DESIGNING SIX SETS OF MONOPOLY GAMES TO DEVELOP MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES AS SEMESTER REVIEW FOR GRADE IV, V, AND VI
OF SD N PURWOBINANGUN YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Wening Tri Widati Student Number: 071214100
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
DESIGNING SIX SETS OF MONOPOLY GAMES TO DEVELOP MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES AS SEMESTER REVIEW FOR GRADE IV, V, AND VI
OF SD N PURWOBINANGUN YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Wening Tri Widati Student Number: 071214100
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
,ddvisor A
$,@ry-Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum.
A Sarjana
Pendidikan Thesis onDESIGNING SIX SETS OF MONOPOLY GAMES TO DEVELOP
MUITIPLE
INTII,I,T6SNCES AS SEIIGSTER REWEW I.ORGRADE rV,v, A,F[D
W
OF SD N PTTRWOBINANGUNTYOGYAKARTA
Approved by
u
Chairperson
Secretary Member Member Member
DESIGhIING STX SETS OF MONOPOLY GAMES TO DEVELOP MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES AS SEMESTER REYIEW FOR GRADE IV, V, AftD VI
OF ^g' IT PUX VOE INANG,T/}r YOGYAKARTA
By
WENING TRI WIDATI Student Number: 07 I 2 14100
Defended before the Board of Examiners on 2 December 201tr
aod Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd.
Made Frida Yulia S.Pd., M.Pd. Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum. Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd.,l\{.Pd. C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd.
Yogyakart4 2 December 2011
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
iv
Finish What I Have Started
Reach What I Have Dreamed
Undergo What I Have Enjoyed
Forget What I Have Left
I dedicate my thesis to:
t#r
relu^\ et[LI I0Z raque oN IZ
"yapd8ol
'p1norls raded cg4uelcs e sa'secuerege.r eql prrB suolplonb eql q peilc esorB ldecxe 'eldoed reqloJo
{roa
eqtJo slred ro {Joa erll we}uoc lou seop 'ue11urtr e^"q I qcr-ry$ 'srseql srqr l3rll erelcep dpseuoq 1AJITVIUSIUO S.XUOIil
fO
INf,rutrIYIS
LEMBAR PERNYATAAI\ PERSETUJUAII
PIJBLIKASI KARYA
ILMIAH T]NTUK
KEPENTINGAN AKADEMISYang bertandatangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama
: Wening Tri WidatiNomorMahasiswa :071214100
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perspustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
DESIGNING SIX SETS OF MONOPOLY GAMES TO DEVELOP MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES AS SEMESTER REVIEW FOR GRADE IV, V, AND VI
OF,SD N PURWOBINANGUII YOGYAKARTA
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta
ijin dari saya atau
memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.Demikian pemyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 21 November 2011
Yatrg menyatakan
AW
vii
ABSTRACT
Widati, Wening Tri. (2011). Designing Six Sets of Monopoly Games to Develop Multiple Intelligences as Semester Review for Grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
SD N Purwobinangun has applied the Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) 2006 in the English teaching and learning process. The result of teaching and learning process will be more satisfactory if there is an existence of innovative media for the students. That is why this research was conducted in order to design Monopoly Games as English material review for each semester of grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun. This research adopted the KTSP
2006 to be integrated with Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligences. There are two questions formulated in this research. First, it is intended to describe how to design six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple Intelligences as semester review. Second, it aims to present six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple Intelligences as material review.
In order to answer the questions, the researcher applied the Research and Development (R&D) method, which was first introduced by Borg and Gall (1983). Since the research was conducted until the product revision, five steps of the R&D method were elaborated with Bell and Wieckert’s guideline (1985) covering eleven steps in the stages of developing and validating the games. Furthermore, two types of instrument were employed to gather the data in the need analysis and validation i.e. the interview and questionnaire.
In designing Monopoly Games, the researcher started with collecting the research and information, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, and main product revision. Library study and need survey were carried out in collecting the research information. In the stage of planning, the research was begun by determining the theme, purpose, grade level, and a number of players. The format, method of checking, materials, players’ roles, procedure and time were determined in the stage of developing preliminary form of product. In preliminary field testing, the researcher conducted the validation of the whole designed games and the trial of the games to grade IV of
SD N Purwobinangun. In addition, the suggestions and evaluations derived from the validation were considered and elaborated in the main product revision.
viii ABSTRAK
Widati, Wening Tri. 2011. Designing Six Sets of Monopoly Games to Develop Multiple Intelligences as Semester Review for Grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
SD N Purwobinangun telah mengaplikasikan Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) 2006 dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris. Hasil dari proses pembelajaran akan lebih memuas apabila media yg inovatif tersedia bagi para siswa. Oleh karena itu penelitian ini dilaksanakan guna merancang permainan monopoli agar dapat membantu para siswa kelas IV, V, and VI di SD N Purwobinangun mengulang materi pelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk setiap semester. Penelitian ini mengadaptasi KTSP 2006 yang diintegrasikan dengan teori dari Gardner mengenai Multiple Intelligences sebagai landasan dalam merancang permainan. Terdapat dua pertanyaan yang dirumuskan dalam penelitian ini. Pertanyaan pertama dimaksudkan untuk menjelaskan bagaimana merancang enam set permainan monopoli untuk mengembangkan Multiple Intelligences sebagai review semester materi. Pertanyaan kedua bertujuan untuk menyajikan tampilan enam set permainan monopoli untuk mengembangkan Multiple Intelligences.
Guna menjawab pertanyaan, peneliti menerapkan metode Penelitian dan Pengembangan (R&D) yang pertama kali diperkenalkan oleh Borg dan Gall (1983). Karena penelitian dilakukan sampai tahap revisi produk, kelima langkah dalam Metode R&D selanjutnya diintegrasikan dengan petunjuk perancangan permainan dari Bell dan Wieckert (1985) yang mencakup sebelas langkah untuk diterapkan pada tahap pengembangan dan validasi. Terdapat dua jenis instrumen yang digunakan dalam pengumpulan data di survey kebutuhan dan tahap validasi, yaitu interview dan kuesioner.
