THE USE OF VISUAL AIDS TO IMPROVE VOCABULARY
MASTERY ON THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMPN 1
KEDUNG JEPARA IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2013/2014
Graduating Paper
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the
Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S.Pd.I)
In the English Department
Tatik Assa’diyah KKI 11310131
International Class Program
English Department of Educational Faculty of
State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) Salatiga.
DECLARATION
BISMILLAHIRROHMANIRROHIM
Hereby the writer declares that this graduating paper is made by the write herself, and it is not containing materials written and has been published by other people and other peoples‘idea except the information from the references.
The writer is capable to account to him graduation paper if in the future it can be proved of containing others‘ idea or in fact, the writer imitates the others‘
graduating paper.
Likewise, this declaration is made by the writer, and she hopes that this declaration can be understood
Salatiga, August 15, 2014 The Writer
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS SALATIGA STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (STAIN) Jl.Tentara Pelajar 02 Phone(0298) 323706, 323433 Fax. 323433 Salatiga
50721
Website: www.stainsalatiga.ac.id E-mail: [email protected] Salatiga, August 15, 2014 Setia Rini, M.Pd
The Lecturer of Educational Faculty Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES Case: Tatik Assa‘diyah‘s Graduating Paper
Dear,
The Head of Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies
Assalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
After reading and correcting Tatik Assa‘diyah‘s graduating paper entitled ―THE USE OF VISUAL AIDS TO IMPROVE VOCABULARY MASTERY ON THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMPN 1 KEDUNG JEPARA IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2013/2014”, I have decided and would like to propose that if it could be accepted by the educational faculty. I hope it could be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
Consultant
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS SALATIGA STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (STAIN) Jl.Tentara Pelajar 02 Phone(0298) 323706, 323433 Fax. 323433 Salatiga
50721
Website: www.stainsalatiga.ac.id E-mail: [email protected] Salatiga, August 15, 2014 Ruwandi, M.A
The Lecturer of Educational Faculty Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES Case: Tatik Assa‘diyah‘s Graduating Paper
Dear,
The Head of Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies
Assalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
After reading and correcting Tatik Assa‘diyah‘s graduating paper entitled ―THE USE OF VISUAL AIDS TO IMPROVE VOCABULARY MASTERY ON THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMPN 1 KEDUNG JEPARA IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2013/2014”, I have decided and would like to propose that if it could be accepted by the educational faculty. I hope it could be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
Consultant
Ruwandi, M.A
MOTTO
Lerning to Do
Doing to Learn
Erning to live
Living to Serve
.
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My God the Almighty
2. My dearest father and mother ( Bisri and Muawanah), who always pray for
me and give their endless love.
3. My dearest brother and sister ( Muntaha Almisbah and Khoirunnisa‘), thank
you for your motivation, kindness, and love.
4. My dearest younger brother and younger sister ( Roisul Umar and Nasriyatur
Rizqiyah), thank you for your kindness and love.
5. My motivator (Taufiqul Muqorrobin ), thank you for your motivation and
your advice,love and everything.
6. All of my big family, thank you for your kindness.
7. My beloved friends khumaira girls (Alif Karyawati, Rizki Parahita A, Khoirul
Bariyyah, Tatik Assa‘diyah, and Kuni Azkal Maroya), thanks for your
support and togetherness.
8. My beloved friends of International Class Program batch 2010, thank for the
togetherness.
9. All my brothers and sisters in International Class Program batch 2011-2013.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, The Most Gracious and The Most Merciful, The Lord of Universe. Because of Him, the writer could finish this thesis as one of the requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan in English Department of Educational Faculty of Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) Salatiga in 2014.
Secondly, peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness.
However, this success would not be achieved without those supports, guidance, advice, help, and encouragement from individual and institution, and I somehow realize that an appropriate moment for me to deepest gratitude for:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd. as the rector of Salatiga State Institute for Islamic Studies.
2. Hammam, S.Pd., M.Pd. as the first director of International Class Program.
3. Setia Rini, M.Pd. as the second director of International Class Program 4. Noor Malikhah, Ph.D as the third director of International Class Program 5. Setia Rini, M.Pd. as the first writer‘s counselor who have educated,
supported, directed and given the writer advices, suggestions, and recommendations for this thesis from beginning until the end.
