THE EFFECT OF TEACHING STRATEGIES
AND SELF EFF
ICACY ON STUDENTS’
ACHIEVEMENT IN READING
COMPREHENSION
Thesis
Submitted to the English Applied Linguistics Study Program in Partial Fullfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Magister
Humaniora
BY
ELFI KHAIRANI NASUTION
Register Number : 8106112031
ENGLISH APPLIED LINGUISTIC PROGRAM
STATE UNIVERSITY OF MEDAN
THE EFFECT OF TEACHING STRATEGIES
AND SELF EFF
ICACY ON STUDENTS’
ACHIEVEMENT IN READING
COMPREHENSION
Thesis
Submitted to the English Applied Linguistics Study Program in Partial Fullfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Magister
Humaniora
BY
ELFI KHAIRANI NASUTION
Register Number : 8106112031
ENGLISH APPLIED LINGUISTIC PROGRAM
STATE UNIVERSITY OF MEDAN
i
ABSTRACT
Elfi Khairani Nasution, The Effect of Teaching Strategy and Self Efficacy on Students´ Achievement in Reading Comprehension. Thesis : English Applied Linguistic Program State University of UNIMED
This research is aimed to find out : (1) The difference of students’ reading comprehension ability between PALS and QARs (2) The difference of students´ reading comprehension ability who have low self efficacy and high self efficacy (3) Interaction between teaching strategy with self efficacy on the students reading comprehension achievement.
The population of this research is all second classes of MTs Negeri Lubuk Pakam, Kabupaten Deli Serdang which have 180 students´ all together and consist of five classes. These samples are taken by using simple random sampling method. The sample of this research is 32 students taught by PALS and 32 students in QARs. The research instrument that used to measure the achievement is test multiple choice with 4 options with 40 questions. To get data of self efficacy used questionnaire Self Efficacy for Children that adapted from Bandura et al. with 30 questions. The research method uses experiment with factorial design 2 x 2. Technique of analyzing data uses ANOVA of two directions at significants α = 0.05.
The findings of the research indicate that : (1) The students´ reading comprehension achievement that taught by PALS (X = 31,31) is higher than the students´ achievement that taught by QARs (X = 30,63) with F observed = (4,34) > F table = (4,00), (2) The students´ reading comprehension achievement who have high self efficacy (X = 33,38) is higher than low self efficacy (X = 29,06) with F observed = (5,60) > F table = (4,00), (3) Be found interaction between teaching strategy and self efficacy on the students´ reading comprehension achievement with F observed = 5,48 > F table = 4,00.
The multiple comparation by Tukey test indicatess that (a) the students´ reading comprehension achievement that taught by PALS is higher than QARs, (b) the students´ reading comprehension achievement that have high self efficacy is higher than the students´reading comprehension achievement that have low self efficacy, (c) be found interaction between teaching strategy with self efficacy, that the students´ reading comprehension achievement that have high self efficacy is higher if use PALS, in the way arround the students´ reading comprehension achievement that have low self efficacy is higher if taught with QARs.
ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The writer’s endless gratitude is primarily expressed to Allah SWT for His forever
Blessing and Mercy that has enabled her to finish writing this piece of academic work.
In the process of writing this thesis, the writer has to confess that many people have
given her the care, attention, and bright ideas. In this connection, she would like to express
her very special appreciation to Prof. Dr. Berlin Sibarani, M.Pd. as her first advisor for his
strong support, comments, criticism, and bright ideas in shaping up this thesis and Dr. Didik
Santoso, M.Pd. her second adviser,for his understanding and the valuable suggestion and
correction.
She would like to thank her deepest gratitude to the reviewers and examiners: Prof.
Dr. Busmin Gurning,M.Pd., Dr. Anni Holila Pulungan, M.Hum., and Dr. Sri Minda Murni,
M.S. for the valuable inputs to be included in this thesis. She also wishes to express thanks to
all lectures who have given her the valuable knowledge during her study at the English
Applied Linguistics Study Program, Postgraduate School, State University of Medan.
Then, she would also like to express her sincere appreciation and love to her parents :
H.M.Yunan Nasutioan and Hj. Dahlia as her inspiration, her beloved husband : Drs Abdul
Malik,M.Pd, and her children : Nurfadhilah Amini, Rafika Hayati and Muhammad Alwi who
always show endless their full support, motivation and pray to finish the study.
