CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Previous Study
The first previous study that is used in this research by Wiwit Wahyuningsih (2005) entitled An Error Analysis of Direct and Indirect Speech (A study at the Second Grade Students of SMU Muhammadiyah Cilacap in Academic Year 2005/206. It is revealed that the students’ ability is good because the mean of the students’
ability is 66.9%. Based on the result it is obtained that the students’ error belong to three categories; over generalization, ignore of the rule restriction, false concept hypothesis, and incomplete application of rule. Those categories belong to intralingual error.
The second previous study that is used in this research by Nur Indrayani (2010) entitled The Students’ Competence in Using Direct
and Indirct Speech ( A study on the Eleventh Grade Students of SMK Muhammadiyah Bobotsari in Academic year 2010/2011. It is revealed that the average of the the stdents’ competence in using direct and
Those previous study give much input in conducting the research because they have same topic that will be able to improve the researcher in conducting research entitle “An Error Analysis on the
Mastery of Direct and Indirect Speech” ( A Study at the Second Grade Students of SMA Negeri 3 Purwokerto in Academic Year 2013/2014). B. Grammar
1. The Definition of Grammar
It is important for us to study grammar, since we will know what it is used for. There are a lot of theories about definition of grammar. Some experts in the world have their own point of view, and opinion about what the grammar exactly is. It may be different from one’s definition to the other definitions, but actually have the
same meaning in principles.
Grammar is the system of a language. According to Hornby (2000:586), “Grammar is the rules in a language for changing the form of words and joining them into sentences.”
While McCarthy and Charter (2006:1) say, “Grammar is concerned with how sentences and utterences are formed.”
correctly. But if students ignore the grammar, they cannot construct sentence correctly which may result in unclear messag
2. The Importance of Learning Grammar
It is important for us to learn grammar. If the students can master the grammar well they will be able to use English well. Then, they know how to produce grammatically correct sentences.
It means that without grammar language can not be conveyed correctly and it is difficult to catch the meaning.
Example :
- Direct speech : Andi said,” The man which sits on the chair is my father.”
- Indirect speech : Andi said that the man which sits on the chair is my father. (incorrect)
Andi said that the man who sat on the chair was his father. (correct)
The error of the sentence above lies at the use of tenseand pronouns because the students do not understand the use of relative pronouns and the changing of tense.
C. Definition of Direct and Indirect Speech 1. Direct Speech
Based on the previous study the definition of direct speech is reporting what someone says by repeating the exact words.
Example: My roommate said, "The door is open. Could you close it?" 2. Indirect Speech
According Muhibin Syah (2006:102), reported speech is also called indirect speech. It refers to using a noun clause to report what someone has said. Unlike in direct speech, in reported speech no quotation marks are used.
Based on the previous study the definition of indirect speech is reporting someone says without repeating the exact words but give the same meaning.
Example of indirect speech:
- My roommate said,” The door is open and could you close it?” - My roommate said that the door was open and asked me whether I
couldclose it.
D. The Concept of Direct and Indirect Speech
There are two ways of relating what a person has said: direct and indirect speech. In direct speech we repeat the original speaker’s exact
words.
Example : He said, “I was hungry.”
In indirect speech if the reporting verb (say, answer, remark, tell, etc) or introductory verb is in the present, present perfect or future there is no change of tense in the reported verb. Whereas if the reporting verb is in past tense there is change of tense.
Example : - He says, “ he is a doctor.” - He says that he is a doctor.
E. Types of Direct and Indirect Speech
ThomsonA.J and A.V Martinet (1980:110) states that indirect speech is classified into fourbut in this research will discuss only three types, such as:
1. Indirect speech of statement. 2. Indirect speech of command. 3. Indirect speech of question. 1. Indirect speech statement
Indirect speech of statement is used to report someone’s statement. Examples:
Table 2.1
Examples of indirect speech
Direct speech Indirect speech
Simple present tense
He said, “Andi study English now.
Past tense
He said that Andi studied English then.
Present continuous tense
“Messi is playing football,” he said.
Past continuous tense
She said that she had bought a book the day before.
He told me, “Eni was cooking.”
Past perfect continuous gone to Jakarta the following week. Future continuous
1) If the reportingverb is in present tense, future tense, and perfect tense there is no change of verb except the pronouns.
Example:
- Present tense
Direct : Andi will say, “ I will write a letter.” Indirect : Andi will say that he willwrite a letter. - Perfect tense
Direct : Andi has said, “ My brother likes this movie.” Indirect : Andi has said that his brother likes this movie. 2) If the reportingverb is related to the general fact or habitual action
there is no change of verb except the pronouns. Example:
Direct : He says, “ Water flow from higher place to lower place.”
