CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’
VOCABULARY MASTERY AND THEIR READING
COMPREHENSION
(a study in second grade of junior high school)
FAJAR FURQON
0608773
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTEMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND ART EDUCATION
INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’
VOCABULARY MASTERY AND THEIR READING
COMPREHENSION
Oleh
Fajar Furqon
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Fajar Furqon 2012
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Desember 2012
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Skripsi ini tidak boleh diperbanyak seluruhya atau sebagian,
PAGE OF APPROVAL
CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY AND THEIR READING COMPREHENSION
(a Study in Second Grade of Junior High School)
By
Fajar Furqon
0608773
Approved by
First Supervisor Second Supervisor
Prof.Dr.Hj. Nenden Sri L. M.Pd. Ika Lestari Damayanti M.A.
NIP. 195111241985032001 NIP. 197709192001122001
Head of English Education Department
Prof.Dr. H. Didi Suherdi, M.Ed
ABSTRACT
TABLE OF CONTENT
Statement ... i
Preface ... ii
Acknowledgement... iii
Abstract ... iv
Table of Content ... v
List of Figures ... viii
List of Table ... ix
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 Background ... 1
1.2 The Scope of the Research ... 3
1.3 Statements of the Problem ... 3
1.4 Aims of the Research ... 3
1.5 Hypothesis ... 4
1.6 Significance of the Research ... 4
1.7 Research Method ... 4
1.7.1 Population and sample ... 4
1.7.2 Data Collection ... 5
1.7.2.1 Instrument ... 5
1.7.2.2 Research Procedure ... 5
1.7.3 Data analysis ... 6
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FOUNDATION ... 8
2.1 Definition of Reading ... 8
2.2 Reading Strategies ... 10
2.3 Reading Comprehension ... 13
2.4 Definition of Vocabulary ... 14
2.5 Related Research ... 16
2.6 Synthesis ... 17
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 18
3.1 Research Design ... 18
3.2 Population and Sample ... 19
3.2.1 Population ... 19
3.2.2 Sample ... 19
3.3 Research Hypothesis ... 19
3.4 Data Collection ... 20
3.4.1 Research Instrument ... 20
3.5 Trying Out the Research Instruments ... 22
3.5.1 Validity ... 23
3.5.2 Reliability ... 25
3.5.3 Difficulty Index ... 26
3.5.4 Discrimination Power Index ... 28
CHAPTER IV: FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 34
4.1 Students’ Reading Comprehension ... 34
4.2 Students’ Vocabulary Mastery ... 38
4.3 Correlation Coefficient ... 41
4.4 Testing the Suggested Hypothesis ... 43
4.5 Discussion ... 44
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 48
5.1 Conclusions ... 48
5.2 Suggestions ... 49
REFERENCES ... 50
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
Introduction
This chapter provides a brief description of the whole contents of the
research, including the background of the research, scope of the research,
statement of the problems, aims of the research, hypothesis, significance of the
research, research method, organization of paper.
1.1 Background of the Research
Reading is one of the important language skills. By reading, people may
get a lot of information. The more he/she reads, the more information he/she will
get. Reading makes someone smarter and creative. As stated by Laddoo (2007)
reading forces the reader’s brain cells to work on a regular basis as this will
keep the reader sharper and smarter. Even though some information can be
obtained without reading, for example by listening to teacher, seminar, radio,
television etc, but by reading someone may get wider information than listening.
For example, someone who reads a newspaper will get more information than
someone who watches news on television. Reader can read the text again when
he/she forgets or tries to get detail information, while listener cannot. This is
supported by Willis (2008) who states that by reading, someone can find the
information he/she needs with specific information.
In order to gain specific information, students at school should be taught
happen (Klingner, Vaughn and Boardman. 2007, p.3). Another way to help the
students to understand the text without knowing all the vocabulary in the text is by
finding key words. It is in line with Lehr & Osborn (2001) who explain that to
understand a text, we need to find the key words of the text. By doing this
strategy, students can cover their vocabulary weaknesses since vocabulary
knowledge is one of the major factors that influence reading comprehension
(Roehrig and Guo, 2011).