Kelima langkah yang terangkum dalam metode R&D diaplikasikan dalam tahap perancangan permainan, yaitu pengumpulan informasi penelitian, perencanaan, pengembangan bentuk awal dari produk, pengujian tahap awal, and revisi utama produk. Studi perpustakaan dan survei kebutuhan dilaksanakan guna mengumpulkan informasi penelitian. Dalam tahap perencanaan, penelitian diawali dengan menentukan tema, tujuan, tingkat kesulitan, dan jumlah pemain dalam permainan. Format, metode pengecekan, materi, peran pemain, prosedure and waktu permainan ditentukan dalam tahap pengembahan awal produk. Dalam pengujian tahap awal permainan, peneliti melaksanakan dan validasi tehadap keseluruhan desain permainan dan percobaan permainan. Selanjutnya, saran dan evaluasi yang terdapat pada tahap validasi dipertimbangkan dan dijabarkan dalam tahap revisi utama produk.
ix
x
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my greatest gratitude to God Almighty
for the guidance to lead me walk on the way of bless. I also would like to extend
my deepest gratitude to all prophets for always being my paragons in undergoing
my life.
My sincere gratitude goes to Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum., for her guidance, kindness, patience, and attention to be my advisor in assisting me
during the research completion. What she has given to me is really beneficial for
improving my ability and competence throughout my study.
I would like to present my deepest gratitude to my parents, Bapak Landjijono and Ibu Siti Widayati, for every single support they have always conferred to me. They are my greatest encouragement for finishing my study
immediately. My sincere gratitude is also addressed to my brothers, Mas Nuri and
Mas Wiwit, and my sister in law, Mbak Kiki, for very often motivating me to always do the best for the sake of my future. In addition, I am also grateful to my
aunt, Endang, for suggesting me conducting the research in the elementary school where she teaches, SD N Purwobinangun.
I am deeply grateful to the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun,
Hartini, S.Pd., for being involved patiently and sincerely in every phase of designing the games. Furthermore, my sincere thanks also go to the students of
xi
the phases of designing the game including in the need survey, trial game, and
game validation.
I also extend my sincere thank to my beloved friend, Wendy Rahmad Biyandi, for always helping and accompanying me in either pleasing or sad moments. I am really grateful to my best friends, Ndud, Trek, Fendi, and Mita, and other friends for their loves, attentions and helps while I am studying at PBI.
My gratitude also goes to my lecturers, Yuseva Iswandari, S.Pd., M.Ed., for being the evaluator of my designed games and Adesti Komalasari, S.Pd., M.A., for being the reader of my research. Last but not least, I would like to express my
sincere thanks to those who have ever encouraged me to always appreciate how
xii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ABSTRACT ... ... vii
ABSTRAK ... ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS . ... x
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ... xii
LIST OF FIGURES ... ... xiv
LIST OF TABLES ... ... xv
LIST APPENDICES ... ... xvi
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Problems ... ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... ... 5
D. Research Objectives .. ... 5
E. Research Benefits ... ... 6
F. Definition of Terms .. ... 7
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 9
A. Theoretical Description ... 9
1. The Ways of the Children Learn English as a Foreign Language .... 9
2. English as a Foreign Language in Elementary Schools... 12
3. The Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) 2006 ... 13
4. Language Game ... ... 14
5. Gardner’s Theory on Multiple Intelligences ... 20
B. Theoretical Framework ... 23
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY ... 28
xiii
B. Research Participants ... 30
C. Research Instruments ... 32
D. Data Gathering Technique ... 34
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 34
F. Research Procedure ... 37
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 38
A. Designing Six Sets of Monopoly Games to Develop Multiple Intelligences as Semester Review ... 38
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 38
2. Planning ... ... 43
3. Develop Preliminary Form of Product ... 46
4. Preliminary Field Testing ... 49
5. Main Product Revision ... 59
B. Presenting Six Sets of Monopoly Game to Develop Multiple Intelligences as Semester Review ... 62
1. The Layout of Monopoly Games ... 63
2. The Procedure of Monopoly Games ... 73
3. The Content of Monopoly Games ... 76
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 82
A. Conclusions ... ... 82
B. Suggestions ... ... 83
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
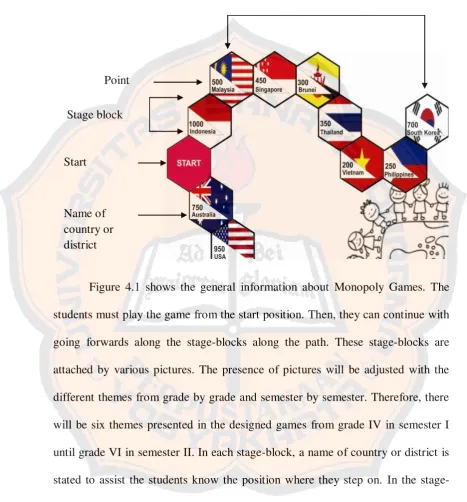
Figure 4.1 The Illustration of General Information
in Monopoly Game ... 64
Figure 4.2 The Illustration of Blank Colorful Blocks ... 65
Figure 4.3 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
of Grade IV for Semester I ... 67
Figure 4.4 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
of Grade IV for Semester II ... 68
Figure 4.5 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
of Grade V for Semester I ... 69
Figure 4.6 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
of Grade V for Semester II ... 71
Figure 4.7 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
of Grade VI for Semester I ... 72
Figure 4.8 The Illustration of Monopoly Game
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1The Draft of Description of Participants ... 31
Table 3.2 Points of Agreement ... 35
Table 3.3 The Draft of Questionnaire Data of Selected Items ... 36
Table 4.1 The Percentage Data of
Students’ Perceptions in the Need Survey ... 41 Table 4.2 The Description of Participants ... 50
Table 4.3 The Questionnaire Data on the Expert Validation ... 51
Table 4.4 The Percentage Data of Students’ Perceptions
in the Material Validation ... 57
xvi
APPENDICES
Appendix A. Permission Letter ... 89
Appendix B. The Blueprint and Raw Data of the Interview in the Need Survey ... 90
Appendix C. The Blueprint of Questionnaire for the Students in the Need Survey ... 92
Appendix D. A List of Multiple Intelligences in the Card Questions ... ... 94
Appendix E. A Sample of One Package of Monopoly Game for Grade IV Semester I ... 103
Appendix F. Questions Based on Notes ... 112
Appendix G. The Monopoly Board of Grade IV Semester II ... 128
Appendix H. The Monopoly Board of Grade V Semester I... 129
Appendix I. The Monopoly Board of Grade V Semester II ... 130
Appendix J. The Monopoly Board of Grade VI Semester I... 131
Appendix K. The Monopoly Board of Grade VI Semester II ... 132
Appendix L. The Blueprint and Raw Data of the Questionnaire in the Expert Validation ... 133
Appendix M. Lesson Plan of Trial ... 138
Appendix N. The Photographs of Trial Run ... 142
Appendix O. The Blueprint of Questionnaire for the Students in the Trial Run ... 143
1
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Research Background
In Indonesia, English has become one of foreign languages to be taught
starting from elementary schools. According to PERMENDIKNAS (The Regulation of National Education Ministry) No. 22, 2006, English as a local
curricular content for grade IV, V and VI is learned at elementary schools for two
teaching hours in a week. Although English is only an elective subject in most of
elementary schools, it is sometimes taught earlier starting from the first grade. By
implementing English starting from elementary schools, the government has been
aware of the importance of English as a global language. In fact, English has been
admitted as the first foreign language to be taught formally starting from the first
or fourth grade of elementary schools.
