhatma Sari, Bachelor Thesis: “
The Effectiveness of Using
Reciprocal Technique on Students’ Reading Ability of Narrative Text”. (Jakarta: UIN Syarif Hidayatullah, 2014).
30 Won-Gay Leung, Bachelor Thesis: “Reciprocal Teaching to improve
English reading comprehension of a group of form three students in
21
reciprocal teaching technique for improving reading comprehension for students group, while this research focused on the improving speaking skill.
The third previous study is about “Applying reciprocal
Teaching Technique to Improve Students Comprehension of
Mathematic Concept”. The author is Munifah Fajarwati from Yogyakarta University. In this research, the writer used Classroom Action Research (CAR) as her method. The researcher used three components to collecting data, there are observation, test and documentation. For the data analysis, the researcher used technique of interactive analysis which include data reduction, data display and conclusion. Finally, the result of this research is reciprocal teaching technique could improve students’ comprehension of mathematic concept, it means that reciprocal technique is success in improving students’ comprehension of mathematic concept.31
The fourth previous study is about “Reciprocal Teaching of
Comprehension Strategies Improves EFL Learners' Writing Ability”.
The author is Mohammad Reza Ghorbani, Faculty of Education in University of Bojnord, Bojnord, Iran. This research is aimed at improving students’ skills of writing by EFL learnes’. This design was an action research study that consisted of planning, action, observation and reflection.32 The difference with researcher is the media implementation and also the design.
The fifth previous study is about “Improving Students Reading
Comprehension Using Reciprocal Questioning Technique a Classroom Action Research in SMK Diponegoro Salatiga in Academic Year 2007/2008” The author is Ani Afida.33 This research was designed by using classroom action research in which this
31 Munifah Fajarwati, Bachelor Thesis: “Applying Reciprocal Teaching
Technique to Improve Students Comprehension of Mathematic Concept”
(Yogyakarta: Yogyakarta University).
32Mohammad Reza Ghorbani, “Reciprocal Teaching of Comprehension Strategies Improves EFL Learners' Writing Ability”. Current Issues in Educaation. Vol. 16 No. 1, January 30, 2016.
33
Ani Afida, Masters Thesis: “Improving Students Reading Comprehension Using Reciprocal Questioning Technique: A Classroom
22
research study concerned with teaching reading comprehension by using reciprocal technique could effectively improved and increased the low ability in reading comprehension in SMK Diponegoro, Salatiga, while teacher focused on the improving speaking skills.
The sixth previous study is about, “The Effectiveness of
Reciprocal Technique Towards Students’ Reading Comprehension
on Report Text”. The author is Lulu Walidaini, UIN Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta. The method that used in the research was quasi-experimental method which divided two different classes. The classes were designed as experiment class and control class.34 In this research, the researcher used quasi-experimental method, while the writer used mixed qualitative and quantitative method. The researcher just focused to use reciprocal teaching technique for the effectiveness of reciprocal technique towards students’ reading comprehension on report text, while this writer focused on the improving speaking skill on article texts.
The seventh previous study is about, “Improving Reading
Comprehension Through Reciprocal Technique to the Tenth Grade
Student of SMK PGRI 4 DENPASAR in Academic Year 2013/2014”. The author is Kadek Suparna, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education in Mahasaraswati University, Denpasar. This research aims to improve the tenth grade student’s reading comprehension through reciprocal technique at the SMK PGRI 4 Denpasar in academic year 2013/2014. The findings of the research are expected to be useful and relevant theoretically and practically.35 In this research, researcher just focused on the influence using reciprocal techniques for the students comprehension in reading, while the writer focused on improving speaking skill with using reciprocal teaching technique methods.
