Journal
of
Biotogy
Agriculture
and
Heatthcare
ts'==='',,5*",,,,..
i'
r
[image:2.612.59.560.14.745.2]VoI
4,
No
I
Q0l4)
Table of
Contents
frrticles
otsody
to Assess the Knowledge Regarding prevention of pneumonia amongDtBc
Aged Adults in Selected Rural Areas of Moodbidri with aview
toetdop
an Informational BookletYathi Kumara Swamy Gowda, Ashok Nayak
il&lcscent's
and Drugs Abuse in NigeriaHanisu Mamman, Ahmad Tajuddin Othman, Lim Hooi
Liqn
EEct
of Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomte exo'Rorke)
seeds on theLiver
dGonads
ofMale
Albino RatsHannah Edim Etta, Cornelia Chinomso Olisaeke, Cletus Inah lboh Efrctiveness of Treatment outcomes of public private
Mix
TuberculosisCmol
Program in Eastern NigeriaHenry A. Efegbere, Arthur E. Anyabolu, prosper O. Adogu, Ebruke K. Efegbere, Emeka H. Enemuo, Robert C. Okonkwo, Obiefuna p. Eze,
Nasiru Sani-Gwqrzo, Amos Omoniyi, Amobi L. Ilika, Anthony O.
Igwegbe, Cyprian I.A. Oyeka
Efects of Different concentrations of Biocides on Fungal populations, Isolated from Biofilms of corroded
oil
pipelines, Nigei Delta Region, NigeriaGodwin U. Akpan, Marian G. Solomon, Godwin Abah Male Genetic Diversity of Siwa Brahmin Clan in Bali Based on
y-Chromosomal Microsatellites
DNA
I
Ketut Junilha, Ni Luh WatiniasihA comparative study on Growth, carcass Traits and rissue Distribution
of
Awassi and Hamdani Lambs
Rabee A. Oramari, Jalat E. Alkass, Kanyaw I. Mahmud
Effectiveness of Enterobacter cloacae to promote the Growth and Increase the Yield of Rice
Datta Ngurah Suprapn, Ni Made Intan Maulina, Khamdqn
Khalimi
Effect of Protein Level on Gonadal Developmont of the African
catfish
IBIMA.7.,
F. D.SIKOK]
Impact of Bat Guano otonycteris hemprichii camd and Seaweed Extract on
Some Growth and Yield Traits of Barakaseed Nigella Sativa
L
ASEEL N. ALMOHAMMEDI, ALI F. ALMEHEMDI,
MFAT
K. ALAJEELEE
Phosphate and Sulphate Adsorptions in Bungor Series Soil
Adzemi Mat Arshad, Ibrahim W
Qualitative Land Evaluation for
oil
palmcultivation
in peninsular MalaysiaAdzemi Mat Arshad
The Efficacy of a Herbal Drug, Schitozim over praziquantel in the Management of Schistosoma mansoni Infection in
BALB/c
miceLynda A Allan, Helen L. Kutima, Shadrack Muya, Darlene Ayonga,
Dorcas Yole
The Influence of Adoption of Improved
oil
parrn production practices on theLivelihood Assets of
oil
Palm Farmers in Kwaebibirem District of GhanaJonathan N. Anaglo, Seth Danlqi Boateng, Felix K. M. Swanzy
10-15
t6-22
23-29
30-35
5 t-56
57-6s
Journal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare
ISSN 2224-3208 (Paper) ISSN 2225493X (Online)
Vol.4, No.l,20l4
Abstract
The Brahmin clan
in
Bali
consistedof
two
groups,th1!
are Siwa Brahmin the descendantof
DangHy4
Nirartha
and
Boda Brahmin, the descendant'or narrg Hyang Asqnaka. Dang Hyang Nirarthacame
to
B{
around
l4g0
anda"."J"Jiirr"
Brahmina"r,
*rttt
"i,.ri.t
oi-s
sub-clans (Kemenuh,Manuaba' Keniten'
Ml
and Patapan).
ffris
nesearch was conducted to ietermine the molecular charactersof Siwa Brahmin clan' The research was conducted by employi"g
th";;i;;;i;; -*[*
-i"tosatellite
Y-chromosomal
DNA
fromJtrc
to october
zor:.