According to Huda (1999) as cited by Lestari (2003: 197), there are four
influential arguments to the roles of English as an important subject in elementary
schools. First, it is related to the demands of tourism industry. In some regions
which have great tourism objects, children need to communicate using English in
order to response and deliver the information to the foreigners. Second, according
to Huda (1999) as cited by Lestari (2003: 197), the quality of English proficiency
can be determined on which the children begin to learn. Third, it is correlated to
how long the individual learner learns English influences the achievement towards
higher if they begin to be familiar with English from elementary schools. Fourth,
the result of English teaching and learning process in the secondary level is
unsatisfactory. Therefore, by teaching English starting from elementary schools,
Huda (1999) believed that the quality of English proficiency among Indonesian
students would be improved significantly.
Since English is considered as a Foreign Language (EFL) in Indonesia, the
researcher believes that learning English is not as easy as learning Indonesian
language. Similar to what happens in SD N Purwobinangun, there are still some problems of teaching English. The first case is related to the lack of supporting
media to teach the students. The English teacher in this school admitted that there
was a limited number of supporting media in accordance with the latest
Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) 2006. In addition, the limited time of teaching English which just covers once in week for each grade also makes the
result of teaching and learning process not too satisfactory. The teacher also added
that it was sometimes difficult to manage the class and to attract the students’
attentions towards the topic discussion.
Dealing with the common and serious problems that the English teacher of
SD N Purwobinangun often faces in teaching English, the researcher believes that an innovative solution is needed to overcome these problems. There are a lot of
effective teaching methods which have been introduced by many educational
experts. One of them is by implementing the interesting classroom activity, for
example game. The nature of game is fun, interesting, challenging and closely
VI in SD N Purwobinangun also acknowledged that they often play the traditional or even electronic games at home.
There are a lot of advantages by implementing games for teaching a
language. Through games, the students will have opportunities for creative
explorations of their individual interests and talents while also learning valued
skills and concepts (Campbell L, Campbell B, and Dickinson, 2004:115). As a
result, the students will be encouraged to learn English and to comprehend the
materials easily. Besides, games also can involve all the basic language skills, i.e.,
listening, speaking, reading, and writing, and a number of skills are often involved
in the same game (Lee, 1979:3). Therefore, games can be used to teach four major
skills covered in learning English in the same time during the game
implementation.
Dealing with the fact that games can be employed for teaching four
language skills, the researcher believes that games will be also effective to review
the semester materials. That is why in this research, the researcher would like to
apply the game as an aid in reviewing the English materials for semester by
semester. Reviewing materials which is sometimes boring can be obviously turned
aside into an interesting activity through a game. By implementing games in
solving the problems happened in SD N Purwobinangun, the researcher expects that games will be effective to assist the students reach a satisfactory result in
mastering the standard competences derived from the KTSP 2006 syllabus.
The designed games will be much beneficial if they can accommodate
intelligences (Gardner, 1999:8). For example, by involving interpersonal
intelligence, visual/spatial intelligence or connected with bodily/kinesthetic
intelligence as well as other intelligences. Therefore, the researcher also employed
Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligences to be elaborated in this researcher. It
aims to present innovative games involving any types of intelligence in reviewing
the materials for semester by semester.
In this research, the researcher would like to design the different type of
games which adapted the commercial games. These designed games enable the
students to go around the world by pretending to have a vacation to some
interesting places. By giving a great image of Indonesia and the world through
some interesting places in these games, the researcher intended to adapt the fun
side of playing Monopoly Games. Furthermore, these games are integrated with
the theory of Multiple Intelligences and the materials covered in the KTSP 2006 syllabus.
B. Research Problems
The researcher formulated two questions in this research covering the
process of designing the games and the presentation of the designed games.
1. How are six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple Intelligences for
2. What do six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple Intelligences for
grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun Yogyakarta as semester review look like?
C. Problem Limitation
Six sets of Monopoly Games based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences
are models of material review for semester by semester based on the KTSP 2006. In Monopoly Games, there will be a lot of questions which are taken from the
indicators have to be achieved by the students in the syllabus. These questions
will be used to know how far the students understand the English materials and
help them to master each indicator for semester by semester. These questions also
cover Gardner’s theory on eight intelligences including linguistic,
logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal and
natural intelligence. In this research, the researcher decided to design Monopoly
Games for the students of grade VI, V and VI of SD N Purwobinangun. The researcher still adapted some basic ways of playing Monopoly Games such as the
existence of dice, tokens, cards and pictures of interesting pictures about
Indonesia and the world.
D. Research Objectives
There are two research objectives presented in this research in accordance
1. To observe how to design six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple
Intelligences for grade IV, V and VI of SD N Purwobinangun Yogyakarta as semester review.
2. To present six sets of Monopoly Games to develop Multiple Intelligences for
grade IV, V and VI of SD N Purwobinangun Yogyakarta as semester review look like.
E. Research Benefits
This research provides some benefits related to the English teaching and
learning process addressed to the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun, the students of SD N Purwobinangun, and future researchers.
1. The English Teacher of SD N Purwobinangun
This research provides the English teacher Monopoly Games as innovative
teaching aids which are different from the commercial and common games. These
games bring a lot of benefits for the teacher. First, the designed games can help
the teacher to review the materials in each semester based on the integration of the
KTSP 2006 and Multiple Intelligences. Second, Monopoly Games can help the teachers to manage the large class. Third, by applying Monopoly Games for
learning English, the teachers are able to know how far the students understand
the materials in semester by semester.
