Chapter 21
Chapter 21
The Global Capital Market:
The Global Capital Market:
Performance and Policy Problems
Introduction
The International Capital Market and the Gains from
Trade
International Banking and the International Capital
Market
Regulating International Banking
How Well Has the International Capital Market
Performed?
Summary
Introduction
International capital market
•
The group of closed interconnected markets in which
residents of different countries trade assets such as
currencies, stocks and bonds
•
This chapter focus on three main questions:
– How has the international capital market enhanced
countries’ gains from trade?
Three Types of Gain From Trade
•
All transactions between the residents of different
countries fall into one of three categories:
– Trades of goods or services for goods or services
– Trades of goods or services for assets
– Trades of assets for assets
The International Capital Market
and the Gains From Trade
Figure 21-1: The Three Types of International Transaction
Risk Aversion
•
The risk associated with a trade of assets is shared when
assets are traded internationally.
– When people are risk averse, countries can gain through
the exchange of risky assets.
– International capital markets make these trades possible.
Portfolio Diversification as a Motive for International
Asset Trade
•
International
portfolio diversification
can allow
residents of all countries to reduce the variability of
their wealth.
– International capital markets make this diversification
possible.
The Menu of International Assets: Debt Versus
Equity
•
International portfolio diversification can be carried
out through the exchange of:
– Debt instruments
– Bonds and bank deposits
» They specify that the issuer of the instrument must repay a fixed
value regardless of economic circumstances.
– Equity instruments
– A share of stock
» It is a claim to a firm’s profits, rather than to a fixed payment,
and its payoff will vary according to circumstance.
International Banking and the
International Capital Market
The Structure of the International Capital Market
•
The main actors in the international capital market are:
– Commercial banks
– Corporations
– Nonbank financial institutions
Figure 21-2: Borrowing in the International Capital Market
Growth of the International Capital Market
•
The removal of barriers to private capital flows across
countries’ borders has contributed to rapid growth in
the international capital market.
•
A policy “trilemma” refers to three available options:
– Fixed exchange rate
– Monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals
– Freedom of international capital movements
Offshore Banking and Offshore Currency Trading
•
Offshore banking
– The business that banks’ foreign offices conduct outside of their home countries
– Banks operate offshore though any of three types of institution:
– Agency office
– Subsidiary bank
– Foreign branch
•
Offshore currency trading
– Trade in bank deposits denominated in currencies of countries other than the one in which the bank is located
– It is referred to as Eurocurrency trading.
•
Eurodollars
– Dollar deposits located outside the U.S.
•
Eurobanks
– Banks that accept deposits denominated in
Eurocurrencies
•
Eurocurrency trading has grown for three reasons:
– Growth in world trade
– Evasion of financial regulations like reserve
The Growth of Eurocurrency Trading
•
London is the leading center of Eurocurrency trading.
•
The early growth in the Eurodollar market was due to:
– Growing volume of international trade
– Cold War
– New U.S. restrictions on capital outflows and U.S.
banking regulations
– Federal Reserve regulations on U.S. banks (e.g., the
Fed’s Regulation Q)
– Move to floating exchange rates in 1973
– Reluctance of Arab OPEC members to place surplus
funds in American banks after the first oil shock
•
International banking facilities (IBFs)
– Banks that accept time deposits and make loans to
foreign customers.
– They are not subject to reserve requirements or interest
rate ceilings.
– They are exempt from state and local taxes.
Regulating International Banking
The Problem of Bank Failure
•
A bank fails when it is unable to meet its obligations to
its depositors.
•
Governments attempt to prevent bank failures through
extensive regulation of their domestic banking
•
The main U.S. safeguards to reduce the risk of bank
failure:
– Deposit insurance
– Reserve requirements
– Capital requirements and asset restrictions
– Bank examination
– Lender of last resort (LLR) facilities
Difficulties in Regulating International Banking
•
Deposit insurance is essentially absent in international
banking.
•
The absence of reserve requirements reduces the
stability of the banking system.
•
Bank examination to enforce capital requirements and
asset restrictions becomes more difficult in an
international setting.
•
There is uncertainty over which central bank is
responsible for providing LLR assistance in
international banking.
International Regulatory Cooperation
•
Offshore banking is largely unprotected by the
safeguards national governments have imposed to
prevent domestic bank failures.
•
Basel Committee
– It is a group of central bank heads from 11
industrialized countries.
– It enhances regulatory cooperation in the international
area.
•
A major change in international financial relations in
the 1990s has been the rapidly growing importance of
new
emerging markets
as sources and destinations
for private capital flows.
•
The trend toward
securitization
has increased the
need for international cooperation in monitoring and
regulating nonbank financial institutions.
How Well Has the International
Capital Market Performed?
The Extent of International Portfolio Diversification
•
The international capital market has contributed to an
increase in international portfolio diversification since
1970.
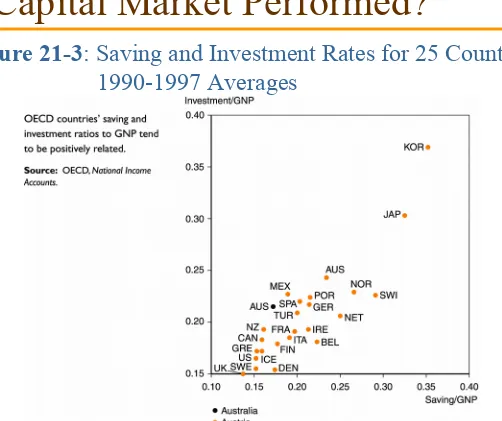
How Well Has the International
Capital Market Performed?
The Extent of Intertemporal Trade
•
Some observers claim that the extent of international
trade, as measured by countries’ current account
balances, has been too small.
Figure 21-3: Saving and Investment Rates for 25 Countries, 1990-1997 Averages
Onshore-Offshore Interest Differentials
•
If the world capital market is functioning well,
international interest rates should move closely
together and not differ too greatly.
– Large interest rate differences would be strong evidence
of unrealized gains from trade.
– Data shows that rates of return on similar deposits issued in the major financial centers are quite close.
Figure 21-4: Comparing Eurodollar and Onshore United States Interest Rates
The Efficiency of the Foreign Exchange Market
•
Exchange rates provide important signals to those who
engage in international trade and investment.
•
Studies Based on Interest Parity
– The interest parity condition:
Rt– R*t = (Eet+1 – Et)/Et (21-1)
where:
Rt is the date-t interest rate on home currency deposits
R*t is the date-t interest rate on foreign currency deposits
Eet+1 is the expected exchange rate
Et is the exchange rate
– The forecast error made in predicting future
depreciation:
ut+1 = (Et+1 – Et)/Et - (Eet+1 – Et)/Et (21-2)
– Under interest parity, this hypothesis can be tested by
writing ut+1 as actual currency depreciation less the
international interest difference:
•
The Role of Risk Premiums
– If bonds denominated in different currencies are
imperfect substitutes for investors, the international interest rate difference equals expected currency
depreciation plus a risk premium, t:
Rt – R*t= (Eet+1 – Et)/Et + t (21-4)
•
Tests for Excessive Volatility
– They yield a mixed verdict on the foreign exchange
performance.
•
The Bottom Line
– Evidence on foreign exchange market is ambiguous;
more research and experience are needed.