ABSTRACT
Topic Map is a standard for the representation and interchange of knowledge, with an emphasis on the findability of information. Index of book, including the Holy Quran, is primarily presented as list of terms, sometimes referring one to another. This kind of association is more advantageous if it can be presented in a way of navigating from one topic to related ones. Topic map is considered suitable for the Holy Quran ibdex representation. Topic Map-based application for Al Quran index was built for representing the main topic of Al Quran into web application so it would be a prototype of the usage of topic-map as navigation tool, visualization, and site-map. The application is able to manage topic-map document according to standard format of XML Topic Map (XTM) including topic, occurrence, and association. Topic-map is visualized by TouchGraph Link Browser applet which can helps users to explore the topics and associations among topics in the Holu Quran topic map. This application was built using Java-servlet with TM4J API and TouchGraph LinkBrowser.
Keywords
Al Quran, Association, Occurrence, TM4J, Topic, Topic Map, TouchGraph LinkBrowser, XTM.
1.
INTRODUCTION
Information nowadays are available in many formats which can be a document, image, book, electronic book, HTML pages, or web site. All these information is increasing rapidly in huge number of size every year. This information overload will cause the difficulties of accessing the right information and has appropriate relevance to a subject or topic within a specific area of interest. Hence, one of the challenges nowadays is no longer how to share the information or knowledge but shifting to how to deliver the right information in the right context to the right person [5].
One of the solutions can be used to that information overload issue is using topic map approach. Topic map uses indexing approach like in a back-of-book index which contain the context and the location of information, as depicted in Figure 1.
Topic maps are designed to manage the info glut, build valuable information networks over any kind of information resources, and enable the structuring of unstructured information. A topic map can be seen as an electronic super index, implementing the back-of-bok index paradigm and much more [5].
Information has unlimited size and domain, and Topic Map is just a standard applicable in many domains. To combine concepts from different domain, each topic maps can be merged to build the larger information domain.
Figure 1 Topics and Back-of-Book Index
This paper describes the usage of topic maps for representing topics in Holy Quran (Al Quran). An application will be built which can be a prototype of topic map application that is possibly developed for other domains.
Al Quran’s topic map document format refers to XML for Topic Map (XTM) ISO standard 13250:2002 [6]. The main topic of this Al Quran topic map is related to the topic ibadah. The index will be managed using application that has several functions to browse, search, and maintain the content of the document exclude the function to manage scope and merge. The knowledge contained in the Topic Map will be presented in a graphical user interface which provides navigation feature instead of just search textually.
2.
HOLY QURAN (AL QURAN)
Al Quran is a holy book contains 114 part, every part contains different number of verses, and every group of verses contains one or more sub-part as known as ruku’ which examine certain theme or topic. This paper will focus on developing topic map for one of Al Quran’s domain, in this case is ibadah.
3.
TOPIC MAP
Topic maps can create an index of information which resides outside that information, as shown in Figure 2. The topic map (the cloud at the top) describes the information in the documents (the little rectangles) and the databases (the little ‘cans’) by linking into them using URIs (the lines) [7].
Figure 2 Topic Map Illustration [7]
Topic map can be defined via an XML document containing all the relevant information. Example of the XML document for topic map is shown in Figure 3.
The topic map document, as shown in Figure 3, starts off with a header specifying the version of XML, followed by the topicMap tag. Inside the topicMap tag, any number of topics and
Figure 3 . Example of XML document for Topic Map
3.1
Topic
Topics are the main elements in topic maps that represent the real world subjects of which the developer wish to present information. A topic can be anything, regardless whether it exists or not, whether it is of physical nature or just an idea or expression [4].
A topic has three characteristics [5]:
1. Names: Human readable name for the subject. A topic can have zero, one, or many names.
2. Occurrences: Link to information resources relevant for the topic.
3. Playing roles in associations: A topic may be associated with other topics.
Regarding to the topic ibadah, in this paper, topics can be: bersuci, doa, haji-umrah, puasa, shalat, sumpah-nazar, tayammum, wudhu, zakat, and zikir.