6. Ruwandi, M.A as the second writer‘s counselor who is so kind in completing this thesis.
8. All the lecturers of International Class Program.
9. All the lecturers of English Department of Educational Faculty.
10.All staff that have helped the writer in processing of thesis administration
Thanks for the support, advices, suggestion, and other helps that you all gives. The writer hopes this research will useful for everyone.
Salatiga, September 4 2014
The Writer
Tatik Assa’diyah
KKI 113 10 131
TABLES OF CONTENTS
TITLE……….. i
DECLARATION………... ii
ATTENTIVE CONSELOR NOTES 1……….. iii
ATTENTIVE CONSELOR NOTES 2……… iv
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION………. v
MOTTO……… vi
DEDICATION……… vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT……… viii
TABLE OF CONTENS……….. ix
ABSTRACK……… x
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1 A.BACKGROUND OF STUDY………. 1
B. IDENTIFICATION OF THE PROBLEM……… 3
C. LIMITATION OF THE PROBLEM……… 4
D. STATEMENTS OF THE PROBLEM………. 4
E. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY………. 5
F. BENEFIT OF STUDY……… 5
G. CLASIFICATION OF KEY TERM……… 6
H. LITERATURE REVIEWS………. 7
I. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY……… 8
K. THE OUTLINE OF THE GRADUATING PAPER……… 19
CHAPTER II: RESEARCH THEORIES 21 A.TEACHING……… 21
1. Term of Teaching………. 22
2. The concept of Teaching……… 23
3. Teaching Strategy……… 24
B. LEARNING……… 27
1. Term of Learning………. 27
2. Type of Learning……… 33
3. Learning Style……… 35
C. VOCABULARY 36 1. Term of Vocabulary……….. 36
2. General View of Vocabulary………. 36
3. Definition of Vocabulary Mastery………. 38
4. Principles of Learning and Teaching Vocabulary……… 38
5. How words are remembered……… 39
6. Type of Vocabulary………. 43
7. The importance of a vocabulary……… 45
D. VISUAL AIDS 46 1. Definition of Visual Aids……… 46
2. How the visual aids can help in teaching language……… 47
3. The component of Visual Aids……… 50
5. Benefit of Visual Aids……… 52
6. Type of Visual Aids……… 53
7. The type of visual aids most commonly used……… 53
8. Tips for Using Visual Effectively……… 54
9. The purpose of using visual aids………. 54
E. THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK……… 55
1. Advantages of Visual Aids……… 60
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH REPORT 62 A.RESEARCH SETTING……… 62
1. Research Location……… 63
2. The History of School……… 63
B. THE PROFILE OF TEACHER AND STAFF 67 1. Teacher………. 67
2. Staff……… 68
A. THE PROFILE OF STUDENTS……… 69
1. The Name of Students……… 69
B. B. THE PROFILE OF SCHOOL FACILITIES……… 71
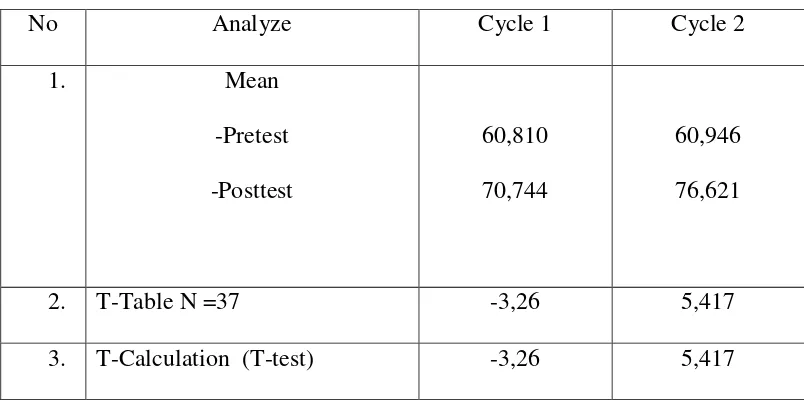
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION 74 A. DATA PRESENTATION SCORE……… 74
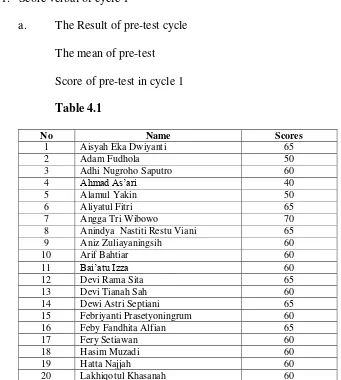
1. Score verbal of cycle ……… 74
a. The Result of pre-test cycle 1……… 74
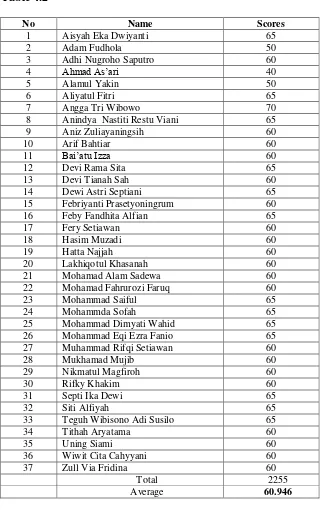
b. The Result of pre-test cycle 2……… 76
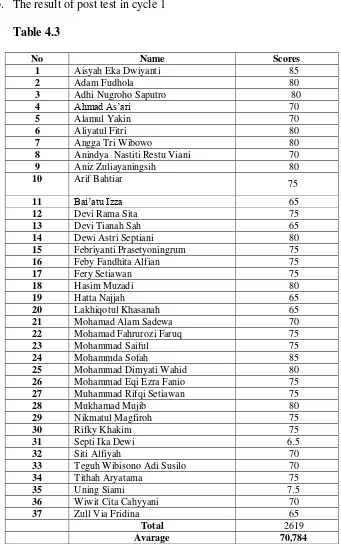
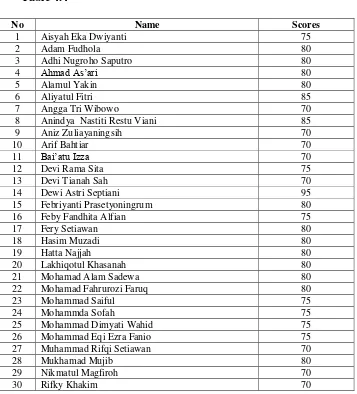
d. The Result of post-test cycle 2……….. 78
B. B.DISCUSSION 81
a. Cycle 1……… 81
b. Cycle II……….. 89
C.RESEARCH SUMMARY……… 93
CHAPTER V : CLOSURE 96
A.CONCLUSIONS……… 96
B. SUGGESTION……… 97
LIST OF TABLES
1. Table 1.1 The Design of CAR... 10
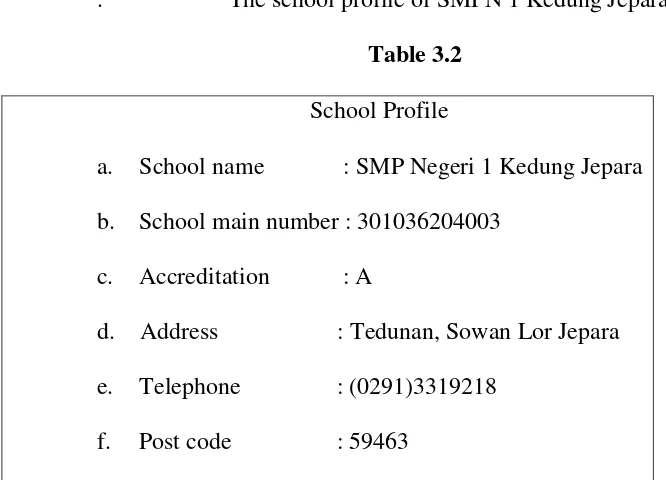
2. Table 3.1 Research Setting……… 62
3. Table 3.2 School Profile……… 63
4. Table 3.3 School organization Structure……….. 66
5. Table 3.4. Teacher……… 67
6. Table 3.5 Staff………. 68
7. Table 3.6 The Profile Students……… 69
8. Table 3.7 The Name of Students………. 69
9. Table 3.8 The Profile of School Facilities……… 71
10. Table 4.1cycle Score pretest I……….. 74
11. Table 4.1cycle Score pretest II……….. 76
12 . Table 4.3 The Result of post test cycle I………. 77
13 Table 4.4 The Result of post test cycle II………. 78
ABSTRACT
Assa‘diyah, Tatik. 2014. The Use of Visual Aids to Improve Vocabulary Mastery on The Eighth Grade Students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara in the Academic Year 2013/2014. Graduating Paper, Educational Faculty. English Department. State Institute for Islamic Studies (STAIN) Salatiga. Conselor: (I) Setia Rini, M.Pd., (II) Ruwandi, M.A.
Keyword: vocabulary mastery, visual aids
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION A. Background of Study
Vocabulary is one language components which should be mastered by SMP or SMA students. Vocabulary is the most important component that will become the basic competence in order to successfully master the four language skills like listening, speaking, reading and writing. If the students have mastered a number of vocabularies required at their level, it will be easier for them to master those elements in English learning. Hardjono defines ―From all aspect foreign language that should be mastered by the students in the learning process, vocabulary is the most important aspect because the students can not use foreign language without vocabulary.‖( 1998:p.71). It means vocabulary is an essential
Teachers have their own priority to manage their classroom, As Richards (1994:p.97) state ‖ teachers have primary responsibility for how they teach; they may assume very different roles within their own classroom‖. So teachers should make their classroom comfortable and
interesting, especially teaching English in junior high school.