One of the previous studies related to the relationship between reading
comprehension and vocabulary mastery was conducted by Liu and Nation (1985).
It is about the success of guessing meanings of a text. The results of this study
show that the participants who have high reading proficiency level could
successfully guess 85% to 100% of the unknown words, and the participants who
have low reading proficiency level guess around 30% to 40% of the unknown
words.
Based on the explanation above, reading comprehension and vocabulary
mastery have a strong relationship. It is in line with Sedita (2005) who states that
vocabulary knowledge is crucial in reading comprehension and determining how
well students are able to comprehend the texts. That is why this study attempts to
find out how strong the vocabulary mastery influences the reading
comprehension. After knowing the correlation, teachers are expected to be able to
From the description above, the present study attempts to find out the
correlation between the students’ vocabulary mastery and their reading
comprehension and to find out how high the correlation between vocabulary
mastery and reading comprehension is. The subjects of this research are the
students of a junior high school in Bandung. The results of this study are expected
to enrich the literature on research regarding to the relation of students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension.
1.2 Scope of the Research
This research focuses on finding out the correlation between reading
comprehension and students’ vocabulary mastery in the 2nd grade of junior high
school because they have learned several types of text. There are 34 students
involved in the present research.
1.3 Statements of the Problem
The problems to be discussed in this research will be summarized in the
following research questions:
1. What is the students’ mastery of reading comprehension?
2. What is the students’ mastery of vocabulary knowledge?
3. What is the correlation between the students’ vocabulary mastery and their
1.4 Aims of the Research
In accordance with the research questions, the aims of the present research
are:
1. to find out the students’ mastery of reading comprehension,
2. to find out the students’ mastery of vocabulary knowledge, and
3. to find out the correlation between the students’ vocabulary mastery and
their reading comprehension.
1.5 Hypothesis
When there is a correlation between students’ vocabulary mastery and
their reading comprehension, the alternative hypothesis is accepted and null
hypothesis is rejected.
1.6 Significance of the Research
The aim of this research is to find out the correlation between student’s
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension in a junior high school. This
study is also expected to give significant contribution to others, especially English
teachers and future researchers. When the teachers know the correlation between
vocabulary mastery and reading comprehension, it may help them to figure out
some appropriate strategies in order to help their students to comprehend the texts.
1.7 Research Method
The present research is a quantitative research. The purpose of this
their reading comprehension. The research method used in this present research
includes population, sample, data collection and data analysis.
1.7.1 Population and sample
The research was conducted at one of Junior high school in Bandung.
The subjects of population were taken from the second grade students
because they had learned several texts. There were 7 classes in this grade.
Each class consisted of 34 students. The total population was 250 students.
The researcher used one of the classes for this research. The students involved
in this present research were 34 students. The subjects of this research were
both male and female.
1.7.2 Data Collection
The technique used to collect the data of this study is achievement
test. The selection of types of test test is based on the intention to screen
students’ current knowledge and skills. Achievement test is a test meant to
measure acquisition of skill (Algarabel and Dasi, 2001). Through this
technique, the information about students’ ability in reading comprehension
and vocabulary mastery is expected to be obtained.
1.7.2.1 Instrument
The main instrument used in this present research is achievement test.
Some questions are given to the subjects to find out their vocabulary mastery
and reading comprehension of the subjects. Tests are taken from questions of
1.7.2.2 Research Procedure
The procedure of research is as follows.
1. Designing the achievement test by compiling test items from UAN
2006 - 2010
2. Giving the achievement test to the students to find out the students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension
3. Organizing the data by dividing the vocabulary scores and reading
scores
4. Analyzing the data collected from the test.
1.7.3 Data analysis
The data collected from achievement test is analyzed using median
formula. Median formula has primary purpose to see the mean score of
vocabulary and reading.