He also thanks the Headmaster of MTsN Lubuk Pakam, Dra Mismah, M.Si., who
gave the permission to conduct the research at school and those teachers especially Mahya
Aini and Nurul Huda, students of MTsN Lubuk Pakam and the researcher’s friends who gave
full supports to this study, they should deserve her sincere gratitude for their cooperative
iii May Allah bless you !
Medan, April 2014
The writer,
iv
2.1 The Nature of Reading Comprehension ... 9
2.1.1 Purposes for Reading ... 12
2.1.2 Level of Comprehension ... 13
2.1.3 The Process of Reading Comprehension ... 15
2.1.4 The Assessment of Reading Comprehension ... 20
2.1.5 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension... 25
2.1.6 Genre ... 26
2.1.7 Narrative text ……… 28
2.2 Teaching Strategy ... 30
2.2.1 Peer Assissted Learning Strategy (PALS) ... 31
2.2.1.1 The Nature of PALS ... 32
3.3 Technique and Instrument of Data Collection ... 57
3.3.1 Technique of Data Collection... 57
3.3.2 Instrument of Data Collection. ... 58
v
3.3.6. Control of Internal and External Validity ... 65
3.3.6.1 Internal Validity ... 66
CHAPTER IV DATA ANALYSIS AND RESEARCH FINDINGS ……… 71
4.1 Data Description ……….. 71 4.1.1 The Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension taught by PALS ……… .. ………. 72
4.1.2 The Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension taught by QARs ………... ….. 73
4.1.3 High Self Efficacy Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension taught by PALS and QARs …… 75
4.1.4 The Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension with Low Self Efficacy taught by PALS and QARs……….. 76 5.1 The Differences on Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension between Students that Taught by PALS and QARs………. 92
5.2 The Difference of Students’ Achievement in Reading
Comprehension between High Self Efficacy and Low
Self Efficacy Student……….. 94 5.3 The Interaction between Teaching Strategies and
vi
Comprehension……… 95 6. The Limitation of the Research………. 97
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND SUGGESTIONS ……. … 99
5.1 Conclusion……… 99
5.2 Implications ………. 100
5.3 Suggestions ………. 101
REFERENCES ………. 102
vii
Table 4.2 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension Taught with PALS ... 71
Table 4.3 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension Taught Using QARs .. 73
Table 4.4 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension with High Self Efficacy Taught with PALS and QARs ... 74
Table 4.5 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension with Low Self Efficacy Taught with PALS and QARs ... 76
Table 4.6 Students’ Achievement with HighSelf Efficacy in Reading Comprehension Taught ... 77
Table 4.7 Students’ Achievement with Low Self Efficacy in Reading Comprehension Taught with PALS ... 78
Table 4.8 Students’ Achievement with High Self Efficacy in Reading Comprehension Taught with QARs ... 80
Table 4.9 Students’ Achievement with Low Self Efficacyin Reading Comprehension Taught with QARs ... 81
Table 4.10 The Summary of the Normality Testing of the Teaching Strategies Data.. 83
Table 4.11 The Summary of the Normality Testing of PALS and Self Efficacy ... 83
Table 4.12 The Summary of the Normality Testing of QARs and Self Efficacy ... 84
Table 4.13 The Summary Analysis of Variance (Anova) Homogeneity Testing between PALS and QARs Using F Test ... 85
Table 4.14 The Summary Analysis of Homogeneity Testing Students’ Self Efficacy Using F Test and Barlet’s Test ... 85
Table 4.15 The Summary Analysis of Homogeneity Testing between Teaching Strategies and Self Efficacy ... 86
Table 4.16 The Summary of Anova Factorial Design 2 x 2 ... 87
viii
LIST OF FIGURES
Pages
Figure
Figure 4.1 Students’ Reading Comprehension Taught with Using PALS ... 72 Figure 4.2 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension
Taught with Using QARs ... 73 Figure 4.3 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension with High
Self Efficacy taught with PALS and QARs ... 75 Figure 4.4 Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension with Low
Self Efficacy Taught by PALS and QARs ... 77 Figure 4.5 Students’ Achievement with High Self Efficacy in Reading
Comprehension Taught with PALS ... 78 Figure 4.6 Students’ Achievement with Low Self Efficacy Taught by PALS ... 79 Figure 4.7 Students’ Achievement with High Self Efficacy in Reading
Comprehension Taught with QARs ... 81 Figure 4.8 Students’ Achievement with Low Self Efficacy in Reading
Comprehension taught with QARs ... 82 Figure 4.9 The Interaction between Teaching Strategies and Self Efficacy ... 91
1
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 The Background of the Study
Developing the students’ competence to comprehend English textbooks in
achieving a certain functional literacy stage is one of the objectives of English teaching.