According to Hatch and Brown (1995: p. 1) there are several difficulties of mastering vocabulary The first is such a test may be used with classes of learners who speak different first languages and thus translation is not a practical approach. Second, there is the likelihood that some learners will have poor reading skills and thus the test needs to be able to be given orally if necessary. And the third is that the contexts for the tested words must not cause too many problems for the learners. The difficulties are faced by students of SMPN 1 KedungJepara. This can be proven from pure research in the eighth grade students the researcher found that students‘ vocabulary mastery is low. It is because the students get difficulties in mastering vocabulary mastery. They are : (1) the students get difficulties in grasping and memorizing the meaning of the words ; (2) they found it hard to spell the words correctly ; and (3) they get difficulties in pronouncing the words correctly; and (4) they get difficulties in using vocabulary in a sentence (Brown 1995: p. 1).
afraid to ask the teacher if they find a difficulty. These problems may give a great influence to their learning process.
The writer suggests using visual aids to solved the problem. The visual aids method can be used in teaching vocabulary, to make the teaching learning process much interesting and fun. It will increase students‘ interest in learning process in the classroom, because the circumstances become more interesting. It is suitable with the characteristic of the young learners who like playing and talking about here and now so using visual aids can be helpful in teaching vocabulary.
According to (Eline: 1997) the advantages of using visual aids they are; (1) Visual aids can make ideas clear and understandable (2.) Visual aids can make a speech more interesting (3.) Visual aids can help an audience remember facts and details (4.) Visual aids can help prove a point.
By using visual aids the expectation an effectively in order that the students can enrich and improve their vocabulary easily. Also helped students understand the motivation in learning and improving learning outcomes in learning vocabulary.
Based on the explanation above, the writer wants to use the visual aids method as the method to improve student‘s vocabulary mastery. The writer is interested in carrying out a study on ―THE USE OF VISUAL
GRADE STUDENTS OF SMPN 1 KEDUNG JEPARA IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2013/2014
B. Identification of the Problem
The on successful study of English may be consul by the following problems:
1. Teacher may not apply the appropriate approach or method in language teaching
2. Teacher may not use the best learning strategies 3. Teacher may not use the best learning sources
4. Teacher have to responsibility decreasing of less learn motivation and less skill even in problem solving of teaching visual aids.
C. Limitation of the Problem
Derived from the problems identified above, the writer focuses ontheuse of visual aids to improve vocabulary mastery on the Eighth grade students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara. This means the writer hopes that the result research can be used as reference for those who want to conduct a research in teaching English .
D. Statements of the Problem
2. Whether or not the implementation of Visual Aids signify the improvement vocabulary on the eighth grade students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara. In the academic year of 2013/2014?
E. Objectives of the Study
Based on the problem formulation above the objective of this research can be specified as follows:
1. To describe the implementation of visual aids to improve vocabulary mastery on the eighth grade students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara. in the academic year of 2013/2014? 2. To analyze and evaluate the improvement of vocabulary
mastery after using visual aids? F. Benefit of Study
The result of this research is expected to give contribution in some ways:
1. Practically
The result of this research can be used by English teacher in teaching, to motivate the students to improve their vocabulary mastery and to suggest the SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara to complete their teaching especially the language teaching using visual aids
Beside Vocabulary is basic component in learning a foreign language and Generally children like thing about visual aids , so they are highly motivated to learnvocabulary and to memorize words that the children watch from visual aids performance. Furthermore, visual aids will make the students relaxed and fun.
The result of this research can be used as reference work for study of the other subject.
G. Classification of Key Term
Here are some definitions as a guidance to understand the terms of this study:
1. Visual aids
Visual aid refers to an instructional aid that is used to supplement spoken and written information. Visual aids can be in the form of videotape, posters, cars models and film.
2. Vocabulary mastery
American, 2000:615). Vocabulary mastery is the knowledge understanding the words.
H. Literature Reviews
In the research paper the writer takes one literature reviews. The first review is entitled ― Improving Students Vocabulary Matery Using Experiential Learning (A Classroom Action Research on The Sixth Grade of SDN Banaran 01 Sukoharjo in The A cademic Years 2009/2010) that was by ―Ike Anisa 2009.
In that paper, she analyzed that the result the use of Experiental Learning can improve students‘ their vocabulary, motivation, interest and achievement. The implementation of visual aids is reasonable because it can give students enrich and improve their vocabulary easily and motivation to learn English. (Ike Anisa, 2009) .
Differ with Ika‘s paper, (Budi, 2011:35) identified that the use of visual aids can help students to improving vocabulary mastery on the text and answer the question. visual aids is not only making students easier to understand the lesson but also motivating and attracting students in learning English particularly in structuring ideas, editing ideas.vocabulary mastery ability as well.
bored since the methods and media are monotonous. When the teacher used usual method, the students will not be attracted with the teaches.
So word wall will gain the interest from the student in junior high school and also can motivate students and improve their vocabulary mastery.
I. Research Methodology
1. Research Approach
An approach that will be done by the writer use quantitative as a primary approach. The quantitative research isolates and defines variables and variables categories. These variable are linked together to frame hypotheses. The data are collected are then tested upon the data (Banner, 1993:4). The secondary approach is descriptive. Descriptive is describing how a technique of learning is applied and the result can be reached (Mukhlis, 2000:57).
2. Method of The Study
Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a research designed to assist a teacher to find out what is happening in his or her own class and to determine actions for future improvement.
3. Research Subject
In conducting this action research, the writer is interested in the students of SMPN 1Kedung Jepara. It is located on Sowan Lor Street –Tedunan . The class is consist of 37 students specifically consist of 10 males and 27 females. They are selected on the basic of the preliminary observation, which is shown the result that students is low vocabulary mastery in visual aids. 4. Research Design
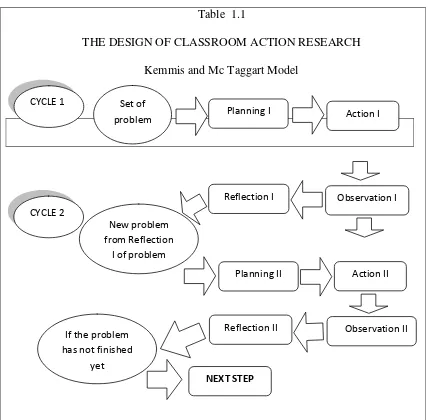
According to Kemmis (1990)cited in Mills (2000:17), action research consists of cycles. Every cycle consists of four steps; planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
Table 1.1
THE DESIGN OF CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH Kemmis and Mc Taggart Model
This research uses a classroom action research. Actually there are varieties of procedures of research, but the researcher selects Kemmis and
CYCLE 1 Set of
problem Planning I Action I
CYCLE 2
Observation I Reflection I
New problem from Reflection
I of problem
Planning II Action II
Observation II Reflection II
If the problem has not finished
yet
Mc Taggart Model in Dr.Hamzah,M.Pd (2012). MenjadiPeneliti PTK yang Profesional as the measurement in this study.