Then, the process is gone to find out the correlation between students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension. SPSS (statistical
package for social sciences) and Pearson Product Moment are used as tools
1.8 Organization of the paper
The paper will be presented into five chapters. The chapter will be
subdivided into subtopics that will elaborate the issue given.
CHAPTER ONE Introduction
It comprises the background of the study, scope of the
research, research question, aims of the study, hypothesis,
significant of the research, research method, data analyses
procedures, clarification of terms, and organization of the
paper.
CHAPTER TWO Theoretical Foundation
Chapter two elaborates the foundation of relevant theories
as a basis for discussing the research problem.
CHAPTER THREE Research Methodology
Chapter three provides the explanation of procedures in
collecting and analyzing data in the research including
research method, research participants, data collecting
techniques, and data analysis.
CHAPTER FOUR Finding and Discussion
Chapter four presents the finding of this study and its
discussion through relevant theories.
CHAPTER FIVE Conclusions and Suggestions
Chapter five delineates the conclusions and suggestions
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Introduction
This chapter presents the explanation about procedures which are taken in
this study in order to find out the answer to the research questions. This chapter
includes research design, Population and sample, Research hypothesis, data
collection, trying out the research instruments, and data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
In this present research, quantitative approach with correlation method is
employed. Quantitative research is used since this research focuses on analyzing
the data through systematic process by using certain computation. Nunan (2003)
and Arikunto (2003) state that quantitative research is an attempt to investigate an
issue by using numerical data and statistical processing.
Correlation method is considered appropriate, since this research
concerns on the investigation to find out the correlation between students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension. It is in line with Sudjana
(1996) who state that correlation method is a process to find out the relationship
between two or more variables and how strong the relationship is. Another
statement comes from Hatch & Farhady (1982) explain that correlation is a
related. Therefore in this study, the variables to be correlated are vocabulary
mastery and reading comprehension.
3.2 Population and Sample
3.2.1 Population
Arikunto (2003) state that population is the whole subject of the research.
The population of the research was the second grade of a junior high school in
Bandung. There were 7 classes consisting of 250 students.
3.2.2 Sample
Sample is a part of the investigated population (Arikunto 2003). The
subject of this study was the second grade of a junior high school. This selection
was based on the reason that those students have learned several types of text and
the researcher had taught the second grade in this school. The present study
chooses one class randomly; the class consisted of thirty four (34) students. It is in
line with Gay, Mills, and Airasian (2006) who suggest that there should be at least
30 (thirty) participants in correlation study to establish a relationship.
3.3 Research Hypothesis
Hypothesis is a prediction about what you expect to happen in the study
(Sudjana, 1996). There are two types of hypothesis, alternative hypothesis (Ha)
According to Weaver (2005) Alternative Hypothesis (Ha) is the hypothesis
that states that there is a relation between the phenomena under investigation. Null
hypothesis (H0) is the opposite of alternative hypothesis, in order words there is
no relation between the phenomena under investigation.
When there is a correlation between students’ vocabulary mastery and
their reading comprehension, the alternative hypothesis is accepted and null
hypothesis is rejected.
3.4 Data Collection
The technique used to collect data in this study is achievement test.
Through this technique, the information about students’ ability in reading
comprehension and vocabulary mastery are expected to be obtained.
3.4.1 Research Instrument
According to Arikunto (2003) research instrument is a tool used by the
researcher to find out or to measure ability with certain rules. Achievement test
was given to the participants in order to measure the ability of students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension.