*rere
was;ri;;
oi utLt" rot"'a,
o""
in
theDYS,9
locus (200bp)' threein DYS390 loc,s
(
z03,2o.7and
21lbp)
""d.'""
alleles were found inDys393
locus(
129 andil:upi
and in DYS395 locus
(lzl
and 131bp). The highest frequency
o!
!n|o^tpe,
from
6 haglot.lrngs recorded, was foundin
haplotype 2 (0.54)
with
the alletecombin"ii",
i,i
ZfiO, ZOl,Oqi
t'Zi.
fhis
ilaplo,tipe was foundin all of
sub-clans: Kemenub"
Manuaba, Keniten, Mas, including sample from unidentified
sub-ilan'
Haplotype2
could be as the
origirnl
haplotyPe of Siwa Brahmin'
^fir*iiO*,
Siwa Brahmin clan,
DNA
microsatellite' allele' haplotypel;r1l#ilirlll;"rociety
today is divided into groups b.ase$ on paternal genealogical lineage ca[ed clanor soroh (Balinese). The society
a"r"ilp"a
from the acculturation betweenp"opi*
who Jame toBali
island earlier' which
isknownasBaliMulaandpeoplewhocametutott'utU'oughtnewthoughtwhatiscalledasReligionbasedon
holly book of Hindu,
v;;.'
Based on trretristoiy,'naii;1".r;d
w^a_s inhab]ted by people who came from variousplace such as China,
r,,jiu,
C*t
a
and Eastlr*i'C"",*uias,
1956; Bellwood' 1985; Ardika'
1996;Wikarman"
1994). The profile
"r
*ipNe
"ouectedfrom the
ieeth
excavated from the tomb at Sembiran village' BulelengRegency was found
,i-itu,
io
that of Indian(1[,i*
etal',,2004)'
farafet
etat'"
(2005) found that 83'7%of
Balinese men have Austronesian genes,
l2ohd";"I"di;"'genes-and
oriy
2,2Yorepresenting gene
from
pre-Neolithic society.
ffr" .r"*
"o*".Jf.o*
.'ru.ioo.ptu"",
entariing Balinese tommunity certainly brought various new genetic prohles*a
"rr*t"
*ttich will
enrich the genetic structurgas well as the culture of Balinese'
Many people
in
Balinese society groups arefunctioi
as Brahmin (Balinese: Sulinggih\to
assist the culturalceremony. They are many
Sulingsih]hai
u.""uff"J
afr"rently
depend on theclan'
For example' Brahmin fromBrahmin (Brahmana)
"lui
i*
"uit;'-
p"donda, Brahmin frorn-Ksatria clancalled Begawan, and Brahmin from
pasek clan called Sri Mpu. Brahmins (pedandal
a"r"""a*t
in_Balinese society was based genealogical lineage'which
is
groupedinto two from two
ancestois. Those arethe
groupor
clanof
Siwa (Siva) Brahmin whodescendant
of
Dang Hyang Nirartha and the "tuo or Boda Brahmin, tire descendantof
f)ang Hyang Astapaka' The descendants of Brahmin clan wascharacter*d
bt
ih"
name b-egin with lda Bagus for the men and lda Ayufor
the woman (Dharma Gosanaof n"g"rr.y
i"t"Urana,
2008;Wi;
andSanteii'
1993)'The
existenceof
Brahmin in Bali was known far earlier than those-the division of Brahmin clans (Siwa andBoda)'
They existedsince the arrival
"r
nJ
r"r*t"raea
at thecutu
v"u'
of
80 ( 152AD)'
the founderof
the-Besakift
Temple (the
largestTempleinBali),thenfollowedltYn]Gana,MpuSemeru,MpuGnijaya,andMpuKuturan(Gingsir,
2000; Dharma Gosana Kab' Jembrana' 2008; Sastrodiwiryo'
2010)'
l
The population
of
siwa Brahmin inBali
*u.