English teaching needs four language skill, namely listening, speaking, reading, and
writing. Reading is one of the four language skills,which should be applied in
comprehending the textbook. In comprehending the textbook involves multiple skills.
The multiple skills not only pronounce the sound of the letter but also all the higher
mental processes, such as memory, thought, imagination, organization, implementation,
and troubleshooting. They are gathered in comprehending text related one another. By
joining multiple skills are hoped to be able to comprehend text correctly.
Reading is an activity with purposes. A person may read in order to gain
information, for enjoyment, or to enhance knowledge of the language being read.
Reading also becomes more important in our lifes because in every aspect of life
reading activity is always envolved. Catering trader does not need going to the market
to know the price of the needed material because they can get information from the
newspaper.
In terms of reading comprehension, students are hoped to comprehend text
and to be interested to do task that teacher ask for them. It is not easy to make the
2
2
teachers just focus on teaching reading not understanding, as the consequence, the
students seem hard to comprehend the reading text.
The reality happened that many students failed in reading because they are not
taught reading well. More teachers focus on teaching “reading” not “understanding” As
the result, the students tend to have poor reading skill and habits. The matter arises
because of some factors: (1) Students do not have good motivation to read because the
text is not interesting, the teaching technique is boring or the text is too hard, (2) they
believe that when comprehending the text, they must comprehend every word in the
text, so they keep on looking up the words in a dictionary to find out the meaning of the
words, (3) they have very limited techniques and strategies in reading, (4) they read
aloud which slows them down and which may inhibit comprehension.
In addition reading comprehension test is one of the dominant test in English
national examination. Persentation reading comprehension test about 50 % of all the
test (Manurung, 2002). The other tests are short functional texts and writing
competence. Remembering students’ ability in vocabulary is less, it becomes a difficult
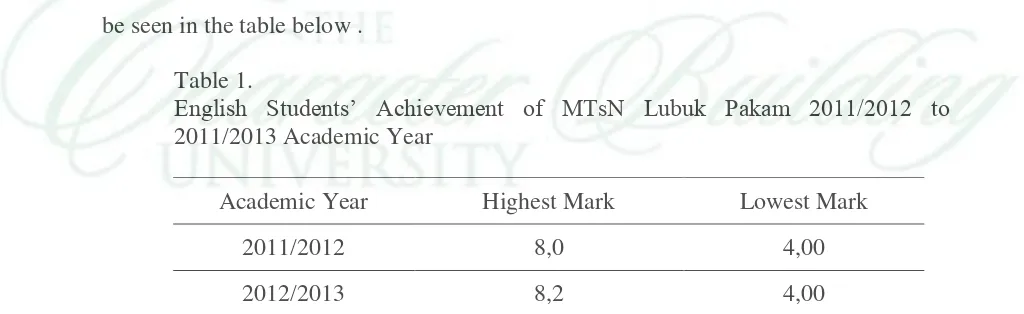
hard for students to answer the tests in the national examination. This case can be seen
English students’ achievement in national examination from 2011/2012 and 2012/2013
academic year in MTs Negeri Lubuk Pakam. Obtaining national examination mark can
be seen in the table below .
Table 1.
English Students’ Achievement of MTsN Lubuk Pakam 2011/2012 to 2011/2013 Academic Year
Academic Year Highest Mark Lowest Mark
2011/2012 8,0 4,00
3
3
Based on researcher’s observation as a teacher in MTsN Lubuk Pakam, reading
comprehension was less to get attention so the instruction was done teacher oriented,
not students oriented. The effort to obtain the comprehension toward the text, the
teachers should use certain strategy. The strategy is choosen by fitting to students, text
and context text. Particular strategy may be well suited for one student, it may not work
for another. Therefore, needing to assess the strengths of their students, fitted by the
text.