The test contains 50 questions, twenty five questions are the questions to
measure students’ reading comprehension and the other twenty five are to
measure students’ vocabulary mastery. The test was taken from 2006-2010 UAN
reasonable to be an
related to reading comprehension are finding t
ing the information about the text. The asp
y test are finding the synonym or antonym, an
tence and correcting the spelling.
the test, the right answer was marked one (1) po
marked zero (0) point, so the overall raw score
ievement test is 50 points. After marking the tes
the final scores by using S formula as below.
core
correct answers
N : number of qu
(
s were interpreted in order to classify partic
003). The classifications are presented in Table
multiple-Table 3.1 Classification of students’ achievement
Score Range Classifications
80 – 100 Excellent
66 – 79 Good
56 – 65 Average
30 – 55 Poor
0 – 29 Fail
In collecting the data, this study took several procedures:
a. Preparing Research instrument (achievement test).
b. Trying out the research instruments to the students in order to check its
validity, reliability, difficulty index and discrimination index.
c. Giving the achievement test to the participants
d. Scoring the participants’ achievement test.
e. Calculating the data by using a median formula and Pearson Product Moment
formula.
f. Analyzing the result through the relevant theories and drawing a conclusion of
this research.
Those procedures above should be taken carefully one by one to prevent
the emergence of mistakes during the research. Furthermore, explanation about
the procedures is clearly presented in the next sections.
3.5 Trying Out the Research Instruments
A good test at least possesses two qualities, which are validity and
2006 – 2010. In order
out before it was actu
order to find out its va
Besides measu
der to get the requirement of a good test, the tes
ctually administered. Then its results then we
validity and reliability.
asuring validity and reliability of the instru
ination power are also calculated. Difficulty
into easy or difficult, while discrimination pow
ificance of test items (Arikunto 2003).
2003) state that a test is valid if it measures wh
r to find out the validity of the achievement te
Table 3.2 r Coefficient Correlation (Validity)
Raw Score Interpretation 0.8 – 1.0 Very high
0.6 – 0.8 High
0.4 – 0.6 Moderate
0.2 – 0.4 Low
0.0 – 0.2 Very Low
(Arikunto, 2003)
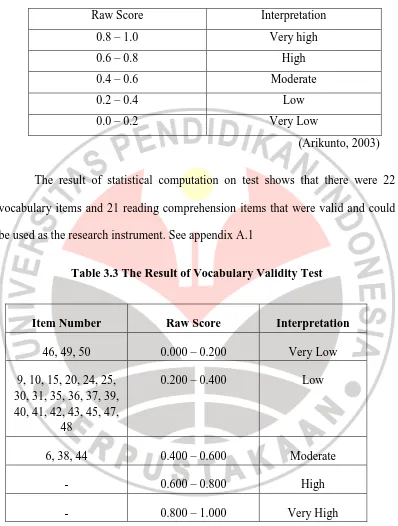
The result of statistical computation on test shows that there were 22
vocabulary items and 21 reading comprehension items that were valid and could
be used as the research instrument. See appendix A.1
Table 3.3 The Result of Vocabulary Validity Test
Item Number Raw Score Interpretation
46, 49, 50 0.000 – 0.200 Very Low
9, 10, 15, 20, 24, 25, 30, 31, 35, 36, 37, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 45, 47,
48
0.200 – 0.400 Low
6, 38, 44 0.400 – 0.600 Moderate
- 0.600 – 0.800 High
Table 3.4 The Result of reading Comprehension Validity Test
Item Number Raw Score Interpretation
11, 26, 29, 33 0.000 – 0.200 Very Low
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 28, 32, 34,
0.200 – 0.400 Low
27 0.400 – 0.600 Moderate
- 0.600 – 0.800 High
- 0.800 – 1.000 Very High
In this correlation research, the items of research instrument must be equal
between two variables. So, one item from vocabulary test must not be used. The
lowest validity score in vocabulary mastery instrument was discarded.
3.5.2 Reliability
According to Arikunto (2003) reliability is related with consistent and
stable indication of test. It means a test can be considered reliable if it is consistent
with the result when it is used more than once to the same objects in different
time.
In finding the reliability of the test, the half method was used.