2. The Students of SD N Purwobinangun
This research was conducted to provide Monopoly Games as effective aids
English. The students can review the materials they have learned in each semester
effectively in a group. These games also can assist the students to master English
well in order to be able to communicate with other people in the real context of
communication. In addition, the students are given a great image of Indonesia and
the world as seen through some interesting pictures as presented in the board
games.
3. Future Researchers
This research provides some beneficial information to help future researchers
in completing their research. It can be an inspiration for future researchers in
designing the other innovative games.
F. Definition of Terms
This section presents the definitions of related term in order to help the
readers understand the contents of the research.
1. Monopoly Games
Orbanes (1988:22) defined Monopoly Game as one of board games in
which the players tried to enrich themselves by developing the real estate in
around the world. In this research, the designed games are presented in a form of
Monopoly Games. However, the designed games will be varied from the
commercial and common monopoly games since they are integrated with the
2. Multiple Intelligences Theory
The theory of Multiple Intelligences was first introduced by
Gardner in 1983. Gardner employed eight different criteria to judge whether the
candidate of ability could be counted as intelligence (Gardner (1983) as cited by
Veenema, Shirley, and Hetland, 1997: 1). This theory was applied in the question
card of the games which also accommodated the materials from KTSP 2006 syllabus.
3. Review
The purpose of review as an evaluation function is to provide the
information to guide decisions and considerations whether the result of learning
system has been satisfactory or not (Hedberg and Reeves, 2003: 97). In this
research, the use of Monopoly Games as material review is to observe whether the
students of grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun have already mastered the materials and to guide them to reach a satisfactory result in the evaluation.
4. SD N Purwobinagun
It is a public elementary school located in Purwobinangun, Kalasan,
Sleman, Yogyakarta where the researcher held the research. In this school, there is
still a lack of innovative teaching media for to assist the students learn English.
During the phase of constructing games, the students of grade IV, V, and VI and
9
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This section presents the theoretical description and theoretical framework
towards the research. It provides the information related to the relevant theories to
be elaborated as the framework of designing the games.
A. Theoretical Description
In this section, the researcher would like to discuss further the theoretical
background of the research in designing Monopoly Games. There will be some
theories and principles directly relevant to the theory of Monopoly Games,
Multiple Intelligences, the latest School Based Curriculum (KTSP) 2006, the characteristics of children as language learners, and the language games
1. The Ways of the Children Learn English as a Foreign Language
In this section, there will be some important aspects towards the ways on
how the children learn English as a first Foreign Language (EFL) to be taught
formally starting from elementary schools. Two major aspects are presented in
this section including the characteristics of children as language learners and how
children learn languages with its teaching implications.
a. The Characteristics of Children as Language Learners
In Indonesia, both adult and young learners have different goals of why
they should learn English. Adult learners are greatly motivated to learn English in
a study abroad. On the other hand, children still undergo to learn their First
Language (L1) as well as other languages instead of having the exact goals in
learning English (Brewster, Ellis, and Gerard, 2004:p. 27). Children do not have
the specific needs towards foreign languages. Therefore, teachers and parents as
children facilitators should work hard and pay more attention to help the children
learn English. In a relation to this case, what teachers and parents have to do first
is identifying the characteristics of children as language learners which make them
different from the adult learners. Moon (1999) as cited by Lestari (2003) divides
the children’ characteristics into seven important points as describe further:
1. Children use language creatively
Children actively try to experiment and deal with the rules of the language to
construct sentences or expressions in their head.
2. Going for meaning
Children concern to the meaning first and tend not to pay attention to the
words which are used to express the meaning.
3. Using ‘chunks’ of language
Children tend to use part by part of foreign language combined to their L1
4. Having fun
Children always enjoy having fun, which make them not aware of learning a
language
5. Joining in the action
Children like working collaboratively in a group with other students, eagerly
6. Talking their heads off
Children’s desire to communicate is very powerful and it carries over and
spreads into foreign language learning.
7. Feeling at home
Children also have a feeling towards learning language. They will easily learn
a language if they feel secured and comfortable with the conditions around
them including the teachers too.
b. How Children Learn Languages and Its Teaching Implications
The innatist view believed that First Language (L1) and Second Language
(L2) learning were both activities which required the children to apply their past
experience to construct the new experience (Brewster et al., 2004: 16). However,
the behaviorist view stated the different idea towards the nature of learning
acquisition. This view sees that the process of L1 and L2 learning acquisition is
very similar from one another since the practice and imitations are usually done
by the children (Brewster et al., 2004: 16). Dealing with Stern's behaviorist view,
the teaching implication will arise in the idea of what the children should learn
foreign language if both L1 and L2 are acquired in the same way (Stern as cited
by Brewster et al., 2004: 3). This idea covers six statements as stated in these
following explanations:
1. Children should spend all of their time in language classes to imitate and
practice language in a common guided way
2. Children should start with separate sounds and then continued to build these
3. Children should spend a lot of time just listening without speaking
4. Reading and writing are introduced in the learning activity after listening and
speaking
5. Grammar taught is not appropriate to young learners.
The behaviorist view on L1 and L2 learning acquisition towards FL learning gives
the implications on the way the children learn FL.
2. English as a Foreign Language in Elementary Schools
Regarding with the nature of language, Ellis (1994:12) believed that
English was considered as a foreign language which was taught in the First
Language (L1) environment often through the medium of L1. From Ellis’ idea, it
can be said that English is taught in a line with the Indonesian language
environment or often by through the medium use of Indonesian language as L1.
In Indonesia, English has been a first foreign language formally taught
starting from the elementary schools. The Indonesian government has issued the
regulation which contains of the guidelines related to the English curriculum
model applied in teaching elementary schools. This phenomenon can be
developed due to the conventional widespread belief that there will be more
advantages by introducing English as a language learning early rather than its
advantages (Brewster et al., 2004: 2). However, the success of learning English in
the elementary level is not achieved easily by the students. In order to create the
best condition to teach English, there must be some requirements to be highlighted
important conditions to be regarded i.e. having appropriate trained teachers,
proper timetabling with sufficient timing, appropriate methodology, continuity
and relation to secondary school, provisions to suitable resources and integrated
with monitoring and evaluation.