Inot"
thentlBoda
Brahmin' which representedby the number
of
people andfamilies.
il;;;;
Brahmin*a
it.
i'edanda were widespreaatto"gtr
outBali, while
the Boda Brahmin was limited and can only be found in Bodakeling and wanasari villages, Karangasem Regency;
Tusan
village, Klungkung Regency, ana SlIaw.ati village,
Gianyar-Reglncy'
The Jynuttyor
clan
of
Siwa Brahminwas started in
fifty
aentury (1430AD)
*h"t
the Foundingfath"',O*g
HyangNirartha came from Java to
Bali
with his family.
At
that time, Gelgel**
'h:-;l"pd,fi;1tf::::*::,'95,:'r:ffl1**:*:"ftt"11ffi'ffi
Male
Genetic
Diversity
of
siwa Brahmin
clan
in Bali
Based on
Chromosomal
Microsatellites
DNA
I Ketut Junitha* and
Ni
Luh WatiniasihBiology Department,
r;*hy
of Mathemltic and Natural Science, udayana UniversityJalan Raya
K;;;;t
Bukit Jimbarano Kuta'Bali'
Indonesia' 80361*
E-mail of ctrresponding [email protected];ft,T#ru'il;#51t15rffi?tl.il
"lt.
Jembrana,ioos;
sastroaiwirvo, 2010;.Ho*"ver,
Riana(201r)
reported that Dang
Hyu-;;;;-t"t
h;
i.i*d.
insati
ubouty"u'
1489' -The Siwa Brahminwas devided into five
groups (sub-clans)
wrrichtsed
on their*ir"*
Jbu"g
H;-g
Nirartha'
He had five wives'the
fint
was fromDaha (Kediri-East Java) who descended Srahmin
;u;clan
Iiemenuh'
The secondwife from
Pasuruan (EastJava) descendeo
sruh-'irr-roi-clan
Manuaba. The,thirdwife
from Blambangan(East Java) desdended Brahmin sub-clan Keniten. The fourth
wife
from vrastcianvar-outif a"o"rra"d
grah;in
sub-clan Mas, and the frfthwife
www.lrste.org
Ifltl
ffifi
descended Brahmin*b-:tl_p."qpan
(Bek,1959; Gingsir ,2OOA).
ffi::,:,f,_.::":j^1,1"-"f,rNA.ui"t
af1'-""t
J.,"od" protein, soit
does nothn'
Microsaterrites"o"ii"
markersrr;;
i""r
rr"J'ffi;1T""k;",il"TlJl:
n
rcrcby
it
isgoJi io
ueempmyeJ;;;;,;;G;"Tff#il1;#1,:ll,.J
rlff
?,Xt
H
;;ffir*,;"X",:":i
:i
:.
:!?!:
;L,r".,.:
i;sl;j.
rjiri.,,,
at,
tee6; ):'Y
DNA
markers that are locatedrt
"r,r*"r"*i1i
ffi.#::#:Xff;*ri::",lrl
l[ffi
]_H:.,,::::::
ji:f
"*i"ri,""-g'J"rsai"*,h"-,i,""i"_r,",arebasedon
trur&
r.Ean
(bride) move andri*
to th"-ui.1brid"g.o"il
rr""r"
.,,fl*|f,"jfl:"?H;
nrir
cbromosom-y markers rruru"",
"r.a_to
determine genetic flows between casted-
ffi61-
Balinese societytx*rr"-
i-"i.,ioosl
*a
for
oene,r^-inor^*
,._^--
-r@r.