The researcher plans to conduct two cycles of classroom action research. There are four steps in one cycle for doing classroom action research. They are planning, action and observation, and reflection.
1. Cycle I
a) Planning
In this stage the researcher conducted some activities to make the teaching and learning process interesting. The researcher arranges the lesson plan based on the teaching material, improves the teaching strategy, prepare the teaching aid and also prepares the sheet of the observation to observe teaching and learning process in this cycle.
b) Action
Doing the activity based lesson plan which is made. In teaching and learning activity, the students are guided to study vocabulary through using Vocabulary game and here are some steps:
1) Giving a brief explanation of the material of vocabulary
2) Applying Vocabulary game. 3) Providing worksheet
5) Closure activity
In the end of teaching and learning activity in every cycle, the teacher gives a test to evaluate the students‘ result for teaching and learning process.
c) Observation
Observation is made during the learning process should be on going and observer does a collaboration in implementation with the English teacher of the class. Here are the instruments used:
1) Field note
2) Recording the situation
3) Collecting data (students‘ score) d) Reflection
analyzing and interpreting data (observation), develop an action planning (reflection).
The researcher‘s reflection is done by discussing with his
collaborator. Note of lack, incompatibility between action and scenario or different response of students that expected. They are analysis of the observation, identification of the problem and find out the alternative decision of the problem.
2. Cycle II
The second cycle is done based on the result of reflection from the first cycle. If the result from observation was still low in quality, it is needed another action in order to make improvement of the quality for the next cycle the topic.
a) Planning
1. The researcher identified the teaching and learning design, such as arranging lesson plan which was according to teaching and learning process.
2. The researcher prepared the teaching and learning resources, such as material, power point (slides), and worksheet and observation sheets.
3. Prepare attendance list in order to know students‘ activeness in participating teaching and learning by using visual aids.
d) Reflection
5. Research Instrument
According to (Eline:1997) it can be concluded that a research Instrument is what you use to collect the information in a qualitative field tudy or observation. It helps you keep track of what you observe and how to reports it. It mus be both valid and precise. the process of collecting data, analyzing, and find the solution.such as a paper and pencil test, a questionnaire, an interview, a research tool, or a set of guidelines for observation.
(Pierce, 2009, p. 159) state "Careful planning for data collection can help with setting realistic goals. Data collection instrumentation, such as surveys, physiologic measures (blood pressure or temperature), or interview guides, must be identified and described. Using previously validated collection instruments can save time and increase the study's credibility. Once the data collection procedure has been determined, a time line for completion should be established."
The researcher use of validated collection instrument consists of Observation, Test and Check list.
1. Observation (Sheet)
researcher will join in class. In this case, the researcher is the teacher. The researcher will used field note, field notes are used to observe and to know the situation and activities during teaching learning process. By using field note I would like to know class situation and participation of students.
2. Test
Test is a method of measuring a person‘s ability,
knowledge, or performance in a given domain (H. Doughlas brown, 2004, 3). Test is done to know students‘ achievement so that the researcher knows the students‘
improvement can be reached by the students. 6. Evaluation criteria
The students‘ success or failure in doing the activities
above was assessed by referring to the criterion issued by Department of Education andCulture. The criterion says that a student can be said to pass the test if he or she cansolve 65% of the whole problems and a class is said to be successful if 85% of themembers pass the test.
7. Data collection a) Test
Test is a method of measuring a person‘s ability,
knowledge, or performance in a given domain (H. Doughlas brown, 2004, 3). In this classroom action research, the researcher provided pre test and post test to evaluate how far the students understand the ability of vocabulary. Test is done to know students‘ achievement so that the researcher knows the students‘ improvement can be reached by the
students.
1. Construction of Instrument
a) Pre-test
Pre-test was given to the students in the first step of collecting data. Pre-test was used to identify the students‘ ability in vocabulary game before the treatment was given. In other words, it told the beginning conditions of the students‗ ability in vocabulary mastery.
b) Formative test
Formative test is a test which is evaluating students in the process of forming their competencies and skills with the goal of helping them to continue that growth process (Brown,2004:6). In this study, the writer conducted the formative tests in the end of cycle1 and cycle2.
c) Post-test
Post-test was conducted to measure the students ‗achievement after the treatments. The test was the same as
the pre-test and formative tests. Result of the post-test was analyzed to see to what extent vocabulary game develop the students ‗invocabulary mastery.
1) Observation
know how the condition of class and students during the teaching and learning process. In conducting observation the researcher used the sheets of checklist to note the activity that might occur in the teaching vocabulary mastery by using visual aids.
2) Documentation
Documentation method is to get a researcher data linked to research object that will be elaborated in this research, and it emphasizes an interview method result, and observation. This method is used to collect data dealing with documentation of teaching and learning process the use visual aids to improve vocabulary mastery.
8. Data Analysis
1. Statistical technique
A statistical technique is used to know there are any influences to student vocabulary mastery or no from the result of pre-test and post test. The researcher uses mean formula from (Sutrisnohadi, 1981:246) to analyze the data:
M =∑
M : the mean obtained
∑x : the sum of the students‘ value
N : the number of subject
2. Descriptive technique
A descriptive technique is used to know the students‘ behavior during teaching and learning process.
In descriptive technique the researcher will analyze the observation sheet which has been made with his collaborator.
J. Hypothesis of the Study
Based on the background of study, statement of the problem, the hypothesis of this study stated that: ―The use of visual aids To improve vocabulary mastery on the eighth grade students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara. in the Academic Year of 2013/2014‖.
K. The Outline of the Graduating Paper
In order to make easy to understand this graduating paper, the researcher uses a system of presentation as follows:
Chapter II is research theories. It contains about theories that relevant toward research, Teaching, Learning, Vocabulary, and visual aids, and about the characteristic the teaching learning process using visual aids .
Chapter III is research report. It contains about general description of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara.
Chapter IV is research finding and discussion. It is about field note and scores of the test.
CHAPTER II RESEARCH THEORIES
This chapter contains two sections. This first section talks about the theoretical reviews underlying this study. The last section describes the research procedure which is used as the basis of this study
A. Teaching
Teaching is derived from word teach. It has meaning; give somebody information about a particular subject to learn something (Oxford-Advanced Learner‘s Dictionary, 1995: 1225).
H. Douglas Brow (2000), in his book Principles of Language Learning and Teaching stated that ―Teaching is showing or helping someone to
learn how to do by something, giving instruction, guiding in the study of something‖.