3. The Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) 2006
The School Level Based Curriculum 2006 or known as KTSP is the latest curriculum applied in Indonesia based on the Regulation of National Education
Ministry (PERMENDIKNAS) No. 22 2002. According to the guideline issued by
Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan (BSNP), KTSP is curriculum developed from the standard contents which are independently constructed by schools based on
different terms of condition. In a relation with the BSNP guideline for elementary schools, each school is also given the opportunity to develop the curriculum in
accordance with its capacities and needs. That is why there will be some
differences in enumerating the standard contents of KTSP from one to another elementary school. Although the KTSP 2006 can be varied in various ways, the government has issued the Governmental Regulation No. 19, 2005 which provides
the guideline to design the KTSP. It emphasizes that KTSP should consist of standard of content, standard competence of graduate, standard of process,
standard of educator and administrator, standard of medium and infrastructure,
standard of funding and standard of assessment.
In a relation to this research, the researcher applied the standard contents
document which contains the statements of what will be learnt passing through
several different stages before achieving the objectives (Hutchinson and Waters,
1994: 10). The definition of syllabus based on the KTSP guideline is similar to what Hutchinson and Waters stated. The English KTSP syllabus which belongs to
SD N Purwobinangun contains some statements covered in the competence standard, teaching materials, indicators, activities and assessments. For each
statement of standard competence, the students are expected to be able to reach
the objective of why they have to master the materials stated in the syllabus. Since
this is an English KTSP syllabus, the standard content of competence to be mastered by the students should cover the four main skills including listening,
speaking, reading and writing.
Regarding with this research, the researcher would like to apply the
standard competence of one semester to be put in the questions provided in
Monopoly Games. As a review of materials, all questions should cover all the
objectives separated into four main skills including listening, speaking, reading
and writing.
4. Language Game
The idea in this section will cover some important aspects towards the
language game. The information about the definition of language game, its roles,
how to construct games, and the nature of Monopoly Games are presented and
a. The Definition of Language Game
Before knowing the roles of language games in learning English, the
researcher would like to present the definition of language games first. Language
games are defined as any fun activities which give young learners opportunities to
practice the foreign language in a relaxing and enjoyable way (Martin, 1995:1).
The nature of language games is fun, interesting, and challenging which can make
the children or young learners enjoy every step of playing these games. What
generally distinguishes language games from other classroom activities in an area
of language teaching is the presence of a visible set of rules which guides the
children’ actions and an element of strategy for children to successfully apply
their language as well as any other skills (Maley, 1999). The presence of rules is
the key to hold a successful learning using a language game as long as it is clear
enough for the students in which the ultimate goal is already defined.
There are a few types of language game used to teach English. Hadfield
(1999) classified language games into two major forms: linguistic games and
communicative games. Linguistic games focus on accuracy, such as supplying the
correct antonym. On the other hand, communicative games focus on successful
exchange of information and ideas, such as two people identifying the differences
between their two pictures which are similar. Whichever form of games the
teachers will use must be appropriate to the learning goals and topic discussions
(Brewster et al., 2004:176). That is why the teachers should be more careful in
determining the proper games to be implemented in teaching English for young
b. The Roles of Language Game
Games play significant roles in teaching languages. There will be a lot of
advantages by implementing language games for young learner classes.
Lee (1995:3) classified the advantages of language game into six major
categories:
1. Games are a welcome break from the usual routine of the language class.
2. They are motivating and challenging.
3. Learning a language requires a great deal of effort. Games help students to
make and sustain the effort of learning.
4. Games provide language practice in the various skills i.e. speaking, writing,
listening and reading.
5. They encourage students to interact and communicate.
6. They create a meaningful context for language use.
Lee’s idea towards several advantages of language game shows the
importance of its presence in the language teaching area. Games usually add
variations to a lesson and increase motivations by providing the language practice
of various major skills by providing the sensible encouragement to the target
language (Maley, 1999). Furthermore, many linguists have proved and believed
that language games bring a lot of advantages in developing the English
c. Constructing Games
There are many guidelines for constructing games. In a line with any other
games, Monopoly Games also can be constructed through various steps. However,
some basic guidelines might be rather different from one another. Bell and
Wieckert (1985: xix) constructed eleven steps in designing the games. Although
this guideline refers to the general type of games, it can be still applied in
designing Monopoly Games as long as it meets its basic demands. Bell and
Wieckert’ guideline is explained further through the sequence steps.
1. Developing the theme of the games
The need is the greatest thing should be put first to start. It begins with
assessing the curriculum to determine the need and always keeping in mind
the relationship between the games and real situation.
2. Determining the purpose
This step can be done by writing down some statements that clearly define the
purpose and scope of the games.
3. Determining the grade level
It deals with adjusting the skills and information to be learned to the range of
abilities in the classroom.
4. Determining the number of players
This step can be done by discovering considerations on how many students are
5. Determining the format
The format of the games will depend on the purpose and the needs and
abilities of the student.
6. Determining the method of checking
The method of checking the games can be carried out by the media specialist,
the teacher, an aide or the students.
7. Designing and gathering the materials
The materials should bear a definite relationship to the established theme and
purpose.
8. Defining players’ roles
It deals with describing the players’ roles and the resources available to them.
9. Deciding upon the procedure and time
This step is correlated to how to play the games and the rule of the games
which should be clearly stated.
10.Carrying out the trial of the games
If the previous steps of designing the games have been done, it is continued
with carrying out the trial of the games to find out whether the games work
properly or not. It may take several trials and modifications before all details
are satisfactory.
11.Conducting the evaluation
Having conducted the trial of the games, the step will be continued by
and unthreatening kinds of questions and determining the rule of games as
covered in the scoring process.
1. The Nature of Monopoly Games
Monopoly Game is one of board games, which is usually played by
children in spare time. It was first introduced by Magie in 1903, which was then
published and distributed by Parker Brothers (Temes, 2006). Monopoly Game has
been used as a teaching model in an economic class as ever done by Scott Nearing
from The Wharton School of Finance. Ender (2005:2) sees Monopoly Games as
simulations of a capitalistic political economy when players can help highlight the
experiences of living in the Western world. This game has a goal to look for the
wealthiest player who can successfully collect more money compared to the
others. For the procedure, how to play Monopoly Game is rather similar to any
other types of board game. It needs some supporting instruments such as a board,
a dice, tokens and cards.