D.rurcsc socretv$Trt:1
etal.,
2005) andfor
genialogical groups or clans in3]: ry*,
et at.,ZOOO; tunithaeia't.:;;i;;
ffi#ffi
?Ji*:'Jj[i,i;ii*".Brahminsub-crant"3:]rh,-uaruaba,
m"
il
rh
r-",il;;;.'.o*rerr
resrtts were re-corded and used a-.{ r,oo,r +^,"
^-,^Io.To:1T3-J
nlarkers,DYslg,
nrys:so,
"*r"ifi"
;iil;:,frf$?"ii,ll,lft
ffi:i:3*
ffi3l:|'j,]:::"t'nt
molecular marker microsateuite y-chromosomarDNA
fiom June,h
,E
mrne nom
nam s,from
r
r
^,"1X|ff:siv1
;amrting
method,b;;J;;;ri,t"s
peopleof
Siwa "itv
r?:ip:.Ti 1d
;;:ffi
,E:::;rlr",,H1:Iil:,fi:r,1il:.:ff
;"*Xffi
f"l.rllml
",1],:,::
I |e.
:t,,r::rum
mucosaceil
was swab using sterilized'ft
frcvolunteers.a"g*r"rrnr"."u".,r""r,'ffi
il#?"".:::,T::;il"ilr:ffi:X*:l
mT":i"'i:1":1j,;1f
Irifr
ar cohoI
prec i p i tat i o:r#f
::::-";::-"-::Triprtrvasextractedusingphenor-:
DIa,
;;;;t,
;,:.
;;;iiliil
?#
ililil:$.H
tr
rp"Tffii
TL-f
"li:U;::::,lf
;ili;i;;'
rorr,
r,
Dys 3 e 0, Dys 3 e 5 and Dy S 3 e s)
rr,l
n s
cl.Ies
in
52-55'c
annearing- iemferatures,then
visuarrr"n'#tij,'j;'?"'rfi::tl;,*:
ffiikT3..Y:^y::'":iropn:tj'^i;
6yo
potvacilamide ger (pAGE) runninsin
r ro r,^rrDNArypingwasdetermin"auvpi"t,i"g;""#;::"fr
_|il;ff
:i'J"^fiTlrTffi:r#;f,l:X
lirru-
2001). The geneticai".i.iiy
.,ur'""i""i""a
foilowing
parra et ar., (1999).htr
r
hqr-r
ce[s
samples were collectedfrom
mal-e SiwaBrahmin clan.
Those were collectedfrom *."qr
rd
otter
eijht
regenciesi,
e"ii,-r;"f, r-rngu;, iil.gk
ng, Bangri, Gianyar, Badung,fir*---
and Bulelens,
u"ro11"ut"lv, i;;'t';iJ., sub-crir
""riJ;;;because,
therefore the samplesffi#
*tl:;:,:**:lt.tfu[f1fem1uh,
2e rrom manuaba, rr
rrom Keniren andF,r*or55volunte"'p."u""a,';ilffi
#;l'ilTJl;',1,'"'it#ffi
;ll;i:il5"T1?n1
min in Bali.
UX=
rntnownJ,rtE
r-fl
ry
fu
0fdl
55 buccal cell samples collected,two of them leaked on the
tilting
process, therefore only 53 samplesffi*T#[i".];ffi1';"X:i:*:,,:j":*i::i:1"-'1111"
#:;*
amprinedin
two primers outorrour
ErililDFrs emploved, whichwere not showing uoy
t*i
i,
Joumal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare
ISSN 2224-3208 (Paper) ISSN 2225493X (Online)
Vol.4, No.l,20l4
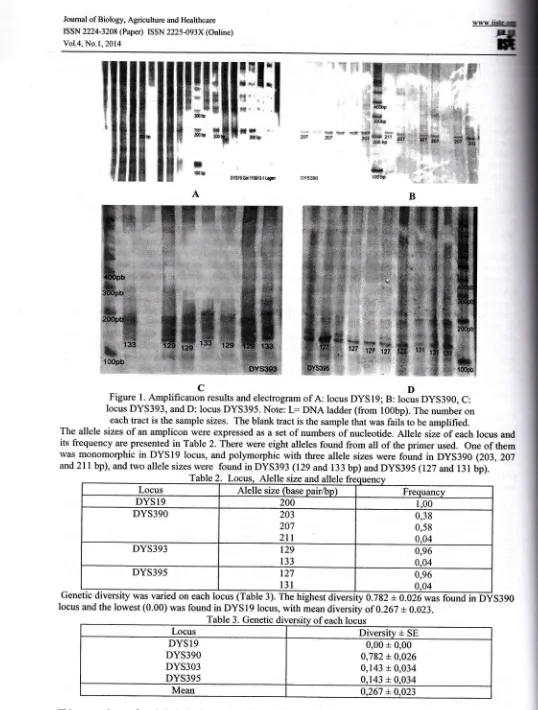
[image:5.612.39.577.33.743.2]0t6}{6.{ ,{t }t lrlr
Figure
l.