Split-half method is a method that uses one achievement test and test once. There are
several steps in this method. The achievement test is equally separated into two
Product Moment co
correlation formula. Then the correlation c
lated by using Spearman Brown formula (Ariku
ormula is as the following.
coefficient
coefficient for each half of the test item
(Ari
lating the reliability (see appendix A.2), it wa
nt of achievement test which is also called r11
reliability coefficient then should be applied
ble (Sugiyono, 2008). The Product Moment ta
hen the result should apply the interpretation.
if robtained > rcritical = valid
if robtained < rcritical = invalid
(S
to Sugiyono (2008) the r critical for this inst
. Since the r obtain exceed the r critical, it me
3.5.3 Difficulty Index
Difficulty index needs to be calculated in order to find out the difficulty
level of a test. Arikunto (2003) state that the index of difficulty or facility value of
an item illustrates how easy or difficult the certain item established in the test. The
value around 0.500 was considered to be ideal with an acceptable range from
around 0.3 to 0.7. In addition, the following formula is used to calculate the index
of difficulty of an item.
=
P = Facility/ Index of difficulty B = The number of correct answers
JS = The number of students taking the test
(Arikunto, 2003:208)
After obtaining the result, the classifications of result were applied to the
table below.
Table 3.5 Criteria of difficulty Index
Index of Difficulty Difficulty Degree 0.00 – 0.30 Difficult item
0.31 -0.70 Moderate item 0.71 – 1.00 Easy item
(Arikunto, 2003)
The result of computing shows that 4 items were considered difficult, 20
Table 3.6 The Difficulty Test
Item Number Index of Difficulty Difficulty Degree
1, 12, 37, 48 0.00 – 0.30 Difficult Item 3, 9, 11, 15, 19, 26, 27, 29, 30,
31, 33, 36, 38, 41, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 50
0.30 -0.70 Moderate Item
2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 21, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 28, 32, 34, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43,
0.70 – 1.00 Easy Item
The result shows that 2 reading items were included into difficult items, 7
reading items were included into moderate items and 16 reading items were
included into easy items. The vocabulary item result was different from reading
result. 2 vocabulary items were included into difficult, 13 vocabulary items were
included into moderate items and 10 items were included into easy items. Detail
calculation see appendix A.4.
3.5.4 Discrimination Power Index
Discrimination power index needs to be calculated in order to find out the
significance of test items in determining participants’ skill (Arikunto 2003).
The present study is able to find the discrimination index by conducting the
procedures.
1. Arranging students’ total score and dividing the score into two groups of
2. Counting the n
Ju : participants in upp
Jl : participants in low
After obtainin
and recommendation
e number of the students in the upper group w
tly, then counting the number of lower grou
tem correctly.
the number of correct answer in the upper gr
the proportion passing in the upper group and
ower group, and
difference by the total number of students in on
ng formula is used to calculate the discriminat
power index Bu : participant in upper grou
upper group Bl : participant in lower grou
ower group
(
ing the result of discrimination power index, th
n should be applied (Arikunto, 2003), as presen
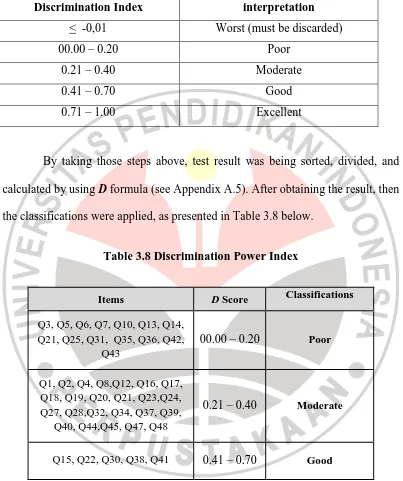
Table 3.7 Classifications of Discrimination Power Index
Discrimination Index interpretation
< -0,01 Worst (must be discarded) 00.00 – 0.20 Poor
0.21 – 0.40 Moderate 0.41 – 0.70 Good 0.71 – 1.00 Excellent
By taking those steps above, test result was being sorted, divided, and
calculated by using D formula (see Appendix A.5). After obtaining the result, then
the classifications were applied, as presented in Table 3.8 below.