In an XML document of topic map, topics are represented using topic tag. Figure 4 shows the example of adding topics into
Figure 4 Defining the main topics
3.2
Occurrence
internal occurrence and external occurrence.Internal occurrence is information about the subject that is typed inside the topic map and included in the XML document for topic map. As an example, for Al Quran topic map, internal occurrence for the topic Sholat might be ‘worship compulsory for Muslims’. External occurrence is a link to information about the topic, which is located elsewhere. Most typically these links are represented as URIs, and point to a web page, or may also point to a file in a file
<topicRef xlink:href="#ibadah"/> </instanceOf>
<occurrence> <resourceData>
Worship compulsory for Muslims </resourceData>
</occurrence> <occurrence>
<resourceRef xlink:href=”http://alislamu.com” />
</occurrence> </topic> </topicMap>
In Figure 5 , an Internal occurrence is represented with resourceData tag, while an external occurrence is represented with resourceRef tag.
3.3
Association
Associations represent the horizontal structure of the topic map ontology which is defining how topics are connected to one another [4]. The number of topics related by one association is not limited, as many as the application requires.
Associations can be rather general like: is located in, lives in, written by, born in; or more specific like: is an academic organization within, or a facility provided by.
Figure 6 Example of association in Al Quran Topic Map
As seen in Figure 6, in Al Quran topic Map, the topic ibadah is related to topic puasa, while topic puasa is related to topic
Albaqoroh. The definition of an association is described in association element using association tag, outside the topic element.
Each member in an association is given a role. This provides extra semantics to how the topics are associated. A topic can have different roles in the different associations where it is a member of. Figure 7 shows the example of association roles.
Figure 7 . Al Quran Topic Map Association Roles
In the Al Quran topic map, the topic puasa has different roles in two associations. In the association with ibadah it has the role ‘included in’. This association can be read that puasa is included in the ibadah. In the association with albaqoroh, puasa
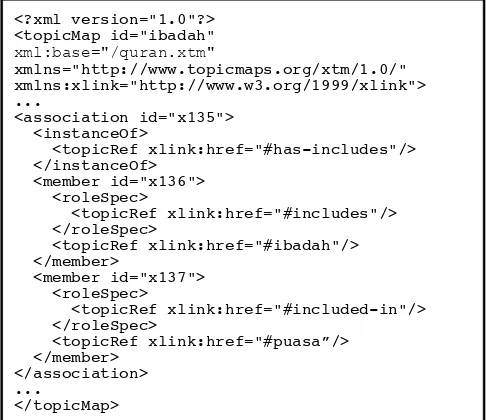
has the role ‘described in’, and albaqoroh has the role ‘describes’. It means albaqoroh describes the topic puasa. Figure 8 shows the syntax to define the association.
3.4
XTM
XML document for topic map described in this paper refers to the international standard called XTM. XML Topic Maps (XTM) is a product of the TopicMaps.Org Authoring Group (AG), formed in 2000 by an independent consortium named TopicMaps.Org, originally chaired by Michel Biezunski and Steven R. Newcomb,
and chaired at the date of delivery of XTM specification version 1.0 by Steve Pepper and Graham Moore [2].
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<topicRef xlink:href="#has-includes"/> </instanceOf>
<member id="x136"> <roleSpec>
<topicRef xlink:href="#includes"/> </roleSpec>
<topicRef xlink:href="#ibadah"/> </member>
<member id="x137"> <roleSpec>
<topicRef xlink:href="#included-in"/> </roleSpec>
<topicRef xlink:href="#puasa”/> </member>
</association> ...
</topicMap>
Figure 8 Defining association
The origins of the topic maps paradigm itself dates back to 1993, when it was first expressed as a working document in the context of the Davenport Group. The paradigm was more fully developed thereafter in the context of the GCA Research Institute (now known as IDEAlliance), in an activity called Conventions for the Application of HyTime, during and after which the paradigm was independently developed, implemented, and promulgated. Early in 2000, after several years of continuous effort by an international group of individuals, the topic map paradigm was fully formalized for the first time as an ISO International Standard, ISO/IEC 13250:2000. Almost immediately thereafter, TopicMaps.Org was founded in order to develop the applicability of the paradigm to the World Wide Web, and to realize its enormous potential to improve the findability and manageability of information [2].