Amplificauon results and electrogram ofA:
locus DYS19; B: locus DYS390, C: locus DYS393, and D: locus DYS395. Note:L:
DNA
ladder (from l00bp). The number oneach tract is the sample sizes. The blank tract is the sample that was fails to be amplified.
The allele sizes
of
an amplicon were expressed as a set of numbers of nucleotide.Allele
sizeof
each locus andits frequency are presented in Table 2. There were eight alleles found from all
of
the primer used. Oneof
them was monomorphicin
DYS19 locus, and polymorphicwith
three allele sizes were foundin DyS390 (203,207
and2ll
bp), and two allele sizeswere
found in DYS393 (129 and 133 bp) and DYS395 (127 andl3l
bp). truE
&
ffiil
MYffi
ffi*ffi
ffi*ry
siit*
W
&i.
{r
,&S
,ffiffi
::::::\ :: ) W
ffi& t
zffi
::ffi
*
**m*"
!'
fiffiM*
il*
zi
H
*
*
ffiffi#r
ffi
,*ffiw
!
--'
ffi[
size and allele
Locus Alelle size (base oair/bo) Frequancv
DYS19 200 1.00
DYS390 203
207
211
0,38 0,58 0.04
DYS393 129
133
0,96
0.04
DYS395 127
l3l
0,960,04Geneticdiversitywasvariedoneachlocus(Table3).Therrigtr@foundinDYS390
locus and the lowest (0.00) was found in
DYSI9
locus, with mean diversity of 0.267 + 0.023.Table2.
Locus. AlelleTable 3. Genetic . Uenetrc didlversl ofeach locus
Locus Diversiw
+
SEDYSI9
DYS390 DYS303 DYS395
0,00 + 0,00
0,782+0,026
0,143
+0,034
0.143 + 0.034Mean 0,267
+0.023
This research was founded six haplotype based and DYS395), there are haplotype
no
1 to 6 ison alleles combination
for
fourloci
(DYSI9,DYS390,DYS393 presented at table 4. The haplotype 2 owning highest frequencyd
Healthcarel[S{ U5{93X
(Ontine)*own
zub-clanwww.iiste.org
t$l3l
ffi[
itt\'12w'207,129,r27
bp)
0.53s folowedby
haploype
no
r
(20a,203,r2g,r27) 0.3g4,
f
d
oo6
u/ith each frequency are 0.19.U+ttype'
alelles coritbinations, frequency and the distribution ofsub-clan of Balinese Siwa
Brahmin
f,ryFtaplotp",
Iod@q:
Freouencv=
Kmuh,
Manb= Manuaba,Kenie
Keniten, and----"";-.,
frrs
6at
there wasno
Patapan sub-clanof
Siwa Brahmin foundin
this study.