34
Lulu Walidaini, Bachelor Thesis: “The Effectiveness of Reciprocal Technique Towards Students’ Reading Comprehension on Report Text” (Jakarta: UIN Syarif Hidayatullah, 2015) p.iii
35
Kadek Suparna, Bachelor Thesis: “Improving Reading
Comprehension Through Reciprocal Technique to the Tenth Grade Student of SMK PGRI 4 Denpasar in Academic Year 2013/2014,
23
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Setting of the Research
This research was conducted at SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto. SMPN 1 Mojoanyar is located in Jabon Village, Mojoanyar District, Mojokerto Regency, East Java. SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto is one of the state junior high school in Mojoanyar District. SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojoanyar has three grades namely the seventh grade, the eighth grade, and the ninth grade. Each grade consists of seven classes. The other buildings are library, teacher office, headmaster office, administration office, computer room, language room and mosque. Teaching and learning process in SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto are done in six days from Monday up to Saturday. The place selection was based on the consideration where the teacher’s of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto and the institution never conducted research about Reciprocal Teaching Technique.
B. Subject of the Research
In this research, the writer choosed SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto as object of the study especially the seventh grade students. The seventh grade students consist of seven class groups, but the writer took one class group, VII-A. The number of the participants are 31 students. They are 17 girls and 14 boys. Their native language is Bahasa Indonesia. The average age of the participants are 13 years old. They have been taught English since the first year of school. They get English lesson which is each meeting along with two hours lesson; one hour lesson is 45 minutes.
24
C. Method of the Research
The research method used in this study is Classroom Action Research (CAR). According to Gay, Classroom Action Research is concerned with a local problem and is conducted in a local setting.1 It means that researcher has to observe and identify the problem at the classroom. In addition, he stated the purpose of action research is to solve classroom through application of the scientific method.2 It means that, in the study the writer also has to provide the solution and an effort about the problem that concern in teaching learning process.
In line with what is said by Wallace, Ebbutt in Hopkins states that classroom action research is about the systematic study of attempts to improve educational practice by groups of participants, by means of their own practical actions, and by means of their own reflection upon the effects of those actions.3
In this study, the classroom action research that is conducted is an attempt to improve students’ speaking skills. This classroom action research is going to be carried out using reciprocal teaching. The effects of the action can be known after using reciprocal teaching technique in speaking skills. The reflection shows whether the technique of reciprocal teaching can improve the students’ speaking skills or not to be higher than before.
D. The Writer’s Role on the Study
In the study, the writer is not only as the observer, he arranges the schedule together with the teacher. In the action, the writer also
1 L. R. Gay, Education Research: Competencies for Analysis an
Application (Colombus: Merril Publishing Company, 1986), p.8. 2 L. R Gay, Education Research Competencies for..., p.8.
3 Dave Ebbutt, Educational Action Research: some general concerns
25
makes lesson planning and the assessment or test before Classroom Action Research pre-test and after post-test in each final cycle. On the other side as the teacher, he carries out the action based upon the lesson planning has been arranged. Furthermore, the writer also collects and analyzes data then reports the result of the study.
E. Procedures of the Research
The writer uses a classroom action research designed by Kurt Lewin model. The cycle contains four phases. They are planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. After the writer and the students accomplish cycle 1 and then there might be found a new problem. They have to continue the next cycle with the same phase of the first cycle. Here are the descriptions in every phase:
1. Planning Phase
In this phase, after the writer observe the class and the writer interviews the teacher. Then, the writer identifies and diagnoses students’ speaking problem occured in the class. At the time, the writer analyses the data that have been identified through observation, interview and makes conclusion. After that, the writer arrange the plan to conduct the classroom in turn. Next, the writer makes lesson plan to applying in VII-A grade class at SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto. The lesson planning also describes teaching procedures, media and resources in every cycle.
2. Acting Phase
According to Arikunto, the acting phase should be implemented at least two cycles continuously, and the time period for each cycle depends on the material needs that existed in the semester or annual program designed by the teacher.4 Related to the condition of limited teaching learning period, the writer take the action phase during two weeks within two cycles in which each cycle consists of two meetings in action.