Table 3.8 Discrimination Power Index
Items D Score Classifications
Q3, Q5, Q6, Q7, Q10, Q13, Q14, Q21, Q25, Q31, Q35, Q36, Q42,
Q43
00.00 – 0.20 Poor
Q1, Q2, Q4, Q8,Q12, Q16, Q17, Q18, Q19, Q20, Q21, Q23,Q24, Q27, Q28,Q32, Q34, Q37, Q39,
Q40, Q44,Q45, Q47, Q48
0.21 – 0.40 Moderate
Q15, Q22, Q30, Q38, Q41 0.41 – 0.70 Good
The result above shows that 14 items were considered poor, 23 items
3.6 Data Analysis
The following are the steps of how the data were analyzed. First, after the
test was taken from the students, the analysis started by scoring the result of the
test. Then, the process was about finding the level of participants’ vocabulary
mastery and reading comprehension. To find out the mastery of the two variables,
computing the mean of each variable was necessary. The formula to compute
mean is as written below.
=∑
=∑
(Arikunto, 2003)
Afterward, it is necessary to make sure that the data were normally
distributed or not (Sudjana, 1996). This study utilized SPSS 17 (Statistical
Package for Social Sciences) as it is one of the oldest and the most widely-used
statistical software package. The equations of Kolmogorov-Smirnov and
Saphiro-Wilk were used to find out the normality distribution.
The result of normality distribution determines the formula which is
employed to analyze the data. If the data are normally distributed, then Pearson
Product Moment formula is applied, as it is also a correlation formula for Where: Mx = Mean x (Vocabulary mastery)
My = Mean y (Reading comprehension)
∑x = The sum of x scores
∑y = The sum of y scores
parametric statistic a
s (variable x and variable y)
(Ariku
sult of correlation coefficient was interpreted
Arikunto, 2003). The interpretations are present
In the other
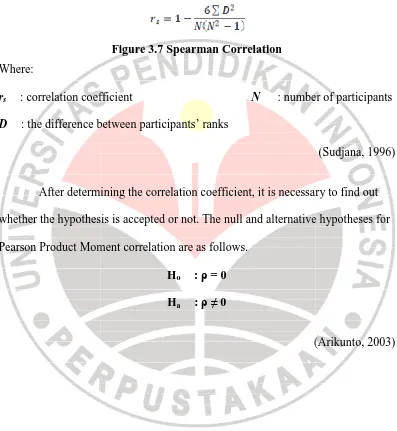
ta are not normally distributed, as it is a correla
istic and ranked data (Sudjana, 1996). The form
Figure 3.7 Spearman Correlation
efficient N : number
e between participants’ ranks
mining the correlation coefficient, it is necessar
esis is accepted or not. The null and alternative
ment correlation are as follows.
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
Introduction
This chapter delineates the conclusions and suggestions of the research.
The conclusions are formulated from the research questions, while the suggestions
present the recommendation for the further research and the related parties.
5.1 Conclusions
This study focuses on the correlation between students’ reading
comprehension and their vocabulary mastery. This study also attempts to find out
the students’ ability in reading comprehension and vocabulary mastery.
Referring to the findings and discussions that have been elaborated in the
previous chapter, it was found out that there is a strong correlation between
students’ reading comprehension and their vocabulary mastery. Although the
scores of reading and vocabulary test are different but the correlation is strong. It
may be caused by the difficult vocabulary in test items. Students who have high
score in reading they also have high score in vocabulary.
There are many factors that help students to comprehend the reading
materials. The result shows that the factors are students’ background knowledge
and experiences. Those factors may help students comprehend reading materials.
When they found unknown words they could guess the meaning of unknown
5.2 Suggestions
After drawing the inferences, there are several suggestions that hopefully
can give the constructive ideas for the readers, especially for English teachers and
future researchers.
Most of English teachers tend to consider that using Indonesian in
English class can dull their students’ ability in using English. Considering to the
result that many students lack of vocabulary knowledge, it is recommended to use
English in English classes, since it facilitates the students to learn materials
efficiently. By using English as medium of instruction, it helps students increase
their vocabulary knowledge. Although using Indonesia language is also needed in
English class to overcome the misunderstanding that may occur in mostly second
language settings. The teachers may want to use different methods in teaching
reading skill to make English class more interesting and fun.