Basedon
the:3pf:r"1,?:qlf*
irir,artlra",.it,*
uv
e"[?leJt;;;
that regarized to be a siwauely4
sub-clans, those are sub-clan Kemenuir, Mauuaba,["rri,*
""jirr"r";fifi;:"rH.H#;
}!ft"ll,:r;:"
"::"*1
Hy_","_"::r^f-:,"rv_aia
""ip,""r"il""uJ*u,uor.,,
but
theymight
be*ancetves
^
Mu* sub-clan.rhis
is,*",r,"i
r,"iil#."ii:";fiT*';ir1'tXlil.t,}1"j[L,ffr,#:
ryks
amplified using-4 pair ofprimers(DySl9, Dys390, Dys393
dan DyS395),one sample was
Ht?XX;3,f"'::"i::::::x****:'*
a
due to mutation occurred on theprr-o'rit"
$i;;:'i1,.L,y
o,e
to the rai,ure in sample which is,"f..J;;;ilffii:
ifirftf:fiT}:f
of alleles varied amongloci'
Eight variety ofalleles were found, which the highest frequency (1.0)
Ir?Illrrl:::'jy::T,.,:g:1*li,"f
rg9!o.
rhis
meanstr,"iir,".'*,s
no mutation occurredsince
-e
father, Dang HvangNirartha.
Thisaneri
*u,
"o*ooro;;';;;;:#tH:ff:tffiil,tT
ffijH:.'2n','it:2:
liz-Linares
et3,!::':)*,::'.:'*-;";;;;;
pr,:,!
r
the worrd (Hammer and Horai,at.
tee6;.-Harmer"i
,i.,
tsitl.
rhe
aueleif
ffi;:
["rff'[fr#ff';l*H#]
frT*::".t"tt"r"::"(r;jr]:_l"yrj-r^ljo,:u)-":1"nslI]
rose]"."]p.o*ry.
rhe
arrere or207bpwal
,ffi
ia
arrnost every casteor
sociar groupin
india
(Rama";
;i."i1liY9ii;'iil;j"1"1#j"
:::y:"iry;;
k
&e
earlier studyin
other BalineJe cian6ayu
slr"r.rlirrra
thar the highest frequencyof
alrerein
mf
2llbp
(Junitha ai<t., zoosy.5.
Conclusiont
lxias found that the siwa Brahmin clanhas low genelic diversity
*iq-6
different haplotypes. The haplotype 2rith
the allele combinations of 200,207,12g,127 could be as the original haplotlpe of Siwa Brahmin.
Achowledgement
This
research
was
possible
due
funded
by
pNBp
lm
lLlcst
Genetic diversity was'foundin DyS390 with
the value
of 0.7g*0.23.
This due to the numberof
ft hd
in this locusYut
th" highest(3).
The total averageoig"*,i"
diversity was low (0,27 +.0,02). Thisk=
of
the low diversityof
dlJe
o,
"u"r,
locus andsiwa'g.ah-;
clan was relatively established recentlyfiM$tr-rug
(Sastrodiwiryo,20rc\.
c*"ii"
airr"rsityof siwa
s;;;in
clan wasro*",
tt
,
renrnyansociety
m.4
hrt
higher than the menort"r,g*u.,
r"grirrgsirgu., t.aaitiorrrl society (0.14)(Junitha
et
al,2[l2;Junitha
,f,
2009, Junitha dan Sudirga 2007;;;ith;-,iaO+1.
h
six haplotlpe wel?
fou3d,rripr"rle"'i..*i
,n:
highest frequencyand
widely
spreadin all
sub-clansrding
the samplewith
unidentineo cran.nre
rraptotyiez
t"r
liLr"-combinations
;ir&,
207,tzg,
r2,1,'*h
could be the oriqinal haplotype"ro".g
rrvr"g
xirurthu,-ine rourroing fatherof
siwa Brahmin clan. ThehTeacy
of haplotypet
"at
o.rs,
trr"*"""ir"gfri
"1"rl
rr"pr"typ"s.