26
3. Observing Phase
In this research, the writer used observation guidance which consists of indicator that is designed according to the focus of research. Besides that, the writer also used some tools such camera or video recorder to analyze the data. This observation focused on students’ activity in class such take a note what can be seen, heard, and observed during the learning process. The data being taken were quantitative and qualitative data. The quantitative data covered the students’ progress while the qualitative data comprised the students’ interest and students’ response.
4. Reflecting Phase
After collecting the data, the writer analyzes the data of teaching learning process. Then, the writer reflects himself by seeing the result of the observation, whether the teaching learning process of speaking using reciprocal teaching technique is good to imply in teaching and learning process at VII-A grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto or not. If the first plan is unsuccesful, proven by students’ achievements, the writer will make the next plan to solve students’ problems and to get a better score in order to achieve at least 75% students who passed KKM 75 (Seventy Five).
F. Technique of Collecting Data
There are two types of collecting data: qualitative and quantitative data. The researcher presents the act of collecting data as follows:
1. Interview
The writer interview the teacher before applying classroom action research. It is to know general description about process of learning speaking skills, to know the students difficulties in speaking skill, to know the situation in speaking activity, the method or any strategies usually implemented by the teacher in teaching speaking.
2. Test
27
learning English especially in speaking lesson. While post-test, is used to measure how far do their improvement after applying the strategy in speaking lesson. Pre and post-test are to knowing the differences between the students ability before and after the teacher used the strategy.
3. Observation
Observation is written note about what is seen, heard, and experienced in collecting data and reflection toward qualitative data. Observation is used to get the certain target which is observed. In this case, the writer uses the unstructured or opened observation directly in the classroom and gets the description about students’ activity and participation in learning process. The process is when the implementation of classroom action research, speaking activity, and students participation in applying reciprocal teaching technique.
G. Technique of Data Analysis
The writer conducted the classroom action research of teaching speaking using Reciprocal Teaching Technique at seventh grade students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto. In analyzing data, the writer used mixing qualitative and quantitative approach. According to Johnson and Christensen, qualitative research relies primarily on the collection of qualitative data (i.e., non-numeric data such as words and pictures).5 While Lodico stated that quantitative approaches summarize data using numbers. Hypotheses and methods of data collection are created before the research begins. This technique is used to know the students’ score of speaking skill in each cycle.6
5 Burke Johnson and Larry Christensen, Educational Research
Quantitative, Qualitative and Mixed Approaches, 2007.
28
To analyze the statistical data, the writer puts on the average of students speaking score per action in one cycle, it uses the formula as follow:7
M = ∑ͯ � Where,
M = Mean of students score ∑ͯ = The sum of students score N = The total number of students
The writer tries to get the class percentages that pass the KKM considering English subject score is 75 (seventy five) in each cycle. In addition, the writer identifies whether or not there might have students’ improvement on speaking from pre-test 1, post-test 1 and post-test 2. The formula used to know the class percentage as follow:
P = �
� x 100% Where,
P = The class percentage F = Frequency are being found N = Number of students
H. The Criteria of the Action Success
Classroom action research is able to to be called successful if it can exceed the criteria that has been determined, and fail if it cannot exceed the criteria that has been determined. In this study, the research will succeed when there is 75% numbers of students could achieve some improvement scores from the pre-test until the second post-test in cycle two or they could pass the target score of the
29
minimal mastery level (KKM).8 The KKM must fulfill considering speaking subject is 75 (seventy five) which is adapted from the school agreement if the criteria of the action is success reached, it means that the next action of the Classroom Action Research would be stopped, but if the criteria has not been achieved yet, the alternative action would be done in the next cycle.
CHAPTER IV RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the writer presents the result of research. It involves the way to the use of reciprocal techniques for teaching speaking skills of VII-A class students in SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto academic year 2016/2017. Related to the result, it consists of four parts. Those are before implementing of the action, implementation of the action, discussion of all the data after implementing the action and the interpretation of the result.