According to Nathan Gage (1964:269) noted that ―to satisfy the
practical demands of education, theories of learning must be stood on their head‘ so as to yield theories of teaching.‖ Teaching is guiding and
successful procedures on a given day for given learners under the various constraints of particular context of learning.
1. Term of Teaching
Term of Teaching as follow as:
a. The first Action plan: Specific proposal developed by a learner, teacher or institution to address problems or difficulties or meet a desired goal.
b. The second active learning methodes:Learning methods that focus on ensure learners and active role in the process of learning instead of passively receiving information.
c. The third is aesthetic response: An effective response a person has to material, which is based on the visual‘s background knowledge,
attitudes, and experiences.
d. The fourthblended learning: An educational formation that integrates learning technique including online delivery of materials through board or other teaching methods.
e. The fifth competencies:Individual abilities as relate to knowledge, understanding, and skill; see also minimal competence.
g. The seventh evaluation: Processing of assessing work completed by an individual, group or institution with the aim of determining whether the individual, group has predetermining standards. h. The eighth exercise: Problem, task or other activity aimed at
developing or improving a person‘s skill or knowledge.
i. And then in the feedback: Responses provided to an individual while completing a task that are intended to guide the individual to desire end.
2. The Concept of Teaching
According to Biggs (1991) an expert on contemporary cognitive psychology stated the concept of teaching divides into three, namely:
a) In quantitative terms, teaching means "the transmission of knowledge" that the transmission of knowledge in this case the teacher only needs to master the knowledge of their field of study and pass on to his students as well as possible.
b) In terms of institutional teaching means "the efficient orchestration of teaching skills", it means the arrangement of all the teaching skills efficiently in this sense teachers are required to always be ready to adapt different teaching techniques for a variety of different students' talents, abilities, and needs.
principle are teaching activities to develop the full potential of the realm of psychological.
3. Teaching Strategy
From (http://www. part-time/strategy) accessed on May 20, 2014) teaching strategy comprise of :
a. Lecturer : The lecture method was the most widely use instructional in college classroom. college classrooms in the late 1970 reported usng some form of the lecture method to teach students (cashin, 1990).Used in conjunction with active learning teaching strategies, the traditional lecture can be an effective way to achieve instructional goals. The advantages of the lecture approach are that it provides a way to communicate a large amount of information to many listeners, maximizes instructor control and is non-threatening to students. The disadvantages are that lecturing minimizes feedback from students, assumes an unrealistic level of student understanding and comprehension, and often disengages students from the learning process causing information to be quickly forgotten. The following recommendations can help make the lecture approach more effective (Cashin, 1990).
1. Fit the lecture to the audience
3. Prepare an outline that includes 5-9 major points you want to cover in one lecture
4. Organize your points for clarity
5. Select appropriate examples or illustrations
6. Present more than one side of an issue and be sensitive to other perspectives
7. Repeat points when necessary
8. Be aware of your audience - notice their feedback
9. Be enthusiastic - you don‘t have to be an entertainer but you should be excited by your topic.
(from Cashin, 1990, pp. 60-61)
a. Case Method: Providing an opportunity for students to apply what they learn in the classroom to real-life experiences has proven to be an effective way of both disseminating and integrating knowledge. The case method is an instructional strategy that engages students in active discussion about issues and problems inherent in practical application. It can highlight fundamental dilemmas or critical issues and provide a format for role playing ambiguous or controversial scenarios.
b. Discussion : There are a variety of ways to stimulate discussion. For example, some faculty begin a lesson with a whole group discussion to refresh students‘ memories about the assigned
points or emerging issues, or generate a set of questions stemming from the assigned reading. These strategies can also be used to help focus large and small group discussions.
c. Give specific feedback rather than general comments. For example (―The beanbag didn‘t get all the way to the hoop, James,
so you might try throwing it harder.
d. Ask questions that provoke children‘s thinking. (―If you couldn’t
talk to your partner, how else could you let him know what to do?‖)
e. Provide information, directly giving children facts, verbal labels, and other information. (―This one that looks like a big mouse with a short tailis called a vole.‖)
f. Give directions for children‘s action or behavior. (―Touch each block only once as you count them.‖ ―You want to move that icon over here? Okay, click on it and hold down, then drag it to wherever you want.‖)
use listserves or on-line notes to extend topic discussions and explore critical issues with students and colleagues, or discipline- specific software to increase student understanding of difficult concepts.
h. Distance Learning. Distance learning is not a new concept. We have all experienced learning outside of a structured classroom setting through television, correspondence courses, etc. Distance learning or distance education as a teaching pedagogy, however, is an important topic of discussion on college campuses today. Distance learning is defined as 'any form of teaching and learning in which the teacher and learner are not in the same place at the same time' (Gilbert, 1995).
B. Learning
Learning is the act or experience of one that learnsknowledge or skill acquired by instruction or study modification of a behavioral tendency by experience (as exposure to conditioning)
(http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/learning)
1. Term of Learning
From (http://theelearningcoach.com/resources/online-learning-glossary-of-terms/) term learning as follow as :
a) ASYNCHRONOUS LEARNING: When learners
called eLearning or web-based training (WBT). Asynchronous learning allows learners to go through a course at their own pace and on their own schedule.
b) AUDIO CONFERENCING: Audio conferencing refers to a connection between three or more locations that involves a voice-only connection. This can be done via telephone or via the computer. When the audio conference is done between computers over the Internet, it uses a technology known as VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol).
c) BLENDED LEARNING: Blended learning is an instructional approach that includes a combination of online and in-person learning activities. For example, students can complete online self-paced assignments by a certain date and then meet on-site or online for additional learning activities.
terms are online learning, eLearning and Web-based Training (WBT).
e) COURSEWARE: Courseware refers to any instructional software that is delivered on a computer.
f) DISTANCE EDUCATION or DISTANCE LEARNING:
Distance Education/Learning occurs when students and their instructors are in different geographical locations and the instruction occurs on an electronic device, such as a computer or mobile phone. The learning can occur in a synchronous environment, in which all participants are connected at the same time or in an asynchronous environment, when participants are engaged in learning at different times.
g) E-LEARNING: eLearning (short for electronic learning) is an umbrella term that refers to all types of training, education and instruction that occurs on a digital medium, like a computer or mobile phone.
h) HYBRID LEARNING: See blended learning.
conversing. It‘s the kind of natural learning humans do
outside of a structured environment.
j) INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN: Instructional design involves the identification of the knowledge, information, and skill gaps of a particular group of people and creating or selecting learning experiences that close this gap. Instructional designers base their learning decisions on cognitive psychology, instructional theory and best practices.
k) INSTRUCTOR LED TRAINING (ILT): ILT typically refers to providing instruction in a classroom environment where the instructor and learners are together at the same time and in the same physical location.
l) INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGNER: An instructional
designer practices the craft and science of instructional design. This person identifies the needs of a targeted audience and determines the best approaches for meeting the audience‘s needs. It could involve designing and writing
m) INTERACTIVE MULTIMEDIA: Interactive multimedia allows learners to provide input to an online course and receive feedback as a result of the input. The input might consist of a mouse click or drag, gestures, voice commands, touching an input screen, text entry and live interactions with connected participants.
n) MOBILE LEARNING: Learning that takes place on a hand-held device, such as a mobile phone, that can take place anytime and anywhere.
o) MULTIMEDIA: Multimedia refers to the presentation of information and instruction through a combination of graphics, audio, text, or video. Multimedia instruction is often interactive.
p) ONLINE LEARNING: The term online learning is often used synonymously with eLearning. It is an umbrella term that includes any type of learning accomplished on a computer and usually over the Internet.
q) SELF-PACED LEARNING: Self-paced learning refers to the type of instruction that allows a person to control the flow of the courseware. It implies the learning environment is asynchronous.
social technologies that allow people to collaborate, converse, provide input, create content and share it. Examples of social media learning can occur through online social networking platforms, blogs and micro blogs (like Twitter), online talk radio and wikis.
s) STREAMING MEDIA: Streaming media refers to video and audio that is downloaded to a computer from the Internet as a continuous stream of data and is played as it reaches the destination computer.
t) SYNCHRONOUS LEARNING: When learners
participate in an online learning course at the same time but in different locations, it is known as synchronous learning. Synchronous learning allows learners to interact with the instructor and other participants. This is done through software that creates a virtual classroom.
u) VIDEO CONFERENCING: Video conferencing refers to the use of video technology (both hardware and software) to create a virtual meeting between two or more people in different physical locations. Participants can see and hear each other through this technology.
implemented through software that allows an instructor and students to interact.
w) WEBINAR: A webinar is a seminar or workshop in which the facilitator and participants view the same screen at the same time. Usually the webinar has an audio component that the facilitator controls and functionality that allows participants to chat by entering text, answering polls, raising their hands and asking questions.
x) WEB-BASED TRAINING (WBT): WBT refers to all types of digital instruction in which the learning material is presented via the Internet.
2. Type of Learning
a. Perceptual learning – ability to learn to recognize stimuli that have been seen before
1) Primary function is to identify and categorize objects and situations
2) Changes within the sensory systems of the brain b. Stimulus-response learning – ability to learn to perform a particular behavior when a certain stimulus is present.
1) Establishment of connections between sensory systems and motor systems.
a. Unconditioned Stimulus (US), Unconditioned Response (UR), Conditioned Stimulus (CS), Conditioned Response (CR)
b. Hebb rule – if a synapse repeatedly becomes active at about the same time that the postsynaptic neuron fires, changes will take place in the structure or chemistry of the synapse that will strengthen it. c. Rabbit experiment – tone paired with puff of air
c . Instrumental conditioning – association between a response and a stimulus; allows an organism to adjust its behavior according to the consequences of that behavior.
1) Reinforcement– positive and negative 2) Punishment
3) Motor learning – establishment of changes within the motor system
4) Relational learning – involves connections between different areas of the association cortex 5) Spatial learning – involves learning about the
relations among many stimuli
6) Episodic learning – remembering sequences of events that we witness
3. .Learning Style
Learning style is the biologically and developmentally imposed set of characteristics that make the same teaching method wonderful for some and terrible for others (Dunn and Grigss, 1988). (Reid, 1987) stated Learning styles are simply put, various approaches or ways of learning. They involve educating methods, particular to an individual that are presumed to allow that individual to learn best. It is commonly believed that most people favor some particular method of interacting with, taking in, and processing stimuli or information (LdPride, 2009).
a. Reid (1995) proposed two major hypotheses about learning styles:
1) All students have their own learning styles and learning strengths and weaknesses.
2) A mismatch between teaching and learning styles causes learning failure, frustration and demoivation.
b. Reid (1987) identifies six learning styles, referred to as PerceptualLearning Styles:
1) Visual learners prefer seeing ideas in writing, e.g: reading handouts.
3) Kinesthetic learners prefer active participation, e.g.: drama, role—play.
4) Tactile learners prefer hands-on work, e.g: handling materials or taking notes.
5) Group learners prefer studying with others. 6) Individual learners prefer studying alone. C. Vocabulary
1. Term of Vocabulary
From (Online edition 2009 Cambridge) the term vocabulary consists of:
Recall the major steps in inverted index construction: a. Collect the documents to be indexed.
b. Tokenize the text.
c. Do linguistic preprocessing of tokens.
d. Index the documents that each term occurs in 2. General View of Vocabulary
needs facility in the use of words. In this definition they try to see the meaning of vocabulary from the general point of view.
According to Hornby , vocabulary is the total numbers of words in a language and vocabulary is a list of words with their meanings ( 1995: p. 131). It means that vocabulary is a number of words along with the meaning in a language that is known by a person. Here, words are symbol that represent, either physical object or idea. Dealing with the vocabulary state that vocabulary can be defined, roughly, as the words we teach in the foreign language. However, new item of vocabulary may be more than a single word (1996:p.60)
Meanwhile vocabulary mastery has always been an essential part of English as a foreign language. There is no doubt that vocabulary mastery is basic in learning English. Here, the word mastery can be defined as a test assessing performance on an objective (Gagne, Briggs, and Wager, (1992:p.262). Furthermore, Zimmerman (in Cody and Huckin, 1997:p.5) state that ―vocabulary
is central to language in critical importance to the typical language learning.
3. Definition of Vocabulary Mastery
Vocabulary mastery are plays an important role in learning a language. There are some definitions of mastery that are proposed by experts. (Swannel (1994:p.656) defines mastery as comprehensive knowledge. This definition is supported by Hornby who states that mastery is complete knowledge or complete skill (1995:p.721). According to culson (1987:p.1050), mastery is skill to use the knowledge. It means that mastery is ability to use one‘s knowledge.