The data shown that haplotypeI
with
&
lnplotpe
combinationsof
20a,
203,l;g,
127 and
*u,
iirt
i[rted
in all
sub-cran, occurredlater than
t{otype
z'
The mutated allele was tr," urr"r"of
207to
203;,,l
rr"p *u,u,ion,
in the locus of Dys3gO(Gusmao
I*iTiJ,"#:,il#i:i$"'irf"o'"t*"
I
occurred rar eariier*,*
ir,"
"th*
r,rpi",),p*-e",q,sand
i)
to
theJoumal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare
ISSN 2224-3208 (Paper) ISSN 2225-093X (Online)
Vo1.4, No.1,2014
17 4.2NN14.2/PNL.0 1.03 .00 120 13, Year 20 I 3
-References
Ardika
I
W.
(1996)."Bali
dalam sentuhan Budaya GlobalAwal
Abad Masehi. Dalam Dinamika Kebudayaa Bali,'. Editor ArdikaI
w
danIM
Sutaba. Upadana sastra. Denpasar. Pp:. 57-72Bek
I.
B.
p.
(1959).',Kitab
Sedjarah Danghyang Nirartha (Peranda Sakti WawuRauhf'-
Pustaka Balimas'Denpasar.
Bali
Bell^wood p. (1985). "Prehistory of the Indo-Malaysian Archipelagio". Academic Press. Sydney
Bhattacharyya N.P., Basu P., 6as
M.,
Pramanik S., Banefee R., Roy B., Roychoundhury S',&
MajumderPI'
(lggg).,,Nlglegible
male geneflow
across etnhic boundariesin
India, revealedby
anlysis on Y-chromosomdDNA
polirnorphism". Genom Research - 9 :7 I 1"7 19
Bowcock A.
M.
Ruaiz-LinaresA.
Tomfohrde J. Minch E.Kidd
J.R.& Cavalli-Sforsza.09s$.
"High resolutioaof
human evolutionary trees with polymorphic microsatellites". Nature- 368:455-457Covarubias
M.
(1956). "Island ofBali".
Alfred A Knopf. NewYork
Dankin E., EAvise ., J.C. (2004)- "Microsatellite
Null
Alleles in Parentage Analysis". JournalHeredity,93:5M-509
Dharma Gosana Kabupaten Jembrana. (2008). "Jati Diriwangsa Brahmana".
Gingsir I D N. (2000). "Babad Brahmana: Babad Bali Agung"' Denpasar
Gusmao
L.,
Sanches-DizP., CalafellF., Martin P., Alonso C'A.,
AlvaresF',
Femandez,Alves
C'
(2005)' .,Mutation Rates atY
Chromosome Specific Microsatellites". Human Mutation.26{6) 520'528Hammer M. F.,
SpurdelA.B.,
Karafet T., Boner M.R., Wood E.T., NovelletoA.,
Malaspina P.,Mitchell R'
Horai S., Jenkins T-.,
&
Zegura3.I-. (tSSZ). "The Geographic Distribution of Human Y-Chromosome Variation"-Genetic. 145:787-805Hammer
M.
F.&
Horai S. (1995). "Y-chromosomeDNA
Variation and The Peoplingof
Japan". Am- J.Hum-Genet. 56:591-962
Hillis
D.M., Moritz C.,
&
Mable B.K..
(1996)."Molecular
Systematics".2"d
ed. Sinauer Assosiates. Inc. Publisher. Sunderland USA.Hutscinson,
F.
(2001). ..DNA Band Size
Semi-logPlotting".
Cancer Research Center. Science EducationPartrnership. 06.26.0
I
Junitha
I.K.
(2004). "Keragaman Genetik Masyarakatdi
desa-desaBali
Aga Berdasarkan AnalisisDNA
danSidik Jari". Disertasi. IPB. Bogor.
Junitha
I K.
(2007). "PengguliaanDNA
Mikrosatelit untuk Penelusuran Kawitan pada Soroh-soroh Masyarakat Bali". J.Biologi
WUD
Il(2):
50-54Junitha
I
K.
&
Sudirgasx.
1zooz1. ..VariasiDNA
Mikrosatelit Kromosom-Y pada MasyarakatBali
MulaTerunyan".
Hayati. l4(2):
59 -64Junitha
I
K.,
Sudirgai. f.,
A
Wijanat M.