Indirect speech : He says that water flow from higher place to lower place.
a. Direct and indirect speech of Question
The function is to report someone question to other. If the direct speech use verbal question the indirect speech must be changed into “if” or “whether”and if the direct speech use WHQuestion (where, when, why, who, what and how)” “if” or “whether” can be replaced by puting the
question words. The pattern as follow:
1) Direct and indirect speech from Nominal Sentence Pattern:
Example:
Indirect : She asked me if (whether)I was interested in her. 2) Dierct and indirect speech from WH Question
Pattern:
Examples:
Direct : He asked me, “ How do you go to school?” Indirect : He asked me How I went to school.
Dirct : My father asked me, “ What are you waiting for?” Indirect: : My father asked me what I was waiting for?
b. Direct and indirect speech of Command
Indirect command can be classified into two types as follow: 1) Positive command
In this type “to” is added between the introductory and reported
command. Pattern :
Table 2.2
Indirect speech of positive command He asked me
To + infinitive He told me
Examples:
Direct : Rani told me, “Open the window, please.” Indirect : Rani told me to open the window.
Direct : Budi asked me, “Come to my house tonight!”
Indirect : Budi asked me to come to his house the following night. 2) Negative command
In this type “not to” is added between the introductory and reported
command. Pattern:
Table 2.3.
Indirect speech of negative command He asked me
Not to + infinitive He told me
Example:
Direct : Our teacher told to us, “Don’t come late!” Indirect : Our teacher told us not to come late.
There are several changes that occur in construction of direct and indirect speech, which are going to be discussed as follow:
1. The change of pronouns and possesive pronouns:
Table 2.4
List of pronouns and possesive pronoun
Direct speech Indirect speech
I I, he or she
my his or her
Our Their
You I
2. The change of Demonstrative Pronouns
The demonstrative pronouns indicating closeness are this and theseand the ones indicating distance are that and those. In indirect speech the change of demonstrative pronouns as follow:
Table 2.5
List of demonstrative pronoun Direct Speech Indirect Speech
this these
that those
3. The change of to be, modal, and auxiliary
Table 2.6
List of to be, modal and auxiliary Direct Speech Indirect Speech
am/is/are was/were
Can could
Will would
Shall should
May might
must had to
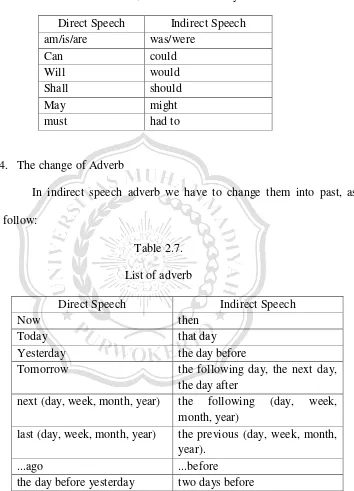
4. The change of Adverb
In indirect speech adverb we have to change them into past, as follow:
Table 2.7. List of adverb
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
Now then
Today that day
Yesterday the day before
Tomorrow the following day, the next day, the day after
next (day, week, month, year) the following (day, week, month, year)
last (day, week, month, year) the previous (day, week, month, year).
...ago ...before
the day before yesterday two days before
F. Error Analysis
1. Error and Mistake
Error is caused by the competence factor, it means that students have not understood yet about the language system used. It happens systematically and will be durable if it is not corrected soon.
It is important for the teacher of target language to analyze carefully the errors a learner made in process of contacting now a system language. All problem of error made by learners should be analyzed accurately to find out the problem solving. The study of error is called “Error Analysis”.
Error analysis is useful for both teacher and students of target language. It show some problems encountered by the students. It is also give further information to te teacher about the process of acquiring of foreign language .
According to Tarigan (1995:76) there are differences between error and mistake. There are six points of view used as standard of comparison, those are:
Table 2.8
Table the differences between error and mistake
Category/ point of view Error Mistakes
5. Result discussed about the types of intralingual error.
1) An Error Analysis on the Mastery of Direct and Indirect Speech ( A Study at the Second Grade Students of SMA Negeri 3 Purwokerto in Academic Year 2013/2014). Intralingual errors refers to errors which are caused by its system of rule of the target language. This error involves:
a) Over generalization
In this case, the learner creates a deviant structure on the basis of other structures in the target language
Example:
"He can sings" where English allows "He can sing" and "He sings").
b) Ignorance of rules restriction
Example:
He made me to go rest" through extension of thepattern "He asked/wanted me to go.
c) False concept hypothesis
The learners do not fully understand a distinction in the target language. The students have the wrong conceptsof language system. They often make error caused by the incorrectness on the difference in target language itself.