From the explanation above vocabulary mastery means an ability to use words in conducting communication, and students understand the sets of words. It can also be said that the set of words likely to be used by those students when constructing new sentences. 4. Principles of learning and teaching vocabulary
However many theories about vocabulary learning process were written, it still remains the matter of memory. Thus, there are several general principles for successful teaching, which are valid for any method. According to Wallace, 1988 the principles are:
a) Aim – what is to be taught, which words, how many
b) Need –target vocabulary should respond students‘ real needs and interests
c) Frequent exposure and repetition
complex process. The students‘ aim to be reached in learning vocabulary process is primarily their ability to recall the word at will and to recognize it in its spoken and written form. Generally, knowing a word involves knowing its form and its meaning at the basic level. In deeper aspects it means the abilities to know its (Harmer 1993):
1) Meaning, i.e. relate the word to an appropriate object or context
2) Usage, i.e. knowledge of its collocations, metaphors and idioms, as well as style and register (the appropriate level of formality), to be aware of any connotations and associations the word might have
3) Word formation, i.e. ability to spell and pronounce the word correctly, to know any derivations (acceptable prefixes and suffixes),
4) Grammar, i.e. to use it in the appropriate grammatical form 5. How words are remembered
memory work? Researchers into the workings of memory distinguish between the following systems ( Thornbury, 2002)
a) Short– term store b) working memory c) Long– term memory a) Short - term store
Short-term store is the brain capacity to hold a limited number of items of information for periods of time up to a few seconds. It is the kind of memory that is involved in repeating a word that you have just heard the teacher modeling. But successful vocabulary learning involves more than holding words for a few seconds. To integrate words into long - term memory they need to be subjected to different kinds of operations.
b) Working memory
memory is a good predictor of language learning aptitude. The better ability to hold words in working memory the smoother the process of learning foreign languages.
c) Long –term memory
Long-term memory can be seen as kind of filling system. Unlike working memory, which has a limited capacity and no permanent content, this kind of memory has an enormous capacity and its contents are durable over time. However, to ensure moving new materials into permanent long-term memory requires number of principles to be followed, described by Thornbury, 2002:
1) Repetition – repetition of encounters with a word is very important, useful and effective. If the word is met several times over space interval during reading activities, students have a very good chance to remember it for a long time. 2) Retrieval - another kind of repetition. Activities, which
require retrieval, such as using the new items in written tasks, help students to be able to recall it again in the future. 3) Spacing - it is useful to split memory work over a period of
time rather than to mass it together in a single block.
5) Use - putting words to use, preferably in an interesting way, is the best way of ensuring they are added to long – term memory. This is so called ―Use it or lose it‖ principle.
6) Cognitive depth - the more decisions students make about the word and the more cognitively demanding these decisions are, the better the word is remembered.
7) Personal organizing - personalization significantly increased the probability that students will remember new items. It is achieved mainly through conversation and role-playing activities.
8) Imaging – easily visualized words are better memorable than those that do not evoke with any pictures. Even abstract words can be associated with some mental image. 9) Mnemonics – tricks to help retrieve items or rules that are
stored in memory. The best kinds of mnemonics are visuals and keyword techniques.
10)Motivation - strong motivation itself does not ensure that words will be remembered. Even unmotivated students remember words if they have to face appropriate tasks. 11)Attention - it is not possible to improve vocabulary without
6. Types of vocabulary
From(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VocabularyThe_importance of a vocabulary) type of vocabulary consists of below:
a. Reading vocabulary
A literate person's reading vocabulary is all the words he or she can recognize when reading. This is generally the largest type of vocabulary simply because a reader tends to be exposed to more words by reading than by listening
b.Listening vocabulary
A person's listening vocabulary is all the words he or she can recognize when listening to speech. People may still understand words they were not exposed to before using cues such as tone, gestures, the topic of discussion and the social context of the conversation.
c.Speaking vocabulary
A person's speaking vocabulary is all the words he or she uses in speech. It is likely to be a subset of the listening vocabulary. Due to the spontaneous nature of speech, words are often misused. This misuse – though slight and unintentional – may be compensated by facial expressions, tone of voice, or hand gestures.
d. Writing vocabulary
communicating: for exampleif there are a number of synonyms, a writer will have his own preference as to which of them to use.he is unlikely to use technical vocabulary relating to a subject in which he has no knowledge or interest.
e. Focal vocabulary
Focal vocabulary is a specialized set of terms and distinctions that is particularly important to a certain group: those with a particular focus of experience or activity. A lexicon, or vocabulary, is a language's dictionary: its set of names for things, events, and ideas. Some linguists believe that lexicon influences people's perception of things, the Sapir–Whorf hypothesis. For example, the Nuer of Sudan have an elaborate vocabulary to describe cattle. The Nuer have dozens of names for cattle because of the cattle's particular histories, economies, and environments [clarification needed]. This kind of comparison has elicited some linguistic controversy, as with the number of "Eskimo words for snow". English speakers with relevant specialised knowledge can also display elaborate and precise vocabularies for snow and cattle when the need arises.
f. Vocabulary growth
reliant on his/her ability to self-express without relying on gestures or babbling. Once the reading and writing vocabularies start to develop, through questions and education, the child starts to discover the anomalies and irregularities of language.
In first grade, a child who can read learns about twice as many words as one who cannot. Generally, this gap does not narrow later. This results in a wide range of vocabulary by age five or six, when an English-speaking child will have learned about 1500 words.
After leaving school, vocabulary growth reaches a plateau [clarification needed]. People usually then expand their vocabularies by e.g. reading, playing word games, and by participating in vocabulary-related programs. Exposure to traditional print media teaches correct spelling and vocabulary, while exposure to text messaging leads to more relaxed word acceptability constraints. 7. The importance of a vocabulary
a. An extensive vocabulary aids expression and communication. b. Vocabulary size has been directly linked to reading comprehension.
c. Linguistic vocabulary is synonymous with thinking vocabulary. d. A person may be judged by others based on his or her vocabulary.
D.Visual Aids
1. Definition of Visual Aids
Visual Aids are devices, sch as films, slides, models, and blackboard, that display in visual from material to be understood or remebered (Collins English Dictionary). The process of understanding speech in a first or second language. The Concept of Visual AidsThe media that used in teaching learning process isvisual. It includes chalkboard, marker board andpicture, other aids model that give the concrete thing.―Visual media present content in breadth and depth‖. Itaroused represent Heinrich R
(1982:63). Ellyawati(2005:11) ―stated that visual aids are the aids that couldbe seen only‖. It can help the teacher in delivering
themessage or the content of education theme to thelearners.
In the classroom situation, the teacher has to try andmake up the class as natural or concrete as possible sothe pupil are interested to study. As the KTSP(2006:36) ―states that one of the
characteristics of the Junior High School students in learning is conceptthing‖. It means that the learning process is startedfrom the
2. How the visual aids can help in teaching languages
The aids that help in teaching languages and that can be seen are called 'visual aids'. They provide practical solutions to the problems of a language teacher whose equipment, as a rule, consists of nothing more than books and classroom. They include black-board, chart maps, pictures, flannel-boards, film strips, slides, epidiascope and actual objects that facilitate the process of teaching. The function of each of these in helping the teaching process is discussed below.
a) BLACK-BOARD: A big strong piece of wood, called black-board is the oldest associate of the teacher but an essential teaching aid. It is used to reading and writing to the pupil. Anything, to which the teacher wants to draw the attention of the pupil, is written on it, e.g. difficult words, phrase patterns, structure patterns, grammar works, questions to test comprehension. In this way the teacher finds his lessons more interesting, lively and effective. It is an important means of picture composition.
accommodate the necessary materials with words written in bold letters. Charts are very useful for presenting and practicing structures, vocabulary items and compositions. Maps may be used for displaying the location of places, mountains, rivers, etc.
c) PICTURES: Pictures comprise text pictures and class pictures. Text pictures are to be found in the texts designed primarily for beginners. The meaning of a single word can be shown in different pictures. For example, the very first lesson of the beginner's text may have different patterns of heads of persons and animals to teach the word head.