A. Research Finding
1. The Result of the Interview before CAR
The interview was held on Thursday, March 23rd 2017 started at 8.30 A.M. and finished at 9.30 A.M. Type of interview in this study was the structured interview. Based on the pre-observation result, the VII-A class showed they are more passive than another class. Most students in VII-A did not participate in class conversation, shy in giving oral presentations and low in vocabulary. They were not courage to involve in the speaking learning process. They were encountered with the hesitance of practicing the material as well as the drilling conducted by the teacher in the learning process. In the other words, the students have the problems with their confidence. Therefore, they need a new technique to improve their speaking skill and make the English speaking lesson more exciting.
2. The Result of the Observation before CAR
31
teaching and learning process, the class of VII-A students face some difficulties when their teacher deliver the materials. It seems at their reactions in learning English. Some of them are bored, sleepy and do not pay attention to their teacher explanation.
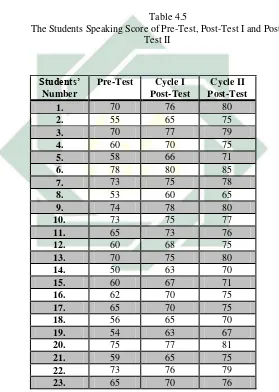
3. The Result of Pre-Test
The pre-test was held before the Classroom Action Research (CAR). It was conducted on Saturday, 25th 2017. It started at 11 A.M. The pre-test was in interview form. Then, the scores was taken in five criteria as stated by Heaton, which are the scores of prononciation, grammar, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension.1 Based on the result of pre-test, the data showed that the mean score of pre-test was 65,48. It means that the students speaking mean score before using reciprocal techniques or before implementing CAR is 65,48. There were 3 students who pass the KKM and there were 28 students still below the KKM. The KKM of the seventh grade students in SMPN 1 Mojoanyar Mojokerto is 75. From the pretest result, it could be seen that students speaking ability was still low. For the result of pre-test, see Appendix J.
4. The Implementation of the Classroom Action Research a. CYCLE I
1) Planning
In this cycle, the writer and the teacher arranged a plan for the action based upon the problems that faced by the students toward speaking skill. In this case, the writer arranged a lesson plan based on the teaching material. Beside of making lesson plan, the writer also prepared observation checklist to observe the students performance during the teaching learning process. Morover, in the lesson planning also consisted of standard competence, basic competence, some indicators that will be reached by the students and the technique that would be implemented.
32
For the lesson plan of cycle 1, see appendix F. The teacher and the writer used a reciprocal teaching technique in which the students will be more active to predict, to ask, to clarify and to summarize. The first cycle will be held in twice meeting. To know the improvement scores from pre-test to post-test, the writer also prepared the instrument of post-test 1 to collect the data.
2) Acting
The cycle of the cycle 1 was done on Monday, March 27th and Saturday, April 1st 2017. In acting phase, the writer implemented lesson plan that had been made before. Greetings and gave a motivation were the first activity did by the teacher at the classroom. The writer also introduce himself to the students. Then, the writer explained the schematic structure about the learning process. After that, the writer shows video from Youtube about Reciprocal Teaching Technique for teaching speaking to the students. The writer gave instruction to the students to make some group, one group consist of four students. Then, the writer give some reading text to the students. Later, the writer implemented the step of reciprocal teaching technique. For the first step, the writer built their background knowledge and their prediction about the text’s title. The writer opened the chance for all students to predict about the text. After that, the writer continued to the next step, it was questioning and clarifying. In reciprocal teaching technique, the writer allowed the students to look up the dictionary.