Adler (2004) stated that comprehension strategies are concious plans sets of
steps that good readers use to make sense of text. Comprehension strategy instruction
helps students to become purposeful, active readers who are in control of their own
reading comprehension. Accordingly, the students will be easier to comprehend the text
if the teacher helps them with strategy in learning.
In terms of this problems, there are desire to compare two kinds of reading
instructions namely Peer Assisted Learning Strategy (PALS) and Question Answer
Relationship strategy (QARs). The PALS are designed to also help children develop
word-level reading skills (Fuch and Fuch,2007: 175) . The students help each other to
read and comprehend the text. Furthermore the Question-Answer Relationship (QAR)
strategy presents a three-way relationship among questions, text content, and reader
knowledge. Simply put, the QAR strategy shows that students who understand how
questions are written are better prepared to answer questions. These activities help
students "demystify" the question-building process as a step toward better reading
4
4
The researcher is interested in these kinds of reading instructions under the
consideration that the PALS provides strategies in which the students comprehend the
text by doing their own activities. They help each other in reading, searching main idea,
and making summary but they do themselves in answering question provided in text. In
contrary, the QAR provides strategies in which the students must comprehend kinds of
question conveyed and then they make categories based on the questions. This strategy
invites the students to think more before answering the question.
Beside the instructions, the students’ ability in reading comprehension is
influenced by other factor that is motivation. “In psychology, motivation is an internal
state or condition (sometimes described as a need, desire, or want) that serves to
activate or energize behavior and give it direction”. Huitt (2011) Accordingly, the
motivation is a force that move person to behaviour toward a goal.
Motivation can be described in many types and the main broad categories are
intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation within an individual, e.g., self
efficacy while extrinsic motivation outside an individual, e.g., grades. Children who
are intrinsically motivated tend to show greater persistence and put more effort into task
through their own volition. On the other hand, students who are extrinsically motivated
may perform tasks with resentment and disinterest, through coercion of an external goal
or reward.
In this study the researcher will analyze one of reading motivation that is self
efficacy . According to Pajares (1996), self efficacy is a persons’ confidence to perform
a specific task successfully and is linked closely to initial task engagement, persistence,
and achievement. Bandura (1997) refers to self-efficacy as one’s convictions to
5
5
provided the foundation for human motivation, well-being and personal accomplishment.
This implies that unless people believe that their actions can produce the outcome they
desire, they have little incentive to act or to persevere in the face of difficulties.
Based on students’ capabilities are hoped they can do task teacher given eagerly,
so it is needed to know influence of self efficacy for the students in learning English.
Research shows that self-efficacy predicts students’ academic motivation and learning
(Pajares, 1996). Therefore a questionnaire based on these constructs measuring self
efficay was used in the current study. It also measures of academic behaviour, social
and emotional students were used so that the importance of self efficacy could be
examined when included with cognitive skills commonly associated with reading.
Therefore, in this study the resercher is interested to discovering the effect of
Peer Assisted Learning Strategy (PALS) and Question Answer Relationship (QAR)
strategy in improving the students’ reading comprehension for those who have high and
low self efficacy of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri (MTsN) Lubuk Pakam where the
researcher teaches English.
1.2 The Identification of the Study
Based on the background of the study, it can be identified, the research problem,
they are :
1. What factors that influence the students’ achievement in reading comprehension ?
2. Does Peer Assisted Learning Strategy (PALS) significantly affect on students’
6
6
3. Does Question Answer Relationship (QAR) significantly affect on the students’
achievement in reading comprehension ?
4. Does the self efficacy significantly affect the students’ achievement in reading
comprehension ?
5. How is the students’ achievement taught by using PALS ?
6. How is the students’ achievement taught by using QAR ?
7. Is the students’ achievement in reading taught by PALS is higher than the students
taught by using QAR ?
8. Is the students’ achievement in reading with high self efficacy higher than the
students with low self efficacy ?
9. How is the students’ achievement with high self efficacy taught by PALS ?
10. How is the students’ achievement with high self efficacy taught by QAR ?
11. Do the teaching strategy and self efficacy significantly affect on the students’
achieving in reading comprehension ?