S. (2009). "Variasi GenetikDNA
Mikrosatelit Kromosom-Y Soroh pasek Kayu Selemdi
Ball". Berkala Penelitian HAYATI. Special Edt No. 3,{ December 2009.Junitha
I
K.,
pharmawatiM.
&
RosianaW.
(2012). "GeneticDiversity
of
Soroh Celagi (Pasek Catur Sanak Cklan) Base don Y-chromosomal MicrosatellitesDNA'.
Procedings on The 4th International Conferences onBiosciencesandBiotecbnology,Denpasar,Bali:2f-22"d September,2012,ISBN:978.,602'777648-7l.239-243'
Karafet,
T.M,
Lansing f.S., deae.f., Wattin
J. C., Surata S. P. K., Arthawiguna W.A',
MeyerL',
BamshadM',
Jorde
L.
3,.,&
Hamm". iU.
f'.
(2005). "Balinese Y-chromosome Perspectiveon
the Peoplingof
Indonesia: Genetic Contributionfrom
Pre-Neolithic Hunther-Gatherer, Austronesia Farmer, and Indian Trader"' HumanBiologt.TT
(1):93-113fansing S.
ReddA.
J., Karafet
T.
M.,
Ardika
I
W.,
SurataS. P.
K.,
SchoenfelderJ'
S',
CampbellM',
Merriwither
A. M.,&
IlammerM.
F. (2004)."An
Indian Trader in Ancient Bali". Antiqur4r. 78 (300): 287-293Mitchel
R.J.,
ReddyB. M,
CampoD.,
Infantino T., KapsM.,
&
CrawfordM. H.
(2006). "Genetic DiversityWithin
a Caste Populationof
India as Measured by Y-Chromosome Haplogroups and Haplotypes: Subcatesof
Golla of Andhra Pradesh". Am.J. Phys. Anthrop. 000;l-9
parra
E. ShriversM.D,
Soemantri A., McGarvey S. T., Hundrieser J., Saha N.,&
Deka R. (1999). "Analysisof
Five Microsatellites Loci in Asian and Pasific Populations". A..J-Phy.Anthrop.110:l-16
Ramana G.V., Su B., Jin
L.,
SinghL.,
Wang N., Underhill P.,&
Chakraborty R. (2001). "Y-Chromosome SNPhaplotypes suggest evidence
of lene flow
among caste, tribe, and migrant Siddi populationof Andhra Pradesh, South India". European J. Hum Genet.9:695-700Riana
I K. (201l;.;'Lelintihan
Sang Catur Sanak Bali. Kayu Selem, Celagi, Tarunya, Kaywan Balingkan, WargaBali Aga". Yayasan tan Mukti Palapa, Bali
Ruiz-LinnaresA., Nayar
K,
Goldsiein D. B., Hebert J.M.,
SeilstadM.
T., Underhill P.A., Linn
A'
A',
FelmenM.
W.,& Cavali-SfoizaL.L.,(1996).
"Geographic Clustering of l{uman Y-chromosome haplotype". Ann Humwww.iiscc
www.iiste.org
's-$
il$r
[.lffil|r
-Perjalanan Dang Hyang Nirartha: Sebuah Dharmayatra (1478-1560) dari Daha sampaimk
ffi61u
-.Ld
B., Dunia W.,&
KantaI M.,
(1983). *Sejarah Klungkung'. Pemerintah Kabupaten-A
lrleasure of Population Subdivision Base on Microsatellite alleles Frequencies". Genetics.ufllfil-
*MitochondrialDNA
in Natural Population: an improved routine for screeningof
geneticD
nsifu
e silver stainin gi' . Electrophoresis. 7 :226-229,ilqc-
( 1993). "Mutation of Human Short Tandem Repeats". Hum. Mol. Genet.B(8): 1123'1128*ni
R- (1993). "Kasta Dalam Hindu Kesalahan Berabad-abad". Yayasan BP.Deqasar