33
On the second meeting in first cycle, the process of CAR was similar with the earlier meeting. The writer reviewed about the students comprehension about the text which has been taught in the previous session and conducted the classroom by using reciprocal teaching technique. It was not only the writer dominated in in process but also the students spoke out and shared about the text. Afterward, the writer gave the post-test 1 to know how well their speaking skill after learning reciprocal teaching technique The writer asks students to speak up in front of the class about their own conclusion from the text. One by one of the students speak up in front of the class to explain their conclusion regarding the content of the text. 3) Observing
34
[image:43.420.47.387.131.496.2]writer instruction carefully. They begun to listen and do what the writer instruction. The participation students in the teaching learning reciprocal teaching technique can be described as the table below:
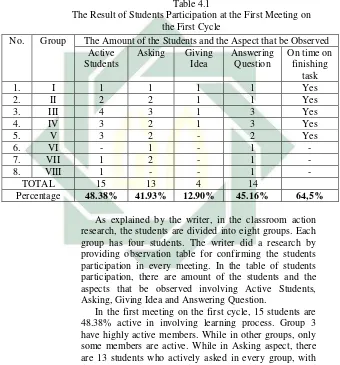
Table 4.1
The Result of Students Participation at the First Meeting on the First Cycle
As explained by the writer, in the classroom action research, the students are divided into eight groups. Each group has four students. The writer did a research by providing observation table for confirming the students participation in every meeting. In the table of students participation, there are amount of the students and the aspects that be observed involving Active Students, Asking, Giving Idea and Answering Question.
In the first meeting on the first cycle, 15 students are 48.38% active in involving learning process. Group 3 have highly active members. While in other groups, only some members are active. While in Asking aspect, there are 13 students who actively asked in every group, with the percentage 41.93%. Then, only 4 students presented their idea bravely during learning because group 5,6,7 and No. Group The Amount of the Students and the Aspect that be Observed
Active Students
Asking Giving Idea
Answering Question
On time on finishing
task
1. I 1 1 1 1 Yes
2. II 2 2 1 1 Yes
3. III 4 3 1 3 Yes
4. IV 3 2 1 3 Yes
5. V 3 2 - 2 Yes
6. VI - 1 - 1 -
7. VII 1 2 - 1 -
8. VIII 1 - - 1 -
TOTAL 15 13 4 14
35
[image:44.420.35.375.142.522.2]8 did not have represent to presented their idea or opinion. Next, there are 14 students actively answer the question of writer as teacher in each group. Group 1,2,3,4,5 were on time for finishing assignment from the writer as teacher.
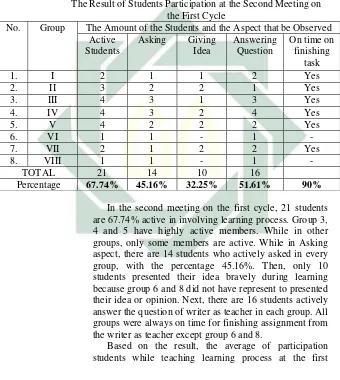
Table 4.2
The Result of Students Participation at the Second Meeting on the First Cycle
No. Group The Amount of the Students and the Aspect that be Observed Active
Students
Asking Giving Idea
Answering Question
On time on finishing
task
1. I 2 1 1 2 Yes
2. II 3 2 2 1 Yes
3. III 4 3 1 3 Yes
4. IV 4 3 2 4 Yes
5. V 4 2 2 2 Yes
6. VI 1 1 - 1 -
7. VII 2 1 2 2 Yes
8. VIII 1 1 - 1 -
TOTAL 21 14 10 16
Percentage 67.74% 45.16% 32.25% 51.61% 90% In the second meeting on the first cycle, 21 students are 67.74% active in involving learning process. Group 3, 4 and 5 have highly active members. While in other groups, only some members are active. While in Asking aspect, there are 14 students who actively asked in every group, with the percentage 45.16%. Then, only 10 students presented their idea bravely during learning because group 6 and 8 did not have represent to presented their idea or opinion. Next, there are 16 students actively answer the question of writer as teacher in each group. All groups were always on time for finishing assignment from the writer as teacher except group 6 and 8.