Regarding with the area of language teaching, many experts believe that
Monopoly Game also can be applied as an educative aid to teach languages. Using
board game including Monopoly Game is an effective, low-anxiety, and fun way
for the students learning and practicing the communication skills as well as
developing their own communication strategies that can be readily applied to the
real world (Changs and Cogswell, 2008). By implementing Monopoly Games in
the classroom activity, the students are able to integrate what they have
5. Gardner’s Theory on Multiple Intelligences
This section deals with the important idea related to the existence of
Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligencesin this research. Furthermore, it covers
some beneficial aspects about the nature of Multiple Intelligences, the roles of
Multiple Intelligences for the students, and the process of teaching and learning
through Multiple Intelligences.
a. The Framework of Multiple Intelligences Theory
In designing six sets of Monopoly Games, the researcher applied
Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligences. Gardner developed the theory of
Multiple Intelligences in 1983. He did a research about human intelligences and
then published the book entitled Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligence. Gardner’s research revealed a wider variety of human intelligences than was previously believed. In this theory, Gardner (1983) defined intelligence
through these three following points:
1. The ability to solve the problems that one encounters in real life.
2. The ability to generate new problems to solve.
3. The ability to make something or offer a service that is valued within one’s
culture.
Dealing with these three definitions, the researcher concluded that intelligence has
been the ability to learn something, to solve problems and to generate a new
concept, which can be valuable from one another.
Gardner introduced seven major intelligences which were possessed
intelligence in 1999. Gardner presented these eight intelligences which have been
considered as Frames of Mind. Campbell et al. (2004: xv) explained Gardner’s idea towards Multiple Intelligences through these following descriptions:
1. Linguistic Intelligence
It is the ability to read, write and communicate with words.
2. Logical-mathematical Intelligence
This intelligence requires the ability to look for patterns, reasons and think in a
logical manner.
3. Visual-spatial Intelligence
It refers to the ability to think in pictures and visualize outcomes.
4. Musical Intelligence
It is the ability to make and compose music, sing and rhythm to learn.
5. Bodily-kinesthetic Intelligence
It refers to the ability to use one’s body movement to solve problem.
6. Interpersonal Intelligence
It requires the ability to use their social skills and good communication.
7. Intrapersonal Intelligence
It is the ability to reflect, analyze, and contemplate problems independently.
8. Naturalist Intelligence
It refers to the ability to make distinctions in the natural world and
The brief descriptions of Multiple Intelligences clearly show that people are
varied from another due to the existence of various intelligences. Some people
might be good in particular intelligences, but not for other intelligences.
b. The Roles of Multiple Intelligences for the Students
In the theory of Multiple Intelligences, Gardner (2004) clearly described
that people have various cognitive strengths. As well as the students, they also
have their own strengths which distinguish them from one another. Svava (2008:
p.5) acknowledged that the students learn differently, for example one can be
excellent at math, but weaker in language area and vice versa. Since the students
have the different abilities to learn particular cases, the innovative teaching and
learning activities should be developed to accommodate the students’ needs
accordance with various dominant abilities.
The theory of Multiple Intelligences presents the breakthrough to the
students’ learning process. It offers the major transformation on how the schools
are run (Svava, 2008:5). The teachers should hold the interesting and innovative
activities, so that all students with their different dominant abilities can be
engaged together in the learning process. The students deserve to have a reputable
education which accommodates their interests. Gardner acknowledged that almost
everyone had the ability to develop all eight intelligences if they were given
appropriate encouragement, enrichment and instruction (Armstrong, 2000:9).
c. Teaching and Learning through Multiple Intelligences
Many educational stakeholders frequently interpret Howard Gardner’s
2004: 251). The theory of Multiple Intelligences presents various models of
learning. Moreover, Campbell et al. (2004: 231) emphasized that the Multiple
Intelligences were typically considered as the instructional processes to enhance
student learning in any discipline. That is why the theory of Multiple
Intelligences theory has been implemented into many forms of instructional media
for the classroom activities and school wide curriculum.
The idea towards the theory of Multiple Intelligences in teaching and
learning processes is often argued by many educators. In fact, Gardner (1994)
stated that individual teachers and entire schools might apply Multiple
Intelligences in diverse and even conflicting ways. Gardner seemed that he
wanted to give the broad opportunities and freedoms for the educators to
implement and elaborate the concept of Multiple Intelligences into various models
of teaching and learning activity. That why it is suggested that teachers should be
better to present their lessons in a wide variety of using music, cooperative
learning, games, role play, multimedia and much more (Amstrong (1999) as cited
by Svava, 2008:6). By having a great variety of classroom activities, the students
are expected to be able to develop their intelligences in a compliance with their
interests to reach an active learning process.
B. Theoretical Framework
Young learners, especially those who live in Indonesia, have their own
characteristics and ways of learning English as Foreign Language (EFL). Similar
have the distinct ways of learning English different from the adult learners. That is
why the innovative teaching media should be implemented to reach a satisfactory
result of learning English. One of the effective media of teaching English is
implementing the language games. Dealing with the roles and benefits of the
games, the researcher believed that games could be effective in presenting the
enjoyable environment of learning English.
In this research, the researcher modified monopoly games as language
games to assist the students of grade IV, V, and VI of SD N Purwobinangun to learn English. The researcher still adapted some basic characteristics of Monopoly
Games as seen in the layout of the games and the additional tools, for example
colorful tokens, a dice and cards. The appearance and rules of playing Monopoly
Games are similar to the commercial games in which the stage-blocks along the
path are still provided. However, the content of Monopoly Games will be partly
varied in accordance with the integration of KTSP 2006 with the theory of Multiple Intelligences.
Monopoly Game is an instructional media in enhancing the students’
ability towards Multiple Intelligences. Campbell et al. (2004) emphasized that a
game with movable pieces often challenged a player’s foresight and imagination
as well as exercise memory skill and visual-spatial intelligence. Since Monopoly
Games can be played by using movable pieces, these games might be applied in
the teaching process to be integrated with Multiple Intelligences. If Monopoly
Games are integrated with the theory of Multiple Intelligences, they will form the
needs of learning English and the students’ interests with various dominant
intelligences.
In order to present the obvious process of designing Monopoly Games, the
researcher adopted the guideline for designing games from Bell and Wieckert
(1985: xix). This guideline consists of eleven steps to construct Monopoly Games.