Class pictures may be sub-divided into picture cards and wall pictures. Picture cards or post cards are extremely helpful in language teaching. They may be captioned or uncaptioned in front or on reverse side.
Wall pictures include maps, posters, photographs, etc. They may be used in place of things such as clouds, sea, mountain, sky, etc., which cannot be brought into the classroom. They are excellent in practice for oral composition and question and answer drill.
Pictures have great importance in the sense that what cannot be described by words, can be described through them.
where there is the need of presenting things in small pieces on very quick rearrangement of smaller units. The advantages of this aid are that items can be prepared beforehand, can be moved about on the flannel and preserved for use on further occasions.
e) FILMS: Film, which is yet another visual aid, may be supplied for language teaching in the form of fixed film strips or slides and motion picture films. The former can be used to convey meaning to teach reading on aids in oral and written composition. The advantages of slides and film strips are that they direct the attention of the whole class to the screen and to the pictures and words on it. Film strips and slides free the teacher room the reality of the situation, leaving the teacher free to control the class. Film strips can depict not only those situations which the teacher can present in the class but also many of these which he cannot. A situation of film strip can be shown over and over again.
film strips. They can show any situation which can and cannot be demonstrated in the classroom. However, it is to be noted that if language teaching by films are to be successful, visual aids have to be designed especially to teaching at a specific level for films, which merely present a teacher in action, are less effective than a good teacher.
Thus we have seen that visual aids play a very vital role in language teaching. The main function of visual teaching material is semantic. It permits the learner to understand what he hears, to learn the situation in which language forms are used and to associate his learning through repetition and limitation.
3. The Component of Visual Aids
Visual Aids consists of five components; class presentation, team, quiz, scoring and team recognition (Robert E. Slavin, 2005, 143). Here are the components:
a. Class presentation
b. Team
Teaming or grouping is a step to gather students in a team from different ethnic, achievement, and gender. Students work in a team that the teacher divides. Teacher prepares worksheet as a guide for the team, so that all members master and each member give contribution. When the team is working, teacher observes, give guidance, motivation and helps if the students need. The aim of team is to determine that all of members can study seriously and to prepare the members work the quiz well.
c. Quiz
Teacher evaluates the result of study with giving quiz about material that is learned and students evaluate other team presentations. In quiz, students are expected to work in a pair and they are allowed to help each other. So every student has to be responsible for understanding the material individually.
d. Score of Individual Development
4. Characteristic of Visual Aids
The Characteristics of Good Visual Aids are as follows:
a. It should be large enough to be clearly visible to the entire group. b. Avoid unnecessary decoration.
c. The important parts should be accentuated by use of effects such as bright color.
d. It should show good workmanship and careful development. e. It should explain ah abstract ideas, show a relationship or present a
sequence of procedure that cannot be clarified without it. f. Whether reduced or enlarged, keep the visual to a scale and
maintain proportionately. g. It should be displayed properly.
h. Avoid too much writing and the writing should be within the comprehension of the learners.
i. After use, it must be preserved using appropriate storage technique. j. It should be mounted in such a way as to make it portable.
5. Benefit of Visual Aids
From (http://members.shaw.ca/toasted/visual_aids.htm) Visual aids can be powerful tools for effective communication. You are encouraged to use them whenever they might enhance a speech. Why use visuals? They have five important benefits:
aids help to convey messages clearly. They save timeInformation that is presented visually is received and processes faster than a verbal message.
2. They enhance retention 3. They promote attentiveness
People think faster than you speak... visuals help keep them focused on your message.
4. They help control nervousness
Displaying visual aids gives you purposeful physical activity that lets your body process nervous energy without distracting the audience.
6. Types of Visual Aids
Visuals range from simple handheld objects to expensive multi-media extravaganzas. Your choice for a particular speech should depend on several factors including:
a) The information you want to convey, b) The size of the audience,
c) The physical environment of the room, d) The equipment available to you,
e) The time available to prepare visual aids, f) The amount of money you can afford. 7. The types of visual aids most commonly used include:
b) White boards, c) Charts and posters, d) Flip charts
e) Overhead transparencies
f) Computer presentations, e.g. Powerpoint.
There are pros and cons associated with using each of the above visual aids.
8. Tips for Using Visuals Effectively
a. Make sure they are visible to the entire audience
1) A good rule of thumb is one-half inch for each ten feet between the visual and the farthest audience member. 2) Print neatly
3) Display them high enough so that all can see 4) Avoid standing in front of them.
b. Keep them simple
1) Use a single visual to illustrate a point
2) Make diagrams and wording simple and accurate 3) With overheads, no more than seven lines and seven words/line.
9. The purpose of using visual aids a. Enliven a difficult/boring subject b. Make a presentation entertaining
E. Theoritical framework
Vocabulary is one language component which has to be mastered by students. But some students vocabulary ability of junior high school, especially in SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara are weak and English Speaking fears for them. Because of that situation, the writer does this research. Before the research, in teaching vocabulary,The English teacher of SMPN 1 Kedung just uses realiaty to teach her students and when doing research the writer uses at vocabulary game to teach students of SMPN 1 Kedung Jepara
The technique that teacher always uses in teaching vocabulary mastery is three phases technique. Although, in this research the writer uses the same technique in teaching vocabulary mastery but the writer assumes that students‘ vocabulary ability will be better than before. It is caused by using vocabulary game students will enjoy the teaching learning process. If the students enjoy the teaching learning process, they will input material easily without compulsively.
To implement Visua Aida is not easy. A teacher is demanded to prepare the instrument and technique well to apply this method in learning. Here are some procedures to apply visual aids in the class:
1. Make a task and summary that is given for students. 2. Arrange the students‘ achievement
5. Suggest students to fill the paper of team summary (Slavin,2008: 143).
a) Implementation Guide and Visual Aids Steps
Robert E. Slavin in his book Cooperative Learning: theory, research and practice 2005 stated Implementation Guide and Visual Aids Steps as follows:
1 . Implementation Guide
a) Make the students enthusiastic to do the question
b) Ask students randomly. It will make the students to prepare their answers every time.
c) Do not give the question that needs long time to do. They will be bored and not be interested in the learning.
2. Visual Aids Steps in cooperative learning. a) Teaching
This step is material delivery step (teaching) to transfer lesson to the student before they learn in their team. A teacher must set the goal includes what aspect will be achieved and state the general concept of the ongoing teaching and learning in the meeting.
b) Team study
Students work with the project paper of their team to master the material.