1.3 The Problems of the Study
The research problems of this study are formulated as follows :
1. Is the students’ reading comprehension ahievement taught by using PAL strategy
significantly higher than taught by using QAR strategy ?
2. Is the students’ achievement in reading comprehension with high self efficacy
higher than low self efficacy ?
3. Is there any significant interaction between PALS and QAR strategies with self
7
7
1.4 The Scope of the Study
There are many strategies that are used in teaching reading, especially reading
comprehension. In this study focused only on the use of the two strategies, they are
PALS and QAR strategies.
Self efficacy influences reading comprehension in doing certain task such as
find main idea, detail information, inferences and paraphrasing. That’s why self
efficacy choosen as the moderator variable. The students in junior high school, where
the researcher teaches English have different self efficacy. They have high and low self
efficacy because they have different background. The different background such as in
their basic education in elementary school, interest, economy, family, environment, ect
may affect the students’ reading comprehension.
1.5 The Objectives of the Study
It is necessary to state clearly what the objectives of the study in relation to the
problems posed. The objectives of the study are :
1) to find out if the students’ achievement in reading comprehension taught by using
PAL strategy is higher than that taught by using QAR strategy.
2) to find out if the reading comprehension achievement of high self efficacy students
is higher than reading comprehension achievement of low self efficacy students.
3) to find out if there is interaction between teaching strategies and self efficacy on
students’ achievement in reading comprehension
1.6 The Significance of the Study
8
8
Theoretically :
1) for the English teachers as the input to improve their students’ ability in reading
comprehension,
2) for students or readers to improve their ability in reading comprehension,
3) can be used as the references for those who want to conduct a research who want to
apply teaching strategies.
Practically :
1) for the English teacher as one of strategies when teaching reading,
2) it can help students who have problem in reading and more enjoyable in learning
English,
3) As comparing for those who want to conduct further in depth research in reading
102
102
CHAPTER
V
CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
Based on the result of the research and discussion that have stated, it is
concluded that :
1. Teaching reading comprehension with PALS and QAR strategy
significantly affect the students’ achievement in reading comprehension.
PALS influences higher to students’ achievement in reading
comprehension than QAR strategy. Hence the PALS is more effective to
be used in teaching reading than QAR strategy in improving students’
achievement.
2. High and low self efficacy give different influence to the students’
achievement in reading comprehension. The students’ achievement in
reading comprehension with high self efficacy is higher than that with low
self efficacy.
3. There is significant interaction between teaching reading strategies and
self efficacy on students’ achievement in reading .comprehension.
Students’ achievement in reading comprehension is influenced by teaching
strategies and self efficacay High self efficacy students showed significant
effect on their reading comprehension achievement if they were taught by
103
103
their reading comprehension achievement if they were taught by using
QAR strategy.
5.2Implications
Based on findings, it can be known that PALS is more effective to be used
in teaching reading comprehension than QAR strategy. The findings give
implication to English teacher and students who wants to improve their
achievement in reading comprehension. In this research the researcher has tested
teaching strategies in reading comprehension, they are Peer Assisted Learning
Stategy (PALS) and Question Answer Relationship (QAR). They are applied on
high self efficacy students and low self efficacy students in order to know which
teaching strategies are appropriate for them in improving their achievement in
reading comprehension.
Based on this research that students’ achievement in reading
comprehension taught by PALS, it is higher than students taught by QAR
strategy. Thus, it implies English teachers should apply PALS.
Furthermore, in this research states that reading comprehension
achievement of high self efficacy students is higher than reading comprehension
of low self efficacy students. Therefore, the teachers should pay attention to the
students’ self efficacy so that the students can obtain better learning achievement,
especially in reading comprehension. Implication of students’ characteristic
difference give sign teachers in selecting strategies have to consider students’ self
104
104
Finally, there is significant interaction between teaching strategies and
students’ self efficacy on students’ achievement in reading comprehension. It
implies that teachers should apply the strategies that are appropriate with students’
self efficacy so that the students can improve students’ achievement in reading
comprehension.