The further explanations towards the guideline of from Bell and Wieckert (1985:
xix) are explained through the following steps.
Step 1: Developing the theme of the games
Designing Monopoly Games is begun by finding and developing the
theme of the games. The theme of games should be based on the latest
KTSP 2006 and the theory of Multiple Intelligences. Since Monopoly Games would be designed as material review, the theme should be closely
related to the children’s world.
Step 2: Determining the purposes
Having developed the theme of designing Monopoly Games, the
researcher continues to determine the purpose of the games. The purposes
are stated through some statements that clearly define the purpose and
scope of the games (Bell and Wieckert, 1985: xix).
Step 3: Determining the grade level
Since Monopoly Games are considered as the additional supporting media
to assist the students in different level of study, the grade level of playing
playing Monopoly Games should be adjusted to the skills and materials
stated in the syllabus.
Step 4: Determining the number of players
In this step, it deals with the researcher’s considerations in determining the
number of players. Since Monopoly Games will be applied in the
classroom learning process, all students should be involved in playing
these games. However, they should work and gather in a small group.
Dealing with the group formation, the researcher should carefully decide
the best number of students to be involved in one group.
Step 5: Determining the format
In this section, some basic concepts of Monopoly Games are adapted to
be elaborated in the format of the games. Hence, Monopoly Games should
cover all important aspects of designing games including the purposes, the
needs, and abilities of the students.
Step 6: Determining the method of checking
After determining the format of the games, the researcher deals with
considering the method of checking the games. It can be done by having
the discussions with media specialists, teachers, an aides or students in
order to know the effectiveness of designed games as classroom learning
aids.
Step 7: Designing and gathering the materials
In this step, the researcher starts to design Monopoly Games by gathering
syllabus of SD N Purwobinangun. The materials are adopted from the materials of grade VI, V, and V and integrated with Multiple Intelligences.
Step 8: Defining players’ roles
Having obtained the materials to be applied in Monopoly Games, the
researcher carries out the step of defining the players’ roles. In this section,
the students should be able to play their roles as players by playing
Monopoly Games in a proper procedure.
Step 9: Deciding upon the procedure and time
When the players’ roles are clearly defined, the next step will be done by
deciding upon the procedure and time. The researcher should consider how
long the games will last a proper allocation of time. The procedure of
playing the games should cover all aspects on how to play the games
including the instructions and rules.
Step 10: Carrying out the trial of the games
This step is the important part in designing Monopoly Games in which the
researcher should carry out the trial of the games in order to know the
effectiveness of the designed games. The trial of the games can be used as
a reflection to improve the quality of Monopoly Games as learning aids.
Step 11: Conducting the evaluation
The last step of designing Monopoly Games is by conducting the
evaluation derived from the trial of the games. It can be done by
discussing the concrete and unthreatening kinds of question and revising
28
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the researcher would like to discuss further the
methodology which was applied in this research. This section consists of six
important aspects including the research method, research participants, research
instruments, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research
procedure.
A. Research Method
In Chapter I, the researcher has already stated two problems formulated in
this research. In order to answer these problems, the researcher applied the
Research and Development (R & D) method in order to design Monopoly Games
as material review for the elementary levels. According to Borg and Gall (1983),
“The R & D method is a process used to develop and validate educational
products” (p. 772). From this definition, there are two important aspects of R & D
method to be considered by the researcher including the development and
validation of educational products. In this research, the educational product refers
to six sets of Monopoly Games for the students of grade IV, V and VI. In applying
the R & D method, the researcher first started from developing Monopoly Games
In conducting a research based on the R & D method, there are some steps
to be carried out in the process of designing Monopoly Games.
The steps of the R and D process referred to as the R and D cycle, which consists of ten steps as follows research and information collecting, planning, develop preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, main product revision, main field testing, operational product revision, operational field testing, final product revision, dissemination and implementation (Borg and Gall, 1983).
The brief explanation above has explained further ten steps of R & D cycle. All
steps in the R & D cycle are important to determine the research result whether it
is successful or not. In this research, the steps of the R & D cycle which have to
be carried out only cover until the fifth steps, i.e. the main product revision
because the five steps of R & D cycle have covered the two main aspects of the R
& D method i.e. developing and validating. The first three steps including
research and information collecting, planning and develop preliminary form,
include to the developing stage whereas the next two steps including preliminary
field testing and main product revision, include to the validating stage. In research
and information collecting, the need survey should be conducted in order to
present the beneficial ideas and current needs to be developed in the research.
Since the products in the research were Monopoly Games, the R & D
cycle was integrated with the guideline of constructing the games by Bell and
Wieckert (1985). As stated in Chapter II, this guideline consists of eleven steps
including determining the theme, purpose, grade of level, number of players,
format, method of checking, materials, players’ roles, procedure and time,
conducting the trial of the game, and evaluation. The steps covered in this
stage of planning. In the stage of planning, it covers the steps of determining the
theme, purpose, grade level, and a number of players. The format, method of
checking, materials, players’ roles, procedure and time would be determined in
the stage of developing preliminary form of product. Preliminary field testing
covers the trial of the games. In addition, the suggestions and evaluations derived
from the validation were considered and elaborated in the main product revision.
B. Research Participants
There were two groups of participants involved in this research. First, the
participants were involved in the need survey. Second, the participants were
participated in the validation.
1. The Participants of the Need Survey
In developing Monopoly Games, the researcher first gathered some
information by conducting the need survey to the English teacher and thirteen
students of grade VI, V and VI in SD N Purwobinangun. Ten students were chosen randomly in each grade to present their points of view in the need survey.
The participants for grade IV are between 9-10 years old, whereas the participants
in grade V are about 11-12 years old. Meanwhile, the participants in grade VI are
between 12-13 years old.