36
meeting is was 42,57% meanwhile the average of the second meeting was 57,35%.
4) Reflecting
The writer and the teacher evaluated about the conclusion of implementing the action. Based on the result of observation toward teaching learning process in this cycle, the students participation were still low because they did not pay attention and they were ashamed to ask and answer question orally. In addition, several students, they thought the question that was given is difficult. Moreover, the reason of students could not achive KKM is they did not comprehend conversation in video acessed from youtube about the use of reciprocal teaching technique for improving skill. In the video, all conversation used English with speed rhythm. Then, the students seemed confused with this technique, although the students have explained clearly. However, the teacher believed that they would be common for using this technique in the next meeting.
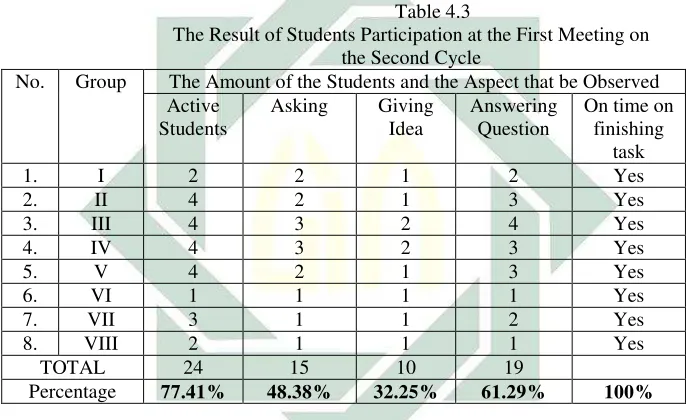
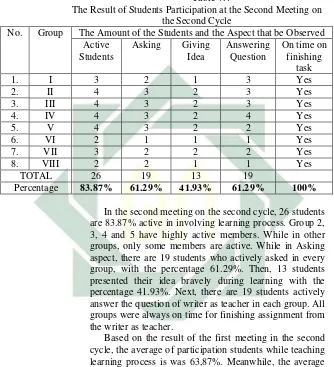
In addition, based on the result of the post-test 1, there were 45.16% students who passed the KKM which increased become 14 students. Then, the writer and the teacher tried to modify the action in order 75% of students in the class could pass the KKM. Instead, the writer and the teacher felt satisfied enough because their efforts to improve students speaking skill had been improved proven by score they get although not all the targets accomplished yet. Beside of that, the students seemed to accept te material easily by using reciprocal teaching technique. From the reflecting phase above, there must be more efforts to the use of reciprocal teaching technique for teaching speaking skill. This efforts was done in the next lesson plan of cycle two. For the result of Post-test 1, see Appendix K.
b. CYCLE II 1) Planning
37
scores, the teacher and the writer rearrange the lesson plan which was used in the previous cycle with some modification. In this cycle, the writer taught the same procedure with the first cycle but he taught by using different texts. It was the same as the activity done in the first cycle. In order to motivate the students to become active learners, the teacher and the writer designed an encouraging teaching learning process in which the students could get involved within the activities optimally. The writer prepared himself with the text that enables the students to comprehend better and more easily. He also gave a students more opportunity to practice that technique. This procedure was aimed for the students to acquire four strategies and applied them to any text with ease. He prepared everything in implementing the second cycle including the teaching materials and lesson plans. For the lesson plan of cycle 2, see Appendix G.
2) Action
The action of the second cycle was done on Monday, April 3rd and Saturday, April 8th 2017. After praying, the teacher and the writer greeted the students. Before the writer continued the lesson, he gave a little review in applying reciprocal teaching technique. After that, he gave some explanations dealing with implementation of reciprocal teaching technique in the first cycle to overcome the students difficulties in making the summary. Firstly, he divided the class into some groups. Each group consisted of four persons. The way to make the group was the student counted the number one up to four. The group was made from