3.5
TM4J
TM4J is a topic map processing engine written in Java providing a pure Java API, support for the Tolog query language, support for importing XTM and LTM syntaxes, support for exporting XTM syntax and persistence of topic map information in a wide variety of databases [8]. As most of othe Java libraries, TM4J is an opensource package available to be further explored.
The engine provides a comprehensive Application Programming Interface (API) to allow programmers to create and modify topic map structures. The engine can be used to manage topic maps which are maintained in-memory or which are persistently stored either in the Ozone object-oriented database, or in a relational database using the Hibernate O-R mapping. TM4J also provides interfaces for querying topic maps structures using the Tolog query language, parsing topic maps from XTM or LTM syntax files, and writing topic maps to XTM syntax files.
3.6
TouchGraph LinkBrowser
TouchGraph LinkBrowser 1 is a Java applet which to visualize information using node and edge. The use of TouchGraph LinkBrowser in topic map application will simplify the exploration and navigation of topics and association between topics.
TouchGraph LinkBrowser will read an XML document which has a specific document type definition as shown in Figure 9. This document type definition has different definition with XTM, so XTM document need to be converted to an XML document that refers to TouchGraph LinkBrowser’s XML.
Regarding to the conversion of XTM to XML, a function has been developed and added to the application. This function will change the topic element with its attributes into node and nodeset, and change the member element inside the association into edge and edgeset.
<TOUCHGRAPH_LB version="1.20"> <NODESET>
<NODE nodeID="node-id1"> …
</NODE> </NODESET> <EDGESET>
<EDGE fromID="node-id1" toID="node-id2" type="1" length="70" visible="false"/> </EDGESET>
</TOUCHGRAPH_LB>
Figure 9 XML DTD to visualize topic map
By the function of TouchGraph LinkBrowser applet, application provide an interface to draws the topic map as a graph, so it can help user to explore the topic map.
4.
AL QURAN TOPIC MAP DESIGN
Al Quran topic map design consists of topic, occurrence, and association related to topics in Al Quran domain to be represented. The main topics in Al Quran are morals/manners, Al Quran, previous, law, private law, worship, science/knowledge, faith, holy war, foods, dress, history, and muamalat [3].
The selected domain for topic map depends primarily on the needs of the application, the user needs, and the author of topic map itself. From the main topics in Al Quran, domain ibadah (worship) has been selected for this paper and from this domain can be expanded to main topics that related to domain as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 . Topic type and main topics
1 http://www.touchgraph.com/newLB/TGLinkBrowser.html and
http://sourceforge.net/projects/touchgraph/
Figure 10 shows the main topics that has been selected for domain ibadah. These main topics can be expanded into more sub-topics that related to main topics.
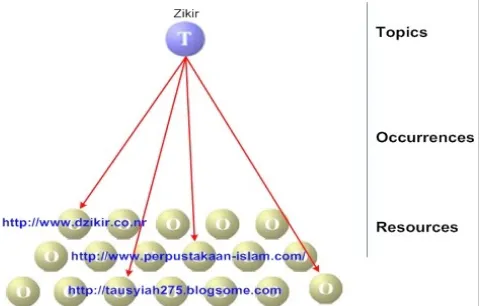
After determining the main topics, the next step is to add the occurrences for each topic. As mentioned before, occurrences can be internal or external. Figure 11 shows the topic zikir with several external occurrences.
Figure 11 Example of adding occurrences into a topic
Other occurrences can be added into another topics in the domain. The process of expanding the main topics into sub-topics and adding occurrences into a topic are repeated until the topic map document considered as complete.
After the topics and sub topics are determined, then the next step is to determine the relationship between topics defined by the association element. Figure 12 shows an example the association for topic puasa.
Figure 12 Example of association between the topics
5.
APPLICATION DESIGN
Figure 13 System design of topic map application
As shown in Figure 13, application uses Java Servlet with TM4J library in processing topic map document (XTM). Processing results are then returned to the servlet to be combined with HTML tags.
6.
IMPLEMENTATION
The process of adding, editing, deleting topics, occurrences and associations, and converting XTM document into XML standard format required by the TouchGraph LinkBrowser applet will produce a web page that can be accessed by the user. In other words, the main menu and contents of this web page are generated from XTM document maintained by administrator. The web page also contains a TouchGraph LinkBrowser applet that visualizes the topic map.