2. The Participants of the Validation
Since there were two phases of conducting the validation, there would be
groups of participants involved in the validation towards the whole designed
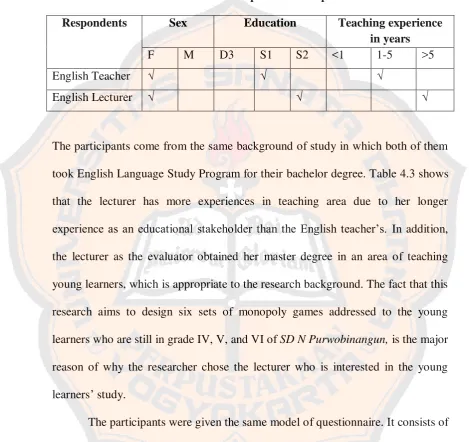
a. The Participants of the Validation towards the Whole Designed Games
After six sets of Monopoly Games were completely designed, the
researcher involved two educational stakeholders the expert validation. The
English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun and the lecturer of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta were
involved in validating the designed games. The lecturer who validated the
designed games should have the background study related to the area of young
learner education for either the bachelor or master degree. In order to present the
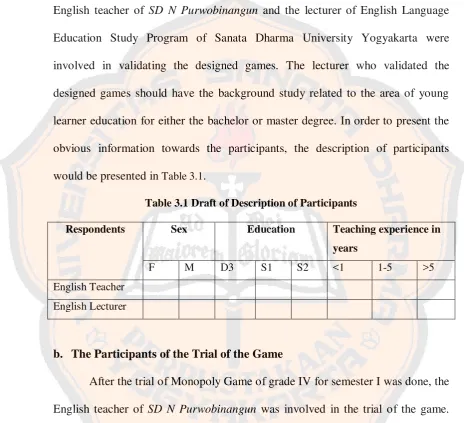
obvious information towards the participants, the description of participants
[image:48.595.60.525.193.616.2]would be presented in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 Draft of Description of Participants
Respondents Sex Education Teaching experience in
years
F M D3 S1 S2 <1 1-5 >5
English Teacher
English Lecturer
b. The Participants of the Trial of the Game
After the trial of Monopoly Game of grade IV for semester I was done, the
English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun was involved in the trial of the game. Furthermore, the researcher also engaged ten students of grade IV who were
randomly chosen to be participated in validating the designed game of the trial of
C. Research Instruments
There were two types of research instruments applied in this research.
Both of them were employed in two phases i.e. the need survey and the validation.
1. The Instruments of the Need Survey
The researcher applied two instruments in the need survey i.e. a list of
interview questions and questionnaire. First, a list questions covered in the
interview was presented to the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun
(Appendix B on page 90). By conducting the interview, the researcher would be
able to explore deeply and analyze some problems related to the teaching and
learning process in SD N Purwobinangun. Second, the questionnaire was also
distributed to draw the students’ perceptions towards their difficulties and
interests in learning English. There are fifteen statements covered in the
questionnaire to be analyzed by the respondents (Appendix C on page 92). Since
the respondents are considered as young learners, the questionnaire was
distributed and constructed in a form of selected items by using two major choices
between yes or no. By distributing the simple model of questionnaire, the students were expected could present their points of view easier towards the provided
statements based on their own experiences.
2. The Instruments of the Validation
In this research, there were two phases of conducting the validation i.e. the
whole designed games and the trial of the game. Thus, there would be also sorts of
a. The Instruments of the Whole Designed Games
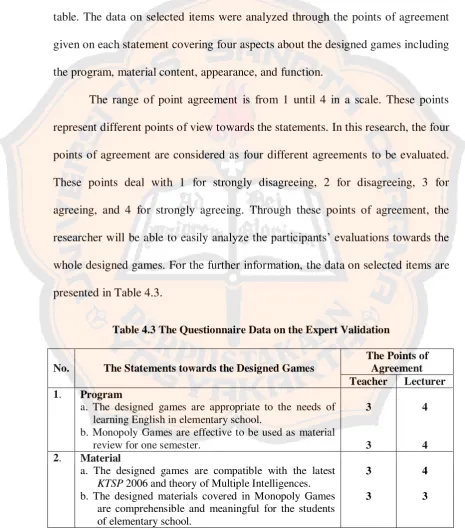
In the phase of validating the designed games, the questionnaire was
distributed to the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun and the lecturer of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The
questionnaire contains not only the statements to be evaluated but also the
open-ended question which cover the important and valuable information towards the
designed games including the experts’ general opinions, comments on
weaknesses, and suggestions (Appendix L on page 133). For the section of
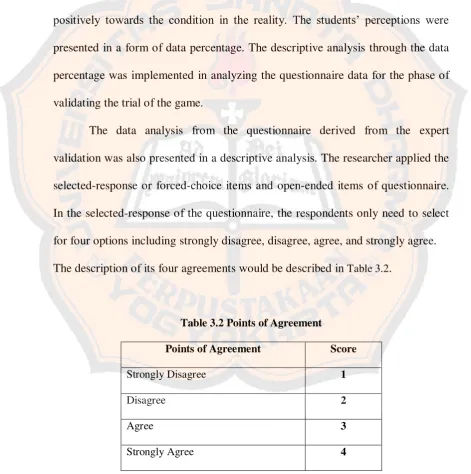
selected-items through statements, there would be four major cases to be analyzed
further including its program, material, appearance, and function. Through the
open-ended items, the respondents are expected to be able to convey their
opinions, suggestions and criticism freely.
b. The Instruments of the Trial of the Game
A list of interview questions and questionnaire were employed in the
validation, which were covered in the phase of trial of the game and the whole
designed games. In the validation of the trial, the questionnaire with a simple
model of yes and no option was also distributed to the students in order to withdraw their perceptions towards the trial of the game (Appendix O on page
143). On the other hand, a list of questions covered in the interview was also
D. Data Gathering Technique
For gathering the data in the need survey, both interview and survey were
conducted in collecting some beneficial information before designing the games.
In conducting the interview, the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun was asked several questions related to any supporting information towards the
teaching and learning process. Meanwhile, the students of SD N Purwobinangun
were also involved in the survey by answering some questions in the simple form
of questionnaire dealing with the teaching and learning process and their interests
in learning English.
For validating the complete design of Monopoly Games, the survey
accomplished with the selected and open–ended items was afterwards addressed
to the lecturer of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma
University and the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun in order to withdraw their opinions, suggestions or even critics towards the designed games. In
addition, after the trial of the game was held, the researcher conducted the
interview with the English teacher of SD N Purwobinangun. In addition, ten students, who were chosen randomly, were involved in the survey by distributing
a simple form of yes and no options in the questionnaire.
E. Data Analysis Technique
Due to the fact that two types of research instruments were applied in this
research, the data analysis technique would be separated into two forms of
1. The Questionnaire Data
Especially for the questionnaire data in a simple model with only yes and
no option, the data was analyzed through the