5.3 Suggesstions
Based on the conclusions and implications above, some suggestions can be
recommended as follow :
1. Teaching strategy with PALS significantly affect the students’
achievement in reading comprehension higher than QAR strategy. It is
suggested to the lecturer or teacher to use PALS in teaching reading
comprehension in improving students’ achievement.
2. The students with higher self efficacy comprehend texts better than those
with lower self efficacy. It is suggested that the lecturer or teacher should
identify their students self efficacy level before doing the teaching and
match his/her teaching technique with the identified levels.
3. There is significant interaction between teaching reading strategies and
self efficacy on students’ achievement in reading comprehension. It is
suggested to the lecturer or teacher should choose appropriate teaching
strategy before doing the teaching and fit it with his students self efficacy
105
105
REFERENCES
Adler.C.R. (2004). Seven Strategies to Teach Students Text Comprehension
Alderson, J.C.(2000). Assessing Reading. London : Cambridge University Press.
Anderson Mark & Kathy Anderson. (2003). Text Types in English 2. South Yarra: MacMillan Education
Ary,D., et al. (2010). Introduction to Research in Education. Wadsworth, Cengange Learning.
Askar, Petek and Davenpot,David. (2009). An Investigation of Factors Related to Self Efficacy for Java Programming Among Engineering Students. Hacettepe University, Beytepe, 06530,Ankara, Turkey. volume 8 Issue 1 Article 3
Baker, L. (2002). Metacognition in Comprehension Instruction. In C. C. Block & M. Pressly (Eds), Comprehension Instruction. Research-based best practices (pp. 77-95). New York : Guilford.
Baker, Linda, and Brown, L. Ann.( 2002). Metacognitive Skills and Reading. In P. David Pearson,ed., Handbook of Reading Research, pp. 353–394. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum
Bandura, A. (1986), Social Foundations of Thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Bandura, A. (1994). Self-efficacy. In V. S. Ramachaudran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Human Behavior,4. New York: Academic Press, pp. 71-81.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The Exercise of Control. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Bandura et al. (1999). See: Bandura, A., Pastorelli, C.,Barbaranelli, C., & Caprara, G.V. (1999). Self- Efficacy Pathways to Childhood Depression. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76, 258-269.
Barrett, T. C. (1994). Taxonomy of Reading Comprehension. In Reading 360 Monograph. Lexington, Mass: Ginn.
106
106
Blackhowicz. C & Ogle (2008). Reading Comprehension. The Guilford Press : New York, Second Edition
Black, P. and Wiliam, D. (1998b). Inside the Black Box: Raising Standards through Classroom Assessment. Phi Delta Kappan, 80 (2): 139-148.
Brassel,Danny, and Rasinski, Timoty. (2008). Comprehension that Works : Taking Students Beyond Ordinary Understanding to Deep Comprehension. Shell education 5301 oceanus Drive Huntington Beach, CA 92649.
Corkett Julie, Hatt Blaine, Benevides Tina. Student and Teacher Self-Efficacy and The Connection to Reading and Writing. (2011) . Canadian Journal of Education 34, 1 (2011).
Coiro, J., Knobel, M., Lankshear, C., & Leu, D. J. (Editors). (2008). Handbook of Research in New Literacies. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Dorn J.Linda and Soffos Carla. (2005) Teaching for Deep Comprehension : A Reading Workshop Approach. Stenhouse Publisher.
Ekwensi, F., Moranski, J., & Townsend-Sweet, M., (2006). E-Learning Concepts and Techniques. Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania's Department of Instructional Technology.
Fletcher J.M., et.al. (1994). Cognitive Profiles of Reading Disability: Comparisons of Discrepancy and Low Achievement Definitions. Journal of Educational Psychology, 86, 6–23.
Fantuzzo, J., and M. Ginsburg-Block. 1998. Reciprocal Peer Tutoring: Developing and Testing Effective Peer Collaborations for Elementary School Students. In Peer-assisted learning, ed. K. Topping and S. Ehly, 121-145. Mahwah, NJ, & London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (1994). Inclusive Schools Movement and the Radicalization of Special Education Reform. Exceptional Children, 60, 294–309.
Fuchs,D., Fuchs, L. S., Mathes, Patricia G. and Simmons, Deborah C.(1997). Responsive to Diversity Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies: Making
107
107
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (2005). Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies: Promoting Word Recognition, Fluency, and Reading Comprehension in Young Children. Journal of Special Education, 39, 34–44.