Furthermore, the further researchers can focus on other issues in reading,
such as reading strategies in improving reading comprehension. Besides, the
further researchers can also investigate the correlation between students’
vocabulary mastery and their reading comprehension more depth to reinforce the
REFERENCES
Apriani, N.S. (2011). Improving Students’ Reading Comprehending Through
Jigsaw. Bandung: Unpublished paper.
Arikunto, Suharsimi. (2003). Prosedur Penelitian: Suatu Pendekatan Praktek
(Edisi Revisi V). Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Cameron, Lynne. (2001). Teaching Languages to Young Learners. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Caverly, D. C., & Peterson, C. L (1996). Foundations for a constructivist: whole
language approach to developmental college reading. Chicago: National
Association of Developmental Education
Day, R. R., & Park, J. (2005). Developing reading comprehension questions. Reading in a Foreign Language, 17(1), 60-73.
Gay, L.R., Mills, G.E., and Airasian P.W. (2006). Educational Research:
Competencies for Analysis and Applications (8th Edition). Upper Saddle
River, New Jersey: Pearson-Merill Prentice Hall.
Grabe, W. and Stoller, F.L. (2002). Teaching and Researching Reading. England: Pearson Education Limited.
Grellet, F. (1985). Developing Reading Skills. Leeds: Leeds University Press.
Guy, Bon L. et.al (1993). Reading Difficulties : their diagnosis and correction. Boston: Allyn and Bacon Publishing co.inc
Hirsch, E.D. (2003). Reading comprehension requires knowledge – of words and
Hatch, Evelyn. and Farhady, Hossein. (1982). Research and Statistic Design for
Applied Linguistic. Massachusetts: Newburry House Publishers, Inc.
Hedgcock, J.S. and Ferris, D.R. (2009). Teaching Readers of English. New York: Routledge, Taylor and Francis
Klingner, Janette K. Sharon V. and Alison B. (2007). Teaching Reading
Comprehension to Students with Learning Difficulties. New York: The
Guilford Press.
Laddoo. (2007). The Importance of Reading. [Online]. Available: http://www.squidoo.com/the-importance-of-reading [13 November 2011]
Lehr Fran & Osborn. (2001). A Focus on Vocabulary. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Liu na and Nation, I.S.P. (1985). Factors Affecting Guessing Vocabulary in
Context. [Online]. available:
http://rel.sagepub.com/cgi/content/abstract/16/1/33 [25 January 2011]
McGinnis, Dorothy & E.Smith Dorothy. (1982). Analyzing and Treating Reading
Problems. New York: Macmilan Publishing co.inc
McEntire, Jo. (2003). Read Ahead 2: Reading and Life Skills Development.
Roehrig, Alysia D. & Guo Ying. . Reading in a foreign language. United States: Florida State University
Sedita, J. (2005). Effective Vocabulary Instruction. [Online]. Available:
http://www.keystoliteracy.com/reading-comprehension/effective-vocabulary-instruction.pdf [12 Desember 2012]
Sudjana. (1996). Metoda Statistika. Bandung: Tarsito
Weaver B. (2005). Probability & Hypothesis Testing. [Online]. Available: http://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=hypothesis%20pdf&source=web &cd=1&sqi=2&ved=0CBcQFjAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.angelfire.co m%2Fwv%2Fbwhomedir%2Fnotes%2Fprob_hyp.pdf&ei=tB24TqG7FsTZrQ eC8LnRAw&usg=AFQjCNHf7qHCyPmkZ8Usd_s37PX9B7xrbg [15 September 2011]
Willis, Dave. (2008). Reading for information: Motivating learners to read
efficiently. [Online]. Available:
http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/articles/reading-information-motivating-learners-read-efficiently [ 19 February 2012 ]
Yildirim, K. Yildiz M. and Ates S. (2011). Is Vocabulary a Strong Variable Predicting