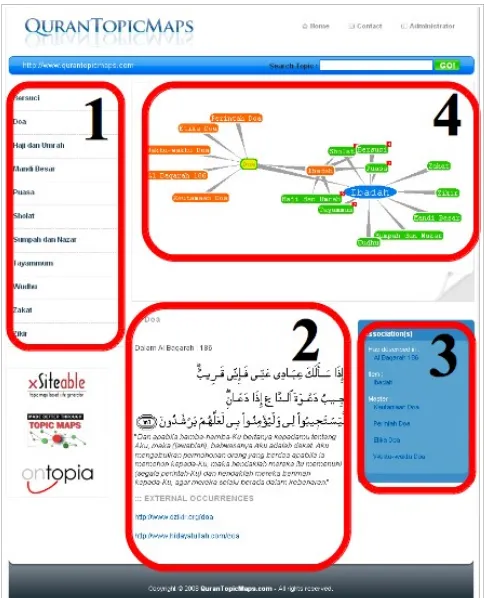
Figure 14 shows the application from user side. Part (1) is the applicatioin menu which contain the main topics from the selected domain. Part (2) is the place for describing the current selected topic which contain the basename of the topic, internal occurrence and external occurrence. If a topic has association, then it will be displayed in part (3). This part can help user to navigate to the related topics. Part (4) is a visualization of topic map contents. In this part, user can see the illustration of topics with its association to other topics. As mentioned before, the visualization of topic map in part (4) is using TouchGraph LinkBrowser applet.
7.
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
From the discussion above, it can be concluded that an open source web-based application for learning Holy Quran has been developed. The system works for presenting and managing knowledge of topics in Al Quran using Topic Map model. Using TouchGraph browser, the Topic Map can be presented in a user-friendly manner after the Topic Map model is converted first to XML format required by the TouchGraph browser. Using this nice GUI, the search, presentation and navigation topics becomes easy.
This paper introduces an approach of wrapping inter-related knowledge, concepts or information existing in the Holy Quran. The approach discussed in this paper can be used and extended for other knowledge domains.
Topic Map presentation used in this research is XTM which keeps all model in a file stored in a file system. The performance issue
should be evaluated if the size or number of concept is increasing from time to time. Another approach which involves persistence store using database management systems (via JDBC, ODBC, Hibernate) could be implemented to compare with the curent achievement as the future works.
Figure 14 . Main page of Al Quran Topic Map application
REFERENCES
[1] Anitta Altenburger, "Authoring XTM Topic Maps, Part I" ,, [online]: http://topicmaps.bond.edu.au/docs/6/toc/ access date 12 Feb 2010
[2] Biezunski, M., Newcomb, S.R., Moore, D.R., Ahmed, K., Altheim, M., and Hunting, S., "XML Topic Maps (XTM) 1.0" ,, [online]: http://www.topicmaps.org/xtm/1.0/xtm1-20010806.html
access date 12 Feb 2010
[3] Fahrudin, A., Widodo, A., Pramono, G.H., Kamal, M.M., Poerbandono, Al Quran Digital,, 2004
[4] Frode Hjeltnes, Development of a Topic Map Application for the Project QUIS – QUality, Interoperability, and Standards in e-Learning,Trodheim, Norwegia, 2006
[5] Holger Rath, "The Topic Maps Handbook" ,2003, [online]:
Http://www.sts.tu-harburg.de/~r.f.moeller/lectures/anatomie-i-und-k-system/empolistopicmapswhitepaper_eng.pdf access date 10 Feb 2010
http://www.y12.doe.gov/sgml/sc34/document/0322_files/iso13250 -2nd-ed-v2.pdf access date 10 Feb 2010
[7] Lars Marius Garshol, "What are Topic Maps" ,2002, [online]:
http://www.xml.com/pub/a/2002/09/11/topicmaps.html access date 10 Feb 2009
[8] - , "TM4J - Topic Maps For Java" ,, [online]: http://tm4j.org
![Figure 2 Topic Map Illustration [7]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok/3987631.1931051/2.612.54.298.126.327/figure-topic-map-illustration.webp)