Fuchs, D., & Fuchs, L. S. (2007). Intervention :Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies (PALS). Practice Guide.
Fuchs, L., Fuchs, D., & Kazdan, S. (1999). Effects of Peer-Assisted Learning Strategies on High School Students with Serious Reading Problems. Remedial and Special Education, 20(5), 309-318.
Gorin, J. S. (2005). Manipulating Processing Difficulty of Reading
Comprehension Questions: The Feasibility of Verbal Item Generations. Journal of Educational Measurement, 4, 351–373.
Grabe, W., and Stoller, F. L. (2002). Teaching and Researching Reading : Health Sciences and Technology contributed to this work.
Grigg, N. & Mann, R. (2008).”Promoting Excellence: An International Study into
Creating Awareness of Business Excellency Models”. The TQM Journal,
20, Iss: 3, pp233-248.
Halliday, M.A.K. (1979). Language as Social Semiotic. London : Edward Arnold.
Hammond, Jenny et.al. 1992. English for Social Purposes. Sydney: National Centre for English Language Teaching and Research Macquarie University
Hardy, Judy & Klarwein, Damien. (1990). Written Genres in the secondary School. Department of Education Queensland
Heilman, W, Arthur. (1981). Discovering Phonics We Use-Book 3.Riverside Publishing Company.
Huitt, W. (2011). Motivation to Learn: An overview. Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University.
108
108
Leo,Jack. (....) Teachers' Assessment Tools eHow Contributor
Macken, Mary. 1991. A Genre-Based Approach to teaching Writing Years 3-6. New south Whales: Common Ground
Manurung,Altur. (2002). Fokus Bahasa Inggris untuk SMP dan MTS. Erlangga : Jakarta
Mathes, P. G., Fuchs, D., Fuchs, L. S., Henley, A. M., & Sanders, A. (1994). Increasing Strategic Reading Practice with Peabody Classwide Peer Tutoring. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 9, 44-48.
McNeil , John D. (1992). Reading Comprehension : New Directions for Classroom Practice, Third edition. HarperCollins Publishers.
Pajares, F. (1996). Self-Efficacy Beliefs in Achievement Settings. Review of Educational Research, 66, 543-578.
Pearson, D. P., ed. (2002). Handbook of Reading Research. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Pearson, P. D., & Hamm, D. N. (2005). The Assessment of Reading Comprehension: A Review of Practices- Past, Present, and Future. In S. G. Paris & S. A. Stahl (Eds.), Children’s Reading Comprehension and Assessment (pp. 17-30). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum.
Raphael, T. (1982). Question-Answering Strategies for Children. The Reading Teacher, 36(2), 186-191.
Raphael, T.E. (1984). Teaching Learners about Sources of Information for Answering Comprehension Questions. Journal of Reading, 27, 303-311.
Raphael, T.E. (1986). Teaching Question-Answer Relationships. The Reading Teacher, 39, 516-520.
Reid,Robert and Lienemann, Ortiz, Torri. (2006). Strategy Instruction for Students with Learning Disabilities. The Guilford Press, New York, London.
S. Arikunto.(2008) Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
109
109
Sari,Indah. (2011). The Effect of Reading Instructions and Students’ Self Efficacy on Reading Comprehension Achievement. Unimed
Schunk, D. H. (2003). "Self-efficacy for Reading and Writing: Influence of Modeling, Goal Setting, and Self-Evaluation". Reading and Writing Quarterly, 19, 159-172.
Snow, C. (2002). Reading for Understanding : Toward an R & D Program in Reading Comprehension. Santa Monica, CA : RAND Education.
Spear-Swerling, L. (2006). Children’s Reading Comprehension and Oral Reading Fluency in Easy Text. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 19, 199-220.
Sudarwati,M.Th. and Grace. (2007). Look A Head 1 an English Courses for Senior High School Students Year X, Jakarta : Erlangga.
Suhermansyah. (2012). The Effect of Teaching Strategies and Instrinsic
Motivation on Students’ Achievement in Reading Comprehension. Unimed
Topping, K., and S. Ehly. (1998). Peer-assisted learning. Mahwah, NJ, & London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.